Point Cloud Inversion: A Novel Approach for the Localization of Trees in Forests from TLS Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
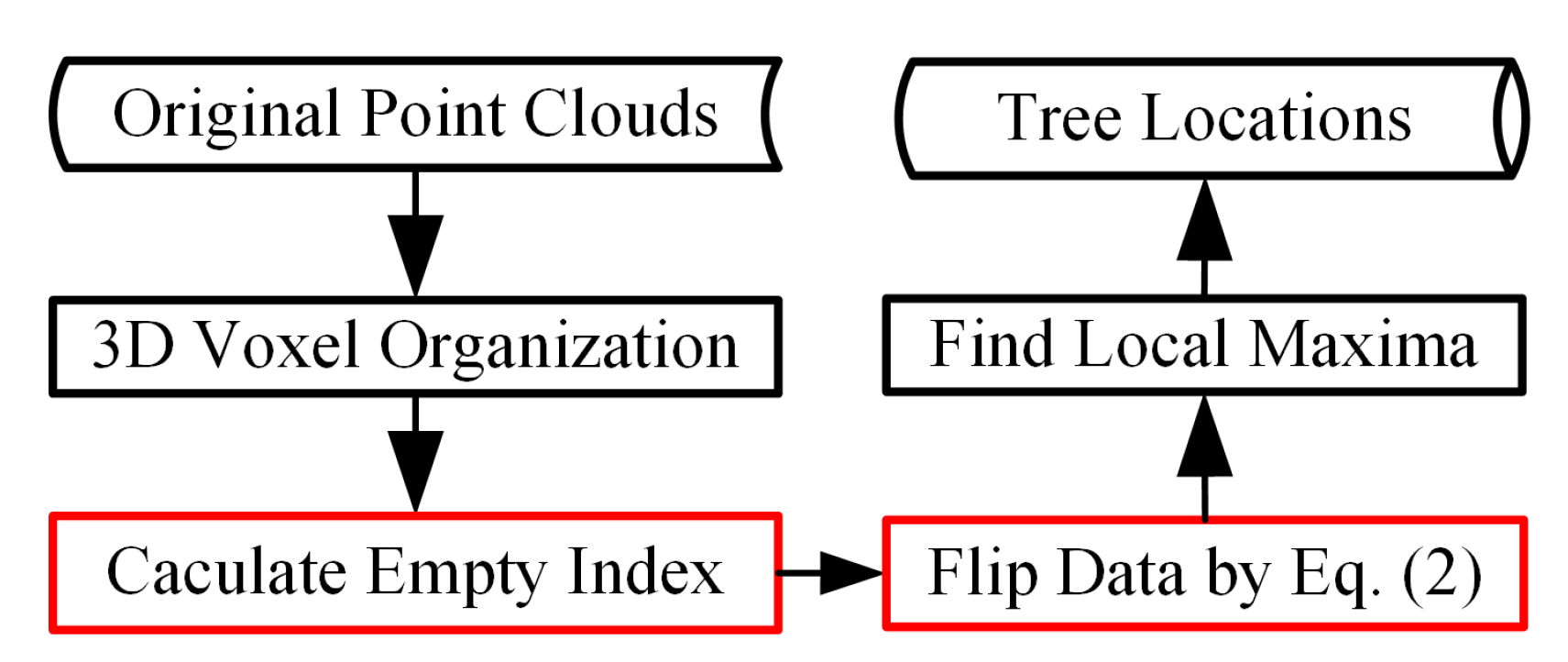
2. Methods
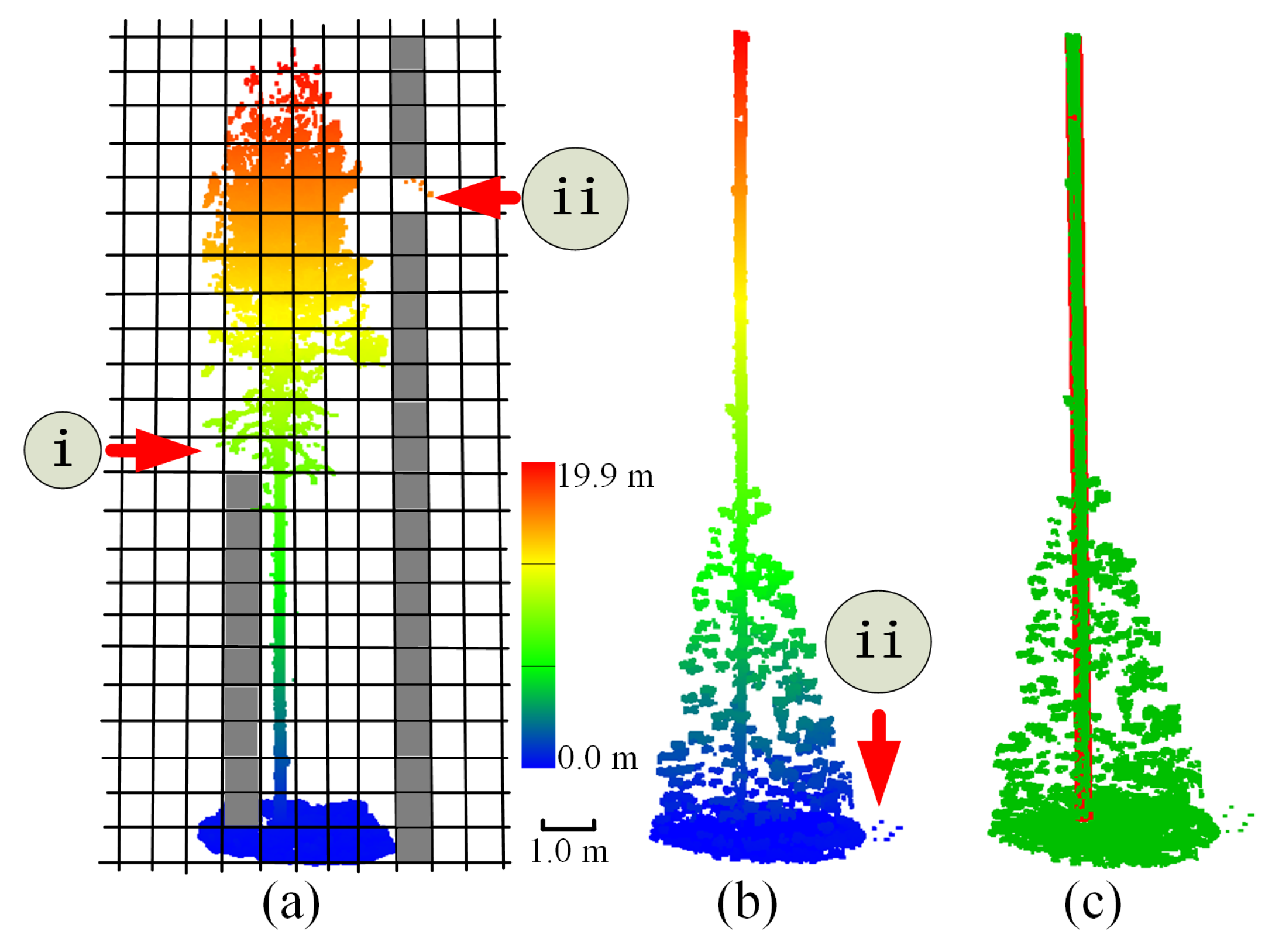
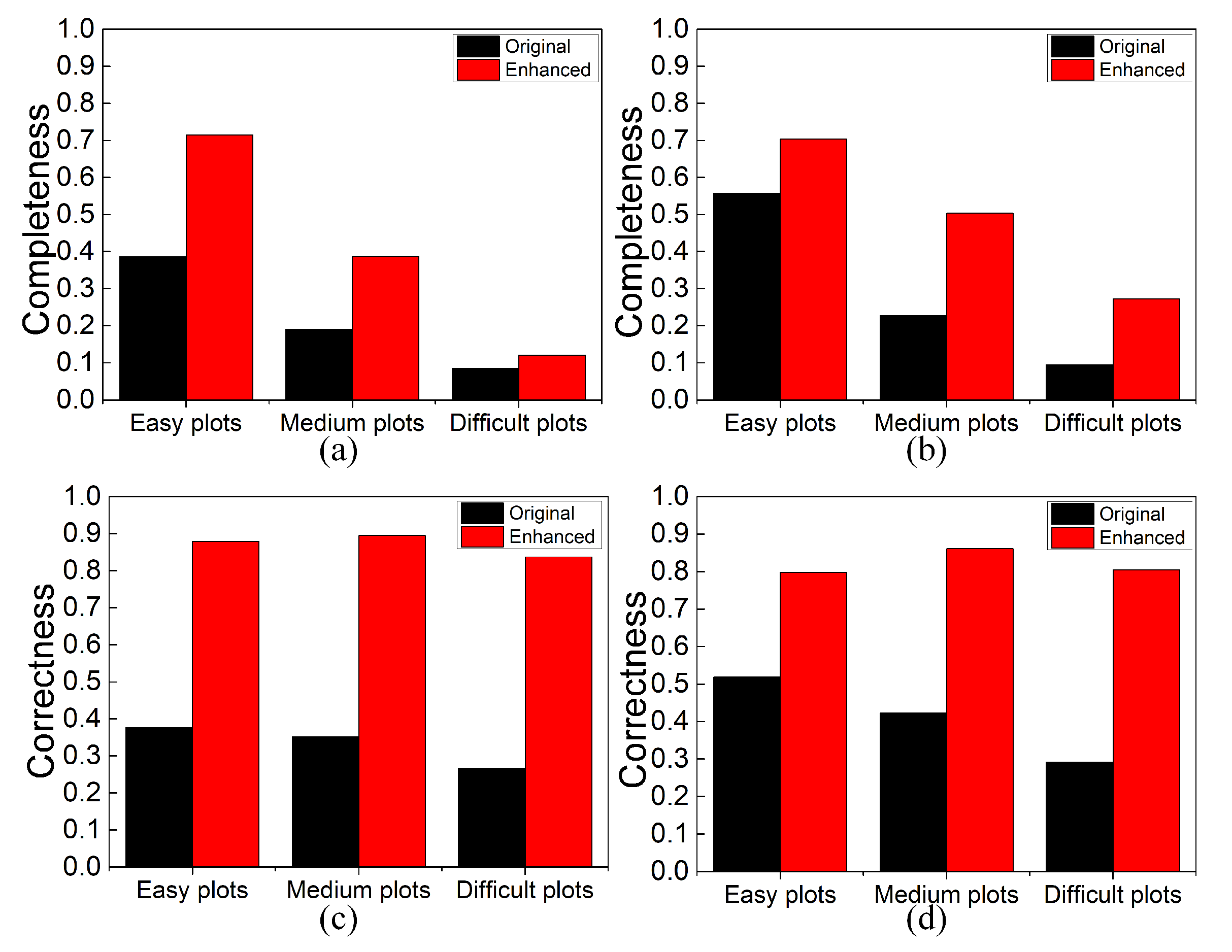
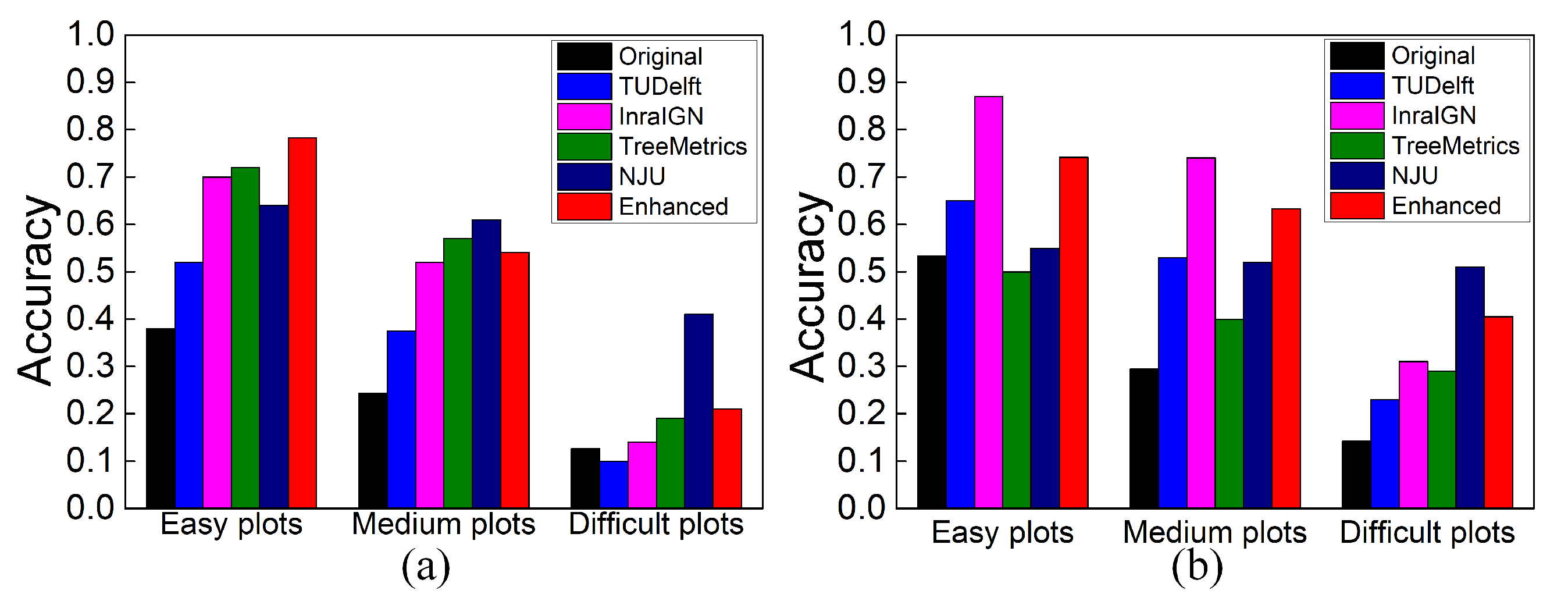
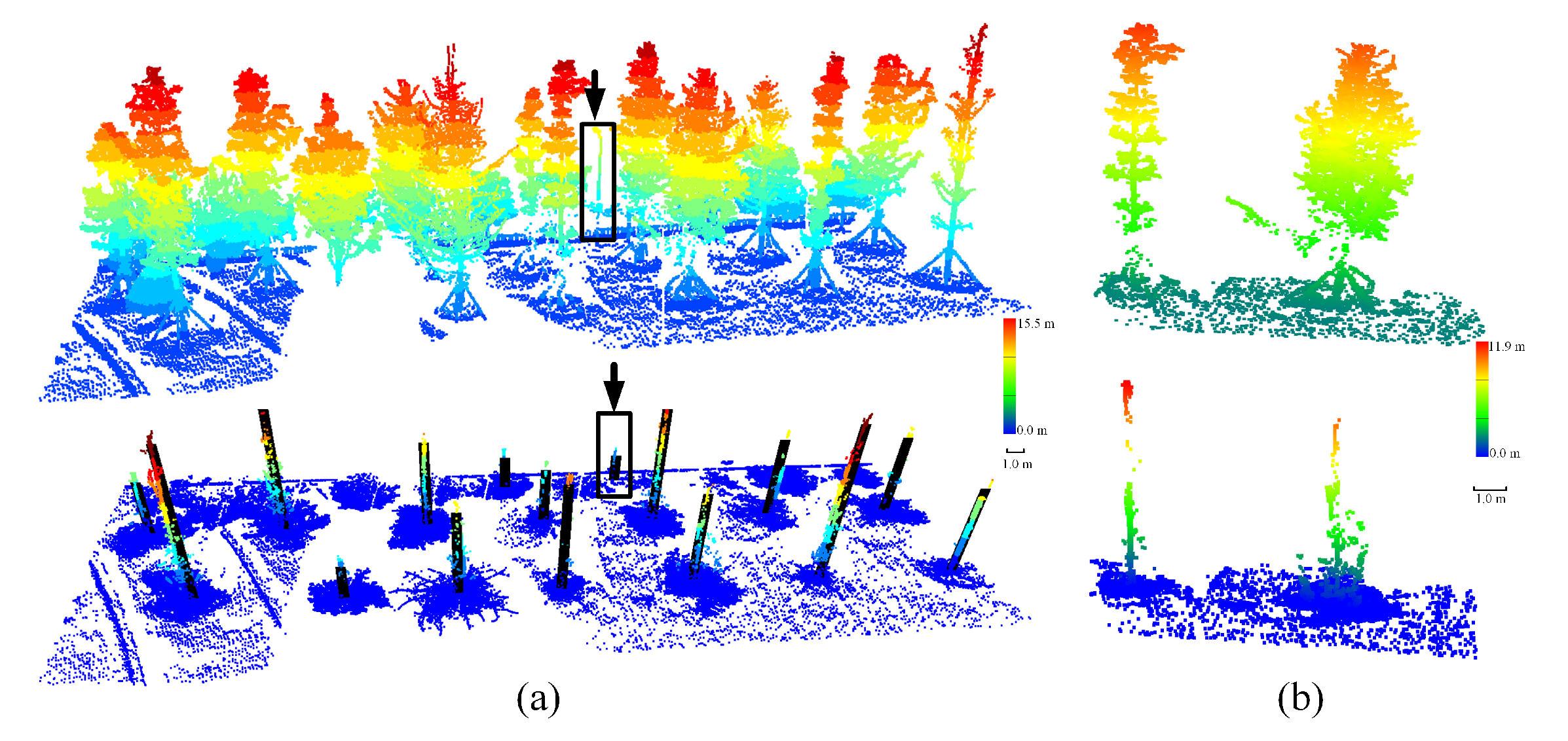
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3D | Three-Dimensional |
| ALS | Airborne Laser Scanning |
| DBH | Diameter at Breast Height |
| DBSCAN | Density-Based Spatial Clustering and Application with Noise |
| PCI | Point Cloud Inversion |
| SS | Single Scans |
| TLS | Terrestrial Laser Scanning |
| MS | Multi-Scans |
References
- Wang, D. Unsupervised semantic and instance segmentation of forest point clouds. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 165, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wan, P.; Wang, T.; Cai, S.; Chen, Y.; Jin, X.; Yan, G. A novel approach for the detection of standing tree stems from plot-level terrestrial laser scanning data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Guo, Q.; Jakubowski, M.K.; Kelly, M. A new method for segmenting individual trees from the lidar point cloud. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2012, 78, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Guo, Q.; Li, W.; Flanagan, J. A bottom-up approach to segment individual deciduous trees using leaf-off lidar point cloud data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 94, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarinen, N.; Kankare, V.; Vastaranta, M.; Luoma, V.; Pyörälä, J.; Tanhuanpää, T.; Liang, X.; Kaartinen, H.; Kukko, A.; Jaakkola, A.; et al. Feasibility of Terrestrial laser scanning for collecting stem volume information from single trees. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 123, 140–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Litkey, P.; Hyyppa, J.; Kaartinen, H.; Vastaranta, M.; Holopainen, M. Automatic stem mapping using single-scan terrestrial laser scanning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutzinger, M.; Pratihast, A.K.; Oude Elberink, S.J.; Vosselman, G. Tree modelling from mobile laser scanning data-sets. Photogramm. Rec. 2011, 26, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Fang, T.; Mathiopoulos, P.T.; Qu, H.; Chen, D.; Wang, Y. A structure-aware global optimization method for reconstructing 3D tree models from terrestrial laser scanning data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 5653–5669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Yang, B.; Liang, X.; Dong, Z.; Huang, R.; Wang, Y.; Pyörälä, J.; Kukko, A. Fast registration of forest terrestrial laser scans using key points detected from crowns and stems. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2020, 13, 1585–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Moskal, L.M. Computational-geometry-based retrieval of effective leaf area index using terrestrial laser scanning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 3958–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, D.; Albert, K.; Ammer, C.; Fehrmann, L.; Kleinn, C. Using terrestrial laser scanning to support biomass estimation in densely stocked young tree plantations. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 8699–8709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Qian, C.; Tang, J.; Liu, H.; Fan, X.; Liang, X.; Zhang, H. Improved 3D Stem Mapping Method and Elliptic Hypothesis-Based DBH Estimation from Terrestrial Laser Scanning Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Zhang, W.; Mellado, N.; Wang, N.; Jin, S.; Cai, S.; Luo, L.; Lejemble, T.; Yan, G. SLAM-aided forest plot mapping combining terrestrial and mobile laser scanning. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 163, 214–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, H.G.; Bienert, A.; Scheller, S.; Keane, E. Automatic forest inventory parameter determination from terrestrial laser scanner data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 1579–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, T.; Schwarz, M.; Tockner, A.; Leisch, F.; Nothdurft, A. Automatic mapping of forest stands based on three-dimensional point clouds derived from terrestrial laser-scanning. Forests 2017, 8, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Wang, C.; Pan, F.; Xi, X.; Zeng, H.; Liu, H. Detecting stems in dense and homogeneous forest using single-scan TLS. Forests 2015, 6, 3923–3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, D.; Zhu, H.; Li, Y. A dual growing method for the automatic extraction of individual trees from mobile laser scanning data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 120, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Wu, F.; Guo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Xue, B.; Hu, X.; Li, P.; Tian, D.; Li, C.; et al. Segmenting tree crowns from terrestrial and mobile LiDAR data by exploring ecological theories. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 110, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ester, M.; Kriegel, H.P.; Sander, J.; Xu, X. A density-based algorithm for discovering clusters in large spatial databases with noise. In Kdd; AAAI: Portland, OR, USA, 1996; Volume 96, pp. 226–231. [Google Scholar]
- Heinzel, J.; Huber, M.O. Detecting tree stems from volumetric TLS data in forest environments with rich understory. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zheng, G.; Eitel, J.U.; Moskal, L.M.; He, W.; Huang, H. Improved salient feature-based approach for automatically separating photosynthetic and nonphotosynthetic components within terrestrial lidar point cloud data of forest canopies. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 679–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wan, Y.; Wang, M.; Xu, J. Automatic stem detection in terrestrial laser scanning data with distance-adaptive search radius. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 2968–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovinskiy, A.; Kim, V.G.; Funkhouser, T. Shape-based recognition of 3D point clouds in urban environments. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision, Kyoto, Japan, 29 September–2 October 2009; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 2154–2161. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Hyyppä, J.; Jaakkola, A.; Yu, X. Three-level frame and RD-schematic algorithm for automatic detection of individual trees from MLS point clouds. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 1701–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Cheng, L.; Xu, H.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, M. Segmentation of individual trees from TLS and MLS Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Int Remote Sens 2016, 99, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lindenbergh, R.; Menenti, M. Scalable individual tree delineation in 3D point clouds. Photogramm. Rec. 2018, 33, 315–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Z.; Hopkinson, C.; Chasmer, L. Automating plot-level stem analysis from terrestrial laser scanning. Forests 2016, 7, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Hyyppä, J.; Kaartinen, H.; Lehtomäki, M.; Pyörälä, J.; Pfeifer, N.; Holopainen, M.; Brolly, G.; Francesco, P.; Hackenberg, J.; et al. International benchmarking of terrestrial laser scanning approaches for forest inventories. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 144, 137–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beutel, J.; Kundel, H.L.; Van Metter, R.L. Handbook of Medical Imaging; SPIE Press: Bellingham, WA USA, 2000; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Arce, G.R.; Bacca, J.; Paredes, J.L. Nonlinear filtering for image analysis and enhancement. In The Essential Guide to Image Processing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 263–291. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Qi, J.; Wan, P.; Wang, H.; Xie, D.; Wang, X.; Yan, G. An easy-to-use airborne LiDAR data filtering method based on cloth simulation. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, J. The synthesis of cloth objects. ACM Siggraph Comput. Graph. 1986, 20, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Liang, F.; Yang, B.; Xu, Y.; Zang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Dai, W.; Fan, H.; Hyyppäb, J.; et al. Registration of large-scale terrestrial laser scanner point clouds: A review and benchmark. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 163, 327–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Baldocchi, D.; Gong, P.; Kelly, M. Isolating individual trees in a savanna woodland using small footprint lidar data. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2006, 72, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, S.; Chen, D.; Peethambaran, J.; Wang, P.; Xu, S. Point Cloud Inversion: A Novel Approach for the Localization of Trees in Forests from TLS Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13030338
Xia S, Chen D, Peethambaran J, Wang P, Xu S. Point Cloud Inversion: A Novel Approach for the Localization of Trees in Forests from TLS Data. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(3):338. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13030338
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Shaobo, Dong Chen, Jiju Peethambaran, Pu Wang, and Sheng Xu. 2021. "Point Cloud Inversion: A Novel Approach for the Localization of Trees in Forests from TLS Data" Remote Sensing 13, no. 3: 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13030338
APA StyleXia, S., Chen, D., Peethambaran, J., Wang, P., & Xu, S. (2021). Point Cloud Inversion: A Novel Approach for the Localization of Trees in Forests from TLS Data. Remote Sensing, 13(3), 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13030338








