Point RCNN: An Angle-Free Framework for Rotated Object Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
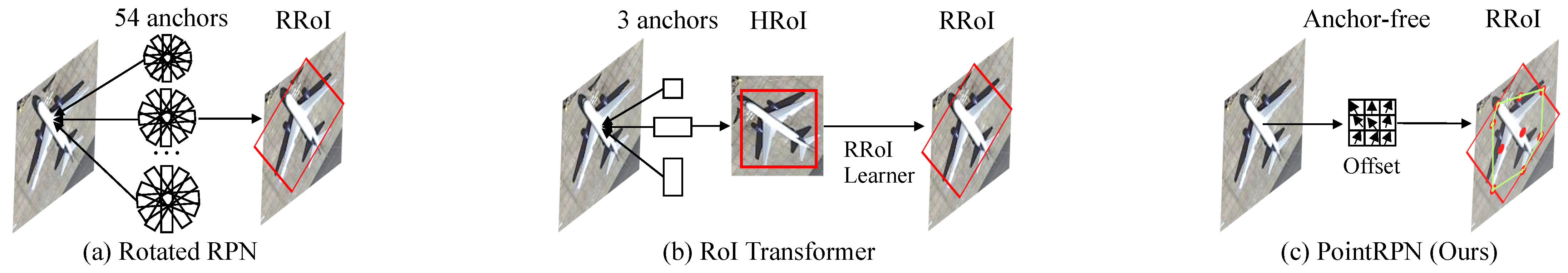
- We propose Point RCNN, a purely angle-free framework for rotated object detection in aerial images. Without introducing angle prediction, Point RCNN is able to address the boundary discontinuity problem.
- We propose PointRPN as an RPN network, which aims to learn a set of representative points for each object of interest, and can provide better detection recall for rotated objects in aerial images.
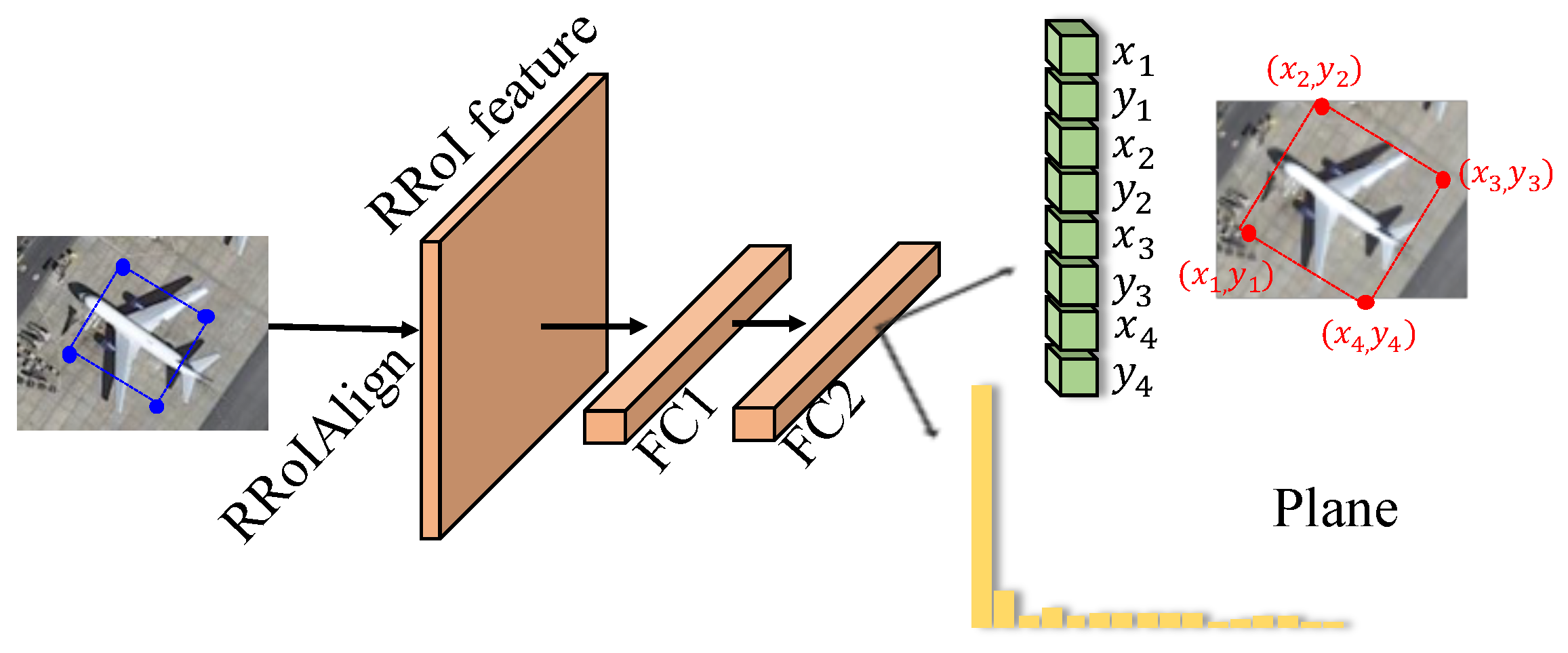
- We propose PointReg as an RCNN head, which can responsively regress and refine the four corners of the rotated proposals generated by PointRPN.
- Aerial images are usually long-tail distributed. We further propose to resample images of rare categories to stabilize training and improve the overall performance.
- Compared with state-of-the-art methods, extensive experiments demonstrate that our Point RCNN framework attains higher detection performance on multiple large-scale datasets and achieves new state-of-the-art performance.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Related Work
2.1.1. Horizontal Object Detection
2.1.2. Rotated Object Detection
2.2. Methods
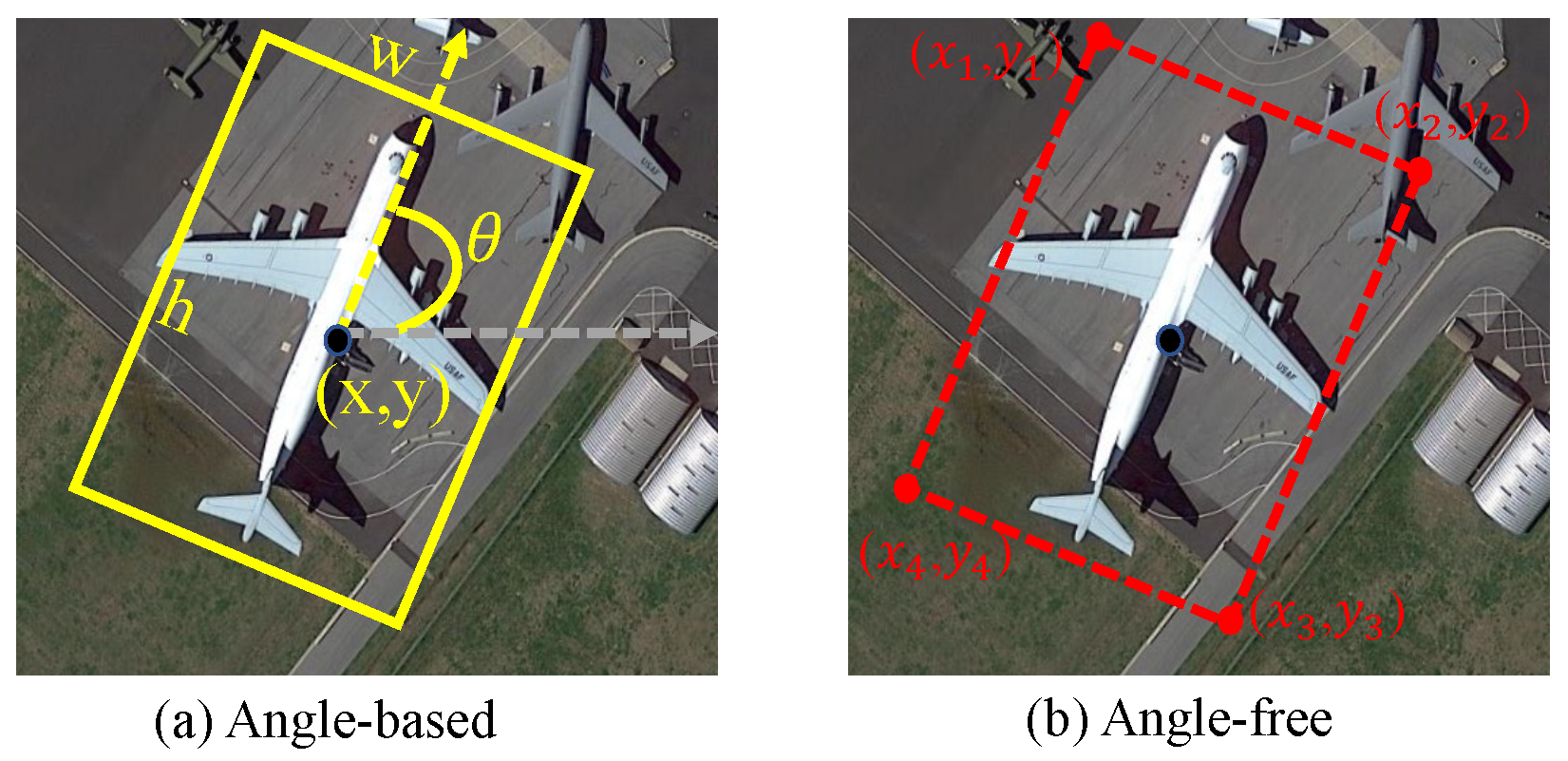
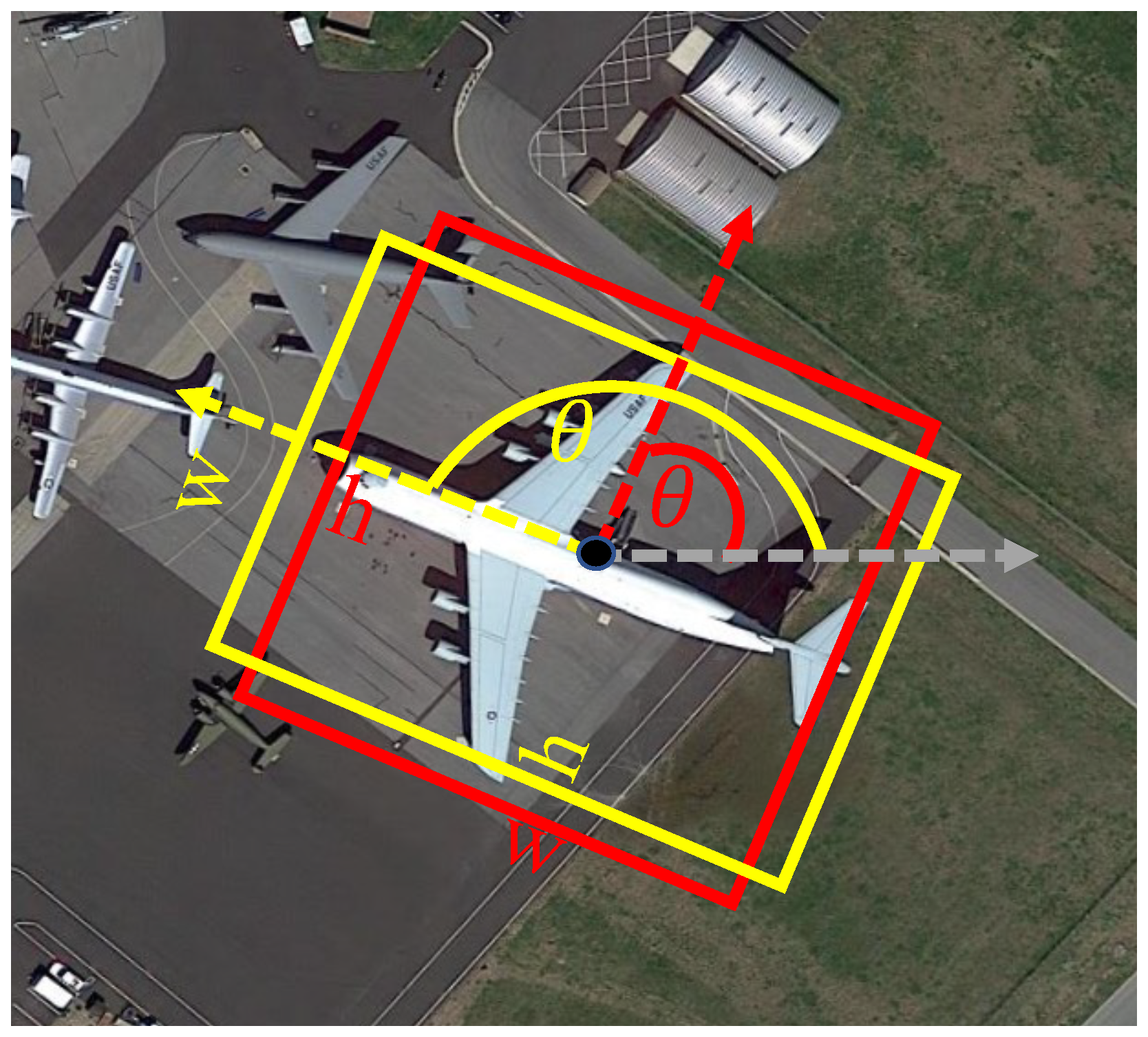
2.2.1. Boundary Discontinuity Problem
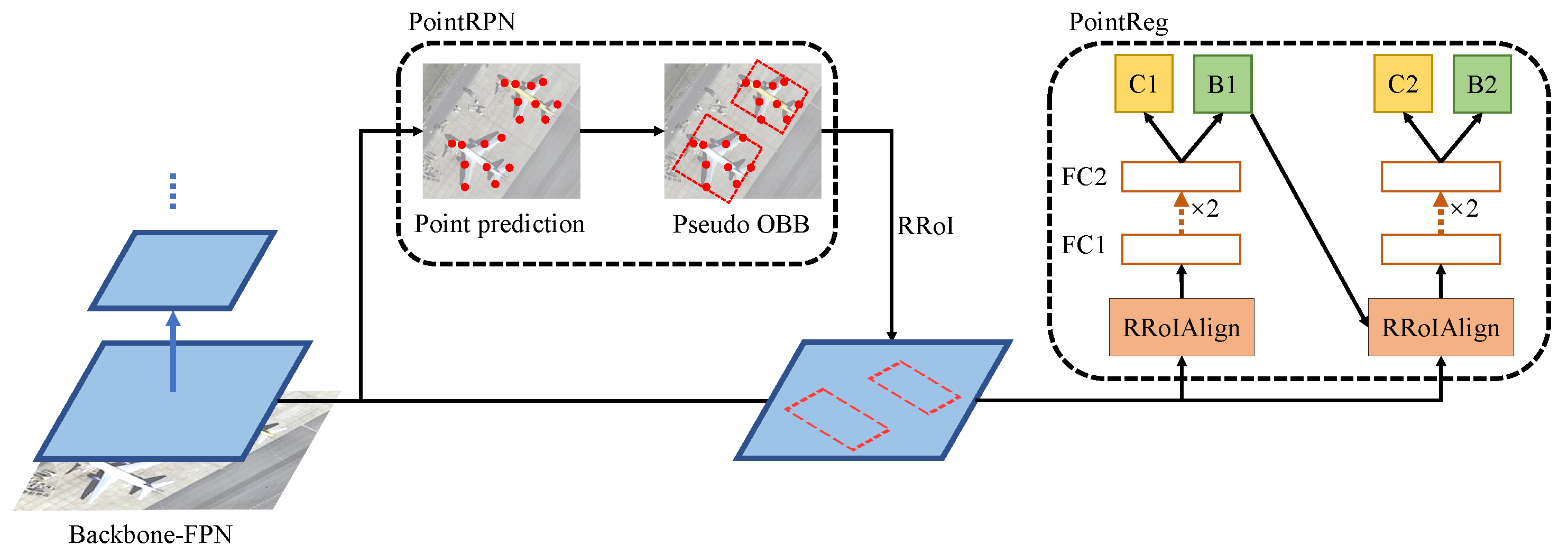
2.2.2. Overview
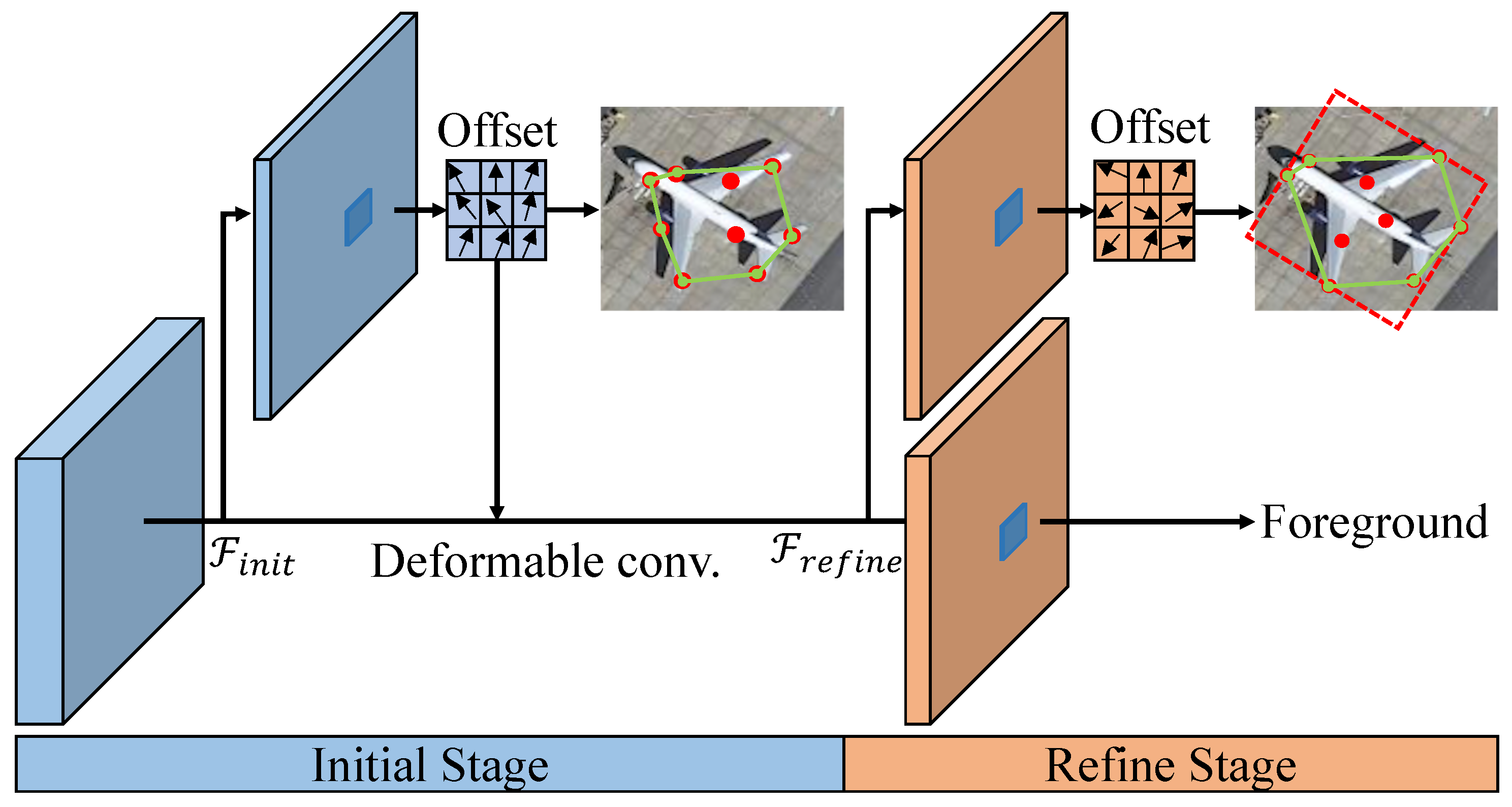
2.2.3. PointRPN
2.2.4. PointReg
2.2.5. Balanced Dataset Strategy
3. Results
3.1. Datasets
3.2. Implementation Details
3.3. Main Results
| Method | Backbone | PL | BD | BR | GTF | SV | LV | SH | TC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RoI Trans. * [13] | R101-FPN | 88.64 | 78.52 | 43.44 | 75.92 | 68.81 | 73.68 | 83.59 | 90.74 |
| O-DNet * [63] | H104 | 89.30 | 83.30 | 50.10 | 72.10 | 71.10 | 75.60 | 78.70 | 90.90 |
| DRN * [64] | H104 | 89.71 | 82.34 | 47.22 | 64.10 | 76.22 | 74.43 | 85.84 | 90.57 |
| Gliding Vertex * [26] | R101-FPN | 89.64 | 85.00 | 52.26 | 77.34 | 73.01 | 73.14 | 86.82 | 90.74 |
| BBAVectors * [27] | R101 | 88.63 | 84.06 | 52.13 | 69.56 | 78.26 | 80.40 | 88.06 | 90.87 |
| CenterMap * [65] | R101-FPN | 89.83 | 84.41 | 54.60 | 70.25 | 77.66 | 78.32 | 87.19 | 90.66 |
| CSL * [19] | R152-FPN | 90.25 | 85.53 | 54.64 | 75.31 | 70.44 | 73.51 | 77.62 | 90.84 |
| SCRDet++ * [23] | R152-FPN | 88.68 | 85.22 | 54.70 | 73.71 | 71.92 | 84.14 | 79.39 | 90.82 |
| CFA [55] | R-152 | 89.08 | 83.20 | 54.37 | 66.87 | 81.23 | 80.96 | 87.17 | 90.21 |
| SA-Net * [21] | R50-FPN | 88.89 | 83.60 | 57.74 | 81.95 | 79.94 | 83.19 | 89.11 | 90.78 |
| ReDet * [15] | ReR50-ReFPN | 88.81 | 82.48 | 60.83 | 80.82 | 78.34 | 86.06 | 88.31 | 90.87 |
| Oriented RCNN * [16] | R101-FPN | 90.26 | 84.74 | 62.01 | 80.42 | 79.04 | 85.07 | 88.52 | 90.85 |
| Point RCNN * (Ours) | ReR50-ReFPN | 82.99 | 85.73 | 61.16 | 79.98 | 77.82 | 85.90 | 88.94 | 90.89 |
| Point RCNN (Ours) | ReR50-ReFPN | 86.21 | 86.44 | 60.30 | 80.12 | 76.45 | 86.17 | 88.58 | 90.84 |
| Point RCNN (Ours) | Swin-T-FPN | 86.59 | 85.72 | 61.64 | 81.08 | 81.01 | 86.49 | 88.84 | 90.83 |
| BC | ST | SBF | RA | HA | SP | HC | mAP | ||
| RoI Trans. * [13] | R101-FPN | 77.27 | 81.46 | 58.39 | 53.54 | 62.83 | 58.93 | 47.67 | 69.56 |
| O-DNet * [63] | H104 | 79.90 | 82.90 | 60.20 | 60.00 | 64.60 | 68.90 | 65.70 | 72.80 |
| DRN * [64] | H104 | 86.18 | 84.89 | 57.65 | 61.93 | 69.30 | 69.63 | 58.48 | 73.23 |
| Gliding Vertex * [26] | R101-FPN | 79.02 | 86.81 | 59.55 | 70.91 | 72.94 | 70.86 | 57.32 | 75.02 |
| BBAVectors * [27] | R101 | 87.23 | 86.39 | 56.11 | 65.62 | 67.10 | 72.08 | 63.96 | 75.36 |
| CenterMap * [65] | R101-FPN | 84.89 | 85.27 | 56.46 | 69.23 | 74.13 | 71.56 | 66.06 | 76.03 |
| CSL * [19] | R152-FPN | 86.15 | 86.69 | 69.60 | 68.04 | 73.83 | 71.10 | 68.93 | 76.17 |
| SCRDet++ * [23] | R152-FPN | 87.04 | 86.02 | 67.90 | 60.86 | 74.52 | 70.76 | 72.66 | 76.56 |
| CFA * [55] | R-152 | 84.32 | 86.09 | 52.34 | 69.94 | 75.52 | 80.76 | 67.96 | 76.67 |
| SA-Net * [21] | R50-FPN | 84.87 | 87.81 | 70.30 | 68.25 | 78.30 | 77.01 | 69.58 | 79.42 |
| ReDet * [15] | ReR50-ReFPN | 88.77 | 87.03 | 68.65 | 66.90 | 79.26 | 79.71 | 74.67 | 80.10 |
| Oriented RCNN * [16] | R101-FPN | 87.24 | 87.96 | 72.26 | 70.03 | 82.93 | 78.46 | 68.05 | 80.52 |
| Point RCNN * (Ours) | ReR50-ReFPN | 88.89 | 88.16 | 71.84 | 68.21 | 79.03 | 80.32 | 75.71 | 80.37 |
| Point RCNN * (Ours) | ReR50-ReFPN | 88.58 | 88.44 | 73.03 | 70.10 | 79.26 | 79.02 | 77.15 | 80.71 |
| Point RCNN * (Ours) | Swin-T-FPN | 87.22 | 88.23 | 68.85 | 71.48 | 82.09 | 83.60 | 76.08 | 81.32 |
| Method | Backbone | PL | BD | BR | GTF | SV | LV | SH | TC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RetinaNet-O [5] | R50-FPN | 71.43 | 77.64 | 42.12 | 64.65 | 44.53 | 56.79 | 73.31 | 90.84 | |
| FR-O [6] | R50-FPN | 71.89 | 74.47 | 44.45 | 59.87 | 51.28 | 68.98 | 79.37 | 90.78 | |
| Mask RCNN [2] | R50-FPN | 76.84 | 73.51 | 49.90 | 57.80 | 51.31 | 71.34 | 79.75 | 90.46 | |
| HTC [67] | R50-FPN | 77.80 | 73.67 | 51.40 | 63.99 | 51.54 | 73.31 | 80.31 | 90.48 | |
| OWSR * [68] | R101-FPN | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Oriented RCNN * [16] | R101-FPN | 87.20 | 84.67 | 60.13 | 80.79 | 67.51 | 81.63 | 89.74 | 90.88 | |
| ReDet * [15] | ReR50-ReFPN | 88.51 | 86.45 | 61.23 | 81.20 | 67.60 | 83.65 | 90.00 | 90.86 | |
| ReDet * [15] | Swin-T-FPN | 80.90 | 85.13 | 60.61 | 80.83 | 67.07 | 83.32 | 89.80 | 90.79 | |
| Point RCNN * (Ours) | ReR50-ReFPN | 83.40 | 86.59 | 60.76 | 80.25 | 79.92 | 83.37 | 90.04 | 90.86 | |
| Point RCNN * (Ours) | ReR50-ReFPN | 83.12 | 86.55 | 60.84 | 82.43 | 80.60 | 83.39 | 90.01 | 90.88 | |
| Point RCNN * (Ours) | Swin-T-FPN | 83.88 | 85.22 | 60.76 | 79.40 | 81.64 | 83.48 | 89.98 | 90.75 | |
| Point RCNN * (Ours) | Swin-T-FPN | 86.93 | 85.79 | 59.52 | 80.42 | 81.91 | 81.92 | 89.95 | 90.35 | |
| BC | ST | SBF | RA | HA | SP | HC | CC | mAP | ||
| RetinaNet-O [5] | R50-FPN | 76.02 | 59.96 | 46.95 | 69.24 | 59.65 | 64.52 | 48.06 | 0.83 | 59.16 |
| FR-O [6] | R50-FPN | 77.38 | 67.50 | 47.75 | 69.72 | 61.22 | 65.28 | 60.47 | 1.54 | 62.00 |
| Mask RCNN [2] | R50-FPN | 74.21 | 66.07 | 46.21 | 70.61 | 63.07 | 64.46 | 57.81 | 9.42 | 62.67 |
| HTC [67] | R50-FPN | 75.12 | 67.34 | 48.51 | 70.63 | 64.84 | 64.48 | 55.87 | 5.15 | 63.40 |
| OWSR * [68] | R101-FPN | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 74.90 |
| Oriented RCNN * [16] | R101-FPN | 82.21 | 78.51 | 70.98 | 78.63 | 79.46 | 75.40 | 75.71 | 39.69 | 76.45 |
| ReDet * [15] | ReR50-ReFPN | 84.30 | 75.33 | 71.49 | 72.06 | 78.32 | 74.73 | 76.10 | 46.98 | 76.80 |
| ReDet * [15] | Swin-T-FPN | 86.04 | 78.69 | 75.35 | 77.38 | 78.48 | 75.41 | 79.51 | 61.95 | 78.20 |
| Point RCNN * (Ours) | ReR50-ReFPN | 87.45 | 84.50 | 72.79 | 77.32 | 78.29 | 77.48 | 78.92 | 47.97 | 78.74 |
| Point RCNN * (Ours) | ReR50-ReFPN | 87.25 | 84.60 | 73.49 | 78.51 | 78.75 | 78.41 | 76.12 | 54.12 | 79.31 |
| Point RCNN * (Ours) | Swin-T-FPN | 87.00 | 84.65 | 70.70 | 77.87 | 78.32 | 79.50 | 74.35 | 63.80 | 79.46 |
| Point RCNN * (Ours) | Swin-T-FPN | 85.72 | 85.84 | 68.57 | 76.35 | 78.79 | 81.24 | 78.64 | 69.23 | 80.14 |
| Method | Backbone | mAP (%) | mAP (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RC2 [69] | VGG16 | 75.70 | - |
| RRPN [17] | R101 | 79.08 | 85.64 |
| RPN [18] | VGG16 | 79.60 | - |
| RRD [70] | VGG16 | 84.30 | - |
| RoI-Trans. [13] | R101-FPN | 86.20 | - |
| Gliding Vertex [26] | R101-FPN | 88.20 | - |
| RDet [20] | R101-FPN | 89.26 | - |
| DRN [64] | H34 | - | 92.7 |
| CenterMap [65] | R50-FPN | - | 92.8 |
| CSL [19] | R152-FPN | 89.62 | - |
| SA-Net [21] | R101-FPN | 90.17 | 95.01 |
| ReDet [15] | ReR50-ReFPN | 90.46 | 97.63 |
| Orient RCNN [16] | R101-FPN | 90.50 | 97.60 |
| Point RCNN (Ours) | ReR50-ReFPN | 90.53 | 98.53 |
| Method | Backbone | Car | Airplane | mAP (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R-Yolov3 [71] | Darknet53 | 74.63 | 89.52 | 82.08 |
| R-RetinaNet [5] | ResNet50 | 84.64 | 90.51 | 87.57 |
| RoI-Trans. [13] | ResNet50 | 88.02 | 90.02 | 89.02 |
| DAL [72] | ResNet50 | 89.25 | 90.49 | 89.87 |
| SA-Net [21] | ResNet50 | 89.56 | 90.42 | 89.99 |
| Point RCNN (Ours) | ReR50-ReFPN | 89.60 | 90.48 | 90.04 |
3.4. Ablation Study
3.4.1. Analysis of PointRPN
3.4.2. Effectiveness of PointReg
3.4.3. Analysis of Balanced Dataset Strategy
3.4.4. Factor-by-Factor Experiment
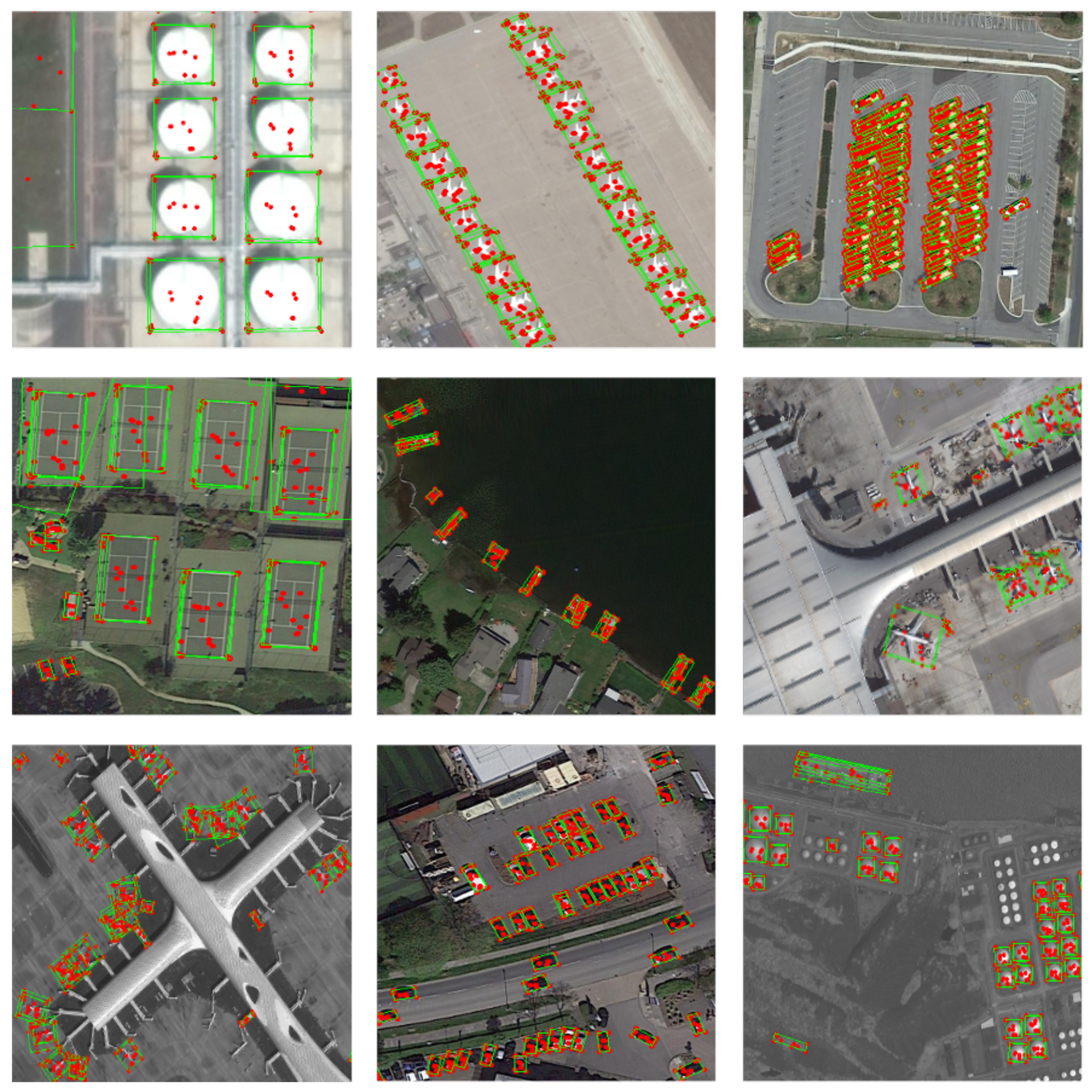
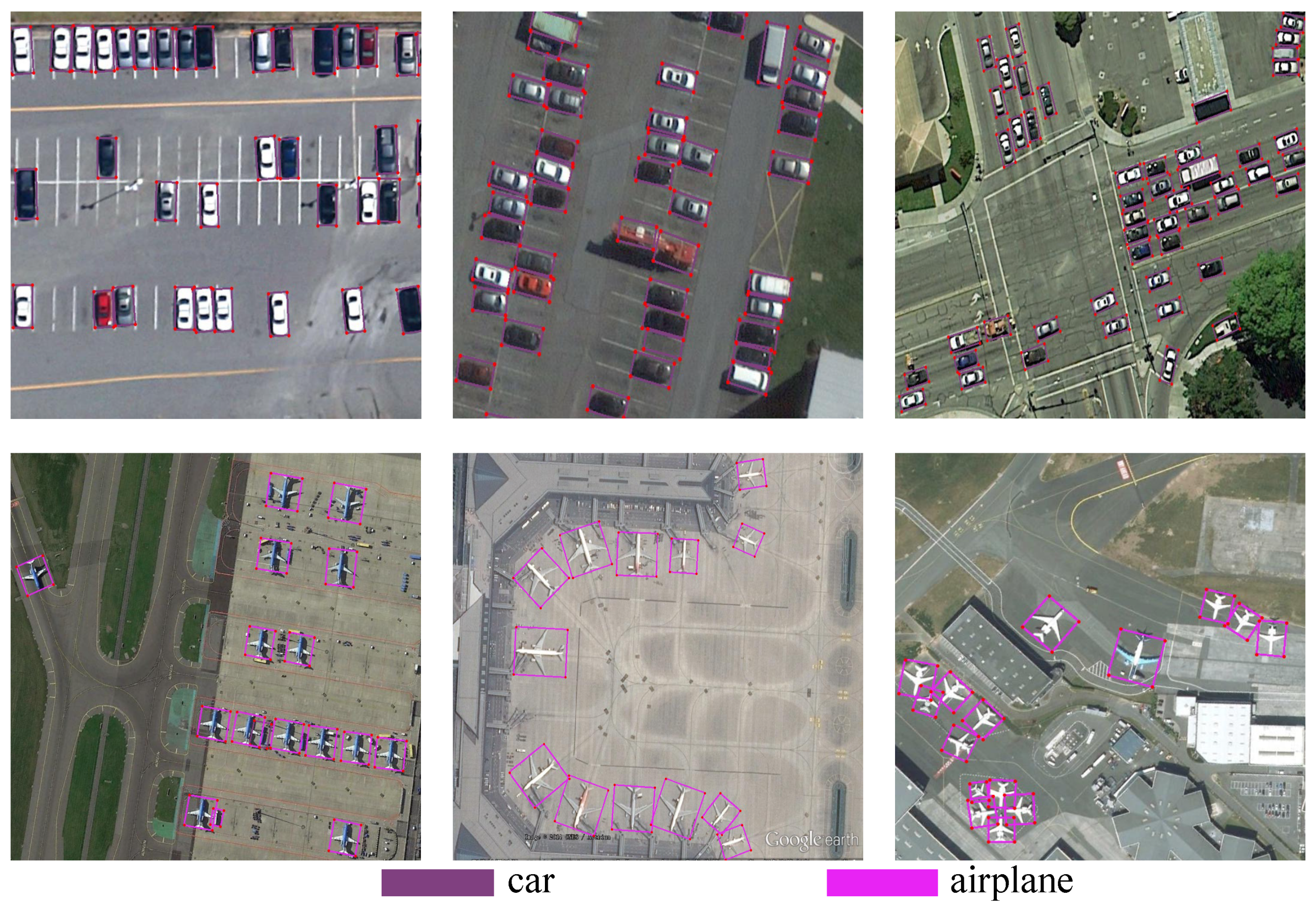
3.4.5. Visualization Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.B.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. In Proceedings of the NeurIPS, Montreal, ON, Canada, 7–12 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2961–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. In Proceedings of the CVPR 2016, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector. In Proceedings of the ECCV 2016, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.B.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision 2017, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, G.S.; Bai, X.; Ding, J.; Zhu, Z.; Belongie, S.; Luo, J.; Datcu, M.; Pelillo, M.; Zhang, L. DOTA: A large-scale dataset for object detection in aerial images. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 3974–3983. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.; Xue, N.; Xia, G.S.; Bai, X.; Yang, W.; Yang, M.Y.; Belongie, S.; Luo, J.; Datcu, M.; Pelillo, M.; et al. Object detection in aerial images: A large-scale benchmark and challenges. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.12219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Pan, Z.; Lei, B.; Hu, Y. LR-TSDet: Towards Tiny Ship Detection in Low-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibakhshikenari, M.; Virdee, B.S.; Althuwayb, A.A.; Aïssa, S.; See, C.H.; Abd-Alhameed, R.A.; Falcone, F.; Limiti, E. Study on on-chip antenna design based on metamaterial-inspired and substrate-integrated waveguide properties for millimetre-wave and THz integrated-circuit applications. J. Infrared. Millim. Terahertz Waves 2021, 42, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althuwayb, A.A. On-chip antenna design using the concepts of metamaterial and SIW principles applicable to terahertz integrated circuits operating over 0.6–0.622 THz. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2020, 2020, 6653095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirkolaei, M.M.; Jafari, M. A new class of wideband microstrip falcate patch antennas with reconfigurable capability at circular-polarization. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2020, 62, 3922–3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, S.; Li, W.; Wang, H.; Fu, P.; Luo, Z. R 2 cnn: Rotational region cnn for arbitrarily-oriented scene text detection. In Proceedings of the 2018 24th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Beijing, China, 20–24 August 2018; pp. 3610–3615. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.; Xue, N.; Long, Y.; Xia, G.S.; Lu, Q. Learning roi transformer for oriented object detection in aerial images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019; pp. 2849–2858. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Yang, J.; Yan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Guo, Z.; Sun, X.; Fu, K. Scrdet: Towards more robust detection for small, cluttered and rotated objects. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019; pp. 8232–8241. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Ding, J.; Xue, N.; Xia, G.S. Redet: A rotation-equivariant detector for aerial object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 2786–2795. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.; Cheng, G.; Wang, J.; Yao, X.; Han, J. Oriented R-CNN for Object Detection. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.05699. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Shao, W.; Ye, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Xue, X. Arbitrary-oriented scene text detection via rotation proposals. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2018, 20, 3111–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, W.; Zhu, S.; Yu, W. Toward arbitrary-oriented ship detection with rotated region proposal and discrimination networks. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 1745–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yan, J. Arbitrary-oriented object detection with circular smooth label. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 677–694. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Liu, Q.; Yan, J.; Li, A.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, G. R3det: Refined single-stage detector with feature refinement for rotating object. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.05612. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Ding, J.; Li, J.; Xia, G.S. Align deep features for oriented object detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Hou, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, W.; Yan, J. Dense Label Encoding for Boundary Discontinuity Free Rotation Detection. In Proceedings of the CVPR 2021, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Yan, J.; Yang, X.; Tang, J.; Liao, W.; He, T. Scrdet++: Detecting small, cluttered and rotated objects via instance-level feature denoising and rotation loss smoothing. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.13316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azimi, S.M.; Vig, E.; Bahmanyar, R.; Körner, M.; Reinartz, P. Towards multi-class object detection in unconstrained remote sensing imagery. In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Perth, Australia, 2–6 December 2018; pp. 150–165. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, W.; Yang, X.; Peng, S.; Guo, Y.; Yan, J. Learning modulated loss for rotated object detection. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.08299. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Fu, M.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, K.; Xia, G.S.; Bai, X. Gliding vertex on the horizontal bounding box for multi-oriented object detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 43, 1452–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yi, J.; Wu, P.; Liu, B.; Huang, Q.; Qu, H.; Metaxas, D. Oriented object detection in aerial images with box boundary-aware vectors. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2021; pp. 2150–2159. [Google Scholar]
- Bradski, G. The OpenCV Library. Dr. Dobb’S J. Softw. Tools 2000, 25, 120–123. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 580–587. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R. Fast r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Z.; Vasconcelos, N. Cascade r-cnn: Delving into high quality object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 6154–6162. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Gu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Dai, J.; Wei, Y. Relation networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) 2018, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 3588–3597. [Google Scholar]
- Law, H.; Deng, J. Cornernet: Detecting objects as paired keypoints. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 734–750. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Z.; Shen, C.; Chen, H.; He, T. Fcos: Fully convolutional one-stage object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 9627–9636. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, K.; Bai, S.; Xie, L.; Qi, H.; Huang, Q.; Tian, Q. Centernet: Keypoint triplets for object detection. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6569–6578. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, S.; Hu, H.; Wang, L.; Lin, S. Reppoints: Point set representation for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 9657–9666. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, L.; Lu, X.; Wang, C. Intersection detection algorithm based on hybrid bounding box for geological modeling with faults. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 29538–29546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premachandra, H.W.H.; Yamada, M.; Premachandra, C.; Kawanaka, H. Low-Computational-Cost Algorithm for Inclination Correction of Independent Handwritten Digits on Microcontrollers. Electronics 2022, 11, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, T.; Sun, F.; Liu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Li, L.; Shi, J. FoveaBox: Beyond Anchor-based Object Detector. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 7389–7398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chi, C.; Yao, Y.; Lei, Z.; Li, S.Z. Bridging the gap between anchor-based and anchor-free detection via adaptive training sample selection. In Proceedings of the CVPR 2020, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 9759–9768. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.; Lee, H.S. Probabilistic Anchor Assignment with IoU Prediction for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the ECCV 2020, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, H.; Ma, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, S.; Sun, J. BorderDet: Border Feature for Dense Object Detection. In Proceedings of the ECCV 2020, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 549–564. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, W.; Wu, L.; Chen, S.; Hu, X.; Li, J.; Tang, J.; Yang, J. Generalized Focal Loss: Learning Qualified and Distributed Bounding Boxes for Dense Object Detection. In Proceedings of the NeurIPS 2020, Online, 6–12 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Carion, N.; Massa, F.; Synnaeve, G.; Usunier, N.; Kirillov, A.; Zagoruyko, S. End-to-End Object Detection with Transformers. In Proceedings of the ECCV 2020, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, R.; Andriluka, M.; Ng, A.Y. End-to-end people detection in crowded scenes. In Proceedings of the CVPR 2016, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Su, W.; Lu, L.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Dai, J. Deformable DETR: Deformable Transformers for End-to-End Object Detection. In Proceedings of the ICLR 2020, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 26–30 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Song, L.; Li, Z.; Sun, H.; Sun, J.; Zheng, N. End-to-End Object Detection with Fully Convolutional Network. In Proceedings of the CVPR 2021, Online, 19–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Yu, C.; Shen, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, H. Object Detection Made Simpler by Eliminating Heuristic NMS. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.11782. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Yan, J.; Ming, Q.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Q. Rethinking Rotated Object Detection with Gaussian Wasserstein Distance Loss. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.11952.2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Yang, X.; Yang, J.; Ming, Q.; Wang, W.; Tian, Q.; Yan, J. Learning High-Precision Bounding Box for Rotated Object Detection via Kullback-Leibler Divergence. In Proceedings of the 2021 Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Online, 6–14 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Pan, C.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X. Constraint Loss for Rotated Object Detection in Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.; Shi, B.; Bai, X. Textboxes++: A single-shot oriented scene text detector. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 3676–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, F.; He, J.; Zhou, G.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Sui, X. Improved Oriented Object Detection in Remote Sensing Images Based on a Three-Point Regression Method. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhang, X.; Jiao, J.; Ji, X.; Ye, Q. Beyond Bounding-Box: Convex-Hull Feature Adaptation for Oriented and Densely Packed Object Detection. In Proceedings of the CVPR 2021, Online, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 8792–8801. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; Qi, H.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y. Deformable convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision 2017, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 764–773. [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis, R.A. On the identification of the convex hull of a finite set of points in the plane. Inf. Process. Lett. 1973, 2, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.B. LVIS: A Dataset for Large Vocabulary Instance Segmentation. In Proceedings of the CVPR 2019, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–25 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Yuan, L.; Weng, L.; Yang, Y. A high resolution optical satellite image dataset for ship recognition and some new baselines. In Proceedings of the 2017 ICPRAM, Porto, Portugal, 24–26 February 2017; Volume 2, pp. 324–331. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Chen, X.; Dai, W.; Fu, K.; Ye, Q.; Jiao, J. Orientation robust object detection in aerial images using deep convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Quebec, QC, Canada, 27–30 September 2015; pp. 3735–3739. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Wang, J.; Pang, J.; Cao, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, S.; Feng, W.; Liu, Z.; Xu, J.; et al. MMDetection: Open MMLab Detection Toolbox and Benchmark. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.07155. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. In Proceedings of the ICLR 2015, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Sun, X. Oriented objects as pairs of middle lines. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 169, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Ren, Y.; Sheng, K.; Dong, W.; Yuan, H.; Guo, X.; Ma, C.; Xu, C. Dynamic refinement network for oriented and densely packed object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2020, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11207–11216. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Yang, W.; Li, H.C.; Zhang, H.; Xia, G.S. Learning center probability map for detecting objects in aerial images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 4307–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.14030. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Pang, J.; Wang, J.; Xiong, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, S.; Feng, W.; Liu, Z.; Shi, J.; Ouyang, W.; et al. Hybrid task cascade for instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2019, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 4974–4983. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Xu, C.; Cui, Z.; Wang, D.; Jie, Z.; Zhang, T.; Yang, J. Learning object-wise semantic representation for detection in remote sensing imagery. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2019, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 20–27. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Pan, Z.; Lei, B. Learning a rotation invariant detector with rotatable bounding box. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.09405. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, M.; Zhu, Z.; Shi, B.; Xia, G.s.; Bai, X. Rotation-sensitive regression for oriented scene text detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2018, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 5909–5918. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. Yolov3: An incremental improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Ming, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Miao, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, L. Dynamic anchor learning for arbitrary-oriented object detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.04150. [Google Scholar]




| Dataset | Source | Annotation | Categories | Instances | Images | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UCAS-AOD [60] | Google Earth | OBB | 2 | 14,596 | 1510 | 2015 |
| HRSC2016 [59] | Google Earth | OBB | 1 | 2976 | 1061 | 2016 |
| DOTA-v1.0 [6] | multi source | OBB | 14 | 188,282 | 2806 | 2018 |
| DOTA-v1.5 | multi source | OBB | 15 | 402,089 | 2806 | 2019 |
| Method | Recall (%) | Recall (%) | Recall (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PointRPN | 85.93 | 89.83 | 90.00 |
| Regression Type of PointReg | mAP (%) |
|---|---|
| () | 77.25 |
| () | 77.60 |
| Oversampling Threshold () | mAP (%) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 73.52 |
| 0.1 | 76.49 |
| 0.2 | 77.44 |
| 0.3 | 77.60 |
| 0.4 | 77.48 |
| Method | PointRPN | Balanced Dataset Strategy | PointReg | mAP (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 71.36 | |||
| Point RCNN | ✓ | 74.17 | ||
| ✓ | 74.22 | |||
| ✓ | ✓ | 77.25 | ||
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 77.60 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Q.; Yu, C. Point RCNN: An Angle-Free Framework for Rotated Object Detection. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2605. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14112605
Zhou Q, Yu C. Point RCNN: An Angle-Free Framework for Rotated Object Detection. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(11):2605. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14112605
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Qiang, and Chaohui Yu. 2022. "Point RCNN: An Angle-Free Framework for Rotated Object Detection" Remote Sensing 14, no. 11: 2605. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14112605
APA StyleZhou, Q., & Yu, C. (2022). Point RCNN: An Angle-Free Framework for Rotated Object Detection. Remote Sensing, 14(11), 2605. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14112605






