Evapotranspiration Retrieval Using S-SEBI Model with Landsat-8 Split-Window Land Surface Temperature Products over Two European Agricultural Crops
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Areas and Data
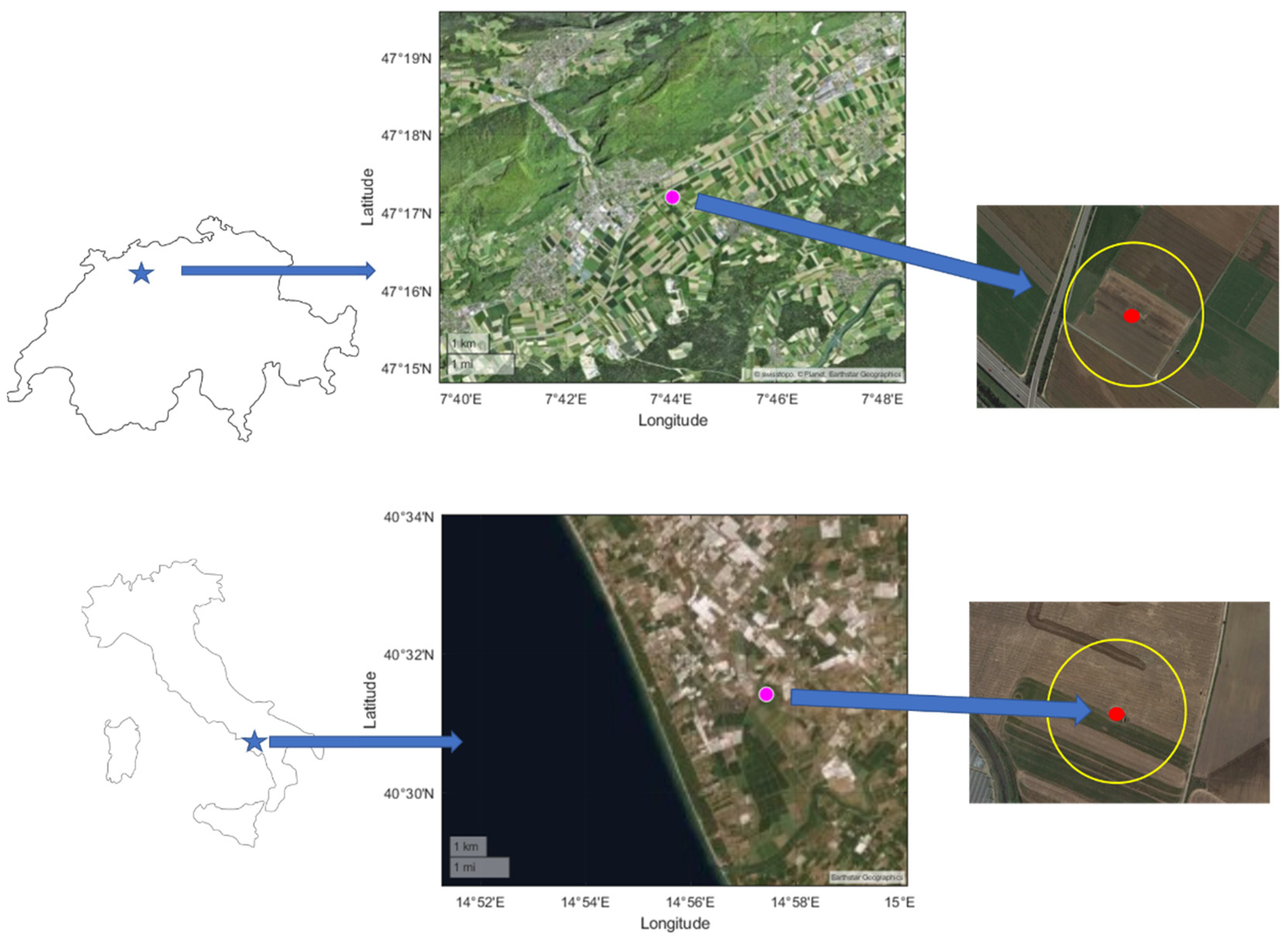
2.1. Description of Sites and Field Flux Data
2.2. Remote Sensing Data
3. Method
3.1. S-SEBI ET Model Description
3.2. LST and Albedo Landsat-8-Derived Products
3.3. Rn and G Fluxes from MSG/Landsat-8-Derived Products
3.4. Daily Evapotranspiration
3.5. ERA5-Land ETd Reanalysis Data
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
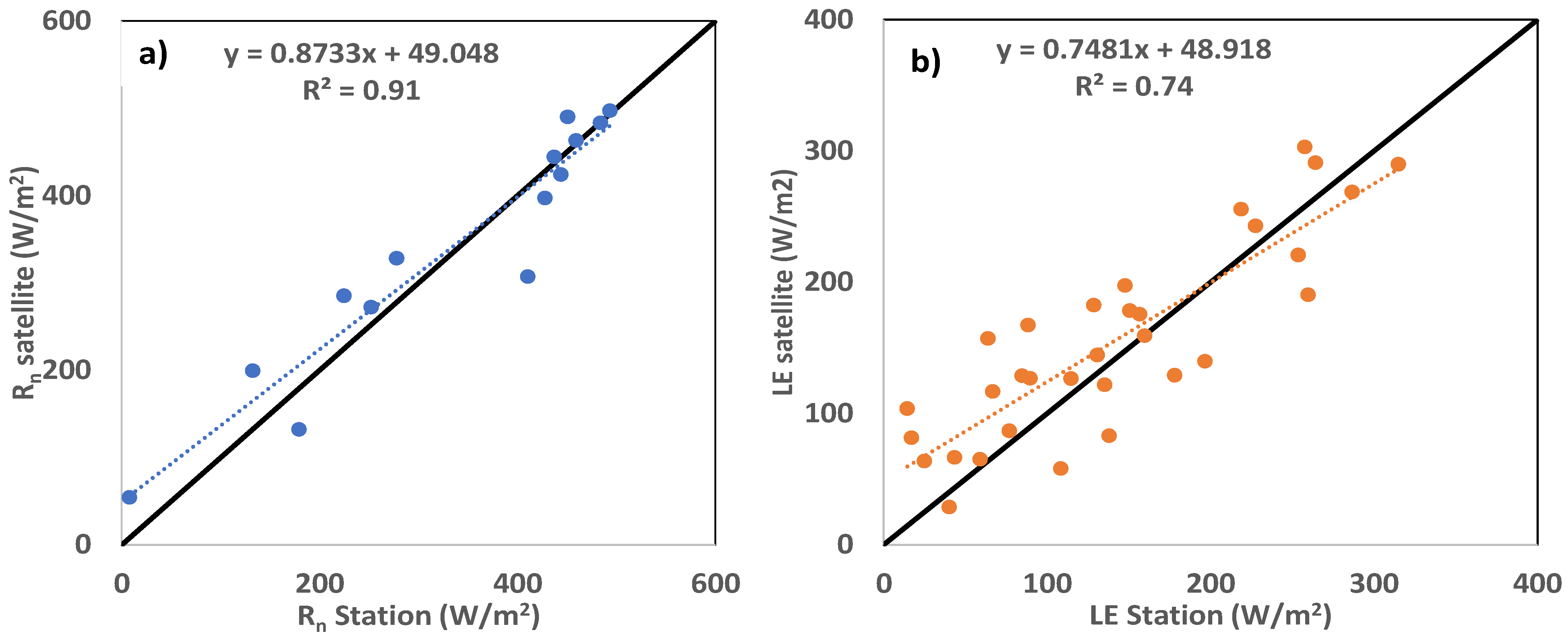
4.1. Comparison with Ground-Measured Data
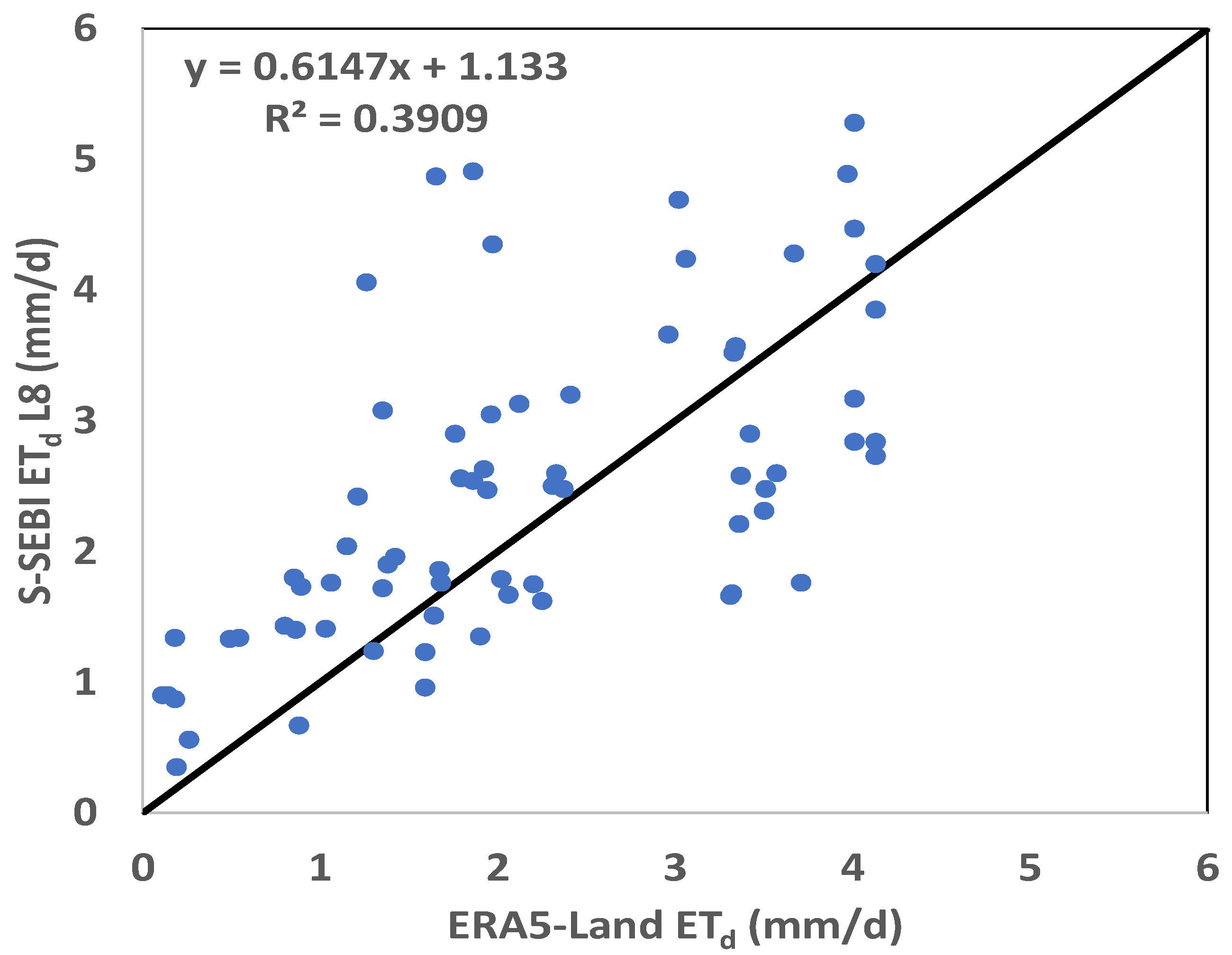
4.2. Comparison with ERA-5/Land Reanalysis Data
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sheffield, J.; Wood, E.F.; Roderick, M.L. Little change in global drought over the past 60 years. Nature 2012, 491, 435–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kljun, N.; Calanca, P.; Rotach, M.W.; Schmid, H.P. A Simple Parameterisation for Flux Footprint Predictions. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2004, 112, 503–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-L.; Tang, R.; Wan, Z.; Bi, Y.; Zhou, C.; Tang, B.; Yan, G.; Zhang, X. A Review of Current Methodologies for Regional Evapotranspiration Estimation from Remotely Sensed Data. Sensors 2009, 9, 3801–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roerink, G.J.; Su, Z.; Menenti, M. S-SEBI: A simple remote sensing algorithm to estimate the surface energy balance. Phys. Chem. Earth Part B Hydrol. Oceans Atmos. 2000, 25, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-L.; Tang, B.-H.; Wu, H.; Ren, H.; Yan, G.; Wan, Z.; Trigo, I.F.; Sobrino, J.A. Satellite-derived land surface temperature: Current status and perspectives. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 131, 14–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhattarai, N.; Wagle, P.; Gowda, P.H.; Kakani, V.G. Utility of remote sensing-based surface energy balance models to track water stress in rain-fed switchgrass under dry and wet conditions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 133, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, B.; Sharma, V. Comparison of Satellite Driven Surface Energy Balance Models in Estimating Crop Evapotranspiration in Semi-Arid to Arid Inter-Mountain Region. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danodia, A.; Patel, N.R.; Chol, C.W.; Nikam, B.R.; Sehgal, V.K. Application of S-SEBI model for crop evapotranspiration using Landsat-8 data over parts of North India. Geocarto Int. 2017, 34, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Yang, Y.; Wu, R.; Gui, D.; Xue, J.; Liu, Y.; Yan, D. Improving Estimation of Cropland Evapotranspiration by the Bayesian Model Averaging Method with Surface Energy Balance Models. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elkatoury, A.; Alazba, A.A.; Mossad, A. Estimating Evapotranspiration Using Coupled Remote Sensing and Three SEB Models in an Arid Region. Environ. Process. 2019, 7, 109–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkatoury, A.; Alazba, A.A.; Abdelbary, A. Evaluating the performance of two SEB models for estimating ET based on satellite images in arid regions. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Käfer, P.S.; da Rocha, N.S.; Diaz, L.R.; Kaiser, E.A.; Santos, D.C.; Veeck, G.P.; Robérti, D.R.; Rolim, S.B.A.; de Oliveira, G.G. Artificial neural networks model based on remote sensing to retrieve evapotranspiration over the Brazilian Pampa. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2020, 14, 038504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrino, J.A.; da Rocha, N.S.; Skoković, D.; Käfer, P.S.; López-Urrea, R.; Jiménez-Muñoz, J.C.; Rolim, S.B.A. Evapotranspiration Estimation with the S-SEBI Method from Landsat 8 Data against Lysimeter Measurements at the Barrax Site, Spain. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Running, S.W.; Baldocchi, D.D.; Turner, D.P.; Gower, S.T.; Bakwin, P.S.; Hibbard, K.A. A Global Terrestrial Monitoring Network Integrating Tower Fluxes, Flask Sampling, Ecosystem Modeling and EOS Satellite Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1999, 70, 108–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietiker, D.; Buchmann, N.; Eugster, W. Testing the ability of the DNDC model to predict CO2 and water vapour fluxes of a Swiss cropland site. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 139, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, L.; Di Tommasi, P.; D’Urso, G.; Magliulo, V. The response of ecosystem carbon fluxes to LAI and environmental drivers in a maize crop grown in two contrasting seasons. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2016, 60, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gobiet, A.; Kotlarski, S.; Beniston, M.; Heinrich, G.; Rajczak, J.; Stoffel, M. 21st century climate change in the European Alps—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 1138–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irons, J.R.; Dwyer, J.; Barsi, J.A. The next Landsat satellite: The Landsat Data Continuity Mission. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 122, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerace, A.; Montanaro, M. Derivation and validation of the stray light correction algorithm for the thermal infrared sensor onboard Landsat 8. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 191, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Santos, V.; Cuxart, J.; Martínez-Villagrasa, D.; Jiménez, M.A.; Simó, G. Comparison of Three Methods for Estimating Land Surface Temperature from Landsat 8-TIRS Sensor Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niclòs, R.; Puchades, J.; Coll, C.; Barberà, M.J.; Pérez-Planells, L.; Valiente, J.A.; Sánchez, J.M. Evaluation of Landsat-8 TIRS data recalibrations and land surface temperature split-window algorithms over a homogeneous crop area with different phenological land covers. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 174, 237–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerace, A.; Kleynhans, T.; Eon, R.; Montanaro, M. Towards an Operational, Split Window-Derived Surface Temperature Product for the Thermal Infrared Sensors Onboard Landsat 8 and 9. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hulley, G.; Hook, S. The ASTER Global Emissivity Database (ASTER GED); Jet Propulsion Laboratory: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, T.; Gu, X.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Yu, S.-S.; Zhang, W.-J.; Li, X. Land Surface Temperature Retrieval from CBERS-02 IRMSS Thermal Infrared Data and Its Applications in Quantitative Analysis of Urban Heat Island Effect. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Erb, A.M.; Schaaf, C.B.; Sun, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Shuai, Y.; Casey, K.; Román, M.O. Early spring post-fire snow albedo dynamics in high latitude boreal forests using Landsat-8 OLI data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jackson, R.D.; Hatfield, J.L.; Reginato, R.J.; Idso, S.B.; Pinter, P.J., Jr. Estimation of daily evapotranspiration from one time-of-day measurements. Agric. Water Manag. 1983, 7, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Dutra, E.; Agustí-Panareda, A.; Albergel, C.; Arduini, G.; Balsamo, G.; Boussetta, S.; Choulga, M.; Harrigan, S.; Hersbach, H.; et al. ERA5-Land: A state-of-the-art global reanalysis dataset for land applications. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 4349–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelosi, A.; Chirico, G.B. Regional assessment of daily reference evapotranspiration: Can ground observations be replaced by blending ERA5-Land meteorological reanalysis and CM-SAF satellite-based radiation data? Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 258, 107169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, C.J. On the Validation Of Models. Phys. Geogr. 1981, 2, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Ren, H.; Qin, Q.; Meng, J.; Zhao, S. A Practical Split-Window Algorithm for Estimating Land Surface Temperature from Landsat 8 Data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 647–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Rn (W/m2) | LE (W/m2) | ETd (mm/d) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | 0.91 | 0.74 | 0.72 |
| StDev | 5 | 8 | 0.2 |
| RMSE | 50 | 50 | 0.9 |
| MAE | 40 | 40 | 0.7 |
| MBE | −7 | −14 | −0.3 |
| NSE | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.6 |
| AI | 0.997 | 0.996 | 0.996 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garcia-Santos, V.; Niclòs, R.; Valor, E. Evapotranspiration Retrieval Using S-SEBI Model with Landsat-8 Split-Window Land Surface Temperature Products over Two European Agricultural Crops. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14112723
Garcia-Santos V, Niclòs R, Valor E. Evapotranspiration Retrieval Using S-SEBI Model with Landsat-8 Split-Window Land Surface Temperature Products over Two European Agricultural Crops. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(11):2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14112723
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcia-Santos, Vicente, Raquel Niclòs, and Enric Valor. 2022. "Evapotranspiration Retrieval Using S-SEBI Model with Landsat-8 Split-Window Land Surface Temperature Products over Two European Agricultural Crops" Remote Sensing 14, no. 11: 2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14112723
APA StyleGarcia-Santos, V., Niclòs, R., & Valor, E. (2022). Evapotranspiration Retrieval Using S-SEBI Model with Landsat-8 Split-Window Land Surface Temperature Products over Two European Agricultural Crops. Remote Sensing, 14(11), 2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14112723








