Abstract
Coal-mining subsidence causes ground fissures and destroys surface structures, which may lead to severe casualties and economic losses. Time series interferometric synthetic aperture radar (TS-InSAR) plays an important role in surface deformation detection and monitoring without the restriction of weather and sunlight conditions. In addition, the probability integral method (PIM) is a surface movement model that is widely used in the field of mining subsidence. In recent years, the integration of TS-InSAR and the PIM has been extensively studied. In this paper, we propose a new method to estimate mining subsidence with the PIM based on TS-InSAR results. This study focuses on the improvement of a boundary constraint and dynamic parameter estimation in the PIM through the inversion of the line-of-sight (LOS) time series deformation derived by TS-InSAR. In addition, 45 Sentinel-1A images from 17 June 2015 to 27 December 2017 of a coal mine in Jiaozuo are utilized to acquire the surface displacement. We apply a time series deformation analysis using small baseline subsets (SBAS) and place the results into an improved PIM to estimate the mining parameters. The simulated mining subsidence is highly consistent with the leveling data, exhibiting an RMSE of 0.0025 m. Compared with the conventional method, the proposed method is more accurate in discovering displacement in mining areas. In the final section of this paper, some sources of error that affect the experiment are discussed.
1. Introduction
During coal mining, coal seam roofs may collapse due to non-homogeneous stress, which may cause cracks above the coal seam and subsidence on the surface. The magnitude of subsidence increases as the goaf area increases. If the strata are horizontal, subsidence may appear as a regular subsidence bowl, which may cause damage to people’s lives and property. Therefore, monitoring coal-mining subsidence is crucial.
Traditional analytical methods include point monitoring, area monitoring and numerical simulation (Table 1). The former two are direct-monitoring methods, while numerical simulation is a forward prediction method. Point-monitoring measurements are collected in the subsidence area by using instruments that collect leveling and GPS measurements. Area monitoring is a method that monitors the surface subsidence area using microwave remote sensing, such as InSAR. Differential InSAR (D-InSAR), as a method for deformation monitoring in mining areas, can accurately identify subsidence areas. In addition, time series InSAR (TS-InSAR) technology improves the monitoring accuracy of D-InSAR. With sufficient data and reasonable acquisition time intervals, it can achieve millimeter-scale monitoring accuracy [1,2,3]. With the help of computers, the numerical simulation method solves practical problems by using numerical calculation, simulation and image display on the basis of finite element, finite volume, discrete element and relevant mathematical models. With the development of rock simulation theories, the simulation of mining subsidence has been widely used. Fast Lagrangian Analysis of Continua in three dimensions (FLAC3D) is a numerical simulation software for rock and coal mines [4,5]. Xia et al. applied FLAC3D to detect illegal mining with the combination of InSAR and the probability integral method (PIM) [6]. Regassa et al. proposed an equivalent discontinuous modeling method that simplifies a complex joint system into a simple joint-system hypothesis and estimates the mechanical parameters in each subarea of the models to simulate the mining-induced rock movement [7]. The probability integral method (PIM), one of the numerical simulation methods, is a normal distribution function of the mining surface subsidence prediction model based on the principle of random medium and has been widely used in predicting and evaluating coal-mining subsidence [8]. This method expresses the surface subsidence caused by underground mining by using a simple formula. It is applicable to the subsidence of horizontally and gently dipping strata [9,10]. Tan et al. improved the PIM to simulate the irregular shape of the goaf, which divides the mining area into a series of triangular elements using Delaunay triangulation [11].

Table 1.
Characteristics of various common measurement methods.
Precise leveling is accurate, but the measurement process is time-consuming and laborious, and it is not applicable to large scale monitoring. The accuracy of the GPS elevation component is much lower than that of leveling. In addition, they all measure sparse points, which cannot describe the total subsidence. Furthermore, the measurement results are impacted by the distribution of GPS points, which is not economically feasible because it is time-consuming and has a high labor cost [9]. The limits of D-InSAR, such as some types of decorrelations, DEM error and atmospheric delay, seriously affect the accuracy of deformation. Due to the side-looking imaging geometry of SAR sensors, InSAR with a single data source can only calculate surface deformation along the line-of-sight (LOS) direction, which cannot obtain the real displacement from coal mining. Karamvasis et al. compared three open-source TS-InSAR methods in an active opencast coal mine and showed that the high deformation areas in active mining regions were not identified by using a simple TS-InSAR method [12]. Chen et al. and Zhang et al. combined SBAS-InSAR and offset tracking to monitor the large gradient subsidence caused by mining [13,14]. The results showed that the fusion method can compensate for the large and nonlinear subsidence. Due to the development of fissures and the inclination of strata, the PIM is affected by the discrepancy between the location and scope of the surface subsidence and the goaf [9].
Combining the probability integral method with TS-InSAR may effectively address the problems associated with mining subsidence monitoring. SBAS-InSAR technology can obtain high-precision monitoring results, which help to explain the details of mining subsidence, draw subsidence profiles, inverse parameters, etc. Integrating the goaf subsidence range calculated by SBAS-InSAR into the PIM as a constraint can improve the efficiency and accuracy in the determination of coal-mining subsidence.
For the integration of InSAR (D-InSAR, TS-InSAR) and the PIM, several methods have been proposed in recent years. Fan et al. simulated the wrapped phase of mining subsidence with a large deformation gradient by using the PIM and subtracted it from the interferometric phase to mitigate the decorrelation and obtain a true subsidence by adding the result calculated by SBAS-InSAR and the simulated deformation results [16]. Yang et al. improved the PIM by integrating the PIM and the Knothe time function, which can predict the dynamic deformation of mining-induced subsidence during the entire period of excavation. In addition, they combined the LOS observation derived by InSAR and eight geometric parameters describing the coal mining-induced goaf by using the PIM and proposed a functional relationship between them [17,18]. Zheng et al. combined the deformation predicted by the PIM and temporarily coherent point SAR interferometry (TCPInSAR) to invert the deformation in low coherent mining areas [19]. Du et al. discussed the location deviation of the real inflection point and proposed an improved PIM by using the back basin boundary derived by D-InSAR in the mining direction to calculate the mining depth [20]. Wang et al. combined the PIM with D-InSAR, subband InSAR and offset tracking to monitor the small-scale, medium-scale and large-scale images, respectively [21]. According to the above research, the improvements of the integration of the PIM and InSAR are mainly focused on the refinement of the InSAR results, but due to the complicated condition underground, the displacement simulated by the PIM may mismatch the real surface displacement derived by InSAR. Although the location of the goaf is obtained, the geological conditions above the goaf are uncertain. Therefore, mining-induced deformation will be delayed and deviated.
In this paper, we propose a new method with a boundary constraint of the goaf in the PIM during the parameter inversion procedure. With the time series deformation derived by TS-InSAR, we predict the mining-induced dynamic deformation during the entire period of the excavation. According to the inverse dynamic parameters, we can estimate the mining process and provide a suitable prediction of mining subsidence.
The content of this paper is arranged as follows. Section 2 introduces the main methodology of the integration of TS-InSAR and the PIM. The establishment of the boundary constraint and the procedures of the proposed method are discussed. Section 3 describes an example to analyze the reliability of the proposed method. Section 4 presents the conclusion and prospects.
2. Materials and Methods
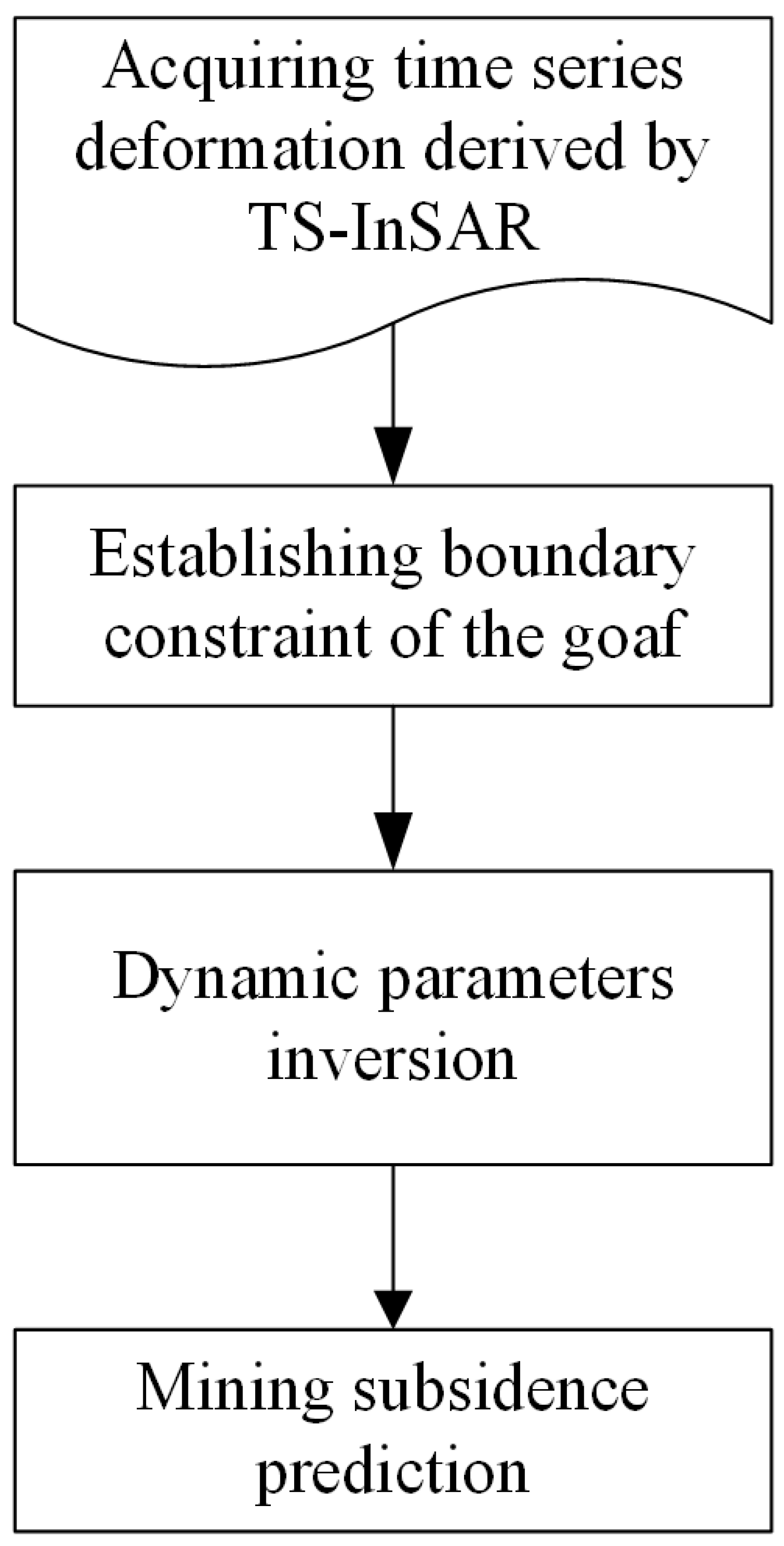
In this study, we utilize the probability integral method and time series InSAR jointly to monitor and estimate coal-mining subsidence. The deformation range derived by the time series InSAR is considered as the ground constraint and introduced into the integration operation. The method flow chart is shown in Figure 1.
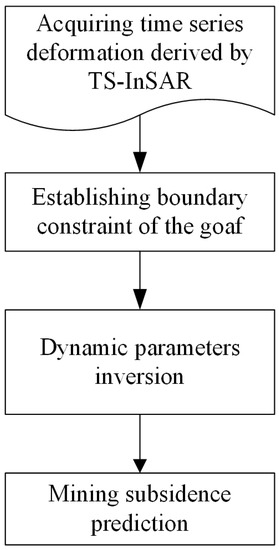
Figure 1.
Flow chart of the proposed method.
2.1. SBAS-InSAR Technology
SBAS-InSAR uses points with stable scattering characteristics and high coherency for inverse surface deformation. This method generates small baseline sets with multiple reference points from different interferometric pairs, which increases repetitive observations and decreases decorrelation caused by a long baseline [2,22,23,24].
The unwrapped phase can be expressed as follows
where is the wavelength of radar, B is the baseline, is the look angle, is the baseline incidence, h is the topographic error of the external DEM, is the deformation expressed as the product of velocity and time interval, is the atmosphere phase consisting of the space-related part and the temporal nonlinear part, and is the noise phase. Thus, Equation (1) can be rewritten as
where the phase component caused by topographic error can be reduced by linear regression. The atmospheric phase can be mitigated with the interpolation method considering the temporal and spatial characteristics of the atmosphere or the relationship between the atmospheric phase and elevation [24,25,26]. The noise phase can be reduced by phase filtering.
After separating the topographic phase, atmospheric phase and noise phase, the differential phase can be expressed by a matrix as
where B is the design matrix. Due to different small baseline sets, B is morbid.
where m is the quantity of SAR data, and j is the quantity of interferometric pairs. Owing to the rank-deficient matrix B, singular value decomposition (SVD) is applied to resolve it.
where V (j × n) and U (n × n) are the orthogonal matrix whose column vector is the eigenvector of BBT, and S is the diagonal matrix whose diagonal element is the eigenvalue of B. Then, deformation can be calculated as
where , and are the deformation of the ith time interval, the deformation rate of the ith time interval and the ith observation time, respectively.
2.2. The Probability Integral Method (PIM)
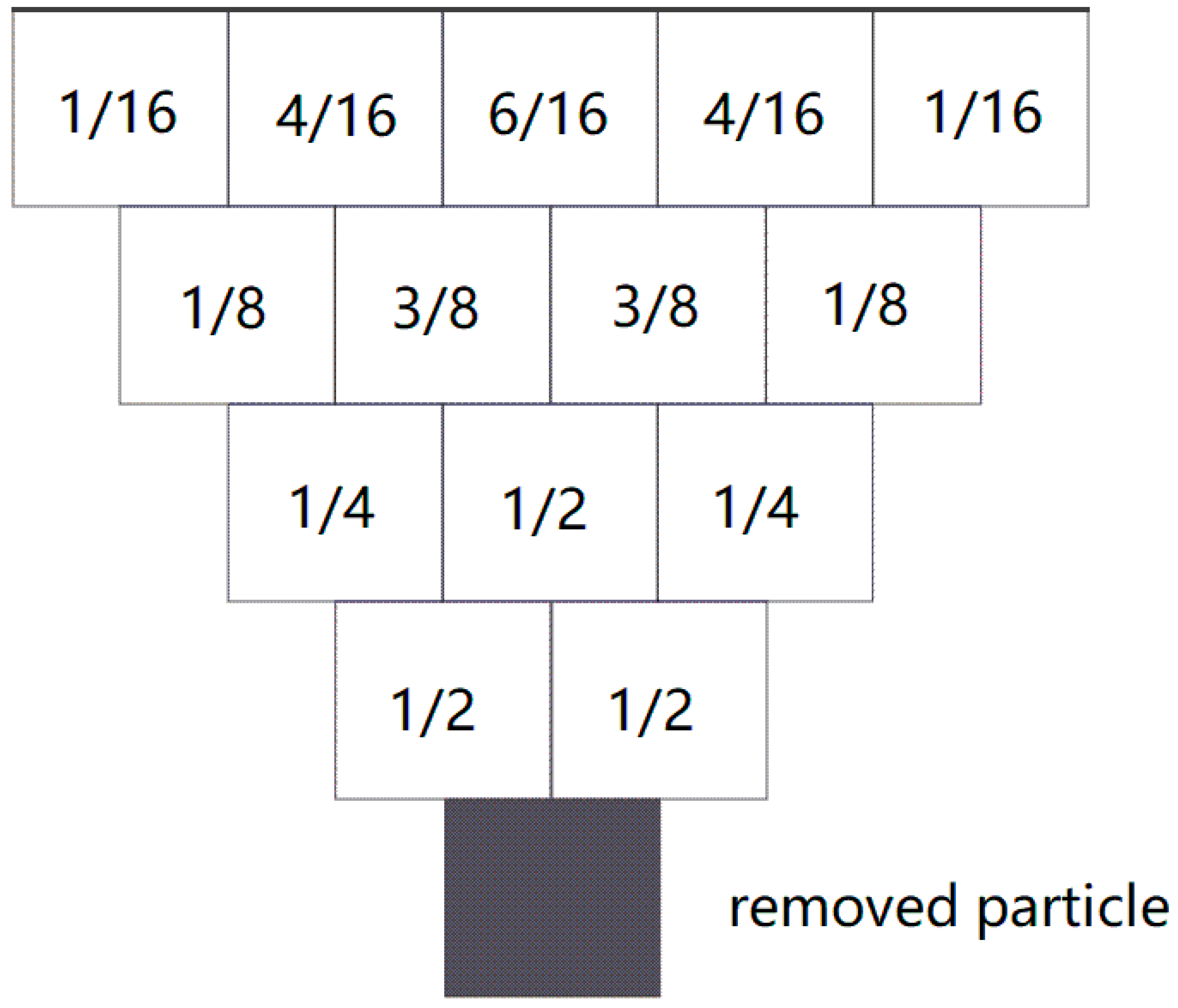
The PIM is a deformation prognosis method based on discontinuous stochastic medium theory, which regards the subsidence of rock particles as a discontinuous medium with the same size obeying statistical law. The surface subsidence profile caused by mining is predicted by the probability density function integral formula. It considers the mining conditions without the influence of geological structure.
Assuming the rock medium underground as small particles, if the particle at the bottom is removed, the particles above will fall due to gravity. The probability of the two particles in the adjacent upper layer will be both 1/2. The probabilities of the upper three particles are 1/4, 1/2 and 1/4 by analogy. Therefore, the subsidence curve obeys the law of normal distribution (Figure 2). For a surface point (x,y), subsidence can be expressed as follows, according to the PIM [16,17,27].
where is the integral function; is the subsidence displacement; is the strike displacement; is the dip displacement; m is the thickness of coal; q is the subsidence coefficient that represents the ratio of the surface vertical displacement to the thickness of the underground mined coal seam; b is the horizontal deformation coefficient; r is the influence radius that could be calculated by r = ; is the function that calculates the strike range of the subsidence W in the subsidence curve function; H is the largest detectable deformation quantity; is the dip angle of coal; is the mining influence propagation angle, and k = [0.5, 0.8]; () is the coordinate of the mining unit; x is the strike range and y is the dip range; , , , , and are the inclined length of the working face, strike length of the working face and displacement distances of the inflection point in the downhill, uphill, left and right directions of the working face, respectively. , . According to principles of radar imaging, the direction of the deformation is the line-of-sight (LOS) observation, which is the synthesis of the up–down, east–west and south–north displacement. Combining the results of InSAR and the PIM, the LOS deformation can be expressed as [18,28]
where , W, , , , and are the LOS deformation, vertical displacement, radar incident angle, radar azimuth angle, working face azimuth angle, east–west displacement and south–north displacement, respectively.
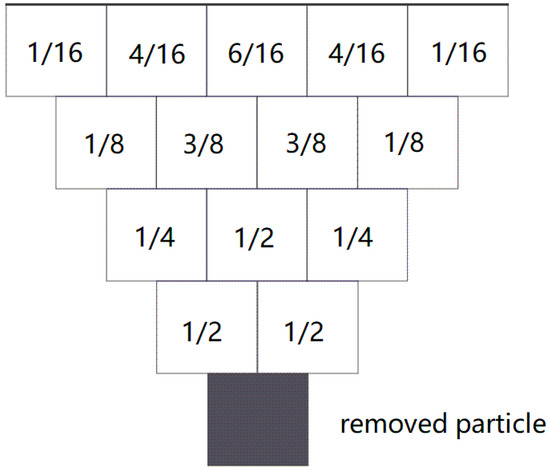
Figure 2.
Probability distribution of particle subsidence according to the stochastic medium theoretical model.
2.3. Parameter Inversion with PSO
Predicting subsidence in a coal mine with the PIM requires many parameters. In this study, m, , , , , , r, , , , , and are given or can be calculated. Only q and B should be inversed. Particle swarm optimization (PSO) is an heuristic algorithm that is applied widely in solution searching. This algorithm solves a problem by generating a population of candidate solutions and moving these particles in the search space according to simple mathematical formulae over the particle’s velocity and position [29,30,31,32], which is expressed as
where is the particle’s velocity update function, is the latest iterative velocity, and are the learning factors, and are two uniform random numbers, is the best individual position, is the latest individual position, and is the best colonial position.
In the traditional PIM, the inversed parameters are set as P(q,b). The known parameters are set as S (m, , , , , , r, , , , , and ). Considering the PIM, the inverse functions are shown as follows.
The fitness function is root mean squared error (RMSE)
where is the LOS deformation simulated by PIM, and is the result of SBAS-InSAR. After inversion, the coefficients are entered the forward model to acquire the 3D coal mine displacement.
2.4. Boundary Constraints
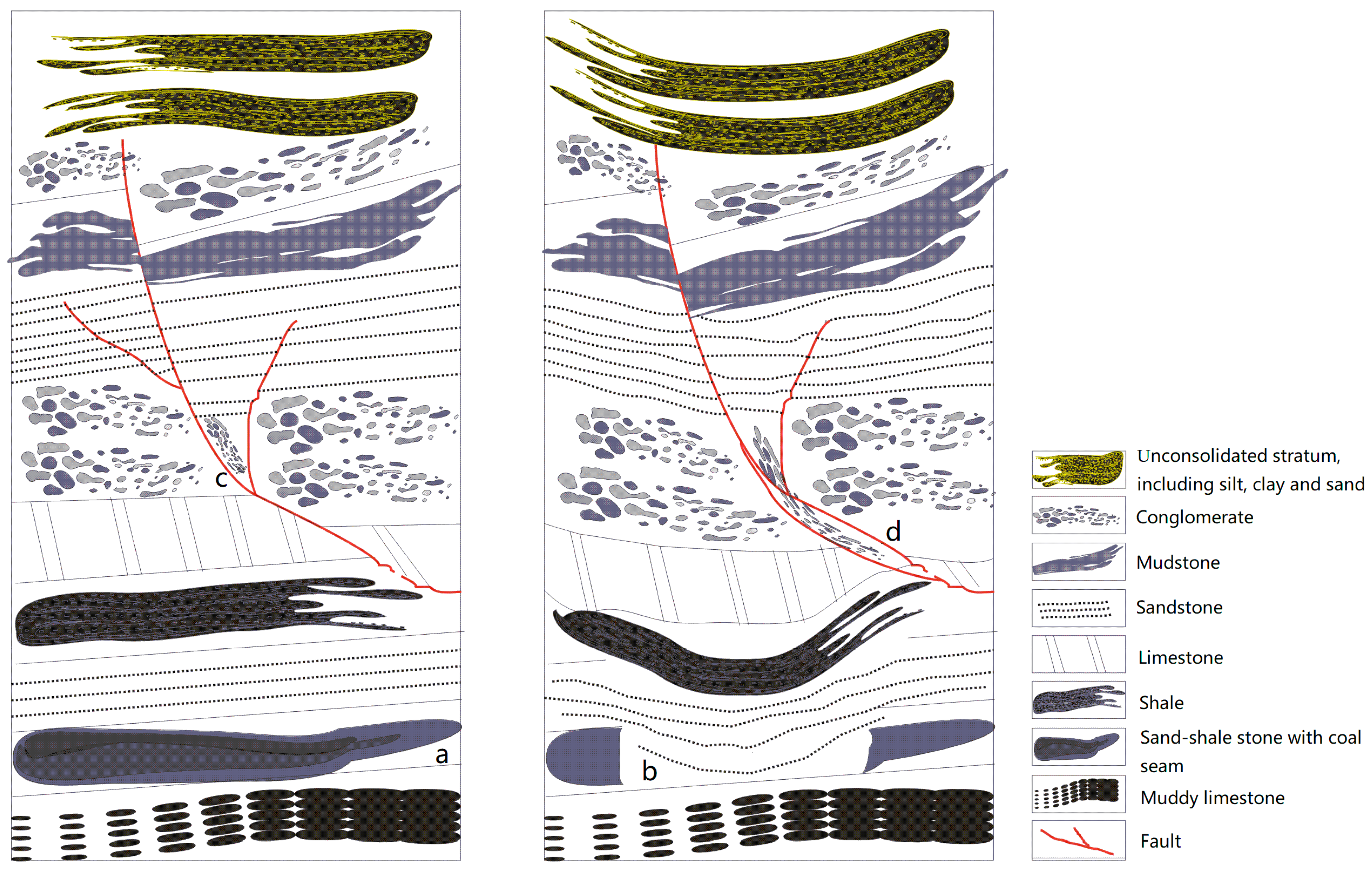
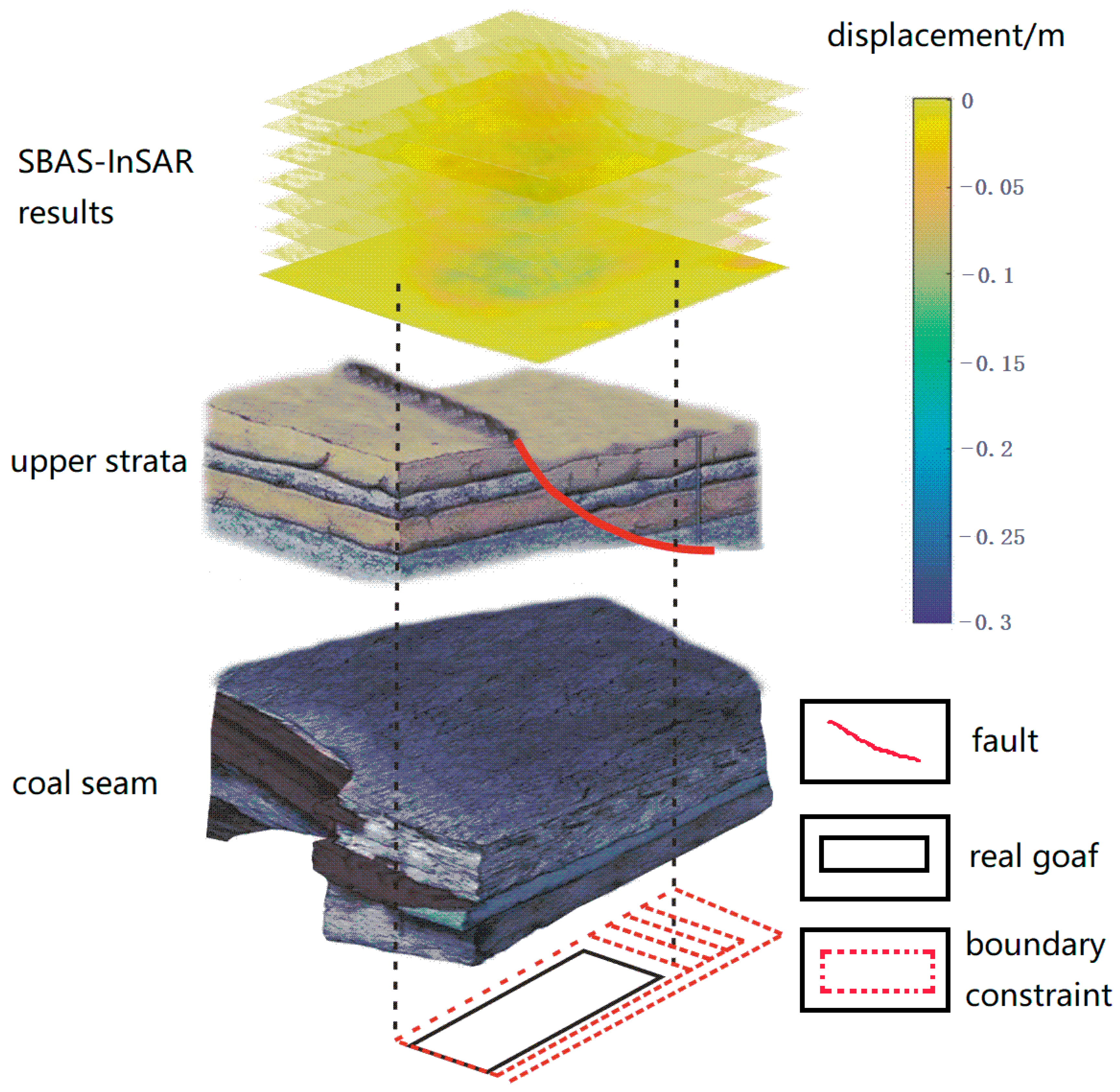
For the conventional PIM, the determination of the location and the extension of the mining subsidence are mainly affected by the influence radius, the influence propagation angle and the integral interval. Furthermore, the influence radius is determined by the sinking curve and calculated by the depth of the coal seam and the main influence angle tangent in full exploitation. The value of the main influence angle tangent is near two and increases with the softness of the upper lithology [33]. Chi et al. discussed the subsidence of a thick unconsolidated layer mining area at the boundary of the basin, which indicates that the boundary of the subsidence in this situation was larger than the conventional conditions [34]. Liu et al. proposed a boundary model to divide total subsidence into four regions according to the inflection points of the terrain reconstruction curve [35]. Du et al. discussed the goaf location due to the deviation of the inflection point when the inflection point is located above the mining excavation [20]. The mining influence propagation angle denotes the inflection of the coal-mining subsidence due to the inflection of the coal seam. In the integral function, the deviation in the dip direction of the surface subsidence was considered by using the depth and influence propagation angle. In this paper, we improved the PIM in the integration function to establish a boundary constraint of surface deformation derived by TS-InSAR. Considering the condition of the coal mine, the real deformation area on the ground is usually larger than the simulation derived by the PIM with local mine data due to complex geological structures such as faults and fissures. Zhu et al. predicted backfill strip mining, which regards surface subsidence as the superposition of backfill mining and strip mining [36]. In fact, if there are faults above the coal seam, the volume of the subsidence must be larger than the volume of mining due to the filling of the fault development interspace (Figure 3). In Figure 3, different strata are distinct at different depths. There is a fault system indicated by the red line representing a kind of unstable geological structure. When coal seam “b” in stratum “a” is fully extracted, the strata above collapse consistently and severely because of the systematic existence of the fault system. “c” and “d” are similar to the fault breccia, which represents the mixture and extrusion of the rock between the upper and lower walls of the fault. If the geological conditions are very complicated underground, this influence would be evident because of the inaccurate assumption of the PIM with isotropic strata and an equal volume of mining and surface subsidence. Therefore, this study regards the displacement unmatched with the PIM theory as equivalent mining. In other words, the extension of the integration interval in the PIM is constrained by surface deformation derived by TS-InSAR.
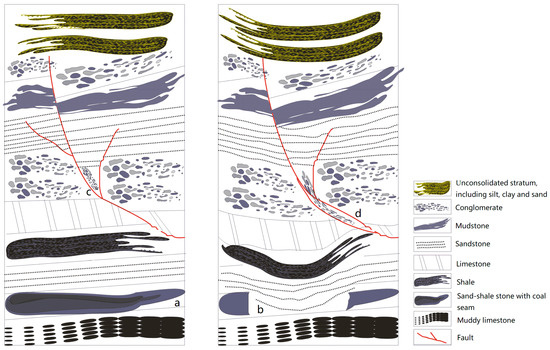
Figure 3.
Sketch map of a coal mine after excavation with a fault system above. The lithology of each strata is illustrated in the legend, and the coal seam is in the penultimate layer (a). Besides, there is a fault system above the coal seam. When the coal seam (b) is extracted, the fault system is activated, and the fault breccia (c) further ruptures into (d).
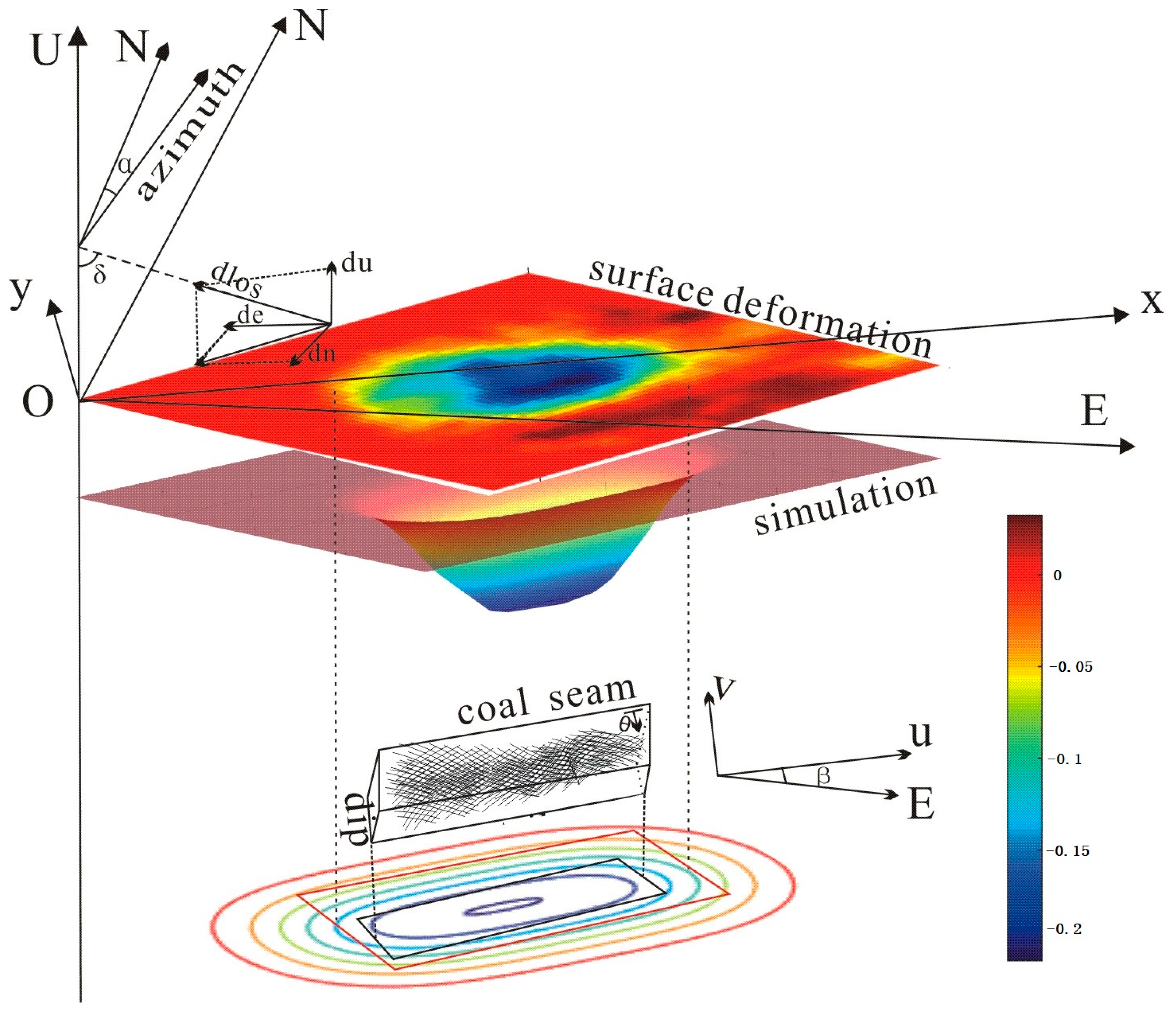
The traditional probability integral method only considers the working face, which constraints from true surface deformation. In this paper, we define a double integral interval , where is the integral interval constrained and determined by the length of the working face and the vertical displacement extension (10 mm) derived by TS-InSAR results. Considering the mining influence propagation and deviation of the inflection point, adjusting the integral interval has the same effect as changing the integral function; therefore, Equation (9) can be expressed as
A sketch of the proposed method is illustrated in Figure 4.
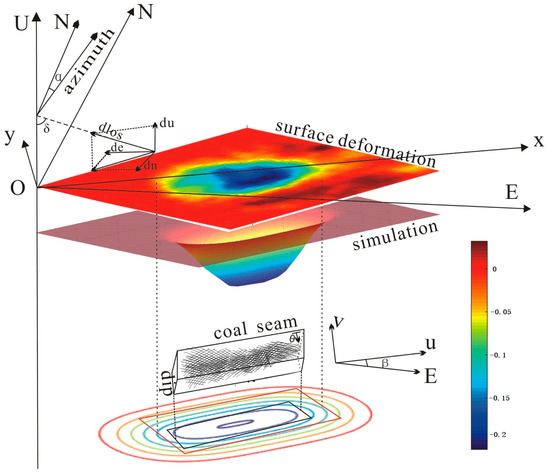
Figure 4.
Sketch of the proposed method. The relationship between the surface deformation and the simulation and angles. Coordinates mentioned before are shown in the figure. The black rectangle represents the real position of the goaf and the minimum of the integral region. The red rectangle represents the defined position of the goaf and the maximum of the integral region.
3. Results
To verify the method discussed above, we select a coal mine located in Jiaozuo, Henan Province, China, to estimate the new method. With SBAS-InSAR technology and the improved PIM, we predict and monitor the coal-mining subsidence.
3.1. Condition of Research Zone
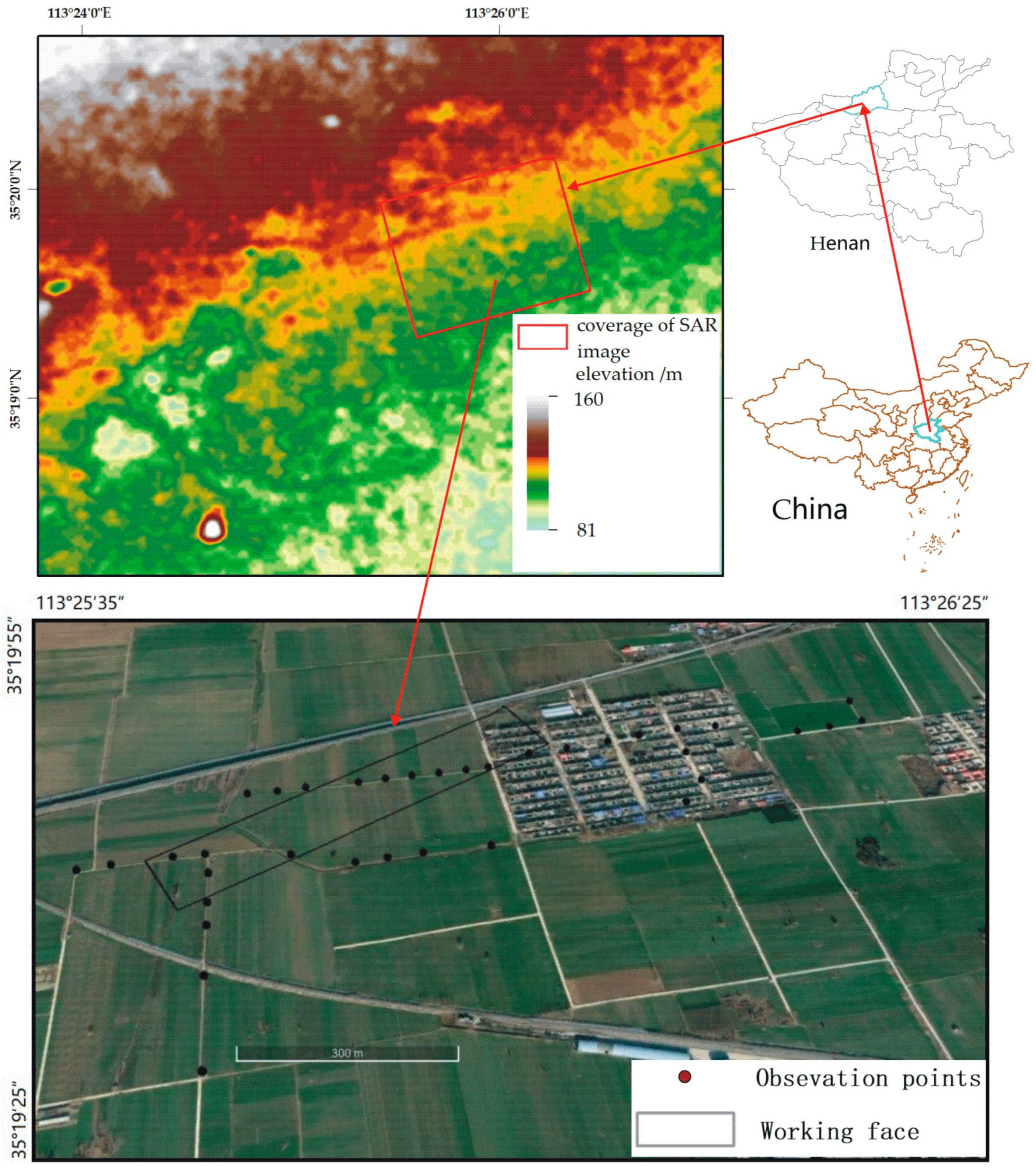
The study area is located in Jiaozuo, Henan Province. There are many coal mines in the research area, and the surface is covered by farmland. Following mine exploration, subsidence has become increasingly serious, which may lead to property damage and risks to human life.
The working face in this study area is a rectangle toward N43°E (Figure 5), and the inclination is toward the SE. The stratum is slightly inclined between 10 and 19° with no folding, forming a monocline structure. The coal seam is under the surface at approximately 547.9–553.64 m. Some leveling data obtained from 36 points from 31 July 2015 to 29 July are used for validation. The leveling points are set on the road or balk for high accuracy.
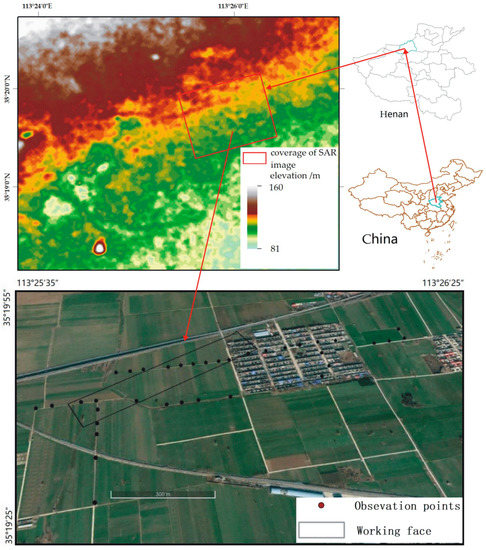
Figure 5.
Location and image of the study area. The black rectangle is the working face of the mine, and the black dots are the leveling points.
3.2. SBAS-InSAR Processing
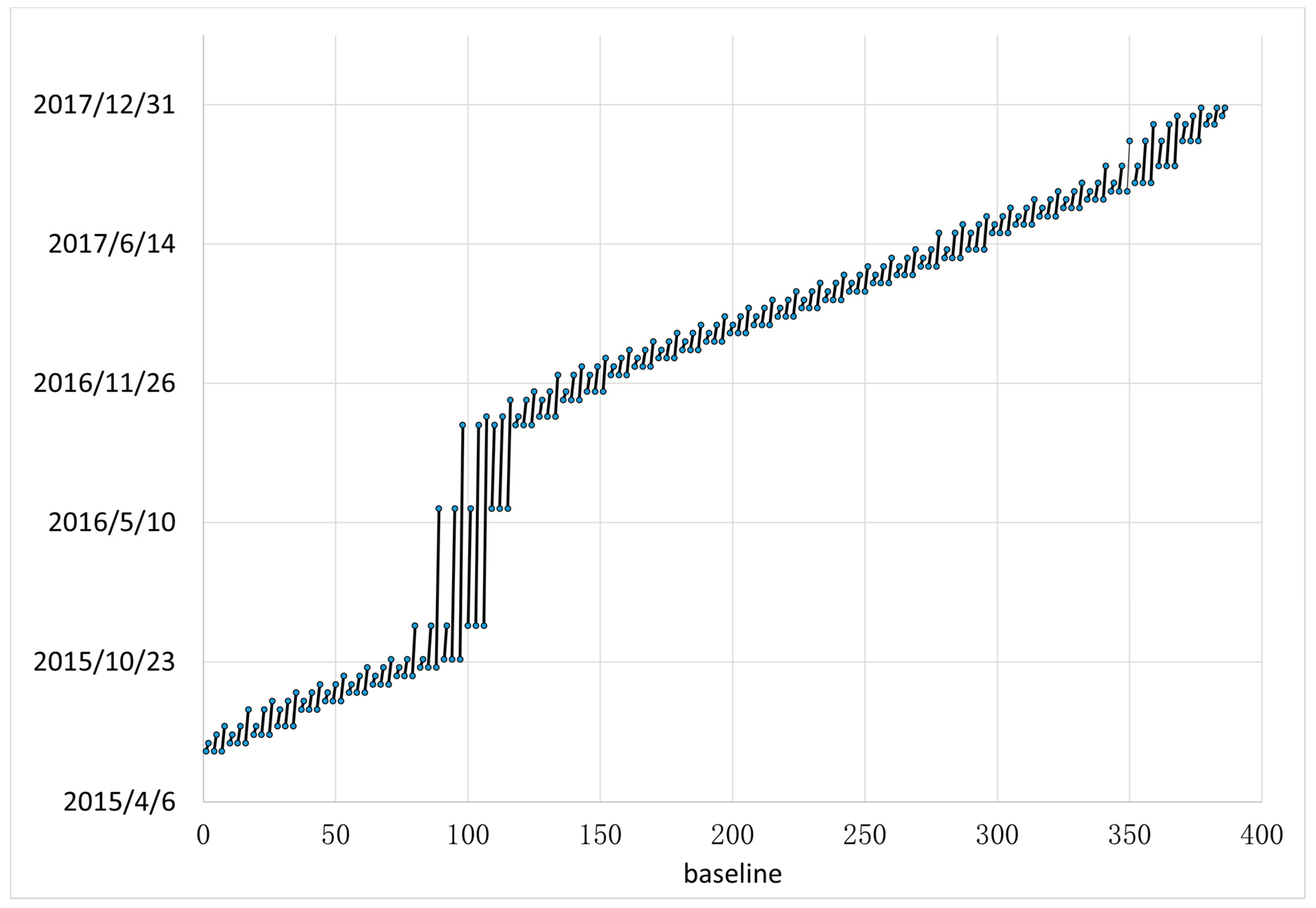
In this study, 45 C-band Sentinel-1A SAR images are acquired to generate 129 interferometric pairs by using SBAS-InSAR technology (Figure 6). The Shuttle Radar Topography Mission 3 (SRTM3) DEM is selected to simulate the elevation phase. Then, a temporal high-pass filter and spatial low-pass filter are applied in the time series process to reduce the atmospheric phase from the mixed interferometry phase. A spatial filter is also adopted to decrease the residual atmosphere. The main procedures are detailed as follows.
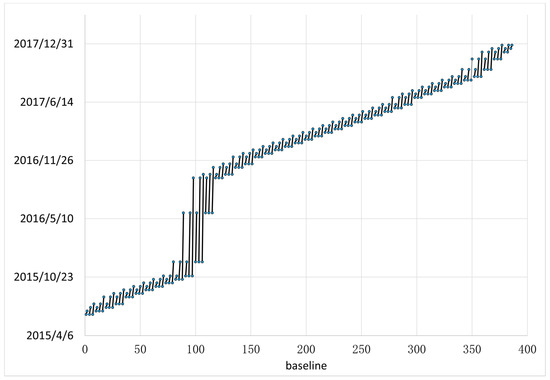
Figure 6.
Condition of interferometric pairs. The black lines are interferometric pairs.
We set the threshold of the perpendicular baseline from 0.4 to 184.4 m. Due to the nonuniform acquisition caused by missing data, the time interval is set from 12 to 336 d. Then, we obtain 129 pairs of interferograms.
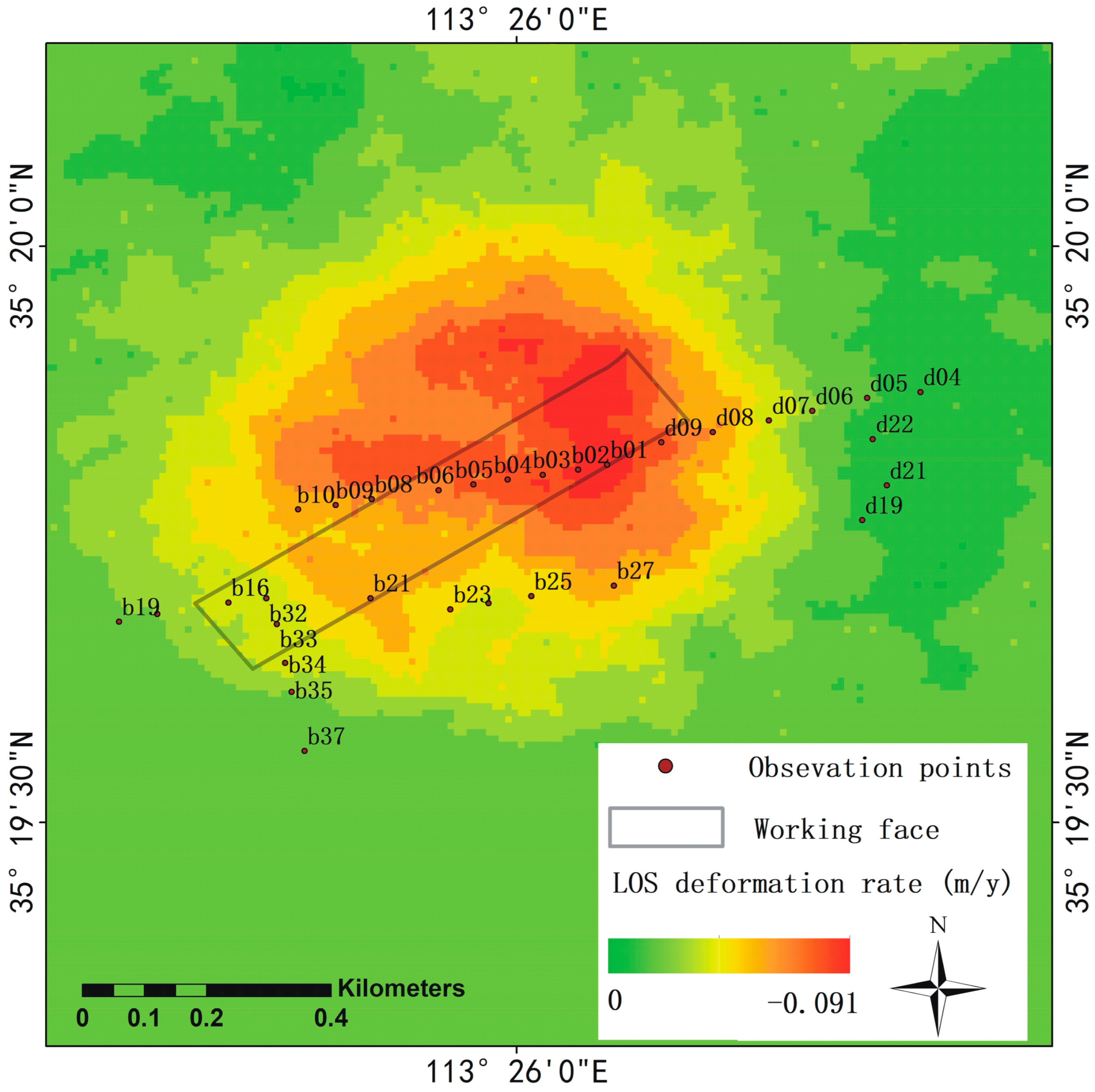
The maximum deformation rate is 0.091 m per year (Figure 7). Darker red regions are associated with larger deformations. The results show that the real deformation is a non-homogeneous deformation with the development of mining. The working face of the coal mine is not in the center of the deformation zone, which is similar to a subsidence bowl in space, but its extension direction is consistent with the surface deformation. The surface deformation did not show concentric subsidence, which may have been due to the heterogeneous stratigraphic structure. Most leveling points are in the range of the deformation zone for further validation.
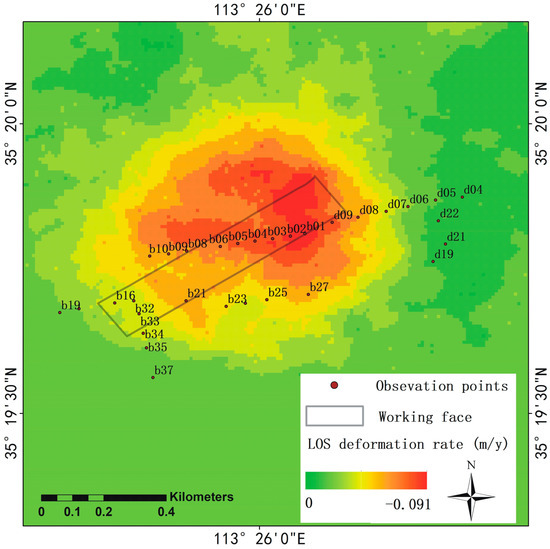
Figure 7.
Line-of-sight (LOS) deformation rate processed by SBAS-InSAR. The red zone is the coal mine, and the green zone is the stable zone. The black rectangle is the working face of the coal mine, and the dots are leveling points.
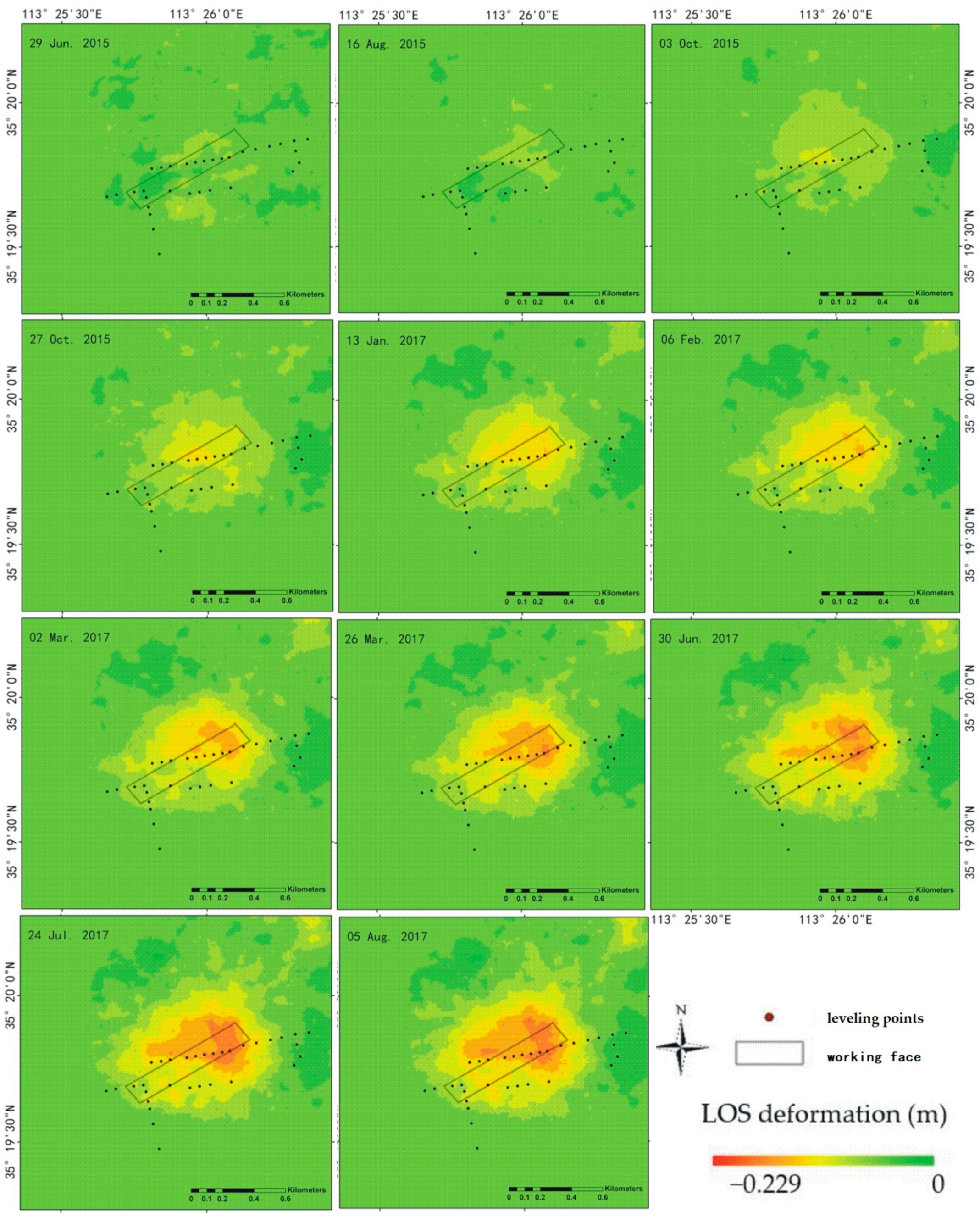
From the equations, the accumulative deformation is calculated (Figure 8). During the observation period, the deformation of the coal mine gradually increased. At the beginning, the displacement is not significant. With time, the deformation zone is increasingly obvious and elliptical in the periphery with irregular polygons in the interior. The maximum subsidence is not in the center of the deformation zone nor in the working face. It changed with mining. In addition, there is another coal mine in the northeastern part of the study area, which shows a similar subsidence. The connecting part is affected by the two mining subsidence areas. Furthermore, the influence of the other coal mine is considered very slight because of the large magnitude of deformation [37,38].
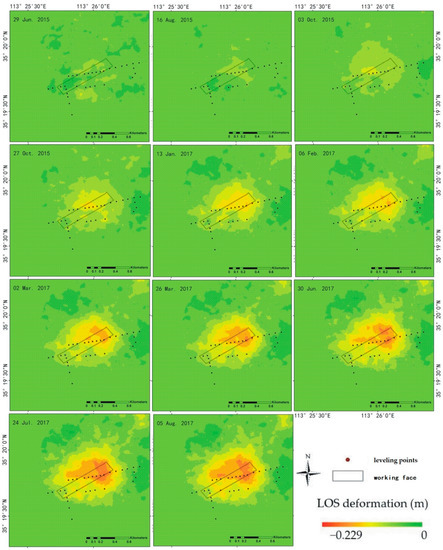
Figure 8.
Typical figures of accumulative deformation. The subsidence center deviated toward the mining direction.
After we calculate the accumulated deformation of the coal mine, the dynamic information on coal-mining subsidence could be clearly illustrated by time series profiles. In this study, we established two profiles along the strike and dip directions and extracted every profile during the observation period (Figure 9). Over time, the surface above the coal mine sank gradually. The subsidence profiles are almost symmetrical at the center and decrease from the center to the edge. There are some differences between the shapes of the two profiles. The length of the strike profile is longer and more symmetrical than the dip profile. Hence, the subsidence on the ground is related to the shape of the working face underground. This characteristic is applied to the proposed method in an integral function to simulate reasonable subsidence.
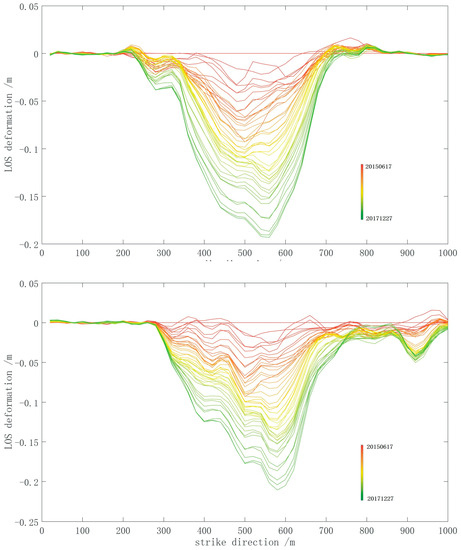
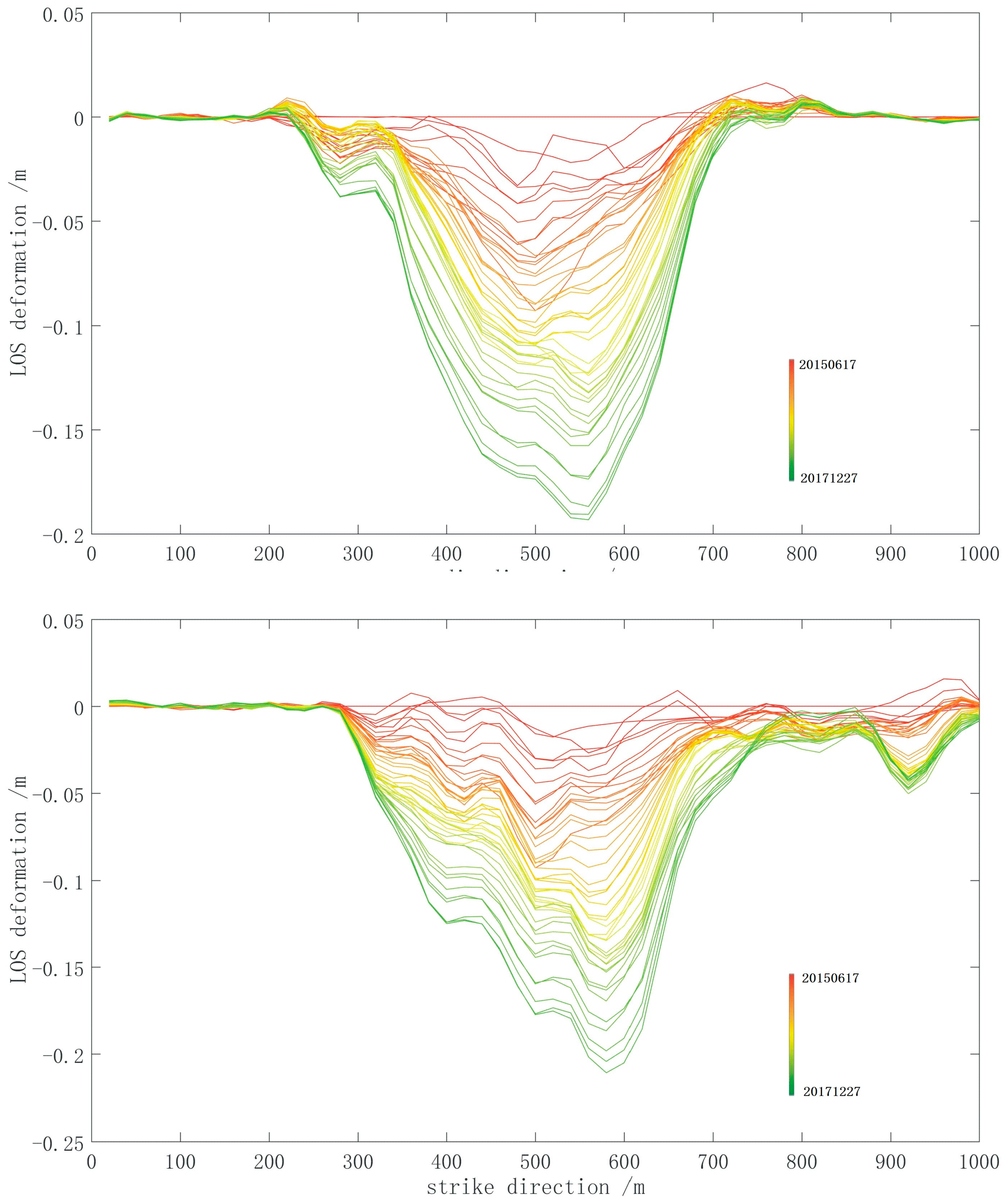
Figure 9.
Profiles of the coal mine in a time series. The upper and lower profiles show the LOS deformation of the coal mine in the strike and dip directions, respectively. From the red to green lines, the subsidence increased gradually during the observation period. During mining, the subsidence center changed with mining and the scope of the collapse basin are different in the two directions.
The profiles show time series information in different directions. However, the curves are not smooth all over, which may have been caused by different geological conditions underground and other decorrelation errors [39]. The maximum subsidence in the two directions approximately is 0.2 m. When the coal mine is excavated, the faults above may have reactivated along with strata movement, which generated non-homogeneous subsidence. Another reason may have been caused by the different surface structures. Different mechanical structures have different responses to subsidence. The major land type in the study area is farmland; however, there are some roads and houses in the study area. Thus, the displacements derived by InSAR in these areas are slightly different.
3.3. Proposed Processing
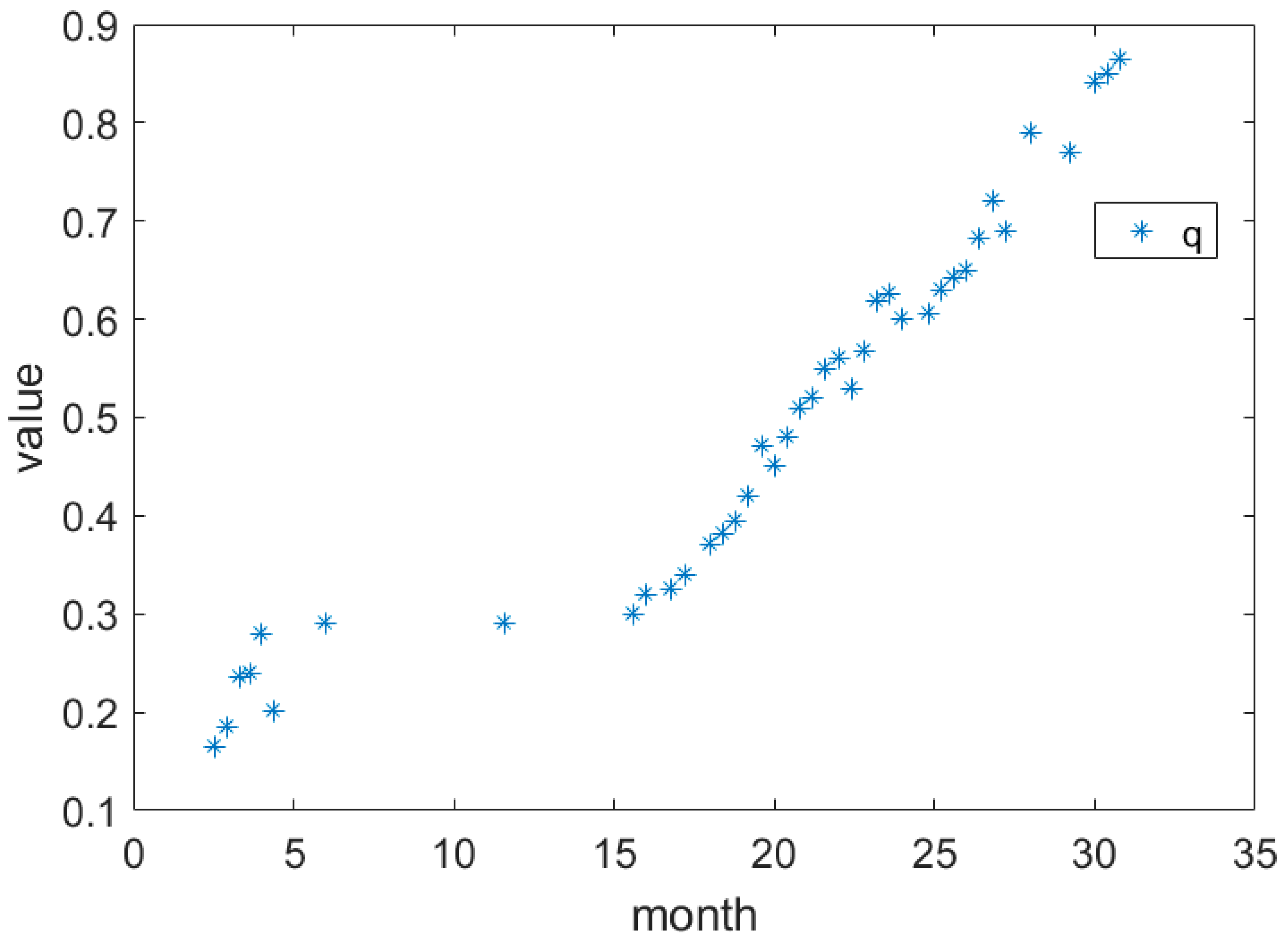
Due to the Yanshan movement, the geological structure in the research zone is complicated and is especially controlled by the high-angle downthrown fault in the northeastern direction. The strata present a monoclinic structure with downfaulted blocks from north to south [39]. The coal seam in the research zone is mainly distributed in anthracolithic strata 547.9–553.64 m underground. The NE-trending fault system affects the mechanism of the surface subsidence process caused by the mining. Therefore, adding a boundary constraint condition on the integral interval can solve this problem (Figure 10). Based on known data and the proposed method (Table 2), we entered the SBAS-InSAR time series results into the proposed method, inversed the dynamic parameters and obtained a continuously changing subsidence coefficient. The subsidence coefficient indicates the conditions of coal mining, such as the strength of the rock, disposal methods of the goaf, repeated mining and the depth of the coal seam. The dynamic subsidence coefficient is illustrated in Figure 11. Due to the nonuniform acquisition of the SAR data, the results are sparse from 5–15 months. After 15 months, the subsidence coefficient increases with the degree of mining.
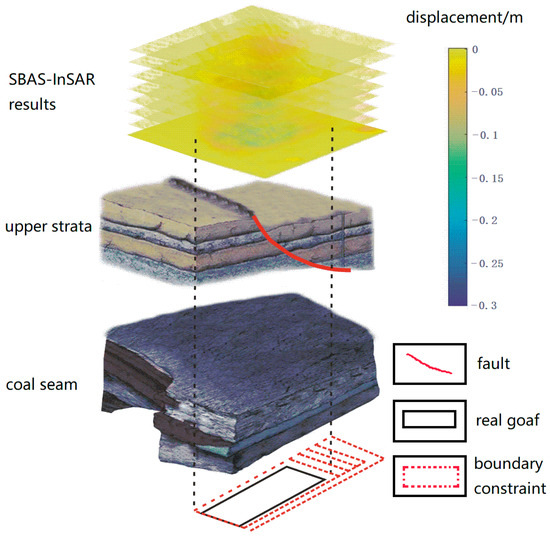
Figure 10.
Sketch map of the proposed method with the boundary constraint.

Table 2.
Value and analytical range of the parameters.
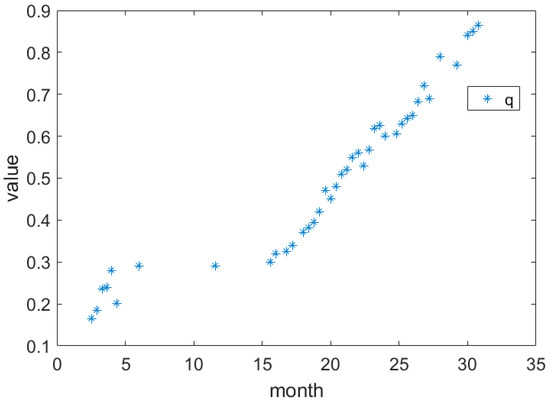
Figure 11.
Change in the inverse dynamic subsidence coefficient with observation time.
3.4. Validation
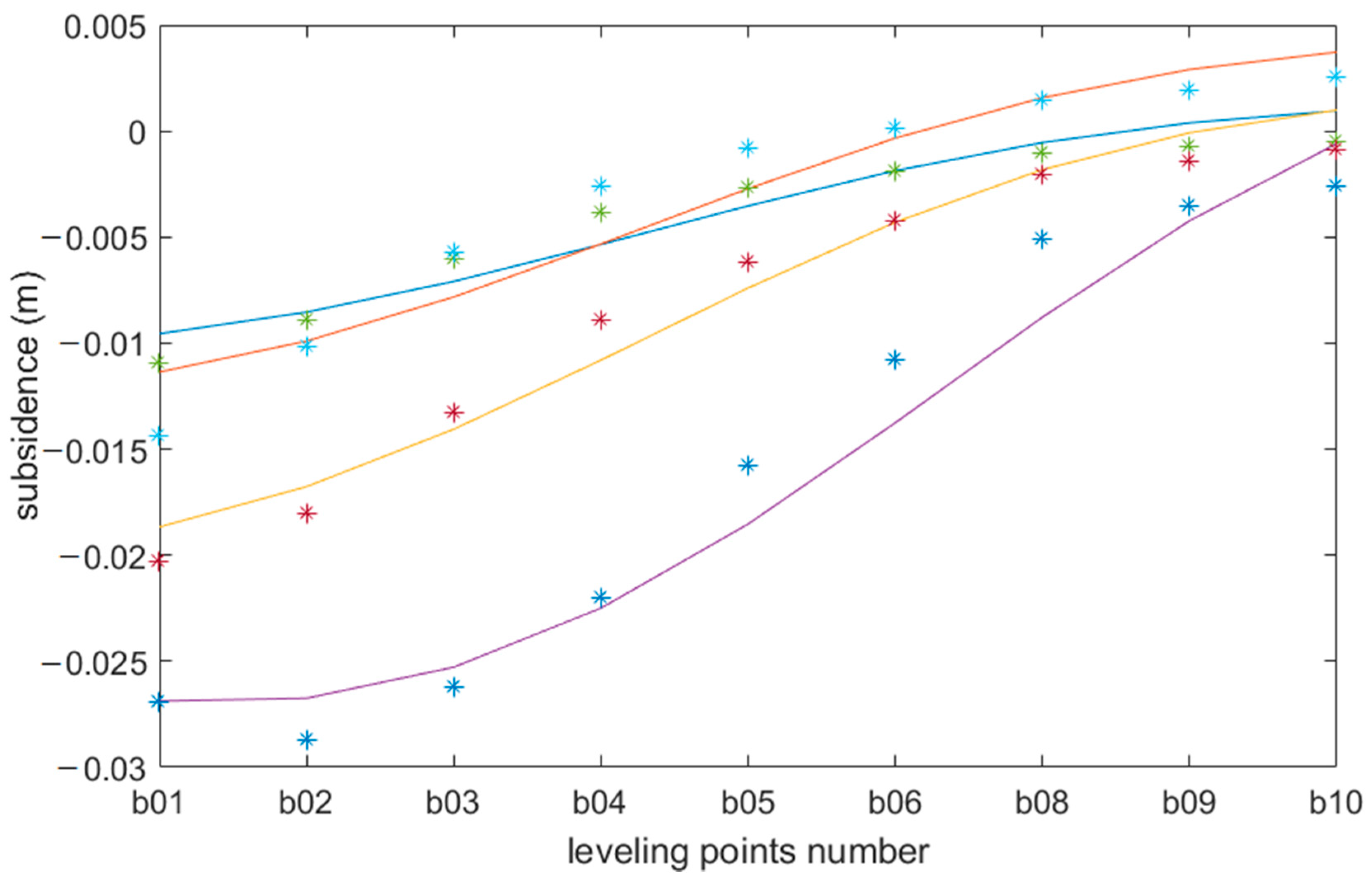
Because not all leveling points are distributed in the subsidence area, we compare the proposed method with the nine typical leveling data within the working face (Figure 12). The abscissa axis is the point number, and the vertical axis is the subsidence value. With time, the leveling data have a decreasing tendency, and the gradient increased gradually. The different colored lines and points represent the results of the proposed method and the field measurements at in different observation times. The results of the leveling data and the proposed method are approximately equal. Considering the precision of leveling, we regard the proposed method as calculating correct results for use.
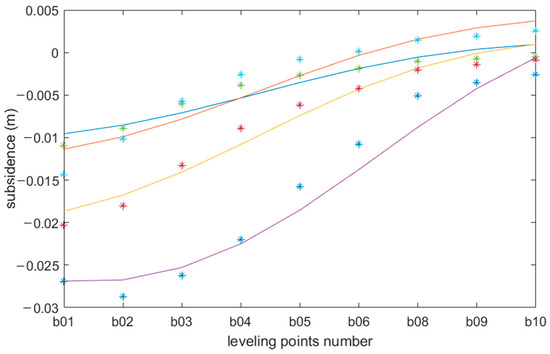
Figure 12.
Comparison between leveling data and SBAS-InSAR results. “*” are the leveling data, and “-” are the results derived by the proposed method. Different colors denote different acquisition times.
In addition, the average RMSE between the results derived by the proposed method and leveling data is 0.0025 m. There is no decreasing trend in the time dimension with the other leveling points away from the working face, which could have been due to the slight deformation magnitude and human disturbance.
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison between the Proposed Method and the Traditional PIM
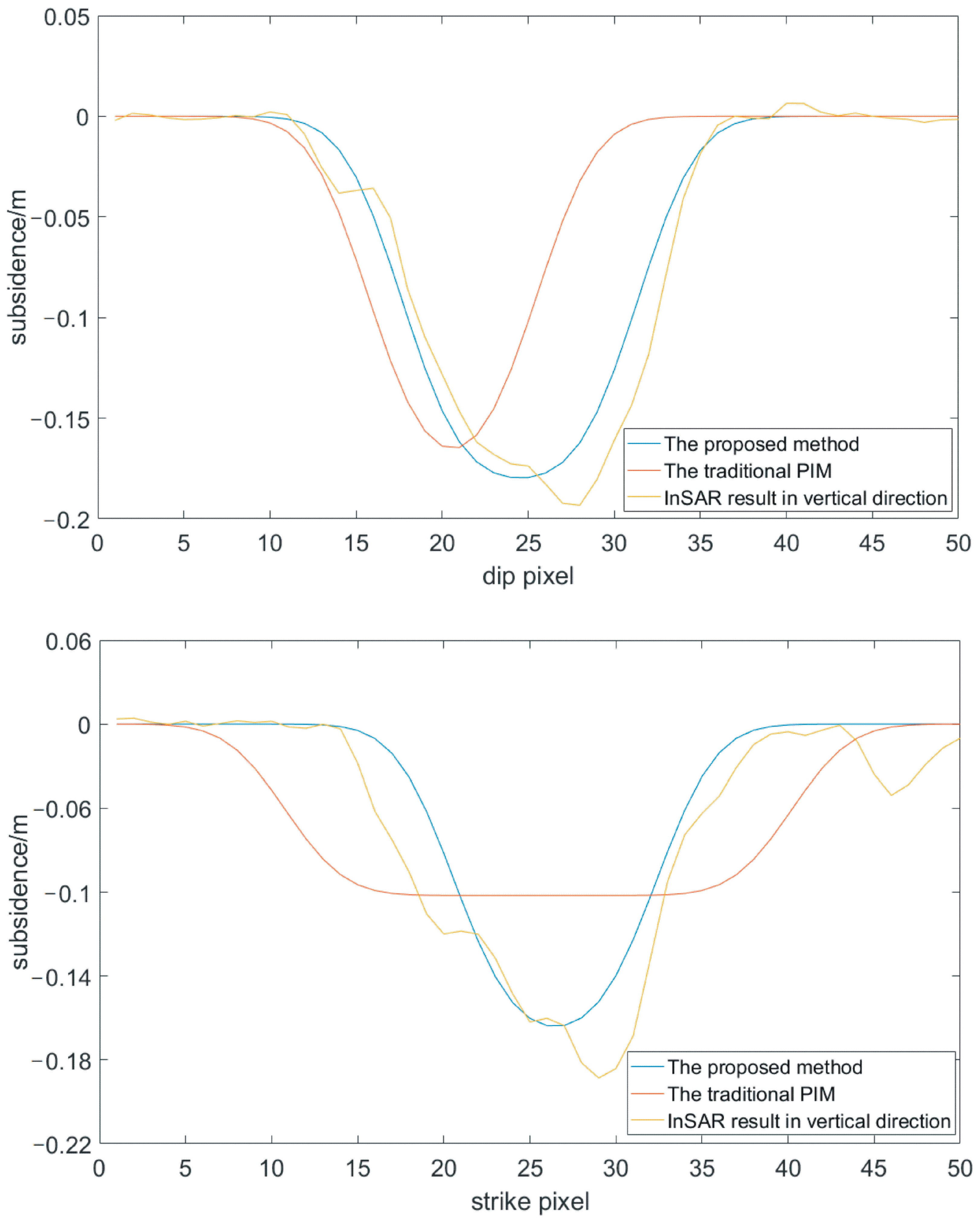
We choose one acquisition time and compared the results of the proposed method with those of the traditional PIM. The profiles show several differences between the proposed method and traditional PIM (Figure 13). In the strike direction, the ranges of these two methods are different because of the longer goaf. The maximum deviation is 0.0918 m, located at point 15; the average error is 0.0395 m, the RMSE is 0.0508 m. On account of different integral intervals, the inverse subsidence coefficient and subsidence are different, which leads to a different forward model. Therefore, the maximum subsidence of the two methods are different. The proposed method shows a deeper subsidence. In the dip direction, the two methods exhibited obvious differences in both range and magnitude, because integral ranges are notably different and the subsidence center deviates by the complex geological condition. The maximum deviation is 0.0478 m, located at point 17; the average error is 0.0272 m, the RMSE is 0.0472 m. Thus, using the proposed method, the coal-mining subsidence simulation is more believable. Due to the smaller range in the dip direction of the working face, the profile of the traditional model in the dip direction is narrow in the subsidence bowl. In comparison, the profile of the proposed method is wider in the subsidence bowl. The maximum of these methods in the dip direction is the same as that in the strike direction. Considering the SBAS-InSAR results, the profiles of the proposed method are more suitable for approximating the real deformation, thus being advantageous compared with the traditional model.
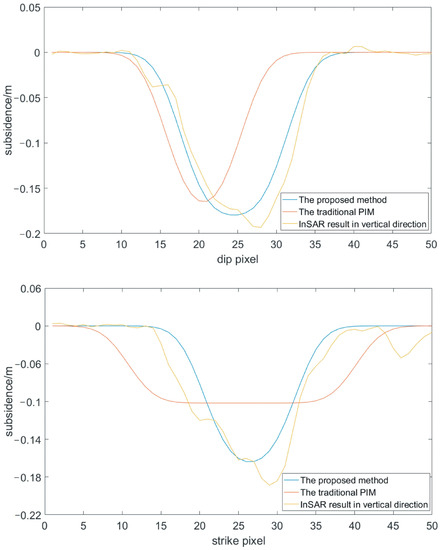
Figure 13.
Profiles of the simulated deformation model. The red lines are the profiles of the SBAS-InSAR results. The blue lines are the profiles of the proposed method and the green lines are the profiles of the traditional PIM. They are drawn in strike and dip directions, respectively.
4.2. Comparison between the Proposed Method and the SBAS-InSAR Results
We compare the proposed method with the SBAS-InSAR results in the vertical direction (Figure 13). The figure indicates that there is little difference between the InSAR results and those of the model with constraints on the subsidence magnitude. In the strike direction, the maximum deviation is 0.061 m, located at point 19; the average error is 0.0172 m, the RMSE is 0.0254 m. In the dip strike direction, the maximum deviation is 0.0436 m, located at point 32; the average error is 0.0096 m, the RMSE is 0.0151 m. The significant difference is the maximum amount of subsidence. The SBAS-InSAR results show a very deep subsidence area that is deeper than that of the simulation model. This may be caused by geologic structures such as faults or springs underground. Additionally, the width of the subsidence bowl in strike direction is different between the proposed method and SBAS-InSAR results. The subsidence bowl of the proposed method is narrower than that calculated by SBAS-InSAR due to the complexity of the surface structure.
In this study, coal-mining subsidence is simulated by the proposed method. It is noteworthy that this improved PIM requires InSAR results to establish inverse parameters related to subsidence prediction and estimation. In fact, TS-InSAR yields a good estimation and monitored coal-mining subsidence. On account of the convenience and speed of the time series InSAR process, the coal mine situation could be obtained in a short period of time. Thus, the key of this study is analyzing the entire process of the coal mine by using the PIM combined with the InSAR time series. The InSAR time series emphasizes the data of the coal-mining subsidence, while the proposed method is used to obtain the deformation model information, which is the mechanism of the subsidence. Only two methods are applied, the entire process occurring in the coal mine could be detected.
4.3. Influence of Complex Geological Conditions and InSAR Geometry
Considering the complex geological conditions, the proposed method regards all surface deformation as resulting from coal mine exploitation. If the stratigraphic dip is small, the simulation could be suitable. Otherwise, the surface subsidence would produce a large deviation, which would not be well simulated by simply changing the integral interval. Besides, the faults and springs in the strata may accelerate the subsidence but deviate the subsidence bowl because they developed low stress region, which could be filled by fragmental rock.
Due to the side-looking imaging geometry of SAR sensors, the result from InSAR is in the LOS direction. However, the surface displacement caused by mining is 3D displacement. Although the subsidence in the subsidence bowl is very significant, the surface deformation is still caused by the horizontal and vertical displacement.
If we ignore the displacement in the dip direction, for a certain point in the subsidence area caused by mining in strike profile, the true displacement can be projected into two directions, while the LOS is another direction. If we just consider the subsidence simulated by PIM or measured by leveling, the true deformation information is not fully considered. Only if we project the vertical and horizontal displacement into LOS and add them together, the deformation information is closest to the real situation. The relevant formula is shown in function 12–14. The inversed horizontal displacement shows a slight horizontal displacement of the coal mine deformation, which helps establish a 3D deformation to fit the LOS deformation derived by SBAS-InSAR.
5. Conclusions
This study utilizes coal-mining monitoring and prediction with the integration of SBAS-InSAR and the PIM and proposes an improved method that creates a boundary constraint in the determination of integral intervals combining SBAS-InSAR and the PIM for locating the goaf and monitoring mining subsidence. Although the traditional PIM provides a suitable prediction for surface subsidence, complex geological conditions exceeds the original assumptions. The improved method is different from the traditional PIM in the integral interval, which regards the change in geological structures as an equivalent boundary constraint. The cumulative displacement derived by SBAS-InSAR is regarded as maximum extension of the equivalent working face. Through PSO, the constrained dynamic parameters in the PIM are inversed and analyzed in the time domain. Therefore, we believe the proposed method will have a wide application in surface deformation caused by extraction.
We select a coal mine located in Jiaozuo, Henan Province, to test the proposed method with 45 Sentinel-1A images. The LOS deformation is transferred into a mining subsidence model to acquire model dynamic parameters (such as the subsidence coefficient and horizontal displacement coefficient). To validate the results of the proposed method, we compare vertical displacement with the leveling data, and the RMSE of leveling point is 0.0025 m. To test the proposed method, profiles of the coal mine in both strike and dip directions are illustrated and compared with the SBAS-InSAR results. Comparisons of the proposed method, traditional PIM and SBAS-InSAR indicate that the proposed method is more consistent with SBAS-InSAR.
The deformation boundary derived by SBAS-InSAR is affected by multiple factors, such as surface resolution, spatial-filtering method and atmospheric conditions. Furthermore, SAR data from different orbits can improve the accuracy of deriving LOS deformation. In the future, more SAR data with high ground resolutions and different types of coal mines may be considered in the method.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.S. and H.Y.; methodology, H.Y.; software, J.P.; validation, Z.G. and B.Z.; formal analysis, B.W.; investigation, B.W.; resources, B.W.; data curation, M.S.; writing—original draft preparation, M.S.; writing—review and editing, M.S.; visualization, M.S.; supervision, H.Y.; project administration, H.Y.; funding acquisition, H.Y. and Z.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the following research projects: the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61427802, 41330634, 41374016 and 41804027); the Science and Technology Project of the State Grid (Research and Application on Intelligent Monitoring and Early Warning Technology of Geological Hazards for Power Transmission Line Based on InSAR, GCB17201700121); the Open Fund of State Key Laboratory of Coal Resources and Safe Mining (Grant No. SKLCRSM20KFA12).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Multibaseline InSAR DEM reconstruction: The wavelet approach. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C. Nonlinear subsidence rate estimation using permanent scatterers in differential SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 2202–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A New Algorithm for Surface Deformation Monitoring Based on Small Baseline Differential SAR Interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Tan, Z.; Yan, L. A Shaft Pillar Mining Subsidence Calculation Using Both Probability Integral Method and Numerical Simulation. Comput. Modeling Eng. Sci. 2018, 117, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, S.H. New open-source ANSYS-SolidWorks-FLAC3D geometry conversion programs. J. Sustain. Min. 2015, 14, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Wang, Y.; In, S.A.R. PIM-Based Inclined Goaf Determination for Illegal Mining Detection. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.R.N.; Mei, G. An equivalent discontinuous modeling method of jointed rock masses for DEM simulation of mining-induced rock movements. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2018, 108, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, S.P.; Costa, J.F.C.L.; Salvadoretti, P.; Koppe, J. Mining simulation for room and pillar coal operation. Rem Rev. Esc. De Minas 2010, 63, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.F.; Li, Z.W.; Zhu, J.J.; Hu, J.; Wang, Y.J.; Chen, G.L. InSAR-Based Model Parameter Estimation of Probability Integral Method and Its Application for Predicting Mining-Induced Horizontal and Vertical Displacements. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 4818–4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.D.; Cheng, D.; Deng, K.Z.; Chen, B.Q.; Zhu, C.G. Subsidence monitoring using D-InSAR and probability integral prediction modelling in deep mining areas. Surv. Rev. 2015, 345, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Song, B.; Bo, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Lu, G. Extraction of Irregularly Shaped Coal Mining Area Induced Ground Subsidence Prediction Based on Probability Integral Method. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamvasis, K.; Karathanassi, V. Performance Analysis of Open Source Time Series InSAR Methods for Deformation Monitoring over a Broader Mining Region. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tong, Y.; Tan, K. Coal Mining Deformation Monitoring Using SBAS-InSAR and Offset Tracking: A Case Study of Yu County, China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 6077–6087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cai, X.; Wang, Y.; Wei, W.; Liu, B.; Jia, S.; Pang, T.; Bai, F.; Wei, Z. Long-term ground multi-level deformation fusion and analysis based on a combination of deformation prior fusion model and OTD-InSAR for longwall mining activity. Measurement 2020, 161, 107911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Mao, Q.; Li, Q.; Zhang, P. An accuracy-improvement method for GPS/INS kinematic levelling for use in linear engineering surveying projects. Measurement 2014, 54, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Lu, L.; Yao, Y. Method Combining Probability Integration Model and a Small Baseline Subset for Time Series Monitoring of Mining Subsidence. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.F.; Li, Z.W.; Zhu, J.J.; Preusse, A.; Yi, H.W.; Wang, Y.J.; Papst, M. An Extension of the InSAR-Based Probability Integral Method and Its Application for Predicting 3-D Mining-Induced Displacements Under Different Extraction Conditions. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 3835–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhu, J.; Yi, H.; Feng, G.; Hu, J.; Wu, L.; Preusse, A.; Wang, Y.J.; Papst, M. Locating and defining underground goaf caused by coal mining from space-borne SAR interferometry. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 135, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Deng, K.; Du, S.; Jie, L.; Feng, J. Joint Probability Integral Method and TCPInSAR for Monitoring Mining Time-Series Deformation. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2018, 47, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, M.; Zhou, D.; Xia, Y. Goaf Locating Based on InSAR and Probability Integration Method. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Deng, K.; Zheng, M. Research on ground deformation monitoring method in mining areas using the probability integral model fusion D-InSAR, sub-band InSAR and offset-tracking. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 85, 101981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, M.E.; Simons, M. A satellite geodetic survey of large-scale deformation of volcanic centres in the central Andes. Nature 2002, 418, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanssen, R.F. Radar Interferometry Data Interpretation and Error Analysis. IEEE 2001, 96–98. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Zhang, L.; Hu, J.; Ding, X.; Li, Z.; Zhu, J. Characterizing sudden geo-hazards in mountainous areas by D-InSAR with an enhancement of topographic error correction. Nat. Hazards 2015, 75, 2343–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.H.; Wdowinski, S.; Kim, S.W.; Won, J.S. Multi-temporal monitoring of wetland water levels in the Florida everglades using interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR). Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2436–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Li, Z.; Penna, N.T. Interferometric synthetic aperture radar atmospheric correction using a GPS-based iterative tropospheric decomposition model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xinpeng, D.; Kan, W.; Dahe, H.; Liang, L.; Dawei, Z. Combining differential SAR interferometry and the probability integral method for three-dimensional deformation monitoring of mining areas. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 5196–5212. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Xu, B.; Li, Z.; Wu, L.; Zhu, J. Prediction of Mining-Induced Kinematic 3-D Displacements from InSAR Using a Weibull Model and a Kalman Filter. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 99, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhu, J.; Preusse, A.; Hu, J.; Feng, G.; Wang, Y.; Papst, M. An InSAR-Based Temporal Probability Integral Method and its Application for Predicting Mining-Induced Dynamic Deformations and Assessing Progressive Damage to Surface Buildings. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J. Particle swarm optimization. Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Neural Netw. 2011, 4, 1942–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Poli, R.; Kennedy, J.; Blackwell, T. Particle swarm optimization. Swarm Intell. 2007, 1, 1942–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Chakrabarti, B.K. Quantum Annealing and Related Optimization Methods; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Yihdego, Y.; Paffard, A. Predicting Open Pit Mine Inflow and Recovery Depth in the Durvuljin soum, Zavkhan Province, Mongolia. Mine Water Environ. 2016, 36, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, S.; Wang, L.; Yu, X.; Fang, X.; Jiang, C. Research on prediction model of mining subsidence in thick unconsolidated layer mining area. IEEE Access 2021, 99, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, M.; Su, L.; Chen, X.; Sun, A. A boundary model of terrain reconstruction in a coal-mining subsidence waterlogged area. Environ. Earth Sci 2021, 80, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Guo, G.; Hui, L.; Yang, X. Surface subsidence prediction method of backfill-strip mining in coal mining. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2019, 78, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casu, F.; Manconi, A.; Pepe, A.; Lanari, R. Deformation Time-Series Generation in Areas Characterized by Large Displacement Dynamics: The SAR Amplitude Pixel-Offset SBAS Technique. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 2752–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhong, L.U.; Zhang, Q. Time-series deformation monitoring over mining regions with SAR intensity-based offset measurements. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 4, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Guo, L.; Guo, Y.; Luo, H.; Liang, Y. Research on the effects of coal mining on the karst hydrogeological environment in Jiaozuo mining area, China. Environ. Geol. 2019, 78, 434. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).