Comparing Luojia 1-01 and VIIRS Nighttime Light Data in Detecting Urban Spatial Structure Using a Threshold-Based Kernel Density Estimation
Abstract
1. Introduction
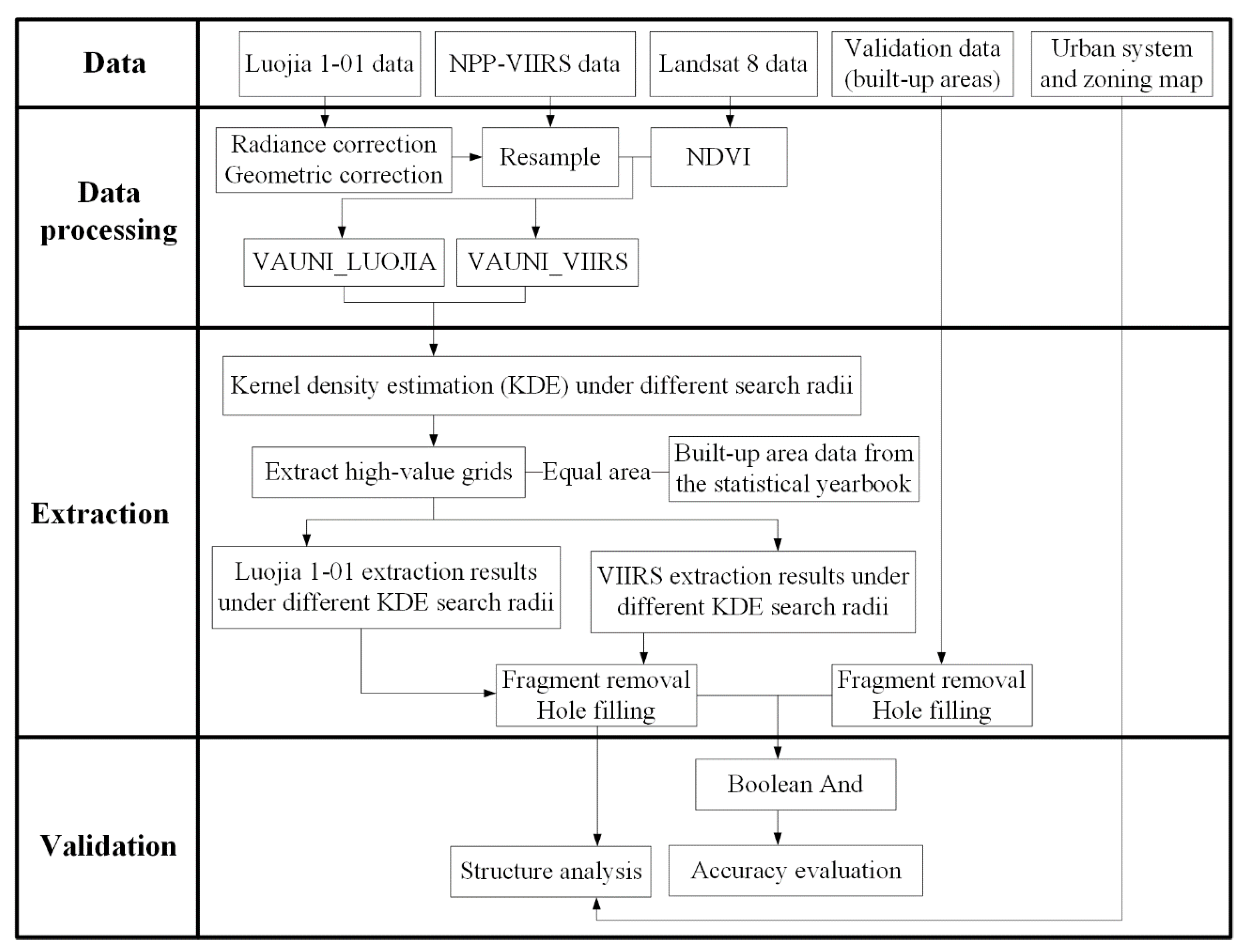
2. Materials and Methods
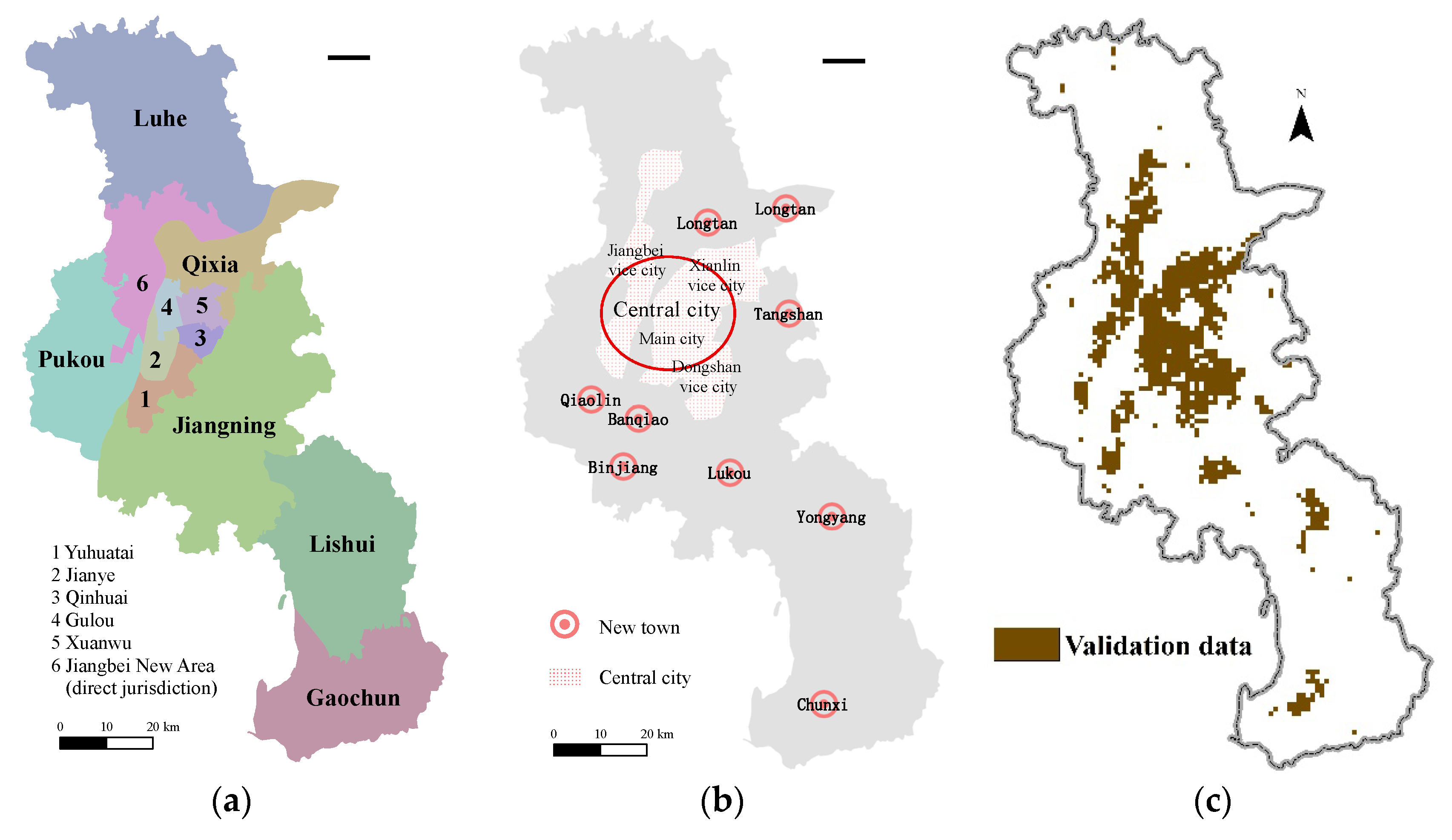
2.1. Study Region and Data
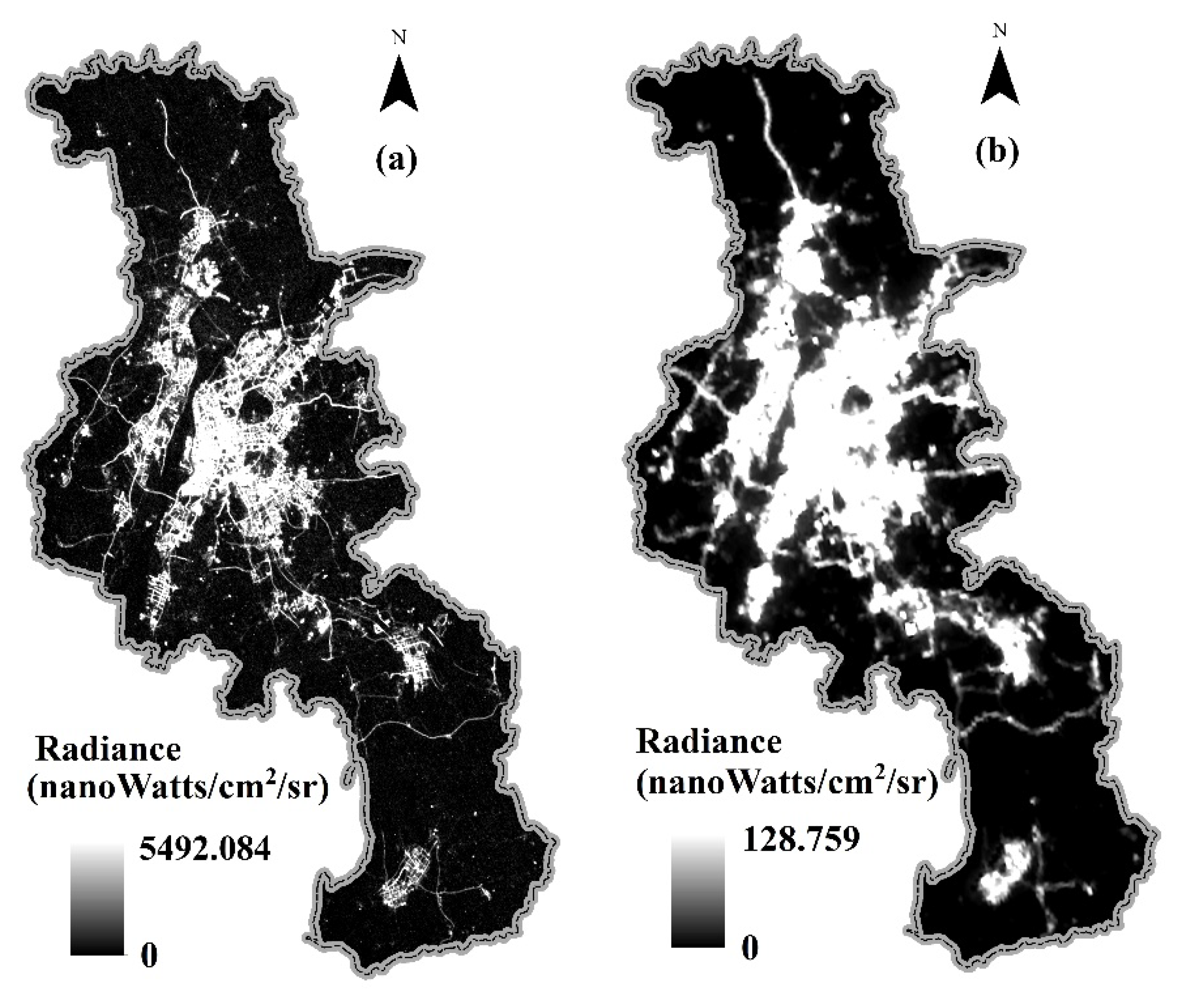
2.1.1. Remote Sensing Data
2.1.2. Validation Data
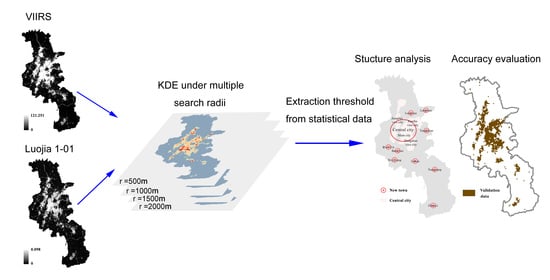
2.2. Analytical Methods
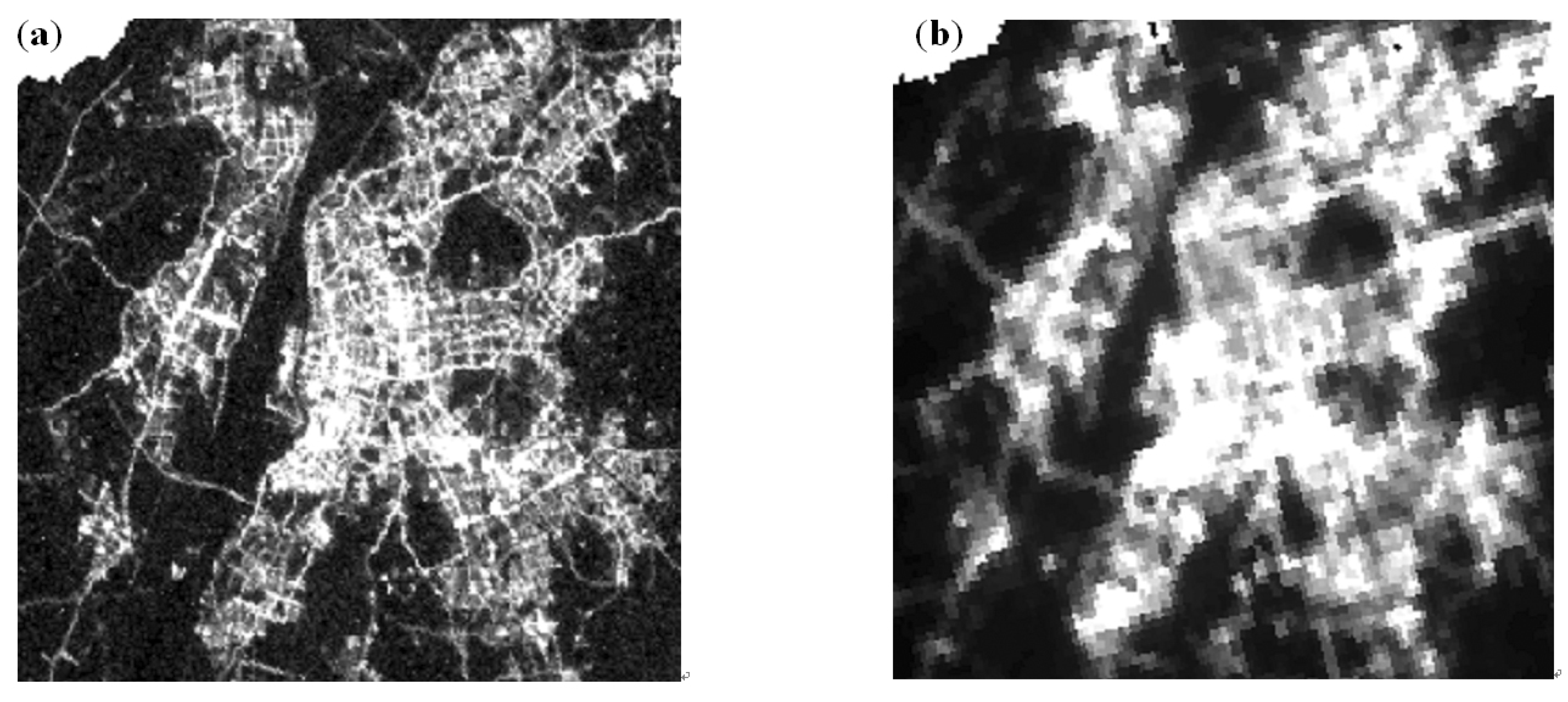
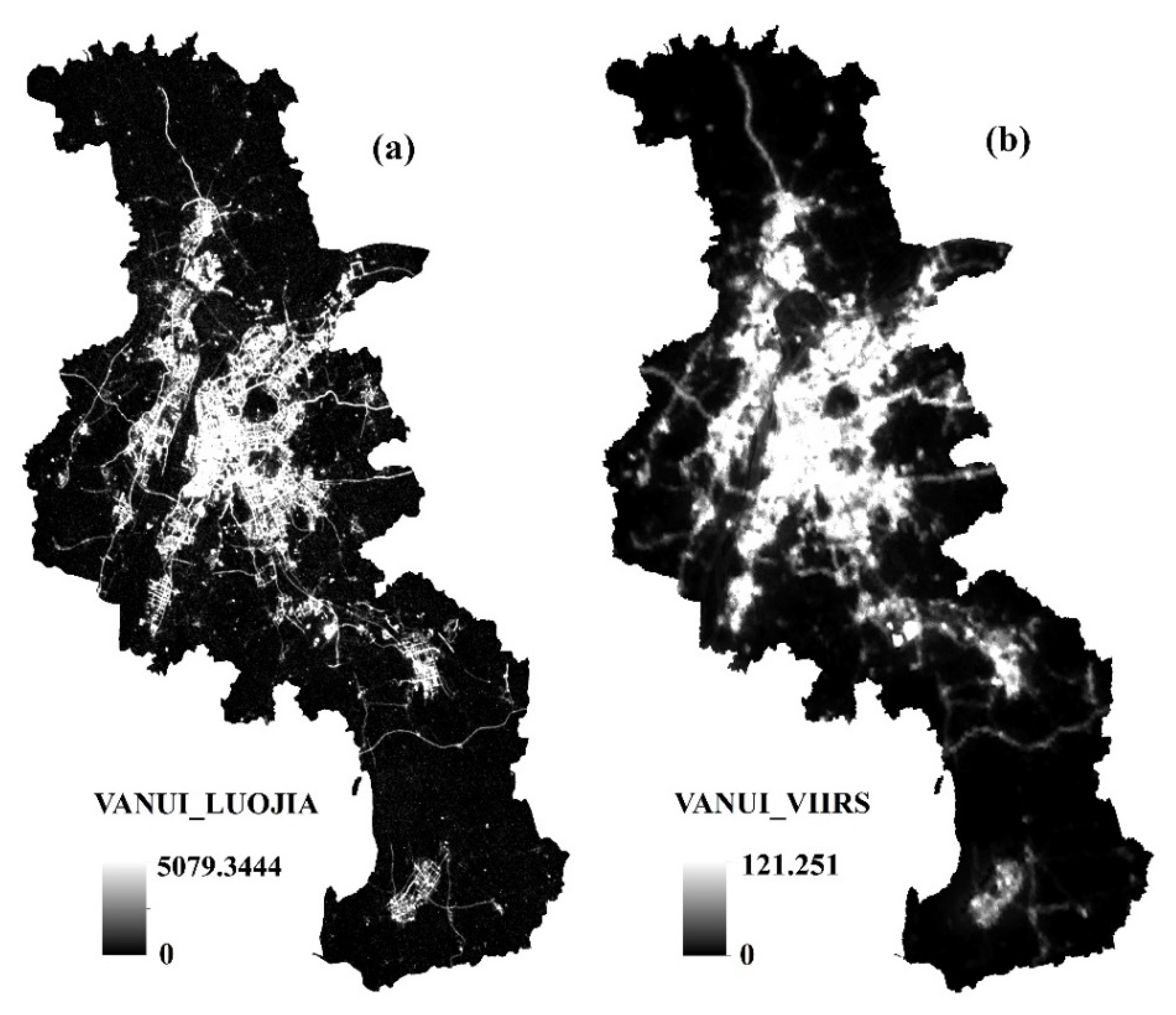
2.2.1. VANUI for Luojia 1-01 and VIIRS
2.2.2. KDE Method
2.2.3. Threshold-Based Urban Built-Up Area Extraction
2.2.4. Extraction Result Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Extraction Results and the Urban Structure
3.2. Accuracy Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Pacione, M. Urban. Geography: A Global Perspective, 2nd ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.S.; He, S.B.; Peng, J.; Huang, X.L.; Zhang, L.Q. Research on spatial characteristics of urban development based on DMSP-OLS data. Geog. Geo-Infor. Sci. 2014, 30, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Ma, J.; Yuan, Y. Research progress and prospect on the identification of urban fringe. Prog. Geog. 2014, 33, 1068–1077. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.R.; Feng, J. Urban spatial expansion in less developed region of China: A case study of Nanchong. Geog. Res. 2010, 29, 43–56. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Urban Surveys National Bureau of Statistics of China. China City Statistical Yearbook 2017; China Statistic Press: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Liu, H.J.; Li, A.M. Urban. Expansion and Remote Sensing Application; Liu, H.J., Li, A.M., Eds.; The Yellow River Water Conservancy Press: Zhengzhou, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, J.R. Urban change detection mapping using Landsat digital data. Am. Cartogr. 1981, 8, 127–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.R.; Toll, D.L. Detecting residential land-use development at the urban fringe. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1982, 48, 629. [Google Scholar]
- Doll, C.N.H.; Muller, J.-P.; Elvidge, C.D. Night-time imagery as a tool for global mapping of socioeconomic parameters and greenhouse gas emissions. AMBIO 2000, 29, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.E.; Kihn, E.A.; Kroehl, H.W.; Davis, E.R. Mapping city lights with nighttime data from the DMSP operational linescan system. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1997, 63, 727–734. [Google Scholar]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Imhoff, M.L.; Baugh, K.E.; Hobson, V.R.; Nelson, I.; Safran, J.; Dietz, J.B.; Tuttle, B.T. Night-time lights of the world: 1994–1995. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2001, 56, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.H.; Li, Z.W.; Guo, H.L.; Tian, Z.H.; Wang, X.L. Analyzing the consistency between built-up areas and human activities and the impacts on the urbanization process: A case study of Zhengzhou, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 6008–6035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.R.; Li, X. An overview on data mining of nighttime light remote sensing. Acta Geodaetica Cartogr. Sin. 2015, 44, 591–601. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.F.; He, C.Y.; Zhang, Q.F.; Huang, Q.X.; Yang, Y. Extracting the dynamics of urban expansion in China using DMSP-OLS nighttime light data from 1992 to 2008. Landscape Urban. Plan. 2012, 106, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.Y.; Smith, S.J.; Elvidge, C.D.; Zhao, K.G.; Thomson, A.; Imhoff, M. A cluster-based method to map urban area from DMSP/OLS nightlights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 147, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, C.N.H.; Muller, J.-P.; Morley, J.G. Mapping regional economic activity from night-time light satellite imagery. Ecol. Econ. 2006, 57, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, E.C.; Seto, K.C. Characterizing urban infrastructural transitions for the sustainable development goals using multi-temporal land, population, and nighttime light data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 234, 111430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, D.R. Can night-time light images play a role in evaluating the Syrian crisis? Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 6648–6661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waluda, C.M.; Yamashiro, C.; Elvidge, C.D.; Hobson, V.R.; Rodhouse, P.G. Quantifying light-fishing for Dosidicus gigas in the Eastern Pacific using satellite remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 91, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Ziskin, D.; Baugh, K.E.; Tuttle, B.T.; Ghosh, T.; Pack, D.W.; Erwin, E.H.; Zhizhin, M. A fifteen year record of global natural gas flaring derived from satellite data. Energies 2009, 2, 595–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.S.; Tian, H.Q.; Zhou, G.M.; Ge, H.L. Regional mapping of human settlements in Southeastern China with multisensor remotely sensed data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3668–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milesi, C.; Elvidge, C.D.; Nemani, R.R.; Running, S.W. Assessing the impact of urban land development on net primary productivity in the Southeastern United States. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 86, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Q.; Yu, B.L.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Liu, H.X.; Yang, C.S.; Shi, K.F.; Wu, J.P. Mapping global urban areas from 2000 to 2012 using time-series nighttime light data and MODIS products. IEEE J.-STARS 2019, 12, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.F.; Huang, C.; Yu, B.L.; Yin, B.; Huang, Y.X.; Wu, J.P. Evaluation of NPP-VIIRS night-time light composite data for extracting built-up urban areas. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, P.; Chen, H.; Huang, Q.L.; Jiang, H.B.; Zhang, Z.J.; Zhang, Y.M.; Luo, X.; Sun, S.J. A novel method for urban area extraction from VIIRS DNB and MODIS NDVI data: A case study of Chinese cities. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 6094–6109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.S.; Hu, D.Y.; Hu, Z.W.; Zhao, W.J.; Mo, Y.; Qiao, K. An integrated soft and hard classification approach for evaluating urban expansion from multisource remote sensing data: A case study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Tangshan metropolitan region, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 3556–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotarba, A.Z.; Aleksandrowicz, S. Impervious surface detection with nighttime photography from the international space station. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 176, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, L.X.; Li, D.R.; Xu, H.M. Mapping urban extent using Luojia 1-01 nighttime light imagery. Sensors 2018, 18, 3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.C.; Zhou, Y.Y. Urban mapping using DMSP/OLS stable night-time light: A review. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 6030–6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; He, G.J.; Long, T.F.; Guo, H.X.; Yin, R.Y.; Leng, W.C.; Liu, H.C.; Wang, G.Z. Potentiality of using Luojia 1-01 nighttime light imagery to investigate artificial light pollution. Sensors 2018, 18, 2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.P.; Liu, X.P.; Liu, P.H.; Liu, X.J. Evaluation of Luojia 1-01 nighttime light imagery for impervious surface detection: A comparison with NPP-VIIRS nighttime light data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2019, 81, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Li, X.; Tong, F.; Li, Z.; Jendryke, M. Mapping urban expansion using night-time light images from Luojia1-01 and international space station. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 2603–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.J.; Tuttle, B.T.; Powell, R.L.; Sutton, P.C. Characterizing relation-ships between population density and nighttime imagery for Denver, Colorado: Issues of scale and representation. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 5733–5746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, M.; Yeh, E.T.; Gong, P.; Elvidge, C.; Baugh, K. Validation of urban boundaries derived from global night-time satellite imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Leung, Y. A study of urban expansion of prefectural-level cities in South China using night-time light images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 5557–5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gong, P.; Liang, L. A 30-year (1984–2013) record of annual urban dynamics of Beijing City derived from Landsat data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 166, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Chen, J.; Imura, H.; Higashi, O. A SVM-based method to extract urban areas from DMSP-OLS and SPOT VGT data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2205–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.T.; Coco, G.; Gao, J. Extraction of urban built-up areas from nighttime lights using artificial neural network. Geocarto Int. 2020, 35, 1049–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldblatt, R.; Stuhlmacher, M.F.; Tellman, B.; Clinton, N.; Hanson, G.; Georgescu, M.; Wang, C.; Serrano-Candela, F.; Khandelwal, A.K.; Cheng, W.H. Using landsat and nighttime lights for supervised pixel-based image classification of urban land cover. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 205, 253–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.L.; Schaaf, C.; Seto, K.C. The vegetation adjusted NTL urban index: A new approach to reduce saturation and increase variation in nighttime luminosity. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 129, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wu, J.; Li, W.; Peng, J.; Liu, H. Evaluating saturation correction methods for DMSP/OLS nighttime light data: A case study from China’s cities. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 9853–9872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, L.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Liu, L. An improved method of night-time light saturation reduction based on EVI. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 4114–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Shi, F.; Zhuo, L.; Chen, J. A simple self-adjusting model for correcting the blooming effects in DMSP-OLS nighttime light images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 224, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.K. Kernel density estimation and k-means clustering to profile road accident hotspots. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2009, 41, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seaman, D.E.; Powell, R.A. An evaluation of the accuracy of kernel density estimators for home range analysis. Ecology 1996, 77, 2075–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.J.; Wu, Z.F.; Cheng, J. Using kernel density estimation to assess the spatial pattern of road density and its impact on landscape fragmentation. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2013, 27, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, L.X.; Shen, Z.H.; Chen, J.D.; Fang, R.; Chen, X.P.; Jiang, R. Spatio-temporal patterns of road network and road development priority in three parallel rivers region in Yunnan, China: An evaluation based on modified kernel distance estimate. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, B.W. Density Estimation for Statistics and Data Analysis; Chapman and Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Imhoff, M.L.; Lawrence, W.T.; Stutzer, D.C.; Elvidge, C.D. A technique for using composite DMSP/OLS ‘City Lights’ satellite data to map urban area. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 61, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, P. Modeling population density with night-time satellite imagery and GIS. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 1997, 21, 227–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.Y.; Shi, P.J.; Li, J.G.; Chen, J.; Pan, Y.Z.; Li, J.; Zhuo, L.; Ichinose, T. Restoring urbanization process in china in the 1990s by using non-radiance-calibrated DMSP/OLS nighttime light imagery and statistical data. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2006, 51, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, S.; Yu, B.; Wu, J.; Liu, H. Methods for deriving urban built-up area using night-light data: Assessment and application. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2011, 26, 169–176. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B.L.; Shu, S.; Liu, H.X.; Song, W.; Wu, J.P.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z.Q. Object-based spatial cluster analysis of urban landscape pattern using nighttime light satellite images: A case study of China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2014, 28, 2328–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.R. Introductory Digital Image Processing: A Remote Sensing Perspective, 2nd ed.; Prentice Hall, Inc.: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.X.; Huang, B.; Song, Y.M. Using multi-source geospatial big data to identify the structure of polycentric cities. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.Y.; Yu, Z.L.; Zhu, S.C.; Zheng, Q.M.; Weston, M.; Wang, K.; Gan, M.Y.; Xu, H.W. Delineating urban boundaries using Landsat 8 multispectral data and VIIRS nighttime light data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, X.Y.; Li, D.R.; He, X.J.; Jendryke, M. A preliminary investigation of Luojia-1 night-time light imagery. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 10, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.J.; Ning, X.G.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.G.; Zhang, H.C.; Meng, J. A rapid and automated urban boundary extraction method based on nighttime light data in China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, J.Y.; Jiang, Y.H.; Zhou, P.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, Y.B. On-orbit geometric calibration and validation of Luojia 1-01 night-light satellite. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noam, L. The impact of seasonal changes on observed nighttime brightness from 2014 to 2015 monthly VIIRS DNB composites. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 193, 150–164. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Levin, N.; Xie, J.; Li, D. Monitoring hourly night-time light by an unmanned aerial vehicle and its implications to satellite remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, R.; Zhang, Q.; Li, D.; Liu, S.; He, T.; Zhao, L. Anisotropic characteristic of artificial light at night—Systematic investigation with VIIRS DNB multi-temporal observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 233, 111357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Search Radius | Raw (0 m) | 500 m | 1000 m | 1500 m | 2000 m | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BA | NA | BA | NA | BA | NA | BA | NA | BA | NA | ||
| Luojia 1-01 | BA | 10.0% | 4.6% | 9.5% | 2.6% | 10.7% | 2.5% | 10.6% | 2.5% | 10.5% | 2.6% |
| NA | 2.4% | 83.0% | 5.1% | 82.8% | 3.9% | 82.9% | 4.0% | 82.9% | 4.1% | 82.8% | |
| VIIRS | BA | 10.3% | 4.3% | 10.5% | 2.8% | 10.6% | 2.7% | 10.7% | 2.7% | 10.4% | 2.6% |
| NA | 2.6% | 82.8% | 4.1% | 82.6% | 4.0% | 82.7% | 3.9% | 82.7% | 4.2% | 82.8% | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Shen, Z. Comparing Luojia 1-01 and VIIRS Nighttime Light Data in Detecting Urban Spatial Structure Using a Threshold-Based Kernel Density Estimation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1574. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13081574
Wang Y, Shen Z. Comparing Luojia 1-01 and VIIRS Nighttime Light Data in Detecting Urban Spatial Structure Using a Threshold-Based Kernel Density Estimation. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(8):1574. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13081574
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yuping, and Zehao Shen. 2021. "Comparing Luojia 1-01 and VIIRS Nighttime Light Data in Detecting Urban Spatial Structure Using a Threshold-Based Kernel Density Estimation" Remote Sensing 13, no. 8: 1574. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13081574
APA StyleWang, Y., & Shen, Z. (2021). Comparing Luojia 1-01 and VIIRS Nighttime Light Data in Detecting Urban Spatial Structure Using a Threshold-Based Kernel Density Estimation. Remote Sensing, 13(8), 1574. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13081574