Abstract
As the largest independent east–west-trending mountain in the world, Mt. Tianshan exerts crucial impacts on climate and pollutant distributions in central Asia. Here, the vertical structures of meteorological elements and black carbon (BC) were first derived at Mt. Tianshan using an unmanned aerial vehicle system (UAVS). Vertical changes in meteorological elements can directly affect the structure of the planet boundary layer (PBL). As such, the influences of topography and meteorological elements’ vertical structure on aerosol distributions were explored from observations and model simulations. The mass concentrations of BC changed slightly with the increasing height below 2300 m above sea level (a.s.l.), which significantly increased with the height between 2300–3500 m a.s.l. and contrarily decreased with ascending altitude higher than 3500 m. Topography and mountain–valley winds were found to play important roles in the distributions of aerosols and BC. The prevailing valley winds in the daytime were conducive to pollutant transport from surrounding cities to Mt. Tianshan, where the aerosol number concentration and BC mass concentration increased rapidly, whereas the opposite transport pattern dominated during nighttime.
1. Introduction
As one of the most important components in the air, aerosols play a great role in the atmospheric environment by reducing visibility [1,2,3,4], and can damage human health as carriers for poisonous heavy metals, organic materials [5,6,7,8], and viruses [9,10]. Meanwhile, aerosols exert complicated impacts on changes in climate ascribed to their absorption and scattering of solar radiation [11,12,13,14]. Precipitation processes can also be modulated by atmospheric aerosols, which act as cloud condensation nuclei (CCN) and further influence the properties and lifetimes of clouds [13,15,16].
Atmospheric aerosols are highly dependent on pollutant emissions, topography, and changes in meteorology [3,17,18,19,20,21]. Several urban agglomerations with dense populations, such as the North China Plain (NCP), Yangtze River Delta (YRD), and Pearl River Delta (PRD), have been suffering from severe air pollution recently [4,22,23,24,25,26,27]. When the emission sources were similar in a certain period, topography was found to significantly impact the transport and dispersion processes of air pollutants in mountainous or basin areas, which may promote heavy pollution events with the control of stagnant weather conditions [3,17,21,28,29,30]. Xu et al. [31] proposed that the “harbor” effect on the eastern lee of the Tibetan Plateau’s large topography on the westerlies was possibly an important factor influencing the regional distribution of haze frequency in eastern China. Zhang, et al. [32] showed that the Sichuan Basin led to an increase of 48 μg m−3 in the basin-averaged surface PM2.5, contributing about 44% to the PM2.5 concentrations during heavy haze pollution, which indicated an important role of the basin topography in worsening air pollution. Meanwhile, high topography was also observed to noticeably affect the local atmospheric circulation, resulting in changes in precipitation and climate [33,34,35,36,37].
As the largest independent east–west-trending mountain in the world, Mt. Tianshan exerts crucial impacts on the climates and air pollutant distributions in central Asia. Many works have been done on the chemistry of snow and ice at the Urumqi River source [38,39,40] in eastern Tianshan, China. However, investigations on aerosols at Mt. Tianshan were scarcely reported, even if the impacts of human activities in this region have been gradually increased. Dong et al. [41] found seasonal variation of dust in precipitation in Tianshan of central Asia. Liu et al. [42] observed that particle size distribution and supersaturation had a major impact on the activation of aerosols into CCN at Mt. Tianshan. Zhao et al. [43] reported that the soot and fly ash particles from anthropogenic pollutions accounted for 15.1 % and 4.7 % in the summer at Mt. Bogda. By measuring the chemical species in snow samples from eastern Tianshan, Wake et al. [44] proposed that anthropogenic pollution had greatly affected the atmospheric compositions. Lee et al. [45] measured the ice core, covering the past 43 years, retrieved from Glacier 1 at the Urumqi River head in east Tianshan, and indicated that anthropogenic activities had released considerable particulate material along with unsaturated hydrocarbons and SO2. Li et al. [46] found noticeable seasonal variations of foehn wind at central Tianshan, which had large impacts on the planet boundary layer (PBL) in Urumqi. Many researchers have pointed out that Mt. Tianshan exerts high influences on the atmospheric environment and PBL in the surrounding areas, which inversely affected the distributions of air pollutants, whereas the vertical profiles of PBL and aerosols at Mt. Tianshan have been rarely studied due to the limitations of observation technology and geographic locations.
As a new measuring method, unmanned aerial vehicle systems (UAVS) have been widely used in the atmospheric environment field in recent years due to their low requirement on operating conditions [47,48,49,50,51]. In this study, a self-developed UAVS, carrying the iMet-XQ2 meteorological sensors and an AE-51 Aethalometer, was used to measure the vertical profiles of temperature, air pressure, and black carbon (BC) in PBL during 18–26 September 2019. The observations were conducted seven times a day, and 57 sequences of meteorology and BC samples were derived in total. The possible interactions between PBL structure and the distributions of aerosols and BC were explored using the in situ measurements, combined with several other datasets including the second Modern-Era Retrospective analysis for Research and Applications (MERRA-2), the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer aerosol optical depth (MODIS AOD), MIX emission inventory, and the Hybrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory (HYSPLIT) model simulation.
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Observation Site and Experiment Description
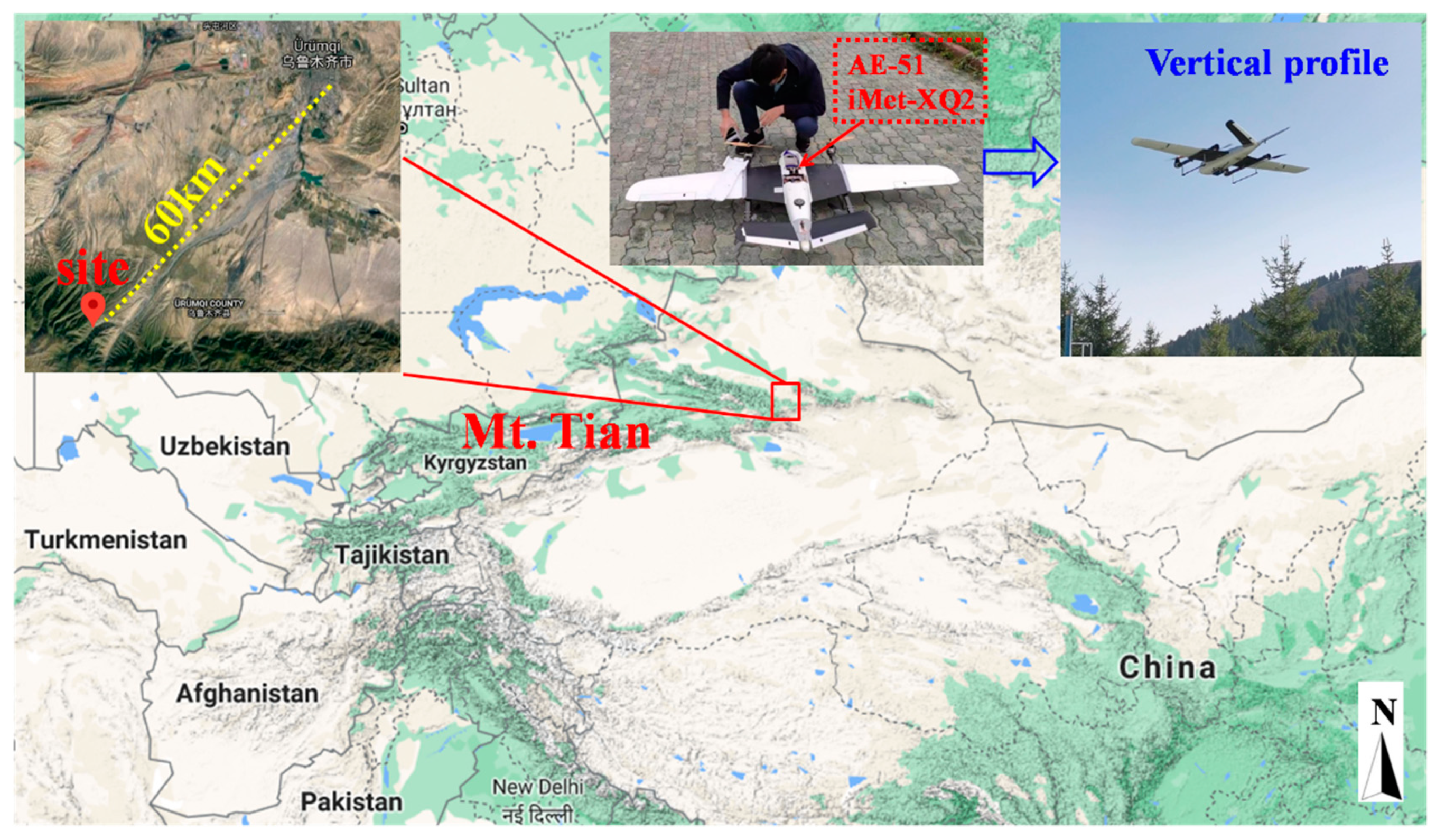
The observation site was located at Urumqi herding test station (43.45° N, 87.18° E; 1930 m a.s.l.), Baiyanggou scenic spot, at Mt. Tianshan, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (Figure 1), which was 60 km away from the Urumqi municipality. The observation was carried out during the period of 18–27 September 2019. A wide-range particle spectrometer (WPS, MSP Corporation, Shoreview, MN, USA) was used to monitor the aerosol number concentration for sizes from 10 nm to 10 μm at the ground, with a time resolution of 5 min. Meteorological elements, including wind speed, wind direction, temperature, relative humidity (RH), precipitation, and visibility, were obtained, with a time resolution of 1 h. Quality control for the meteorological dataset was implemented based on the surface observation criteria of the China Meteorological Administration.
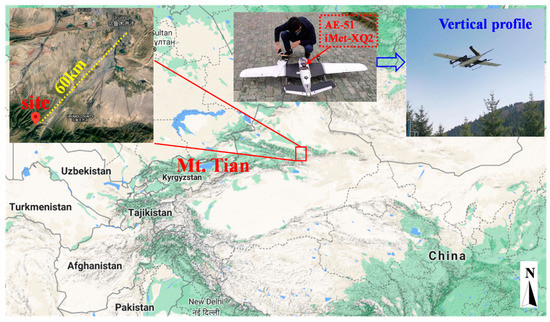
Figure 1.
Locations of the observation site and surrounding areas.
The UAVS (Jiangsu Environmental Innovation & Service Ltd. Co, Nanjing, China) can measure the vertical profiles of meteorological elements and BC mass concentration. The UAVS with a fixed wing had a length of 1.2 m and a wingspan of 2.16 m, which was made of expanded polyolefin (EPO) foam, as shown in Figure 1. A meteorological sensor, iMet-XQ2 (Inter MET Inc., Grand Rapids, MI, USA), a self-contained sensor package designed for the UVAS to measure atmospheric pressure, temperature, and relative humidity, was carried by the UVAS. It was also equipped with a built-in GPS and an internal data logger, along with a rechargeable battery. Detailed information about the iMet-XQ2 can be referred to in reference [52]. The mass concentration of BC was observed by a micro-aethalometer AE-51 (Magee Scientific, Berkeley CA, USA), which measures the light transmission through a Teflon-coated glass fiber filter at 880 nm. A change in filter attenuation is then translated to the mass concentration of BC particles. The introduction of AE-51 can be found in the related documents [53,54]. The UAVS takes off and lands at a speed of 1 m/s−1.
2.2. Datasets
2.2.1. MODIS
In this study, Terra MODIS C6.1 Level 3 aerosol products (MOD08_M3) with 1° × 1° resolution were used. The data were downloaded from the NASA Level 1 and Atmosphere Archive and Distribution System (https://ladsweb.nascom.nasa.gov/data/search.html (accessed on 1 January 2021)). The dark target and deep blue merged AOD data at 550 nm (hereafter referred to as AOD) were principally used in this study. The details of the MODIS can be found in Lee et al. [2] and de Leeuw et al. [55]. The MODIS data was used during the period of 18–27 September 2019.
2.2.2. MERRA-2
The modern-era retrospective analysis for research and applications, version 2 (MERRA-2) is a global atmospheric reanalysis produced by the NASA Global Modeling and Assimilation Office (GMAO). It spans the satellite observing era from 1980 to the present. Horizontal and vertical meteorological data of wind speed during the pollution episodes were obtained from the MERRA-2 reanalysis dataset with a horizontal resolution of 0.5° × 0.625° (https://disc.gsfc.nasa.gov/datasets?project=MERRA-2 (accessed on 1 January 2021)). The detailed introductions can be found in Gelaro et al. [56] and Bosilovich et al. [57]. The MERRA-2 data was used during the period of 18–27 September 2019, and the time resolution was 3 h.
2.2.3. Emission Inventory
MIX is a new anthropogenic emission inventory over Asia for the years 2008 and 2010. It was developed to support the Model Inter-Comparison Study for Asia Phase III (MICS-Asia III) and the Task Force on Hemispheric Transport of Air Pollution (TF HTAP) projects by a mosaic of up-to-date regional and national emission inventories, including REAS inventory version 2.1 for the whole of Asia [58], the Multi-resolution Emission Inventory for China (MEIC) developed by Tsinghua University, a high-resolution NH3 emission inventory by Peking University [59], an Indian emission inventory developed by Argonne National Laboratory (ANL-India) [60,61], and the official Korean emission inventory from the Clean Air Policy Support System (CAPSS) [62]. The details of these inventories can be found in Li et al. [63].
2.3. The HYSPLIT Model
Air mass backward trajectories above the observation sites were simulated by the Hybrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory (HYSPLIT) model (http://ready.arl.noaa.gov/HYSPLIT.php (accessed on 1 March 2021)), which was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Air Resources Laboratory (ARL). The National Weather Service’s National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP) Global Data Assimilation System (GDAS) archive was used for the meteorological input field, with a horizontal resolution of 1.0° × 1.0°. The details of the HYSPLIT can be found in Stein et al. [64] and Draxler and Rolph [65] Air mass backward trajectories for 48 h at the observation sites were simulated by the HYSPLIT.
2.4. Planet Boundary Layer Height (PBLH)
In addition to the collected temperature (T), air pressure (P), relative humidity (RH), wind speed (WS), and wind direction (WD), two important parameters, the virtual potential temperature () and specific humidity (q), were used to reflect the evolution of the PBL. The calculation of is as follows:
where T is the collected temperature (K), P and P0 are the collected pressure and the standard sea-level pressure (hPa), respectively, Rd is the specific gas constant for dry air (287 J kg−1 K−1), and Cpd is the specific heat capacity at constant pressure for dry air at standard temperature (1005 J kg−1 K−1);
q (g kg−1) was calculated from:
where ε is the ratio of the molecular weight of water vapor to dry air (0.622), e is the water vapor pressure (hPa), which is the product of the RH (%) measured at each T and the calculated saturated vapor pressure.
The calculation of is as follows:
In this paper, PBLH was determined from the profiles according to the gas block method [53,66]. During the daytime period, PBLH was determined from the bottom of the inverse virtual potential temperature layer, where increased significantly.
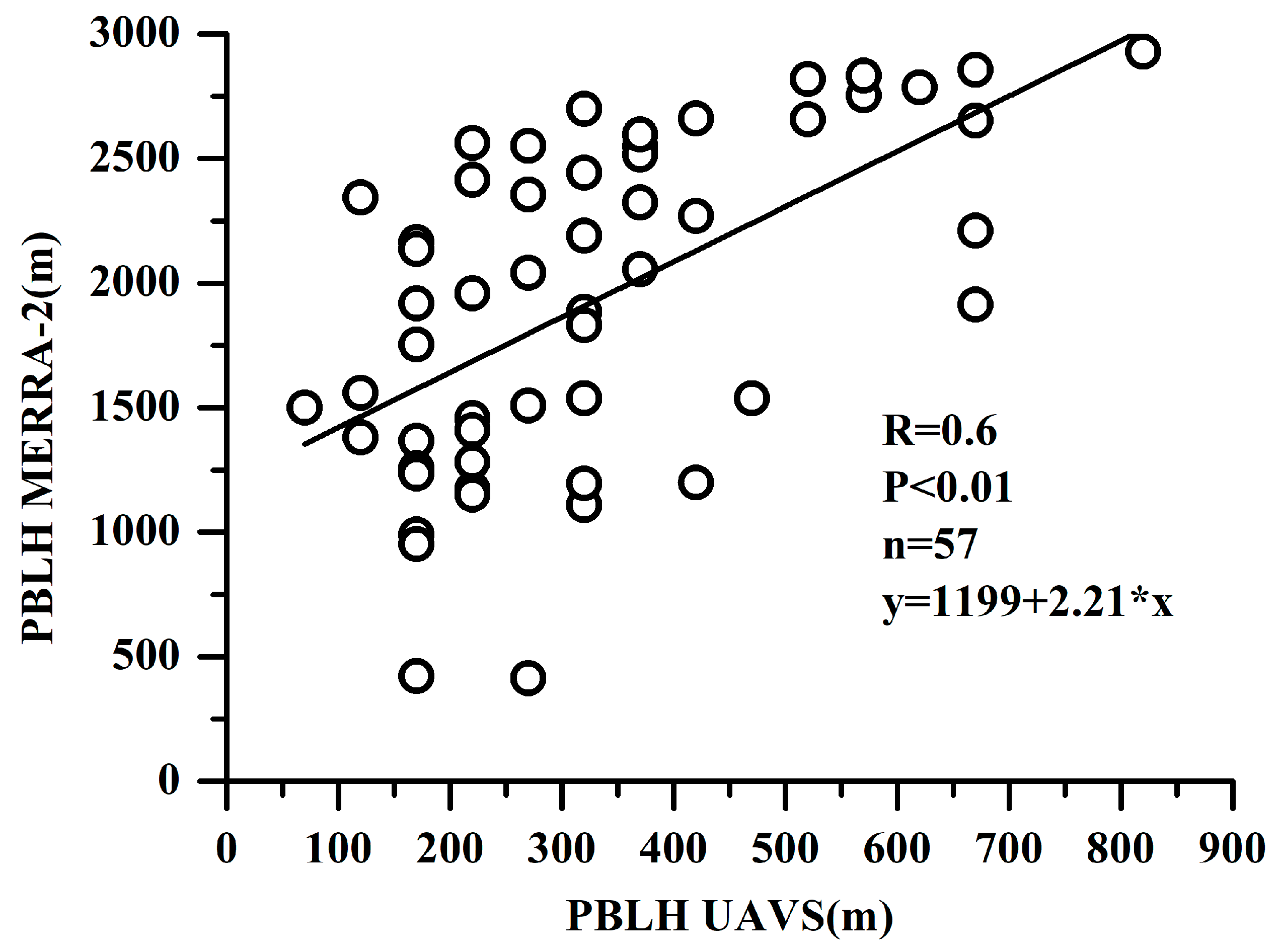
As shown in Figure 2, the PBLH derived from the UAVS had a good relationship with those by MERRA-2 products, with a correlation coefficient of 0.6. However, the UAVS-derived PBLH were generally lower than the MERRA-2, probably due to the coarse resolution of the MERRA-2 dataset with an average value of grid points that cannot well reflect the PBLH at Mt. Tianshan, where the field measurements were more essential to explore its environmental evolution.
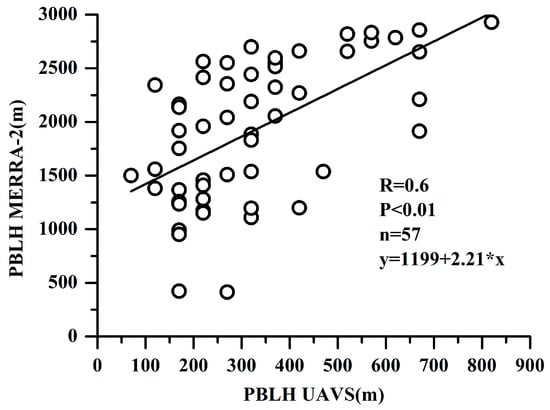
Figure 2.
Comparisons of PBLH derived from the UAVS and MERRA-2.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Overall Description
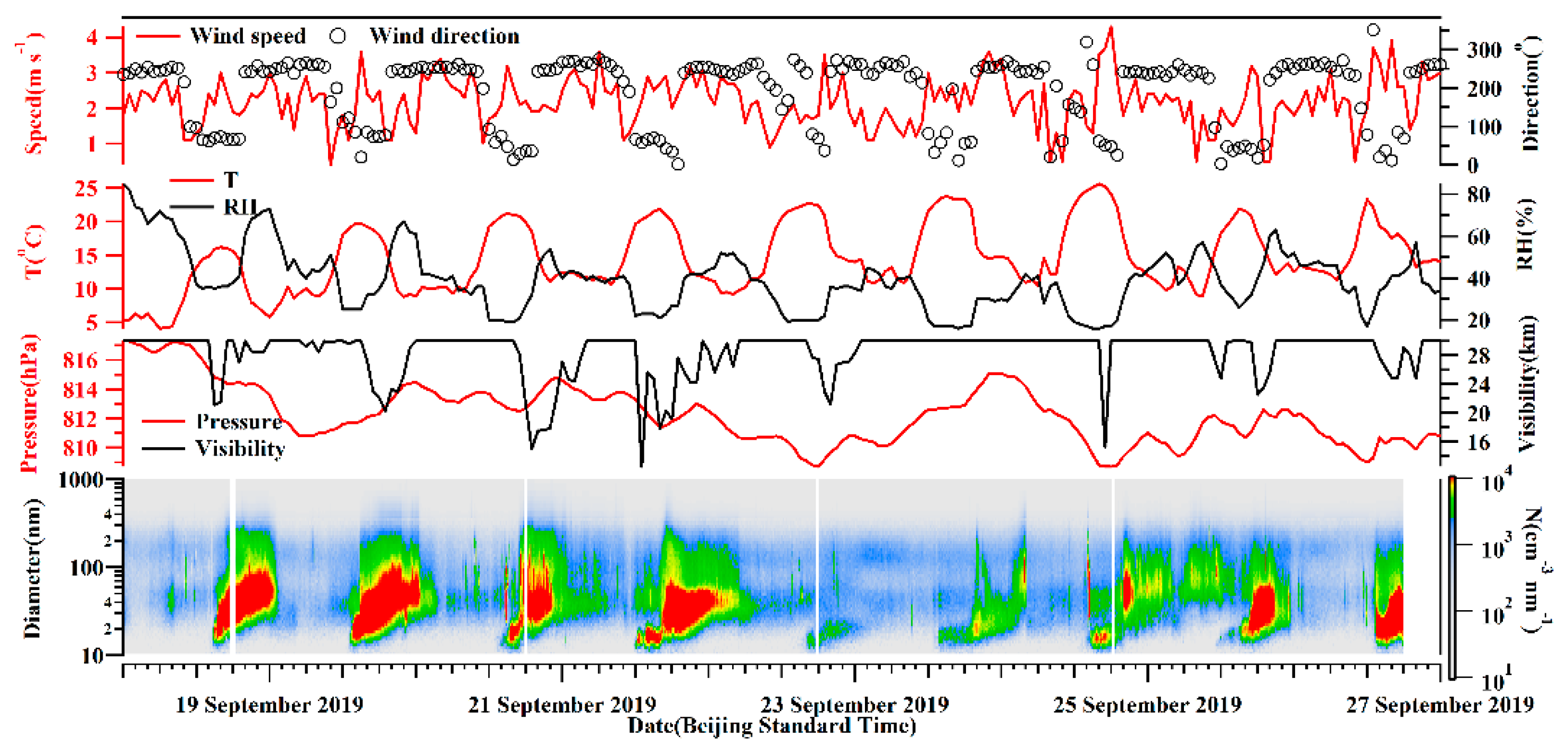
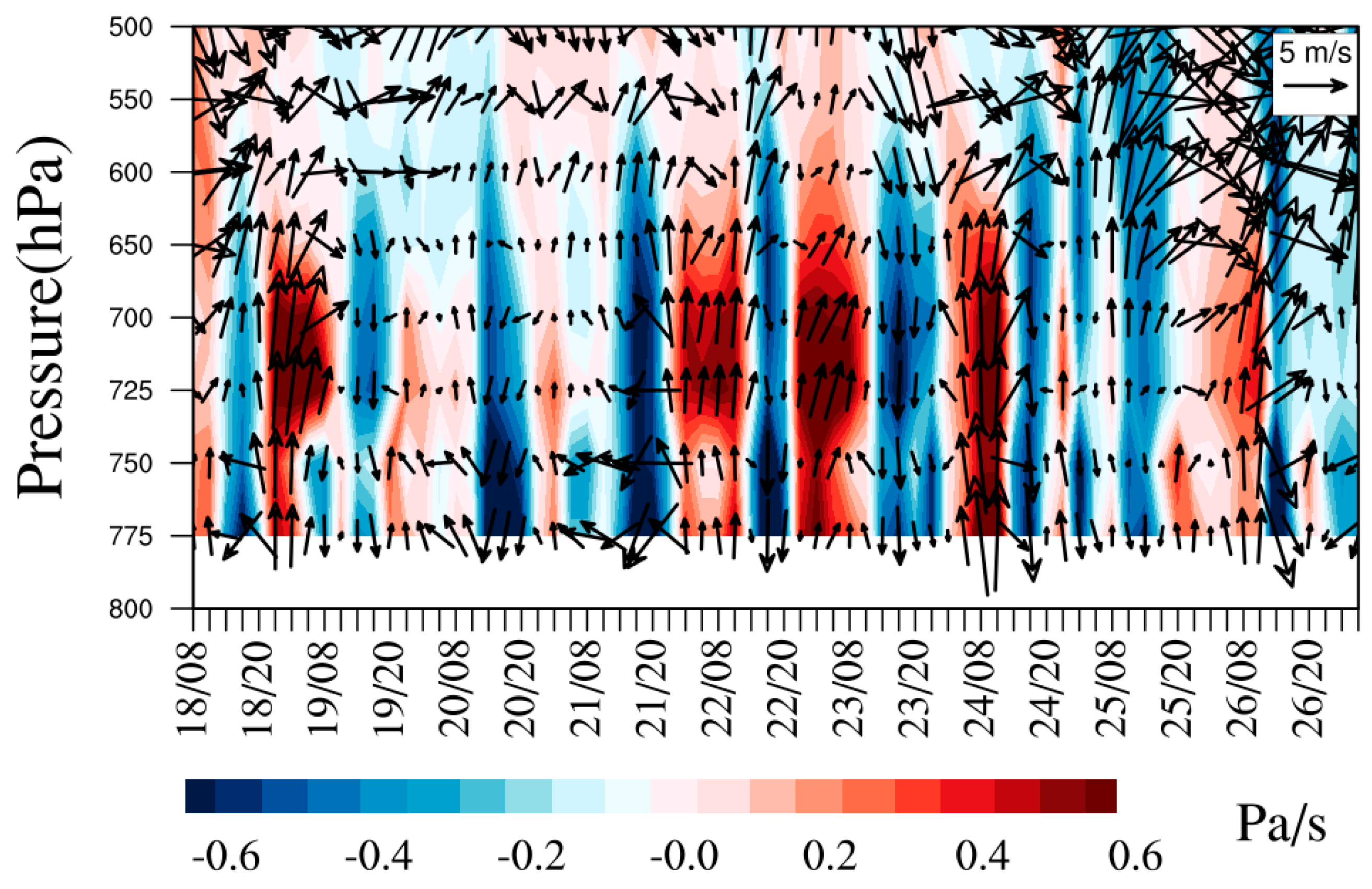
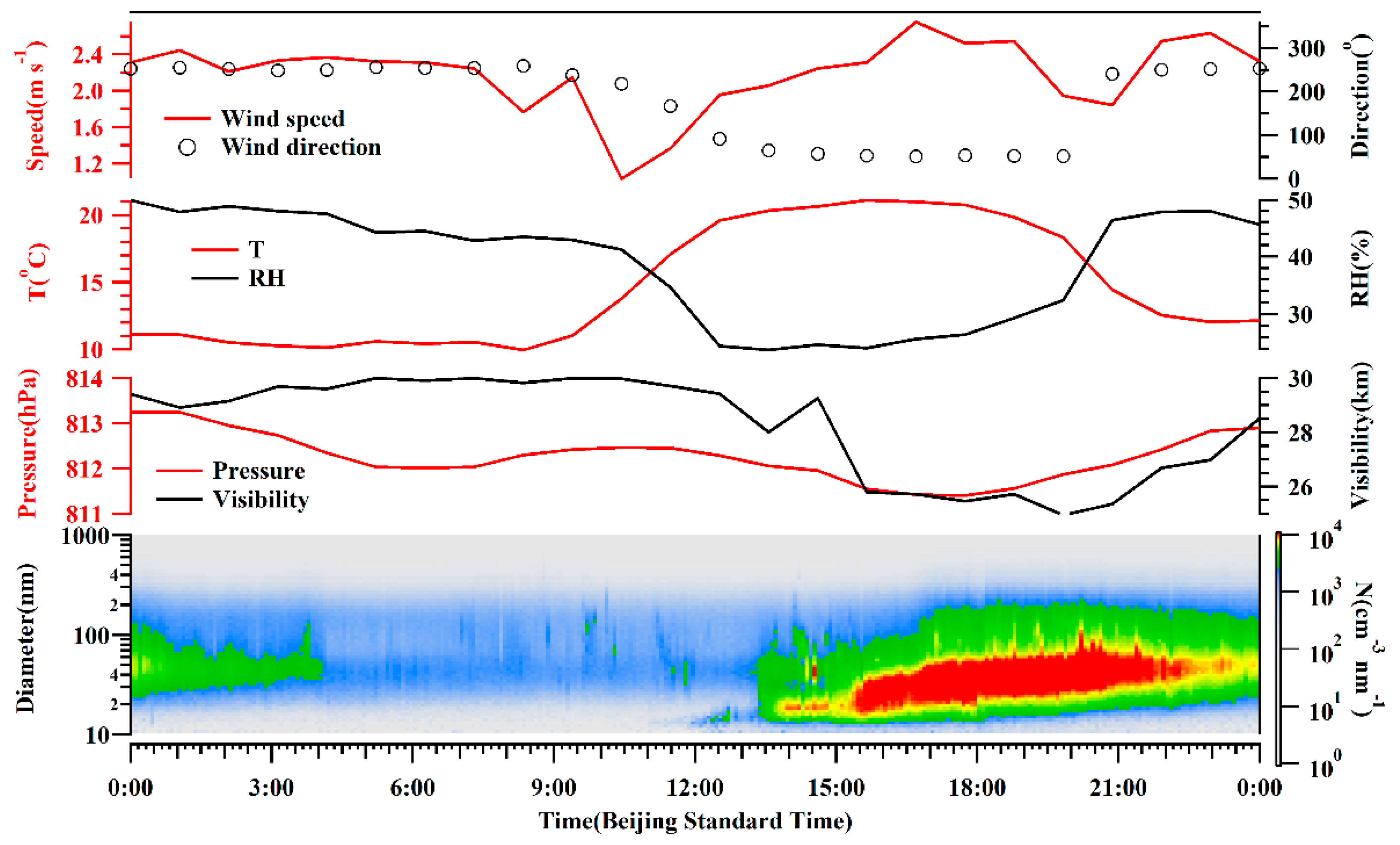
The diurnal variations of the aerosol number concentrations were notable, as shown in Figure 3, with higher and lower values in the daytime and nighttime, respectively. Aerosols increased sharply from 14:00 (Beijing time, BST) when higher temperature and lower RH were observed. The observation site at Mt. Tianshan has an altitude around 1900 m a.s.l, which was near the top of the PBL. As such, the concentrations of background aerosols at Mt. Tianshan were low, resulting in high visibility with an average of 28.4 km and a minimum value of 12.5 km at 13:00 on September 21. The fluctuations in visibility were found to entirely correspond to the increases in aerosol number concentrations (Figure 3). Hence, air pollutants, especially aerosol particles, from surrounding areas can be transported to the observation site in the daytime ascribed to the development of PBL, further decreasing the visibility. In addition, the formation and elimination processes of orographic clouds at Mt. Tianshan can largely affect the visibility. The mountain winds with southerlies and sinking motion (the positive values of vertical velocity) were dominant in the nighttime (Figure 4), resulting in the pollutants’ transport from Mt. Tianshan to Urumqi, lower aerosol number concentrations were noticed consequently at Mt. Tianshan. The PBL developed gradually when the sun rose, with the highest PBLH after noon, when aerosol concentrations began to increase, attributed to the vertical mixing of near-surface pollutants. Table 1 lists a low PBLH of 170 ± 65 m at 10:00 (BST) when the sun heats the ground, the BC and aerosol number concentrations were low as well. Hereafter, the BPLH gradually elevated with the continuous heating process of the sun and reached the maximums of 464 ± 147 m and 460 ± 178 m at 15:00 and 17:00, respectively, when the concentrations of BC and aerosols were also high. Meanwhile, the valley winds prevailing in the daytime featured as northerlies and ascending flows (Figure 4). As such, it was conducive to carrying air pollutants from Urumqi to Mt. Tianshan in the daytime, which were found to be the strongest during 14:00–20:00, when the valley winds were the highest, and a sharp increase in aerosol number concentrations at 14:00 was noticed. Generally, the concentrations of background aerosols were low due to the low emission sources at Mt. Tianshan at high altitudes. However, air pollutants from the surrounding areas may transport to Mt. Tianshan with the evolution of the PBL in the daytime, where the pollutants increased rapidly as a result.
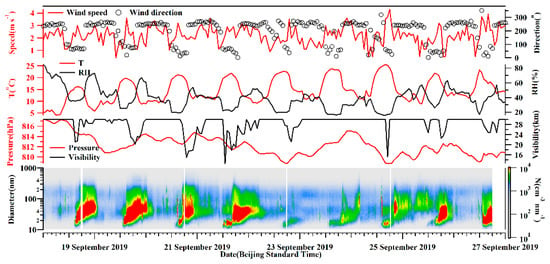
Figure 3.
Time series of aerosol number concentration and meteorological elements near the ground observation.
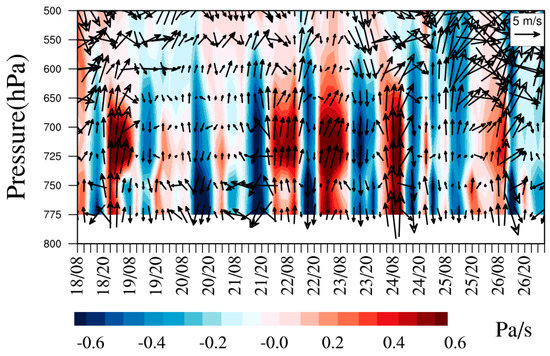
Figure 4.
Time series of the wind field and vertical velocity for MERRA-2 during the observation period.

Table 1.
Statistical summary of launches and near-ground parameters. Hmax and PBLH are the maximum height reached by the UAVS and planet boundary layer height, respectively. Tsur, RHsur, WSsur, BC, NNucleation, NAitken, NAcc, and NCoarse denote the temperature, relative humidity, wind speed, mass concentration of BC, number concentration of nucleation aerosol (10–20 nm), Aitken aerosol (20–100 nm), accumulation aerosol (100–1000 nm), and coarse aerosol (1.0–10.0 μm), respectively, near the ground, presented as the average value ± standard deviation.
The meteorological elements wavered slightly during the observation period (Figure 3), with an average wind speed of 2.2 m/s−1, mostly from the north direction. The temperature and RH indicated notable diurnal variations. The visibility was normally high with an average of 28.3 km, which was also observed to fluctuate shortly due to the impacts of orographic cloud, for instance, the visibility was 24.8 km at 15:00 on 21 September, and decreased down to 7.8 km at 16:00 on that day.
Overall, the aerosol distributions were affected noticeably by the PBL structure. Here, we used the UVAS to explore the diurnal variations of PBL and its impacts on the aerosol distribution. Table 1 lists UVAS launches and near-ground parameters. It can be noticed that the observation heights of UVAS were normally between 3350–4300 m, the diurnal variations of meteorological elements were significant, with low temperature, high RH, and low wind speed in the morning and nighttime, when the aerosol number concentration and BC mass concentration were low as well, which were the contrary to those in the daytime.
3.2. Vertical Profiles of BC Mass Concentration and Meteorological Element
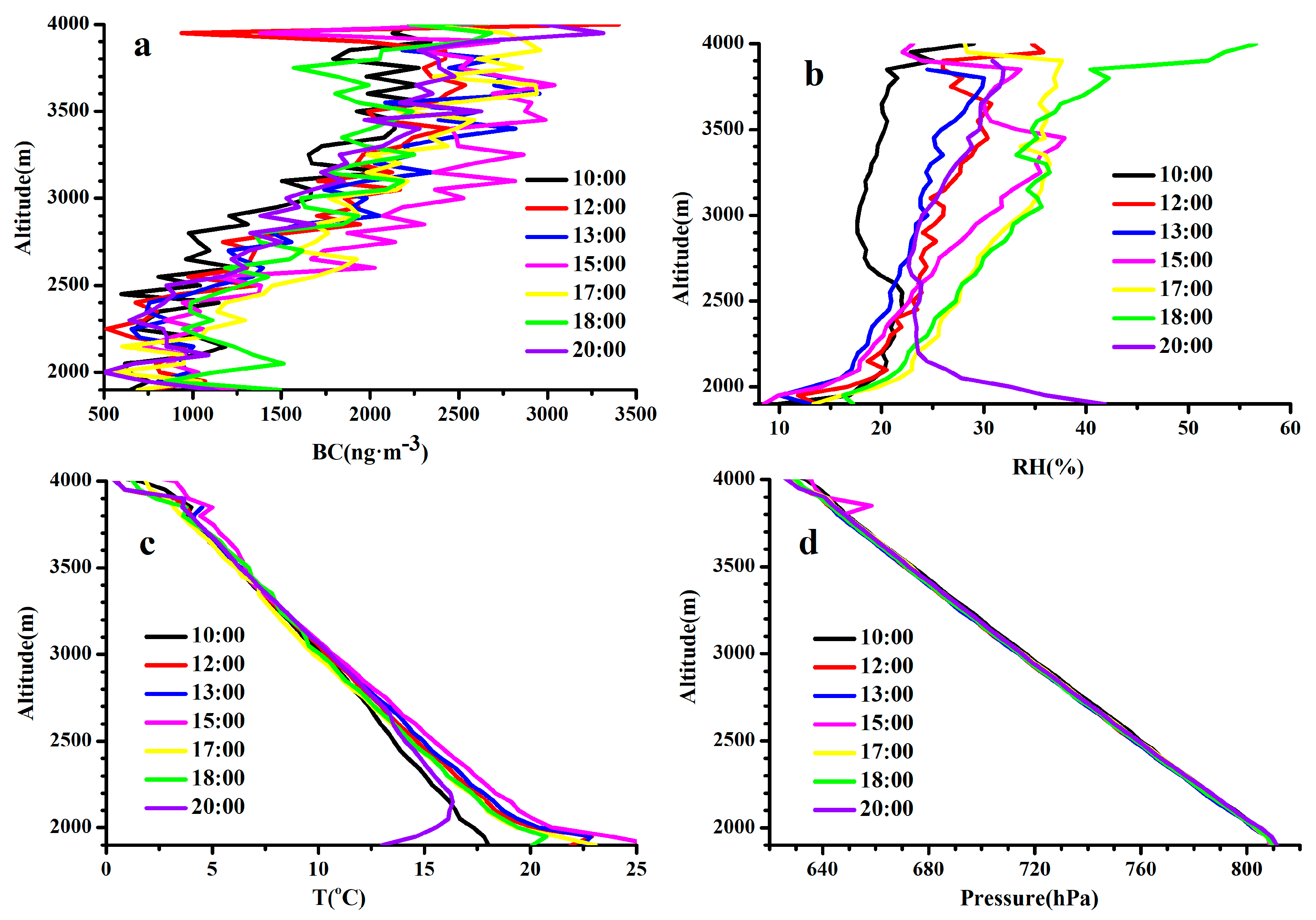
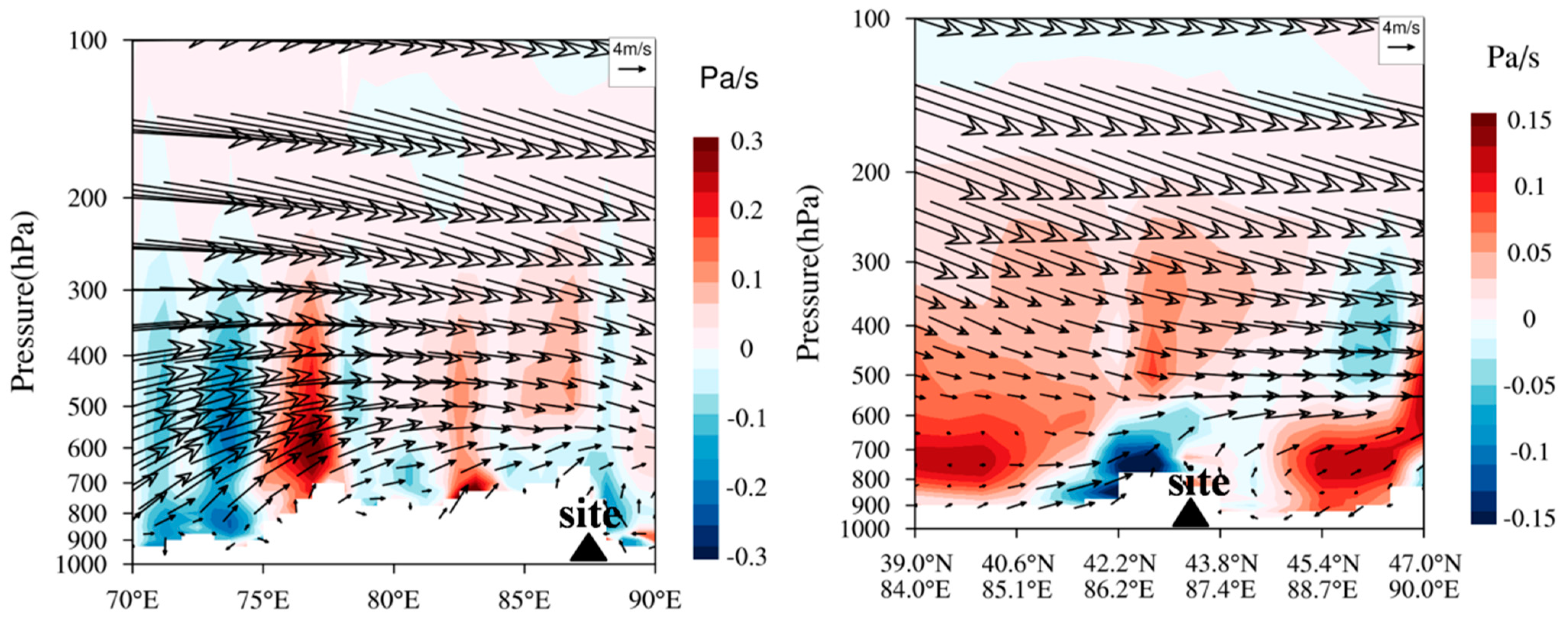
Figure 5a demonstrates that the vertical profiles of BC were similar at different time periods, which changed slightly with the increasing height below 2300 m a.s.l. and enhanced obviously with the height above 2300 m, with the maximum value at ~3500 m, hereafter, the BC decreased again with ascending altitude. Mt. Tianshan, at the south direction of the site, has an altitude of 3500–4000 m. As shown in Figure 4, the valley winds dominated in the daytime with air masses from Urumqi in the north, which were found to be lifted and returned at Mt. Tianshan due to its terrain blocking effects (Figure 6), resulting in larger BC concentrations at higher altitudes. It is also worth noting that the strong westerly winds with a weak sinking motion were dominated above 650 hPa and changed to low winds due to the topography effects with uplifting flows below 650 hPa over Mt. Tianshan during the observation period (Figure 6), which were consistent with those in Figure 4 with strong ascending flows below 650 hPa and weak vertical velocity above 650 hPa. Figure 5d reveals that the top of Mt. Tianshan near the observation site was approximately 3700 m (650 hPa), hence, the decrease in BC concentrations with the increasing height over 3500 m can be attributed to strong diffusion conditions.
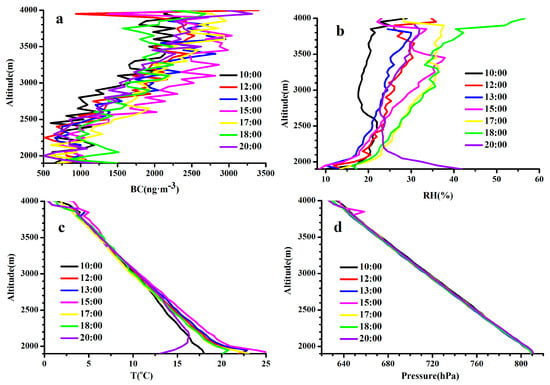
Figure 5.
Vertical profiles of BC mass concentration and meteorological elements during the observation period. (a) BC, (b) RH, (c) T, (d) pressure.
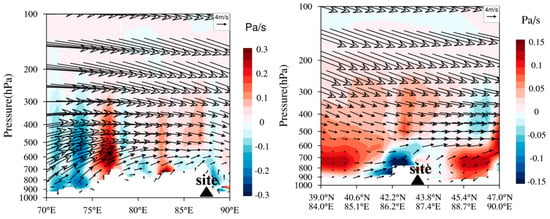
Figure 6.
Vertical sections of the wind field and vertical velocity during the observation period.
The surface temperature increased sharply after sunrise (Figure 5c), resulting in a lower RH (Figure 5b). It can be seen that the PBL structure was extremely unstable below 2300 m, where the temperature and RH decreased and increased noticeably with height, respectively, which can also be seen in Figure 4 with strong uplifting flows in the daytime. As such, the BC concentrations changed slightly below 2300 m because of the well-mixed PBL. Meanwhile, temperature inversions near the surface were also observed at most of the time segments (Figure 5c), with the largest strength and thickness appearing at 20:00, which led to high BC concentrations near the surface due to the strong inhibition of vertical mixing process.
Figure 7 also reveals the obvious impacts of mountain–valley winds on the aerosol distributions. The aerosol number concentrations were low in the nighttime when the mountain winds dominated with stable southerlies, which was contrary to those in the daytime. The wind speeds reached the minimum value of 1.0 m s−1 at 10:00 and the maximum of 2.8 m s−1 at 16:00. The temperature and RH began to increase and decrease, respectively, from 9:00, when the mountain winds began to turn into valley winds. It was characterized by slight changes in temperature and RH from 12:00, when the valley winds prevailed with the control of large wind speeds, the aerosol number concentrations thus increased, attributed to the pollutant transport from surrounding cities. The winds converted gradually from valley to mountain again in view of the decreasing temperature and increasing RH after 19:00, when high air pressure was observed. The mountain winds dominated from 22:00 as the stable air pressure was characterized, the aerosol concentrations started to reduce consequently. The visibility was noticed to be low in the daytime and high in the nighttime because of the aerosol extinction effects.
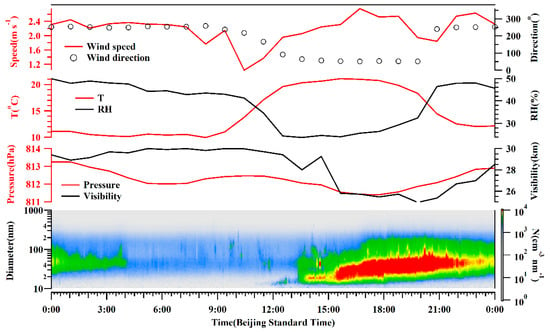
Figure 7.
Diurnal variations of aerosol size distribution and meteorological elements near ground observation.
3.3. Backward Trajectories during the Observation Period
Given the high aerosol number concentrations at 15:00 (BST), when the valley winds prevailed with high temperature and low RH (Figure 7), we analyzed the 48 h backward trajectories of air masses at different heights above the observation site at 15:00. Figure 8 indicated that the trajectory lengths of air masses were mostly short, within 400 km at the heights of 0–1000 m above the site; however, the directions changed greatly in view of the topographic effects. Table 1 indicates the highest PBLH at 15:00, when the solar radiation and the vertical convection were strong (Figure 4) and the horizontal wind speeds were relatively low, which resulted in short trajectories but various changes in their directions at lower heights. The westerly air masses were dominant, with relatively long trajectory lengths higher than 1600 m above the site, where the top of the Mt. Tianshan was located. Overall, the air masses changed noticeably in the lower and higher altitudes above the observation site due to the terrain effects of Mt. Tianshan.
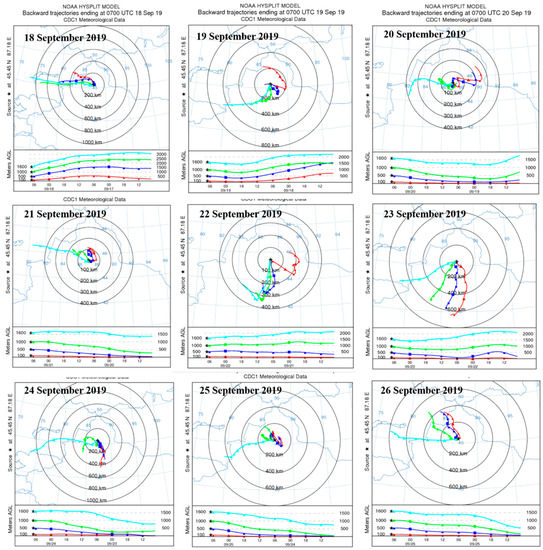
Figure 8.
48 h backward trajectories at different heights above observation site at 15:00.
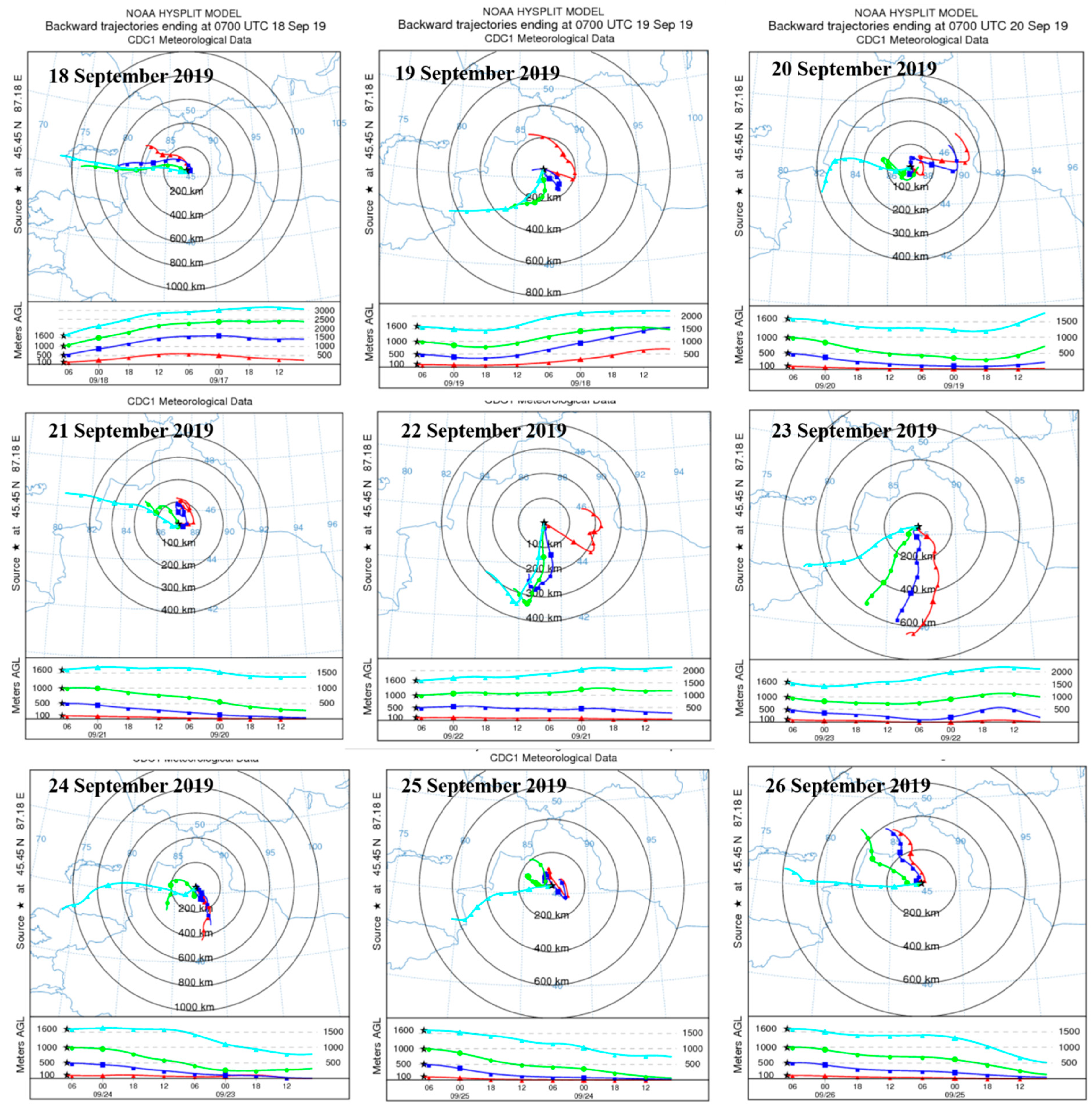
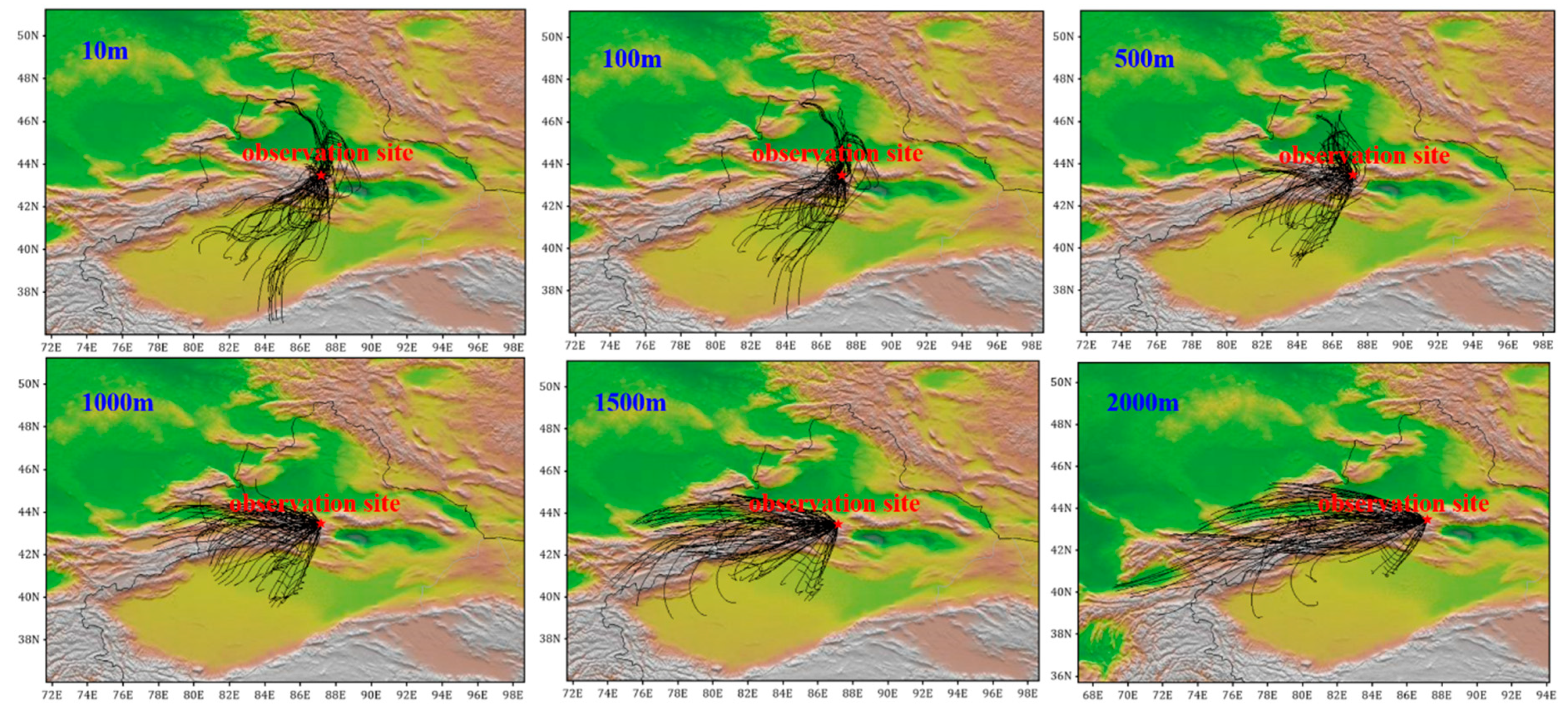
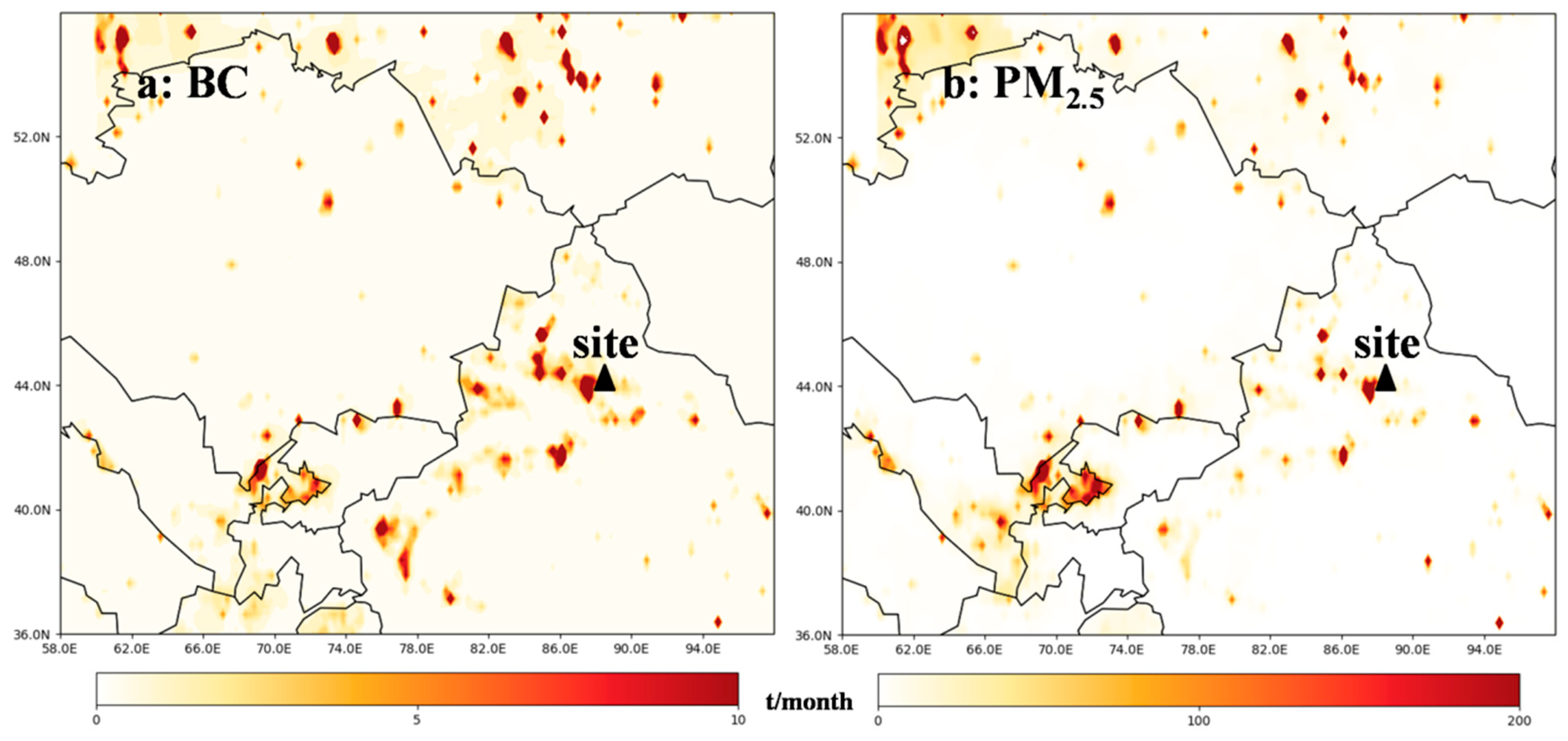
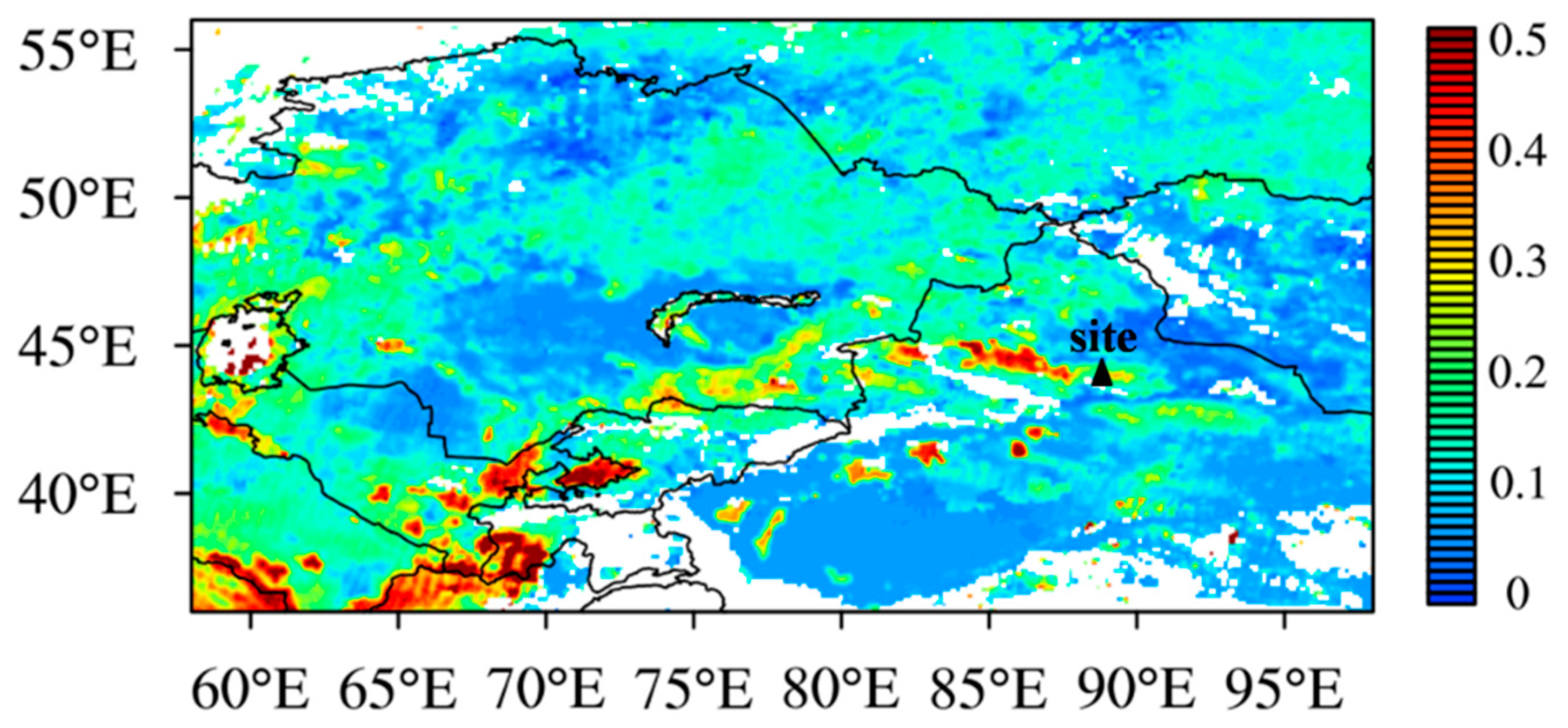
To better characterize the air masses at Mt. Tianshan, the 48 h backward trajectory at different heights above the observation site were also conducted every 3 h (Figure 9). It was found that the air masses at 10 and 100 m heights above the site were mainly from the southwest and northeast, respectively, implying large impacts of mountain–valley winds as well. Meanwhile, the pollutant emissions of BC and PM2.5 distributed densely around Mt. Tianshan (Figure 10), where high AOD values were also observed (Figure 11), such high concentrations of air pollutants can be transported by the air masses from the surroundings to the observation site via mountain–valley wind effects.
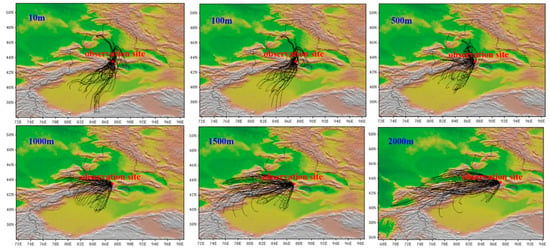
Figure 9.
48 h backward trajectory at different heights above observation site every 3 h.
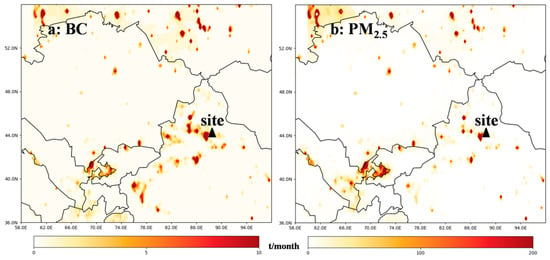
Figure 10.
Distributions of (a) BC and (b) PM2.5 from the MIX emission inventory.
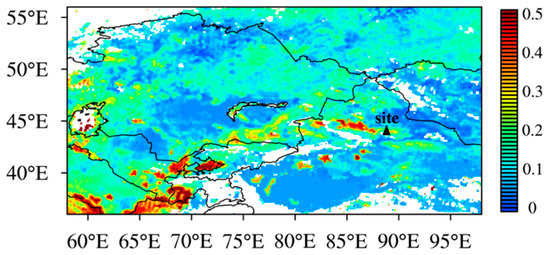
Figure 11.
AOD distributions during the observation period.
The westerly air masses were initially observed above 500 m above the site, implying the topographic impact on the local air masses weakened, such effects were noticed to be less important at heights over 1000 m above the site, where westerly and southwest air masses prevailed, and finally disappeared at the altitude exceeding 1500 m above the site where the western air masses dominated. The length of the air mass was enhanced with the increasing heights, revealing the greater diffusion conditions at higher altitudes. It can be seen that the air masses were mostly sourced from regions with low pollutant emissions and AOD values at higher altitudes (Figure 10 and Figure 11), leading to the decreases in BC concentrations with heights exceeding 3500 m a.s.l. (Figure 5), i.e., 1600 m above the observation site.
4. Conclusions
In this study, the vertical structures of meteorological elements and BC were first derived using an UAVS. Subsequently, the impact mechanisms of topography and meteorological elements’ vertical structure on the distributions of aerosols and BC were explored at Mt. Tianshan, from observations and model simulations. We found that the PBLH had large impacts on the distributions of air pollutants at Mt. Tianshan, with the concentration increase in the daytime due to the pollutant transport from surrounding areas to the mountain under high BPLH. The PBLH had a minimum value of 170 ± 65 m at 10:00 and maximums of 464 ± 147 m and 460 ± 178 m at 15:00 and 17:00, respectively. A high correlation was also observed between the PBLH derived by the UAVS and MERRA-2, with the former much lower than the latter, revealing that the observation data can amend the reanalysis data and model results. Topography and mountain–valley winds exerted great influences on the distributions of aerosol size and BC mass concentrations. Large discrepancies in the dominant air masses were observed in the lower and higher altitudes of Mt. Tianshan, ascribed to the topographic effects. The prevailing valley winds in the daytime were conducive to pollutant transport from the surrounding cities to Mt. Tianshan, where the aerosol number concentrations and BC mass concentrations increased rapidly as a result, which was contrary to the changes in the nighttime. The topographic effects on the air masses disappeared when the height above sea level exceeded 3500 m, where long-range transport and favorable diffusion conditions featured, resulting in low BC concentrations. Topography and mountain–valley winds also played important roles in the vertical distributions of BC, the mass concentrations of BC changed slightly with the increasing height below 2300 m a.s.l., which significantly increased with the height between 2300–3500 m and contrarily decreased with the ascending altitude higher than 3500 m.
This study demonstrated the discrepancies of air masses in the lower and higher altitudes of Mt. Tianshan, which exerted significant impacts on the aerosol size distributions and chemical composition. Such changes in aerosols can directly alter their hygroscopicity and residence time, further modifying the distributions of CCN at Mt. Tianshan. Overall, the aforementioned effects may change the physicochemical characteristics of orographic clouds, which further alter the precipitation mechanisms of clouds at different altitudes that should be discussed explicitly in future research.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.L. and H.W.; investigation, H.W., A.L., Z.Z. and K.C.; methodology, H.W. and J.X.; visualization, H.W.; writing—original draft, A.L. and H.W.; funding acquisition, Y.Y.; writing—review and editing, A.L., H.W., Y.L., Y.Y., B.L. and K.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Weather Modification Ability Construction Project of Northwest China (ZQCR18211); the Weather Modification Construction Research and Test Project in northwest China of China Meteorological Administration (RYSY201902); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (91644224 and 41805022).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article. The ground observation data and UAVS data are available from the authors upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of internet.
References
- Huang, R.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Bozzetti, C.; Ho, K.-F.; Cao, J.-J.; Han, Y.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Slowik, J.G.; Platt, S.M.; Canonaco, F.; et al. High secondary aerosol contribution to particulate pollution during haze events in China. Nature 2014, 514, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, M.J. Characteristics of aerosol observed during two severe haze events over Korea in June and October 2004. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 5146–5155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.; Huang, R.-J.; Zhang, R.; Tie, X.; Li, G.; Cao, J.; Zhou, W.; Shi, Z.; Han, Y.; Gu, Z.; et al. Severe haze in northern China: A synergy of anthropogenic emissions and atmospheric processes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 8657–8666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; An, J.; Shen, L.; Zhu, B.; Pan, C.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Duan, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y. Mechanism for the formation and microphysical characteristics of submicron aerosol during heavy haze pollution episode in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Kong, S.; Yan, Q.; Wu, F.; Cheng, Y.; Zheng, S.; Wu, J.; Yang, G.; Zheng, M.; Tang, L.; et al. The impacts of pollution control measures on PM2.5 reduction: Insights of chemical composition, source variation and health risk. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 197, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Chen, Y.; Ye, X. Haze, air pollution, and health in China. Lancet 2013, 382, 2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, X.; Wu, D.; Brasseur, G. Lung cancer mortality and exposure to atmospheric aerosol particles in Guangzhou, China. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 2375–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lighty, J.S.; Veranth, J.M.; Sarofim, A.F. Combustion Aerosols: Factors Governing Their Size and Composition and Implications to Human Health. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2000, 50, 1565–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolli, S.; Chen, Y.-C.; Wang, S.-H.; Vivone, G. Impact of meteorological conditions and air pollution on COVID-19 pandemic transmission in Italy. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattorini, D.; Regoli, F. Role of the chronic air pollution levels in the Covid-19 outbreak risk in Italy. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaas, J.; Boucher, O.; Bellouin, N.; Kinne, S. Satellite-based estimate of the direct and indirect aerosol climate forcing. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Wang, C.; Ekman, A.M.L.; Barth, M.C.; Rasch, P.J. Distribution and direct radiative forcing of carbonaceous and sulfate aerosols in an interactive size-resolving aerosol–climate model. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Ariya, P. Atmospheric organic and bio-aerosols as cloud condensation nuclei (CCN): A review. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 795–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemura, T.; Nozawa, T.; Emori, S.; Nakajima, T.Y.; Nakajima, T. Simulation of climate response to aerosol direct and indirect effects with aerosol transport-radiation model. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singla, V.; Mukherjee, S.; Kashikar, A.S.; Safai, P.D.; Pandithurai, G. Black carbon: Source apportionment and its implications on CCN activity over a rural region in Western Ghats, India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 7071–7081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, G.; Tyagi, B.; Singh, J.; Sarangi, C.; Tripathi, S. Aerosol-orography-precipitation—A critical assessment. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 214, 116831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oanh, N.T.K.; Leelasakultum, K. Analysis of meteorology and emission in haze episode prevalence over mountain-bounded region for early warning. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 2261–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caramagna, A.; Famoso, F.; Lanzafame, R.; Monforte, P. Analysis of Vertical Profile of Particulates Dispersion in Function of the Aerodynamic Diameter at a Congested Road in Catania. Energy Procedia 2015, 82, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Qiao, L.; Gong, D.; Kim, S.-J.; Wang, Y.; Mao, R. Numerical simulations of the effects of regional topography on haze pollution in Beijing. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, N.; Wang, N.; Huang, X.; Liu, P.; Chen, L. The effects of terrain and atmospheric dynamics on cold season heavy haze in the Guanzhong Basin of China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 1805–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yao, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Ji, D.; Tang, G.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Hu, B.; Xin, J. Mechanism for the formation of the January 2013 heavy haze pollution episode over central and eastern China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Huang, X.; Zhang, J.; Luo, B.; Zhang, W.; Song, H. Characterization of aerosol particles during the most polluted season (winter) in urban Chengdu (China) by single-particle analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 17685–17695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Hu, B.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Y. Characteristics of aerosol size distributions and chemical compositions during wintertime pollution episodes in Beijing. Atmos. Res. 2016, 168, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, J.; Luo, B.; Wang, L.; Tang, G.; Liu, Z.; Song, H.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, L.; Wang, Y. Water-soluble ions in PM2.5 during spring haze and dust periods in Chengdu, China: Variations, nitrate formation and potential source areas. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 1740–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Ma, T.; Duan, F.; Li, H.; He, K.; Xia, J.; Yang, S.; Zhu, L.; Ma, Y.; Huang, T.; et al. Characteristics and formation mechanisms of winter haze in Changzhou, a highly polluted industrial city in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 253, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Wang, S.; Jiang, J.; Fu, Q.; Chen, C.; Xu, B.; Yu, J.; Fu, X.; Hao, J. Long-term trend of haze pollution and impact of particulate matter in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 182, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, W.; Liu, T.; Du, Q.; Li, J.; Xiao, J.; Guo, L.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Xu, X.; Wan, D.; et al. The interplay of haze characteristics on mortality in the Pearl River Delta of China. Environ. Res. 2020, 184, 109279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, J.; Dou, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Q.; Sun, Z.; Pan, Y.; Jia, X.; Cheng, Z.; Ma, P.; Su, J.; et al. Regional atmospheric pollutant transport mechanisms over the North China Plain driven by topography and planetary boundary layer processes. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 221, 117098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Zhao, T.; Bai, Y.; Shen, L.; Sun, X.; Gu, Y. Contribution of Regional PM2.5 Transport to Air Pollution Enhanced by Sub-Basin Topography: A Modeling Case over Central China. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, G.; Yim, S.H.L.; Wang, S.; Duan, B.; Nie, C.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Shang, K. Synergistic effects of synoptic weather patterns and topography on air quality: A case of the Sichuan Basin of China. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 53, 6729–6744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Ding, G.; Cheng, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhao, T. “Harbor” effect of large topography on haze distribution in eastern China and its climate modulation on decadal variations in haze. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 1132–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Guo, X.; Zhao, T.; Gong, S.; Xu, X.; Li, Y.; Luo, L.; Gui, K.; Wang, H.; Zheng, Y.; et al. A modelling study of the terrain effects on haze pollution in the Sichuan Basin. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 196, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, D.; Amir, G. Evidence of orographic precipitation suppression by air pollution–induced aerosols in the western United States. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2006, 45, 893–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirak, I.L.; Cotton, W.R. Effect of Air Pollution on Precipitation along the Front Range of the Rocky Mountains. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2006, 45, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, D.; Dai, J.; Yu, X.; Yao, Z.; Xu, X.; Yang, X.; Du, C. Inverse relations between amounts of air pollution and oro-graphic precipitation. Science 2007, 315, 1396–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathias, J.M.; Thomas, R.B. Disentangling the effects of acidic air pollution, atmospheric CO2, and climate change on recent growth of red spruce trees in the Central Appalachian Mountains. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 3938–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.M.; Lee, H.; Moon, S.; Baik, J.-J. How Mountain Geometry Affects Aerosol-Cloud-Precipitation Interactions: Part I. Shallow Convective Clouds. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2020, 98, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Edwards, R.; Mosley-Thompson, E.; Wang, F.; Dong, Z.; You, X.; Li, H.; Li, C.; Zhu, Y. Seasonal variability of ionic concentrations in surface snow and elution processes in snow–firn packs at the PGPI site on Ürümqi glacier No. 1, eastern Tien Shan, China. Ann. Glaciol. 2006, 43, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, F.; Zhang, M. Characteristics of atmospheric dust deposition in snow on the glaciers of the eastern Tien Shan, China. J. Glaciol. 2009, 55, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Li, Z.; Xiao, C.; Wang, F.; Zhang, M. Characteristics of aerosol dust in fresh snow in the Asian dust and non-dust periods at Urumqi glacier no. 1 of eastern Tian Shan, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2009, 60, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Li, Z.; Edwards, R.; Wu, L.; Zhou, P. Temporal characteristics of mineral dust particles in precipitation of Urumqi River Valley in Tian Shan, China: A comparison of alpine site and rural site. Atmos. Res. 2011, 101, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Wang, H.; Cui, Y.; Shen, L.; Yin, Y.; Wu, Z.; Guo, S.; Shi, S.; Chen, K.; Zhu, B.; et al. Characteristics of Aerosol during a Severe Haze-Fog Episode in the Yangtze River Delta: Particle Size Distribution, Chemical Composition, and Optical Properties. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Li, Z.; Zhou, P. Ion chemistry and individual particle analysis of atmospheric aerosols over Mt. Bogda of eastern Tianshan Mountains, Central Asia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 180, 409–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wake, C.P.; Paul, A.M.; Wang, P.; Yang, Q.; Han, J.; Xie, Z. Anthropogenic sulfate and Asian dust signals in snow from Tien Shan, northwest China. Ann. Glaciol. 1992, 16, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, X.; Qin, D.; Jiang, G.; Duan, K.; Zhou, H. Atmospheric pollution of a remote area of Tianshan Mountain: Ice core record. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xia, X.; Zhong, S.; Luo, L.; Yu, X.; Jia, J.; Zhao, K.; Li, N.; Liu, Y.; Ren, Q. Shallow foehn on the northern leeside of Tianshan Mountains and its influence on atmospheric boundary layer over Urumqi, China—A climatological study. Atmos. Res. 2020, 240, 104940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieber, P.; Seifried, T.M.; Burkart, J.; Gratzl, J.; Kasper-Giebl, A.; Schmale, D.G.; Grothe, H. A Drone-Based Bioaerosol Sampling System to Monitor Ice Nucleation Particles in the Lower Atmosphere. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilinski, M.; Markowicz, K.; Markowicz, J. Observation of vertical variability of black carbon concentration in lower troposphere on campaigns in Poland. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 137, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Zhu, B.; Lu, W.; Yan, S.; Fang, C.; Liu, X.; Liu, D.; Liu, C. Estimation of radiative forcing and heating rate based on vertical observation of black carbon in Nanjing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 144135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Park, Y.; Fan, X.; Bai, D.; Zong, P.; Qin, B.; Cai, X.; Ahn, K.-H. Measurements of atmospheric aerosol vertical distribution above North China Plain using hexacopter. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 665, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, T.; Jayaratne, E.; Gonzalez, L.; Morawska, L. Determination of the vertical profile of particle number concentration adjacent to a motorway using an unmanned aerial vehicle. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.; Houston, A.L.; Shankar, A.; Detweiler, C. Design and Evaluation of Sensor Housing for Boundary Layer Profiling Using Multirotors. Sensors 2019, 19, 2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhu, B.; Huang, Y.; Shi, S.; Wang, H.; An, J.; Yu, X. Vertical distributions of black carbon aerosols over rural areas of the Yangtze River Delta in winter. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 661, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowicz, K.; Ritter, C.; Lisok, J.; Makuch, P.; Stachlewska, I.; Cappelletti, D.; Mazzola, M.; Chilinski, M. Vertical variability of aerosol single-scattering albedo and equivalent black carbon concentration based on in-situ and remote sensing techniques during the iAREA campaigns in Ny-Ålesund. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 164, 431–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leeuw, G.; Sogacheva, L.; Rodriguez, E.; Kourtidis, K.; Georgoulias, A.K.; Alexandri, G.; Amiridis, V.; Proestakis, E.; Marinou, E.; Xue, Y.; et al. Two decades of satellite observations of AOD over mainland China using ATSR-2, AATSR and MODIS/Terra: Data set evaluation and large-scale patterns. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2018, 18, 1573–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelaro, R.; Mccarty, W.; Suárez, M.J.; Todling, R.; Molod, A.; Takacs, L.; Randles, C.A.; Darmenov, A.; Bosilovich, M.G.; Reichle, R.; et al. The Modern-Era Retrospective Analysis for Research and Applications, Version 2 (MERRA-2). J. Clim. 2017, 30, 5419–5454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosilovich, M.G.; Lucchesi, R.; Suarez, M. MERRA-2: File Specification; NASA GSFC: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2015.
- Kurokawa, J.; Ohara, T.; Morikawa, T.; Hanayama, S.; Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Fukui, T.; Kawashima, K.; Akimoto, H. Emissions of air pollutants and greenhouse gases over Asian regions during 2000–2008: Regional Emission inventory in ASia (REAS) version 2. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2013, 13, 11019–11058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Song, Y.; Li, M.; Li, J.; Huo, Q.; Cai, X.; Zhu, T.; Hu, M.; Zhang, H. A high-resolution ammonia emission inventory in China. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2012, 26, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Streets, D.G. Increase in NOx Emissions from Indian Thermal Power Plants during 1996–2010: Unit-Based Inventories and Multisatellite Observations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 7463–7470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Streets, D.G. Sulfur dioxide and primary carbonaceous aerosol emissions in China and India, 1996–2010. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2011, 11, 9839–9864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Lee, Y.-M.; Jang, K.-W.; Yoo, C.; Kang, K.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Jung, S.-W.; Park, J.-M.; Lee, S.-B.; Han, J.-S.; et al. Korean National Emissions Inventory System and 2007 Air Pollutant Emissions. Asian J. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 5, 278–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, Q.; Kurokawa, J.-I.; Woo, J.-H.; He, K.; Lu, Z.; Ohara, T.; Song, Y.; Streets, D.G.; Carmichael, G.R.; et al. MIX: A mosaic Asian anthropogenic emission inventory under the international collaboration framework of the MICS-Asia and HTAP. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2017, 17, 935–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, A.F.; Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D.; Stunder, B.J.B.; Cohen, M.D.; Ngan, F. NOAA’s HYSPLIT Atmospheric Transport and Dispersion Modeling System. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 2059–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D. HYSPLIT (HYbrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory) Model; NOAA Air Resources Laboratory: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2010. Available online: http://ready.arl.noaa.gov/HYSPLIT.php (accessed on 1 March 2021).
- Zhang, X.; Cai, X.; Chai, F. Structures and characteristics of the atmospheric boundary layer over Beijing area in autumn. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Pekin. 2006, 42, 220–225. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).