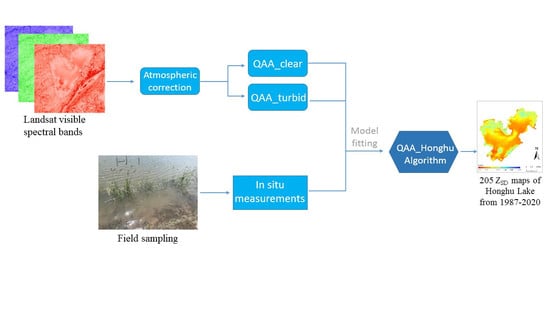
An Improved QAA-Based Method for Monitoring Water Clarity of Honghu Lake Using Landsat TM, ETM+ and OLI Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Region and Datasets
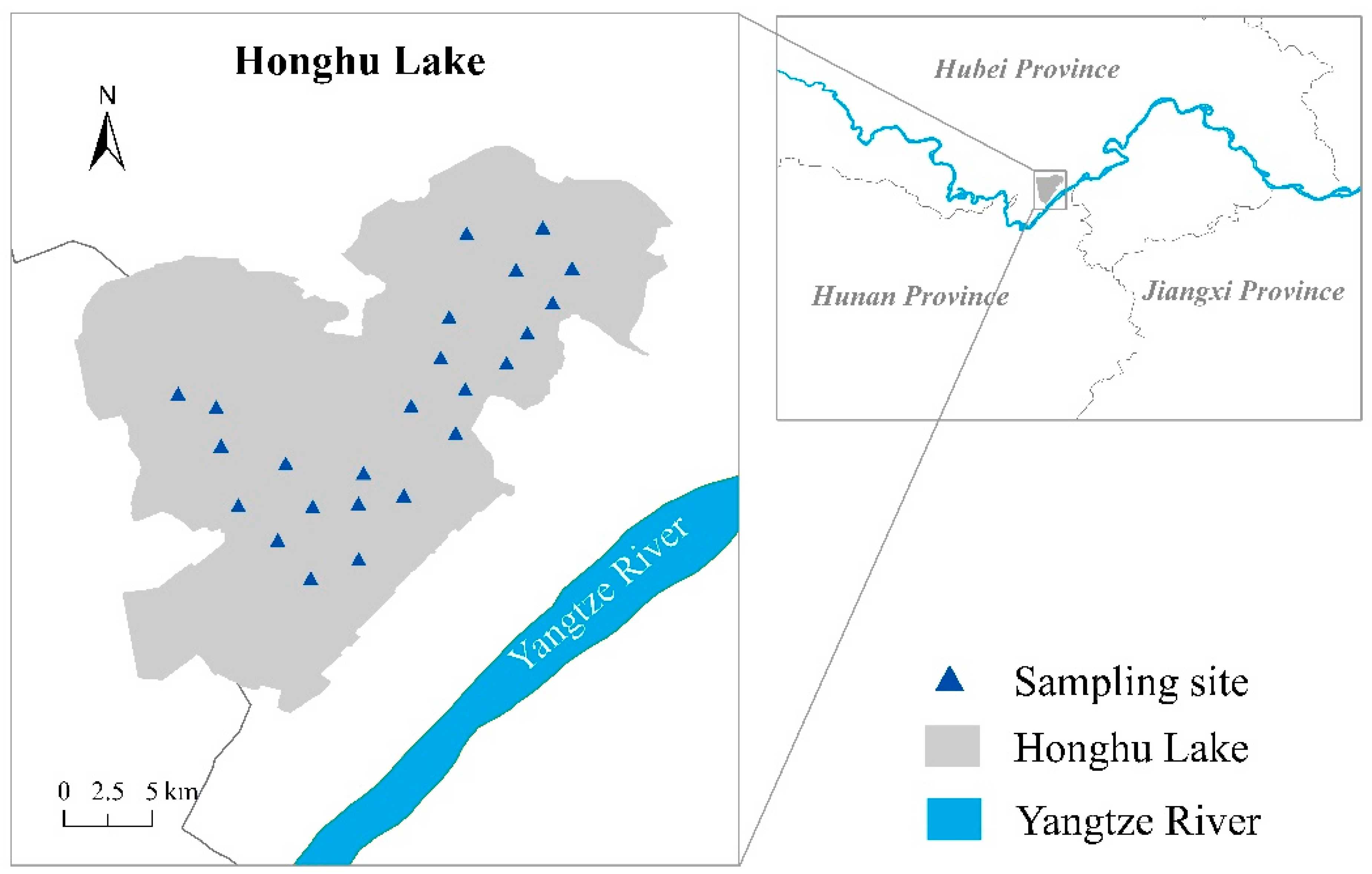
2.1. Study Region
2.2. Datasets
3. Methods
3.1. The Original OLI ZSD Algorithm
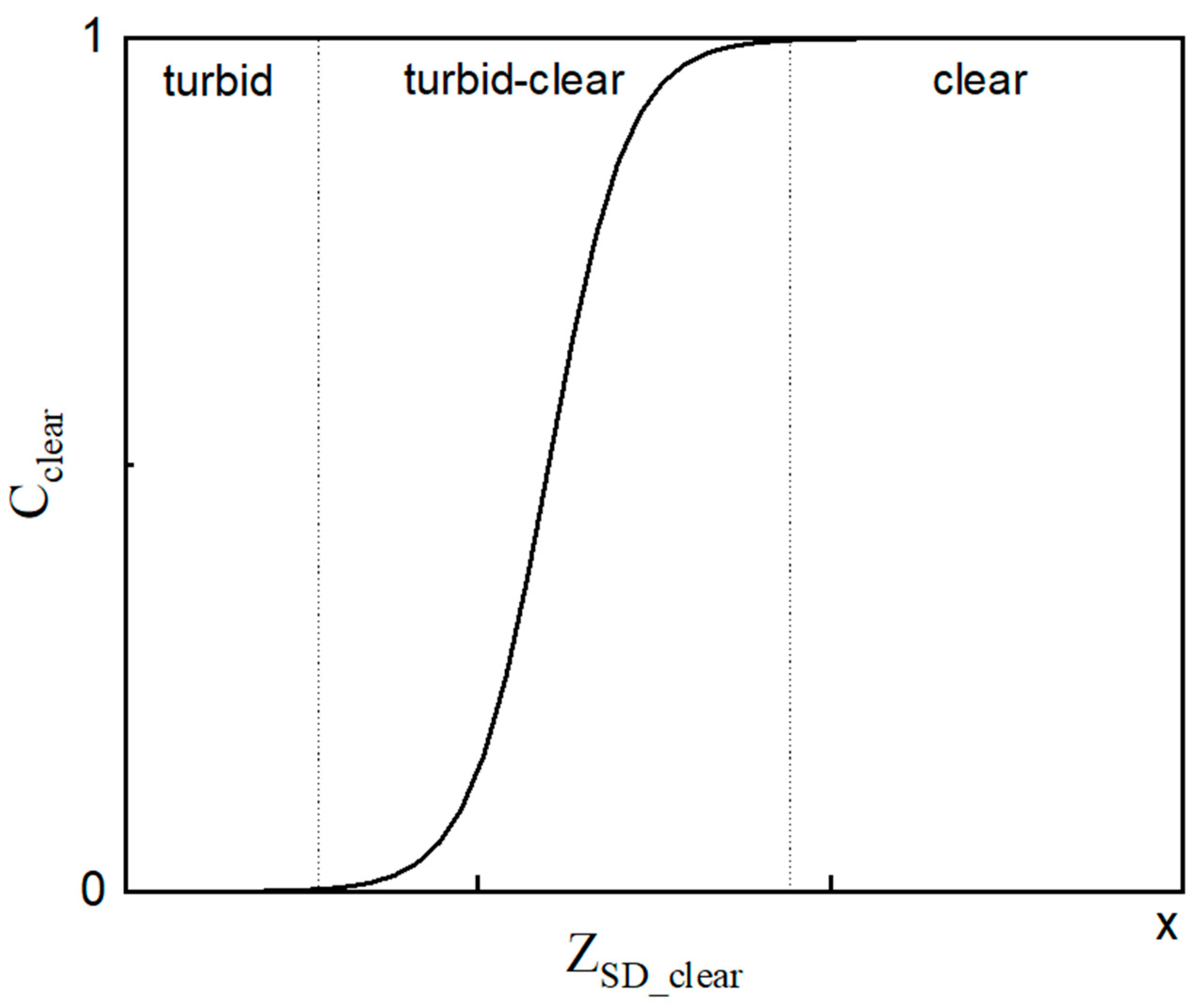
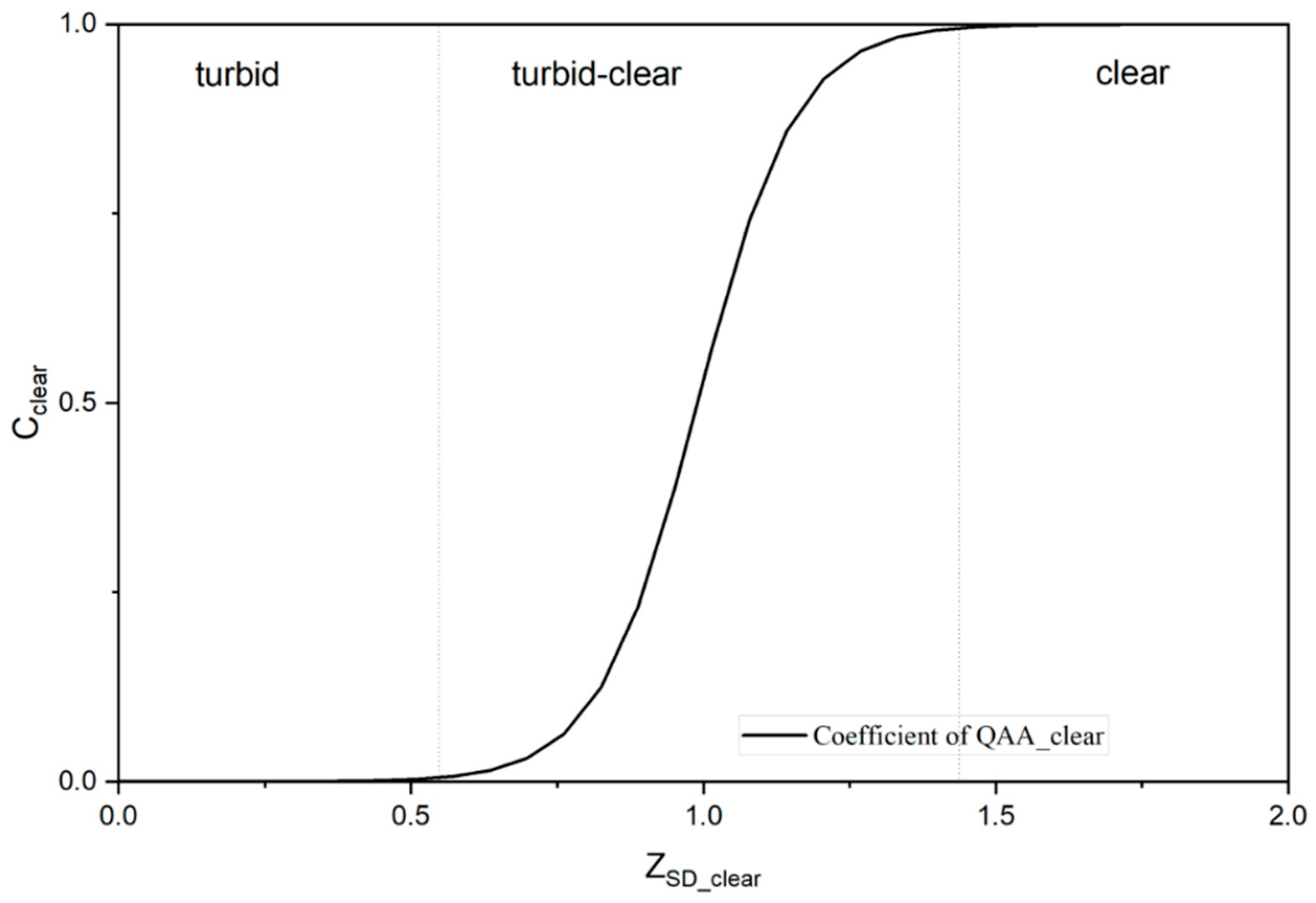
3.2. Developing a Combined Model for Honghu Lake
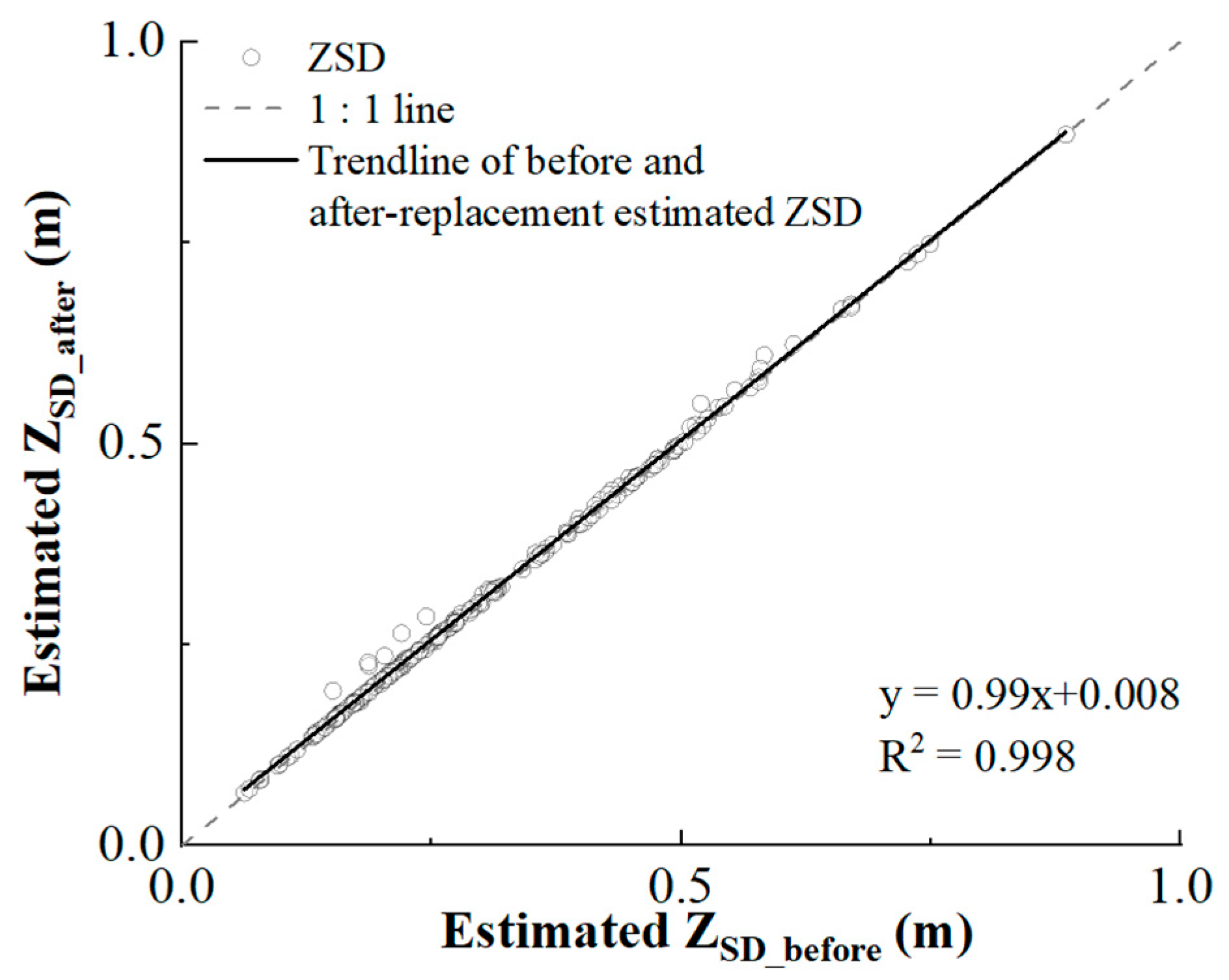
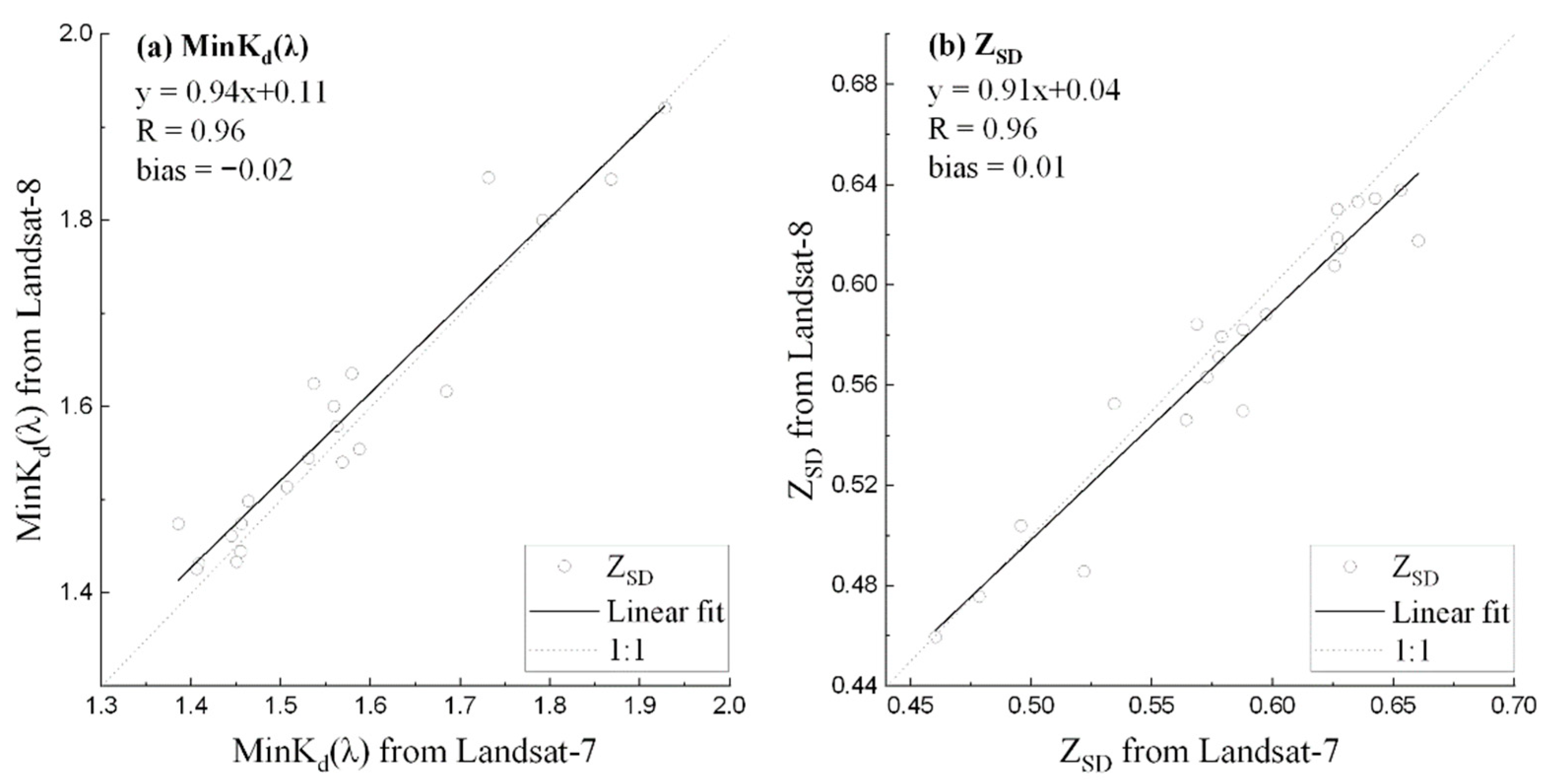
3.3. Applying QAA to Landsat TM and ETM+ Data
3.4. Error Metics and Statistical Indicators
4. Results
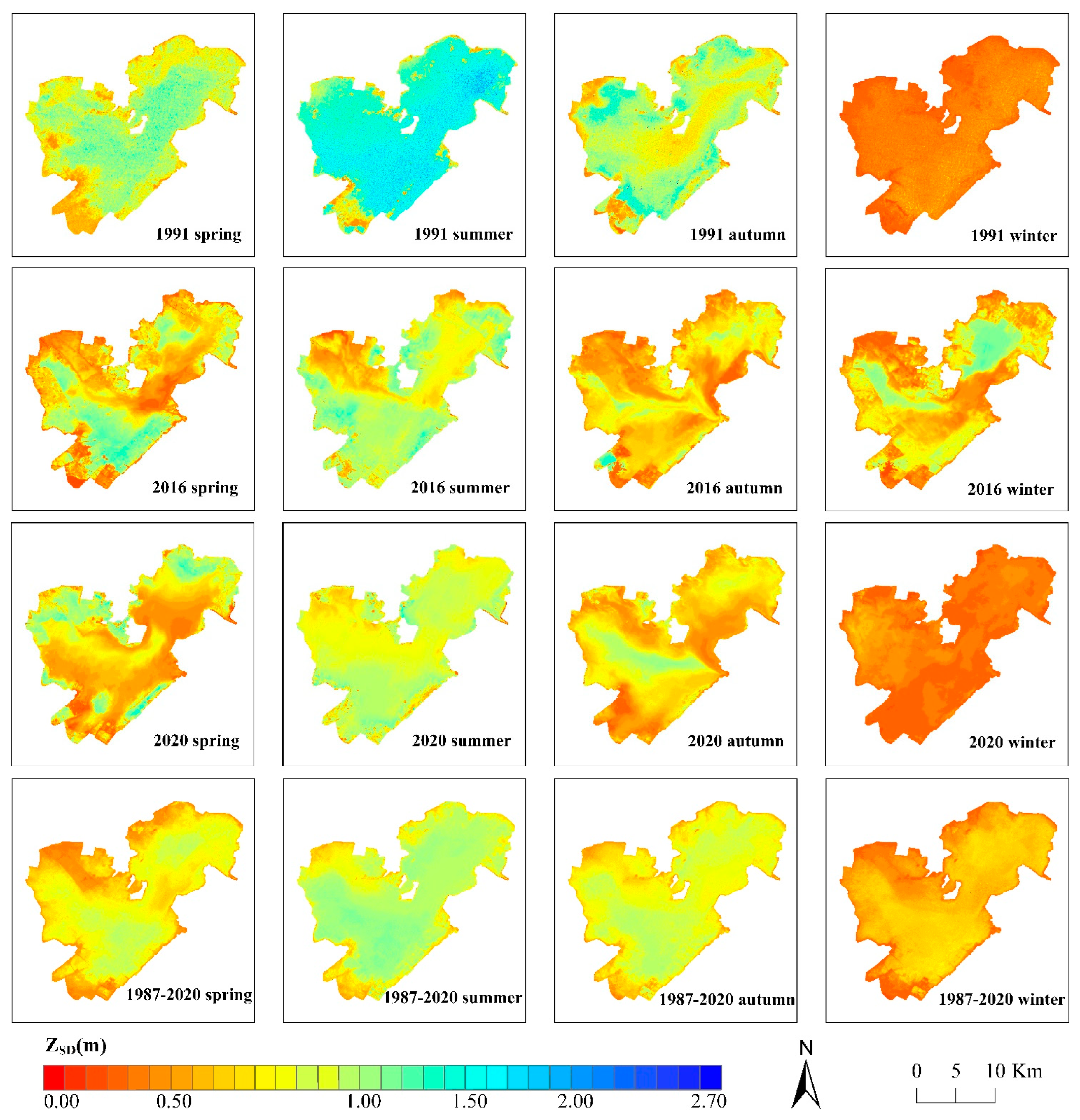
4.1. ZSD Estimation from Landsat Data by QAA_Honghu
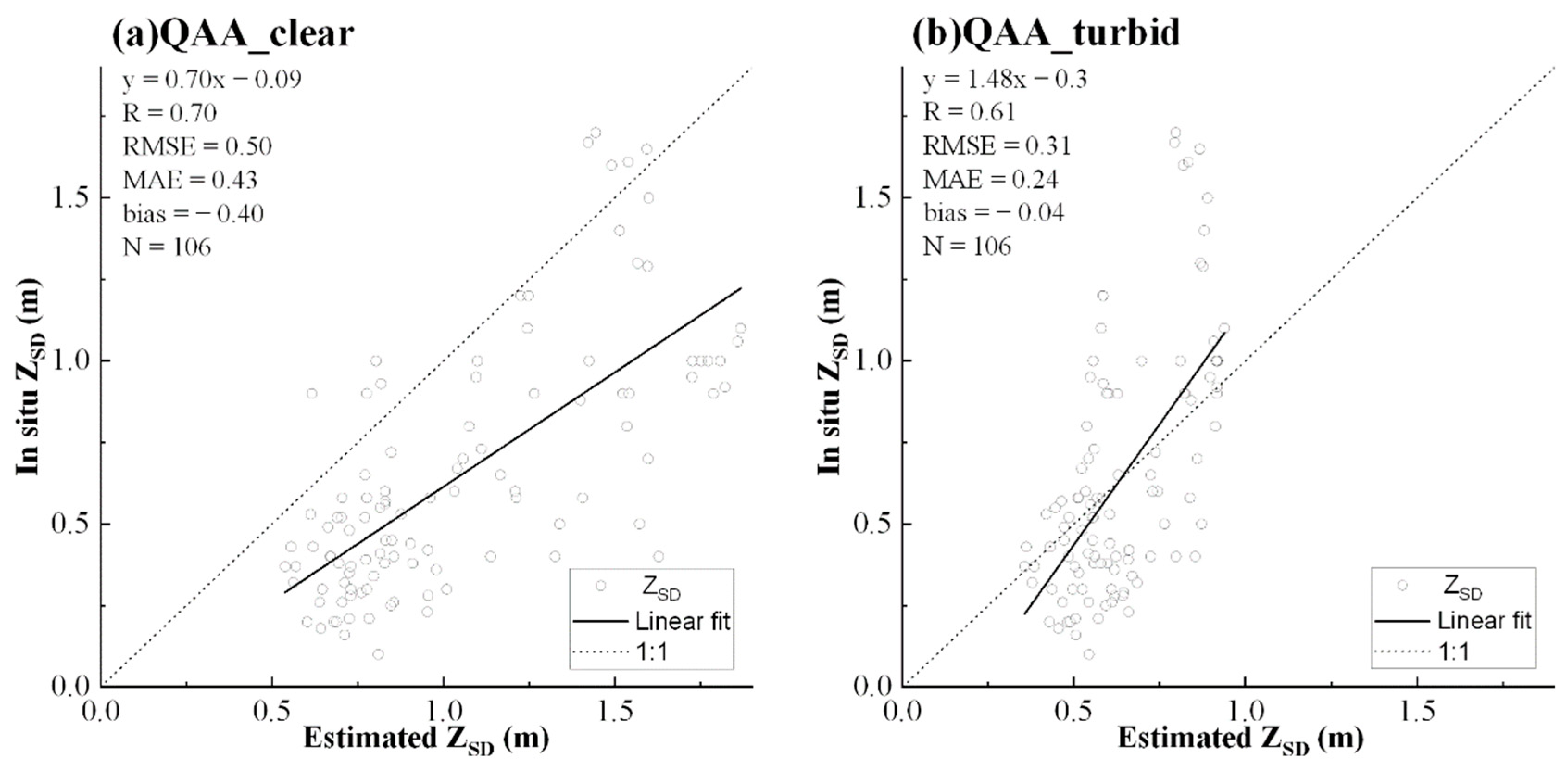
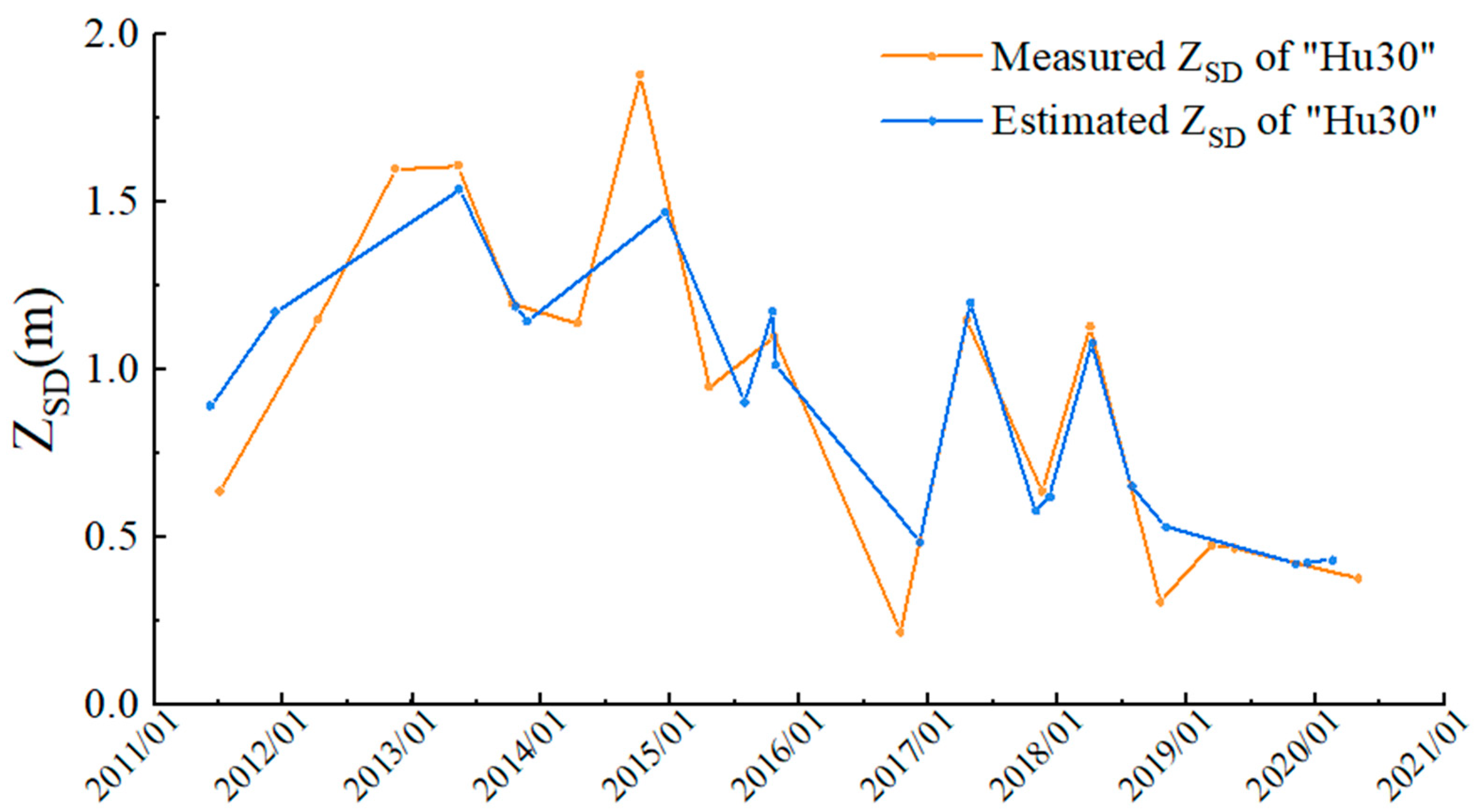
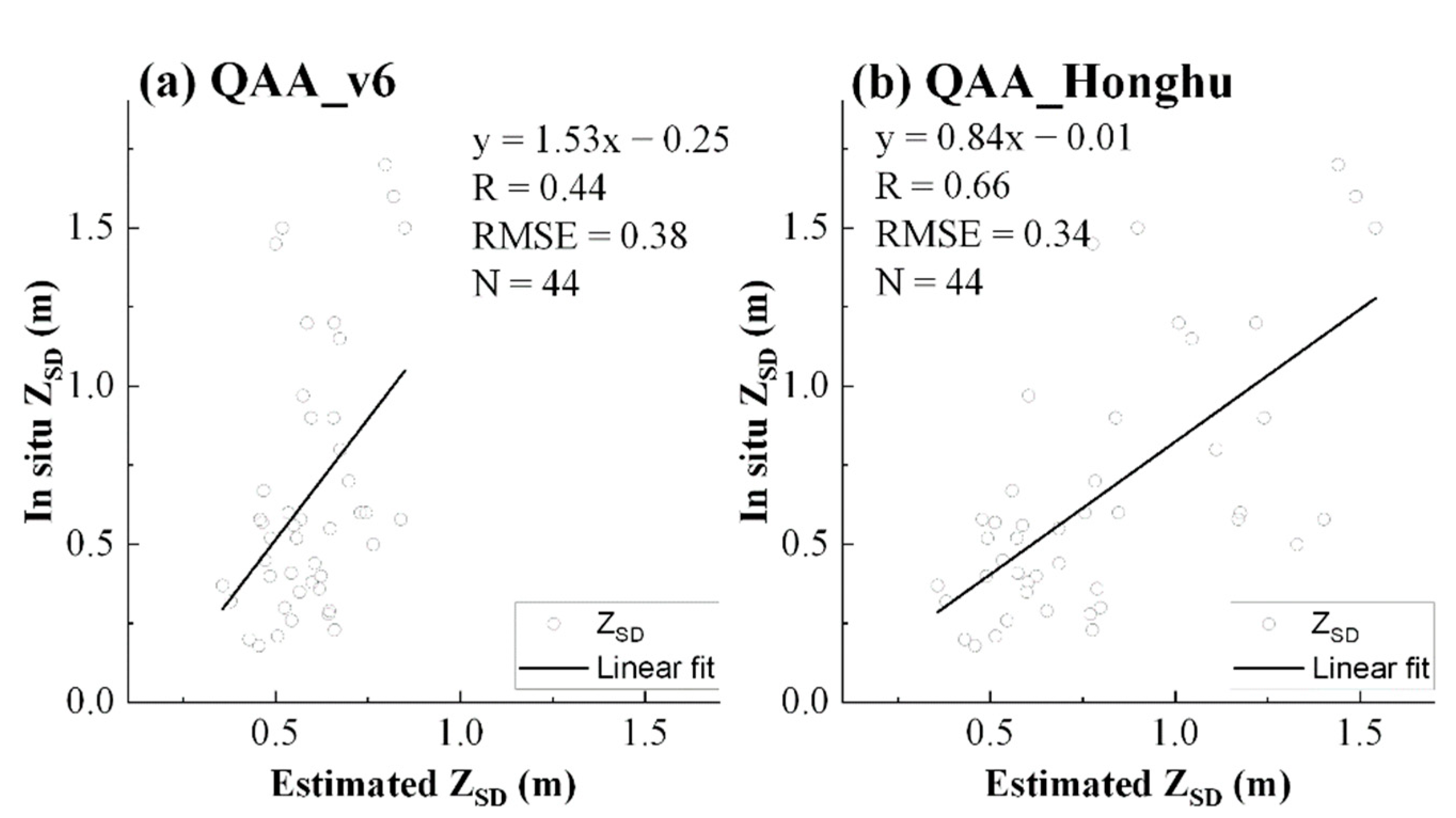
4.2. Validation of QAA_Honghu Using in Situ Measurements
5. Discussion
5.1. The Performance of QAA_Honghu
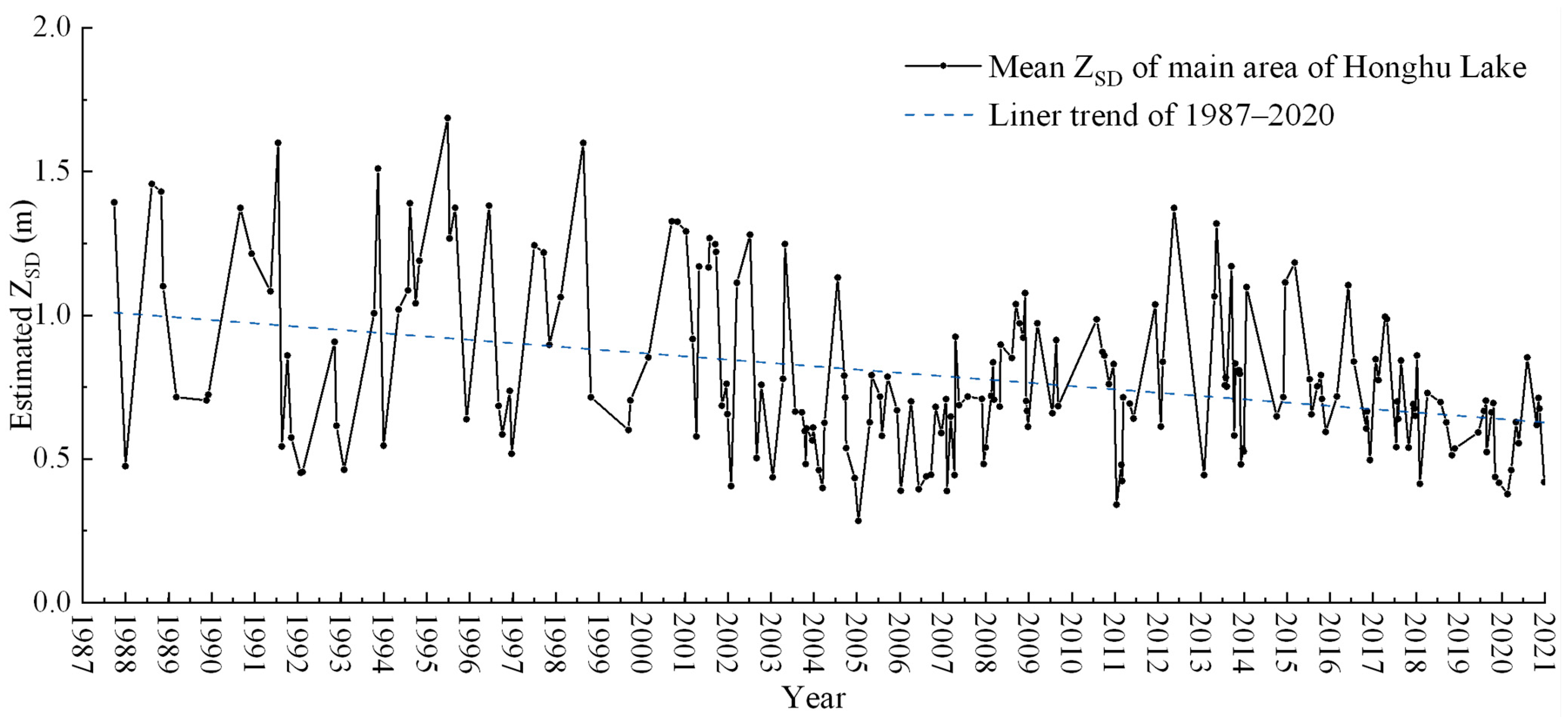
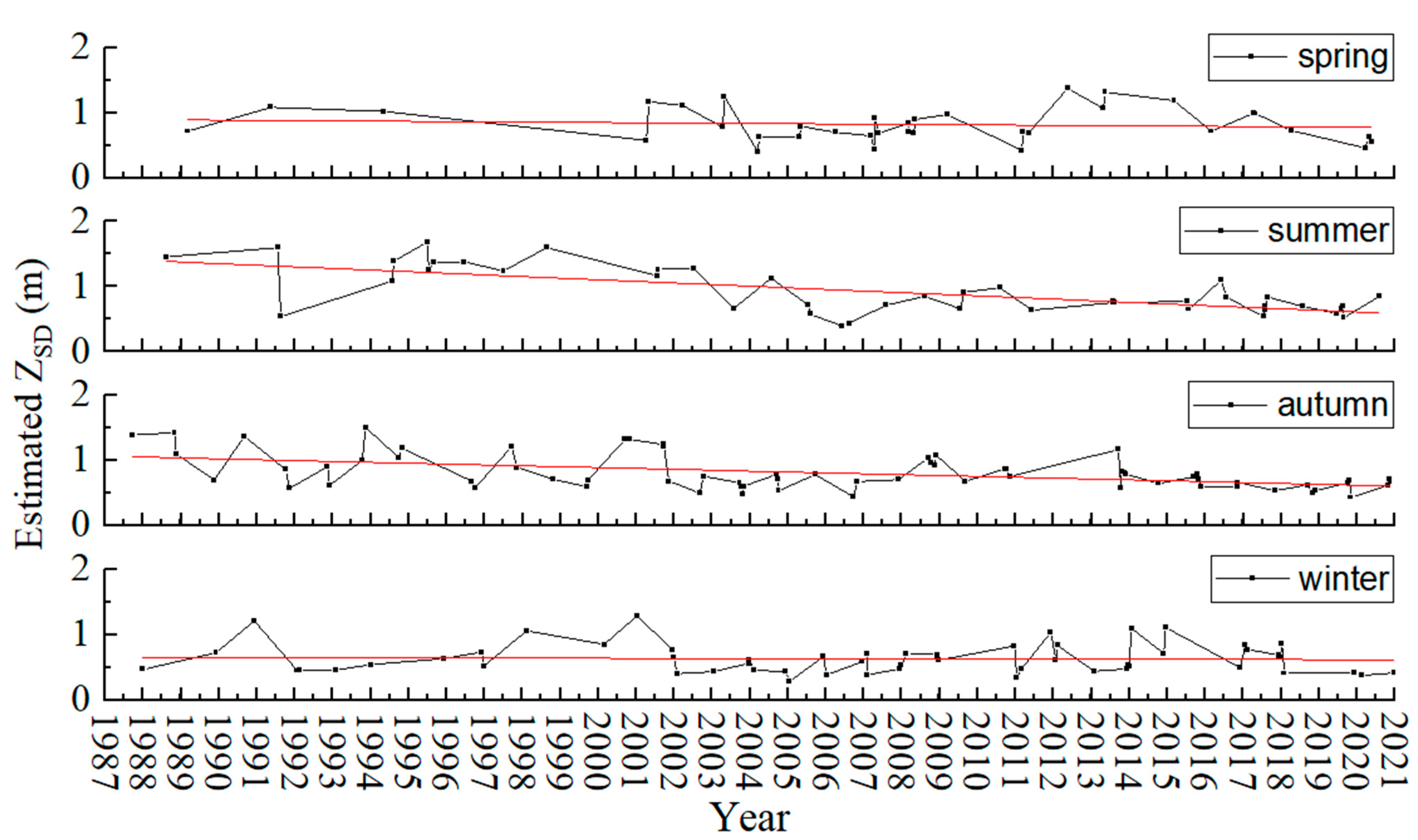
5.2. ZSD Trend of Honghu Lake
5.3. Future Implication
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, Y.; Wang, M.; Qin, B. Wind and submerged aquatic vegetation influence bio-optical properties in large shallow Lake Taihu, China. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosciences 2013, 118, 713–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyce, D.G.; Lewis, M.; Worm, B. Integrating global chlorophyll data from 1890 to 2010. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2012, 10, 840–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Muller-Karger, F.E.; Hu, C. Remote sensing of water clarity in Tampa Bay. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 109, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, I.M.; Loftin, C.S.; Sader, S.A. Combining lake and watershed characteristics with Landsat TM data for remote estimation of regional lake clarity. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 123, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majozi, N.P.; Salama, M.S.; Bernard, S.; Harper, D.M.; Habte, M.G. Remote sensing of euphotic depth in shallow tropical inland waters of Lake Naivasha using MERIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 148, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsch, E.S.; Cardille, J.A.; Koll-Egyed, T.; Fortin, M.-J. Landsat 8 Lake Water Clarity Empirical Algorithms: Large-Scale Calibration and Validation Using Government and Citizen Science Data from across Canada. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Ma, R.; Duan, H.; Pahlevan, N.; Melack, J.; Shen, M.; Xue, K. A machine learning approach to estimate chlorophyll-a from Landsat-8 measurements in inland lakes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 248, 111974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Carder, K.L.; Arnone, R.A. Deriving inherent optical properties from water color: A multiband quasi-analytical algorithm for optically deep waters. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 5755–5772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Lyu, H.; Wang, Y.; Jin, Q.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Fu, Q. An Improved Approach to Retrieve IOPs Based on a Quasi-Analytical Algorithm (QAA) for Turbid Eutrophic Inland Water. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 5177–5189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogashawara, I.; Mishra, D.R.; Nascimento, R.F.F.; Alcântara, E.H.; Kampel, M.; Stech, J.L. Re-parameterization of a quasi-analytical algorithm for colored dissolved organic matter dominant inland waters. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 53, 128–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoge, F.E.; Lyon, P.E. Satellite retrieval of inherent optical properties by linear matrix inversion of oceanic radiance models: An analysis of model and radiance measurement errors. J. Geophys. Res. 1996, 101, 16631–16648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukata, R.P.; Jerome, J.H.; Kondratyev, K.Y.; Pozdnyakov, D.V. Optical Properties and Remote Sensing of Inland and Coastal Waters; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Z.; Shang, S.; Hu, C.; Du, K.; Weidemann, A.; Hou, W.; Lin, J.; Lin, G. Secchi disk depth: A new theory and mechanistic model for underwater visibility. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 169, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, T. Evaluation of a QAA-based algorithm using MODIS land bands data for retrieval of IOPs in the Eastern China Seas. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 13953–13971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Hou, X.; Zheng, Y. Monitoring and understanding the water transparency changes of fifty large lakes on the Yangtze Plain based on long-term MODIS observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 221, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitarch, J.; Bellacicco, M.; Organelli, E.; Volpe, G.; Colella, S.; Vellucci, V.; Marullo, S. Retrieval of Particulate Backscattering Using Field and Satellite Radiometry: Assessment of the QAA Algorithm. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S.; Sun, X.; Zhang, B. Water clarity changes in Lake Taihu over 36 years based on Landsat TM and OLI observations. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng Feng, L.; Yun Mei, L.; Yong, Z.; Deyong, S.; Bin, Y. Validation of a Quasi-Analytical Algorithm for Highly Turbid Eutrophic Water of Meiliang Bay in Taihu Lake, China. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 2492–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Matsushita, B.; Chen, J.; Yoshimura, K.; Fukushima, T. Retrieval of Inherent Optical Properties for Turbid Inland Waters From Remote-Sensing Reflectance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 3761–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Mishra, D.R.; Lee, Z. Bio-Optical Inversion in Highly Turbid and Cyanobacteria-Dominated Waters. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, F.; Mishra, D.R.; Astuti, I.; Rodrigues, T.; Alcântara, E.; Imai, N.N.; Barbosa, C. Parametrization and calibration of a quasi-analytical algorithm for tropical eutrophic waters. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 121, 28–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, F.; Sokoletsky, L.; Sun, X. Validation and Calibration of QAA Algorithm for CDOM Absorption Retrieval in the Changjiang (Yangtze) Estuarine and Coastal Waters. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Matsushita, B.; Setiawan, F.; Vundo, A. An improved algorithm for estimating the Secchi disk depth from remote sensing data based on the new underwater visibility theory. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 152, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lee, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, J.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.; Qin, B.; Sun, Z. Remote Sensing of Secchi Depth in Highly Turbid Lake Waters and Its Application with MERIS Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Lei, S.H.; Li, Y.M.; Lyu, H.; Xu, J.F.; Dong, X.Z.; Wang, R.; Yang, Z.Q.; Li, J.C. Retrieval of Secchi Disk Depth in Turbid Lakes from GOCI Based on a New Semi-Analytical Algorithm. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somasundaram, D.; Zhang, F.; Ediriweera, S.; Wang, S.; Yin, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, B. Patterns, Trends and Drivers of Water Transparency in Sri Lanka Using Landsat 8 Observations and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Song, K.; Mu, G.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, J.; Ren, J. Evaluation of the Quasi-Analytical Algorithm (QAA) for Estimating Total Absorption Coefficient of Turbid Inland Waters in Northeast China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 4022–4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najah, A.; Al-Shehhi, M.R. Performance of the Ocean Color Algorithms: QAA, GSM, and GIOP in Inland and Coastal Waters. Remote Sens. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 4, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, S.; Dong, Q.; Lee, Z.; Li, Y.; Xie, Y.; Behrenfeld, M. MODIS observed phytoplankton dynamics in the Taiwan Strait: An absorption-based analysis. Biogeosciences 2011, 8, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; He, X.; Liu, Z.; Lin, N.; Xing, Q.; Pan, D. Sun glint correction with an inherent optical properties data processing system. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 42, 617–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, M.A.; Simis, S.G.H.; Selmes, N. Complementary water quality observations from high and medium resolution Sentinel sensors by aligning chlorophyll-a and turbidity algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 265, 112651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Z.; Shang, S.; Qi, L.; Yan, J.; Lin, G. A semi-analytical scheme to estimate Secchi-disk depth from Landsat-8 measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 177, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhellemont, Q. Adaptation of the dark spectrum fitting atmospheric correction for aquatic applications of the Landsat and Sentinel-2 archives. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 225, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhellemont, Q.; Ruddick, K. Atmospheric correction of metre-scale optical satellite data for inland and coastal water applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 216, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jukić, D.; Scitovski, R. Solution of the least-squares problem for logistic function. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2003, 156, 159–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Carpenter, D.J.; Carpenter, S.M. Modeling inland water quality using Landsat data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1983, 13, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloiber, S.M.; Brezonik, P.L.; Bauer, M.E. Application of Landsat imagery to regional-scale assessments of lake clarity. Water Res. 2002, 36, 4330–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Liu, G.; Wang, Q.; Wen, Z.; Lyu, L.; Du, Y.; Sha, L.; Chong, F. Quantification of lake clarity in China using Landsat OLI imagery data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 243, 111800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.; Li, N. Remote sensing estimation of water clarity for various lakes in China. Water Res. 2021, 192, 116844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.P.; Kovalskyy, V.; Zhang, H.K.; Vermote, E.F.; Yan, L.; Kumar, S.S.; Egorov, A. Characterization of Landsat-7 to Landsat-8 reflective wavelength and normalized difference vegetation index continuity. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackleson, S.G. Diffuse attenuation in optically-shallow water: Effects of bottom reflectance. Ocean. Opt. XIII 1997, 2963, 326–330. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, A.; Gao, J.; Ahmad, W.; Neil, D.; Bell, P. A composite DOP approach to excluding bottom reflectance in mapping water parameters of shallow coastal zones from TM imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 92, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, S.; Qin, W.; Lu, T.; Li, J.; Cao, Y. A Semi-Empirical Chlorophyll-a Retrieval Algorithm Considering the Effects of Sun Glint, Bottom Reflectance, and Non-Algal Particles in the Optically Shallow Water Zones of Sanya Bay Using SPOT6 Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, R.; Gianey, H.K. Comprehensive review on supervised machine learning algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Machine Learning and Data Science (MLDS), Noida, India, 14–15 December 2017; pp. 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Ban, X.; Yu, C.; WeiI, K.; Du, Y. Analysis of Influence of Enclosure Aquaculture on Water Quality of Honghu Lake. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 33, 125–129. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Wang, X.; EnHua, L.; Cai, X.; Deng, F. Water Quality Change Characteristics and Driving Factors of Honghu Lake before and after Ecological Restoration. Wetl. Sci. 2012, 10, 188–193. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Wang, H.; Wand, H.; Liang, Y.; Li, X. Lake Demolition Monitoring and Estimation of Ecological Environment Benefits in Jianghan Plain: A Case Study of the Honghu Lake. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2020, 29, 2760–2769. [Google Scholar]
- LI, E.; Yang, C.; Cai, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X. Plant Diversity and Protection Measures in Honghu Wetland. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2021, 30, 623–635. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Zhou, S.; Huang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Li, R. The Impact of Land Use Changes on Flood Disaster in the Honghu Lake Watershed. Adv. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 63–66. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, H.; Qin, B.; Liu, G.; Li, Y. Long-term remote monitoring of total suspended matter concentration in Lake Taihu using 250 m MODIS-Aqua data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 164, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Feng, L.; Duan, H.; Chen, X.; Sun, D.; Shi, K. Fifteen-year monitoring of the turbidity dynamics in large lakes and reservoirs in the middle and lower basin of the Yangtze River. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 190, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Lee, Z.; Ma, R.; Yu, K.; Li, D.; Shang, S. Moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) observations of cyanobacteria blooms in Taihu Lake. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, Y.; Lyu, H.; Wang, S.; Du, C.; Huang, C. An improved land target-based atmospheric correction method for Lake Taihu. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 9, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, W.J.; Sterckx, S.; Montes, M.J.; De Keukelaere, L.; Knaeps, E. Atmospheric correction for inland waters. In Bio-Optical Modeling and Remote Sensing of Inland Waters; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 69–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Cao, W.; Li, D.; Lou, X.; Fan, K. An Exponential Algorithm for Bottom Reflectance Retrieval in Clear Optically Shallow Waters from Multispectral Imagery without Ground Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Image Type | Image Date | Sampling Date |
|---|---|---|
| Landsat-8 | 12 May 2013 | 9 May 2013 |
| Landsat-7 | 11 October 2013 | 9 October 2013 |
| Landsat-8 | 6 October 2014 | 7 October 2014 |
| Landsat-8 | 25 October 2015 | 21 October 2015 |
| Landsat-7 | 13 April 2017 | 17 April 2017 |
| Landsat-8 | 8 April 108 | 2 April 2018 |
| Landsat-8 | 1 August 2019 | 26 July 2019 |
| Landsat-8 | 5 November 2019 | 14 November 2019 |
| Landsat-8 | 29 April 2020 | 29 April 2020 |
| Step | Calculation | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||
| 2 | , where =0.089, =0.1245 | |
| 3 | QAA_clear () | QAA_turbid (Else) |
| 4 | ||
| 5 | ||
| 6 | ||
| 7 | ||
| 8 | ||
| 9 | ||
| 10 | ||
| Band Wavelength (nm) | TM | ETM+ | OLI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Band 1 | 486 | 479 | 443 |
| Band 2 | 571 | 561 | 481 |
| Band 3 | 668 | 661 | 554 |
| Band 4 | 656 |
| Landsat-7 Date | Landsat-8 Date |
|---|---|
| 23 July 2013 | 31 July 2013 |
| 30 December 2013 | 22 December 2013 |
| 17 October 2015 | 25 October 2014 |
| 4 November 2016 | 12 November 2016 |
| 9 December 2017 | 17 December 2017 |
| 25 August 2019 | 17 August 2019 |
| 15 November 2020 | 7 November 2020 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, M.; Xiao, F.; Wang, Z.; Feng, Q.; Ban, X.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, Z. An Improved QAA-Based Method for Monitoring Water Clarity of Honghu Lake Using Landsat TM, ETM+ and OLI Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3798. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153798
Chen M, Xiao F, Wang Z, Feng Q, Ban X, Zhou Y, Hu Z. An Improved QAA-Based Method for Monitoring Water Clarity of Honghu Lake Using Landsat TM, ETM+ and OLI Data. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(15):3798. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153798
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Miaomiao, Fei Xiao, Zhou Wang, Qi Feng, Xuan Ban, Yadong Zhou, and Zhengzheng Hu. 2022. "An Improved QAA-Based Method for Monitoring Water Clarity of Honghu Lake Using Landsat TM, ETM+ and OLI Data" Remote Sensing 14, no. 15: 3798. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153798
APA StyleChen, M., Xiao, F., Wang, Z., Feng, Q., Ban, X., Zhou, Y., & Hu, Z. (2022). An Improved QAA-Based Method for Monitoring Water Clarity of Honghu Lake Using Landsat TM, ETM+ and OLI Data. Remote Sensing, 14(15), 3798. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153798