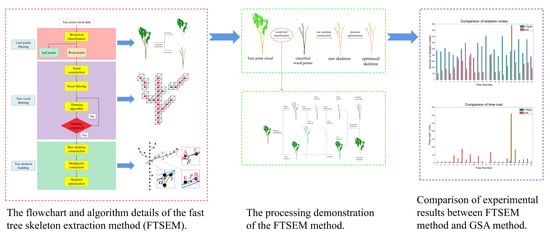
Fast Tree Skeleton Extraction Using Voxel Thinning Based on Tree Point Cloud
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Data
2.2. Method
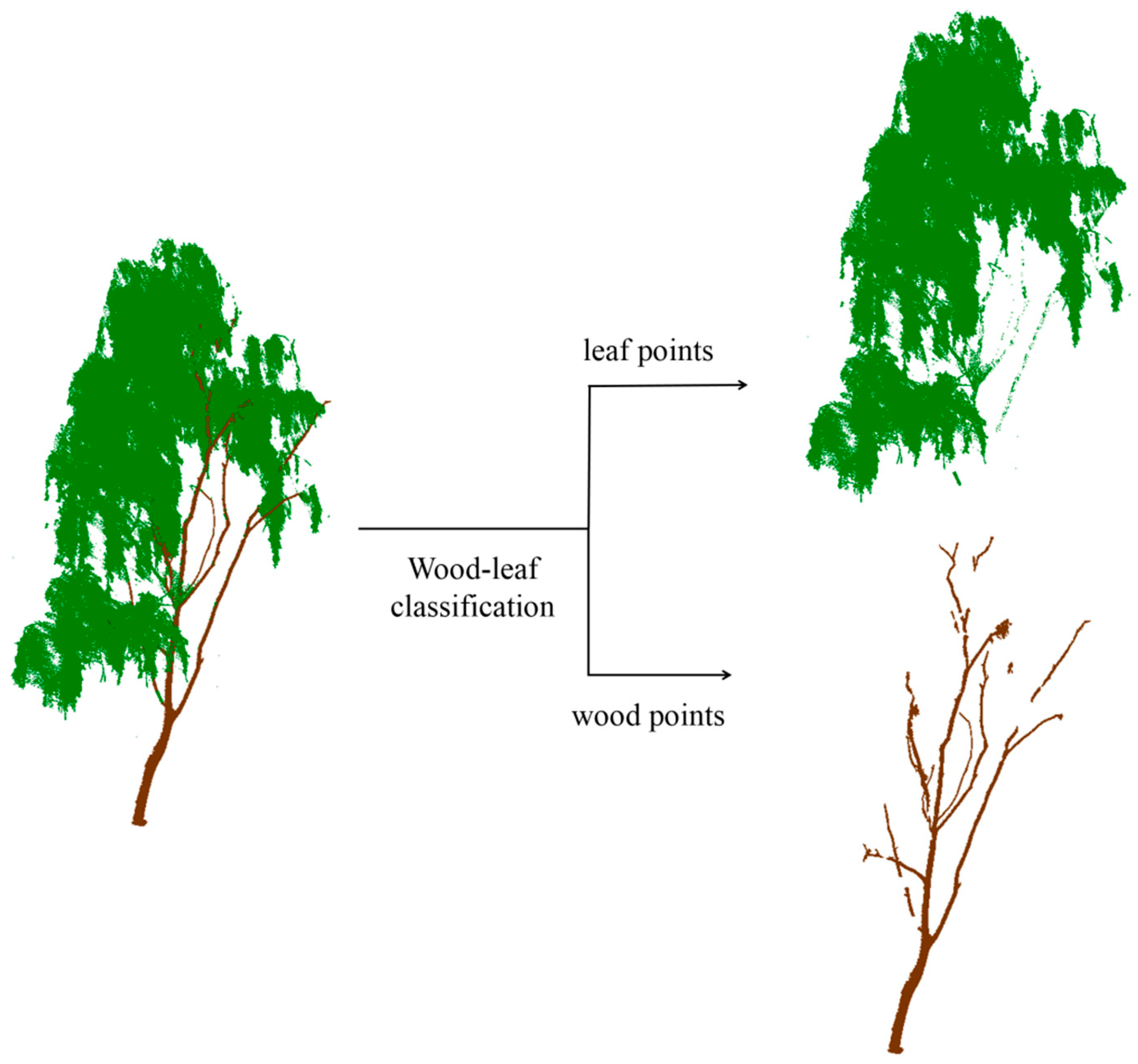
2.2.1. Leaf Points Filtering
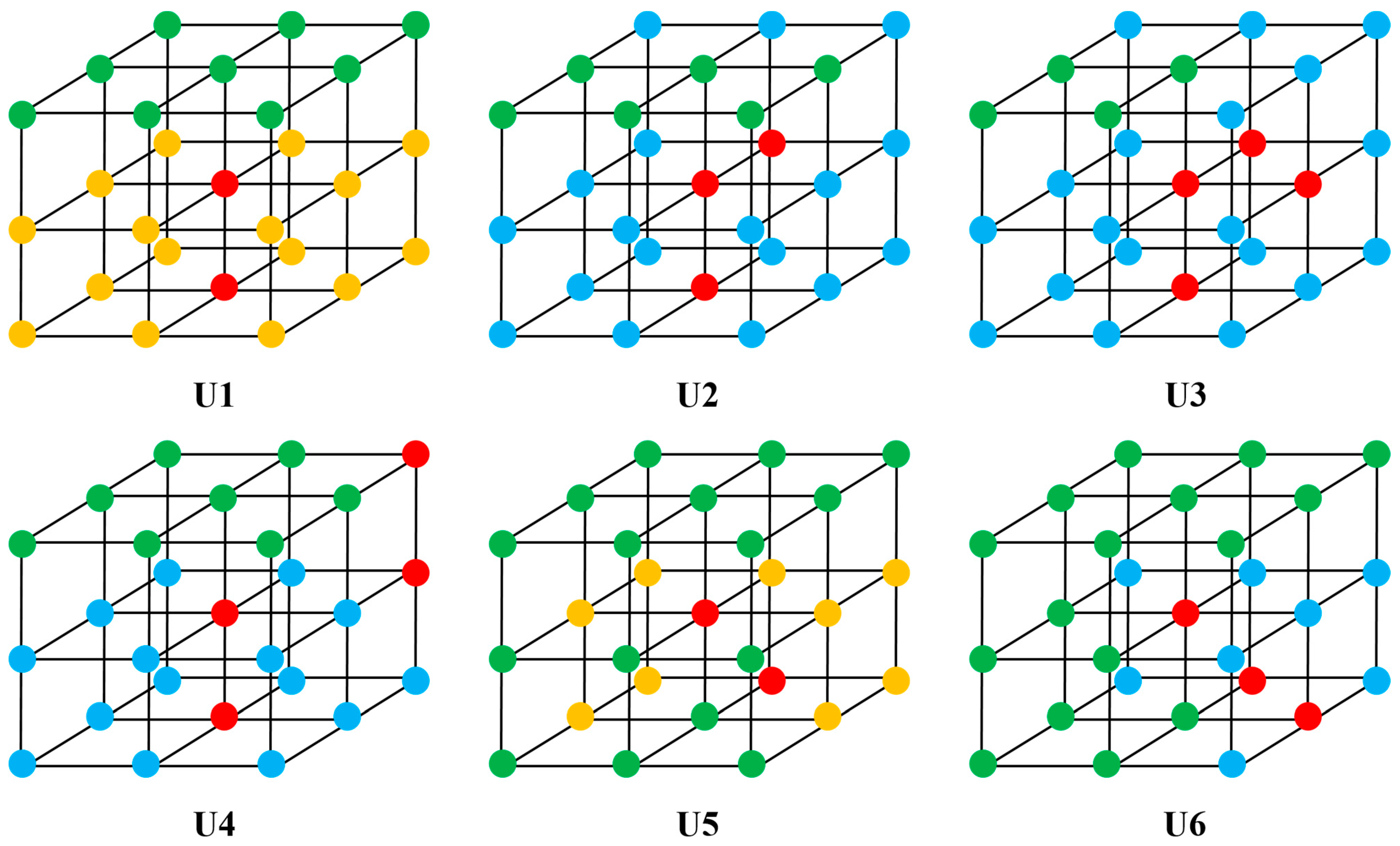
2.2.2. Tree Voxel Thinning
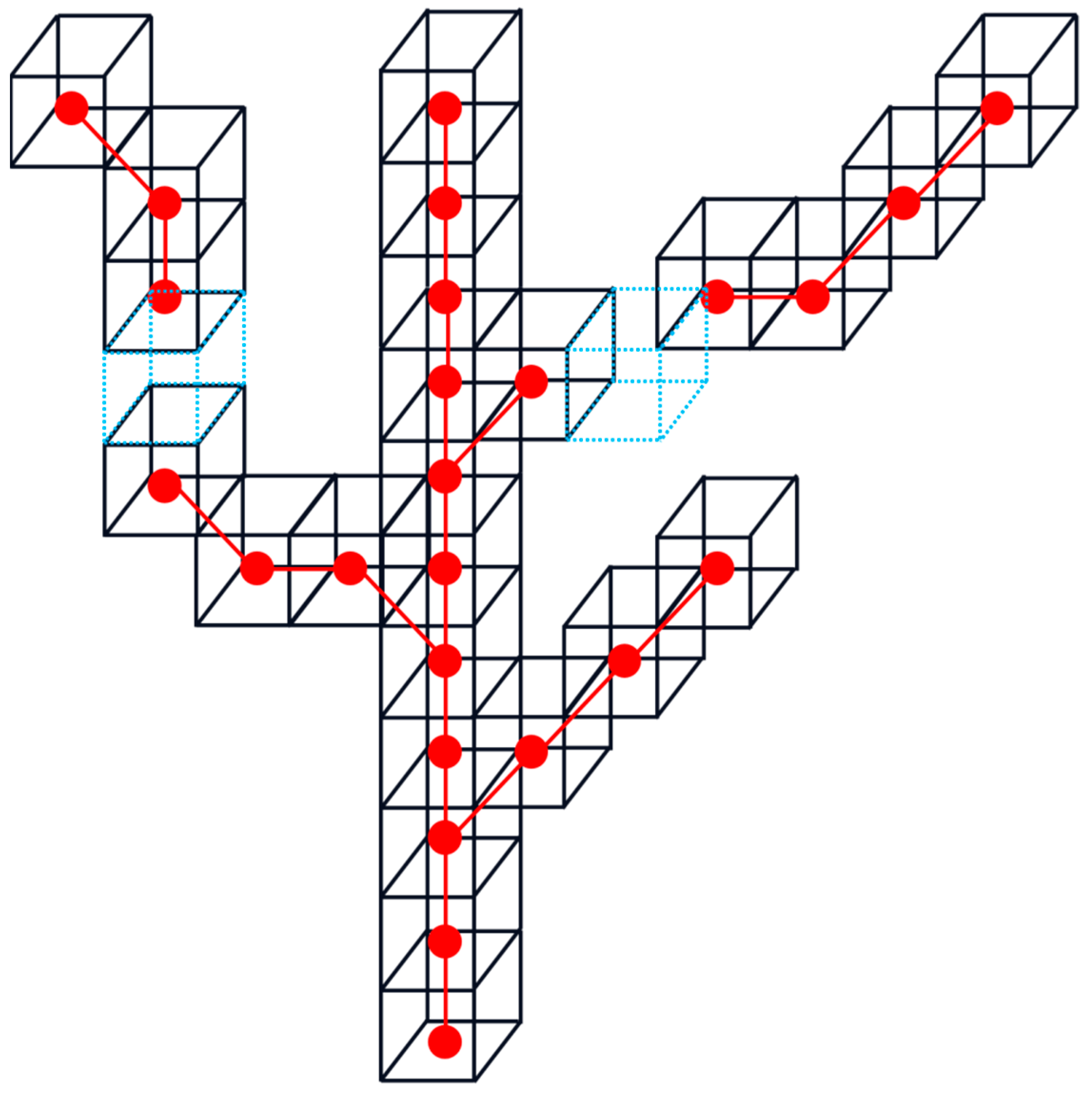
2.2.3. Tree Skeleton Building
Raw Skeleton Construction
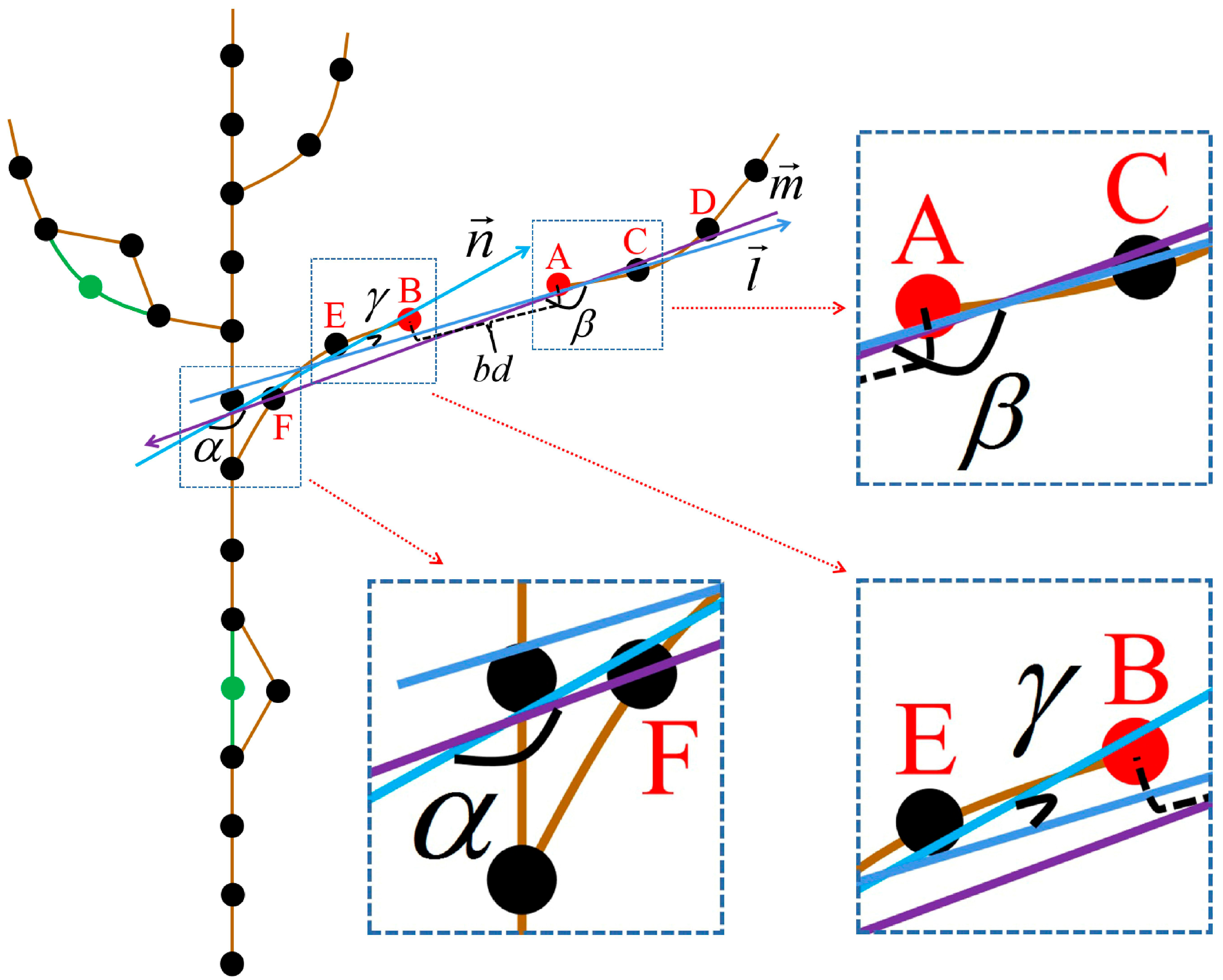
Breakpoint Connection
Skeleton Optimization
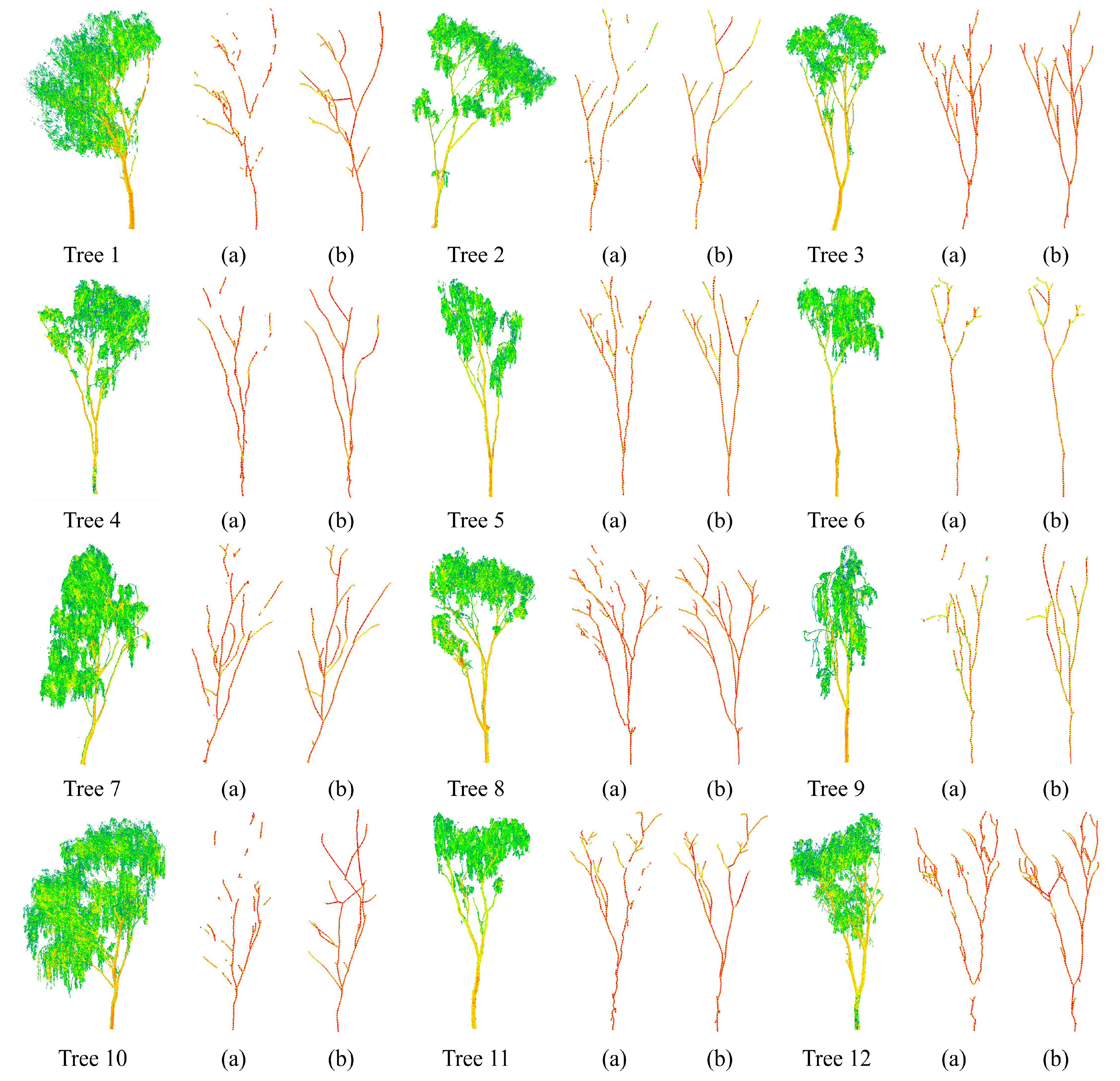
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Li, A.; Liu, F. Large-Scale Urban Point Cloud Labeling and Reconstruction. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 138, 86–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, M.; Tagliasacchi, A.; Seversky, L.M.; Alliez, P.; Guennebaud, G.; Levine, J.A.; Sharf, A.; Silva, C.T. A Survey of Surface Reconstruction from Point Clouds. Comput. Graph. Forum 2017, 36, 301–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, S.; MacLean, D.; Hennigar, C.; Pitt, D. Forecasting Forest Inventory Using Imputed Tree Lists for LiDAR Grid Cells and a Tree-List Growth Model. Forests 2018, 9, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandare, K.; Ørka, H.O.; Dalponte, M.; Næsset, E.; Gobakken, T. Individual Tree Crown Approach for Predicting Site Index in Boreal Forests Using Airborne Laser Scanning and Hyperspectral Data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 60, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palace, M.; Sullivan, F.B.; Ducey, M.; Herrick, C. Estimating Tropical Forest Structure Using a Terrestrial Lidar. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Ma, L.; He, W.; Eitel, J.U.H.; Moskal, L.M.; Zhang, Z. Assessing the Contribution of Woody Materials to Forest Angular Gap Fraction and Effective Leaf Area Index Using Terrestrial Laser Scanning Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 1475–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsoy, P.J.; Mitchell, J.J.; Levia, D.F.; Clark, P.E.; Glenn, N.F. Estimation of Big Sagebrush Leaf Area Index with Terrestrial Laser Scanning. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 61, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Yan, W.; Zheng, G.; Yin, H.; Cavan, G.; Zhan, W.; Zhang, N.; Cheng, L. Retrieval of Three-Dimensional Tree Canopy and Shade Using Terrestrial Laser Scanning (TLS) Data to Analyze the Cooling Effect of Vegetation. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 217, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oveland, I.; Hauglin, M.; Gobakken, T.; Næsset, E.; Maalen-Johansen, I. Automatic Estimation of Tree Position and Stem Diameter Using a Moving Terrestrial Laser Scanner. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauglin, M.; Astrup, R.; Gobakken, T.; Næsset, E. Estimating Single-Tree Branch Biomass of Norway Spruce with Terrestrial Laser Scanning Using Voxel-Based and Crown Dimension Features. Scand. J. For. Res. 2013, 28, 456–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Bu, G.; Wang, P. An Automatic Tree Skeleton Extracting Method Based on Point Cloud of Terrestrial Laser Scanner. Int. J. Opt. 2017, 2017, 5408503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Han, J.; Li, N.; Huang, H.; Chen, B. Mass-Driven Topology-Aware Curve Skeleton Extraction from Incomplete Point Clouds. IEEE Trans. Visual. Comput. Graph. 2020, 26, 2805–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiteanu, F.; Klein, R. Hybrid Tree Reconstruction from Inhomogeneous Point Clouds. Vis. Comput. 2014, 30, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bournez, E.; Landes, T.; Saudreau, M.; Kastendeuch, P.; Najjar, G. From TLS Point Clouds to 3d Models of Trees: A Comparison of Existing Algorithms for 3d Tree Reconstruction. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2017, XLII-2/W3, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez, V.; Rosell-Polo, J.R.; Pascual, M.; Escolà, A. Multi-Tree Woody Structure Reconstruction from Mobile Terrestrial Laser Scanner Point Clouds Based on a Dual Neighbourhood Connectivity Graph Algorithm. Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 148, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, G.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, B.; Li, X.; Zhu, Y.; Lei, L.; Chen, R.; Dong, Z.; Yang, H. Apple Tree Branch Information Extraction from Terrestrial Laser Scanning and Backpack-LiDAR. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calders, K.; Newnham, G.; Burt, A.; Murphy, S.; Raumonen, P.; Herold, M.; Culvenor, D.; Avitabile, V.; Disney, M.; Armston, J.; et al. Nondestructive Estimates of Above-ground Biomass Using Terrestrial Laser Scanning. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2015, 6, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Gossett, N.; Chen, B. Knowledge and Heuristic-Based Modeling of Laser-Scanned Trees. ACM Trans. Graph. 2007, 26, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.-M.; Wintz, J.; Mourrain, B.; Wang, W.; Boudon, F.; Godin, C. Efficient and Robust Reconstruction of Botanical Branching Structure from Laser Scanned Points. In Proceedings of the 2009 11th IEEE International Conference on Computer-Aided Design and Computer Graphics, Huangshan, China, 19–21 August 2009; pp. 572–575. [Google Scholar]
- Livny, Y.; Yan, F.; Olson, M.; Chen, B.; Zhang, H.; El-Sana, J. Automatic Reconstruction of Tree Skeletal Structures from Point Clouds. In ACM SIGGRAPH Asia 2010 Papers, Proceedings of the SIGGRAPH ASIA 2010, Seoul, South Korea, 15–18 December 2010; ACM Press: New York, NY, USA, 2010; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, C.; Guo, X.; Li, Z. Skeleton Extraction for Tree Models. Math. Comput. Model. 2011, 54, 1115–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delagrange, S.; Jauvin, C.; Rochon, P. PypeTree: A Tool for Reconstructing Tree Perennial Tissues from Point Clouds. Sensors 2014, 14, 4271–4289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verroust, A.; Lazarus, F. Extracting Skeletal Curves from 3D Scattered Data. In Proceedings of the Proceedings Shape Modeling International ‘99. International Conference on Shape Modeling and Applications, Aizu-Wakamatsu, Japan, 1–4 March 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Fang, T.; Tong, X.; Mathiopoulos, P.T.; Zhang, L.; Mei, J. A Local Structure and Direction-Aware Optimization Approach for Three-Dimensional Tree Modeling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 4749–4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Fang, T.; Mathiopoulos, P.T.; Qu, H.; Chen, D.; Wang, Y. A Structure-Aware Global Optimization Method for Reconstructing 3-D Tree Models from Terrestrial Laser Scanning Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 5653–5669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackenberg, J.; Spiecker, H.; Calders, K.; Disney, M.; Raumonen, P. SimpleTree—An Efficient Open Source Tool to Build Tree Models from TLS Clouds. Forests 2015, 6, 4245–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.; Zhang, L.; Wu, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L. 3D Tree Modeling from Incomplete Point Clouds via Optimization and L1-MST. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2017, 31, 999–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Huang, X.; Fan, J.; Eichhorn, M.; An, F.; Chen, B.; Cao, L.; Zhu, Z.; Yun, T. Retrieval of Aerodynamic Parameters in Rubber Tree Forests Based on the Computer Simulation Technique and Terrestrial Laser Scanning Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, A.; Liu, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, M. Skeleton Extraction from Point Clouds of Trees with Complex Branches via Graph Contraction. Vis. Comput. 2020, 37, 2235–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorte, B.; Pfeifer, N. Structuring Laser-scanned Trees Using 3D Mathematical Morphology. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2004, 35, 929–933. [Google Scholar]
- Bucksch, A.; Lindenbergh, R. CAMPINO—A Skeletonization Method for Point Cloud Processing. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2008, 63, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucksch, A.; Lindenbergh, R.; Menenti, M. SkelTre: Robust Skeleton Extraction from Imperfect Point Clouds. Vis. Comput. 2010, 26, 1283–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Liu, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, M.; Lin, Y. Tree Skeletonization for Raw Point Cloud Exploiting Cylindrical Shape Prior. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 27327–27341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremer, M.; Rutzinger, M.; Wichmann, V. Derivation of Tree Skeletons and Error Assessment Using LiDAR Point Cloud Data of Varying Quality. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 80, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Yang, J.; Behnke, S. Research on Geometric Features and Point Cloud Properties for Tree Skeleton Extraction. Pers. Ubiquit. Comput. 2018, 22, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zhang, D.; Li, N.; Chen, L. Force Field Driven Skeleton Extraction Method for Point Cloud Trees. Earth Sci. Inf. 2019, 12, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, M.; Yao, Y.; Hu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W. An Automatic Tree Skeleton Extraction Approach Based on Multi-View Slicing Using Terrestrial LiDAR Scans Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Wu, S.; Cohen-Or, D.; Gong, M.; Zhang, H.; Li, G.; Chen, B. L1-Medial Skeleton of Point Cloud. ACM Trans. Graph. 2013, 32, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, M. Curve Skeleton Extraction via K-Nearest-Neighbors Based Contraction. Int. J. Appl. Math. Comput. Sci. 2020, 30, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wen, W.; Xiao, B.; Guo, X.; Du, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y. An Accurate Skeleton Extraction Approach From 3D Point Clouds of Maize Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Bao, Y.; Tang, L.; Ortiz, D.; Salas-Fernandez, M.G. Automated Morphological Traits Extraction for Sorghum Plants via 3D Point Cloud Data Analysis. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 162, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, P.; Gao, Z.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Gan, X.; Liu, Z. Wood-Leaf Classification of Tree Point Cloud Based on Intensity and Geometric Information. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palàgyi, K.; Kuba, A. A 3D 6-Subiteration Thinning Algorithm for Extracting Medial Lines. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 1998, 19, 613–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liang, G.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, D. A New Method of Breakpoint Connection Using Curve Features for Contour Vectorization. ElAEE 2012, 18, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bu, G.; Wang, P. Adaptive Circle-Ellipse Fitting Method for Estimating Tree Diameter Based on Single Terrestrial Laser Scanning. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2016, 10, 026040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Technical Parameters | |
|---|---|
| The farthest distance measurement | 600 m (natural object reflectivity ≥ 90%) |
| The scanning rate (points/s) | 300,000 (emission), 125,000 (reception) |
| The vertical scanning range | −40°~60° |
| the horizontal scanning range | 0°~360° |
| Laser divergence | 0.3 mrad |
| The scanning accuracy | 3 mm (single measurement), 2 mm (multiple measurements) |
| The angular resolution | better than 0.0005° (in both vertical and horizontal directions) |
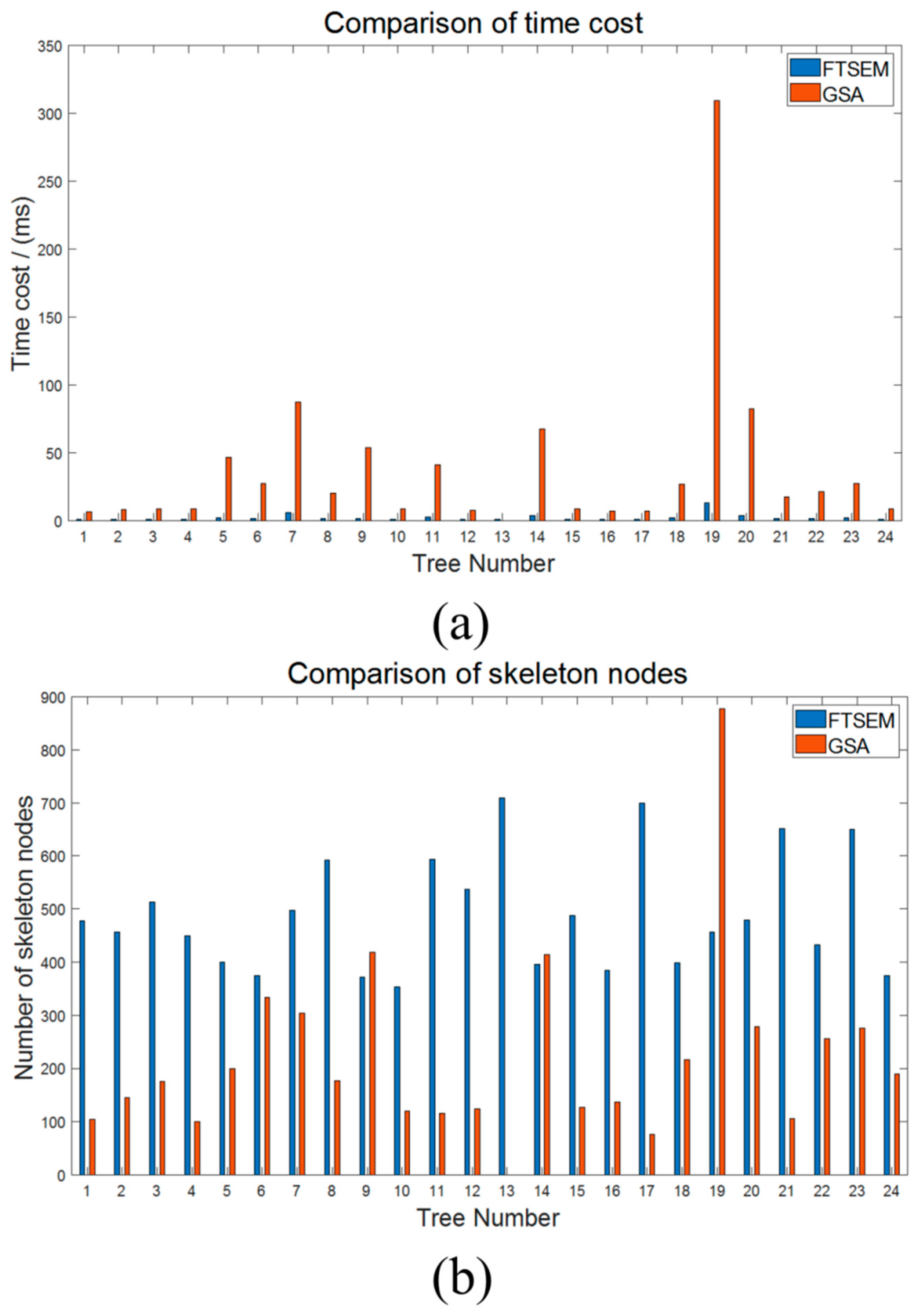
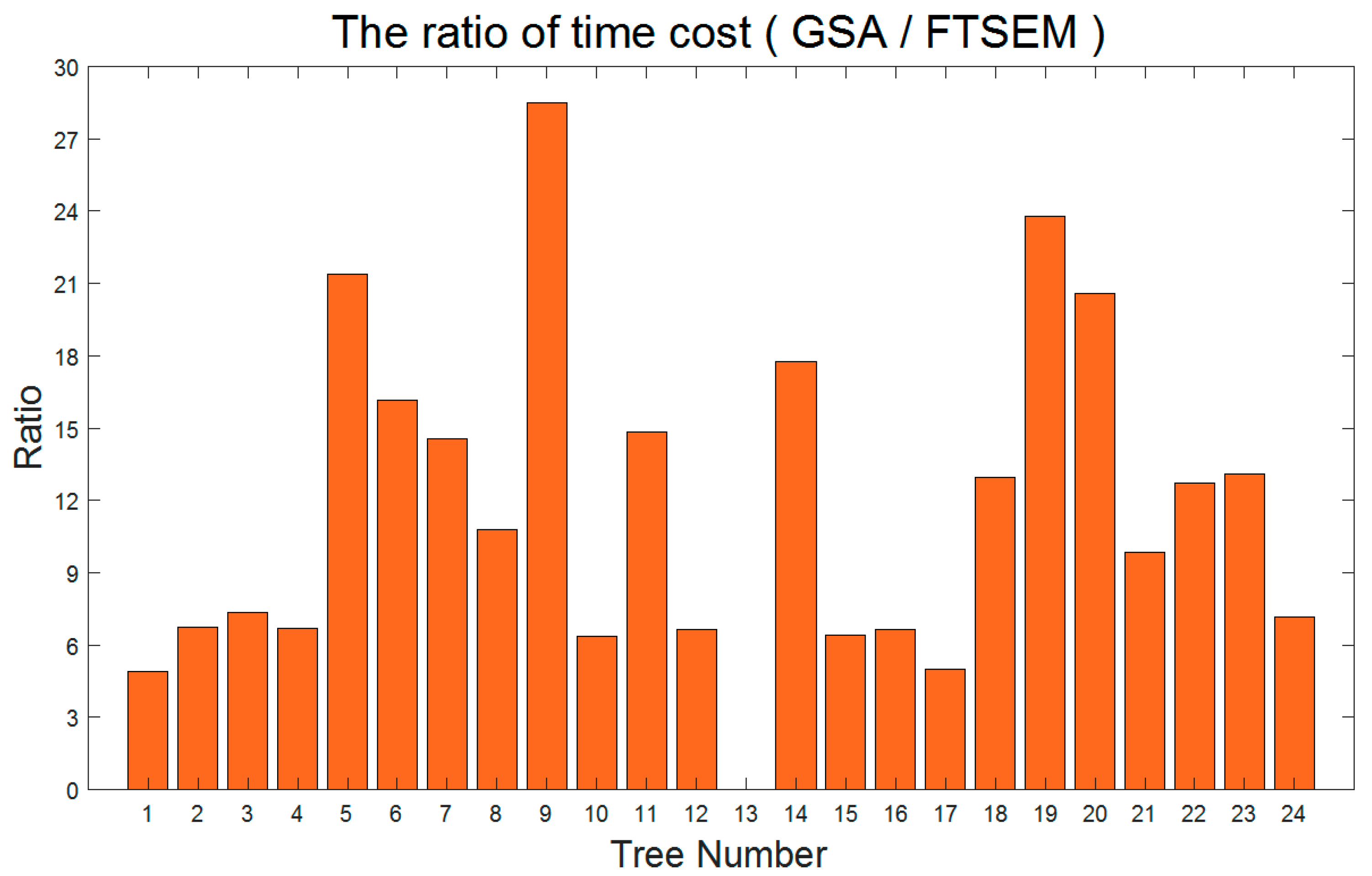
| Tree Number | Point Number | Node Number | Runtime (s) | TPMP (s) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FTSEM | GSA | FTSEM | GSA | FTSEM | GSA | ||
| 1 | 876,657 | 477 | 105 | 1.3 | 6.4 | 1.5 | 7.3 |
| 2 | 716,701 | 456 | 146 | 1.2 | 8.1 | 1.7 | 11.3 |
| 3 | 629,250 | 513 | 175 | 1.2 | 8.8 | 1.9 | 14.0 |
| 4 | 733,233 | 450 | 101 | 1.3 | 8.7 | 1.8 | 11.9 |
| 5 | 1,064,546 | 400 | 199 | 2.2 | 47.0 | 2.1 | 44.2 |
| 6 | 971,915 | 374 | 334 | 1.7 | 27.5 | 1.7 | 28.3 |
| 7 | 3,398,859 | 497 | 304 | 6.0 | 87.3 | 1.8 | 25.7 |
| 8 | 1,162,123 | 592 | 177 | 1.9 | 20.5 | 1.6 | 17.6 |
| 9 | 1,068,644 | 372 | 418 | 1.9 | 54.1 | 1.8 | 50.6 |
| 10 | 1,210,685 | 354 | 120 | 1.4 | 8.9 | 1.2 | 7.4 |
| 11 | 1,318,700 | 593 | 116 | 2.8 | 41.5 | 2.1 | 31.5 |
| 12 | 742,280 | 537 | 125 | 1.2 | 8.0 | 1.6 | 10.8 |
| 13 | 203,303 | 709 | / | 1.0 | / | 4.9 | / |
| 14 | 1,896,619 | 395 | 414 | 3.8 | 67.5 | 2.0 | 35.6 |
| 15 | 1,080,397 | 487 | 127 | 1.4 | 9.0 | 1.3 | 8.3 |
| 16 | 980,776 | 384 | 137 | 1.1 | 7.3 | 1.1 | 7.4 |
| 17 | 841,575 | 700 | 77 | 1.4 | 7.0 | 1.7 | 8.3 |
| 18 | 1,357,196 | 398 | 216 | 2.1 | 27.2 | 1.5 | 20.0 |
| 19 | 4,925,230 | 457 | 877 | 13.0 | 309.3 | 2.6 | 62.8 |
| 20 | 1,716,488 | 479 | 279 | 4.0 | 82.4 | 2.3 | 48.0 |
| 21 | 1,275,620 | 651 | 106 | 1.8 | 17.7 | 1.4 | 13.9 |
| 22 | 1,301,100 | 433 | 256 | 1.7 | 21.6 | 1.3 | 16.6 |
| 23 | 1,315,914 | 650 | 275 | 2.1 | 27.5 | 1.6 | 20.9 |
| 24 | 771,395 | 374 | 189 | 1.2 | 8.6 | 1.6 | 11.1 |
| Average TPMP (s) | / | / | / | / | / | 1.8 | 22.3 |
| Articles | Tree Name | Point Number | Runtime (s) | TPMP (s) | Average TPMP (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [32] | Simple tree | 49,669 | 66 | 1328.8 | 17,146.4 |
| Apple tree | 385,772 | 11,520 | 29,862.2 | ||
| Tulip tree | 816,670 | 16,536 | 20,248.1 | ||
| [35] | Sample 1 | 658,423 | 55.7 | 84.6 | 81.3 |
| Sample 2 | 821,416 | 63.2 | 76.9 | ||
| Sample 3 | 583,217 | 48.1 | 82.5 | ||
| [37] | Leaf-on ginkgo tree | 1,974,535 | 1980 | 1002.8 | 2049.3 |
| Leaf-off ginkgo tree | 348,868 | 1080 | 3095.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, J.; Wang, P.; Li, R.; Zhou, M.; Wu, Y. Fast Tree Skeleton Extraction Using Voxel Thinning Based on Tree Point Cloud. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2558. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14112558
Sun J, Wang P, Li R, Zhou M, Wu Y. Fast Tree Skeleton Extraction Using Voxel Thinning Based on Tree Point Cloud. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(11):2558. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14112558
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Jingqian, Pei Wang, Ronghao Li, Mei Zhou, and Yuhan Wu. 2022. "Fast Tree Skeleton Extraction Using Voxel Thinning Based on Tree Point Cloud" Remote Sensing 14, no. 11: 2558. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14112558
APA StyleSun, J., Wang, P., Li, R., Zhou, M., & Wu, Y. (2022). Fast Tree Skeleton Extraction Using Voxel Thinning Based on Tree Point Cloud. Remote Sensing, 14(11), 2558. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14112558