Assessment of the Feasibility of PPP-B2b Service for Real-Time Coseismic Displacement Retrieval
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Correction Strategy for Orbit and Clock Offsets
2.2. Assessment Strategy for Orbit and Clock Offsets
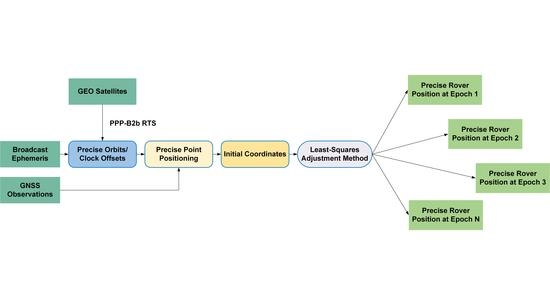
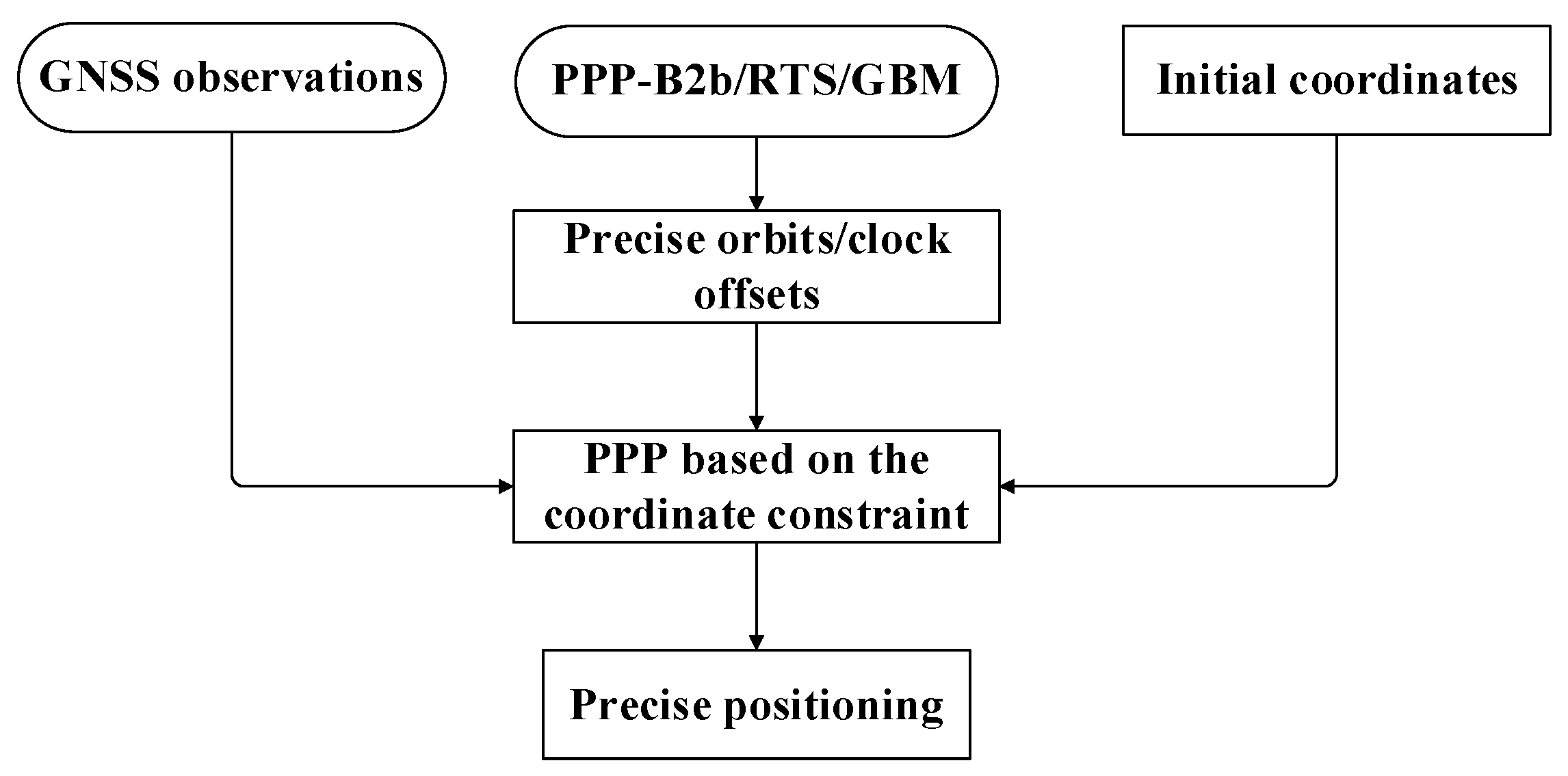
2.3. PPP Model Based on Constrained Coordinates
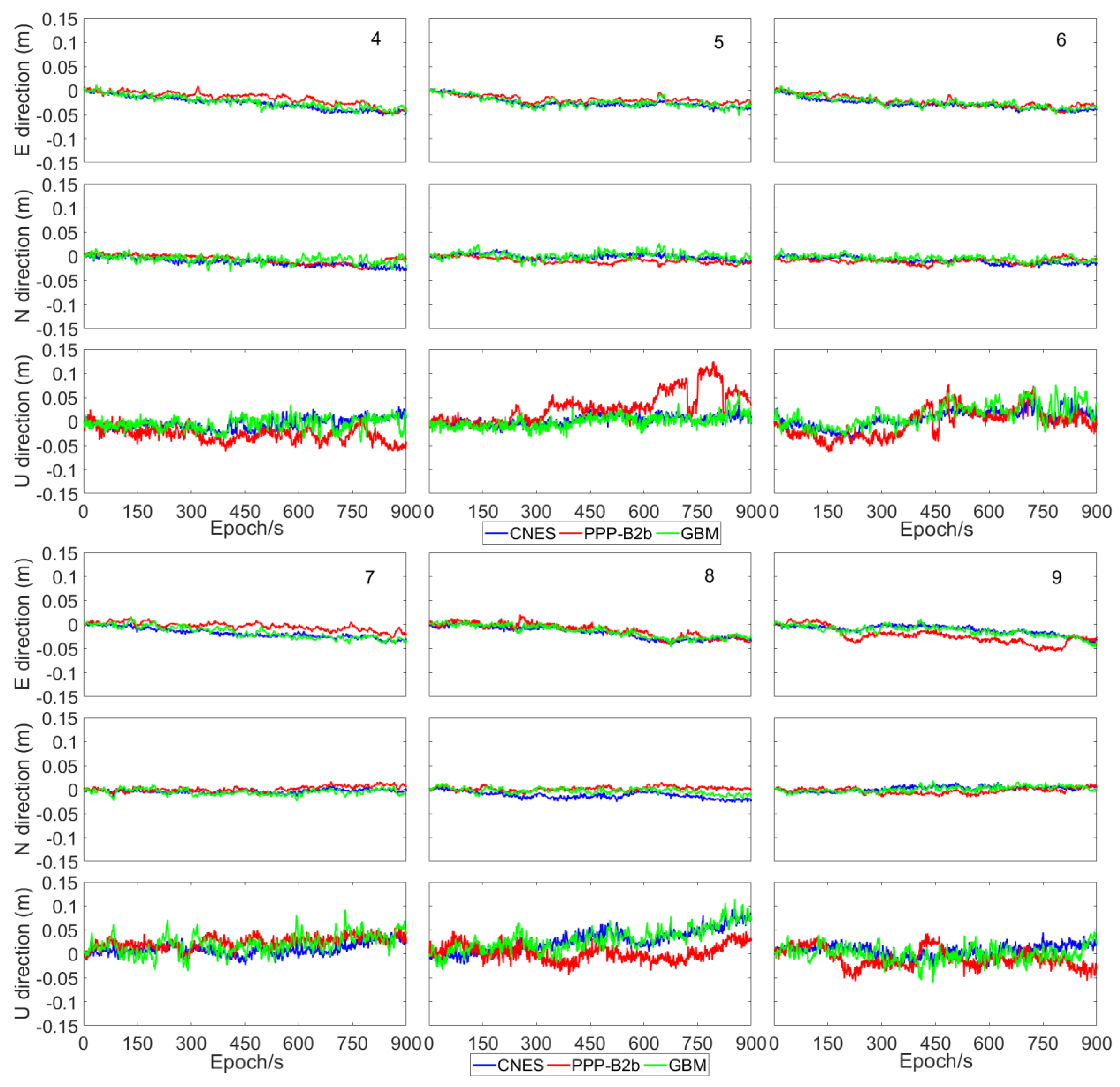
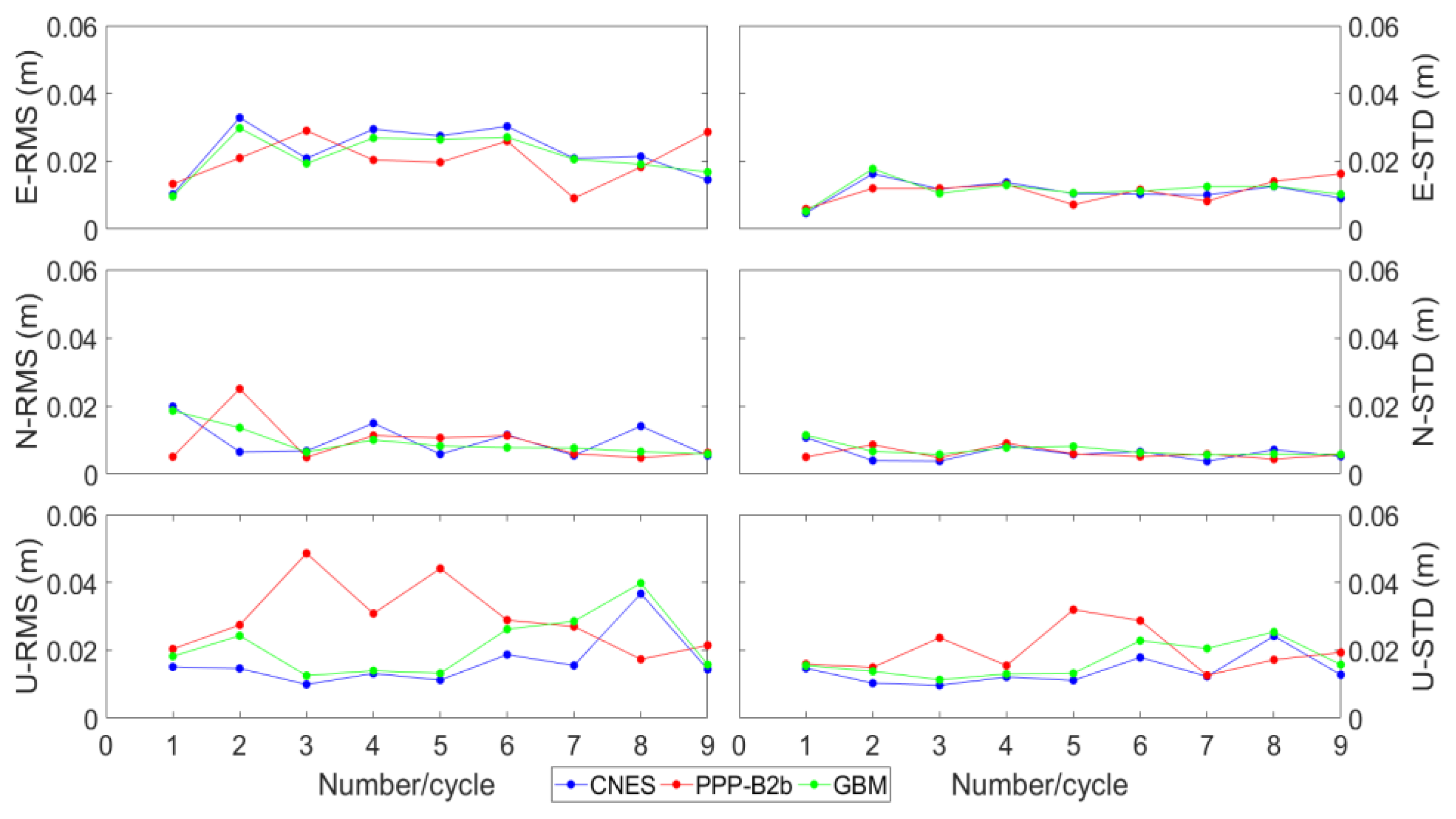
3. Numerical Results
3.1. Evaluation of Orbit and Clock Offsets
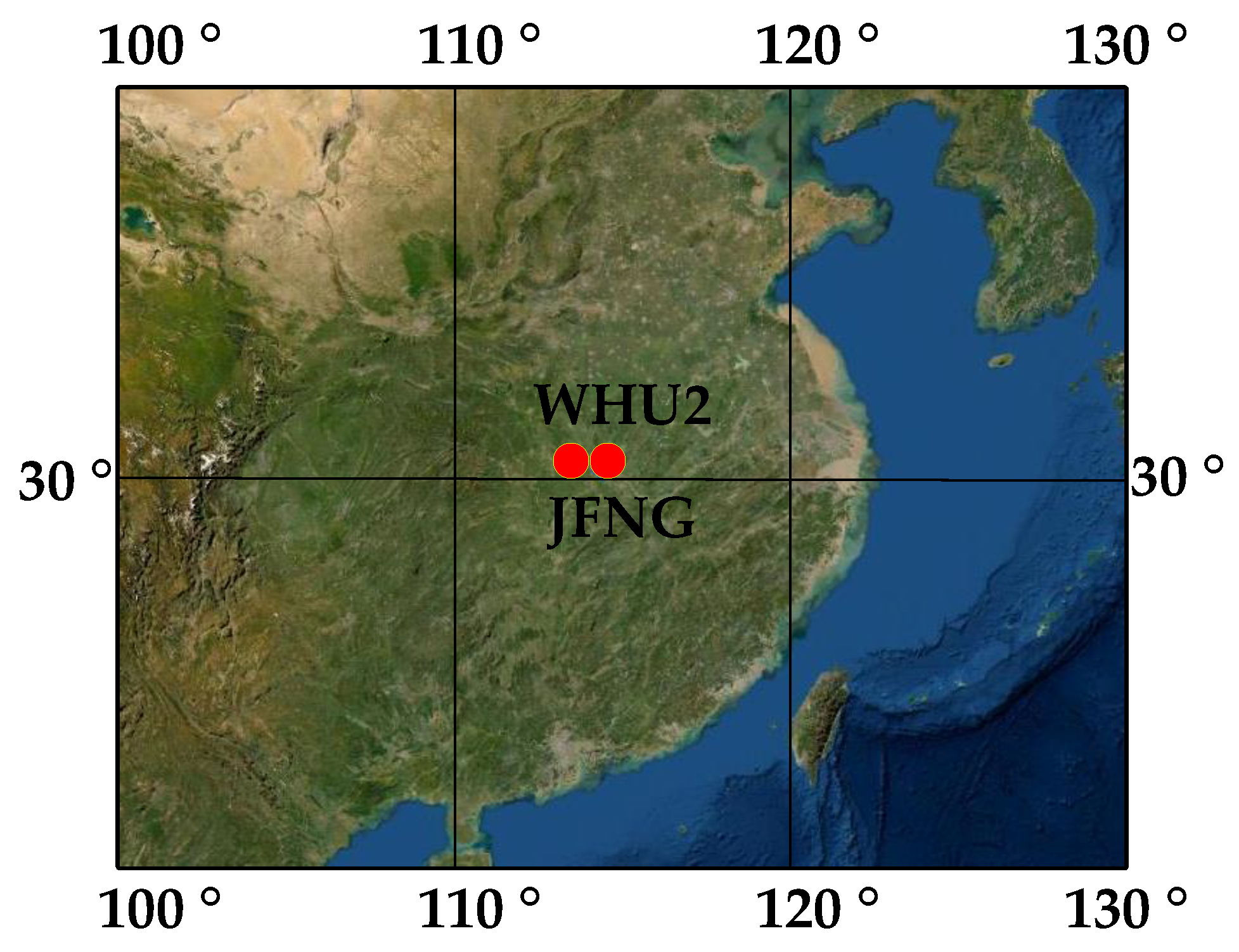
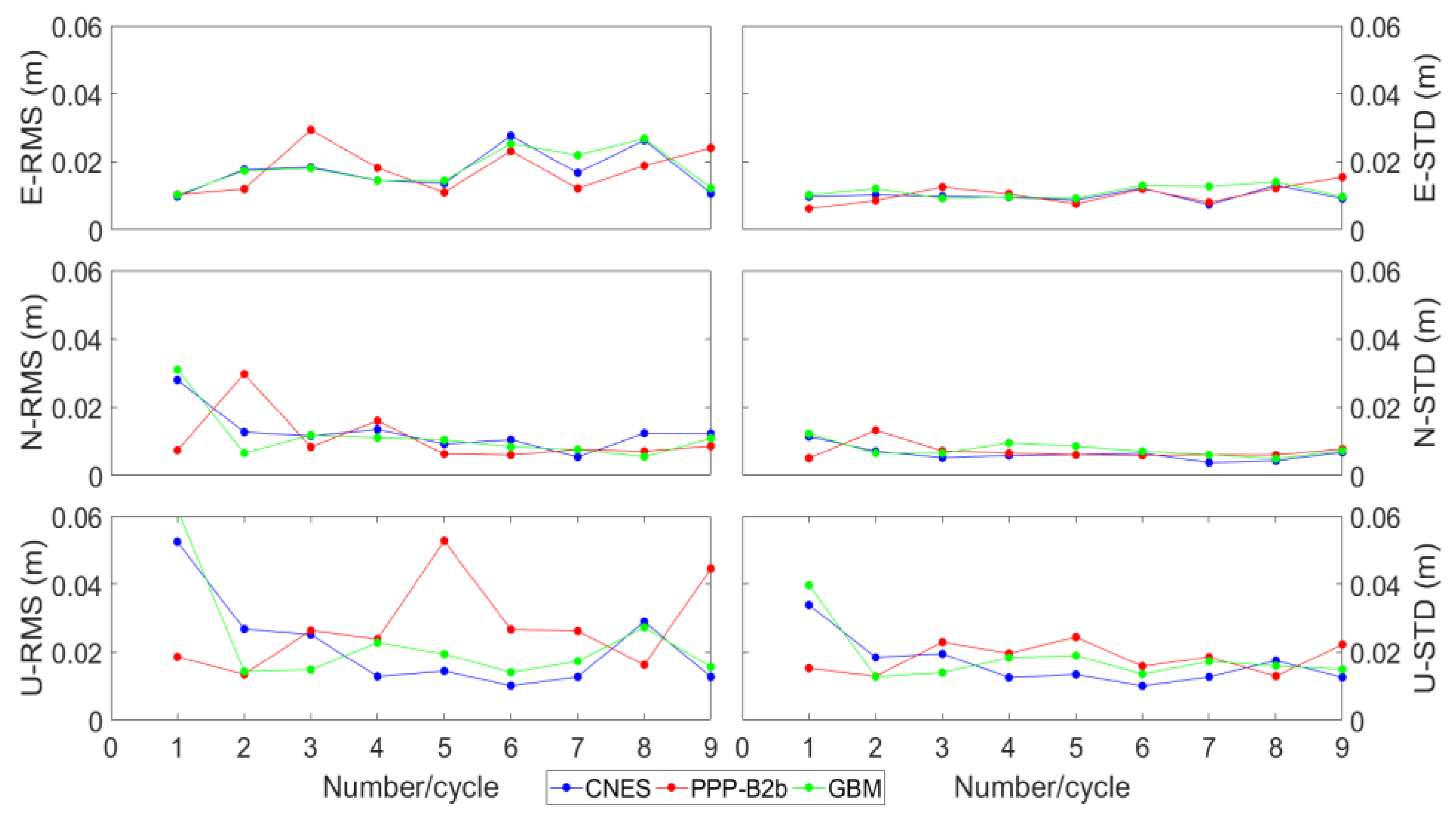
3.2. Positioning Test
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.; Yang, Y.; He, H.; Guo, H. Benefits of BDS-3 B1C/B1I/B2a triple-frequency signals on precise positioning and ambiguity resolution. GPS Solut. 2020, 24, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.M.; Ziv, A. Application of real-time GPS to earthquake early warning. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L16310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Li, Y.; Shan, X.; Zhu, C. Earthquake Magnitude Estimation from High-Rate GNSS Data: A Case Study of the 2021 Mw 7.3 Maduo Earthquake. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Liang, R.; Shi, X.; Dai, K.; Cheng, J.; Cao, J. Detecting and Analyzing the Displacement of a Small-Magnitude Earthquake Cluster in Rong County, China by the GACOS Based InSAR Technology. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G.; Khodabandeh, A. Review and principles of PPP-RTK methods. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 217–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, X.; Yin, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Qu, C.; Zhang, G.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Jiang, Y. High-rate real-time GNSS seismology and early warning of earthquakes. Chin. J. Geophys. 2019, 62, 3043–3052. [Google Scholar]
- Brack, A.; Männel, B.; Schuh, H. GLONASS FDMA data for RTK positioning: A five-system analysis. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouba, J. Measuring Seismic Waves Induced by Large Earthquakes with GPS. Stud. Geophys. Geod. 2003, 47, 741–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blewitt, G.; Kreemer, C.; Hammond, W.C.; Plag, H.P.; Stein, S.; Okal, E. Rapid determination of earthquake magnitude using GPS for tsunami warning systems. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L11309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zumberge, J.F.; Heflin, M.B.; Jefferson, D.C.; Watkins, M.M.; Webb, F.H. Precise point positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1997, 102, 5005–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, F.; Dong, D.; Li, W.; Jiang, X.; Wickert, J.; Schuh, H. GAMP: An open-source software of multi-GNSS precise point positioning using undifferenced and uncombined observations. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, B.; Liu, H.; Xu, L.; Qian, C.; Gong, X.; An, X. Performance Analysis of BDS Medium-Long Baseline RTK Positioning Using an Empirical Troposphere Model. Sensors 2018, 18, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, L.; Eslinger, D.; Sharpe, T. Innovative algorithms to improve long range RTK reliability and availability. In Proceedings of the ION NTM, San Diego, CA, USA, 22–24 January 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Jin, S.; Roberts, G.W. Prior Position- and ZWD-Constrained PPP for Instantaneous Convergence in Real-Time Kinematic Application. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkan, R.M.; Saka, M.H.; Ozulu, M.; İlçi, V. Kinematic precise point positioning using GPS and GLONASS measurements in marine environments. Measurement 2017, 109, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Shi, C.; Fang, R.; Liu, J.; Niu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yanagidani, T. High-rate precise point positioning (PPP) to measure seismic wave motions: An experimental comparison of GPS PPP with inertial measurement units. J. Geod. 2013, 87, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouba, J.; Héroux, P. Precise Point Positioning using IGS Orbit and Clock Products. GPS Solut. 2001, 5, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Su, K. Co-seismic displacement and waveforms of the 2018 Alaska earthquake from high-rate GPS PPP velocity estimation. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 1559–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Gao, X.; Hu, J.; Ma, F.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, W. Performance assessment of real-time multi-GNSS integrated PPP with uncombined and ionospheric-free combined observables. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 67, 234–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, X.; Wickert, J. Multi-GNSS phase delay estimation and PPP ambiguity resolution: GPS, BDS, GLONASS, Galileo. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 579–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banville, S.; Geng, J.; Loyer, S.; Schaer, S.; Spring, T.; Strasser, S. On the interoperability of IGS products for precise point positioning with ambiguity resolution. J. Geod. 2020, 94, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colosimo, G.; Crespi, M.; Mazzoni, A. Real-time GPS seismology with a stand-alone receiver: A preliminary feasibility demonstration. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2011, 116, B11302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Branzanti, M.; Colosimo, G.; Crespi, M.; Mazzoni, A. GPS Near-Real-Time Coseismic Displacements for the Great Tohoku-oki Earthquake. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ge, M.; Guo, B.; Wickert, J.; Schuh, H. Temporal point positioning approach for real-time GNSS seismology using a single receiver. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 5677–5682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, K.; Zamora, N.; Babeyko, A.; Li, X.; Ge, M. Precise Positioning of BDS, BDS/GPS: Implications for Tsunami Early Warning in South China Sea. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 15955–15968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, K.; Ge, M.; Babeyko, A.; Li, X.; Diao, F.; Tu, R. Retrieving real-time co-seismic displacements using GPS/GLONASS: A preliminary report from the September 2015 Mw 8.3 Illapel earthquake in Chile. Geophys. J. Int. 2016, 206, 941–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weinbach, U.; Schön, S. Improved GPS-based coseismic displacement monitoring using high-precision oscillators. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 3773–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Zhang, X.; Ren, X.; Li, X. High-precision coseismic displacement estimation with a single-frequency GPS receiver. Geophys. J. Int. 2015, 202, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, K.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Li, P.; Sang, J.; Ma, T.; Schuh, H. Capturing coseismic displacement in real time with mixed single- and dual-frequency receivers: Application to the 2018 Mw7.9 Alaska earthquake. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yue, D.; Huang, Z.; Chen, J. Performance of real-time undifferenced precise positioning assisted by remote IGS multi-GNSS stations. GPS Solut. 2020, 24, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsobeiey, M.; Al-Harbi, S. Performance of real-time Precise Point Positioning using IGS real-time service. GPS Solut. 2016, 20, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadas, T.; Bosy, J. IGS RTS precise orbits and clocks verification and quality degradation over time. GPS Solut. 2015, 19, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdelazeem, M.; Çelik, R.; El-Rabbany, A. An Enhanced Real-Time Regional Ionospheric Model Using IGS Real-Time Service (IGS-RTS) Products. J. Navig. 2016, 69, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Ge, M.; Neitzel, F.; Wang, X.; Yuan, H. Investigation of the performance of real-time BDS-only precise point positioning using the IGS real-time service. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhao, L.; Li, L.; Feng, S.; Cheng, J. Performance Evaluation of Kinematic BDS/GNSS Real-Time Precise Point Positioning for Maritime Positioning. J. Navig. 2019, 72, 34–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Diasty, M.; Elsobeiey, M. Precise Point Positioning Technique with IGS Real-Time Service (RTS) for Maritime Applications. Positioning 2015, 6, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nie, Z.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ji, S.; Yang, H. An approach to GPS clock prediction for real-time PPP during outages of RTS stream. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Nie, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wu, H.; Xu, X. Real-Time Coseismic Displacement Retrieval Based on Temporal Point Positioning with IGS RTS Correction Products. Sensors 2021, 21, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Z.; Xu, X.; Wang, Z.; Du, J. Initial Assessment of BDS PPP-B2b Service: Precision of Orbit and Clock Corrections, and PPP Performance. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Liu, J.; Hu, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, G.; Ju, B. Initial Assessment of the BDS-3 PPP-B2b RTS compared with the CNES RTS. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, J. Performance evaluation of BDS-3 PPP-B2b precise point positioning service. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Satellite Navigation Office. BeiDou Navigation Satellite System Signal in Space Interface Control Document Precise Point Positioning Service Signal PPP-B2b (Beta Version). Available online: http://www.beidou.gov.cn/xt/gfxz/201912/P020191227331847498839.pdf (accessed on 30 September 2020).
- Petit, G.; Luzum, B. IERS Conventions (2010); Bureau International Des Poids et Mesures Sevres: Frankfurt am Main, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
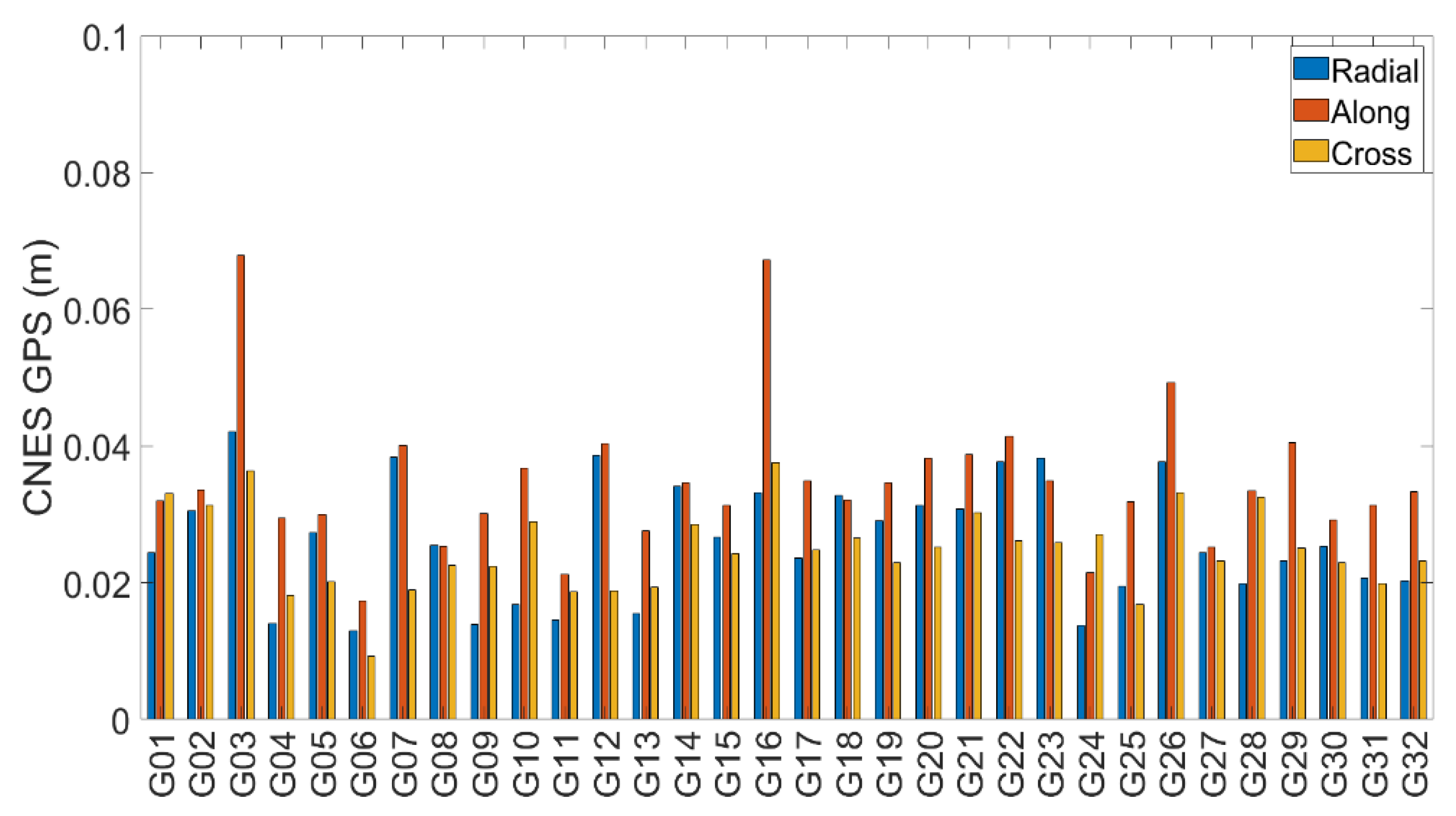
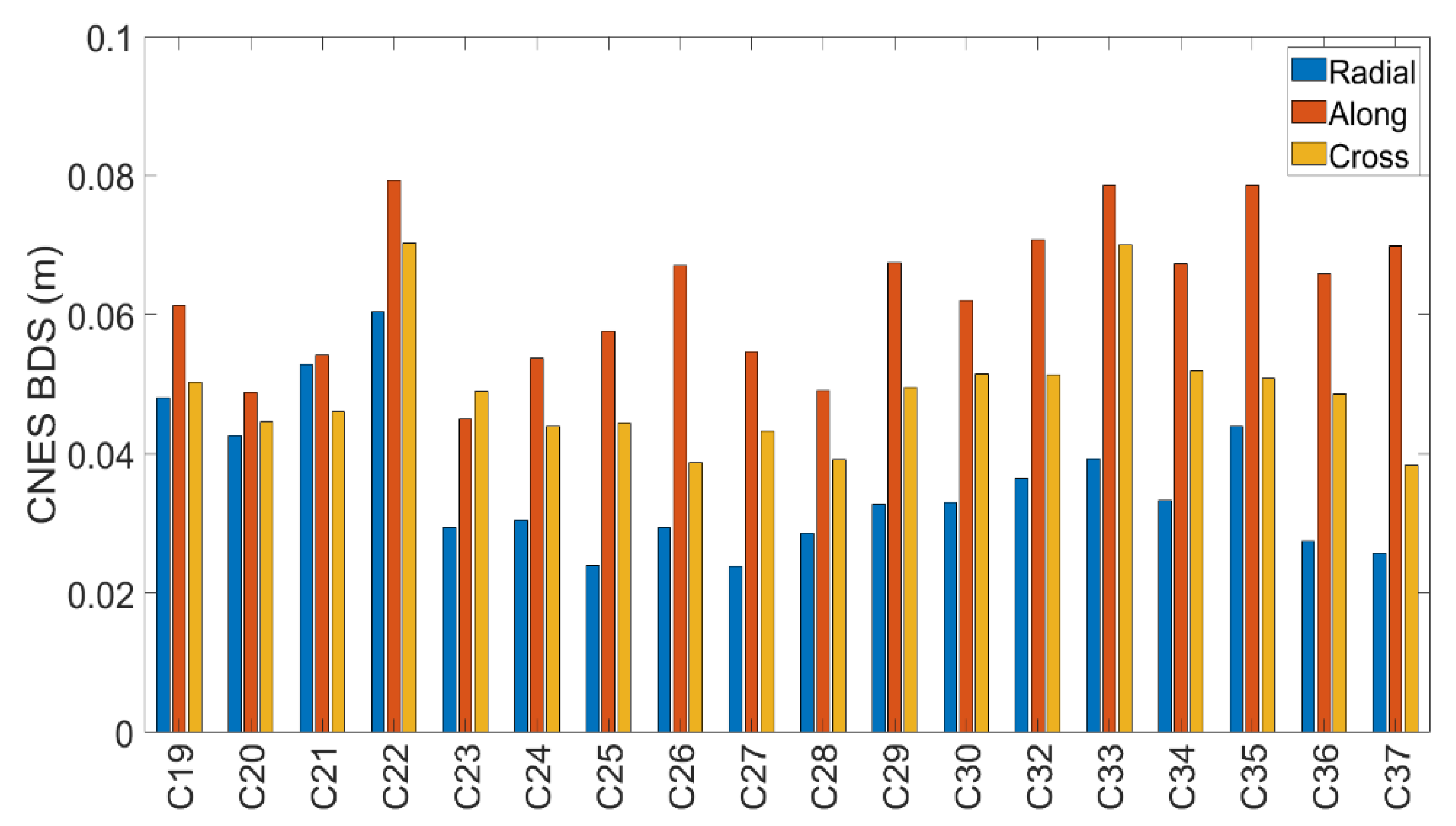
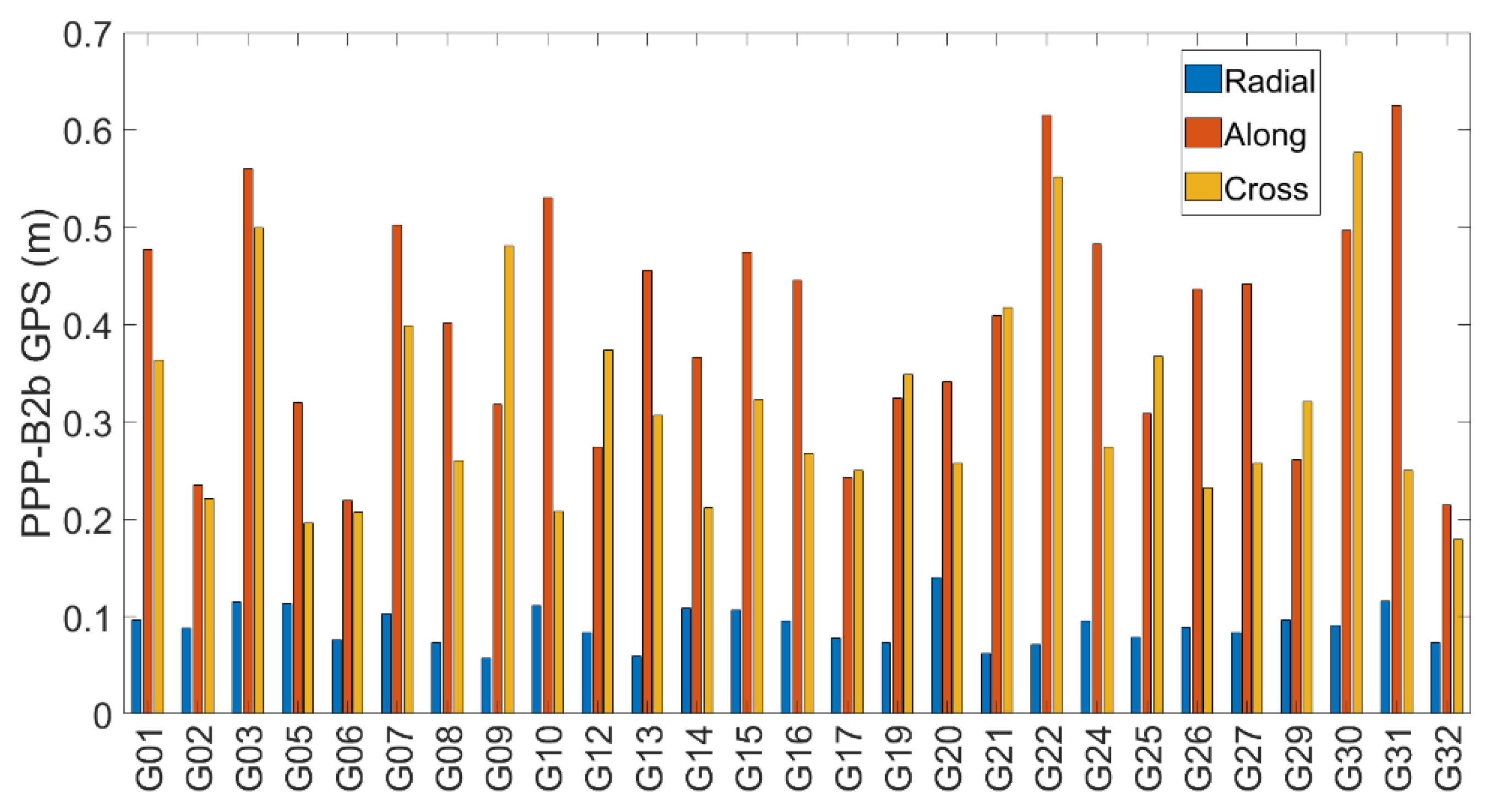
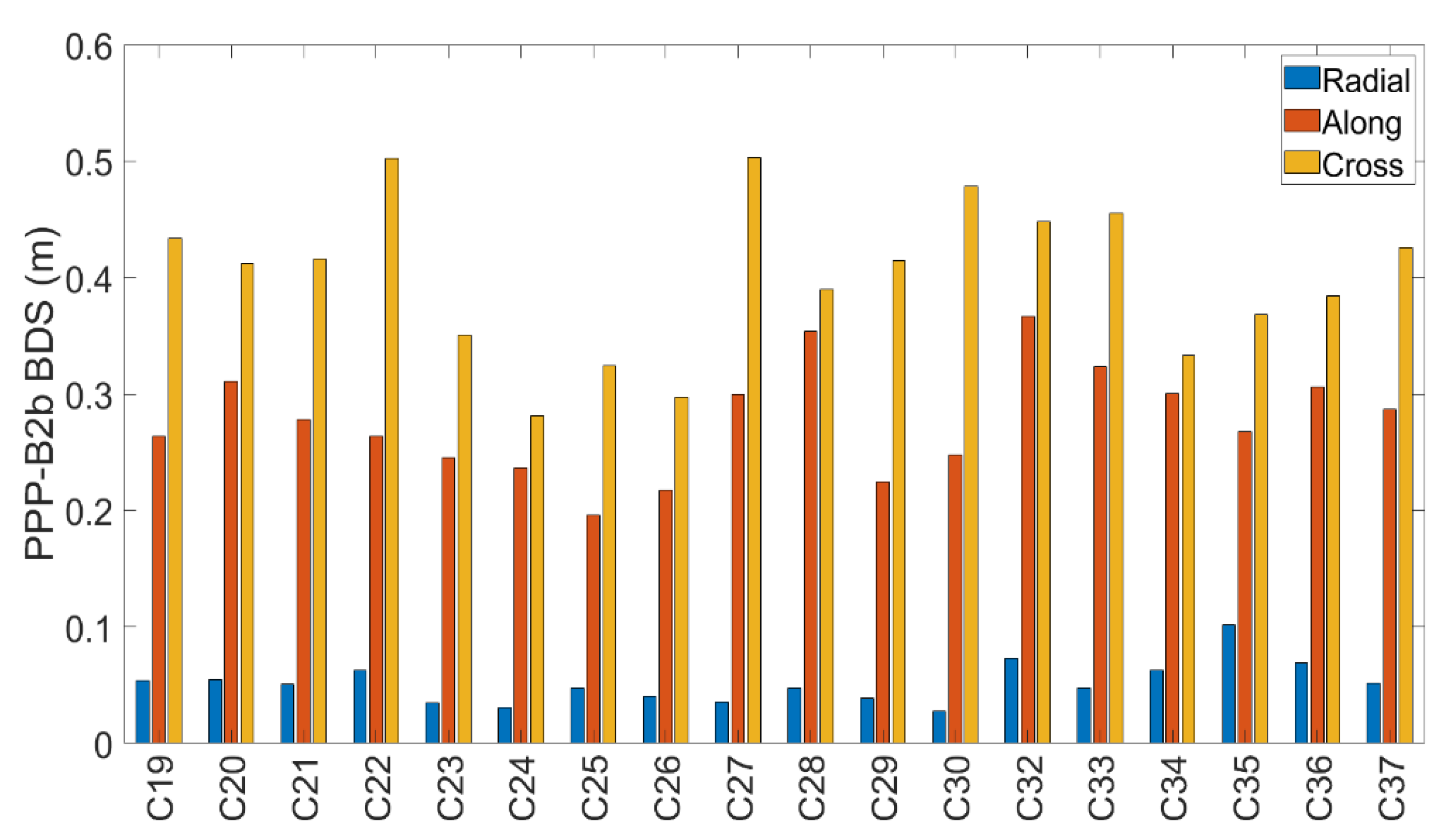


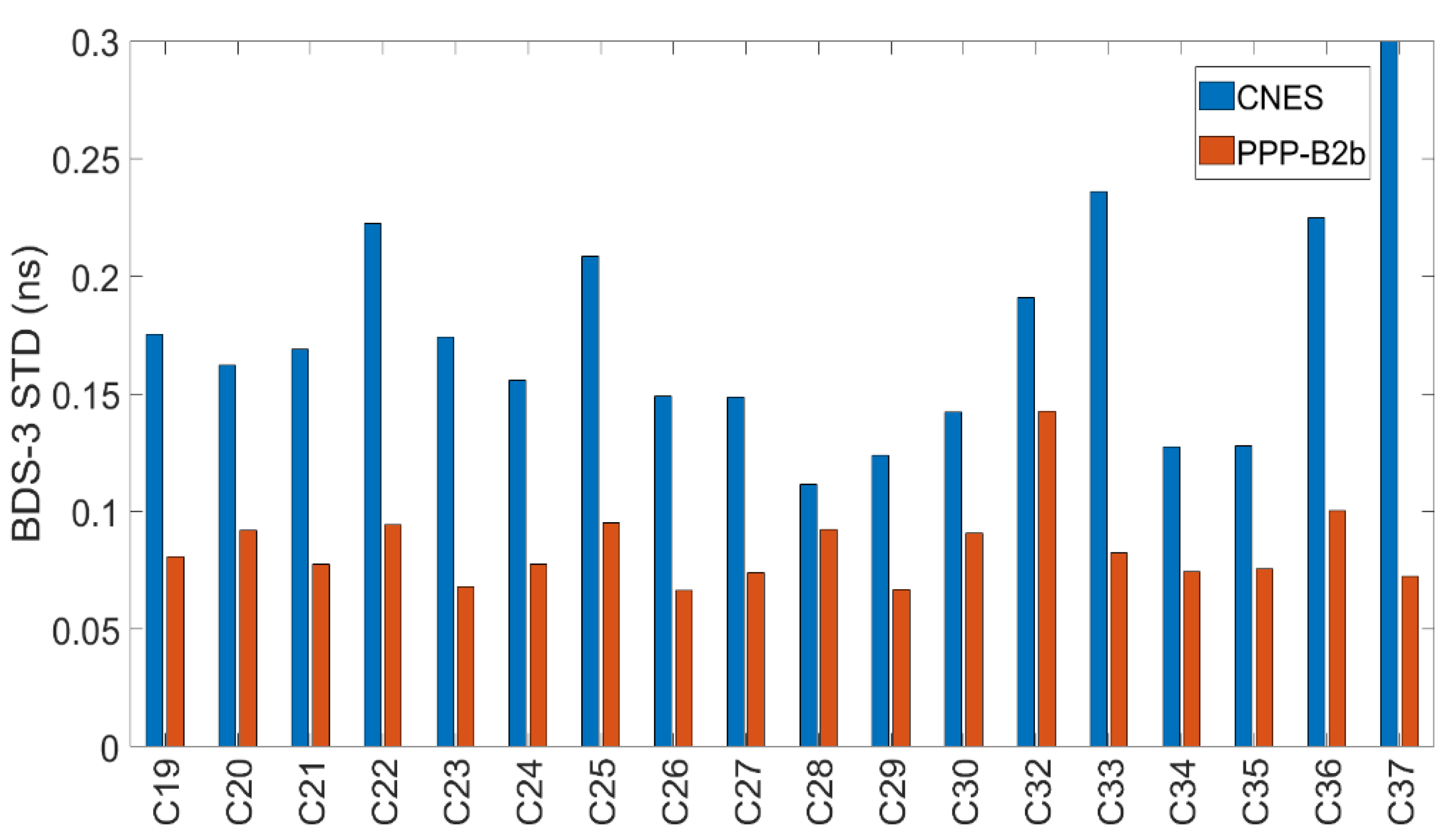
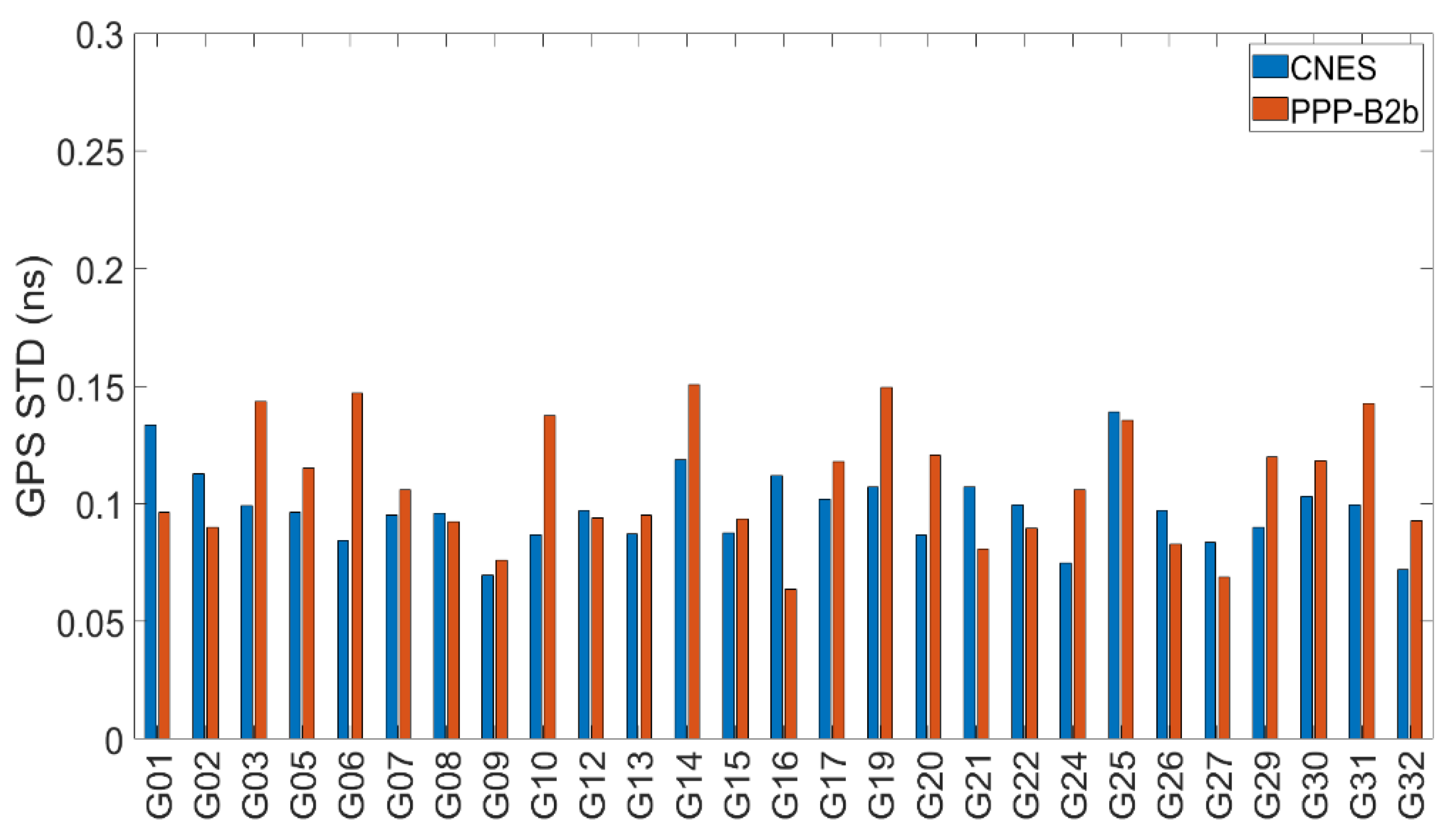
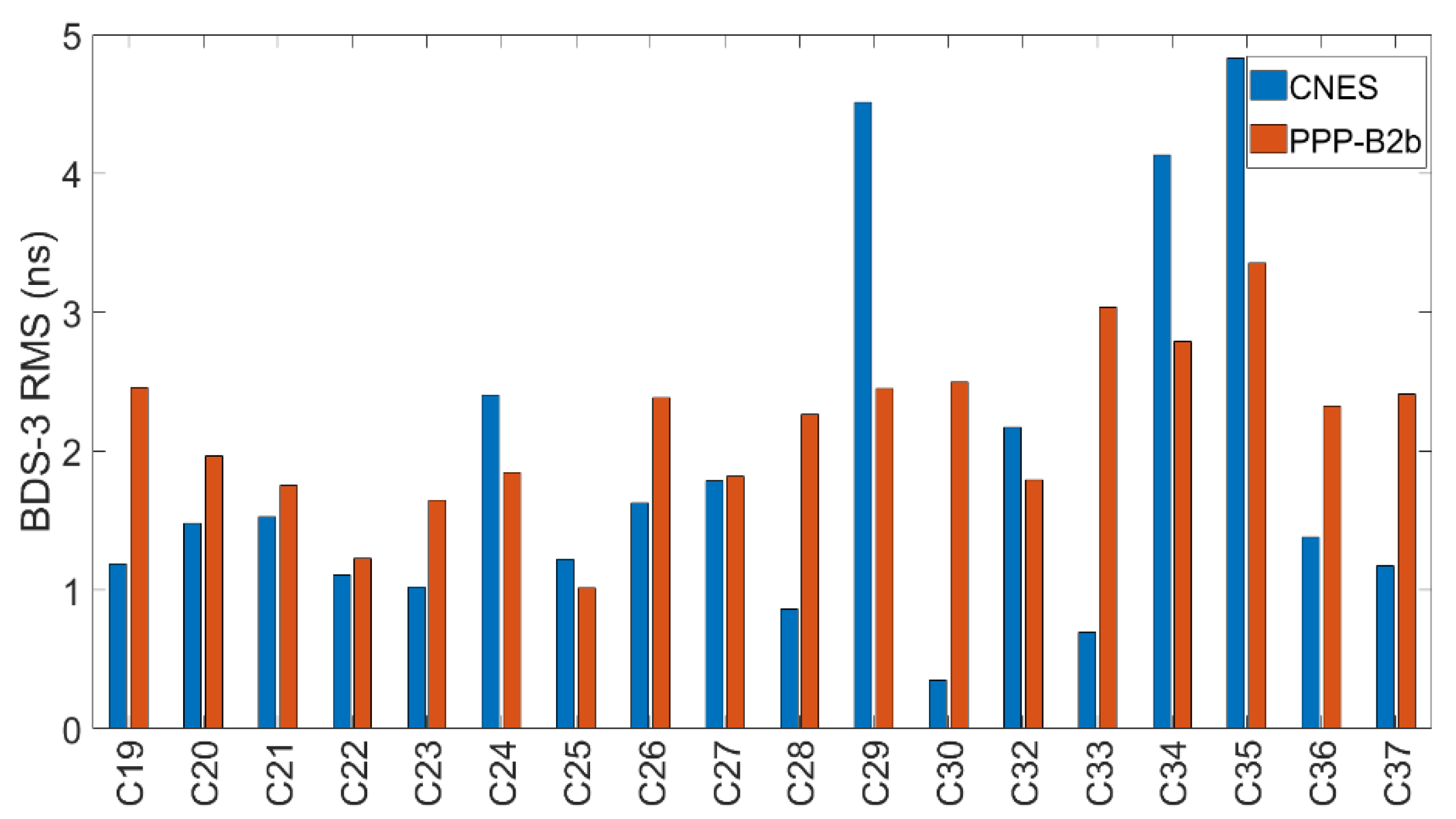
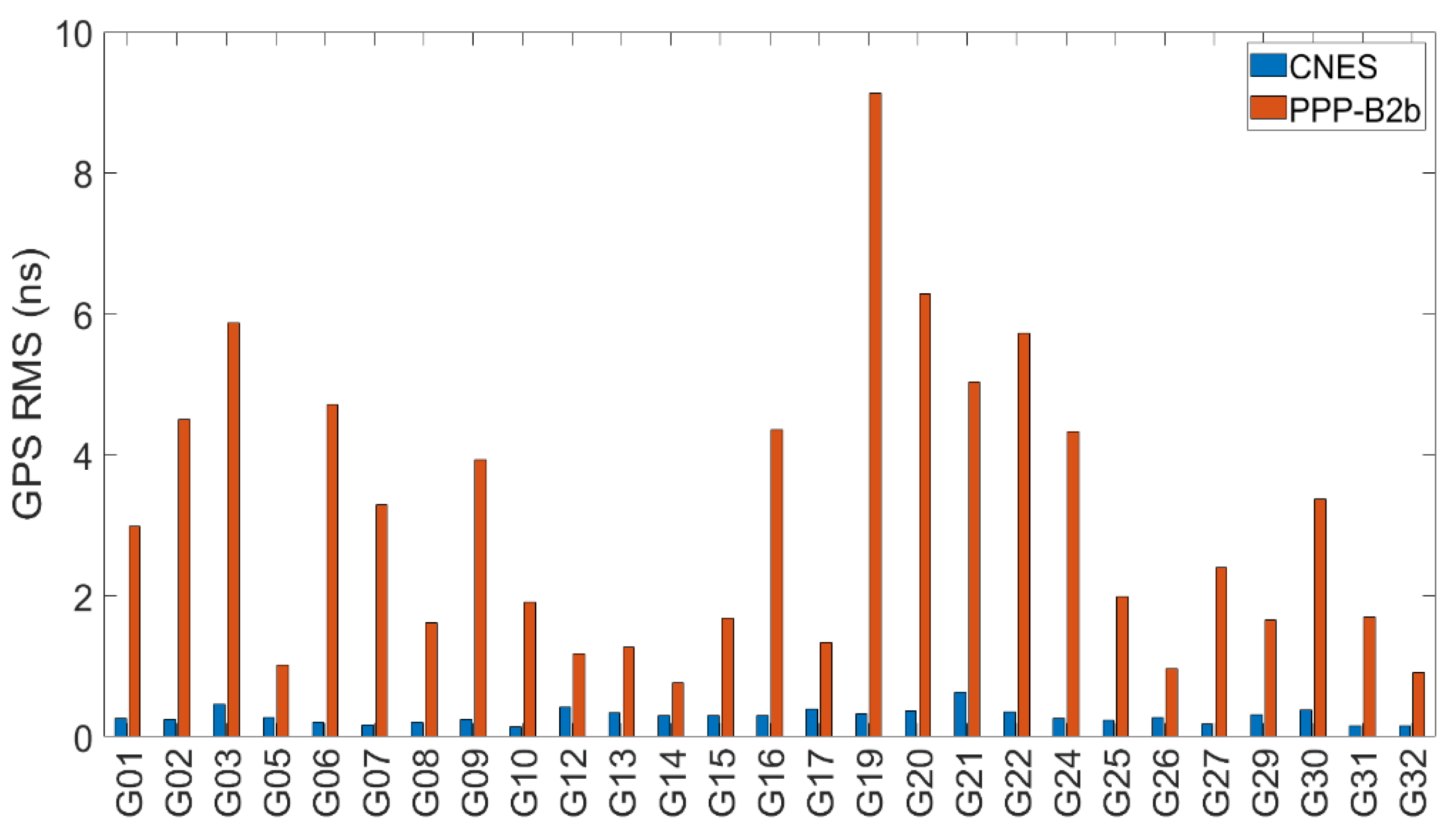




| Service | System | Radial | Along | Cross | Clock |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPP-B2b | BDS-3 | 0.077 | 0.314 | 0.422 | 0.025 |
| GPS | 0.090 | 0.399 | 0.319 | 0.032 | |
| CNES | BDS-3 | 0.036 | 0.063 | 0.049 | 0.052 |
| GPS | 0.026 | 0.035 | 0.025 | 0.029 |
| Item | Processing Strategies |
|---|---|
| Observation type | GPS L1/L2, BDS B1/B3 |
| Elevation mask | 10° |
| Troposphere | Saastamoinen model |
| Solid tide | IERS Conventions 2010 [43] |
| Ocean loading | IERS Conventions 2010 [43] |
| Relativistic effect | Empirical model |
| Ambiguity | Float |
| PCO/Phase center variation (PCV) | IGS14.atx |
| Satellite orbit and clock | PPP-B2b/CNES |
| Station | Type | E | N | U | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMS | STD | RMS | STD | RMS | STD | ||
| PPP-B2b | 0.0177 | 0.0104 | 0.0107 | 0.0070 | 0.0276 | 0.0183 | |
| JFNG | CNES | 0.0173 | 0.0100 | 0.0128 | 0.0063 | 0.0218 | 0.0167 |
| GBM | 0.0178 | 0.0111 | 0.0114 | 0.0076 | 0.0231 | 0.184 | |
| PPP-B2b | 0.0206 | 0.0112 | 0.0095 | 0.0060 | 0.0296 | 0.0200 | |
| WHU2 | CNES | 0.0231 | 0.0110 | 0.010 | 0.0061 | 0.0166 | 0.0139 |
| GBM | 0.0217 | 0.0115 | 0.0094 | 0.0070 | 0.0214 | 0.0168 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, H.; Ji, S.; Weng, D.; Wang, Z.; He, K.; Chen, W. Assessment of the Feasibility of PPP-B2b Service for Real-Time Coseismic Displacement Retrieval. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5011. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13245011
Yang H, Ji S, Weng D, Wang Z, He K, Chen W. Assessment of the Feasibility of PPP-B2b Service for Real-Time Coseismic Displacement Retrieval. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(24):5011. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13245011
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Hao, Shengyue Ji, Duojie Weng, Zhenjie Wang, Kaifei He, and Wu Chen. 2021. "Assessment of the Feasibility of PPP-B2b Service for Real-Time Coseismic Displacement Retrieval" Remote Sensing 13, no. 24: 5011. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13245011
APA StyleYang, H., Ji, S., Weng, D., Wang, Z., He, K., & Chen, W. (2021). Assessment of the Feasibility of PPP-B2b Service for Real-Time Coseismic Displacement Retrieval. Remote Sensing, 13(24), 5011. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13245011