Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity Analysis of Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration: Evidence from Nighttime Light Data (2001–2019)
Abstract
1. Introduction
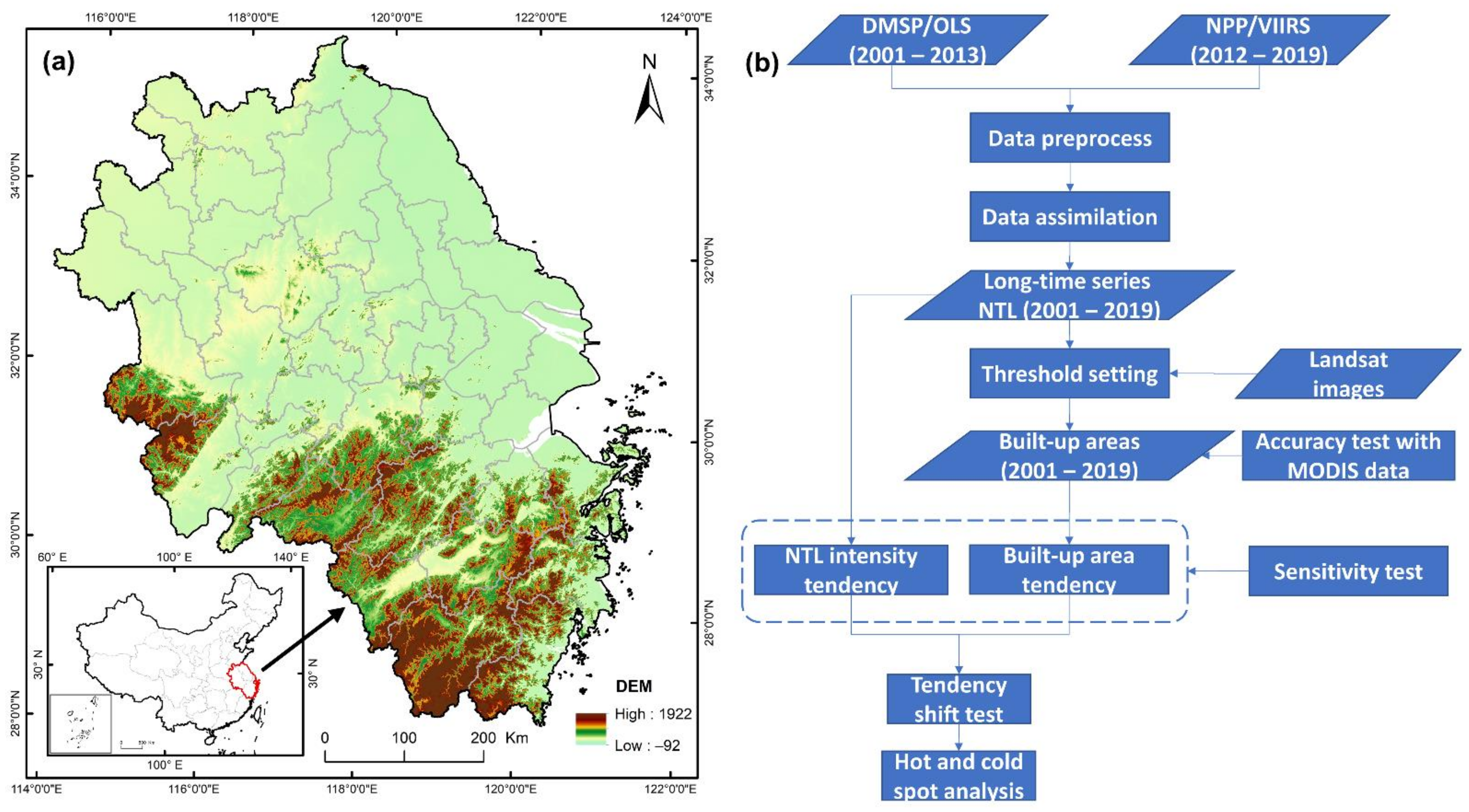
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data and Preprocessing
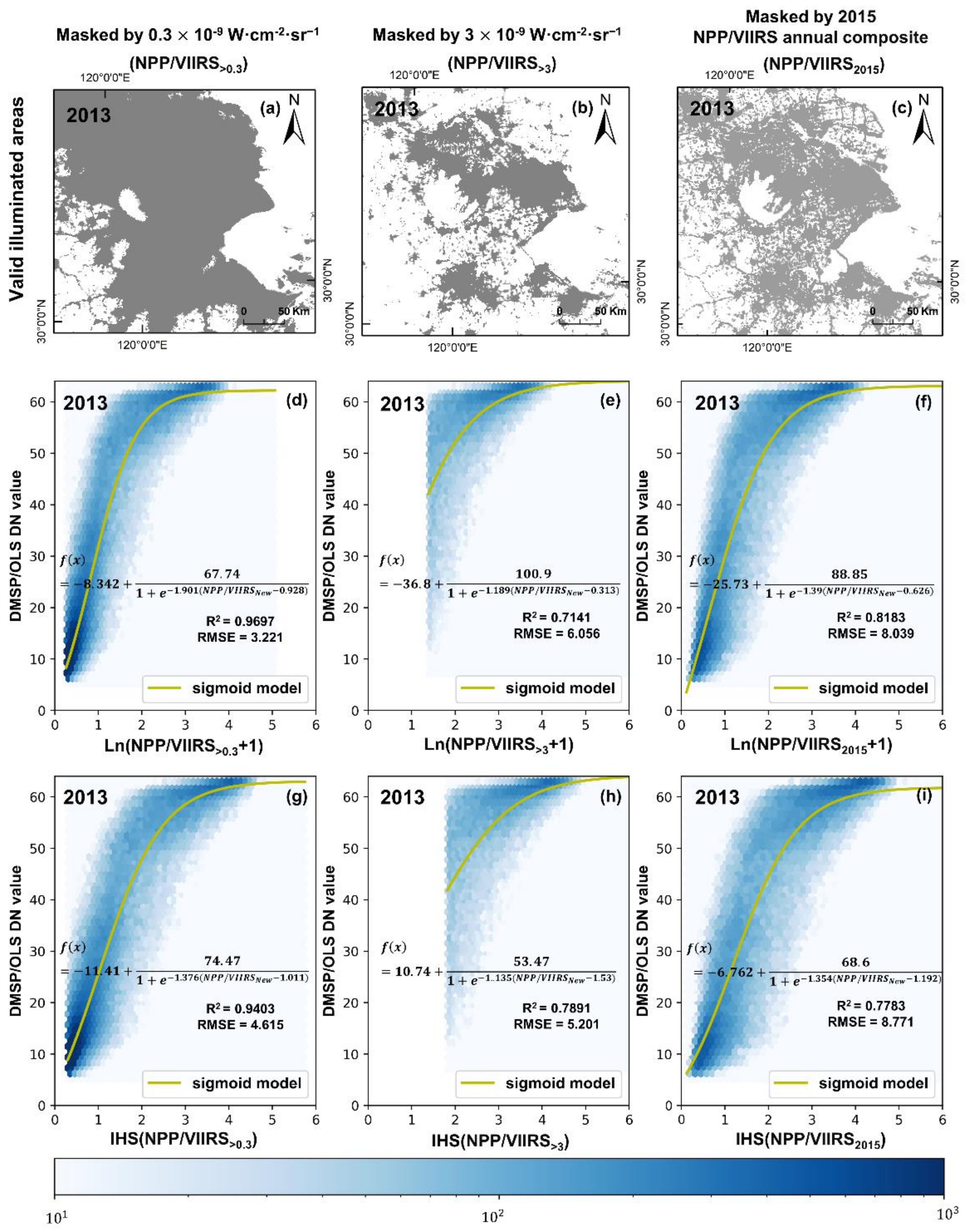
2.2. Background Noise Mask
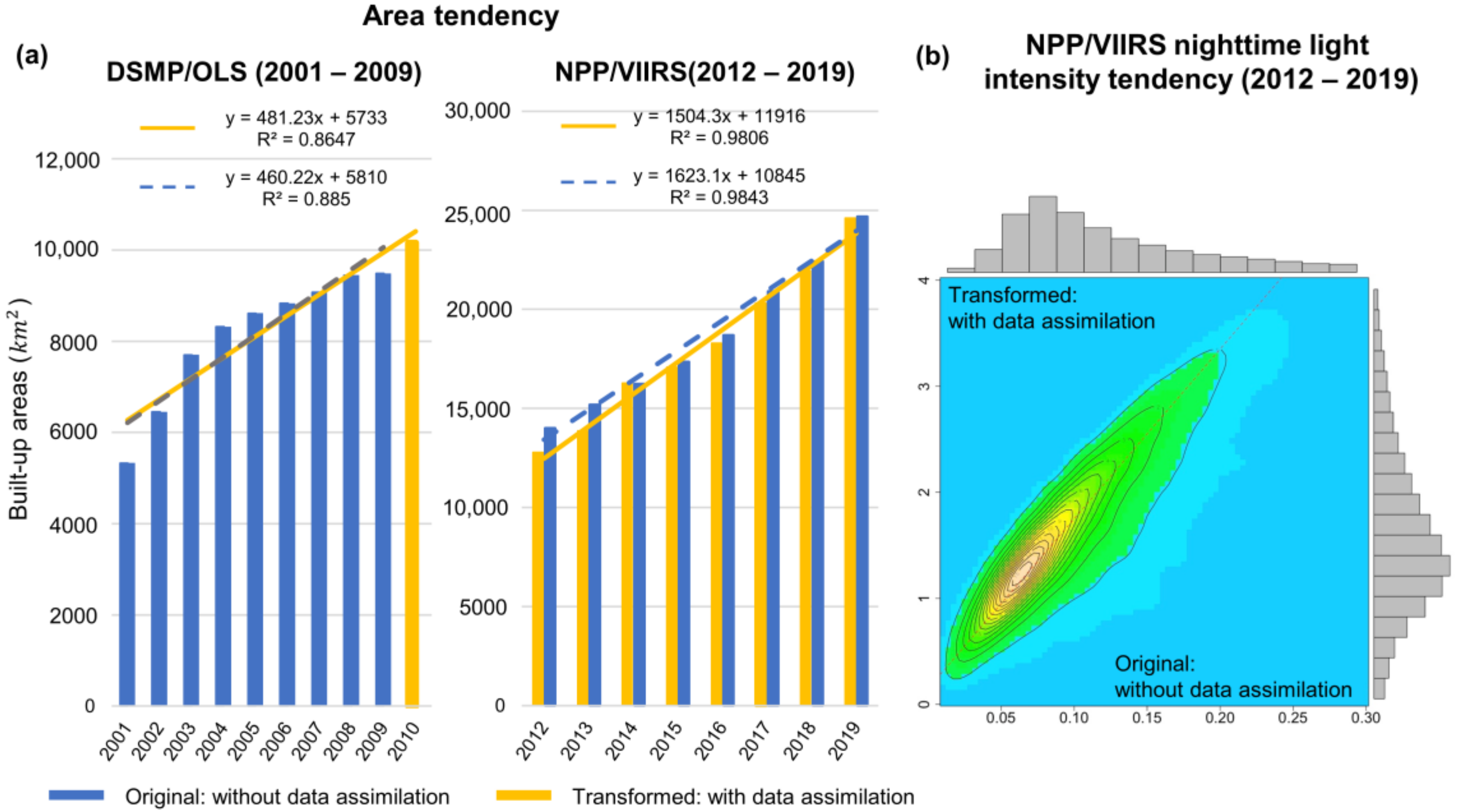
2.3. Data Assimilation
2.4. Threshold Setting for the Built-up Area
2.5. Area Tendency and Light Intensity Tendency
2.6. Hot and Cold Spot Analysis
2.7. Tendency Shift
3. Results
3.1. Background Noise Mask and Data Assimilation
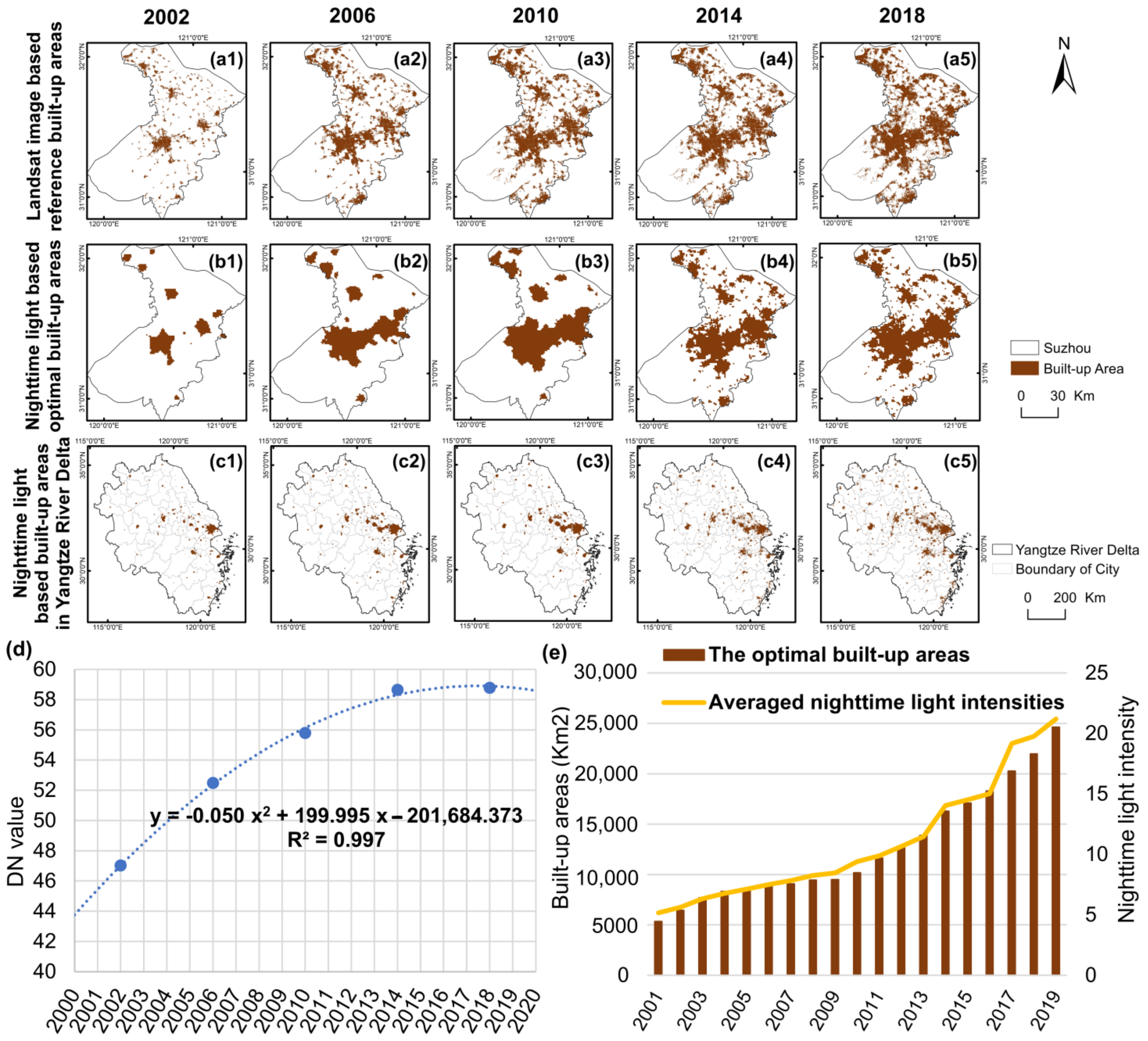
3.2. Threshold Setting for the Built-Up Areas
3.3. Accuracy Test with MODIS Data
4. Analyses and Discussion
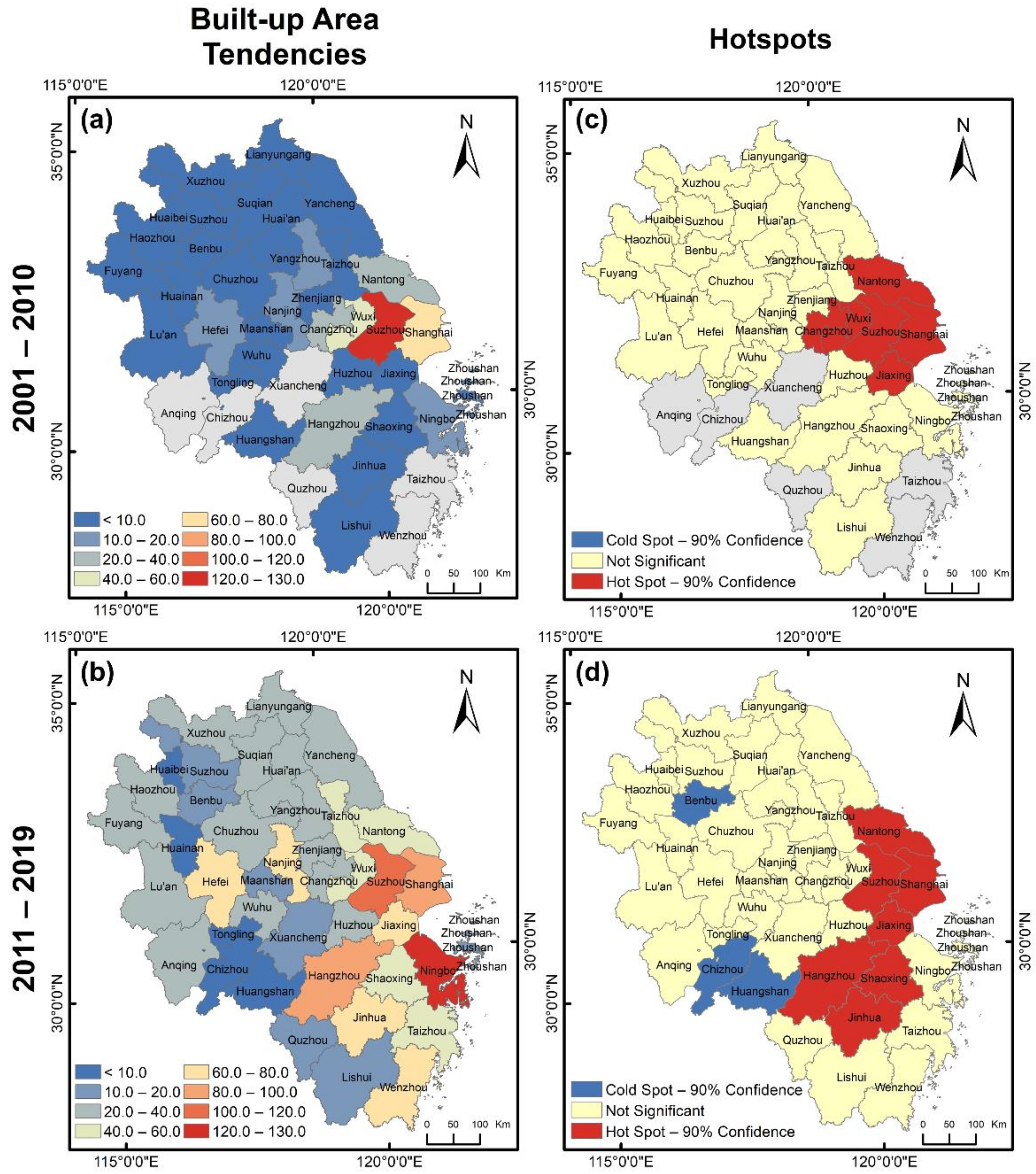
4.1. Spatial Heterogeneity in the Administrative City Scale
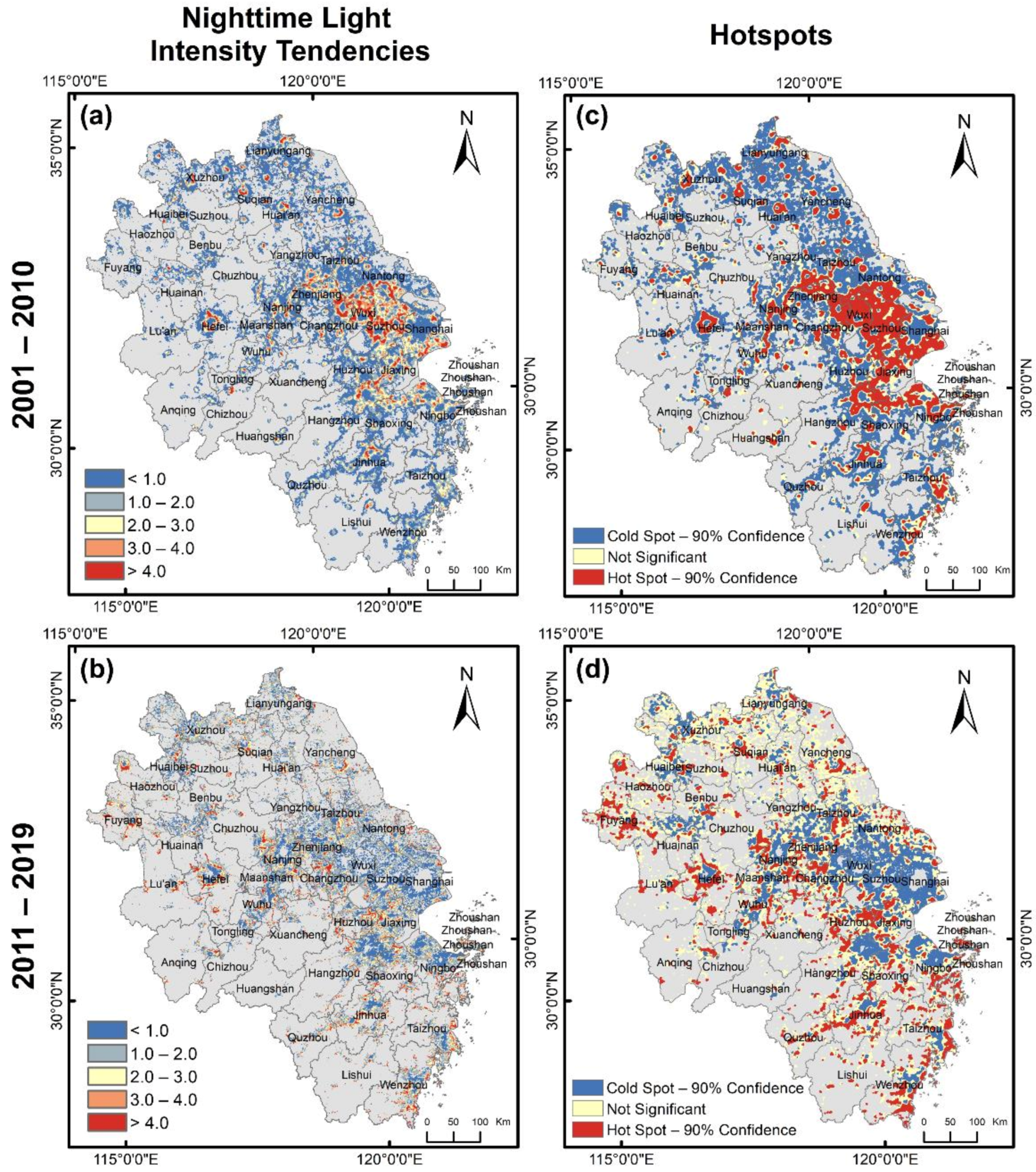
4.2. Temporal Heterogeneity in the Pixel Scale
4.3. Spatial-Temporal Joint Analysis
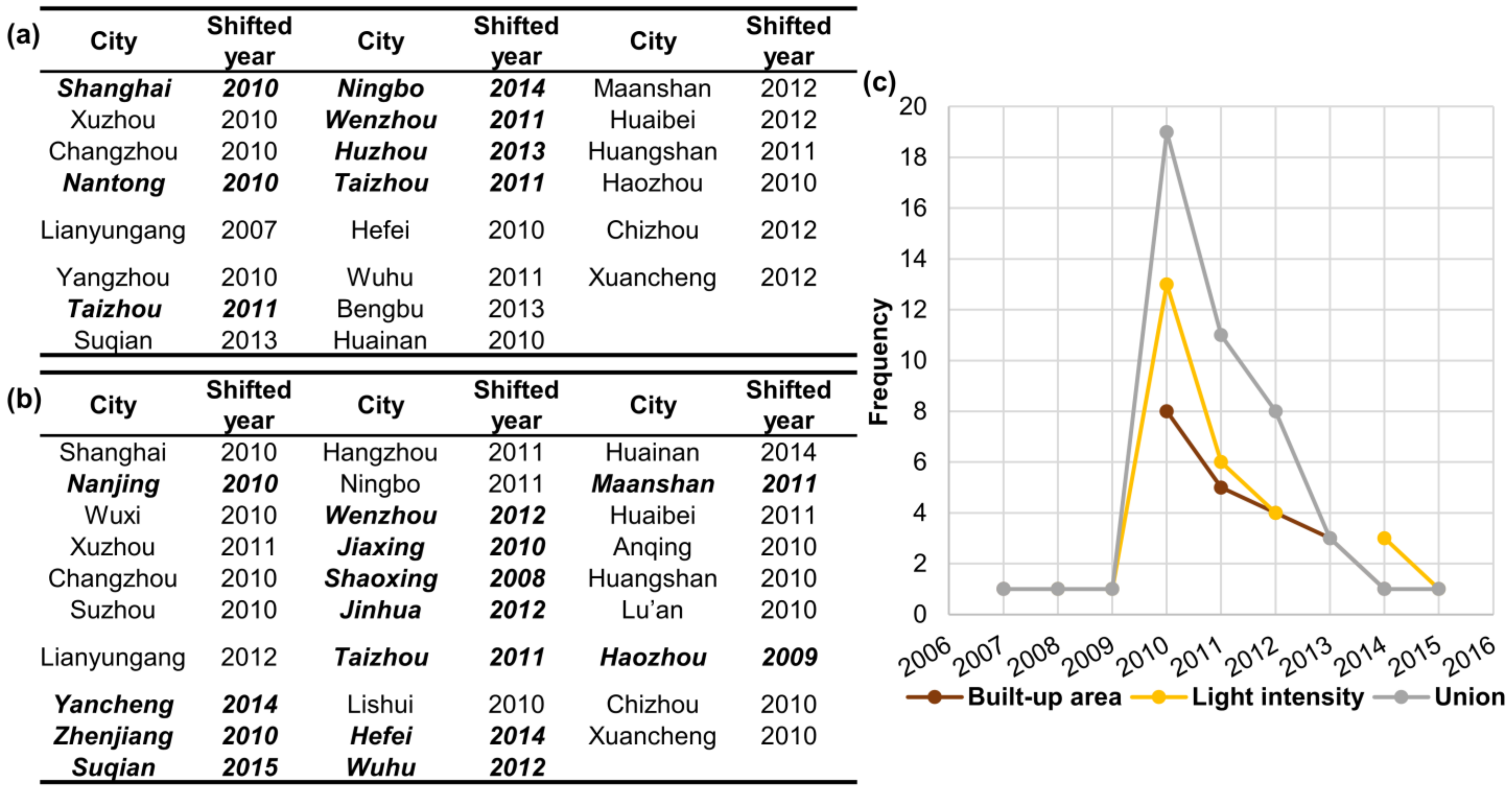
4.3.1. Tendency Shift Detection
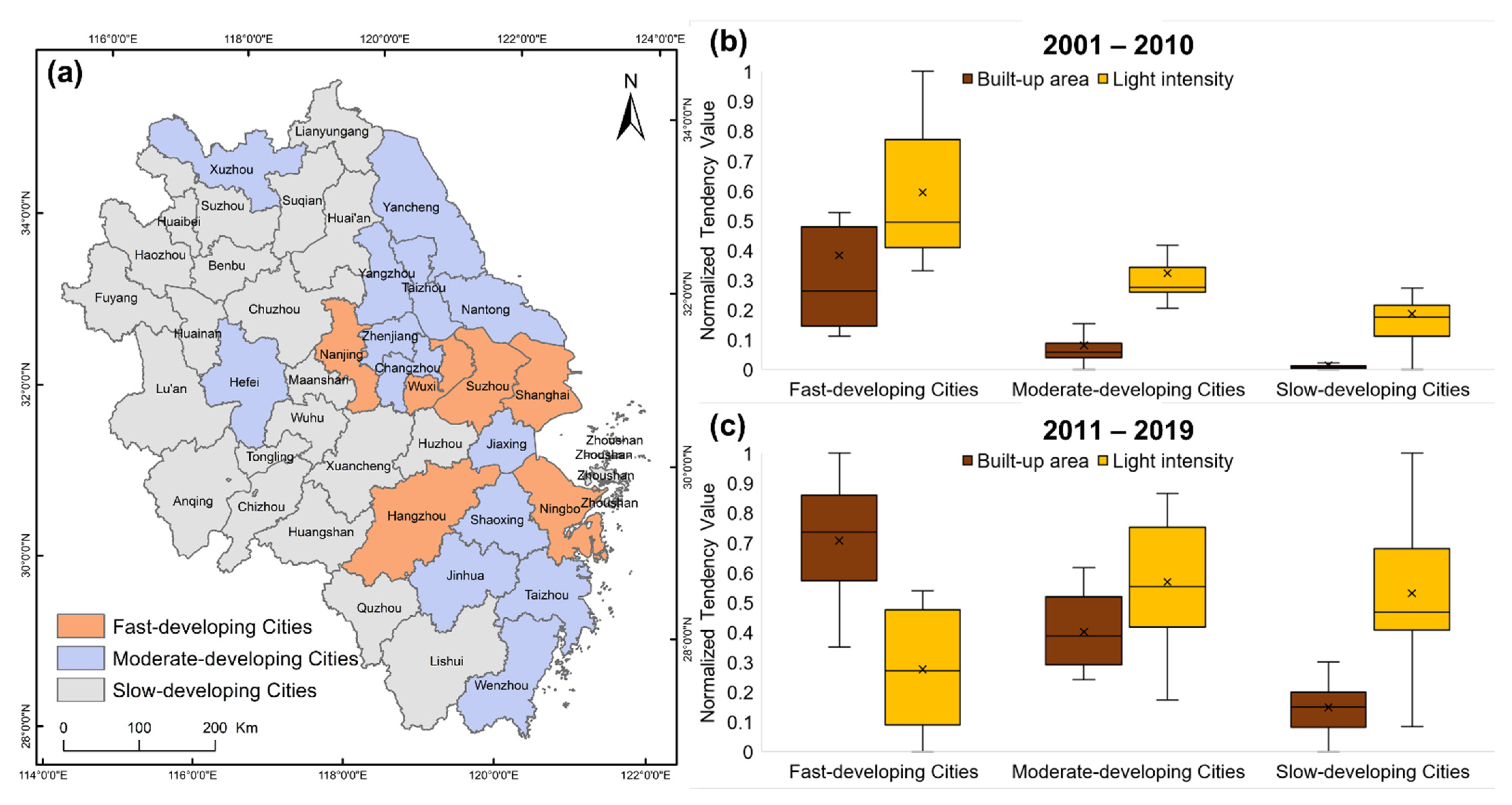
4.3.2. GDP Associated Spatiotemporal Variability
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gottmann, J. Megalopolis or the urbanization of the northeastern seaboard. Econ. Geogr. 1957, 33, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taubenböck, H.; Wiesner, M.; Felbier, A.; Marconcini, M.; Esch, T.; Dech, S. New dimensions of urban landscapes: The spatio-temporal evolution from a polynuclei area to a mega-region based on remote sensing data. Appl. Geogr. 2014, 47, 137–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florida, R.; Gulden, T.; Mellander, C. The rise of the mega-region. Camb. J. Reg. Econ. Soc. 2008, 1, 459–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedmann, J. Four Theses in the Study of China’s Urbanization. Int. J. Urban Reg. Res. 2006, 30, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN. World Urbanization Prospects: The 2018 Revision; UN: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Li, X.; Xie, H.; Lu, C. Urban land expansion and arable land loss in China—A case study of Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region. Land Use Policy 2005, 22, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Huang, J.; Rozelle, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z. Impact of urbanization on cultivated land changes in China. Land Use Policy 2015, 45, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Xia, Z.-G.; Clarke, K.C.; Frei, A. Impact of Urban Sprawl on Water Quality in Eastern Massachusetts, USA. Environ. Manag. 2007, 40, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houghton, R.; Hackler, J. Sources and sinks of carbon from land-use change in China. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2003, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Fraedrich, K.; Guan, Y.; Guo, S.; Zhang, C. Urbanization and the thermal environment of Chinese and US-American cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 589, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhou, W.; Han, L.; Qian, Y. Uneven urban-region sprawl of China’s megaregions and the spatial relevancy in a multi-scale approach. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 97, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Shi, P.; Liu, Y. Society: Realizing China’s urban dream. Nat. News 2014, 509, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R. Rebalancing the Spatial Economy: The Challenge for Regional Theory. Territ. Politics Gov. 2015, 3, 235–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Liu, J.; Xie, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhuang, D.; Niu, Z. Analysis of spatio-temporal dynamic pattern and driving forces of urban land in China in 1990s using TM images and GIS. Cities 2005, 22, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Jiang, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y. The urban growth, size distribution and spatio-temporal dynamic pattern of the Yangtze River Delta megalopolitan region, China. Ecol. Model. 2011, 222, 865–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.Y. The Distribution of Population in China, With Statistics and Maps. Acta Geogr. Sin. 1935, 2, 33–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Gong, Y.; Li, Y.; Lu, D.; Zhang, H. Population distribution and urbanization on both sides of the Hu Huanyong Line: Answering the Premier’s question. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 1593–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Liu, S.; Zhao, M.; Liu, Z. China’s different spatial patterns of population growth based on the “Hu Line”. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 1611–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Fraedrich, K.; Guan, Y.; Guo, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, X. Urbanization and climate change: Insights from eco-hydrological diagnostics. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 647, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Huang, C.; Yu, B.; Yin, B.; Huang, Y.; Wu, J. Evaluation of NPP-VIIRS night-time light composite data for extracting built-up urban areas. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Lu, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J. Mapping impervious surface distribution with integration of SNNP VIIRS-DNB and MODIS NDVI data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 12459–12477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhao, H.; Jiang, S. A Zipf’s Law-Based Method for Mapping Urban Areas Using NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Weng, Q.; Weng, A. A comparative study of NPP-VIIRS and DMSP-OLS nighttime light imagery for derivation of urban demographic metrics. In Proceedings of the 2014 Third International Workshop on Earth Observation and Remote Sensing Applications (EORSA), Changsha, China, 11–14 June 2014; pp. 335–339. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, K.; Yu, B.; Huang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yin, B.; Chen, Z.; Chen, L.; Wu, J. Evaluating the Ability of NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light Data to Estimate the Gross Domestic Product and the Electric Power Consumption of China at Multiple Scales: A Comparison with DMSP-OLS Data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1705–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Zhou, C.; Pei, T.; Haynie, S.; Fan, J. Responses of Suomi-NPP VIIRS-derived nighttime lights to socioeconomic activity in China’s cities. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, H.; Chen, X.; Li, C. Potential of NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light Imagery for Modeling the Regional Economy of China. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 3057–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Yu, B.; Hu, Y.; Huang, C.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wu, J. Modeling and mapping total freight traffic in China using NPP-VIIRS nighttime light composite data. GIScience Remote Sens. 2015, 52, 274–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Cao, C.; Zhang, B.; Qiu, S.; Elvidge, C.; Von Hendy, M. Radiometric calibration of DMSP-OLS sensor using VIIRS day/night band. In Proceedings of the Earth Observing Missions and Sensors: Development, Implementation, and Characterization III, Beijing, China, 13–15 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, D.; Xu, H.; Wu, C. Intercalibration between DMSP/OLS and VIIRS night-time light images to evaluate city light dynamics of Syria’s major human settlement during Syrian Civil War. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 5934–5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, C.; Cheng, W.; Li, M.; Huang, K. Building a Series of Consistent Night-Time Light Data (1992–2018) in Southeast Asia by Integrating DMSP-OLS and NPP-VIIRS. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 1843–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Guo, J.; Ahmad, S.; Li, Z.; Hong, J. Constructing a New Inter-Calibration Method for DMSP-OLS and NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, S.; Guan, Y.; Cai, D.; Zhang, C.; Fraedrich, K.; Xiao, H.; Tian, Z. Urbanization and Spillover Effect for Three Megaregions in China: Evidence from DMSP/OLS Nighttime Lights. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Qi, W.; Jin, H. Urban sprawl among Chinese cities of different population sizes. Habitat Int. 2018, 79, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Qi, W.; Fu, B.; Wang, K. Geographical transformations of urban sprawl: Exploring the spatial heterogeneity across cities in China 1992–2015. Cities 2020, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Liu, S.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, Q. Measuring urban sprawl in Beijing with geo-spatial indices. J. Geogr. Sci. 2007, 17, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Li, M.; Li, W. Evaluation of NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light Data for Mapping Global Fossil Fuel Combustion CO2 Emissions: A Comparison with DMSP-OLS Nighttime Light Data. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, X.; Shao, X.; Cao, C.; Fu, X.; Yan, L. Comparison between the Suomi-NPP Day-Night Band and DMSP-OLS for Correlating Socio-Economic Variables at the Provincial Level in China. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, J.; Olivia, S.; Boe-Gibson, G. Night Lights in Economics: Sources and USES1. J. Econ. Surv. 2020, 34, 955–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.; Ziskin, D.; Baugh, K.; Tuttle, B.; Ghosh, T.; Pack, D.; Erwin, E.; Zhizhin, M. A Fifteen Year Record of Global Natural Gas Flaring Derived from Satellite Data. Energies 2009, 2, 595–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.B.; Weiss, S.; Mills, S.; Hauss, B. Suomi NPP VIIRS day-night band on-orbit performance. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 12705–12718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, J. Better Night Lights Data, For Longer*. Oxf. Bull. Econ. Stat. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, J.; Olivia, S.; Boe-Gibson, G.; Li, C. Which night lights data should we use in economics, and where? J. Dev. Econ. 2021, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, J.; Datt, G.; Murgai, R.; Ravallion, M. For India’s Rural Poor, Growing Towns Matter More Than Growing Cities. World Dev. 2017, 98, 413–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C.; Pozzi, F.; Elvidge, C. Spatial analysis of global urban extent from DMSP-OLS night lights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 96, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; He, C.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Q.; Yang, Y. Extracting the dynamics of urban expansion in China using DMSP-OLS nighttime light data from 1992 to 2008. Landsc. Urban. Plan. 2012, 106, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleasby, I.R.; Owen, E.; Wilson, L.; Wakefield, E.D.; O’Connell, P.; Bolton, M. Identifying important at-sea areas for seabirds using species distribution models and hotspot mapping. Biol. Conserv. 2020, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwitira, I.; Murwira, A.; Zengeya, F.M.; Shekede, M.D. Application of GIS to predict malaria hotspots based on Anopheles arabiensis habitat suitability in Southern Africa. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 64, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratcliffe, J.H. Damned If You Don’t, Damned If You Do: Crime Mapping and its Implications in the Real World. Polic. Soc. 2002, 12, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Systems Research Institute. ArcGIS Desktop: Release 10; Environmental Systems Research Institute: Redlands, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Getis, A.; Ord, J.K. The analysis of spatial association by use of distance statistics. In Perspectives on Spatial Data Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 127–145. [Google Scholar]
- Pettitt, A.N. A Non-Parametric Approach to the Change-Point Problem. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C (Appl. Stat.) 1979, 28, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, B.; Anderson, S.; Elvidge, C.; Ghosh, T.; Baugh, K.; Sutton, P. Aladdin’s Magic Lamp: Active Target Calibration of the DMSP OLS. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 12708–12722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Development and Reform Commission; Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development. The Development Plan for the Yangtze River Delta Megaregion (2015–2030). Available online: https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/xxgk/zcfb/tz/201606/W020190905517021091604.pdf (accessed on 11 January 2021).
- Wang, L.; Zhao, P. From dispersed to clustered: New trend of spatial restructuring in China’s metropolitan region of Yangtze River Delta. Habitat Int. 2018, 80, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Xing, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, R.S. Spatio-temporal analysis on built-up land expansion and population growth in the Yangtze River Delta Region, China: From a coordination perspective. Appl. Geogr. 2018, 96, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Hou, G. The spatiotemporal coupling characteristics of regional urbanization and its influencing factors: Taking the Yangtze River Delta as an example. Sustainability 2019, 11, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics. Anhui: Analysis and Thoughts on Economic Operation in Northern Anhui. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/ztjc/ztfx/fxbg/200407/t20040713_14765.html (accessed on 11 January 2021).
- Xu, S. On the Management of World Heritage in China—The Evaluation and Renewal of Huangshan Model. Tour. Trib. 2002, 6, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Che, Q. Urban Spatial Expansion Process, Pattern and Mechanism in Yangtze River Delta. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2011, 66, 446–456. [Google Scholar]
- Jenks, G.F. The data model concept in statistical mapping. Int. Yearb. Cartogr. 1967, 7, 186–190. [Google Scholar]
- Sutton, P.C.; Elvidge, C.; Ghosh, T. Estimation of Gross Domestic Product at Sub-National Scales using Nighttime Satellite Imagery. Int. J. Ecol. Econ. Stat. 2007, 8, 5–21. [Google Scholar]
- Angel, S.; Parent, J.; Civco, D.L.; Blei, A.; Potere, D. The dimensions of global urban expansion: Estimates and projections for all countries, 2000–2050. Prog. Plan. 2011, 75, 53–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.; Kihn, E.; Kroehl, H.W.; Davis, E. Mapping City Lights With Nighttime Data from the DMSP Operational Linescan System. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1997, 63, 727–734. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Nordhaus, W. A Test of the New VIIRS Lights Data Set: Population and Economic Output in Africa. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 4937–4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, N.B.; Faeth, S.H.; Golubiewski, N.E.; Redman, C.L.; Wu, J.; Bai, X.; Briggs, J.M. Global change and the ecology of cities. Science 2008, 319, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, G. Urbanization as a major driver of urban climate change. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2015, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Yang, X. Urbanization and heterogeneous surface warming in eastern China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 1363–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landsberg, H.E. The Urban Climate; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Oke, T.R. Boundary Layer Climates; Routledge: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Platt, R.H.; Rowntree, R.A.; Muick, P.C. The Ecological City: Preserving and Restoring Urban Biodiversity; University of Massachusetts Press: Amherst, MA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
| 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overall accuracy (%) | 97.56 | 97.29 | 95.49 |
| Kappa coefficient | 0.66 | 0.68 | 0.65 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, M.; Guo, S.; Guan, Y.; Cai, D.; Zhang, C.; Fraedrich, K.; Liao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Z. Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity Analysis of Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration: Evidence from Nighttime Light Data (2001–2019). Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13071235
Yu M, Guo S, Guan Y, Cai D, Zhang C, Fraedrich K, Liao Z, Zhang X, Tian Z. Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity Analysis of Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration: Evidence from Nighttime Light Data (2001–2019). Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(7):1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13071235
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Min, Shan Guo, Yanning Guan, Danlu Cai, Chunyan Zhang, Klaus Fraedrich, Zhouwei Liao, Xiaoxin Zhang, and Zhuangzhuang Tian. 2021. "Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity Analysis of Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration: Evidence from Nighttime Light Data (2001–2019)" Remote Sensing 13, no. 7: 1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13071235
APA StyleYu, M., Guo, S., Guan, Y., Cai, D., Zhang, C., Fraedrich, K., Liao, Z., Zhang, X., & Tian, Z. (2021). Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity Analysis of Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration: Evidence from Nighttime Light Data (2001–2019). Remote Sensing, 13(7), 1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13071235







