Increasing Shape Bias to Improve the Precision of Center Pivot Irrigation System Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.3. Training Data
2.4. Methods
2.4.1. Edge Image Sample Data Augmentation to Increase Shape Bias
2.4.2. PVANET
2.4.3. YOLOv4
2.4.4. Training of PVANET and YOLOv4
2.4.5. Evaluation
3. Results
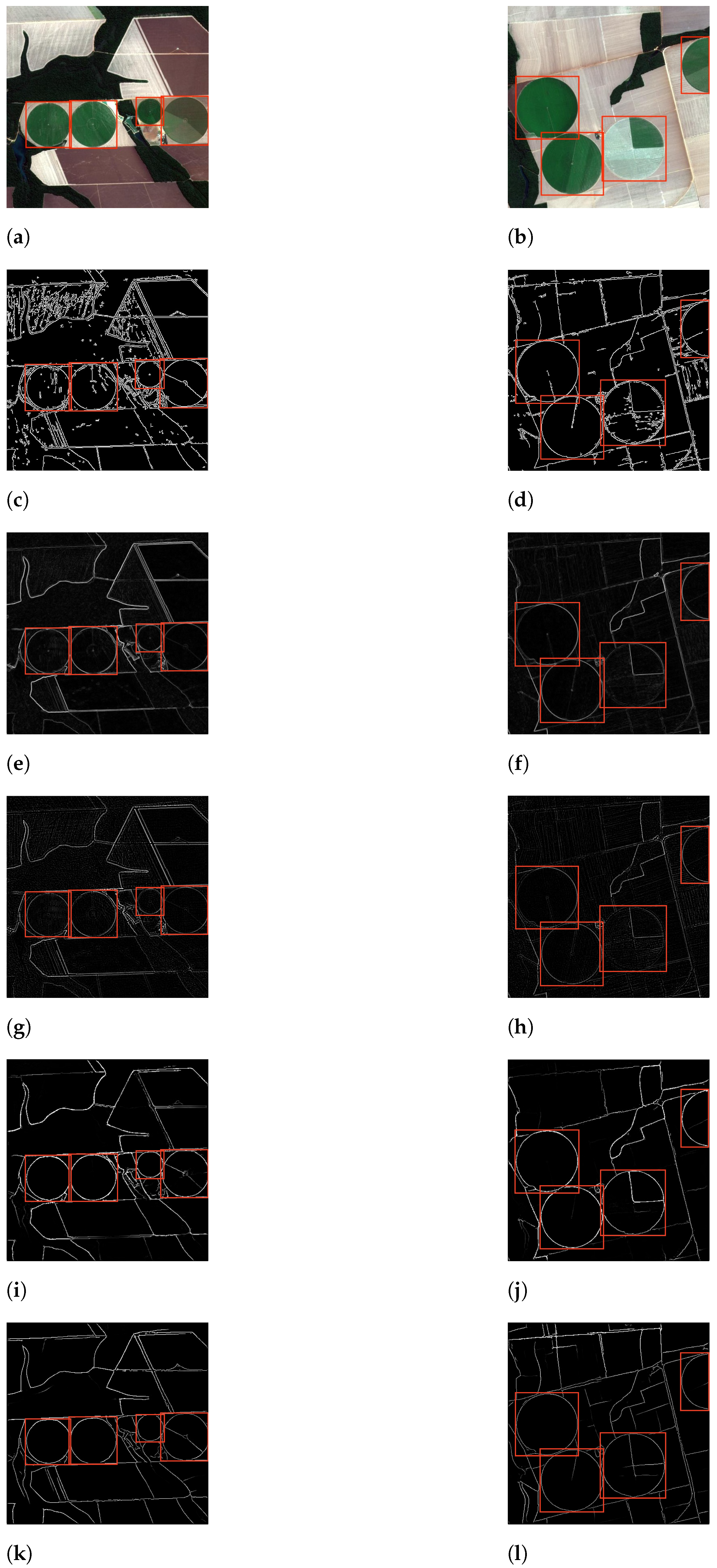
3.1. Edge Image Samples Extracted Using Canny Edge Detector in the Training Data
3.2. More Edge Image Samples in the Training Data
3.3. Edge Image Samples Extracted Using Different Methods in the Training Data
3.4. Only Edge Image Samples in the Training Data
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arvor, D.; Meirelles, M.; Dubreuil, V.; Bégué, A.; Shimabukuro, Y.E. Analyzing the agricultural transition in Mato Grosso, Brazil, using satellite-derived indices. Appl. Geogr. 2012, 32, 702–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rundquist, D.C.; Hoffman, R.O.; Carlson, M.P.; Cook, A.E. The Nebraska Center-Pivot Inventory: An Example of Operational Satellite Remote Sensing on a Long-Term Basis. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1989, 55, 587–590. [Google Scholar]
- Duda, R.O.; Hart, P.E. Use of the Hough transformation to detect lines and curves in pictures. Commun. ACM 1972, 15, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q.V. EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks. arXiv 2020, arXiv:1905.11946. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLOv3: An Incremental Improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Shelhamer, E.; Long, J.; Darrell, T. Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1605.06211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takikawa, T.; Acuna, D.; Jampani, V.; Fidler, S. Gated-SCNN: Gated Shape CNNs for Semantic Segmentation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.05740. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Yue, P.; Di, L.; Wu, Z. Automatic Identification of Center Pivot Irrigation Systems from Landsat Images Using Convolutional Neural Networks. Agriculture 2018, 8, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraiva, M.; Protas, É.; Salgado, M.; Souza, C. Automatic Mapping of Center Pivot Irrigation Systems from Satellite Images Using Deep Learning. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1505.04597. [Google Scholar]
- De Albuquerque, A.O.; de Carvalho Júnior, O.A.; Carvalho, O.L.F.D.; de Bem, P.P.; Ferreira, P.H.G.; de Moura, R.D.S.; Silva, C.R.; Trancoso Gomes, R.A.; Fontes Guimarães, R. Deep Semantic Segmentation of Center Pivot Irrigation Systems from Remotely Sensed Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.W.; Arvor, D.; Corpetti, T.; Tang, P. PVANET-Hough: Detection and location of center pivot irrigation systems from sentinel-2 images. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2020, V-3-2020, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, N.; Lu, H.; Erlikhman, G.; Kellman, P.J. Deep convolutional networks do not classify based on global object shape. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2018, 14, e1006613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geirhos, R.; Rubisch, P.; Michaelis, C.; Bethge, M.; Wichmann, F.A.; Brendel, W. ImageNet-trained CNNs are biased towards texture; increasing shape bias improves accuracy and robustness. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1811.12231. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.H.; Hong, S.; Roh, B.; Cheon, Y.; Park, M. PVANET: Deep but Lightweight Neural Networks for Real-time Object Detection. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1608.08021. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv4: Optimal Speed and Accuracy of Object Detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar]
- Arvor, D.; Jonathan, M.; Meirelles, M.S.P.; Dubreuil, V.; Durieux, L. Classification of MODIS EVI time series for crop mapping in the state of Mato Grosso, Brazil. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 7847–7871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catálogo de Metadados da ANA. Available online: https://metadados.snirh.gov.br/geonetwork/srv/por/catalog.search#/metadata/e2d38e3f-5e62-41ad-87ab-990490841073 (accessed on 2 January 2021).
- Xie, S.; Tu, Z. Holistically-Nested Edge Detection. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, X.; Riba, E.; Sappa, A. Dense Extreme Inception Network: Towards a Robust CNN Model for Edge Detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Snowmass Village, CO, USA, 1–5 March 2020; pp. 1912–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, W.; Sohn, K.; Almeida, D.; Lee, H. Understanding and improving convolutional neural networks via concatenated rectified linear units. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning, New York, NY, USA, 20–22 June 2016; pp. 2217–2225. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going Deeper with Convolutions. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.4842. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, T.; Yao, A.; Chen, Y.; Sun, F. HyperNet: Towards Accurate Region Proposal Generation and Joint Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, S.; Zitnick, C.L.; Bala, K.; Girshick, R. Inside-Outside Net: Detecting Objects in Context with Skip Pooling and Recurrent Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2874–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y.M.; Yeh, I.H.; Wu, Y.H.; Chen, P.Y.; Hsieh, J.W. CSPNet: A New Backbone that can Enhance Learning Capability of CNN. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.11929. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Spatial Pyramid Pooling in Deep Convolutional Networks for Visual Recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1904–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, M.; Nahavandi, S. Multi-Residual Networks: Improving the Speed and Accuracy of Residual Networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1609.05672. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.06521. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, P.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Ye, R.; Ren, D. Distance-IoU Loss: Faster and Better Learning for Bounding Box Regression. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.08287. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, S.; Han, D.; Chun, S.; Oh, S.J.; Yoo, Y.; Choe, J. CutMix: Regularization Strategy to Train Strong Classifiers With Localizable Features. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6022–6031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.; Chien, J.; Chen, H. Self Adversarial Training for Human Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2018 Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA ASC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 12–15 November 2018; pp. 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the Inception Architecture for Computer Vision. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiasi, G.; Lin, T.Y.; Le, Q.V. DropBlock: A regularization method for convolutional networks. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.12890. [Google Scholar]
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. SGDR: Stochastic Gradient Descent with Warm Restarts. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1608.03983. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Li, F.-F. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Shelhamer, E.; Donahue, J.; Karayev, S.; Long, J.; Girshick, R.; Guadarrama, S.; Darrell, T. Caffe: Convolutional Architecture for Fast Feature Embedding. In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia (MM ’14), Orlando, FL, USA, 3–7 November 2014; ACM Press: Orlando, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darknet: Open Source Neural Networks in C. Available online: https://pjreddie.com/darknet/ (accessed on 2 January 2021).

| Detected Candidate Pivots | Correctly Detected Pivots | Precision | Recall | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVANET | 846 | 619 | 73.2% | 96.6% |
| PVANET-Hough | 737 | 614 | 83.3% | 95.8% |
| Shape-Biased-PVANET | 706 | 627 | 88.8% | 97.8% |
| YOLOv4 | 707 | 623 | 88.1% | 97.2% |
| YOLOv4-Hough | 682 | 614 | 90.0% | 95.8% |
| Shape-Biased-YOLOv4 | 680 | 624 | 91.8% | 97.3% |
| Detected Candidate Pivots | Correctly Detected Pivots | Precision | Recall | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVANET | 846 | 619 | 73.2% | 96.6% |
| Shape-Biased-PVANET | 706 | 627 | 88.8% | 97.8% |
| Shape-Biased-PVANET-2 | 709 | 629 | 88.7% | 98.1% |
| Shape-Biased-PVANET-3 | 660 | 632 | 95.8% | 98.6% |
| Shape-Biased-PVANET-4 | 699 | 632 | 90.4% | 98.6% |
| Shape-Biased-PVANET-5 | 712 | 626 | 87.9% | 97.7% |
| YOLOv4 | 707 | 623 | 88.1% | 97.2% |
| Shape-Biased-YOLOv4 | 680 | 624 | 91.8% | 97.3% |
| Shape-Biased-YOLOv4-2 | 677 | 629 | 92.9% | 98.1% |
| Shape-Biased-YOLOv4-3 | 675 | 630 | 93.3% | 98.3% |
| Shape-Biased-YOLOv4-4 | 673 | 632 | 93.9% | 98.6% |
| Shape-Biased-YOLOv4-5 | 678 | 625 | 92.2% | 97.5% |
| Detected Candidate Pivots | Correctly Detected Pivots | Precision | Recall | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVANET | 846 | 619 | 73.2% | 96.6% |
| Shape-Biased-PVANET-Canny | 706 | 627 | 88.8% | 97.8% |
| Shape-Biased-PVANET-Sobel | 690 | 630 | 91.3% | 98.3% |
| Shape-Biased-PVANET-Laplacian | 692 | 627 | 90.6% | 97.8% |
| Shape-Biased-PVANET-HED | 692 | 629 | 90.9% | 98.1% |
| Shape-Biased-PVANET-DexiNed | 680 | 628 | 92.4% | 98.0% |
| YOLOv4 | 707 | 623 | 88.1% | 97.2% |
| Shape-Biased-YOLOv4-Canny | 680 | 624 | 91.8% | 97.3% |
| Shape-Biased-YOLOv4-Sobel | 665 | 622 | 93.5% | 97.0% |
| Shape-Biased-YOLOv4-Laplacian | 683 | 629 | 92.1% | 98.1% |
| Shape-Biased-YOLOv4-HED | 664 | 627 | 94.4% | 97.8% |
| Shape-Biased-YOLOv4-DexiNed | 679 | 626 | 92.2% | 97.7% |
| Detected Candidate Pivots | Correctly Detected Pivots | Precision | Recall | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVANET | 846 | 619 | 73.2% | 96.6% |
| Shape-Biased-PVANET | 706 | 627 | 88.8% | 97.8% |
| PVANET-edge | 661 | 568 | 85.9% | 88.6% |
| PVANET-edge-2 | 630 | 581 | 92.2% | 90.6% |
| PVANET-edge-3 | 658 | 580 | 88.1% | 90.5% |
| YOLOv4 | 707 | 623 | 88.1% | 97.2% |
| Shape-Biased-YOLOv4 | 680 | 624 | 91.8% | 97.3% |
| YOLOv4-edge | 728 | 572 | 78.6% | 89.2% |
| YOLOv4-edge-2 | 655 | 585 | 89.3% | 91.3% |
| YOLOv4-edge-3 | 664 | 582 | 87.7% | 90.8% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Tang, P. Increasing Shape Bias to Improve the Precision of Center Pivot Irrigation System Detection. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 612. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13040612
Tang J, Zhang Z, Zhao L, Tang P. Increasing Shape Bias to Improve the Precision of Center Pivot Irrigation System Detection. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(4):612. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13040612
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Jiwen, Zheng Zhang, Lijun Zhao, and Ping Tang. 2021. "Increasing Shape Bias to Improve the Precision of Center Pivot Irrigation System Detection" Remote Sensing 13, no. 4: 612. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13040612
APA StyleTang, J., Zhang, Z., Zhao, L., & Tang, P. (2021). Increasing Shape Bias to Improve the Precision of Center Pivot Irrigation System Detection. Remote Sensing, 13(4), 612. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13040612







