Calibration and Validation of CYGNSS Reflectivity through Wetlands’ and Deserts’ Dielectric Permittivity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (a)
- To identify areas that exhibit theoretical scattering properties and suitable dielectric conditions so that the reflectivity values are minimally affected by contributions such as BSR and VOD.
- (b)
- From the zones in the previous objective, verify the potential and capacity of desert areas to obtain a calibration bias parameter using GNSS-R reflectivities.
- (c)
- Once the bias parameter is estimated, verify the suitability of a scale factor based on wetlands’ reflectivity, according to the method proposed by [25].
- (d)
- To perform the conversion of calibrated GNSS-R reflectivities into SMC values.
- (e)
- To validate the SMC values estimated from the calibrated reflectivities.
2. Study Areas and Data
2.1. Calibration Areas
2.2. SMAP BSR, VOD, and SMC Data from the Calibration Areas
2.3. CYGNSS Data
- (1)
- CYGNSS reflectivity values range between −35 dB and −5 dB;
- (2)
- Incidence angles range between 0° and 25°;
- (3)
- DDM signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is greater than 3 dB;
- (4)
- Gr (receiver antenna gain towards the specular point) is greater than 5 dB;
- (5)
- Land surface heights are lower than 700 m.
3. Methodology
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Theoretical Water/Dry Soil Dielectric Properties
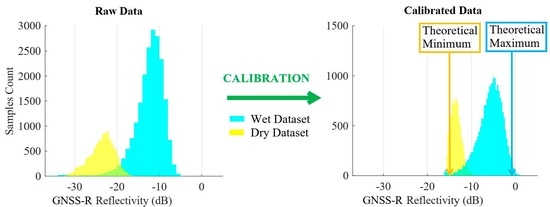
4.2. Analysis and Calibration of CYGNSS Reflectivity
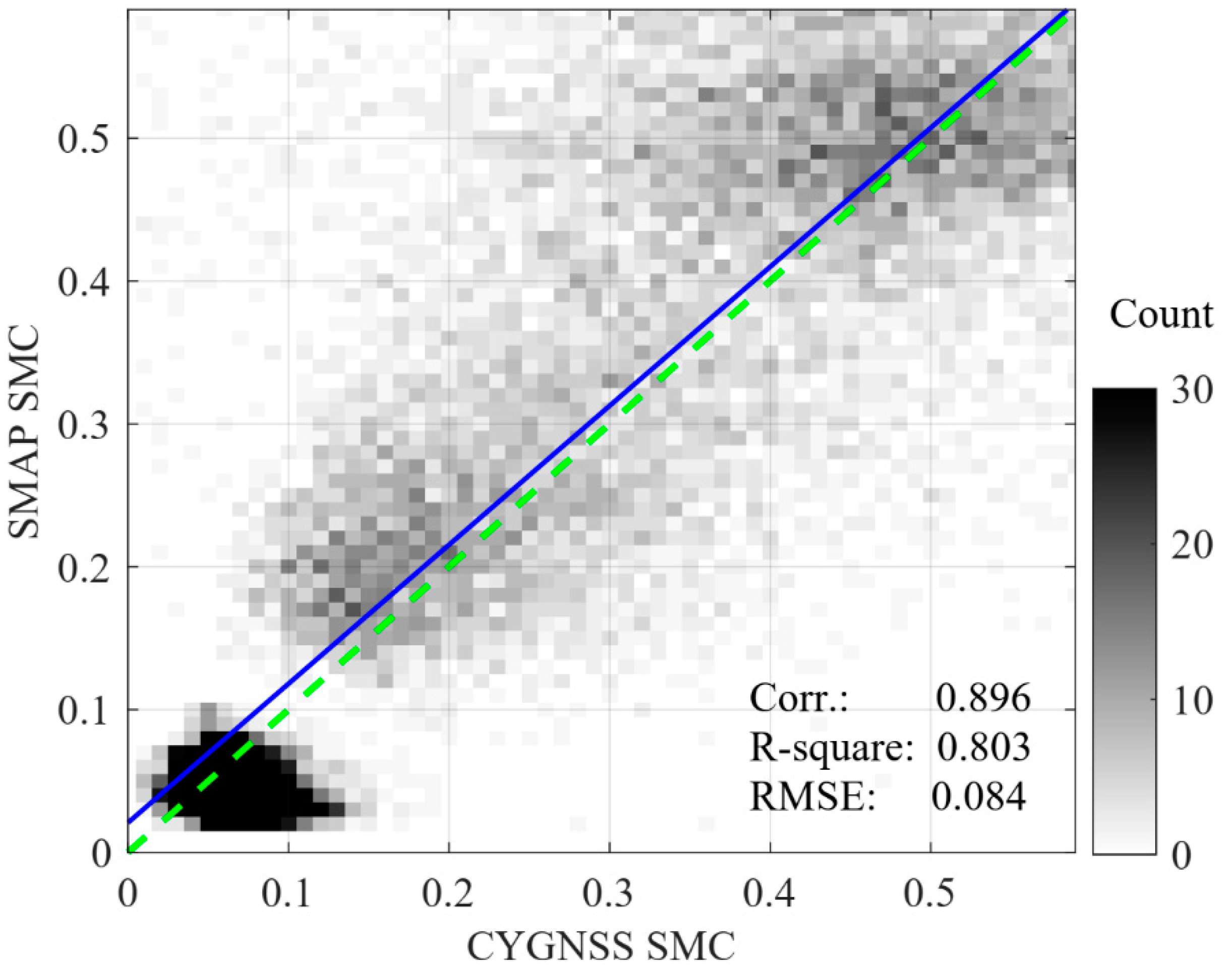
4.3. Validation of CYGNSS SMC with SMAP SMC
4.4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, H.; Lakshmi, V. Use of Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System (CyGNSS) Observations for Estimation of Soil Moisture. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 8272–8282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santi, E.; Paloscia, S.; Pettinato, S.; Fontanelli, G.; Clarizia, M.P.; Comite, D.; Dente, L.; Guerriero, L.; Pierdicca, N.; Floury, N. Remote Sensing of Forest Biomass Using GNSS Reflectometry. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 2351–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Komjathy, A. GNSS reflectometry and remote sensing: New objectives and results. Adv. Space Res. 2010, 46, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Jin, S. GNSS-Reflectometry: Forest canopies polarization scattering properties and modeling. Adv. Space Res. 2014, 54, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masters, D.; Zavorotny, V.; Katzberg, S.; Emery, W. GPS signal scattering from land for moisture content determination. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Honolulu, HI, USA, 24–28 July 2000; pp. 3090–3092. [Google Scholar]
- Masters, D.; Axelrad, P.; Katzberg, S. Initial results of land-reflected GPS bistatic radar measurements in SMEX02. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 92, 507–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, C.C.; Colliander, A.; Shah, R.; Zuffada, C.; Burgin, M. The sensitivity of ground-reflected GNSS signals to near-surface soil moisture, as recorded by spaceborne receivers. In Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017; pp. 2661–2663. [Google Scholar]
- Ruf, C.S.; Chew, C.; Lang, T.; Morris, M.G.; Nave, K.; Ridley, A.; Balasubramaniam, R. A New Paradigm in Earth Environmental Monitoring with the CYGNSS Small Satellite Constellation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Egido, A.; Caparrini, M.; Ruffini, G.; Paloscia, S.; Santi, E.; Guerriero, L.; Pierdicca, N.; Floury, N. Global navigation satellite systems reflectometry as a remote sensing tool for agriculture. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 2356–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egido, A.; Paloscia, S.; Motte, E.; Guerriero, L.; Pierdicca, N.; Caparrini, M.; Santi, E.; Fontanelli, G.; Floury, N. Airborne GNSS-R polarimetric measurements for soil moisture and above-ground biomass estimation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 1522–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camps, A.; Park, H.; Pablos, M.; Foti, G.; Gommenginger, C.P.; Liu, P.W.; Judge, J. Sensitivity of GNSS-R Spaceborne Observations to Soil Moisture and Vegetation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 4730–4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, Y.; Savi, P. Sensing soil moisture and vegetation using GNSS-R polarimetric measurement. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 59, 858–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleason, S.; Hodgart, S.; Sun, Y.; Gommenginger, C.; Mackin, S.; Adjrad, M.; Unwin, M. Detection and processing of bistatically reflected GPS signals from low earth orbit for the purpose of ocean remote sensing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 1229–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Song, Y.; Xu, J.; Duan, Z.; Jin, S.G. Bistatic scattering simulations of circular and linear polarizations over land surface for signals of opportunity reflectometry. Geosci. Lett. 2021, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavorotny, V.U.; Gleason, S.; Cardellach, E.; Camps, A. Tutorial on Remote Sensing Using GNSS Bistatic Radar of Opportunity. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 2, 8–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Privette, C.V.; Khalilian, A.; Torres, O.; Katzberg, S. Utilizing space-based GPS technology to determine hydrological properties of soils. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 3582–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Savi, P.; Canone, D.; Notarpietro, R. Estimation of Surface Characteristics Using GNSS LH-Reflected Signals: Land Versus Water. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 4752–4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, R.; Gleason, S.; Ruf, C. The NASA CYGNSS mission: A pathfinder for GNSS scatterometry remote sensing applications. In Remote Sensing of the Ocean, Sea Ice, Coastal Waters, and Large Water Regions; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 9240, p. 924005. [Google Scholar]
- Carreño-luengo, H.; Luzi, G.; Crosetto, M. Sensitivity of CyGNSS Bistatic Reflectivity and SMAP Microwave Radiometry Brightness Temperature to Geophysical Parameters Over Land Surfaces. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 12, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarizia, M.P.; Pierdicca, N.; Costantini, F.; Floury, N. Analysis of CyGNSS Data for Soil Moisture Retrieval. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 2227–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabia, A.; Molina, I.; Jin, S.G. Soil Moisture Content from GNSS Reflectometry using Dielectric Permittivity from Fresnel Reflection Coefficients. Remote Sens. 2022, 12, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camps, A.; Vall·llossera, M.; Park, H.; Portal, G.; Rossato, L. Sensitivity of TDS-1 GNSS-R Reflectivity to Soil Moisture: Global and Regional Differences and Impact of Different Spatial Scales. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chew, C.; Small, E. Soil Moisture Sensing Using Spaceborne GNSS Reflections: Comparison of CYGNSS Reflectivity to SMAP Soil Moisture. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 4049–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chew, C.; Small, E. Description of the UCAR/CU Soil Moisture Product. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Ji, R.; Liu, B.; Li, H.; Zhu, S. A Two-Step Method to Calibrate CYGNSS-Derived Land Surface Reflectivity for Accurate Soil Moisture Estimations. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 2500405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindlish, R.; Barros, A.P. Parameterization of vegetation backscatter in radar-based, soil moisture estimation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 76, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egido, A.; Ruffini, G.; Caparrini, M.; Martín, C.; Farrés, E.; Banqué, X. Soil moisture monitorization using GNSS reflected signals. In Proceedings of the 1st Colloquium Scientific and Fundamental Aspects of the Galileo Programme, Toulouse, France, 25–27 October 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Biome. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biome (accessed on 1 January 2022).
- Lim; Hwang; Kuang. The Sahara Desert Northern Africa. Available online: https://biomania-saharadesert.weebly.com/climatelocation.html (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Henchiri, M.; Igbawua, T.; Javed, T.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, S.; Essifi, B.; Ujoh, F.; Zhang, J. Meteorological Drought Analysis and Return Periods over North and West Africa and Linkage with El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO). Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stilla, D.; Zribi, M.; Pierdicca, N.; Baghdadi, N.; Huc, M. Desert Roughness Retrieval Using CYGNSS GNSS-R Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gleason, S.; O’Brien, A.; Russel, A.; Al-Khaldi, M.M.; Johnson, J.T. Geolocation, Calibration and Surface Resolution of CYGNSS GNSS-R Land Observations. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beauducel, F. READHGT: Import/Download NASA SRTM Data Files (.HGT). MATLAB Central File Exchange. 2022. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/36379-readhgt-import-download-nasa-srtm-data-files-hgt (accessed on 1 February 2022).
- Das, N.; Entekhabi, D.; Dunbar, R.S.; Kim, S.; Yueh, S.; Colliander, A.; O’Neill, P.E.; Jackson, T. SMAP/Sentinel-1 L2 Radiometer/Radar 30-Second Scene 3 km EASE-Grid Soil Moisture, Version 2; 1 to 30 April 2019; NASA National Snow and Ice Data Center Distributed Active Archive Center: Boulder, CO, USA, 2018; Available online: https://nsidc.org/data/SPL2SMAP_S/versions/2 (accessed on 1 February 2022).
- OPeNDAP-PODAAC FTP Layout. Available online: https://podaac-opendap.jpl.nasa.gov (accessed on 1 September 2019).
- Jia, Y.; Pei, Y. Remote Sensing in Land Applications by Using GNSS-Reflectometry. In Recent Advances and Applications in Remote Sensing; Hung, M.-C., Wu, Y.-H., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gleason, S. Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document Level 1A DDM Calibration. In CYGNSS Level 1 Science Data Record Version 2.1; PO.DAAC: Ann Arbor, MI, USA; Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System (CYGNSS): Pasadena, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gleason, S. Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document Level 1B DDM Calibration. In CYGNSS Level 1 Science Data Record Version 2.1; PO.DAAC: Ann Arbor, MI, USA; Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System (CYGNSS): Pasadena, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ruf, C.; Chang, P.; Clarizia, M.P.; Gleason, S.; Jelenak, Z.; Murray, J.; Morris, M.; Musko, S.; Posselt, D.; Provost, D.; et al. CYGNSS Handbook Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System: Deriving Surface Wind Speeds in Tropical Cyclones; National Aeronautics and Space Administration: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2016; p. 154. ISBN 978-1-60785-380-0. [Google Scholar]
- Katzberg, S.J.; Torres, O.; Grant, M.S.; Masters, D. Utilizing calibrated GPS reflected signals to estimate soil reflectivity and dielectric constant: Results from SMEX02. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 100, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiao, X.; Khalilian, A.; Payero, J.O.; Maja, J.M.; Privette, C.V.; Han, Y.J. Evaluating Reflected GPS Signal as a Potential Tool for Cotton Irrigation Scheduling. Adv. Remote Sens. 2016, 5, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chew, C.; Lowe, S.; Parazoo, N.; Esterhuizen, S.; Oveisgharan, S.; Podest, E.; Zuffada, C.; Freedman, A. SMAP radar receiver measures land surface freeze/thaw state through capture of forward-scattered L-band signals. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 198, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrazzoli, P.; Guerriero, L.; Pierdicca, N.; Rahmoune, R. Forest biomass monitoring with GNSS-R: Theoretical simulations. Adv. Space Res. 2011, 47, 1823–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, C.; Reager, J.T.; Small, E. CYGNSS data map flood inundation during the 2017 Atlantic hurricane season. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, W.; Liu, B.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, X.; Wu, G.; Xu, L.; Chen, X.; Hong, Y. Using CYGNSS Data to Monitor China’s Flood Inundation during Typhoon and Extreme Precipitation Events in 2017. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajabi, M.; Nahavandchi, H.; Hoseini, M. Evaluation of CYGNSS Observations for Flood Detection and Mapping during Sistan and Baluchestan Torrential Rain in 2020. Water 2020, 12, 2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edokossi, K.; Calabia, A.; Jin, S.G.; Molina, I. GNSS-Reflectometry and Remote Sensing of Soil Moisture: A Review of Measurement Techniques, Methods, and Applications. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shahidi, M.; Hasted, J.; Jonscher, A. Electrical properties of dry and humid sand. Nature 1975, 258, 595–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, M.C.; Ulaby, F.T.; Hallikainen, M.T.; El-Rayes, M.A. Microwave Dielectric Behavior of Wet Soil-Part II: Dielectric Mixing Models. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1985, 23, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artemov, V.G.; Volkov, A.A. Water and Ice Dielectric Spectra Scaling at 0 °C. Ferroelectrics 2014, 466, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mätzler, C. Microwave permittivity of dry sand. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 317–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, N.J. Chapter 2-Electrical and Magnetic Properties of Rocks, Soils and Fluids; Harry, M.J., Ed.; Ground Penetrating Radar Theory and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 41–72. ISBN 9780444533487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitterman, D.V. 11.10-Tools and Techniques: Active-Source Electromagnetic Methods. In Treatise on Geophysics, 2nd ed.; Schubert, G., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 295–333. ISBN 9780444538031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallikainen, M. Microwave Dielectric Properties of Materials. In Encyclopedia of Remote Sensing; Encyclopedia of Earth Sciences Series; Njoku, E.G., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speight, J.G. 2-The properties of water. In Speight, Natural Water Remediation, Butterworth-Heinemann, James, G., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 53–89. ISBN 9780128038109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, T.; Wentz, F.J. The complex dielectric constant of pure and sea water from microwave satellite observations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42–49, 1836–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vijay, R.; Jain, R.; Sharma, K.S. Dielectric Spectroscopy of Grape Juice at Microwave Frequencies. Int. Agrophysics 2015, 29, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fano, W.G.; Trainotti, V. Dielectric properties of soils. In Proceedings of the 2001 Annual Report Conference on Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomena (Cat. No. 01CH37225), Kitchener, ON, Canada, 14–17 October 2001; pp. 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mätzler, C.; Murk, A. Complex Dielectric Constant of Dry Sand in the 0.1 to 2 GHz Range; Research Report No. 2010-06-MW.; Institute of Applied Physics, University of Bern: Bern, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calla, O.P.N. Study of the properties of dry and wet loamy sand soils at microwave frequencies. Indian. J. Radio Space Phys. 1999, 28, 109–112. [Google Scholar]
- Ulaby, F.T.; Moore, R.K.; Fung, A.K. Microwave Remote Sensing. In From Theory to Applications; Artech House: New York, NY, USA, 1986; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Ulaby, F.; Long, D.G. Microwave Radar and Radiometric Remote Sensing; The University of Michigan Press: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2014; 984p, ISBN 978-0-472-11935-6. [Google Scholar]
- USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service. Soil Quality Indicators. Available online: https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/portal/nrcs/detail/soils/health/assessment/?cid=stelprdb1237387 (accessed on 15 February 2020).
- Global Gridded Surfaces of Selected Soil Characteristics. 2005. International Geosphere Biosphere Programme. Initiative I. Volumes 1–5. Global Data Sets for Land-Atmosphere Models. The International Satellite Land Surface Climatology Project. 1996. Available online: https://databasin.org/datasets/6fa1816931124221b1d55e0dd4a0e7c3/ (accessed on 15 February 2020).
- Ahmad, H.A.; Tarek, M.S. Measured Dielectric Permittivity of Contaminated Sandy Soil at Microwave Frequency. J. Microw. Optoelectron. Electromagn. Appl. 2016, 15, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meyer, K.; Erdogmus, E.; Morcous, G.; Naughtin, M. Use of Ground Penetrating Radar for Accurate Concrete Thickness Measurements. In Proceedings of the Architectural Engineering Conference (AEI) 2008, Denver, CO, USA, 24–27 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Complex Dielectric Constant of Water. Available online: https://www.random-science-tools.com/electronics/water_dielectric.htm (accessed on 15 February 2022).
- Topp, G.C.; Davis, J.L.; Annan, A.P. Electromagnetic determination of soil water content: Measurements in coaxial transmission lines. Water Resour. Res. 1980, 16, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, K.; Kumar Paul, P. Present status of soil moisture estimation by microwave remote sensing. Cogent Geosci. 2015, 1, 1084669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Soil Moisture Network. Available online: https://ismn.geo.tuwien.ac.at/en/ (accessed on 1 February 2022).













| Location, Country | From Coordinates | To Coordinates |
|---|---|---|
| Sahara Desert, Mali | (18°N, 6°W) | (21°N, 3°W) |
| Rub’Al Khali Desert, Saudi Arabia | (19°N, 50°E) | (22°N, 53°E) |
| Savanna of Beni District, Bolivia | (15°S, 67°W) | (12°S, 64°W) |
| Ganges Delta, Bangladesh | (22°N, 88°E) | (25°N, 91°E) |
| Location, Country | Median | Quantile at 99% |
|---|---|---|
| Sahara Desert, Mali | 0.0047 | - |
| Rub’Al Khali Desert, Saudi Arabia | 0.0015 | - |
| Savanna of Beni District, Bolivia | - | 0.2047 |
| Ganges Delta, Bangladesh | - | 0.2095 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Molina, I.; Calabia, A.; Jin, S.; Edokossi, K.; Wu, X. Calibration and Validation of CYGNSS Reflectivity through Wetlands’ and Deserts’ Dielectric Permittivity. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3262. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14143262
Molina I, Calabia A, Jin S, Edokossi K, Wu X. Calibration and Validation of CYGNSS Reflectivity through Wetlands’ and Deserts’ Dielectric Permittivity. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(14):3262. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14143262
Chicago/Turabian StyleMolina, Iñigo, Andrés Calabia, Shuanggen Jin, Komi Edokossi, and Xuerui Wu. 2022. "Calibration and Validation of CYGNSS Reflectivity through Wetlands’ and Deserts’ Dielectric Permittivity" Remote Sensing 14, no. 14: 3262. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14143262
APA StyleMolina, I., Calabia, A., Jin, S., Edokossi, K., & Wu, X. (2022). Calibration and Validation of CYGNSS Reflectivity through Wetlands’ and Deserts’ Dielectric Permittivity. Remote Sensing, 14(14), 3262. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14143262