A Blueprint for the Estimation of Seagrass Carbon Stock Using Remote Sensing-Enabled Proxies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Background
3. Processes and Drivers of Carbon Sequestration in Seagrass Meadows
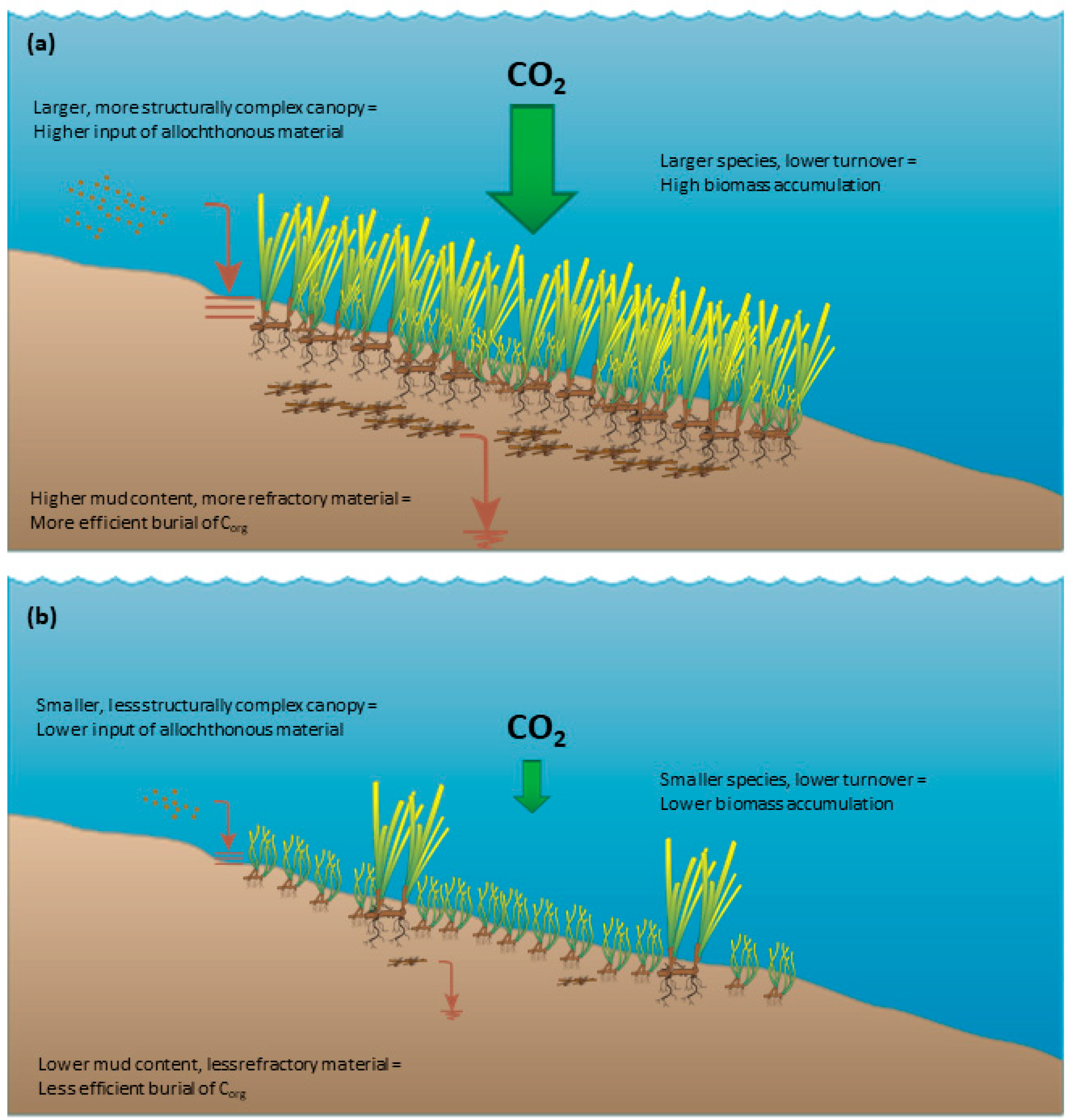
3.1. Biomass Accumulation and Autochthonous Contributions to Corg Stocks
3.2. Input of Allochthonous Corg into the Ecosystem
3.3. Efficient Burial of Corg
3.4. Summary: Processes and Drivers of Seagrass Carbon Stocks
4. Review Method
- Contained a clearly described and repeatable method;
- Used optical satellite remote sensing data to attempt to measure at least one biophysical characteristic of seagrass;
- Did not exclusively use manual image interpretation techniques.
5. Identifying Remote Sensing Proxies for Seagrass Carbon Stock: Possibilities and Challenges
5.1. Meadow Characteristics and Dynamics as Proxy Indicators of Carbon Stock
5.1.1. Aboveground Biomass (AGB)
5.1.2. Meadow Species Composition
5.1.3. Intra-Annual Variation in Seagrass Growth
5.2. Landscape Ecology Metrics and Spatial Characteristics as Proxies for Carbon Stock
5.2.1. Landscape Ecology Metrics Applied to Seagrass Meadows
5.2.2. Landscape Context
5.3. Seagrass Life History and Phenological Time Series Analysis
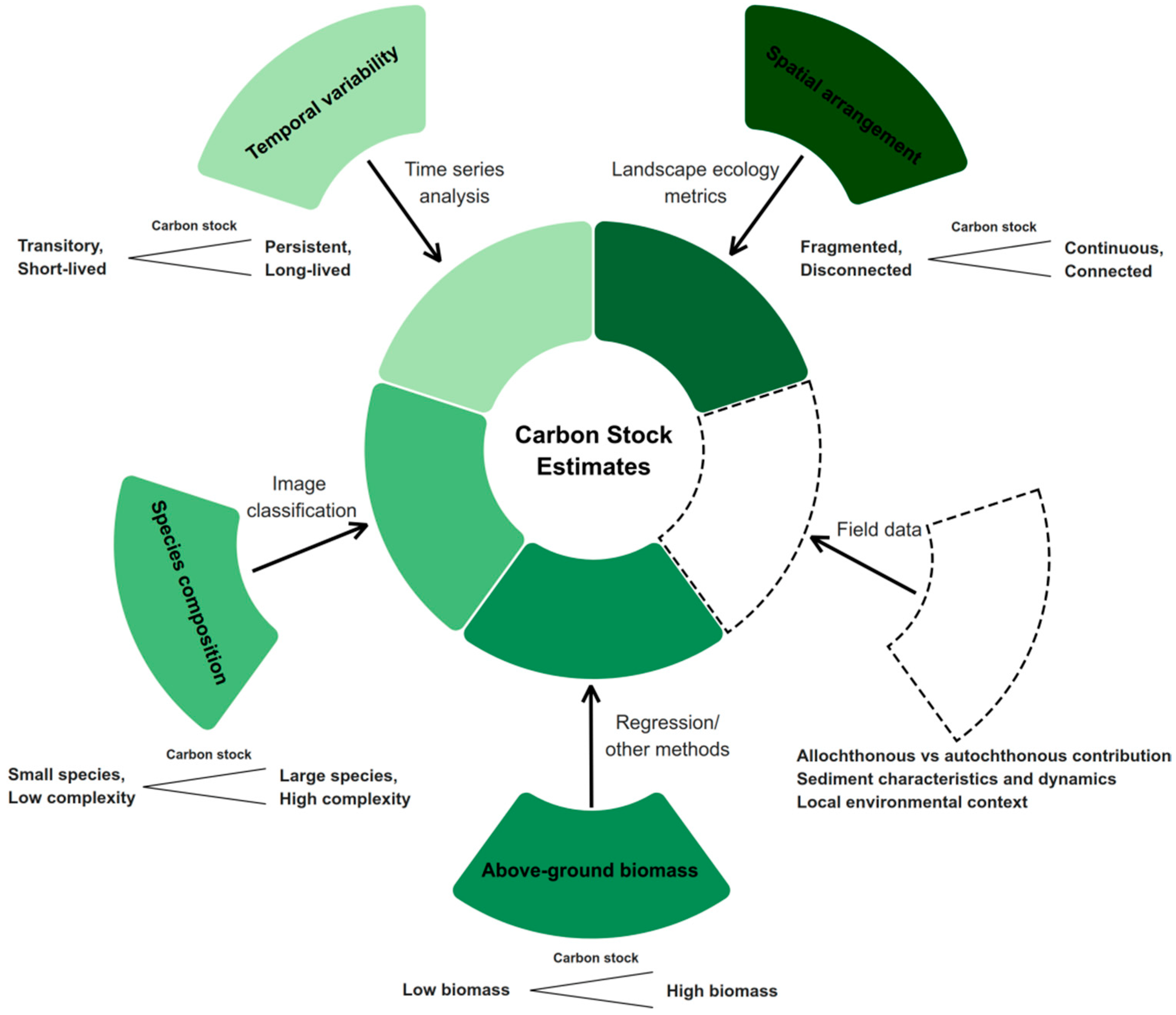
6. Enabling Carbon Stock Estimates from Space
- Estimate AGB and its heterogeneity across space;
- Classify seagrass ecosystems by species composition or dominant species;
- Characterise the spatial configuration and landscape context of seagrass ecosystems, and quantify these characteristics using landscape ecology metrics;
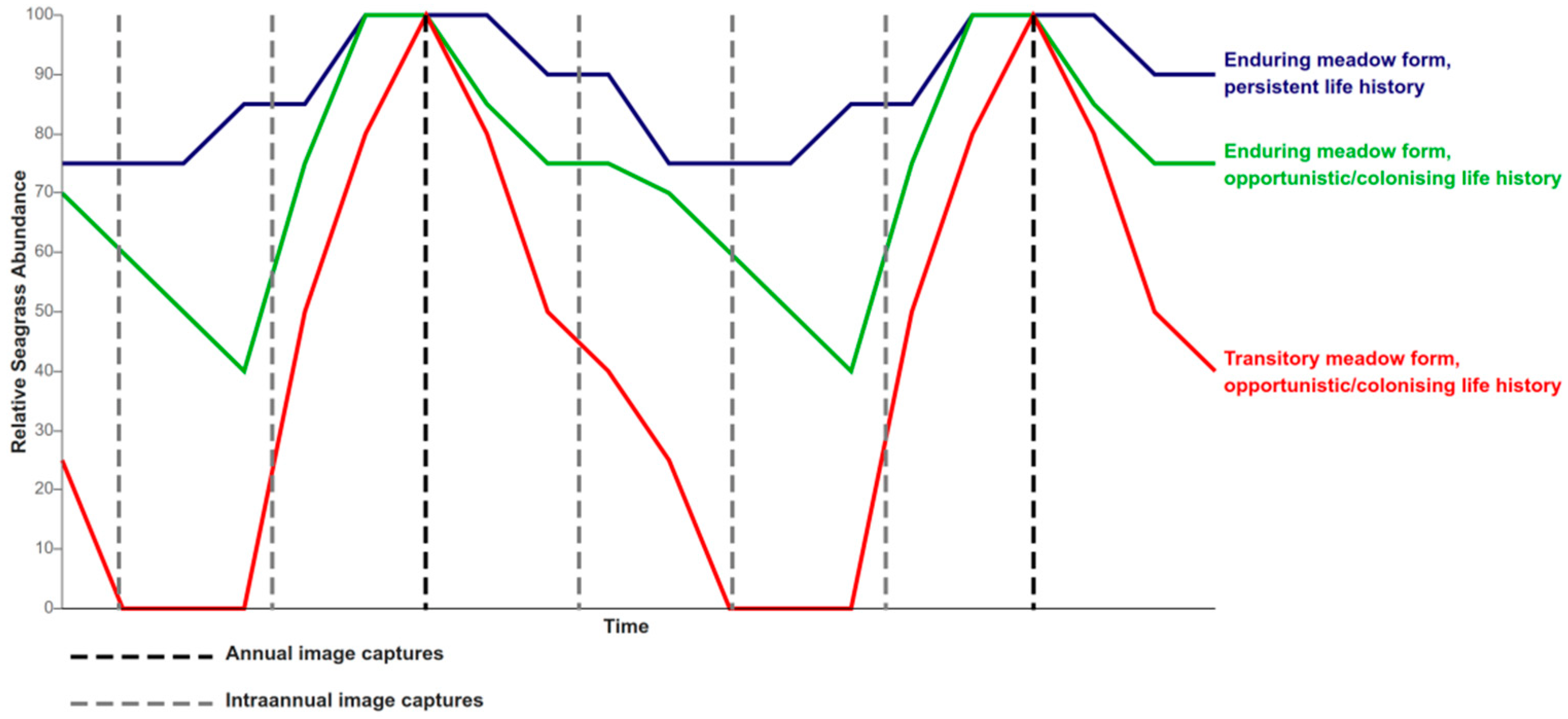
- Capture intra-annual variability of seagrass species composition and AGB to monitor seagrass life cycles and temporal change (Figure 4).
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Macreadie, P.I.; Costa, M.D.; Atwood, T.B.; Friess, D.A.; Kelleway, J.J.; Kennedy, H.; Lovelock, C.E.; Serrano, O.; Duarte, C.M. Blue carbon as a natural climate solution. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 826–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thayer, G.W.; Wolfe, D.A.; Williams, R.B. The Impact of Man on Seagrass Systems: Seagrasses must be considered in terms of their interaction with the other sources of primary production that support the estuarine trophic structure before their significance can be fully appreciated. Am. Sci. 1975, 63, 288–296. [Google Scholar]
- Oreska, M.P.; McGlathery, K.J.; Aoki, L.R.; Berger, A.C.; Berg, P.; Mullins, L. The greenhouse gas offset potential from seagrass restoration. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, A.D.; Fatoyinbo, T.; Charles, S.P.; Bourgeau-Chavez, L.L.; Goes, J.; Gomes, H.; Halabisky, M.; Holmquist, J.; Lohrenz, S.; Mitchell, C.; et al. A review of carbon monitoring in wet carbon systems using remote sensing. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 025009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourqurean, J.W.; Duarte, C.M.; Kennedy, H.; Marbà, N.; Holmer, M.; Mateo, M.A.; Apostolaki, E.T.; Kendrick, G.A.; Krause-Jensen, D.; McGlathery, K.J. Seagrass ecosystems as a globally significant carbon stock. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeod, E.; Chmura, G.L.; Bouillon, S.; Salm, R.; Björk, M.; Duarte, C.M.; Lovelock, C.E.; Schlesinger, W.H.; Silliman, B.R. A blueprint for blue carbon: Toward an improved understanding of the role of vegetated coastal habitats in sequestering CO2. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2011, 9, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hemminga, M.A.; Duarte, C.M. Seagrass Ecology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Nordlund, L.; Koch, E.W.; Barbier, E.B.; Creed, J.C. Seagrass Ecosystem Services and Their Variability across Genera and Geographical Regions. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Unsworth, R.K.; Nordlund, L.M.; Cullen-Unsworth, L.C. Seagrass meadows support global fisheries production. Conserv. Lett. 2019, 12, e12566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, J.; Hoyt, S.; Isensee, K.; Telszewski, M.; Pidgeon, E. Coastal Blue Carbon: Methods for Assessing Carbon Stocks and Emissions Factors in Mangroves, Tidal Salt Marshes, and Seagrasses; Conservation International: Arlington, VA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Environment Programme. Out of the Blue: The Value of Seagrasses to the Environment and to People; UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lavery, P.S.; Mateo, M.A.; Serrano, O.; Rozaimi, M. Variability in the carbon storage of seagrass habitats and its implications for global estimates of blue carbon ecosystem service. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanders, C.J.; Maher, D.T.; Smoak, J.M.; Eyre, B.D. Large variability in organic carbon and CaCO3 burial in seagrass meadows: A case study from three Australian estuaries. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2019, 616, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricart, A.M.; York, P.H.; Bryant, C.V.; Rasheed, M.A.; Ierodiaconou, D.; Macreadie, P.I. High variability of Blue Carbon storage in seagrass meadows at the estuary scale. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.H.; Suonan, Z.; Qin, L.-Z.; Kim, H.; Park, J.-I.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.-G.; Kang, C.-K.; Lee, K.-S. Variability in blue carbon storage related to biogeochemical factors in seagrass meadows off the coast of the Korean peninsula. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 813, 152680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramante, J.F.; Ali, S.M.; Ziegler, A.D.; Sin, T.M. Decadal biomass and area changes in a multi-species meadow in Singapore: Application of multi-resolution satellite imagery. Bot. Mar. 2018, 61, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poursanidis, D.; Traganos, D.; Teixeira, L.; Shapiro, A.; Muaves, L. Cloud-native seascape mapping of Mozambique’s Quirimbas National Park with Sentinel-2. Remote Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 7, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topouzelis, K.; Makri, D.; Stoupas, N.; Papakonstantinou, A.; Katsanevakis, S. Seagrass mapping in Greek territorial waters using Landsat-8 satellite images. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 67, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randazzo, G.; Italiano, F.; Micallef, A.; Tomasello, A.; Cassetti, F.P.; Zammit, A.; D’Amico, S.; Saliba, O.; Cascio, M.; Cavallaro, F. WebGIS Implementation for Dynamic Mapping and Visualization of Coastal Geospatial Data: A Case Study of BESS Project. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, L.J.; Langlois, L.A.; Roelfsema, C.M. Improving Approaches to Mapping Seagrass within the Great Barrier Reef: From Field to Spaceborne Earth Observation. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herr, D.; Pidgeon, E.; Laffoley, D.d.A. Blue Carbon Policy Framework 2.0: Based on the Discussion of the International Blue Carbon Policy Working Group; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. 2013 Supplement to the 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories: Wetlands; Hiraishi, T., Krug, T., Tanabe, K., Srivastava, N., Baasunsuren, J., Fukuda, M., Troxler, T.G., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ralph, P.J.; Crosswell, J.; Cannard, T.; Steven, A.D. Estimating seagrass blue carbon and policy implications: The Australian perspective. In Seagrasses of Australia; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 743–758. [Google Scholar]
- Orth, R.J.; Carruthers, T.J.; Dennison, W.C.; Duarte, C.M.; Fourqurean, J.W.; Heck, K.L.; Hughes, A.R.; Kendrick, G.A.; Kenworthy, W.J.; Olyarnik, S. A global crisis for seagrass ecosystems. Bioscience 2006, 56, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hopkinson, C.S.; Cai, W.-J.; Hu, X. Carbon sequestration in wetland dominated coastal systems—A global sink of rapidly diminishing magnitude. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2012, 4, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovelock, C.E.; Atwood, T.; Baldock, J.; Duarte, C.M.; Hickey, S.; Lavery, P.S.; Masque, P.; Macreadie, P.I.; Ricart, A.M.; Serrano, O. Assessing the risk of carbon dioxide emissions from blue carbon ecosystems. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2017, 15, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greiner, J.T.; McGlathery, K.J.; Gunnell, J.; McKee, B.A. Seagrass restoration enhances “blue carbon” sequestration in coastal waters. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72469. [Google Scholar]
- Griscom, B.W.; Adams, J.; Ellis, P.W.; Houghton, R.A.; Lomax, G.; Miteva, D.A.; Schlesinger, W.H.; Shoch, D.; Siikamäki, J.V.; Smith, P.J. Natural climate solutions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 11645–11650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- UNEP-WCMC; Short, F.T. Global Distribution of Seagrasses (Version 7.1). Seventh Update to the Data Layer Used in Green and Short (2003); UN Environment Programme World Conservation Monitoring Centre: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories, Prepared by the National Greenhouse Gas Inventories Programme; Eggleston, H.S., Buendia, L., Miwa, K., Ngara, T., Tanabe, K., Eds.; IGES: Hayama, Japan, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. 2019 Refinement to the 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories; Calvo Buendia, E., Tanabe, K., Kranjc, A., Baasunsuren, J., Fukuda, M., Ngarize, S., Osako, A., Pyrozhenko, Y., Shermanau, P., Federici, S., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Macreadie, P.I.; Baird, M.E.; Trevathan-Tackett, S.M.; Larkum, A.W.; Ralph, P.J. Quantifying and modelling the carbon sequestration capacity of seagrass meadows—A critical assessment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 83, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyajima, T.; Hori, M.; Hamaguchi, M.; Shimabukuro, H.; Adachi, H.; Yamano, H.; Nakaoka, M. Geographic variability in organic carbon stock and accumulation rate in sediments of East and Southeast Asian seagrass meadows. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2015, 29, 397–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, M.; Deyanova, D.; Gutschow, S.; Asplund, M.E.; Lyimo, L.D.; Karamfilov, V.; Santos, R.; Bjork, M.; Gullstrom, M. Sediment Properties as Important Predictors of Carbon Storage in Zostera marina Meadows: A Comparison of Four European Areas. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazarrasa, I.; Marbà, N.; Garcia-Orellana, J.; Masqué, P.; Arias-Ortiz, A.; Duarte, C.M. Effect of environmental factors (wave exposure and depth) and anthropogenic pressure in the C sink capacity of Posidonia oceanica meadows. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2017, 62, 1436–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asplund, M.E.; Dahl, M.; Ismail, R.O.; Arias-Ortiz, A.; Deyanova, D.; Franco, J.N.; Hammar, L.; Hoamby, A.I.; Linderholm, H.W.; Lyimo, L.D. Dynamics and fate of blue carbon in a mangrove–seagrass seascape: Influence of landscape configuration and land-use change. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 1489–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Bryan, B.A.; Connor, J.D.; Nolan, M.; Gao, L. Land use mapping error introduces strongly-localised, scale-dependent uncertainty into land use and ecosystem services modelling. Ecosyst. Serv. 2015, 15, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattsson, E.; Ostwald, M.; Wallin, G.; Nissanka, S. Heterogeneity and assessment uncertainties in forest characteristics and biomass carbon stocks: Important considerations for climate mitigation policies. Land Use Policy 2016, 59, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewers Lewis, C.J.; Carnell, P.E.; Sanderman, J.; Baldock, J.A.; Macreadie, P.I. Variability and Vulnerability of Coastal ‘Blue Carbon’ Stocks: A Case Study from Southeast Australia. Ecosystems 2017, 21, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, O.; Lovelock, C.E.; Atwood, T.B.; Macreadie, P.I.; Canto, R.; Phinn, S.; Arias-Ortiz, A.; Bai, L.; Baldock, J.; Bedulli, C.; et al. Australian vegetated coastal ecosystems as global hotspots for climate change mitigation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armitage, A.R.; Fourqurean, J.W. Carbon storage in seagrass soils: Long-term nutrient history exceeds the effects of near-term nutrient enrichment. Biogeosciences 2016, 13, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serrano, O.; Gómez-López, D.I.; Sánchez-Valencia, L.; Acosta-Chaparro, A.; Navas-Camacho, R.; González-Corredor, J.; Salinas, C.; Masque, P.; Bernal, C.A.; Marbà, N. Seagrass blue carbon stocks and sequestration rates in the Colombian Caribbean. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, J.E.; Benedetti-Cecchi, L.; Trinanes, J.; Muller-Karger, F.E.; Ambo-Rappe, R.; Boström, C.; Buschmann, A.H.; Byrnes, J.; Coles, R.G.; Creed, J.; et al. Toward a Coordinated Global Observing System for Seagrasses and Marine Macroalgae. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazarrasa, I.; Samper-Villarreal, J.; Serrano, O.; Lavery, P.S.; Lovelock, C.E.; Marba, N.; Duarte, C.M.; Cortes, J. Habitat characteristics provide insights of carbon storage in seagrass meadows. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 134, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, C.M.; Chiscano, C.L. Seagrass biomass and production: A reassessment. Aquat. Bot. 1999, 65, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pergent, G.; Romero, J.; Pergent-Martini, C.; Mateo, M.-A.; Boudouresque, C.-F. Primary production, stocks and fluxes in the Mediterranean seagrass Posidonia oceanica. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1994, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lirman, D.; Cropper, W.P. The influence of salinity on seagrass growth, survivorship, and distribution within Biscayne Bay, Florida: Field, experimental, and modeling studies. Estuaries 2003, 26, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdie, M.; Fourqurean, J.W. Responses of seagrass communities to fertilization along a gradient of relative availability of nitrogen and phosphorus in a carbonate environment. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2004, 49, 2082–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collier, C.J.; Lavery, P.S.; Ralph, P.J.; Masini, R.J. Physiological characteristics of the seagrass Posidonia sinuosa along a depth-related gradient of light availability. Mar. Ecol. Progr. Ser. 2008, 353, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, O.; Lavery, P.S.; Rozaimi, M.; Mateo, M.Á. Influence of water depth on the carbon sequestration capacity of seagrasses. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2014, 28, 950–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, P.G. Detrital processing in seagrass systems: A review of factors affecting decay rates, remineralization and detritivory. Aquat. Bot. 1989, 35, 263–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemminga, M.; Harrison, P.; Van Lent, F. The balance of nutrient losses and gains in seagrass meadows. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1991, 71, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourqurean, J.W.; Schrlau, J.E. Changes in nutrient content and stable isotope ratios of C and N during decomposition of seagrasses and mangrove leaves along a nutrient availability gradient in Florida Bay, USA. Chem. Ecol. 2003, 19, 373–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, M.A.; Cebrian, J.; Dunton, K.; Mutchler, T. Carbon Flux in Seagrass Ecosystems. In Seagrasses: Biology, Ecology and Conservation; Larkum, A.W.D., Orth, R.J., Duarte, C.M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 159–192. [Google Scholar]
- Trevathan-Tackett, S.M.; Macreadie, P.I.; Sanderman, J.; Baldock, J.; Howes, J.M.; Ralph, P.J. A global assessment of the chemical recalcitrance of seagrass tissues: Implications for long-term carbon sequestration. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozaimi, M.; Serrano, O.; Lavery, P. Comparison of carbon stores by two morphologically different seagrasses. J. Royal Soc. West. Aust. 2013, 96, 81. [Google Scholar]
- Stankovic, M.; Panyawai, J.; Jansanit, K.; Upanoi, T.; Prathep, A. Carbon content in different seagrass species in Andaman Coast of Thailand. Sains Malays. 2017, 46, 1441–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, O.; Almahasheer, H.; Duarte, C.M.; Irigoien, X. Carbon stocks and accumulation rates in Red Sea seagrass meadows. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bañolas, G.; Fernández, S.; Espino, F.; Haroun, R.; Tuya, F. Evaluation of carbon sinks by the seagrass Cymodocea nodosa at an oceanic island: Spatial variation and economic valuation. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2020, 187, 105112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazarrasa, I.; Lavery, P.; Duarte, C.M.; Lafratta, A.; Lovelock, C.E.; Macreadie, P.I.; Samper-Villarreal, J.; Salinas, C.; Sanders, C.; Trevathan-Tackett, S. Factors determining seagrass Blue Carbon across bioregions and geomorphologies. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2021, e2021GB006935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilminster, K.; McMahon, K.; Waycott, M.; Kendrick, G.A.; Scanes, P.; McKenzie, L.; O’Brien, K.R.; Lyons, M.; Ferguson, A.; Maxwell, P.; et al. Unravelling complexity in seagrass systems for management: Australia as a microcosm. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 534, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thayer, G.W.; Kenworthy, W.J.; Fonseca, M.S. The Ecology of Eelgrass Meadows of the Atlantic Coast: A Community Profile; Fish and Wildlife Service; US Department of the Interior: Washington, DC, USA, 1984.
- Walker, D.I.; Olesen, B.; Phillips, R.C. Reproduction and phenology in seagrasses. In Global Seagrass Research Methods; Short, F.T., Coles, R.G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 59–74. [Google Scholar]
- Duarte, C.M. Temporal biomass variability and production/biomass relationships of seagrass communities. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1989, 51, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, M.S.; Fisher, J.S. A comparison of canopy friction and sediment movement between four species of seagrass with reference to their ecology and restoration. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1986, 29, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambi, M.C.; Nowell, A.R.; Jumars, P.A. Flume observations on flow dynamics in Zostera marina (eelgrass) beds. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1990, 61, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- France, R.L.; Holmquist, J.G. Delta13C variability of macroalgae: Effects of water motion via baffling by seagrasses and mangroves. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1997, 149, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Potouroglou, M.; Bull, J.C.; Krauss, K.W.; Kennedy, H.A.; Fusi, M.; Daffonchio, D.; Mangora, M.M.; Githaiga, M.N.; Diele, K.; Huxham, M. Measuring the role of seagrasses in regulating sediment surface elevation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Katwijk, M.; Bos, A.; Hermus, D.; Suykerbuyk, W. Sediment modification by seagrass beds: Muddification and sandification induced by plant cover and environmental conditions. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 89, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widdows, J.; Pope, N.D.; Brinsley, M.D.; Asmus, H.; Asmus, R.M. Effects of seagrass beds (Zostera noltii and Z. marina) on near-bed hydrodynamics and sediment resuspension. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 358, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serrano, O.; Ricart, A.M.; Lavery, P.S.; Mateo, M.A.; Arias-Ortiz, A.; Masque, P.; Rozaimi, M.; Steven, A.; Duarte, C.M. Key biogeochemical factors affecting soil carbon storage in Posidonia meadows. Biogeosciences 2016, 13, 4581–4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gullström, M.; Lyimo, L.D.; Dahl, M.; Samuelsson, G.S.; Eggertsen, M.; Anderberg, E.; Rasmusson, L.M.; Linderholm, H.W.; Knudby, A.; Bandeira, S.; et al. Blue Carbon Storage in Tropical Seagrass Meadows Relates to Carbonate Stock Dynamics, Plant–Sediment Processes, and Landscape Context: Insights from the Western Indian Ocean. Ecosystems 2017, 21, 551–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lima, M.d.A.C.; Ward, R.D.; Joyce, C.B. Environmental drivers of sediment carbon storage in temperate seagrass meadows. Hydrobiologia 2020, 847, 1773–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, O.; Lavery, P.S.; Duarte, C.M.; Kendrick, G.A.; Calafat, A.; York, P.H.; Steven, A.; Macreadie, P.I. Can mud (silt and clay) concentration be used to predict soil organic carbon content within seagrass ecosystems? Biogeosciences 2016, 13, 4915–4926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samper-Villarreal, J.; Lovelock, C.E.; Saunders, M.I.; Roelfsema, C.; Mumby, P.J. Organic carbon in seagrass sediments is influenced by seagrass canopy complexity, turbidity, wave height, and water depth. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2016, 61, 938–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oreska, M.P.J.; McGlathery, K.J.; Porter, J.H. Seagrass blue carbon spatial patterns at the meadow-scale. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricart, A.M.; Pérez, M.; Romero, J. Landscape configuration modulates carbon storage in seagrass sediments. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 185, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricart, A.M.; York, P.H.; Rasheed, M.A.; Pérez, M.; Romero, J.; Bryant, C.V.; Macreadie, P.I. Variability of sedimentary organic carbon in patchy seagrass landscapes. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 100, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhitya, A.; Bouma, T.; Folkard, A.; Van Katwijk, M.; Callaghan, D.; De Iongh, H.; Herman, P. Comparison of the influence of patch-scale and meadow-scale characteristics on flow within seagrass meadows: A flume study. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 516, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Allaoui, N.; Serra, T.; Colomer, J.; Soler, M.; Casamitjana, X.; Oldham, C. Interactions between fragmented seagrass canopies and the local hydrodynamics. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Azkab, M.H.; Chmura, G.L.; Chen, S.; Sastrosuwondo, P.; Ma, Z.; Dharmawan, I.W.E.; Yin, X.; Chen, B. Mangroves as a major source of soil carbon storage in adjacent seagrass meadows. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemminga, M.; Slim, F.; Kazungu, J.; Ganssen, G.; Nieuwenhuize, J.; Kruyt, N. Carbon outwelling from a mangrove forest with adjacent seagrass beds and coral reefs (Gazi Bay, Kenya). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1994, 106, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra-Vargas, L.A.; Gillis, L.G.; Mancera-Pineda, J.E. Stronger Together: Do Coral Reefs Enhance Seagrass Meadows “Blue Carbon” Potential? Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, O.; Rozaimi, M.; Lavery, P.S.; Smernik, R.J. Organic chemistry insights for the exceptional soil carbon storage of the seagrass Posidonia australis. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2020, 237, 106662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemu, J.B.; Yaakub, S.M.; Yando, E.S.; San Lau, R.Y.; Lim, C.C.; Puah, J.Y.; Friess, D.A. Geomorphic gradients in shallow seagrass carbon stocks. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2022, 265, 107681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackleson, S.; Klemas, V. Remote sensing of submerged aquatic vegetation in lower Chesapeake Bay: A comparison of Landsat MSS to TM imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 1987, 22, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phinn, S.; Roelfsema, C.; Dekker, A.; Brando, V.; Anstee, J. Mapping seagrass species, cover and biomass in shallow waters: An assessment of satellite multi-spectral and airborne hyper-spectral imaging systems in Moreton Bay (Australia). Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3413–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelfsema, C.; Phinn, S.; Udy, N.; Maxwell, P. An integrated field and remote sensing approach for mapping seagrass cover, Moreton Bay, Australia. J. Spat. Sci. 2009, 54, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, M.B.; Phinn, S.R.; Roelfsema, C.M. Long term land cover and seagrass mapping using Landsat and object-based image analysis from 1972 to 2010 in the coastal environment of South East Queensland, Australia. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 71, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, R.; Bell, S.; Meyer, C.; Baggett, L.; Zhao, Y. Mapping and assessing seagrass along the western coast of Florida using Landsat TM and EO-1 ALI/Hyperion imagery. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 115, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicaksono, P.; Hafizt, M. Mapping seagrass from space: Addressing the complexity of seagrass LAI mapping. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 46, 18–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wabnitz, C.C.; Andréfouët, S.; Torres-Pulliza, D.; Müller-Karger, F.E.; Kramer, P.A. Regional-scale seagrass habitat mapping in the Wider Caribbean region using Landsat sensors: Applications to conservation and ecology. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3455–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, M.; Roelfsema, C.; Kovacs, E.; Samper-Villarreal, J.; Saunders, M.; Maxwell, P.; Phinn, S. Rapid monitoring of seagrass biomass using a simple linear modelling approach, in the field and from space. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2015, 530, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stankovic, M.; Tantipisanuh, N.; Rattanachot, E.; Prathep, A. Model-based approach for estimating biomass and organic carbon in tropical seagrass ecosystems. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2018, 596, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zoffoli, M.L.; Gernez, P.; Rosa, P.; Le Bris, A.; Brando, V.E.; Barillé, A.-L.; Harin, N.; Peters, S.; Poser, K.; Spaias, L.; et al. Sentinel-2 remote sensing of Zostera noltei-dominated intertidal seagrass meadows. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 251, 112020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borfecchia, F.; De Cecco, L.; Martini, S.; Ceriola, G.; Bollanos, S.; Vlachopoulos, G.; Valiante, L.M.; Belmonte, A.; Micheli, C. Posidonia oceanica genetic and biometry mapping through high-resolution satellite spectral vegetation indices and sea-truth calibration. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 4680–4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, R.; Bell, S. A protocol for improving mapping and assessing of seagrass abundance along the West Central Coast of Florida using Landsat TM and EO-1 ALI/Hyperion images. J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 83, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barillé, L.; Robin, M.; Harin, N.; Bargain, A.; Launeau, P. Increase in seagrass distribution at Bourgneuf Bay (France) detected by spatial remote sensing. Aquat. Bot. 2010, 92, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, G.; Stelzer, K.; Smollich, S.; Gade, M.; Adolph, W.; Melchionna, S.; Kemme, L.; Geißler, J.; Millat, G.; Reimers, H.-C.; et al. Remotely sensing the German Wadden Sea—A new approach to address national and international environmental legislation. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, N.T.; Manley-Harris, M.; Pham, T.D.; Hawes, I. The use of radar and optical satellite imagery combined with advanced machine learning and metaheuristic optimization techniques to detect and quantify above ground biomass of intertidal seagrass in a New Zealand estuary. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 42, 4712–4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, S.S.; Borum, J.; Fortes, M.D.; Duarte, C. Species composition and plant performance of mixed seagrass beds along a siltation gradient at Cape Bolinao, The Philippines. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1998, 174, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, C.J.; Lavery, P.S.; Masini, R.J.; Ralph, P.J. Morphological, growth and meadow characteristics of the seagrass Posidonia sinuosa along a depth-related gradient of light availability. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 337, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyons, M.; Phinn, S.; Roelfsema, C. Integrating Quickbird Multi-Spectral Satellite and Field Data: Mapping Bathymetry, Seagrass Cover, Seagrass Species and Change in Moreton Bay, Australia in 2004 and 2007. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 42–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fyfe, S. Spatial and temporal variation in spectral reflectance: Are seagrass species spectrally distinct? J. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 464–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorhaug, A.; Richardson, A.; Berlyn, G. Spectral reflectance of the seagrasses: Thalassia testudinum, Halodule wrightii, Syringodium filiforme and five marine algae. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 1487–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, A.G.; Brando, V.E.; Anstee, J.M. Retrospective seagrass change detection in a shallow coastal tidal Australian lake. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 97, 415–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traganos, D.; Aggarwal, B.; Poursanidis, D.; Topouzelis, K.; Chrysoulakis, N.; Reinartz, P. Towards Global-Scale Seagrass Mapping and Monitoring Using Sentinel-2 on Google Earth Engine: The Case Study of the Aegean and Ionian Seas. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Traganos, D.; Reinartz, P. Interannual Change Detection of Mediterranean Seagrasses Using RapidEye Image Time Series. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mumby, P.J.; Edwards, A.J. Mapping marine environments with IKONOS imagery: Enhanced spatial resolution can deliver greater thematic accuracy. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 82, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelfsema, C.M.; Lyons, M.; Kovacs, E.M.; Maxwell, P.; Saunders, M.I.; Samper-Villarreal, J.; Phinn, S.R. Multi-temporal mapping of seagrass cover, species and biomass: A semi-automated object based image analysis approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 150, 172–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, E.; Roelfsema, C.; Lyons, M.; Zhao, S.; Phinn, S. Seagrass habitat mapping: How do Landsat 8 OLI, Sentinel-2, ZY-3A, and Worldview-3 perform? Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 9, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, S.; Clark, K.B. Seasonal variation in standing crop of the seagrass Syringodium filiforme and associated macrophytes in the northern Indian River, Florida. Estuaries 1981, 4, 223–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaría-Gallegos, N.A.; Sánchez-Lizaso, J.L.; Félix-Pico, E.F. Phenology and growth cycle of annual subtidal eelgrass in a subtropical locality. Aquat. Bot. 2000, 66, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samper-Villarreal, J.; Mumby, P.J.; Saunders, M.I.; Roelfsema, C.; Lovelock, C.E. Seagrass Organic Carbon Stocks Show Minimal Variation Over Short Time Scales in a Heterogeneous Subtropical Seascape. Estuaries Coasts 2018, 41, 1732–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McComb, A.; Cambridge, M.; Kirkman, H.; Kuo, J. The Biology of Australian Seagrasses; University of Western Australia Press: Crawley, WA, Australia, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- de Boer, W.F. Biomass dynamics of seagrasses and the role of mangrove and seagrass vegetation as different nutrient sources for an intertidal ecosystem. Aquat. Bot. 2000, 66, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, Y.S.; Collier, C.; Ow, Y.X.; Kendrick, G.A. Global Warming and Ocean Acidification: Effects on Australian Seagrass Ecosystems. In Seagrasses of Australia: Structure, Ecology and Conservation; Larkum, A.W., Kendrick, G.A., Ralph, P.J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 705–742. [Google Scholar]
- Pittman, S.; Yates, K.; Bouchet, P.; Alvarez-Berastegui, D.; Andréfouët, S.; Bell, S.; Berkström, C.; Boström, C.; Brown, C.; Connolly, R. Seascape ecology: Identifying research priorities for an emerging ocean sustainability science. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2021, 663, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, B.D.; Bell, S.S. Seagrass landscapes: A terrestrial approach to the marine subtidal environment. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1994, 9, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, B.; Walker, B.K.; Dijkstra, J.A. Mapping and Quantifying Seascape Patterns. In Seascape Ecology; Pittman, S.J., Ed.; Wiley Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2018; pp. 27–56. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, S.S.; Fonseca, M.S.; Stafford, N.B. Seagrass ecology: New contributions from a landscape perspective. In Seagrasses: Biology, Ecology and Conservation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 625–645. [Google Scholar]
- Hamylton, S.; Spencer, T. Geomorphological modelling of tropical marine landscapes: Optical remote sensing, patches and spatial statistics. Cont. Shelf Res. 2011, 31, S151–S161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhrin, A.V.; Townsend, P.A. Improved seagrass mapping using linear spectral unmixing of aerial photographs. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 171, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhrin, A.V.; Turner, M.G. Physical drivers of seagrass spatial configuration: The role of thresholds. Landsc. Ecol. 2018, 33, 2253–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rioja-Nieto, R.; Barrera-Falcón, E.; Hinojosa-Arango, G.; Riosmena-Rodríguez, R. Benthic habitat β-diversity modeling and landscape metrics for the selection of priority conservation areas using a systematic approach: Magdalena Bay, Mexico, as a case study. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2013, 82, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmi, M.; Purwanto, W.A.; Subardjo, P.; Aysira, A. Benthic Diversity Mapping and Analysis Base on Remote Sensing and Seascape Ecology Approach at Parang Islands, Karimunjawa National Park, Indonesia. Int. J. Civ. Eng. Technol. 2018, 9, 227–235. [Google Scholar]
- Cajica, A.K.O.; Hinojosa-Arango, G.; Garza-Pérez, J.R.; Rioja-Nieto, R. Seascape metrics, spatio-temporal change, and intensity of use for the spatial conservation prioritization of a Caribbean marine protected area. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2020, 194, 105265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbański, J.; Mazur, A.; Janas, U. Object-oriented classification of QuickBird data for mapping seagrass spatial structure. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2009, 38, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, R.; Bell, S. Mapping seagrass coverage and spatial patterns with high spatial resolution IKONOS imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 54, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewers Lewis, C.J.; Young, M.A.; Ierodiaconou, D.; Baldock, J.A.; Hawke, B.; Sanderman, J.; Carnell, P.E.; Macreadie, P.I. Drivers and modelling of blue carbon stock variability in sediments of southeastern Australia. Biogeosciences 2020, 17, 2041–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stankovic, M.; Hayashizaki, K.-I.; Tuntiprapas, P.; Rattanachot, E.; Prathep, A. Two decades of seagrass area change: Organic carbon sources and stock. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 163, 111913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madonsela, S.; Cho, M.A.; Mathieu, R.; Mutanga, O.; Ramoelo, A.; Kaszta, Ż.; Van De Kerchove, R.; Wolff, E. Multi-phenology WorldView-2 imagery improves remote sensing of savannah tree species. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 58, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyons, M.B.; Roelfsema, C.M.; Phinn, S.R. Towards understanding temporal and spatial dynamics of seagrass landscapes using time-series remote sensing. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 120, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelfsema, C.; Kovacs, E.M.; Saunders, M.I.; Phinn, S.; Lyons, M.; Maxwell, P. Challenges of remote sensing for quantifying changes in large complex seagrass environments. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 133, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalek, J.L.; Wagner, T.W.; Luczkovich, J.J.; Stoffle, R.W. Multispectral change vector analysis for monitoring coastal marine environments. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1993, 59, 381–384. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, A.C.; Rohmann, S.O. Mapping changes in submerged aquatic vegetation using Landsat imagery and benthic habitat data: Coral reef ecosystem monitoring in Vieques Sound between 1985 and 2000. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2006, 79, 375–388. [Google Scholar]
- Blakey, T.; Melesse, A.; Hall, M.O. Supervised classification of benthic reflectance in shallow subtropical waters using a generalized pixel-based classifier across a time series. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 5098–5116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fauzan, M.A.; Wicaksono, P. Characterizing Derawan seagrass cover change with time-series Sentinel-2 images. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 48, 102048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, J.R.; Hinojosa-Corona, A.; Gray, A.B.; Burke Watson, E. Emerging Sensor Platforms Allow for Seagrass Extent Mapping in a Turbid Estuary and from the Meadow to Ecosystem Scale. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Simpson, J.; Bruce, E.; Davies, K.P.; Barber, P. A Blueprint for the Estimation of Seagrass Carbon Stock Using Remote Sensing-Enabled Proxies. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3572. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153572
Simpson J, Bruce E, Davies KP, Barber P. A Blueprint for the Estimation of Seagrass Carbon Stock Using Remote Sensing-Enabled Proxies. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(15):3572. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153572
Chicago/Turabian StyleSimpson, Jamie, Eleanor Bruce, Kevin P. Davies, and Paul Barber. 2022. "A Blueprint for the Estimation of Seagrass Carbon Stock Using Remote Sensing-Enabled Proxies" Remote Sensing 14, no. 15: 3572. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153572
APA StyleSimpson, J., Bruce, E., Davies, K. P., & Barber, P. (2022). A Blueprint for the Estimation of Seagrass Carbon Stock Using Remote Sensing-Enabled Proxies. Remote Sensing, 14(15), 3572. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153572





