Influence of Plasma Sheath’s Velocity Field on ISAR Imaging of Hypersonic Target
Abstract
:1. Introduction
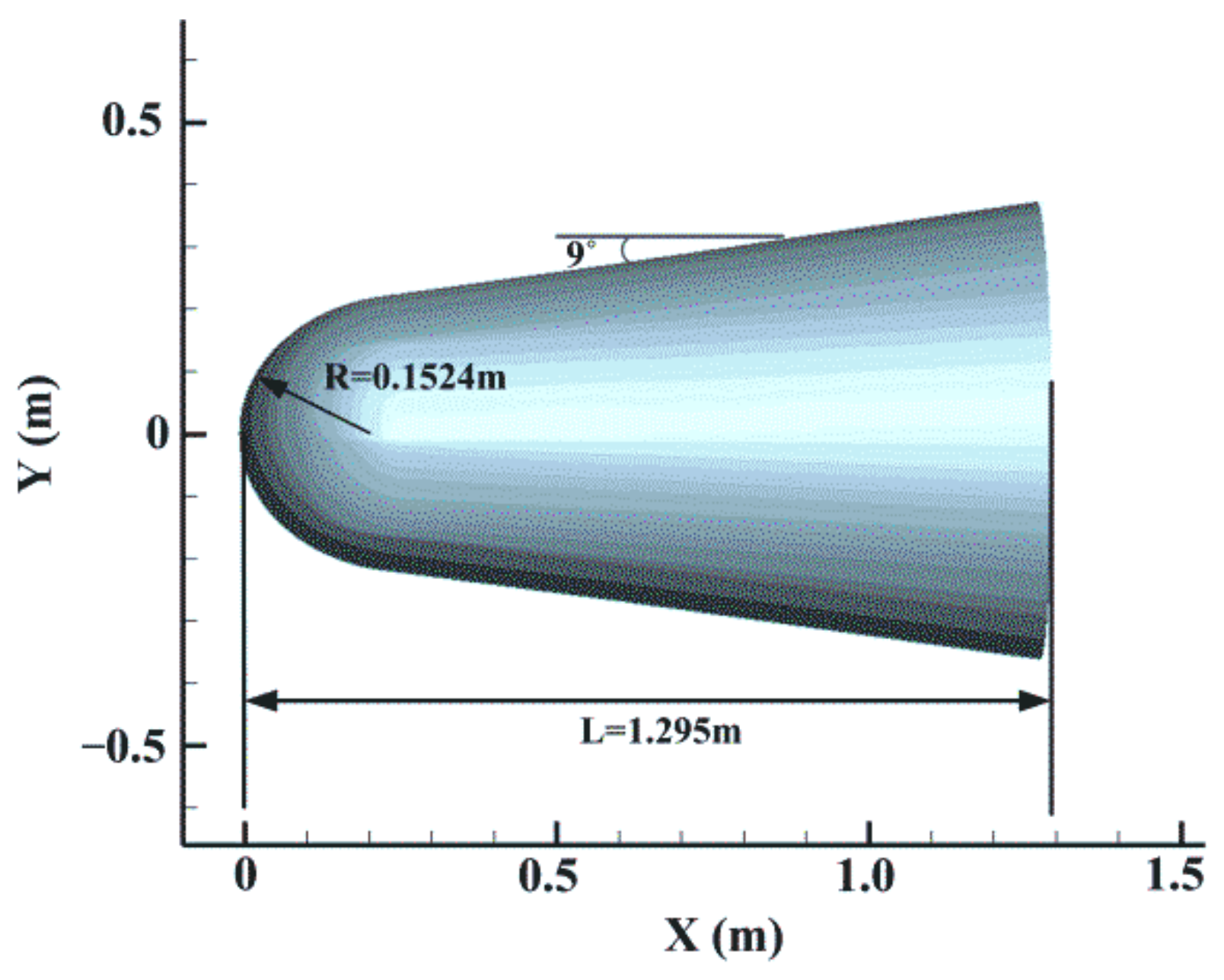
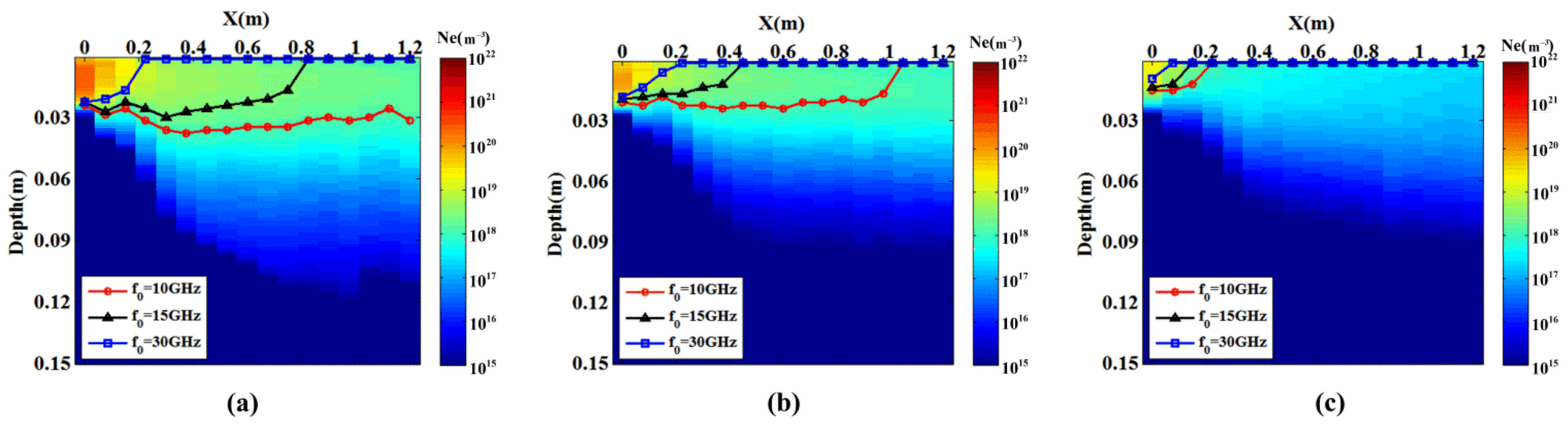
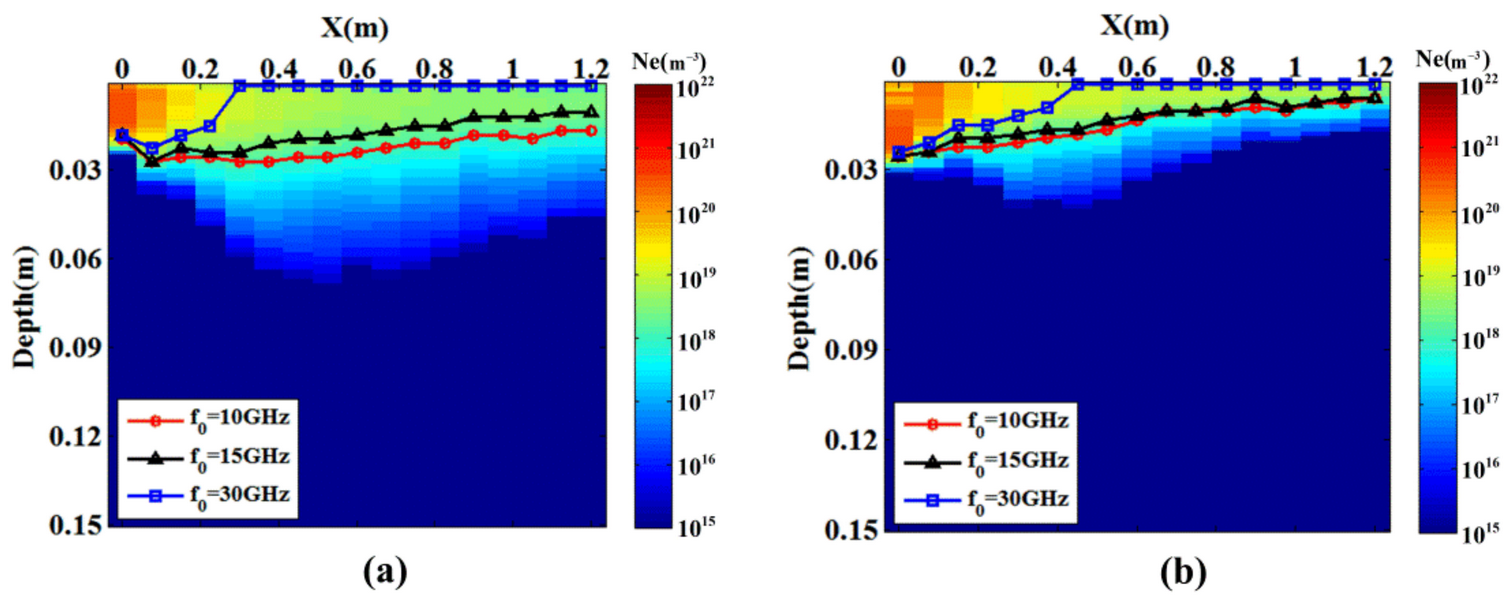
2. Distribution Characteristics of Plasma Sheath
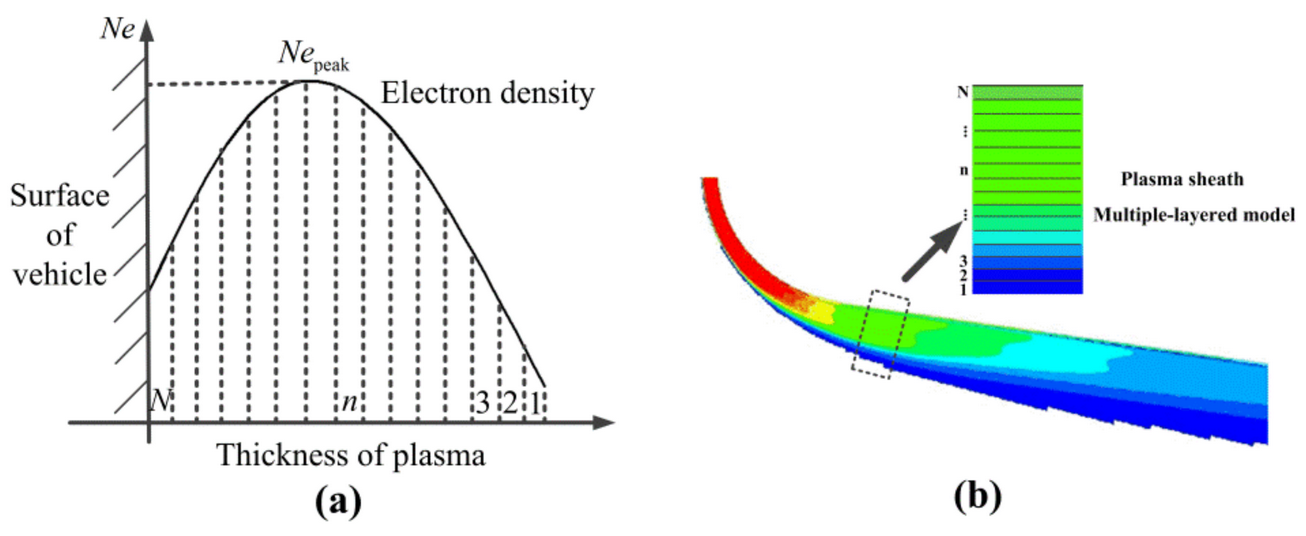
2.1. Electron Density of Plasma Sheath
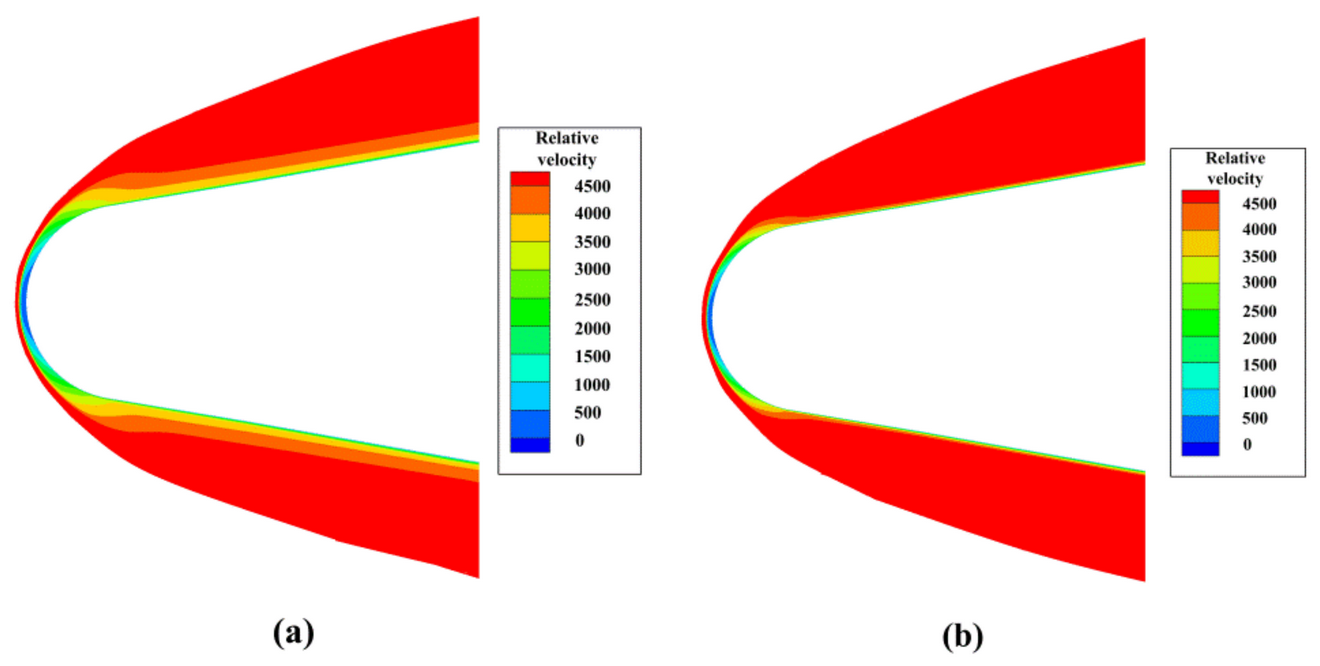
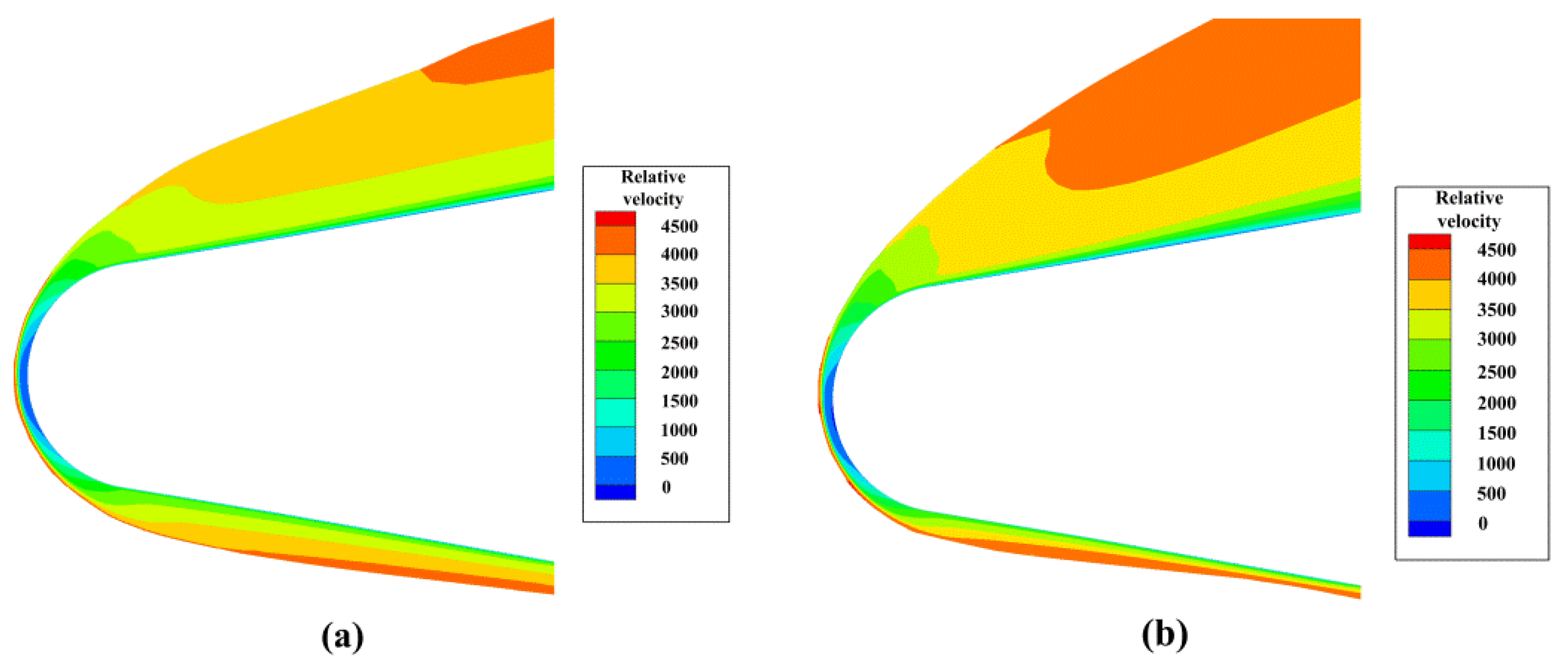
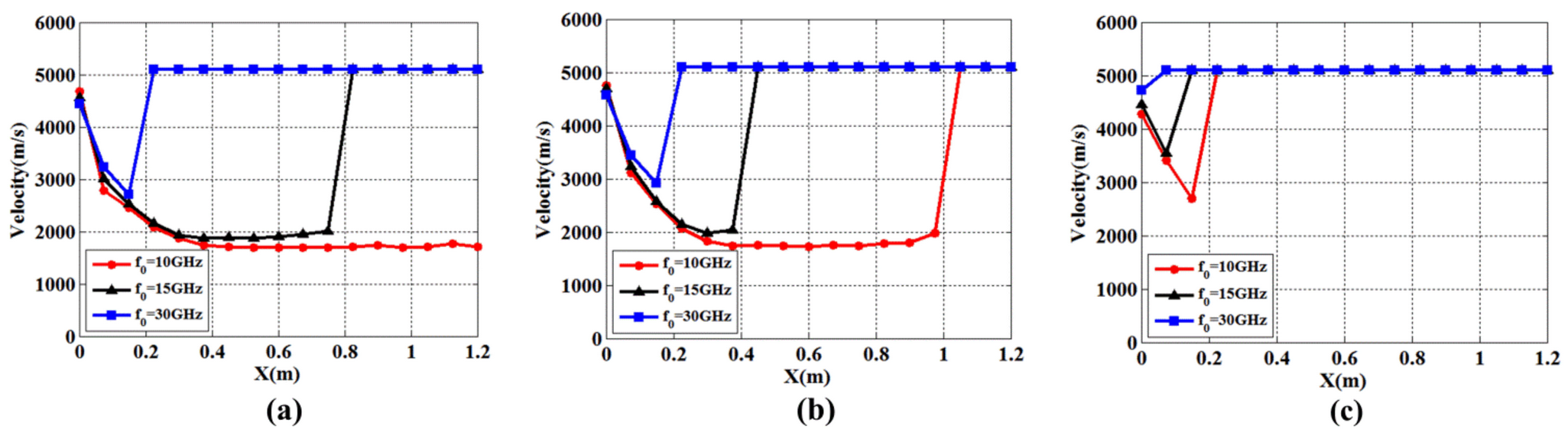
2.2. Velocity Field of the Plasma Sheath
3. Reflection of EM Wave in Plasma Sheath
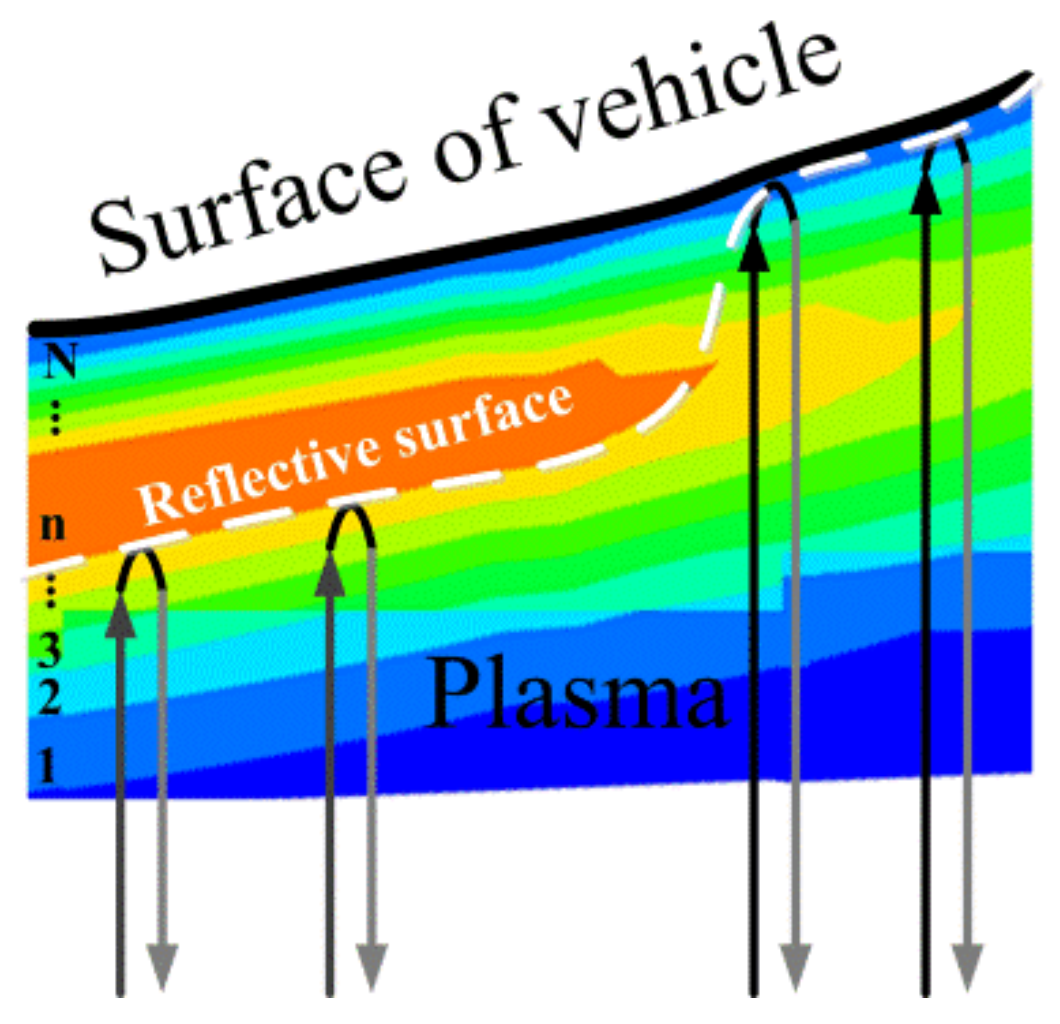
3.1. Reflective Surface in the Plasma Sheath
3.2. Velocities of the Reflective Surface
4. Influence of Plasma Sheath on One-Dimensional Range Profile
4.1. The Stop-and-Go Model
4.2. The Intra-Pulse Motion Model
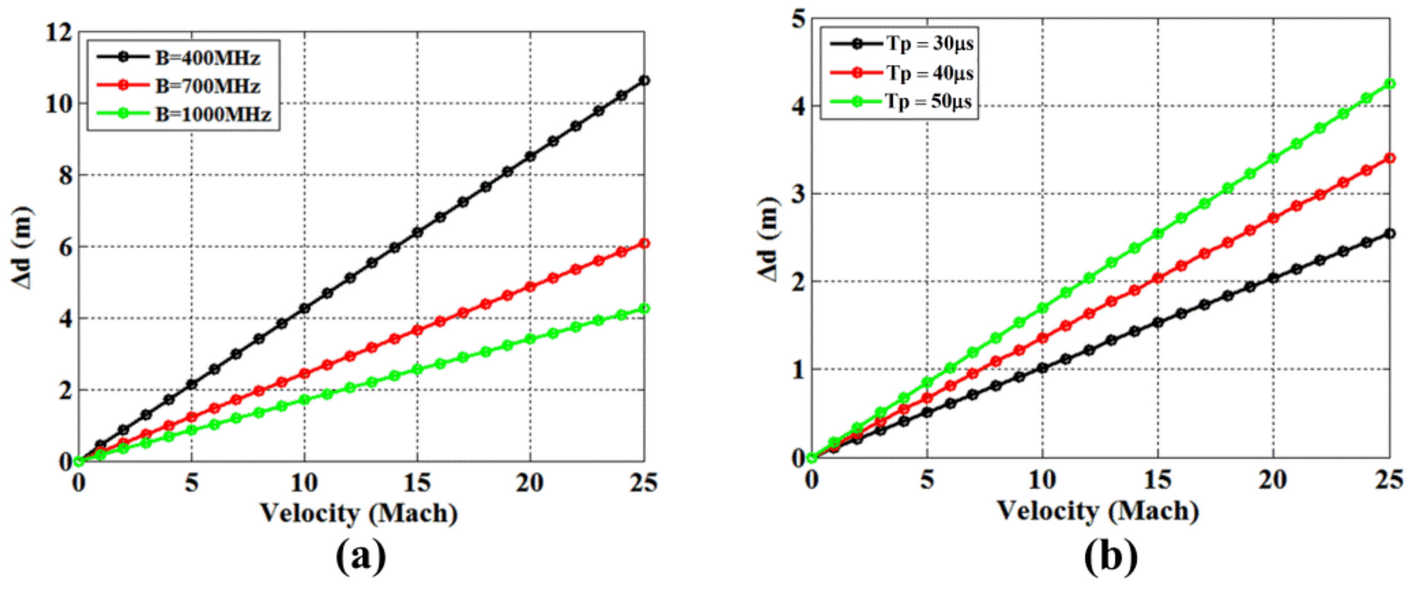
4.3. The Displacement and Diffusion in One-Dimensional Range Profile
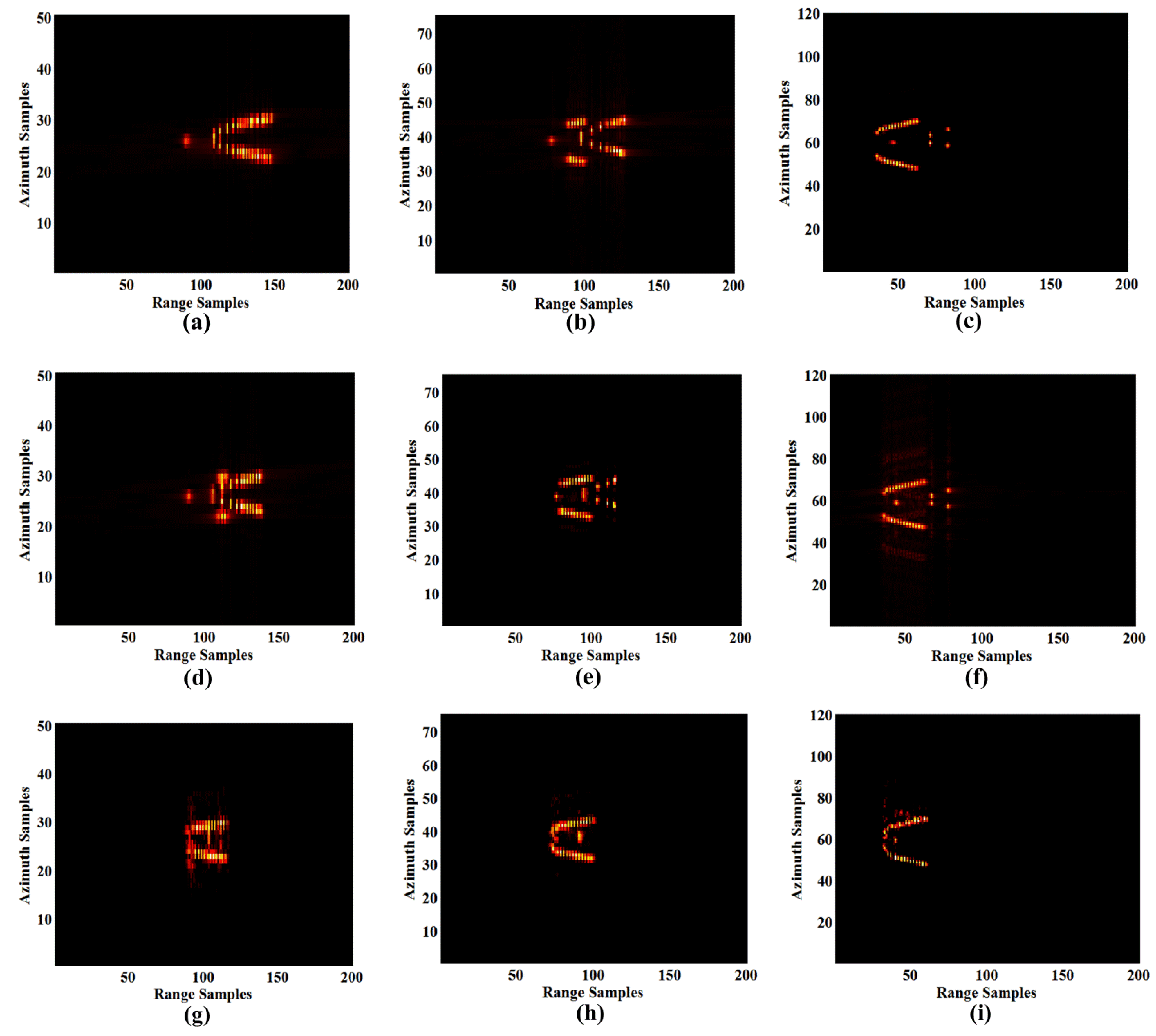
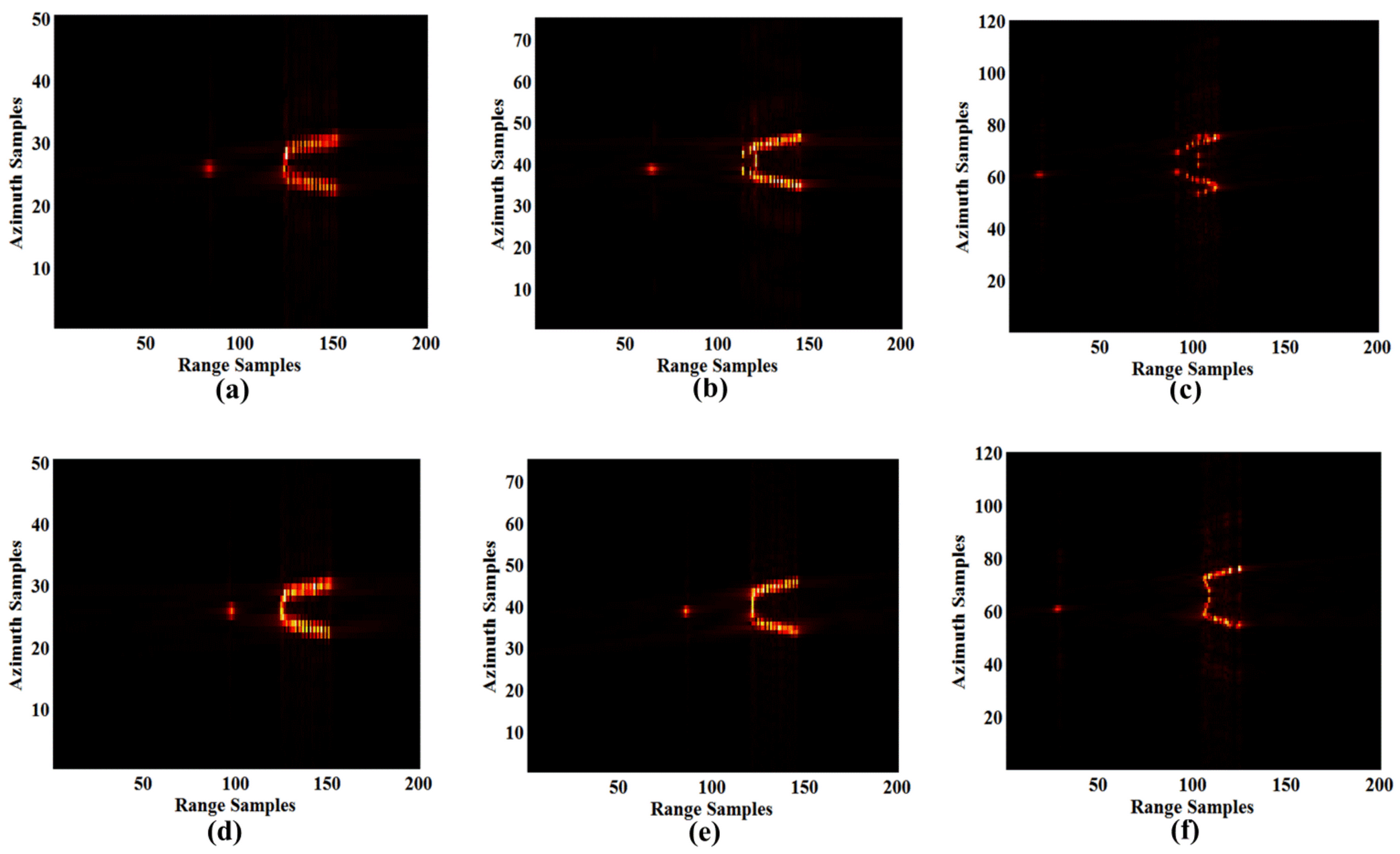
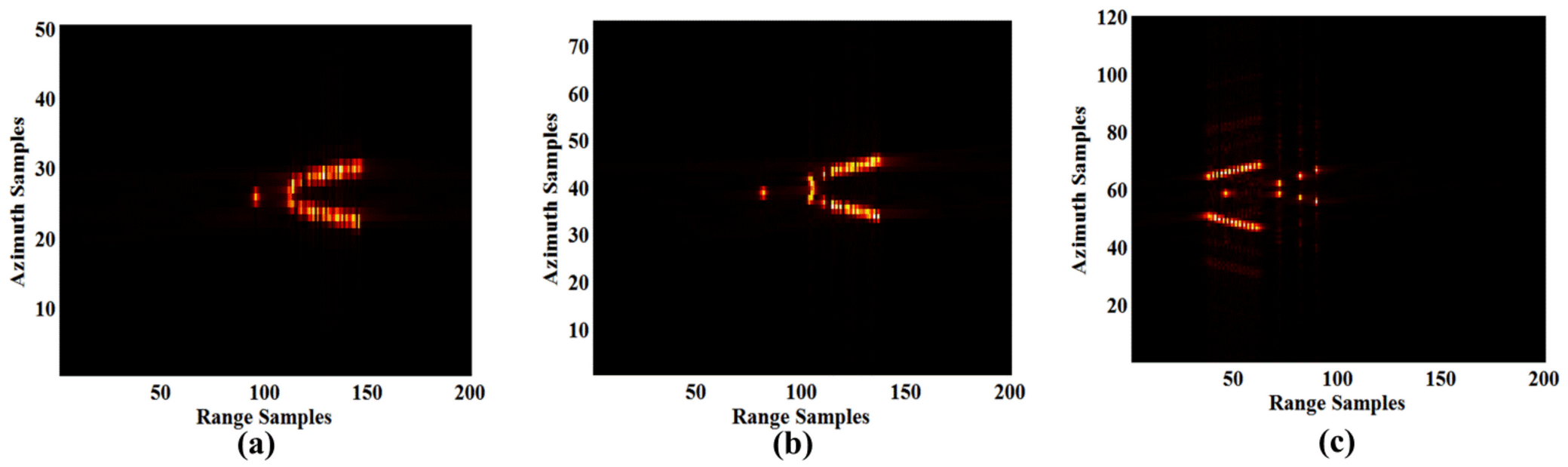
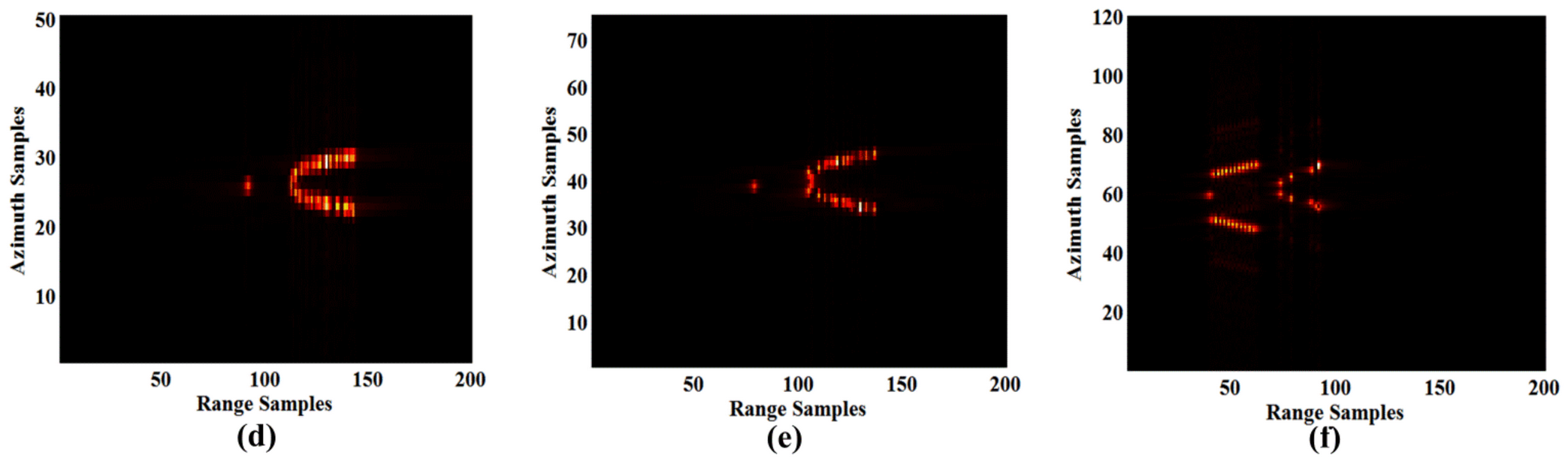
5. Simulation Analysis on ISAR Imaging
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- EM waves cannot penetrate plasma if the plasma frequency is greater than their own. For plasma sheaths of hypersonic targets with non-uniform electron density distribution, EM waves are reflected by plasma layers of varying depths to form an irregular reflective surface.
- (2)
- The incident depth depends on two frequencies, the frequency of incident EM waves and the plasma frequency determined by the electron density. Changes in flight scenes could alter the distribution of electron density, thus affecting the incident depth. Therefore, the flight scene and radar frequency selection both impact the distribution of reflective surfaces.
- (3)
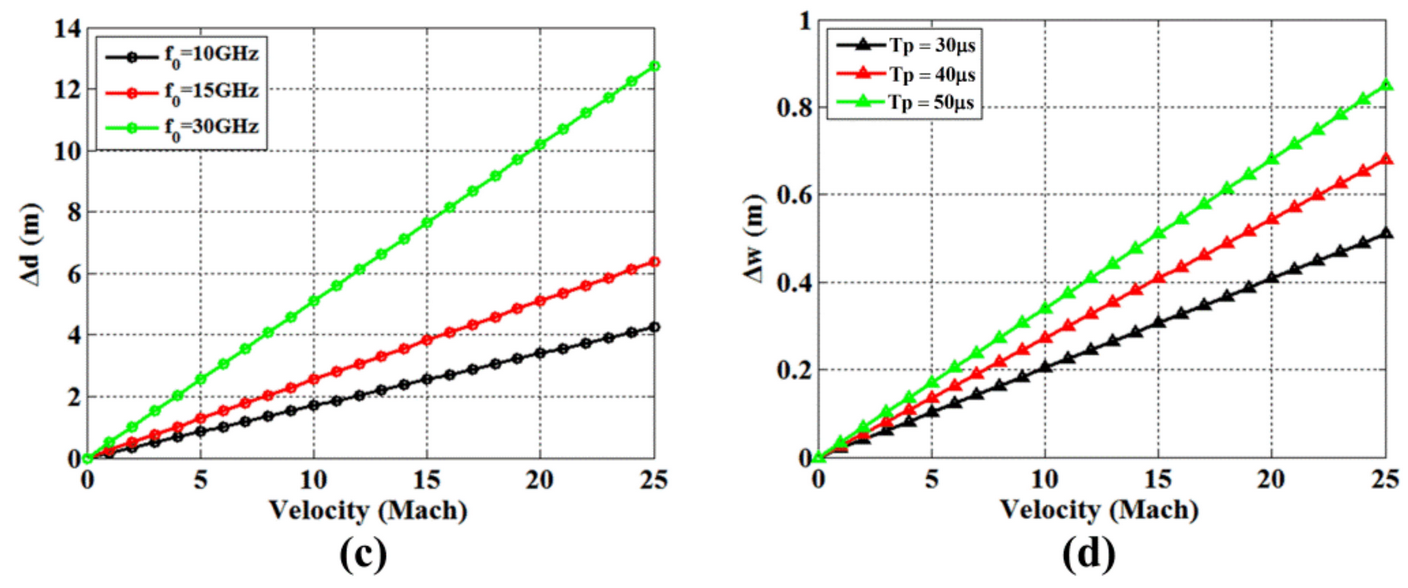
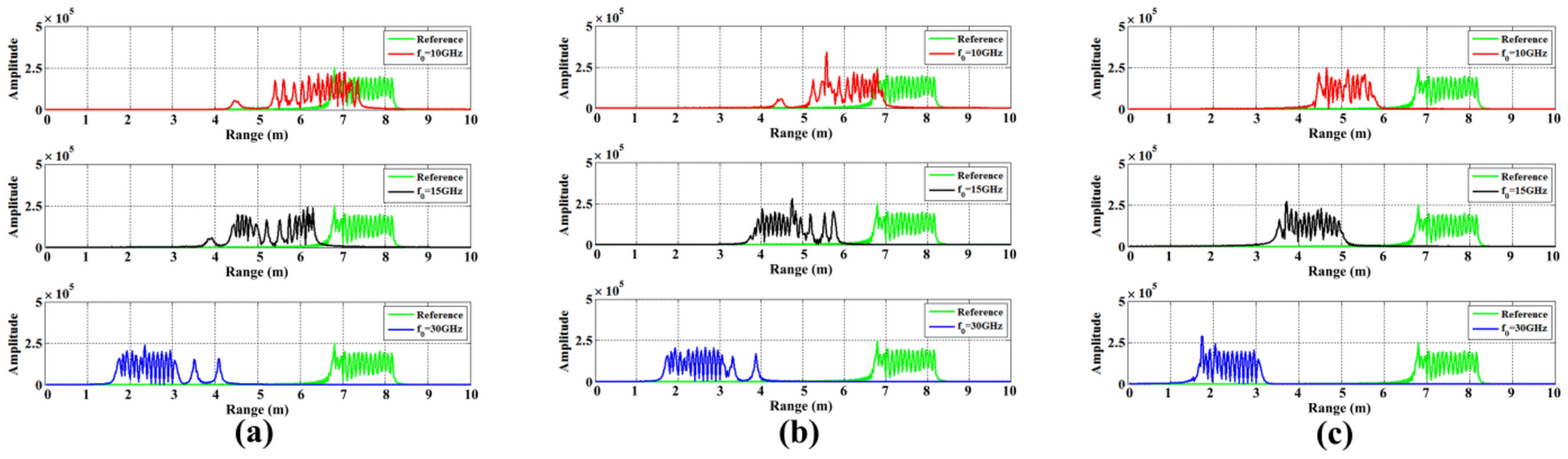
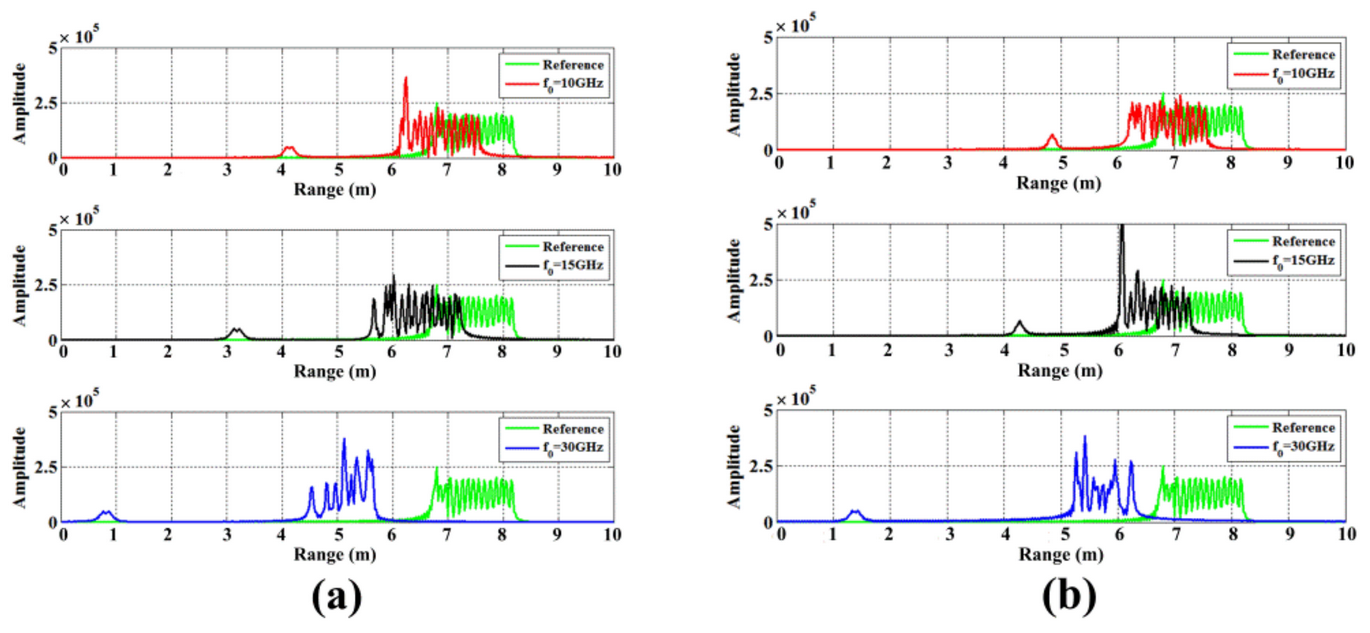
- The velocity of the reflective surface is coupled to the radar echo, resulting in varying degrees of displacement and diffusion of the scattering points along with the one-dimensional range profile. Displacement and diffusion have a positive correlation with the coupled velocity and frequency of the EM wave.
- (4)
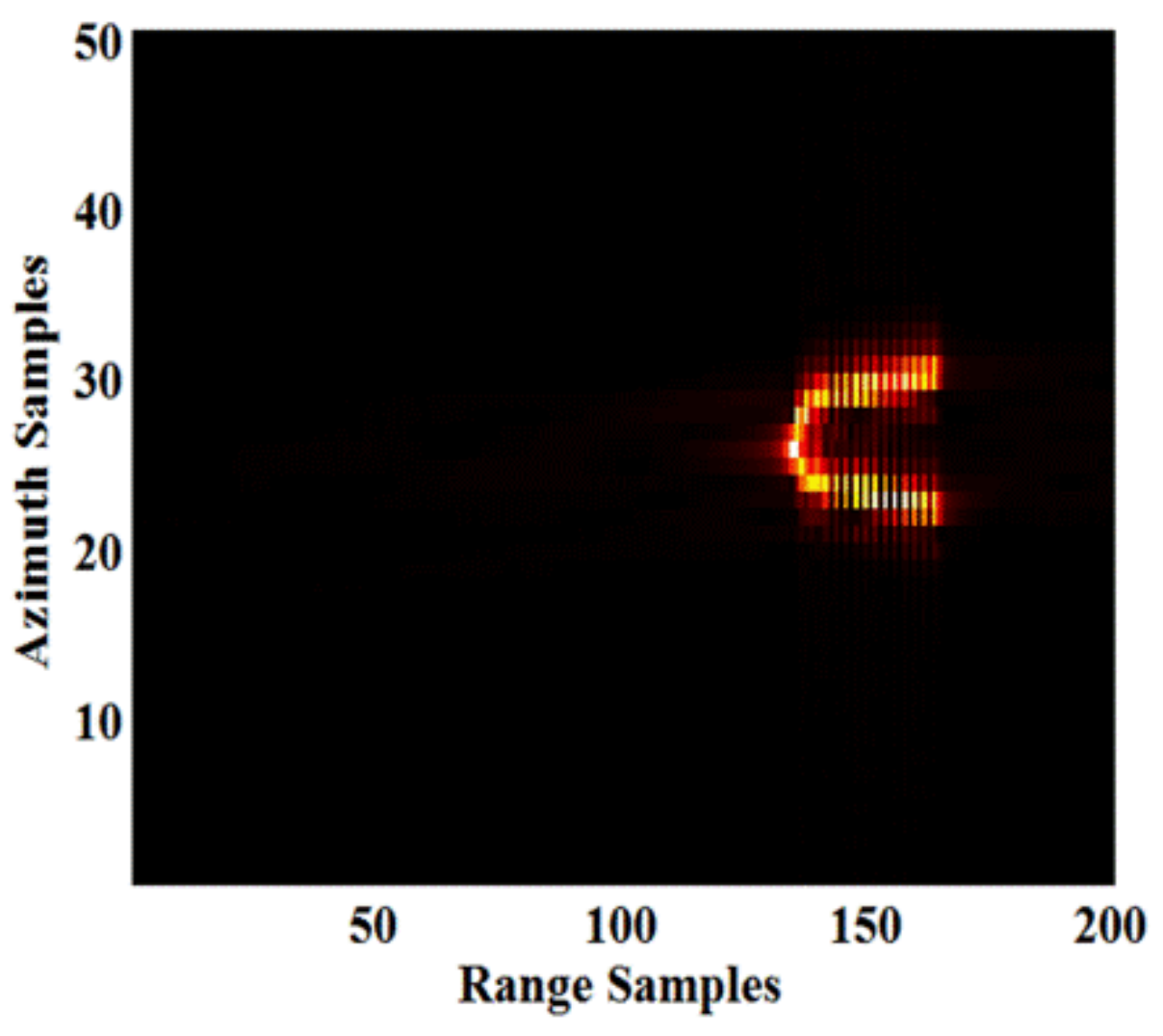
- The velocity of the reflective surface stretches the range dimension of the ISAR image. The stagnation point and scattering points in EM-penetrated regions typically experience the greatest displacement.
- (5)
- The X-band radar provides the best imaging quality for scenes 4, 5, 6, and 7, whereas Ka-band is appropriate for scenes 1, 2, and 3. The ISAR image quality of the X-band radar is more stable in all scenes, whereas the imaging performance of the Ka-band radar is scene-dependent.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gupta, R.N.; Lee, K.P.; Moss, J.N.; Sutton, K. Viscous Shock-Layer Solutions with Coupled Radiation and Ablation for Earth Entry. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 1992, 29, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodara, H. The Use of Magnetic Fields in the Elimination of the Re-Entry Radio Blackout. Proc. IRE 1961, 49, 1825–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, I.D. Modeling of associative ionization reactions in hypersonic rarefied flows. Phys. Fluids 2007, 19, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Li, K.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X. Study of the Influence of Time-Varying Plasma Sheath on Radar Echo Signal. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2017, 45, 3166–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Z. Electromagnetic Reflection from Conductive Plate Coated with Nonuniform Plasma. Int. J. Infrared Milli. Waves 2007, 28, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guo, L. Research on electromagnetic scattering characteristics of reentry vehicles and blackout forecast model. J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 2012, 26, 1767–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Liu, Y.; Lin, X.; Li, X. Effects of a reentry plasma sheath on the beam pointing properties of an array antenna. AIP Adv. 2018, 8, 035023. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Shen, F.; Liu, Y.; Ai, W.; Li, X. Improved Scattering-Matrix Method and Its Application to Analysis of Electromagnetic Wave Reflected by Reentry Plasma Sheath. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2018, 46, 1755–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, H. Reflection Properties of Electromagnetic Wave in a Bounded Plasma Slab. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2010, 38, 3348–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, X. Reflection and Absorption Analysis of Obliquely Incident Wave in Reentry Plasma Sheath. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 4th International Conference on Signal and Image Processing (ICSIP), Wuxi, China, 19–21 July 2019; pp. 385–390. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, B.; Liu, Y.; Song, L.; Li, X.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, X. Passive Radar Jamming: A Novel Method Using Time-Varying Plasma. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 120082–120088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Bai, B.; Gao, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, M. Method of Detecting a Target Enveloped by a Plasma Sheath Based on Doppler Frequency Compensation. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2020, 48, 4103–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wei, B.; Yin, W. Analysis on the Characteristics of EM Waves Propagation in the Plasma Sheath Surrounding a Hypersonic Vehicle. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2017, 45, 2922–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, X. The study of spatial dispersion effect on electromagnetic waves propagation in the warm non-uniform re-entry plasma sheath. Phys. Plasmas 2020, 27, 022104. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, Z.; Li, J.; Guo, L. ISAR Imaging Analysis of a Hypersonic Vehicle Covered with Plasma Sheath. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 2002413. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Bai, B.; Li, X.; Shen, F.; Chen, X.; Zhao, L. Establishment of a Wideband Radar Scattering Center Model of a Plasma Sheath. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 140402–140410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wu, J.; Yang, J.; Huang, Y.; Yang, H.; Yang, X. Non-Stop-and-Go Echo Model for Hypersonic-Vehicle-Borne Bistatic Forward-Looking Sar. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2018—2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018; pp. 545–548. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Liao, G. MPD model for radar echo signal of hypersonic targets. J. Eng. 2014, 8, 399–406. [Google Scholar]
- Farbar, E.; Boyd, I.D.; Kim, M.; Martin, A. Investigation of the Effects of Electron Translational Nonequilibrium on Numerical Predictions of Hypersonic Flow Fields. In Proceedings of the 42nd AIAA Thermophysics Conference, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27–30 June 2011; pp. 2011–3136. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.C.; Sproul, L.K. Influence of reentry turbulent plasma fluctuation on EM wave propagation. Comput. Fluids 2006, 35, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, W.; Cross, A.E. Electrostatic-Probe Measurements of Plasma Parameters for Two Reentry Flight Experiments at 25,000 Feet per Second; NASA Technical Note; National Aeronautics and Space Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1972; NASA-TN-D-6617.
- Shao, C.; Tian, D.; Qian, K.; Chen, W. Numerical Simulation of Weakly Ionized Dynamic Plasma for Reentry Vehicles. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 2016, 53, 900–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybak, J.; Churchill, R.J. Progress in reentry communications. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1971, AES-7, 879–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Xu, J.; Shi, L.; Xie, K. Effects of Reentry Plasma Sheath on the Polarization Properties of Obliquely Incident EM Waves. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2014, 42, 3365–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Bai, B.; Gao, H. An Analysis of Radar Detection on a Plasma Sheath Covered Reentry Target. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2021, 57, 4255–4268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Li, X.; Shi, L.; Liu, Y.; Bai, B. A layered fluctuation model of electron density in plasma sheath and instability effect on electromagnetic wave at Ka band. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2018, 78, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Shen, F.; Liu, Y.; Ai, W.; Li, X. Study of plasma-based stable and ultra-wideband electromagnetic wave absorption for stealth application. Plasma Sci. Technol. 2018, 20, 065503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalluri, D.K.; Goteti, V.R.; Sessler, A.M. WKB solution for wave propagation in a time-varying magnetoplasma medium: Longitudinal propagation. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 1993, 21, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.; Xing, M.D.; Wang, T. Radar Imaging Technology; Publishing House of Electronics Industry: Beijing, China, 2005; pp. 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Horé, A.; Ziou, D. Image quality metrics: PSNR vs. SSIM. In Proceedings of the 2010 20th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Istanbul, Turkey, 23–26 August 2010; pp. 2366–2369. [Google Scholar]
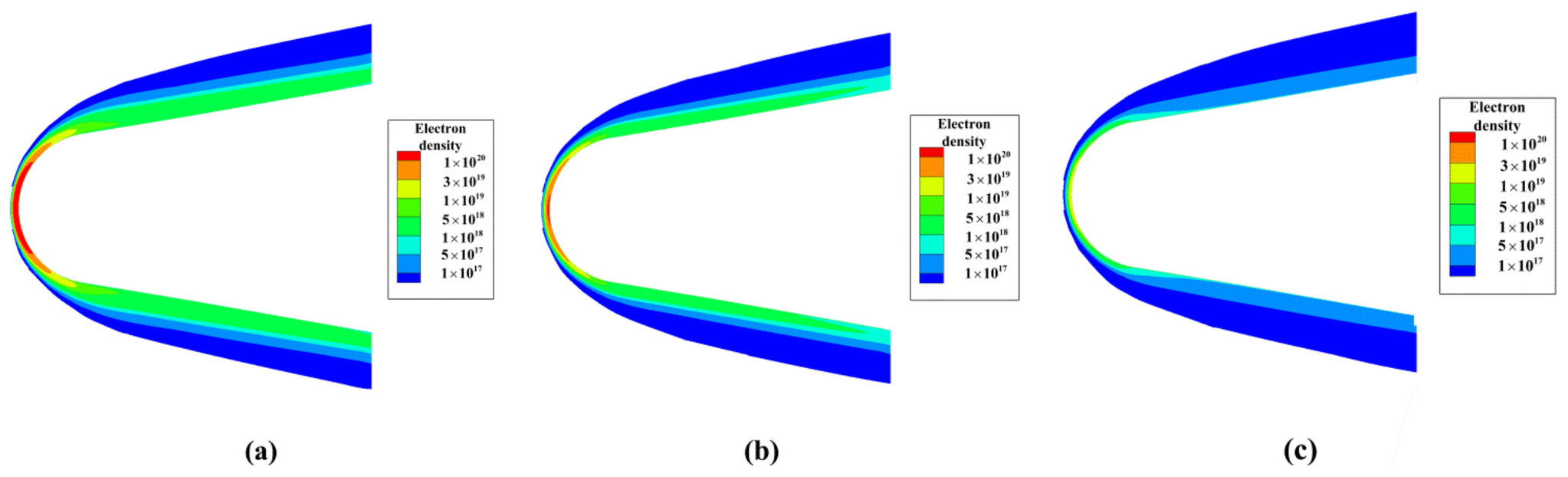
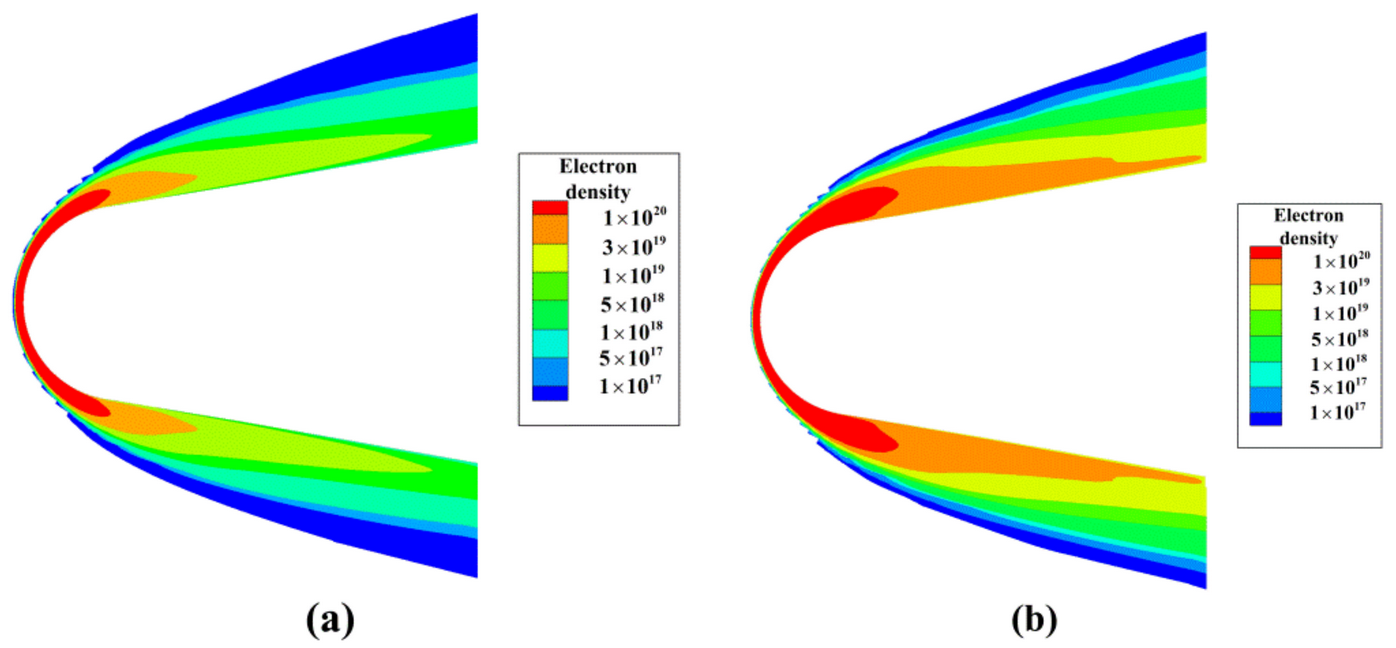

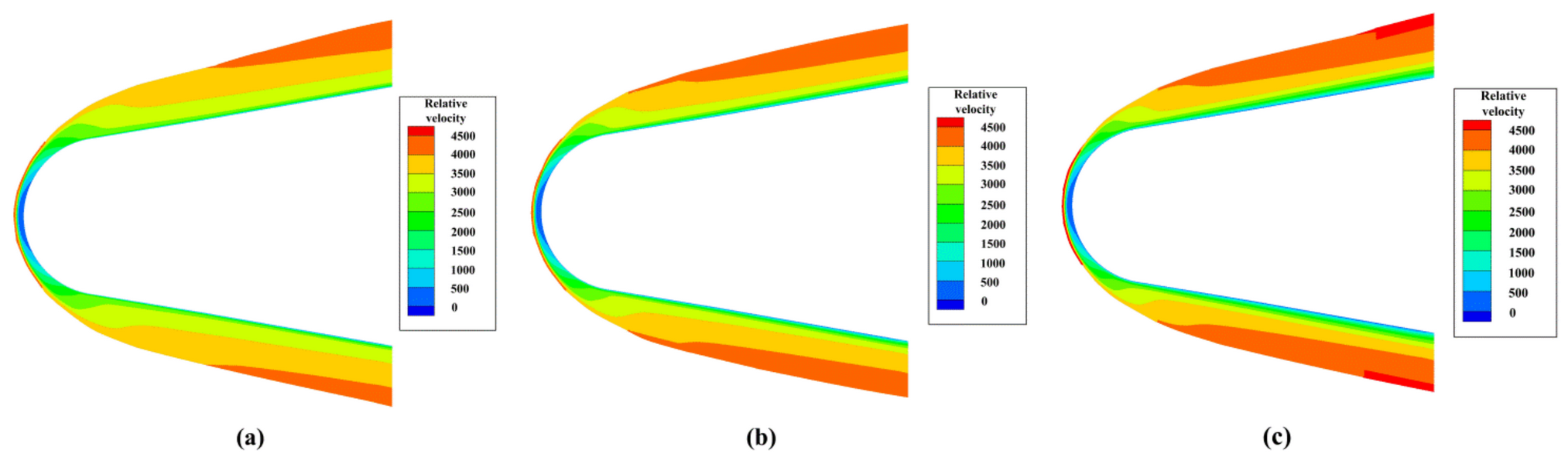




| Scene | Altitude | Velocity | Attack Angle |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 30 km | Mach 15 | 0° |
| 2 | 40 km | Mach 15 | 0° |
| 3 | 50 km | Mach 15 | 0° |
| 4 | 30 km | Mach 20 | 0° |
| 5 | 30 km | Mach 25 | 0° |
| 6 | 30 km | Mach 15 | 10° |
| 7 | 30 km | Mach 15 | 20° |
| Scene | X-Band | Ku-Band | Ka-Band |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 26.85 dB | 25.77 dB | 28.12 dB |
| 2 | 26.43 dB | 26.48 dB | 28.86 dB |
| 3 | 25.62 dB | 26.60 dB | 28.43 dB |
| 4 | 28.61 dB | 25.35 dB | 24.85 dB |
| 5 | 28.80 dB | 26.52 dB | 24.49 dB |
| 6 | 27.37 dB | 25.89 dB | 25.23 dB |
| 7 | 27.53 dB | 26.34 dB | 25.78 dB |
| SD | 1.14 dB | 0.47 dB | 1.86 dB |
| Scene | X-Band | Ku-Band | Ka-Band |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.683 | 0.435 | 0.711 |
| 2 | 0.658 | 0.526 | 0.718 |
| 3 | 0.585 | 0.553 | 0.714 |
| 4 | 0.777 | 0.398 | 0.285 |
| 5 | 0.828 | 0.498 | 0.298 |
| 6 | 0.716 | 0.482 | 0.489 |
| 7 | 0.721 | 0.501 | 0.487 |
| SD | 0.079 | 0.053 | 0.191 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, Y.; Li, X.; Shen, F.; Mao, Z.; Bai, B.; Chen, X. Influence of Plasma Sheath’s Velocity Field on ISAR Imaging of Hypersonic Target. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3799. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153799
Xie Y, Li X, Shen F, Mao Z, Bai B, Chen X. Influence of Plasma Sheath’s Velocity Field on ISAR Imaging of Hypersonic Target. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(15):3799. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153799
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Yaocong, Xiaoping Li, Fangfang Shen, Zheng Mao, Bowen Bai, and Xuyang Chen. 2022. "Influence of Plasma Sheath’s Velocity Field on ISAR Imaging of Hypersonic Target" Remote Sensing 14, no. 15: 3799. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153799
APA StyleXie, Y., Li, X., Shen, F., Mao, Z., Bai, B., & Chen, X. (2022). Influence of Plasma Sheath’s Velocity Field on ISAR Imaging of Hypersonic Target. Remote Sensing, 14(15), 3799. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153799






