Challenges in Reconciling Satellite-Based and Locally Reported Estimates of Wetland Change: A Case of Topographically Constrained Wetlands on the Eastern Tibetan Plateau
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
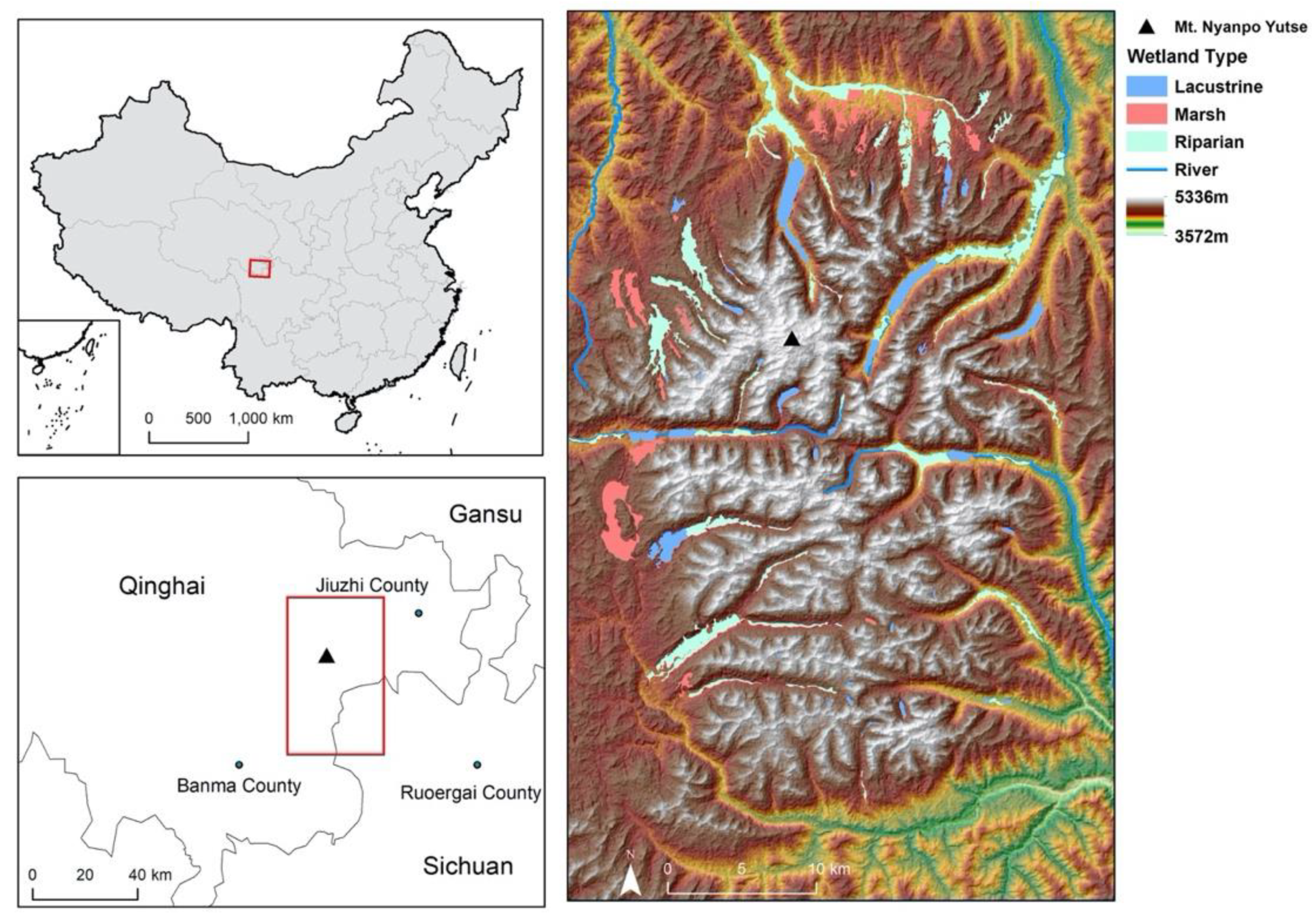
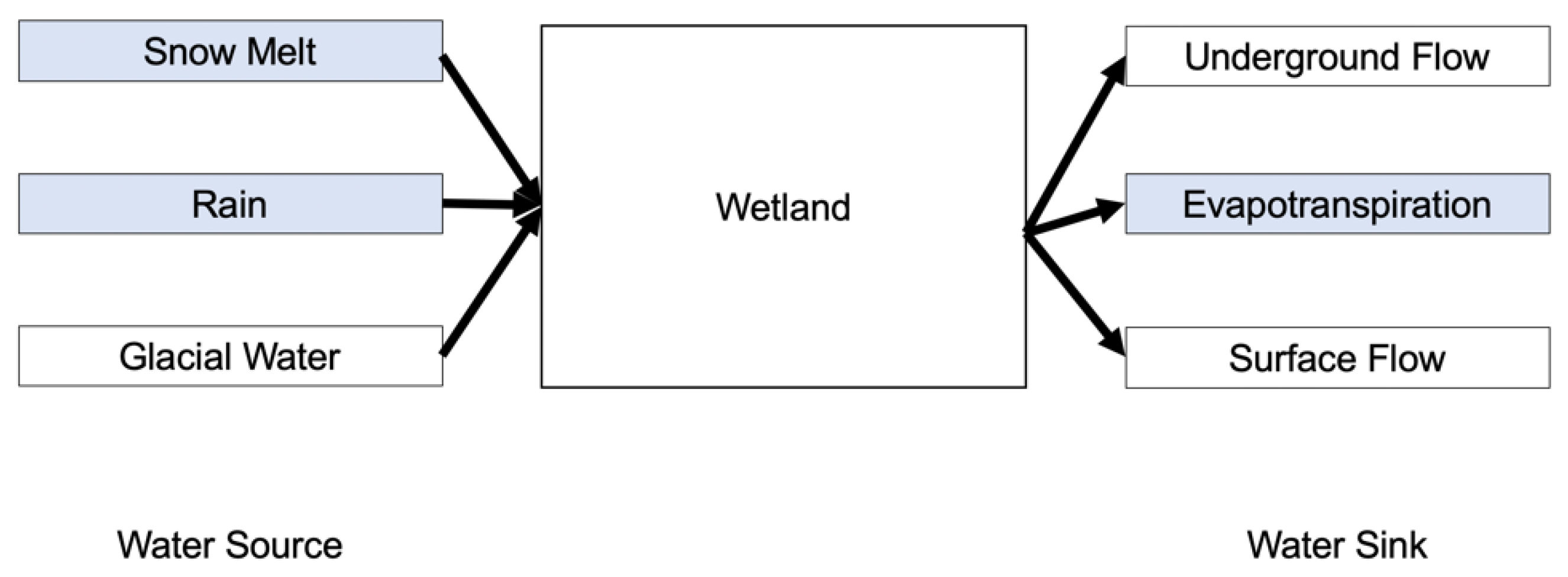
2.1. Regional Setting
2.2. Analysis of Satellite-Based Evidence of Wetland Change
2.3. Analysis of Potential Climate Drivers of Wetland Change
3. Results
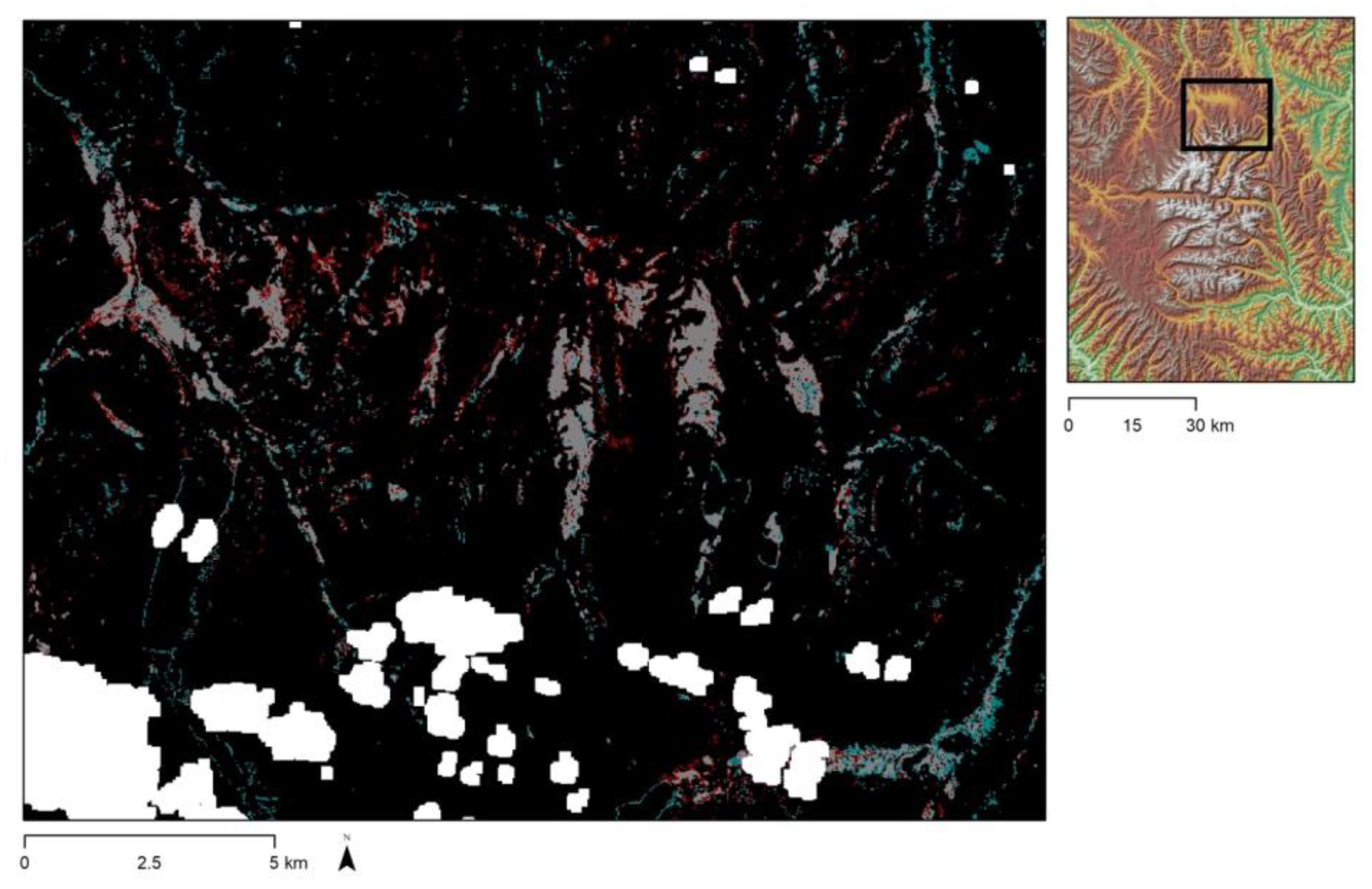
3.1. Wetland Area
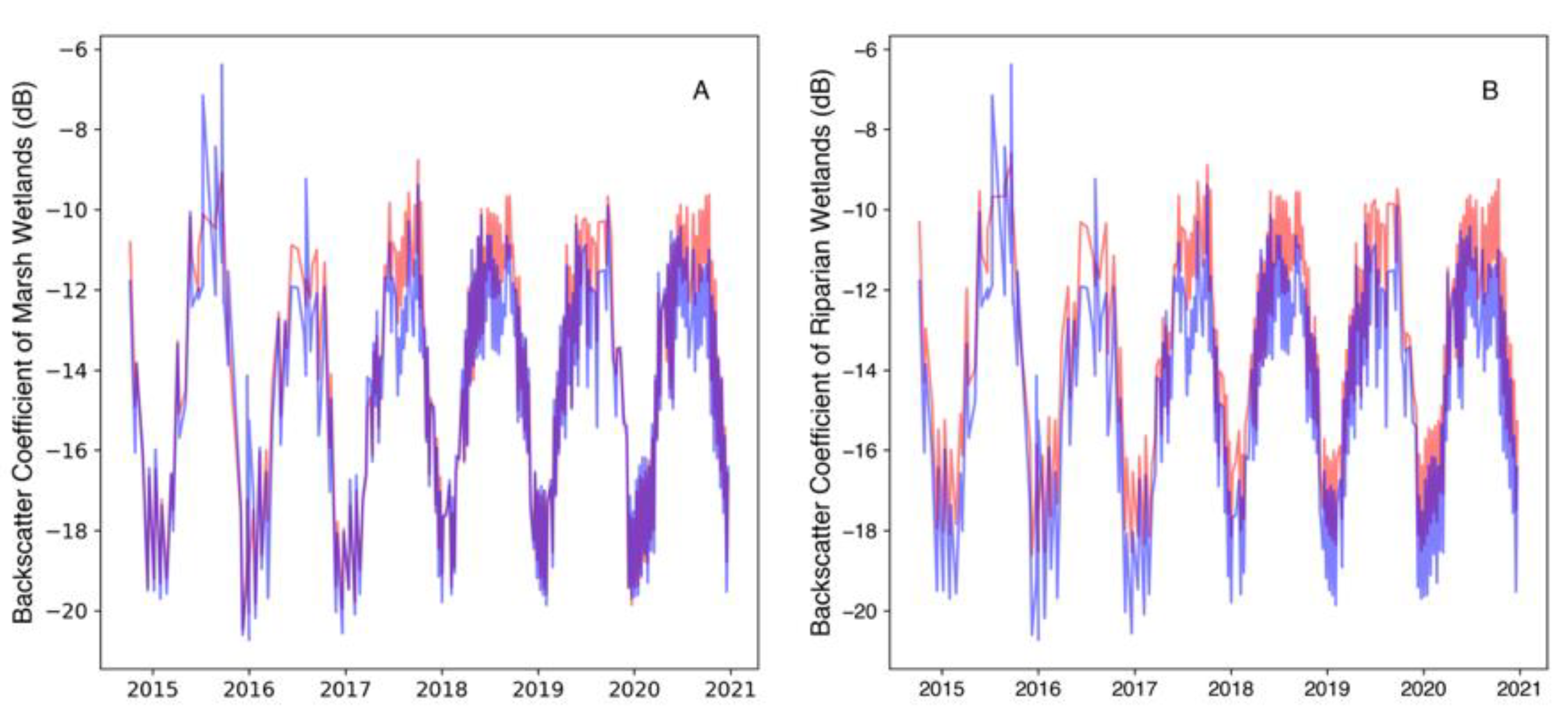
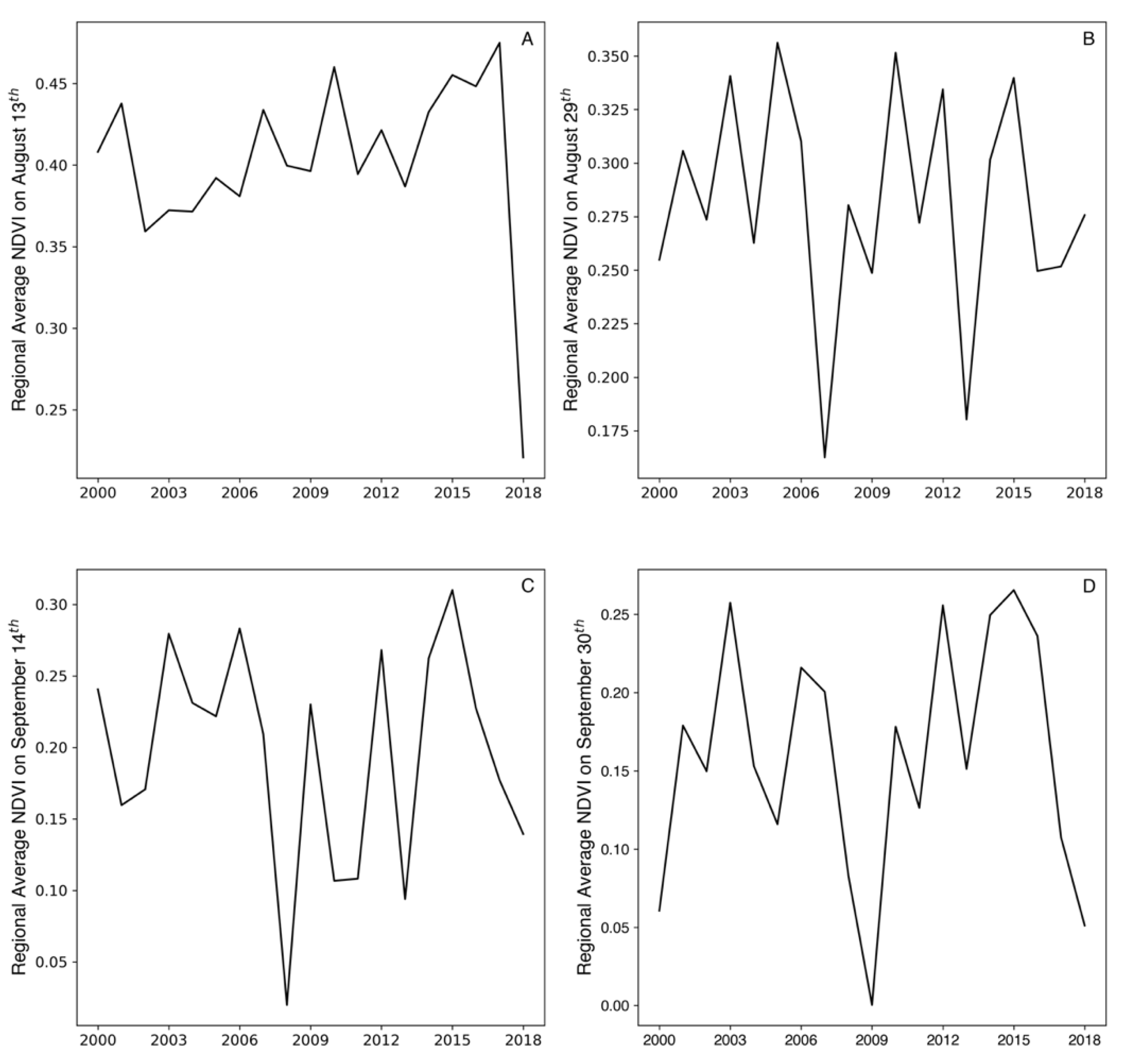
3.2. Wetland Vegetation and Water
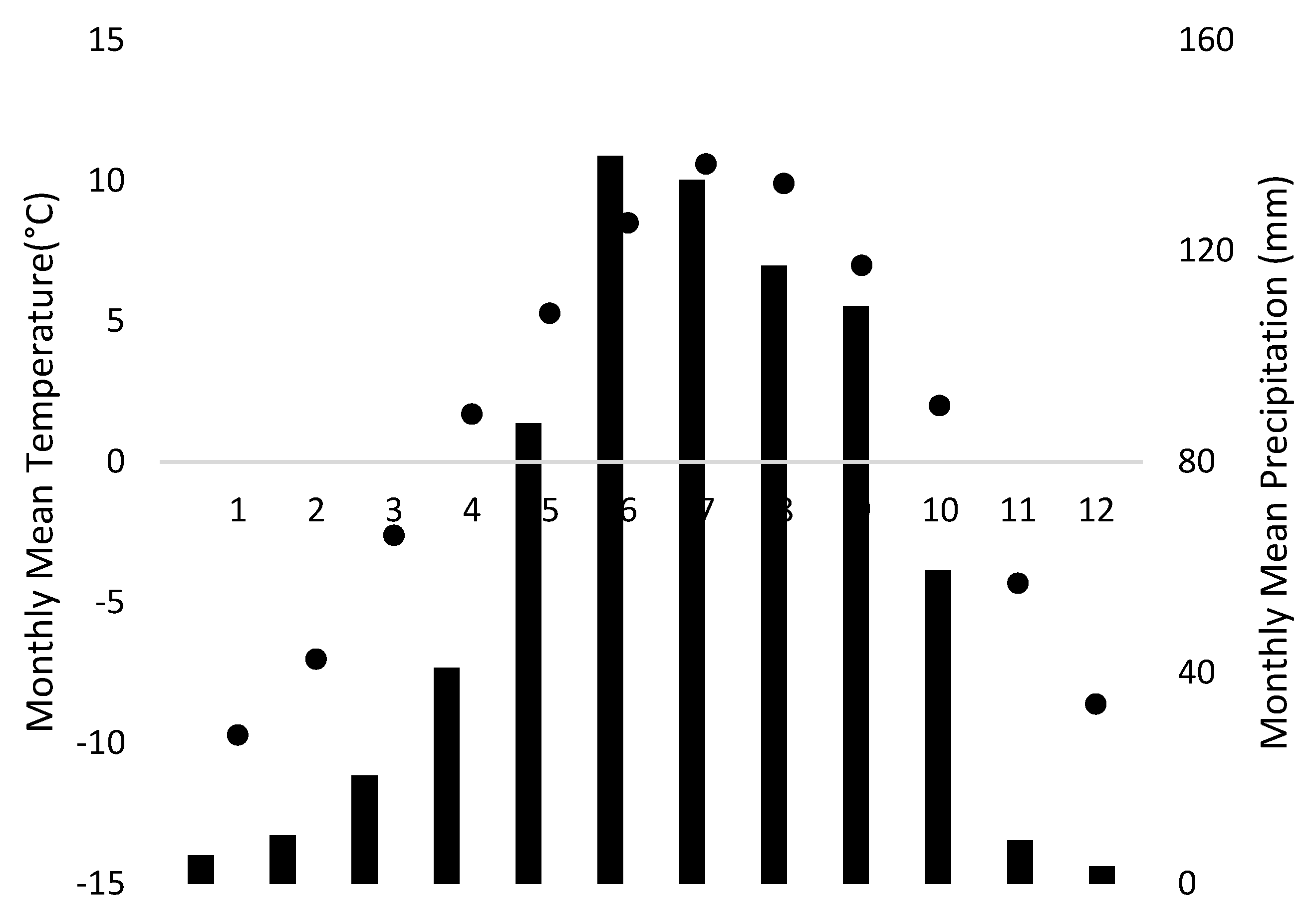
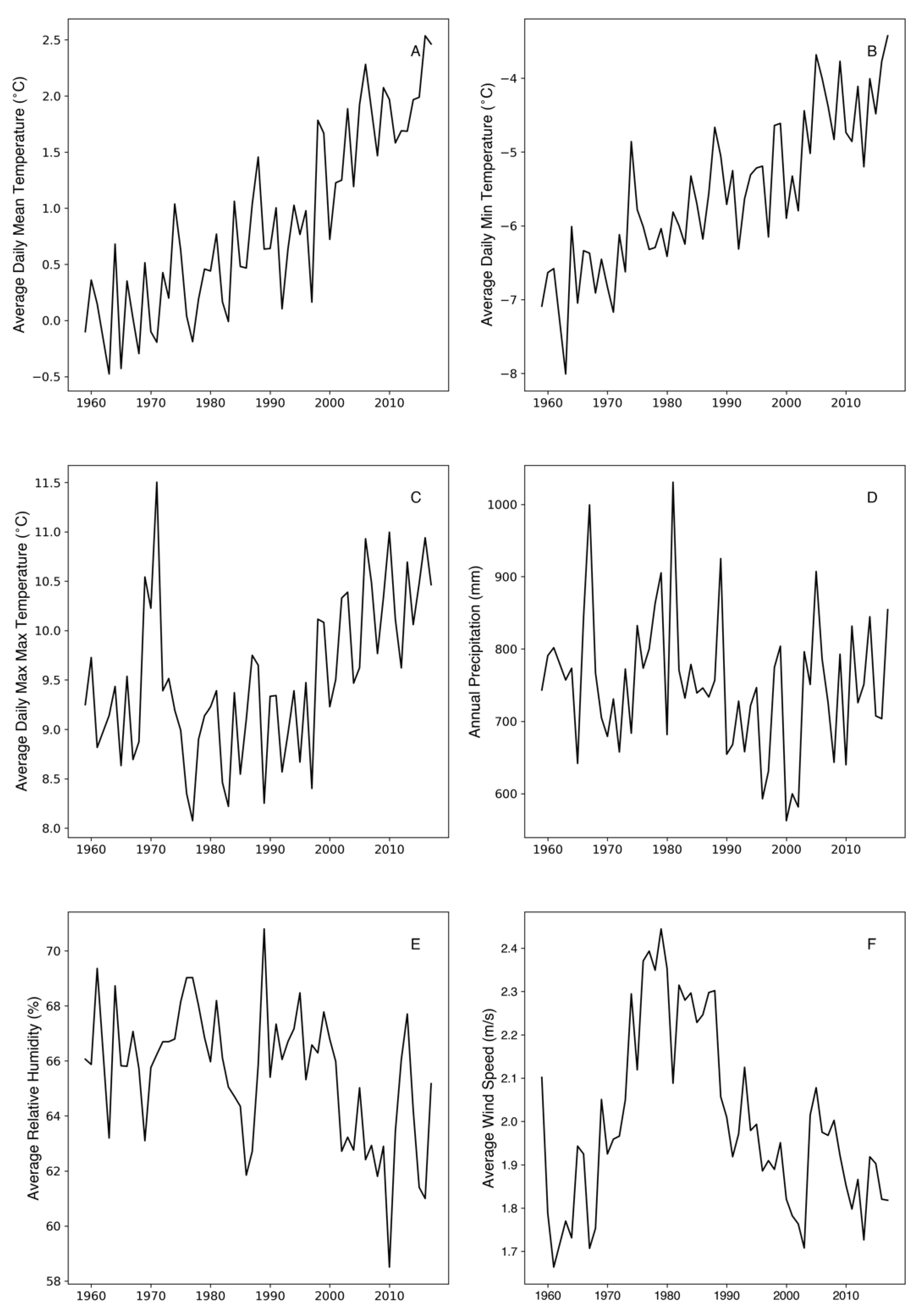
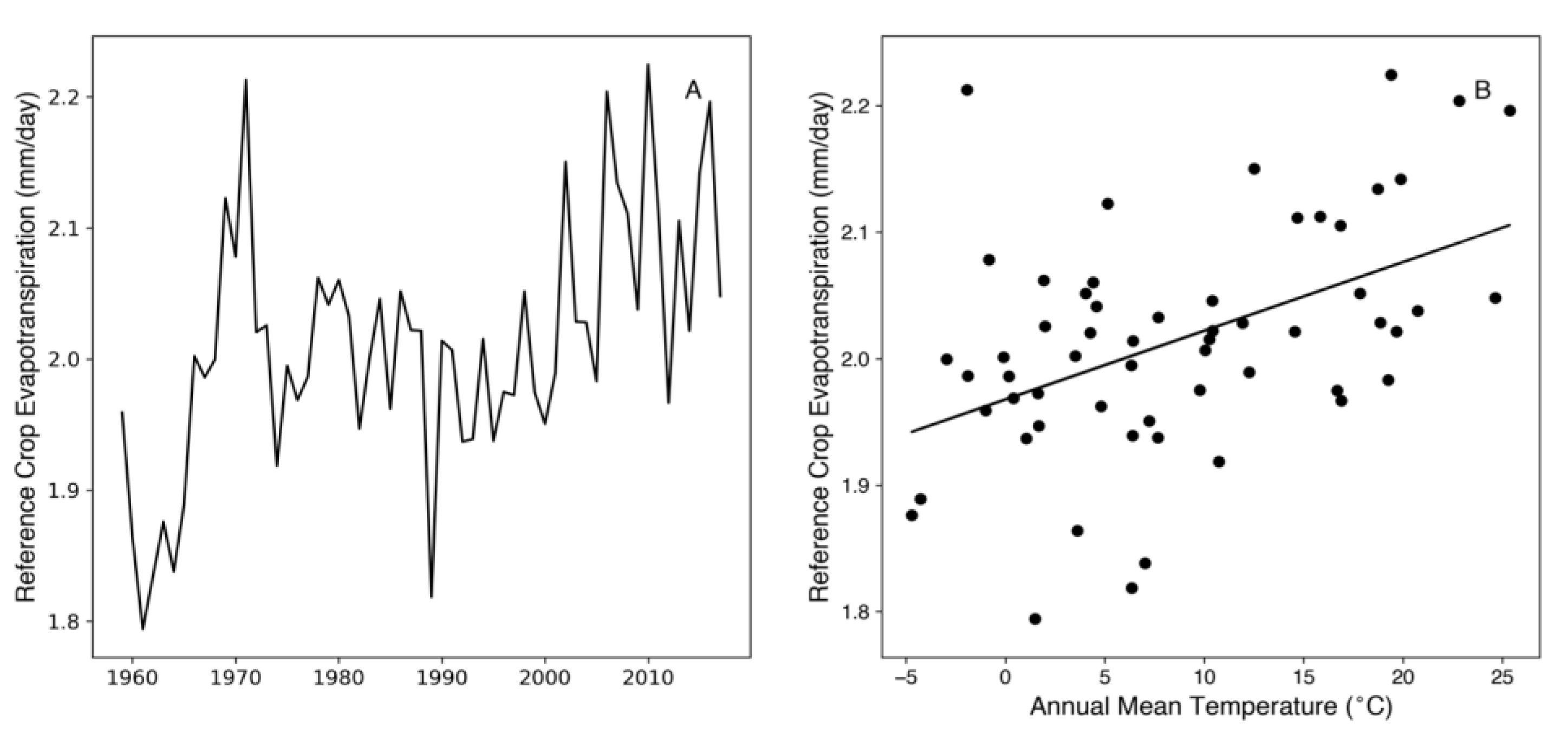
3.3. Meteorological Record
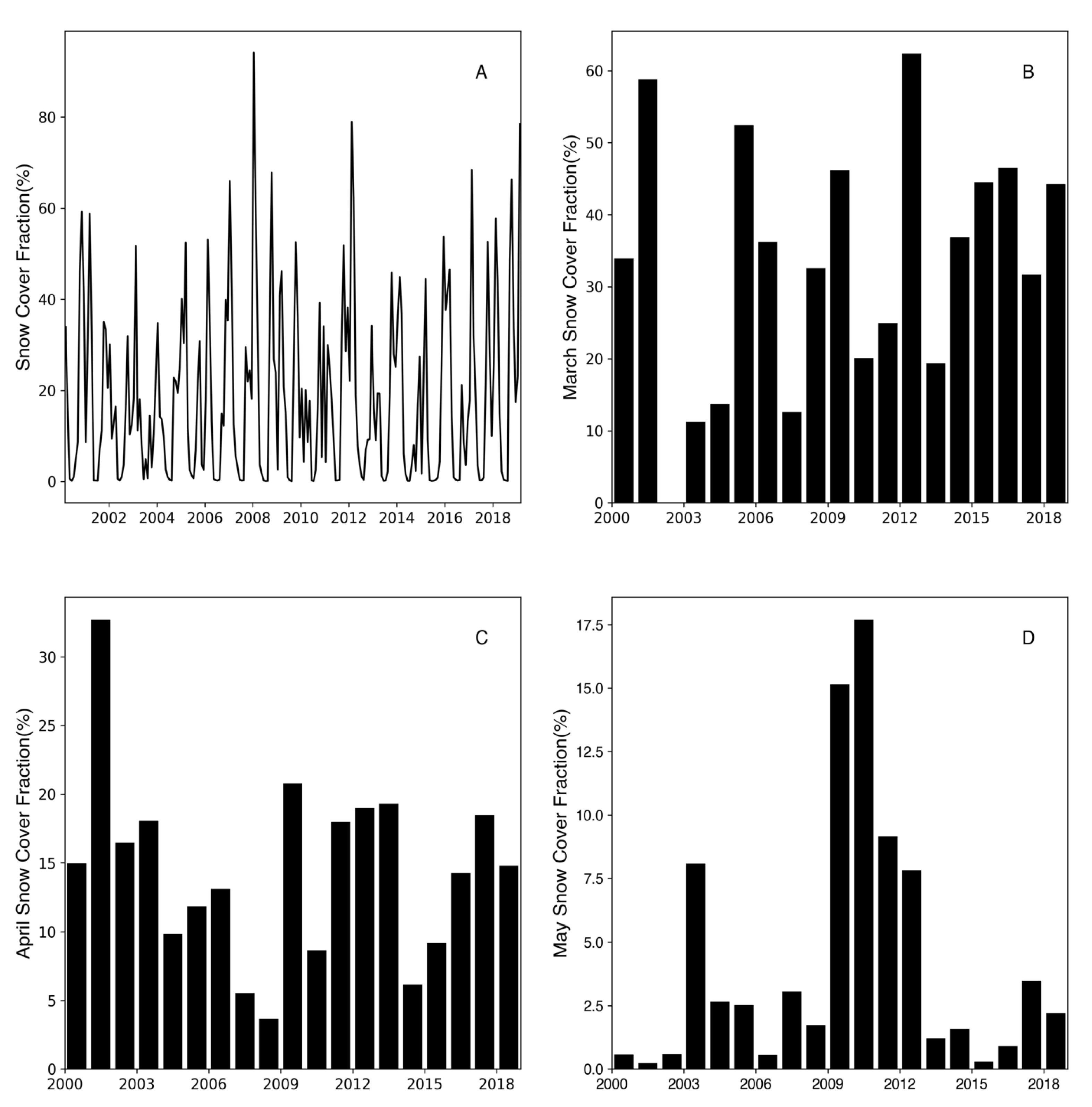
3.4. Snow Cover Fraction
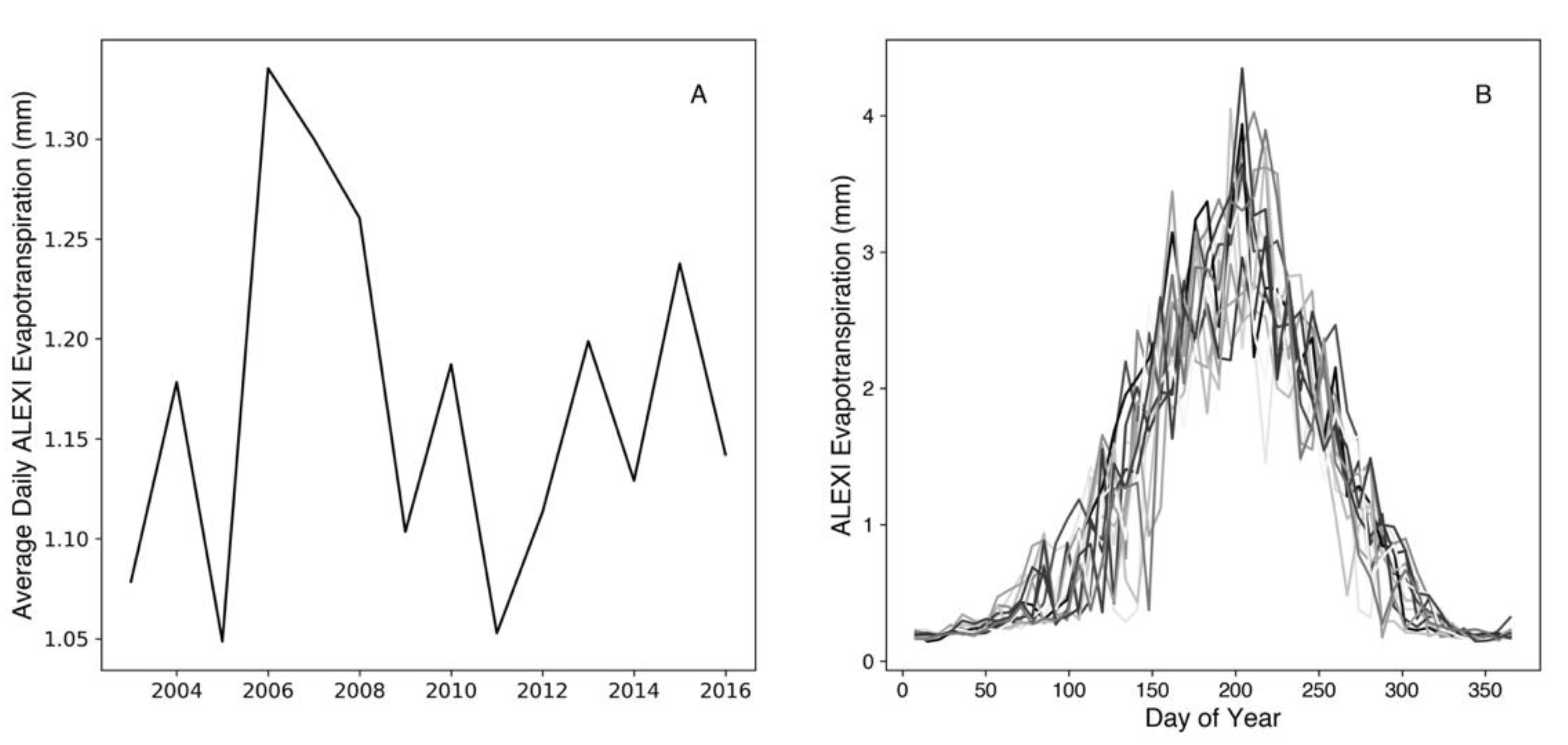
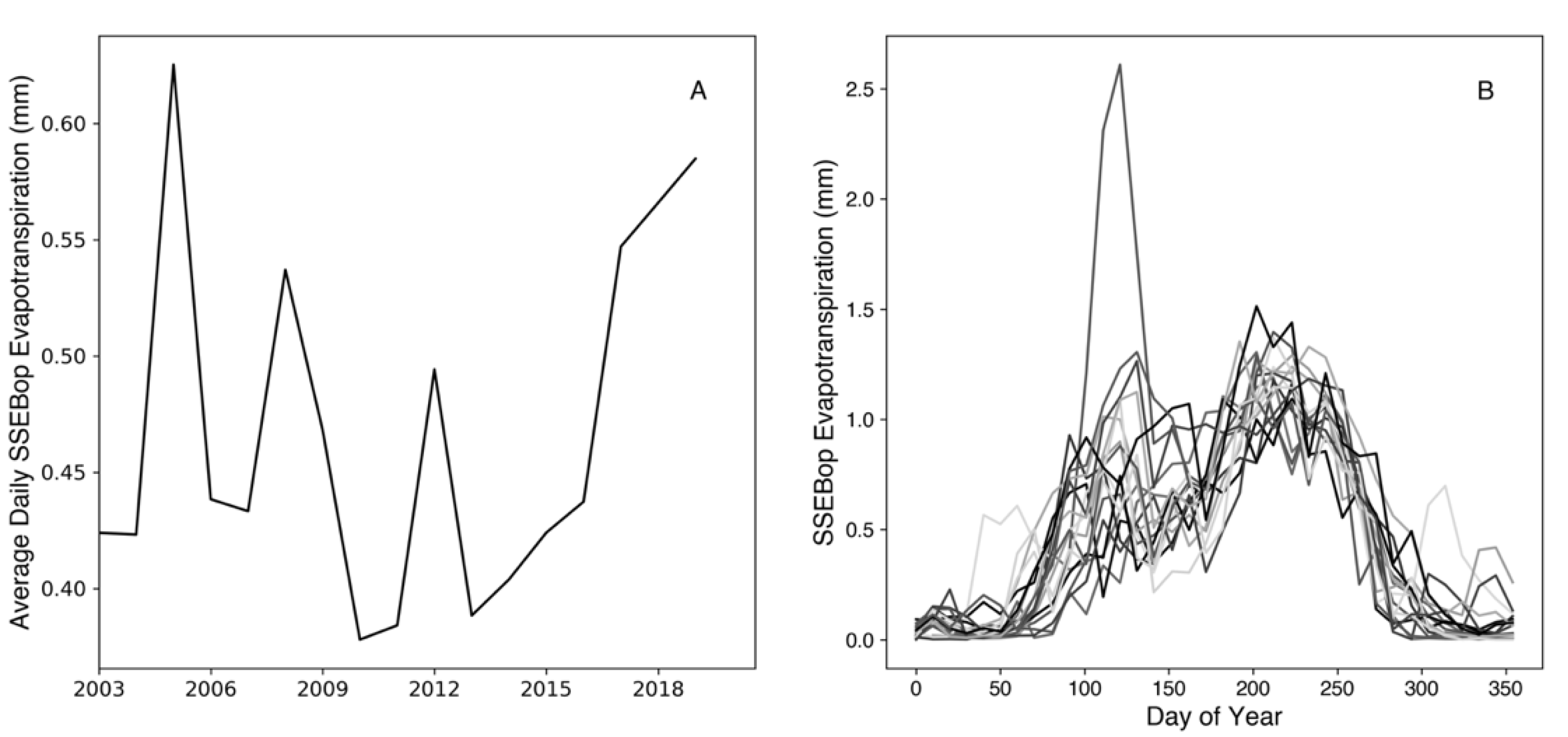
3.5. Evapotranspiration Trends
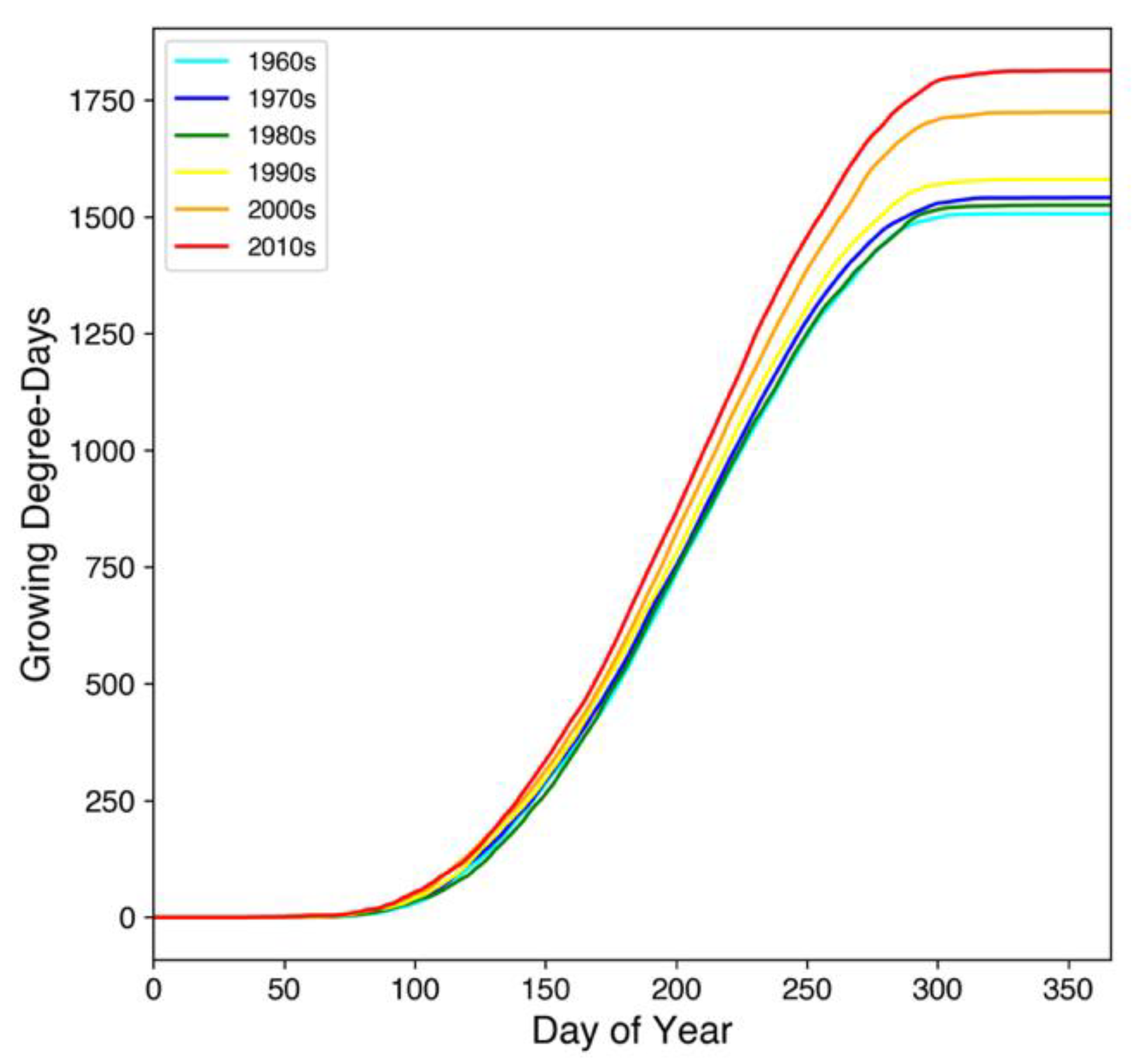
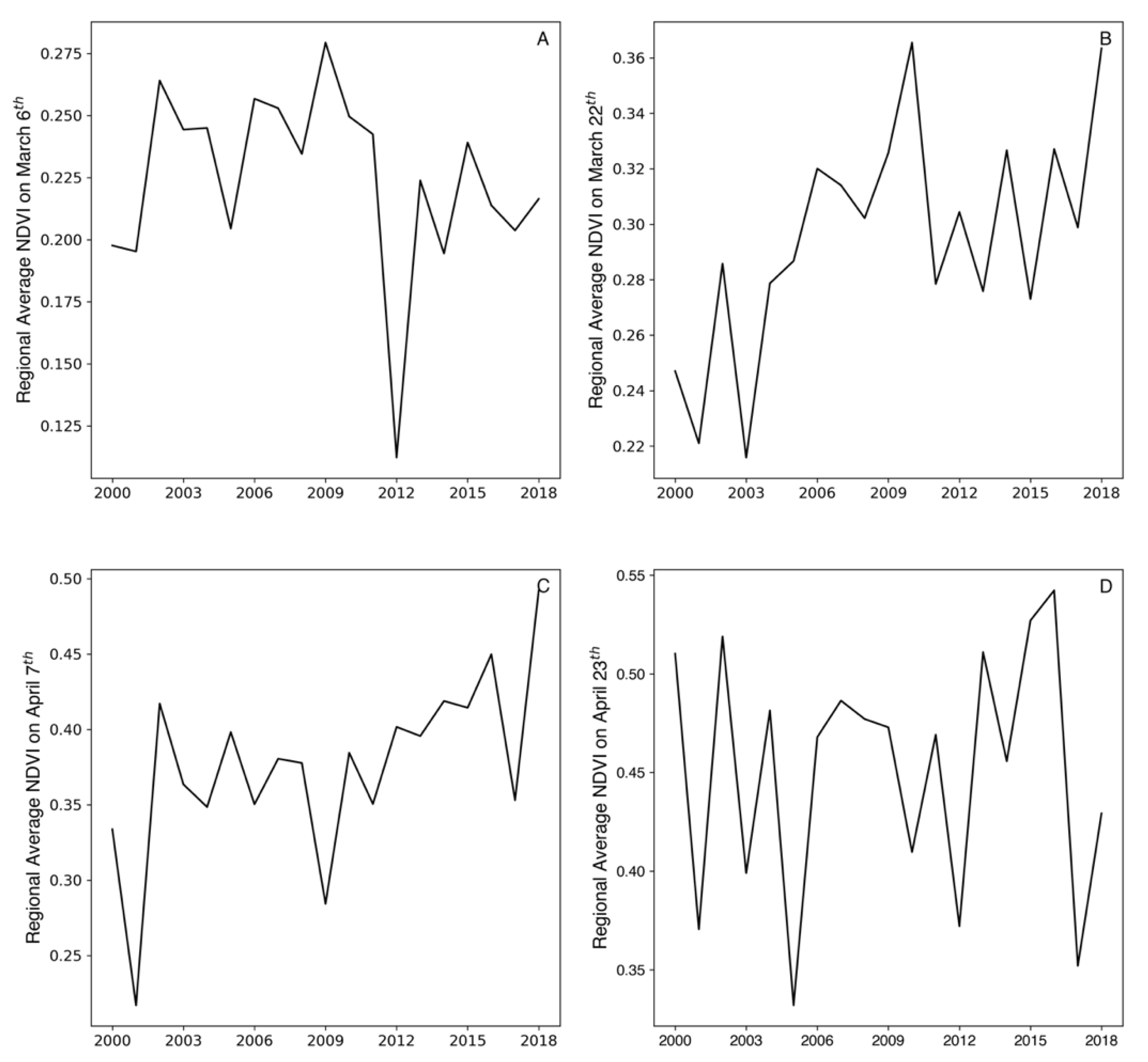
3.6. Phenology
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bullock, A.; Acreman, M. The Role of Wetlands in the Hydrological Cycle. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2003, 7, 358–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, F.; Zhang, H. Recent Changes in Wetlands on the Tibetan Plateau: A Review. J. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 879–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, B. Climatic Warming in the Tibetan Plateau during Recent Decades. Int. J. Climatol. 2000, 20, 1729–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Bao, Q.; Hoskins, B.; Wu, G.; Liu, Y. Tibetan Plateau Warming and Precipitation Changes in East Asia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y. Changes in Alpine Wetland Ecosystems of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau from 1967 to 2004. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 180, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, X.; Zou, Y.; Lu, Y.; Jiang, M.; Tong, S.; Zhang, K. Predicted Areas of Potential Distributions of Alpine Wetlands under Different Scenarios in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Glob. Planet. Change 2014, 123, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Xu, M. Dynamic Changes of the Alpine Wetlands in Tibet, China. In Proceedings of the IGARSS, Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018; pp. 9229–9232. [Google Scholar]
- Erwin, K.L. Wetlands and Global Climate Change: The Role of Wetland Restoration in a Changing World. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 17, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xu, J. Typical Alpine Wetland Landscape Changes in Eastern Tibetan Plateau under Climate Change over 15 Years. Int. Geosci. Remote Sens. Symp. 2012, 4907–4910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Xu, Y.; You, Q.; Flügel, W.A.; Pepin, N.; Yao, T. Review of Climate and Cryospheric Change in the Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Res. Lett. 2010, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, J.; Shilpakar, R.L.; Ma, X. Mapping Wetland Cover in the Greater Himalayan Region: A Hybrid Method Combining Multispectral and Ecological Characteristics. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 1083–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Wu, T. Responses of Permafrost to Climate Change and Their Environmental Significance, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2007, 112, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Li, X.L.; Cheung, A.; Yang, Y.W. Degradation of Wetlands on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: A Comparison of the Effectiveness of Three Indicators. J. Mt. Sci. 2013, 10, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Gao, P.; Hu, X.; Yi, Y.; Pan, B.; You, Y. Coupled Impact of Decadal Precipitation and Evapotranspiration on Peatland Degradation in the Zoige Basin, China. Phys. Geogr. 2020, 41, 145–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Hao, M.; Li, Y.; Tong, L. Monitoring the Changes of Wetlands in the Source Region of Three Rivers with Remote Sensing Data from 1976 to 2013. In Proceedings of the 2016 4th International Workshop on Earth Observation and Remote Sensing Applications (EORSA), Guangzhou, China, 4–6 July 2016; pp. 198–201. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, Y.; Li, A. Assessment of Alpine Wetland Dynamics from 1976–2006 in the Vicinity of Mount Everest. Wetlands 2011, 31, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, P.; Wu, N.; Luo, P.; Wang, Z.; Li, M. Analysis of Dynamics and Driving Factors of Wetland Landscape in Zoige, Eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. J. Mt. Sci. 2009, 6, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Yang, X.; Jin, Y.; Xu, B.; Zhou, Q. Remote Sensing and Evaluation of the Wetland Ecological Degradation Process of the Zoige Plateau Wetland in China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 104, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Xiao, P.; Feng, X.; Li, H.; Ma, R.; Duan, H.; Zhao, L. Monitoring Lake Changes of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau over the past 30 Years Using Satellite Remote Sensing Data. Chinese Sci. Bull. 2014, 59, 1021–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yi, Y.; Song, K.; Kimball, J.S.; Lu, Q. Hydrological Response of Alpine Wetlands to Climate Warming in the Eastern Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.F.; Lehmkuhl, F.; Falk, D. Quantifying Land Degradation in the Zoige Basin, NE Tibetan Plateau Using Satellite Remote Sensing Data. J. Mt. Sci. 2017, 14, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Dong, Z.; Wei, Z.; Lu, J. Land Use and Land Cover Change Monitoring in the Zoige Wetland by Remote Sensing. In Proceedings SPIE Volume 7841, In Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on Digital Earth: Data Processing and Applications, Beijing, China, 9–12 September 2009; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2010; p. 78410V. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, X.; Hao, Y.; Cui, X.; Chen, H.; Huang, S.; Du, Y.; Li, W.; Kardol, P.; Xiao, X.; Cui, L. Variability and Changes in Climate, Phenology, and Gross Primary Production of an Alpine Wetland Ecosystem. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guang-Yin, H.; Zhi-Bao, D.; Jun-Feng, L.; Chang-Zhen, Y. Driving Forces of Land Use and Land Cover Change (LUCC) in the Zoige Wetland, Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Cold Arid Reg. 2012, 4, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, W.; Hu, G.; Wei, Z. Changes in Ecosystem Service Values in Zoige Plateau, China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 139, 766–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foggin, J.M. Environmental Conservation in the Tibetan Plateau Region: Lessons for China’s Belt and Road Initiative in the Mountains of Central Asia. Land 2018, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Yu, L.; Yang, C.; Chang, L.; Yang, J.; Zhang, S. China’s Wetland Databases Based on Remote Sensing Technology. Chinese Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 374–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- General Schema of Sanjiangyuan National Park; National Development and Reform Commission: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Shen, X.; Tan, J. Ecological Conservation, Cultural Preservation, and a Bridge between: The Journey of Shanshui Conservation Center in the Sanjiangyuan Region, Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Ecol. Soc. 2012, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L. Alpine Habitat Dynamics and Avian Biodiversity in Different Land-use Regimes on the Eastern Tibetan Plateau; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Fassnacht, F.E.; Storch, I.; Bürgi, M. Land-use Regime Shift Triggered the Recent Degradation of Alpine Pastures in Nyanpo Yutse of the Eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Landsc. Ecol. 2017, 32, 2187–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, E.T. ‘How Can Experience of Local Residents be “Knowledge”?’ Challenges in Interdisciplinary Climate Change Research. Area 2016, 48, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallant, A.L.; Sadinski, W.; Brown, J.F.; Senay, G.B.; Roth, M.F. Challenges in Complementing Data from Ground-based Sensors with Satellite-derived Products to Measure Ecological Changes in Relation to Climate—lessons from Temperate Wetland-upland Landscapes. Sensors 2018, 18, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Mischke, S. A Lateglacial and Holocene Lake Record from the Nianbaoyeze Mountains and Inferences of Lake, Glacier and Climate Evolution on the Eastern Tibetan Plateau. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2009, 28, 1970–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlütz, F.; Lehmkuhl, F. Holocene Climatic Change and the Nomadic Anthropocene in Eastern Tibet: Palynological and Geomorphological Results from the Nianbaoyeze Mountains. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2009, 28, 1449–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environment and Culture of the Tibetan Plateau (Nyanpo Yutse Volume); China Tibetology Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Stein, E.D.; Mattson, M.; Fetscher, A.E.; Halama, K.J. Influence of Geologic Setting on Slope Wetland Hydrodynamics. Wetlands 2004, 24, 244–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, L.; Brisco, B.; Dabboor, M.; Schmitt, A.; Pratt, A. A Collection of SAR Methodologies for Monitoring Wetlands. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 7615–7645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sentinel-1 Algorithms. Available online: https://developers.google.com/earth-engine/sentinel1 (accessed on 10 October 2020).
- Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Peterson, S.; Shukla, S.; Davenport, F.; Michaelsen, J.; Knapp, K.R.; Landsfeld, M.; Husak, G.; Harrison, L.; et al. A high-resolution 1983–2016 TMAX Climate Data Record Based on Infrared Temperatures and Stations by the Climate Hazard Center. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 5639–5658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Z.; Xu, L.; Salomonson, V.V. MODIS/Terra Observed Seasonal Variations of Snow Cover over the Tibetan Plateau. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Tang, Y.; Yang, Y. Trends in Pan Evaporation and Reference and Actual Evapotranspiration across the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senay, G.B.; Bohms, S.; Singh, R.K.; Gowda, P.H.; Velpuri, N.M.; Alemu, H.; Verdin, J.P. Operational Evapotranspiration Mapping Using Remote Sensing and Weather Datasets: A New Parameterization for the SSEB Approach. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2013, 49, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.C.; Norman, J.M.; Mecikalski, J.R.; Otkin, J.A.; Kustas, W.P. A Climatological Study of Evapotranspiration and Moisture Stress Across the Continental United States Based on Thermal Remote Sensing: 1. Model Formulation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMaster, G.S.; Wilhelm, W.; Wilhelm, W.W. Growing Degree-days: One Equation, Two Interpretations. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1997, 87, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, L.; Liang, L.; Donnelly, A.; Park, I.; Schwartz, M.D. Effects of Elevation on Spring Phenological Sensitivity to Temperature in Tibetan Plateau Grasslands. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2014, 59, 4856–4863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; He, M.; Niu, Z. Responses of Alpine Wetlands to Climate Changes on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau Based on Remote Sensing. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Chen, D.; Ren, G.; Chen, Y.; Liao, Y. Spatial and Temporal Variations and Controlling Factors of Potential Evapotranspiration in China: 1956–2000. J. Geogr. Sci. 2006, 16, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Axel, T. Climatic Change on the Tibetan Plateau: Potential Evapotranspiration Trends from 1961–2000. Clim. Change 2006, 76, 291–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.C.; Norman, J.M.; Mecikalski, J.R.; Otkin, J.A.; Kustas, W.P. A Climatological Study of Evapotranspiration and Moisture Stress Across the Continental United States Based on Thermal Remote Sensing: 2. Surface Moisture Climatology. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senay, G.B.; Budde, M.E.; Verdin, J.P. Enhancing the Simplified Surface Energy Balance (SSEB) Approach for Estimating Landscape ET: Validation with the METRIC Model. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 98, 606–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Luedeling, E.; Xu, J. Winter and Spring Warming Result in Delayed Spring Phenology on the Tibetan Plateau. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 22151–22156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, J.; Xiao, X. Green-up Dates in the Tibetan Plateau Have Continuously Advanced from 1982 to 2011. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 4309–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Peng, S.; Lin, X.; Chang, J. Declining Snow Cover May Affect Spring Phenological Trend on the Tibetan Plateau. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E2854–E2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Article | Focus | Spatial Extent | Timespan | Main Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [5] | Area change Fragmentation | Entire Tibetan Plateau | 1967–2014 | 10% loss of wetland across the Tibetan Plateau. Greatest degradation occurred in Yangtze source region. Wetland fragmentation accelerated in Yellow river headwaters region and Zoige basin. |
| [7] | Area change | Entire Tibetan Plateau | 1990–2010 | Lake area increased of 35.3%. River and swamp decreased by with 833.49 km2 and 2761.30 km2. |
| [9] | Area change Structure change Vegetation diversity | Maqu County | 1995–2010 | Temperature rise causes drying of wetland and reduction in biodiversity. |
| [14] | Area change Driver | Zoige basin | 1967–2011 | Changes in evapotranspiration does not completely explain peatland degradation as precipitation > evapotranspiration during the study period |
| [15] | Area change | Three River Source Region | 1976–2013 | Lake increase steadily by a small amount Marsh wetland significant decreases Wetland in Yangtze River Basin has been decreasing since 2004, while wetland in Yellow River Basin has been increasing. |
| [16] | Area change | Mt. Everest Region | 1988–2016 | Total area changed (expansion and contraction) by 94.5 km2 (5.6%). Regressive succession occurred in some regions. |
| [17] | Area change Succession | Zoige Basin | 1977–2001 | Succession between lake, marsh, semi-marsh, and grassland was found. |
| [18] | Area change Structural change Biodiversity change | Zoige Basin | 2000–2015 | Area decreased in the study period. Fragmentation varied in the period. Vegetation biomass dropped in 2015. |
| [19] | Area, number | Entire Tibetan Plateau | 1960s–2006 (maps) | Patterns of changes in the area of lakes differ by regions. No consistent trend. |
| [20] | Runoff production Growing season length Evapotranspiration Vertical temperature gradient | Zoige Basin | 1985–2007 | Basins with larger wetlands have lower runoff Increasing trend of non-freeze period and growing season. Increasing trend in evapotranspiration and vertical temperature gradient. |
| [21] | Area change Type Conversion | Zoige Basin | 1994–2009 | Wetland decreased by 440 km2, deep wetland decreased by 78 km2 and humid meadow decreased by 80 km2 |
| [22] | Area change Type Conversion | Zoige Basin | 1975–2005 | Wetland steadily converted to other types, mainly various kinds of grasslands and sandy lands. |
| [13] | Soil moisture Vegetative cover | Maduo County | 2011 | Degree of wetland degradation is assessed a priori. Density of pika burrows is a less reliable indicators for wetland change, vegetation cover and soil moisture content are more reliable. |
| [23] | Gross-primary production Phenology | Zoige Basin | 2000–2011 | Simulation shows increasing EVI, LSWI, and growing season GPP |
| [24] | Area change | Zoige Basin | 1990–2005 | Wetland shrank from 5308 km2 to 4980 km2 Sandy land expanded from 112 km2 to 137 km2 Forest land decreased from 5686 km2 to 5443 km2 Grassland degraded from 12,309 km2 to 10,672 km2 |
| [25] | Ecosystem service | Zoige Basin | 1975–2015 | The value of ecosystem services dropped from 61.46 × 109 yuan in 1975 to 58.61 × 109 yuan in 2005. |
| Wetland | Lake | Rock | Meadow | Shrub | Total | User’s Accuracy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wetland | 78 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 7 | 89 | 0.88 |
| Lake | 0 | 34 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 34 | 1 |
| Rock | 1 | 8 | 80 | 0 | 0 | 89 | 0.90 |
| Meadow | 12 | 0 | 0 | 69 | 30 | 111 | 0.62 |
| Shrub | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 28 | 30 | 0.93 |
| Total | 93 | 42 | 80 | 73 | 65 | 353 | |
| Producer’s Accuracy | 0.84 | 0.81 | 1 | 0.95 | 0.43 | ||
| Kappa | 0.77 |
| Non-Wetland | Wetland | Total | User’s Accuracy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Wetland | 253 | 7 | 260 | 0.97 |
| Wetland | 18 | 75 | 93 | 0.81 |
| Total | 271 | 82 | 353 | |
| Producer’s Accuracy | 0.93 | 0.91 | ||
| Kappa | 0.81 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, J.; Zaitchik, B. Challenges in Reconciling Satellite-Based and Locally Reported Estimates of Wetland Change: A Case of Topographically Constrained Wetlands on the Eastern Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1484. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13081484
Fang J, Zaitchik B. Challenges in Reconciling Satellite-Based and Locally Reported Estimates of Wetland Change: A Case of Topographically Constrained Wetlands on the Eastern Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(8):1484. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13081484
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Jianing, and Benjamin Zaitchik. 2021. "Challenges in Reconciling Satellite-Based and Locally Reported Estimates of Wetland Change: A Case of Topographically Constrained Wetlands on the Eastern Tibetan Plateau" Remote Sensing 13, no. 8: 1484. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13081484
APA StyleFang, J., & Zaitchik, B. (2021). Challenges in Reconciling Satellite-Based and Locally Reported Estimates of Wetland Change: A Case of Topographically Constrained Wetlands on the Eastern Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sensing, 13(8), 1484. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13081484






