Capability of IMERG V6 Early, Late, and Final Precipitation Products for Monitoring Extreme Precipitation Events
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Areas
2.2. Datasets
2.2.1. Gauge-Based Precipitation Data
2.2.2. Satellite Precipitation Products
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Statistical Metrics
2.3.2. Categorical Metrics
3. Results
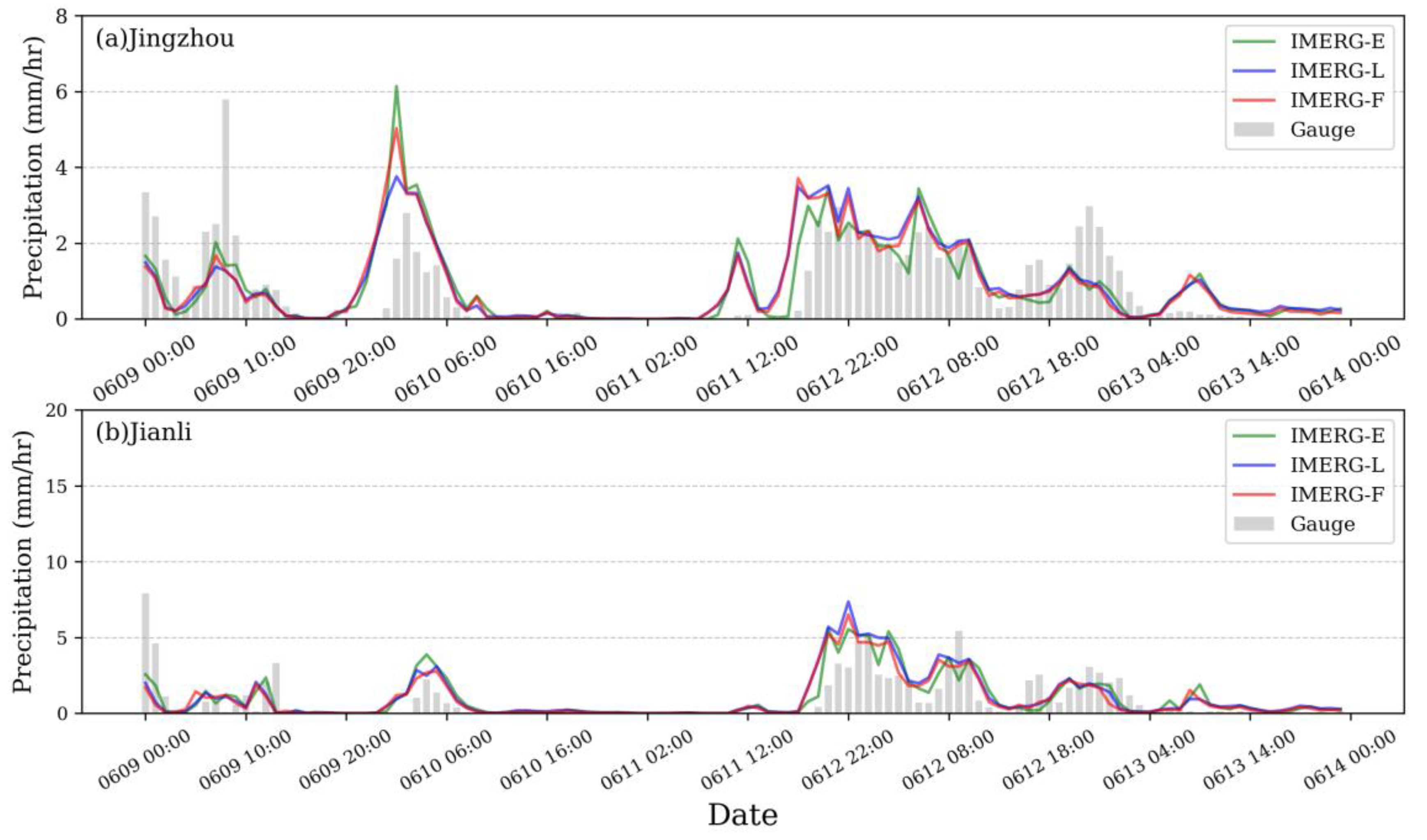
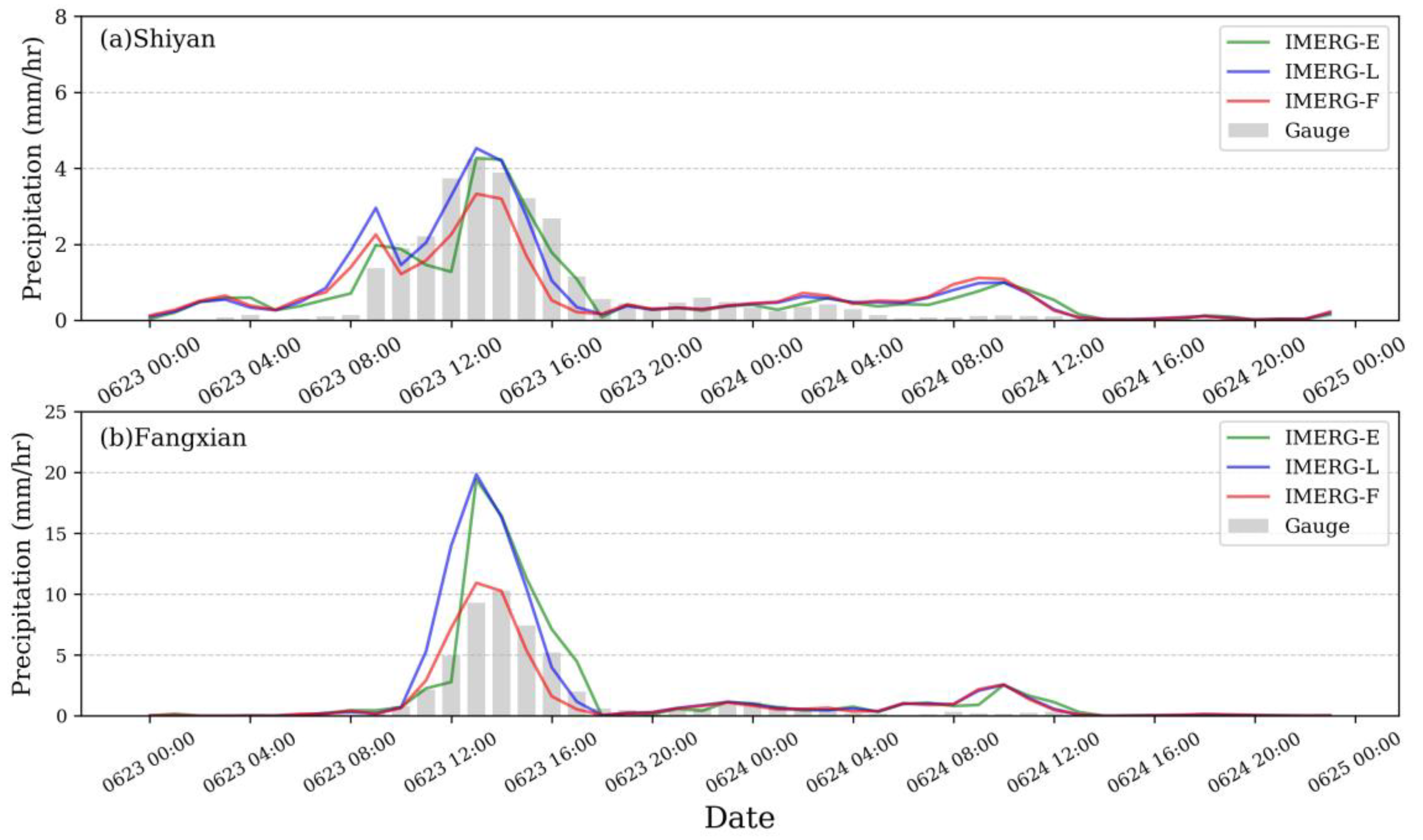
3.1. Spatial and Temporal Assessments
3.2. Statistical Assessments
3.3. Precipitation Detection Ability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akinbile, C.O.; Ogunmola, O.O.; Abolude, A.T.; Akande, S.O. Trends and spatial analysis of temperature and rainfall patterns on rice yields in nigeria. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2020, 21, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC 2014. Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. In Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Core Writing Team, Pachauri, R.K., Meyer, L.A., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; p. 151. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F. Temporal pattern analysis of local rainstorm events in china during the flood season based on time series clustering. Water 2020, 12, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buarque, D.C.; de Paiva, R.C.D.; Clarke, R.T.; Mendes, C.A.B. A comparison of amazon rainfall characteristics derived from trmm, cmorph and the brazilian national rain gauge network. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2011, 116, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Chen, S.; Bao, A.M.; Hu, J.J.; Yang, B.H.; Stepanian, P.M. Comprehensive evaluation of high-resolution satellite-based precipitation products over china. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, W.L.; Zhang, P.Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, X.D. Reconstructing satellite-based monthly precipitation over northeast china using machine learning algorithms. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Li, Z.; Xue, X.; Hu, Q.; Yong, B.; Hong, Y.J.W.S. A study of substitutability of trmm remote sensing precipitation for gauge-based observation in ganjiang river basin. Adv. Water Sci. 2015, 26, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.L.; Guo, B.; Ye, B.; Ye, Q.; Chen, H.N.; Ju, X.H.; Guo, J.Y.; Wang, Z.L. Systematical evaluation of gpm imerg and trmm 3b42v7 precipitation products in the huang-huai-hai plain, china. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantas, V.M.; Liu, Z.; Caro, C.; Pereira, A. Validation of trmm multi-satellite precipitation analysis (tmpa) products in the peruvian andes. Atmos. Res. 2015, 163, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, R.J.; Janowiak, J.E.; Arkin, P.A.; Xie, P. Cmorph: A method that produces global precipitation estimates from passive microwave and infrared data at high spatial and temporal resolution. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, K.-L.; Gao, X.; Sorooshian, S.; Gupta, H.V. Precipitation estimation from remotely sensed information using artificial neural networks. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1997, 36, 1176–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shige, S.; Yamamoto, T.; Tsukiyama, T.; Kida, S.; Ashiwake, H.; Kubota, T.; Seto, S.; Aonashi, K.; Okamoto, K. The gsmap precipitation retrieval algorithm for microwave sounders-part i: Over-ocean algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2009, 47, 3084–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guoqiang, T.; Wei, W.; Ziyue, Z.; Xiaolin, G.; Na, L.; Di, L.; Yang, H. An overview of the global precipitation measurement (gpm) mission and it’s latest development. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2015, 30, 607–615. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, F.; Zhang, L.M.; Win, K.W.W.; Ren, L.L.; Zhao, C.X.; Zhu, Y.H.; Jiang, S.H.; Liu, Y. Assessment of gpm and trmm multi-satellite precipitation products in streamflow simulations in a data-sparse mountainous watershed in myanmar. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.F.; Xu, Z.X.; Pang, B.; Liu, W.F.; Liu, J.T.; Du, L.G.; Wang, R. Assessment of satellite-derived precipitation products for the beijing region. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, W.; Wang, G.J.; Ali, G.; Hagan, D.F.T.; Bhatti, A.S.; Lou, D. Comparing multiple precipitation products against in-situ observations over different climate regions of pakistan. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.K.; Yong, B. Evaluation and hydrological utility of the latest gpm imerg v5 and gsmap v7 precipitation products over the tibetan plateau. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.Q.; Ma, Y.Z.; Long, D.; Zhong, L.Z.; Hong, Y. Evaluation of gpm day-1 imerg and tmpa version-7 legacy products over mainland china at multiple spatiotemporal scales. J. Hydrol. 2016, 533, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asong, Z.E.; Razavi, S.; Wheater, H.S.; Wong, J.S. Evaluation of integrated multisatellite retrievals for gpm (imerg) over southern canada against ground precipitation observations: A preliminary assessment. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 1033–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.L.; Ibrahim, A.; Duan, Z.; Cracknell, A.P.; Chaplot, V. Evaluation of six high-resolution satellite and ground-based precipitation products over malaysia. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 1504–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.Z.; Tang, G.Q.; Long, D.; Yong, B.; Zhong, L.Z.; Wan, W.; Hong, Y. Similarity and error intercomparison of the gpm and its predecessor-trmm multisatellite precipitation analysis using the best available hourly gauge network over the tibetan plateau. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, A.Y.; Kakar, R.K.; Neeck, S.; Azarbarzin, A.A.; Kummerow, C.D.; Kojima, M.; Oki, R.; Nakamura, K.; Iguchi, T. The global precipitation measurement mission. Bull. Amer. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 701–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.X.; Li, R.; He, J.X.; Wang, H.; Fan, X.G.; Yao, S.Y. Comparative evaluation of the gpm imerg early, late, and final hourly precipitation products using the cmpa data over sichuan basin of china mdpi. Water 2020, 12, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, A.; Garcia-Ortega, E.; Merino, A.; Sanchez, J.L.; Kummerow, C.; Tapiador, F.J. Assessment of imerg precipitation estimates over europe. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandridge, C.; Lakshmi, V.; Bolten, J.; Srinivasan, R. Evaluation of satellite-based rainfall estimates in the lower mekong river basin (southeast asia). Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.Y.; Lu, Y.; Tan, M.L.; Li, X.G.; Wang, G.Q.; He, R.M. Nine-year systematic evaluation of the gpm and trmm precipitation products in the shuaishui river basin in east-central china. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.S.; Xiao, L.S.; Min, C.; Chen, S.; Kulie, M.; Huang, C.Y.; Liang, Z.Q. Evaluation of latest gpm-era high-resolution satellite precipitation products during the may 2017 guangdong extreme rainfall event. Atmos. Res. 2019, 216, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Braithwaite, D.; Hsu, K.; Joyce, R.; Xie, P.; Yoo, S.-H. Nasa global precipitation measurement (gpm) integrated multi-satellite retrievals for gpm (imerg). Algorithm Theor. Basis Doc. 2015, 4, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Administration, C.M. Quality Control of Surface Meteorological Observational Data. Available online: http://www.cmastd.cn/ (accessed on 18 January 2021).
- Tan, J.; Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J. Imerg v06: Changes to the morphing algorithm. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2019, 36, 2471–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoglio, P.; Laio, F.; Balbo, S.; Boccardo, P.; Disabato, F. Improving an extreme rainfall detection system with gpm imerg data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Maggioni, V. Assessment of level-3 gridded global precipitation mission (gpm) products over oceans. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ren, D.; Nan, Z.; Wang, W.; Wu, X. Interpolated or satellite-based precipitation? Implications for hydrological modeling in a meso-scale mountainous watershed on the qinghai-tibet plateau. J. Hydrol. 2020, 583, 124629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.H.; Lue, H.S.; Crow, W.T.; Zhu, Y.H.; Wang, J.Q.; Su, J.B. Evaluation of satellite-based precipitation products from imerg v04a and v03d, cmorph and tmpa with gauged rainfall in three climatologic zones in china. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.R.; Gao, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.G.; Li, X. A downscaling-merging method for high-resolution daily precipitation estimation. J. Hydrol. 2020, 581, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Q.; Yong, B.; Gourley, J.J.; Liu, J.F.; Ren, L.L.; Wang, W.G.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, J.Y. Impact of the crucial geographic and climatic factors on the input source errors of gpm-based global satellite precipitation estimates. J. Hydrol. 2019, 575, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjad, M.; Yilmaz, M.T.; Yucel, I.; Yilmaz, K.K. Performance evaluation of satellite- and model-based precipitation products over varying climate and complex topography. J. Hydrol. 2020, 584, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, W.J.; Du, H.B.; Wu, Z.F.; Shen, X.J.; Ma, S. Decreasing precipitation occurs in daily extreme precipitation intervals across china in observations and model simulations. Clim. Dynam. 2020, 54, 2597–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hu, Q.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cui, T.; Cao, S. Monitoring and analysis of the extreme heavy rainfall process on june 10, 2017 in nanjing using five near real time satellite rainfall estimations. Plateau Meteorol. 2018, 37, 806–814. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.X.; Liu, G.D.; Chen, T.; Chen, Y.; Xia, C.C. Evaluation of gpm imerg precipitation products with the point rain gauge records over sichuan, china. Atmos. Res. 2020, 246, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.B.; Aguilar, E.; Sensoy, S.; Melkonyan, H.; Tagiyeva, U.; Ahmed, N.; Kutaladze, N.; Rahimzadeh, F.; Taghipour, A.; Hantosh, T.H.; et al. Trends in middle east climate extreme indices from 1950 to 2003. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2005, 110, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camarasa-Belmonte, A.M.; Butron, D. Estimation of flood risk thresholds in mediterranean areas using rainfall indicators: Case study of valencian region (spain). Nat. Hazards 2015, 78, 1243–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
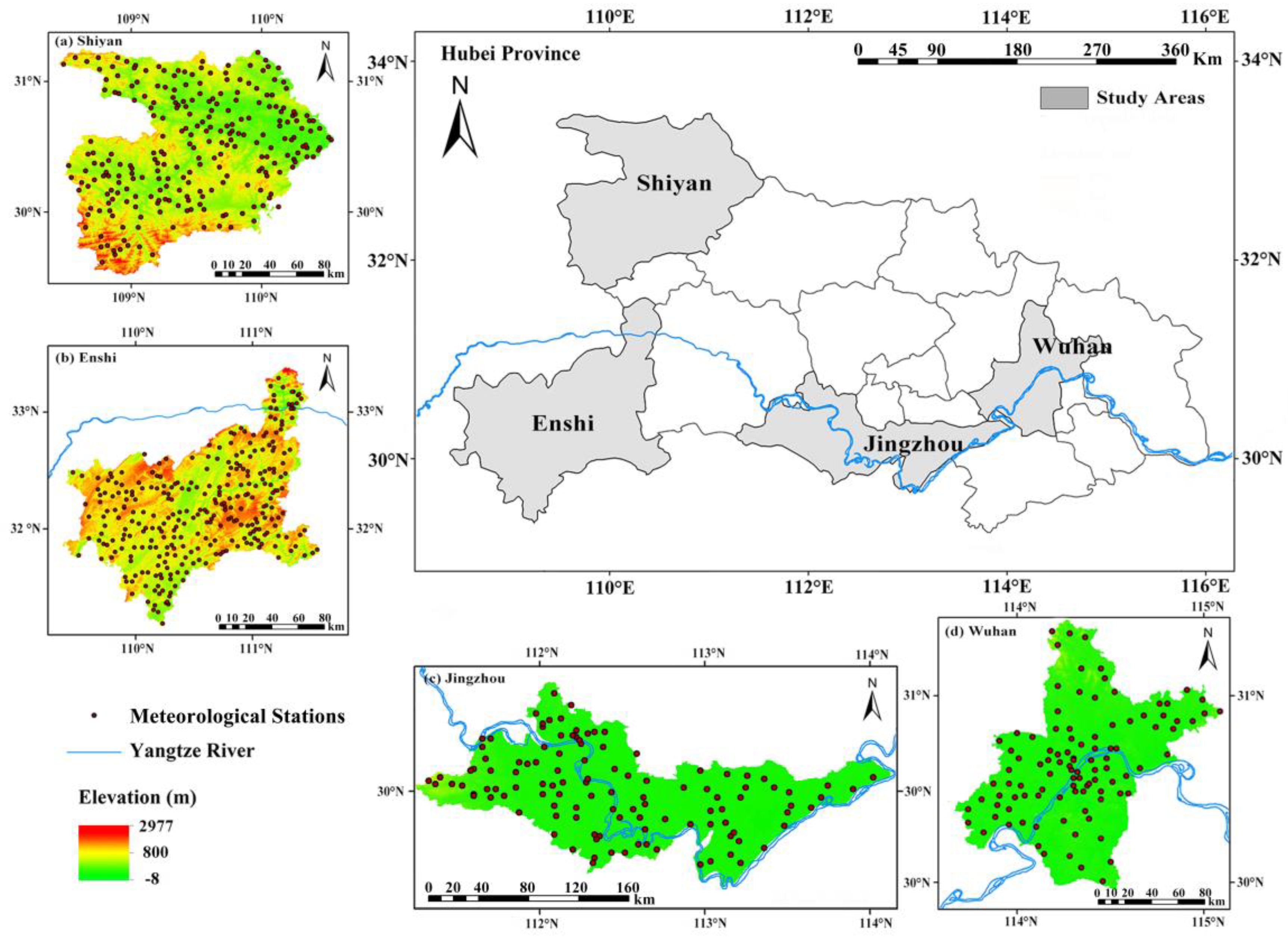
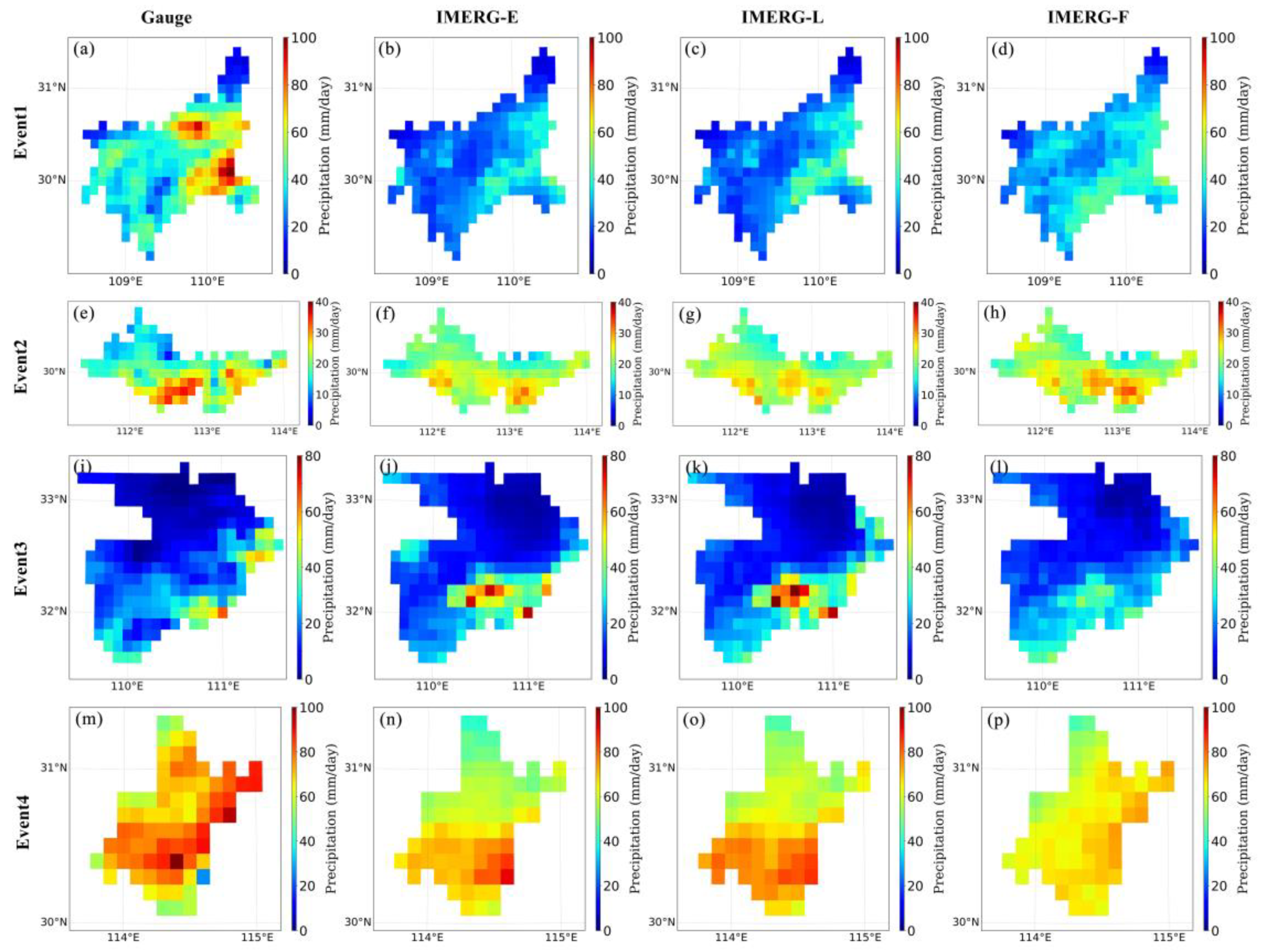

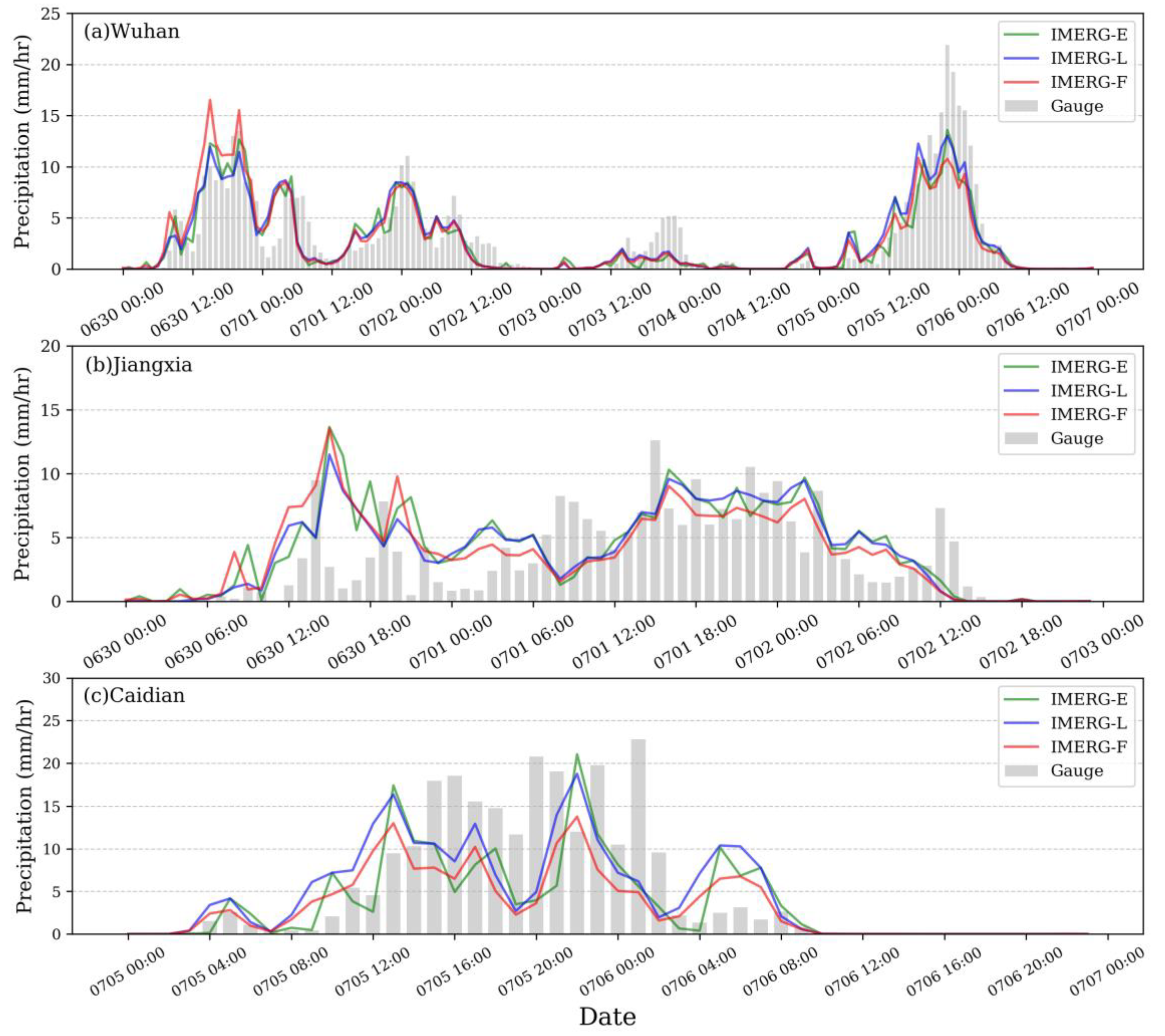
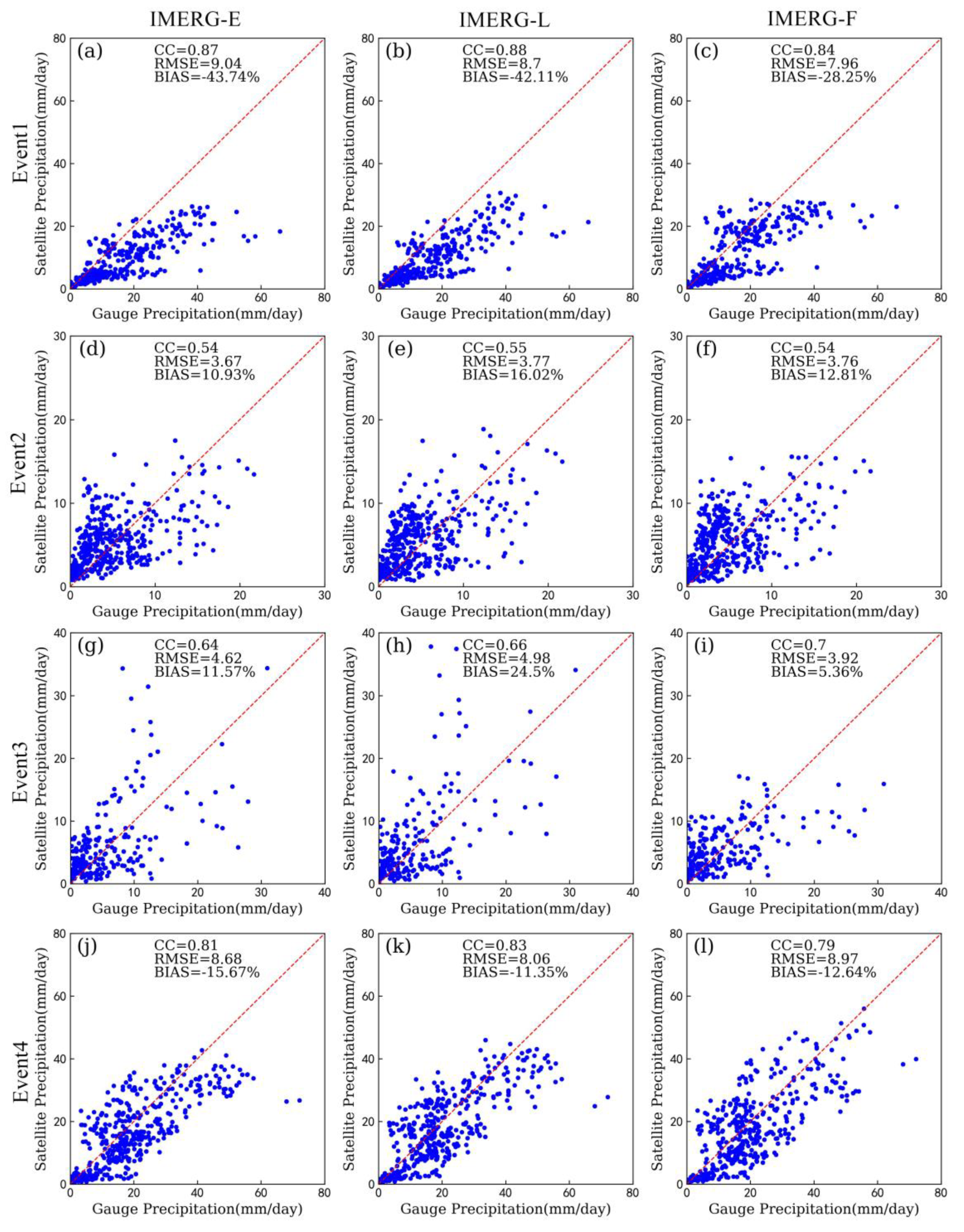

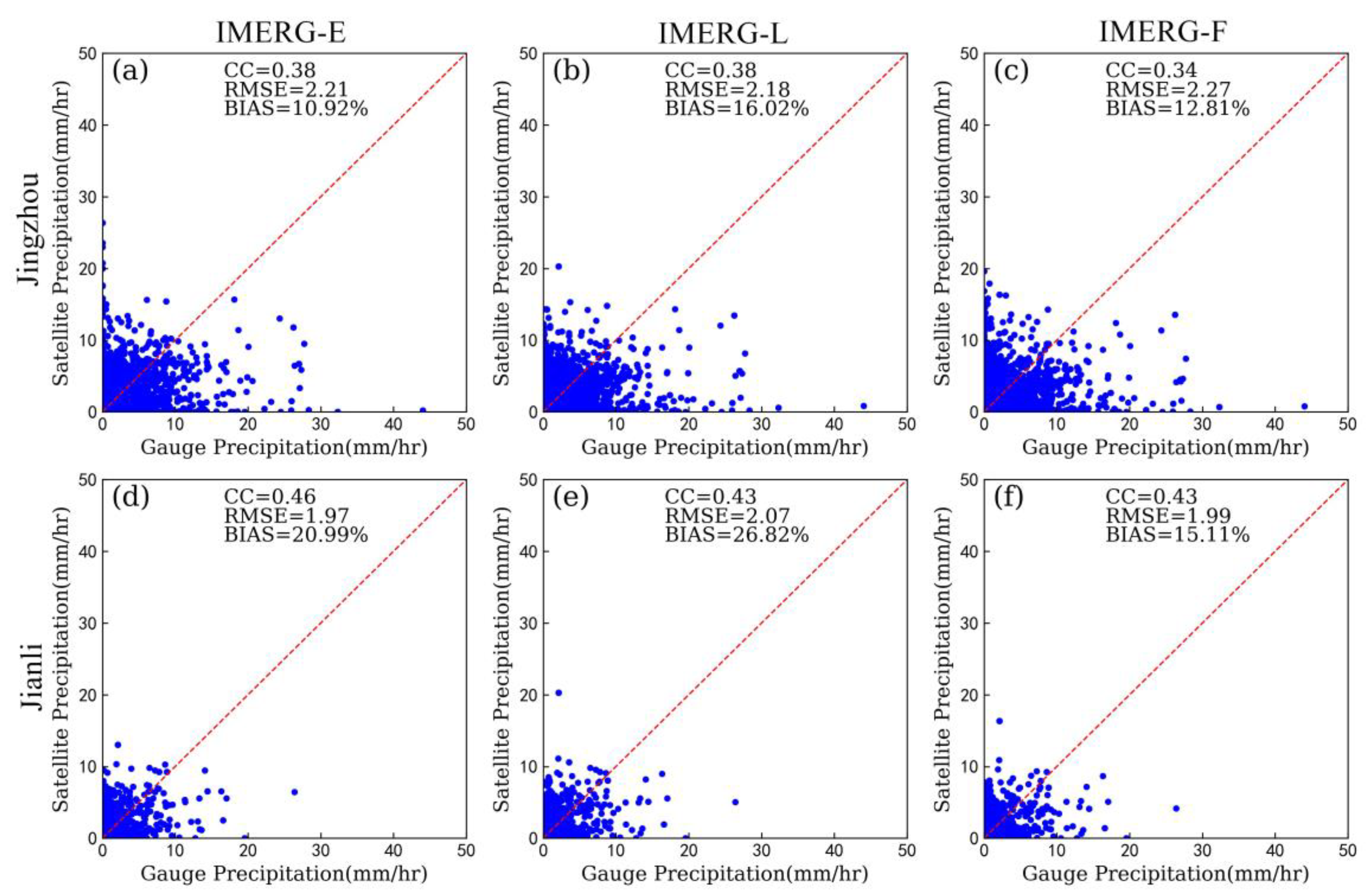

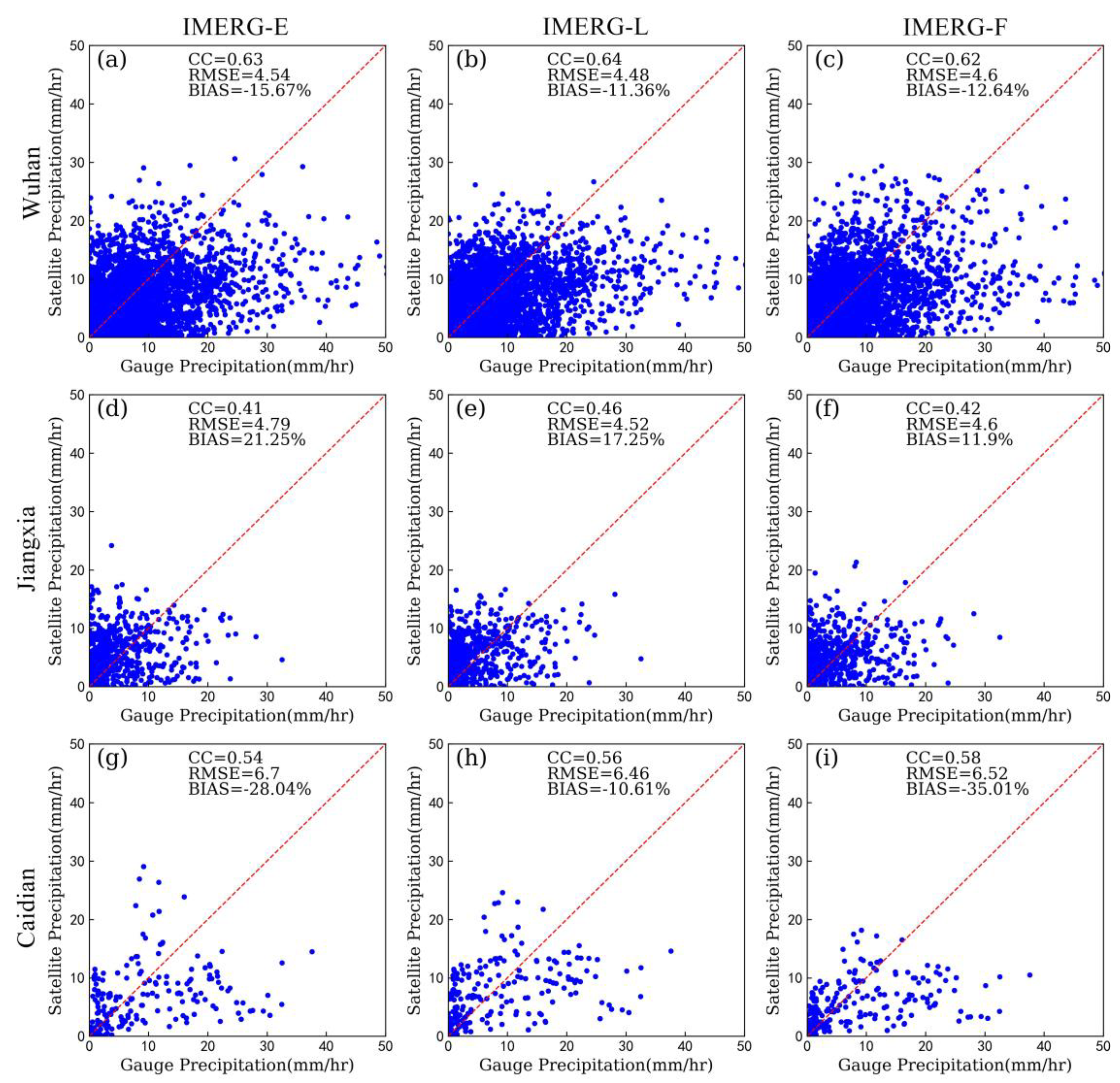
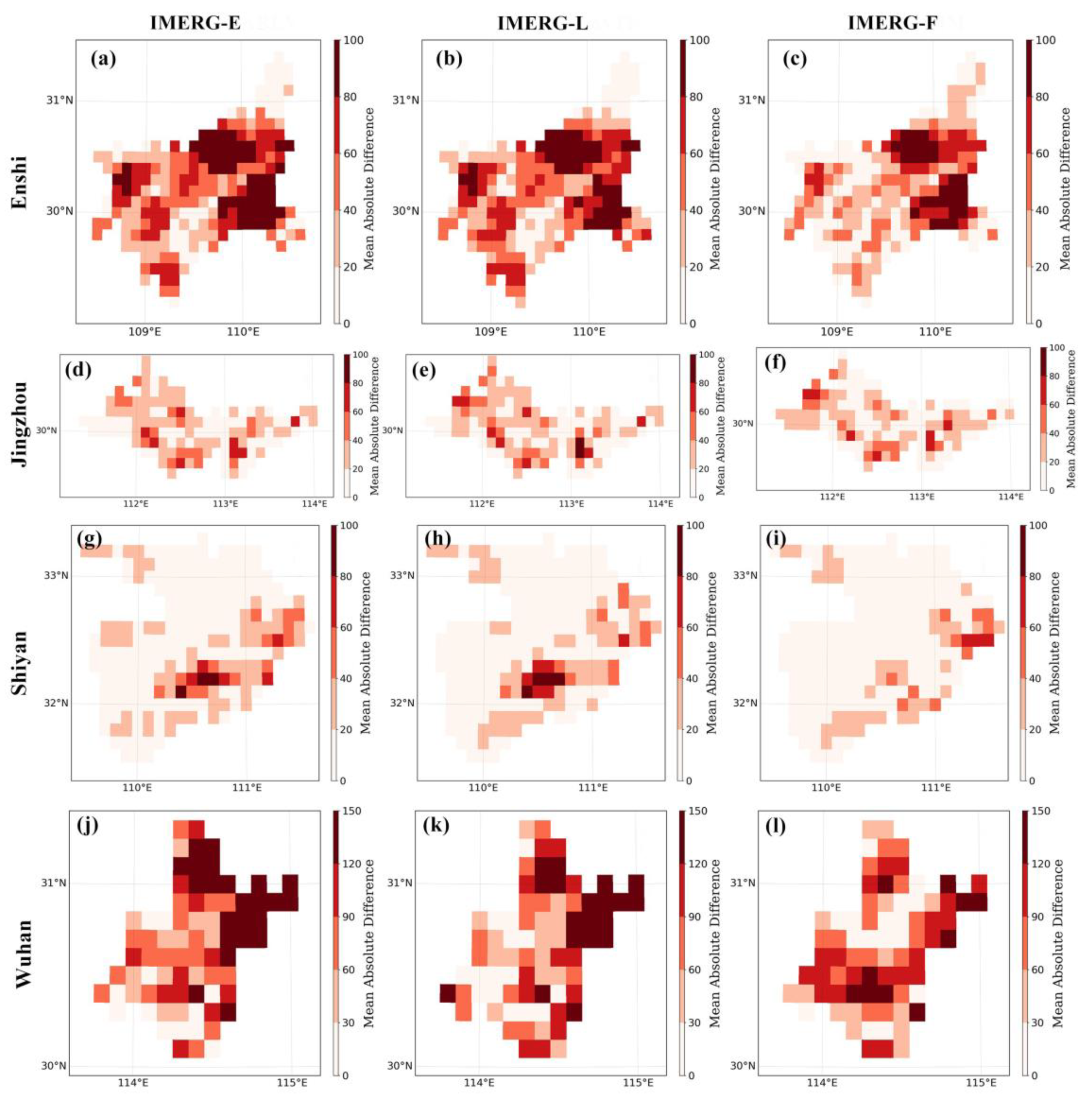

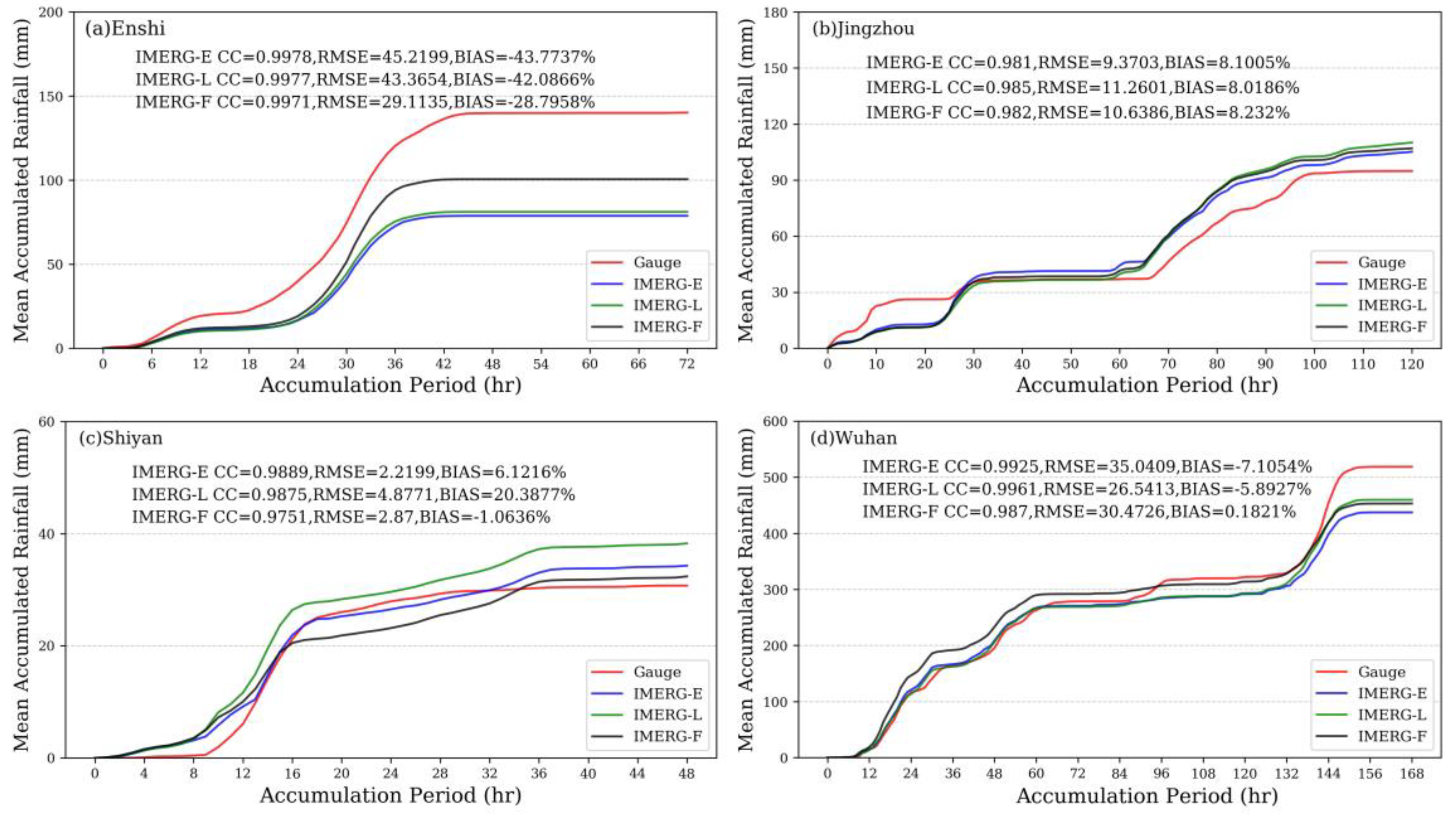
| Event | Region | Time | Longitude | Latitude | Number of Stations | Rainfall Centers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Event 1 | Enshi | 18–20 July 2016 | 109.08°–109.98°E | 29.83°–30.65°N | 260 | Hefeng, Jianshi |
| Event 2 | Jingzhou | 9–13 June 2017 | 111.25°–114.08°E | 29.43°–31.62°N | 114 | Jianli |
| Event 3 | Shiyan | 23–24 June 2016 | 109.48°–111.27°E | 31.50°–33.53°N | 260 | Fangxian |
| Event 4 | Wuhan | 30 June–6 July 2016 | 113.68°–115.08°E | 29.97°–31.37°N | 102 | Jiangxia, Caidian |
| IMERG Precipitation Estimates in Threshold Interval | IMERG Precipitation Estimates Not in Threshold Interval | |
|---|---|---|
| Gauges in Threshold Interval | Hit (H) | Missed (M) |
| Gauges Not in Threshold Interval | False (F) | — |
| Event | Region | Product | CC | RMSE (mm) | BIAS (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Event1 | Enshi | IMERG-E | 0.63 | 3.33 | −43.74 |
| IMERG-L | 0.61 | 3.38 | −42.11 | ||
| IMERG-F | 0.61 | 3.38 | −28.25 | ||
| Hefeng | IMERG-E | 0.52 | 4.77 | −51.19 | |
| IMERG-L | 0.55 | 4.65 | −48.51 | ||
| IMERG-F | 0.56 | 4.60 | −45.10 | ||
| Jianshi | IMERG-E | 0.75 | 3.43 | −47.39 | |
| IMERG-L | 0.74 | 3.46 | −44.45 | ||
| IMERG-F | 0.76 | 3.25 | −36.68 | ||
| Event2 | Jingzhou | IMERG-E | 0.38 | 2.21 | 10.92 |
| IMERG-L | 0.38 | 2.18 | 16.02 | ||
| IMERG-F | 0.34 | 2.27 | 12.81 | ||
| Jianli | IMERG-E | 0.46 | 1.97 | 20.99 | |
| IMERG-L | 0.43 | 2.07 | 26.82 | ||
| IMERG-F | 0.43 | 1.99 | 15.11 | ||
| Event3 | Shiyan | IMERG-E | 0.49 | 2.44 | 11.57 |
| IMERG-L | 0.47 | 2.68 | 24.50 | ||
| IMERG-F | 0.49 | 2.07 | 5.35 | ||
| Fangxian | IMERG-E | 0.63 | 4.10 | 60.27 | |
| IMERG-L | 0.62 | 4.37 | 75.23 | ||
| IMERG-F | 0.64 | 2.68 | 11.30 | ||
| Event4 | Wuhan | IMERG-E | 0.63 | 4.54 | −15.67 |
| IMERG-L | 0.64 | 4.48 | −11.36 | ||
| IMERG-F | 0.62 | 4.60 | −12.64 | ||
| Jiangxia | IMERG-E | 0.41 | 4.79 | 21.25 | |
| IMERG-L | 0.46 | 4.52 | 17.25 | ||
| IMERG-F | 0.42 | 4.60 | 11.90 | ||
| Caidian | IMERG-E | 0.54 | 6.70 | −28.04 | |
| IMERG-L | 0.56 | 6.46 | −10.61 | ||
| IMERG-F | 0.58 | 6.52 | −35.01 |
| Metrics | Precipitation Intensity | IMERG-E | IMERG-L | IMERG-F |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| POD | Light rain | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.75 |
| Moderate rain | 0.62 | 0.61 | 0.62 | |
| Heavy rain | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.24 | |
| Rainstorm | 0.55 | 0.51 | 0.76 | |
| CSI | Light rain | 0.33 | 0.29 | 0.35 |
| Moderate rain | 0.21 | 0.22 | 0.28 | |
| Heavy rain | 0.10 | 0.12 | 0.18 | |
| Rainstorm | 0.52 | 0.47 | 0.68 | |
| FAR | Light rain | 0.62 | 0.67 | 0.60 |
| Moderate rain | 0.76 | 0.75 | 0.67 | |
| Heavy rain | 0.80 | 0.78 | 0.60 | |
| Rainstorm | 0.10 | 0.12 | 0.12 |
| Metrics | Precipitation Intensity | IMERG-E | IMERG-L | IMERG-F |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| POD | Light Rain | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.52 |
| Moderate Rain | 0.54 | 0.34 | 0.39 | |
| Heavy Rain | 0.34 | 0.37 | 0.37 | |
| Rainstorm | 0.23 | 0.30 | 0.21 | |
| CSI | Light Rain | 0.41 | 0.38 | 0.45 |
| Moderate Rain | 0.31 | 0.21 | 0.24 | |
| Heavy Rain | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.15 | |
| Rainstorm | 0.20 | 0.23 | 0.18 | |
| FAR | Light Rain | 0.21 | 0.31 | 0.24 |
| Moderate Rain | 0.57 | 0.67 | 0.61 | |
| Heavy Rain | 0.78 | 0.80 | 0.80 | |
| Rainstorm | 0.42 | 0.48 | 0.47 |
| Metrics | Precipitation Intensity | IMERG-E | IMERG-L | IMERG-F |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| POD | Light rain | 0.65 | 0.61 | 0.57 |
| Moderate rain | 0.36 | 0.32 | 0.49 | |
| Heavy rain | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.38 | |
| Rainstorm | 0.49 | 0.62 | 0.14 | |
| CSI | Light rain | 0.54 | 0.50 | 0.53 |
| Moderate rain | 0.17 | 0.15 | 0.22 | |
| Heavy rain | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.20 | |
| Rainstorm | 0.27 | 0.33 | 0.11 | |
| FAR | Light rain | 0.23 | 0.25 | 0.14 |
| Moderate rain | 0.76 | 0.79 | 0.72 | |
| Heavy rain | 0.72 | 0.72 | 0.70 | |
| Rainstorm | 0.62 | 0.58 | 0.62 |
| Metrics | Precipitation Intensity | IMERG-E | IMERG-L | IMERG-F |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| POD | Light Rain | 0.79 | 0.93 | 0.99 |
| Moderate Rain | 0.22 | 0.30 | 0.16 | |
| Heavy Rain | 0.14 | 0.19 | 0.12 | |
| Rainstorm | 0.79 | 0.81 | 0.76 | |
| CSI | Light Rain | 0.42 | 0.55 | 0.54 |
| Moderate Rain | 0.14 | 0.21 | 0.12 | |
| Heavy Rain | 0.07 | 0.10 | 0.05 | |
| Rainstorm | 0.70 | 0.72 | 0.68 | |
| FAR | Light Rain | 0.52 | 0.43 | 0.46 |
| Moderate Rain | 0.73 | 0.59 | 0.72 | |
| Heavy Rain | 0.87 | 0.82 | 0.91 | |
| Rainstorm | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.13 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, C.; Gao, W.; Hu, J.; Du, L.; Du, L. Capability of IMERG V6 Early, Late, and Final Precipitation Products for Monitoring Extreme Precipitation Events. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 689. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13040689
Zhou C, Gao W, Hu J, Du L, Du L. Capability of IMERG V6 Early, Late, and Final Precipitation Products for Monitoring Extreme Precipitation Events. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(4):689. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13040689
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Chenguang, Wei Gao, Jiarui Hu, Liangmin Du, and Lin Du. 2021. "Capability of IMERG V6 Early, Late, and Final Precipitation Products for Monitoring Extreme Precipitation Events" Remote Sensing 13, no. 4: 689. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13040689
APA StyleZhou, C., Gao, W., Hu, J., Du, L., & Du, L. (2021). Capability of IMERG V6 Early, Late, and Final Precipitation Products for Monitoring Extreme Precipitation Events. Remote Sensing, 13(4), 689. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13040689







