Abstract
Highland barley is the unique germplasm resource and dominant crop in Tibet with low-level precipitation and a severe shortage of available water resources. Understanding the characteristics and dynamics of evapotranspiration (ET) components (vegetation transpiration (Ec), soil evaporation (Es), and canopy interception evaporation (Ei)) of highland barley can help better optimize water management practices. The seasonal and interannual variations in ET components of highland barley were investigated using the PML-V2 ET product during 2001–2020. The results suggested that Es was the most important ET component and accounted for 77% of total ET for highland barley in Tibet. ET components varied obviously over the altitude, Es, and Es/ET ratio; a decreasing trend was observed with the increase in altitude from 3500 m to 3800 m and then this changed to an increasing trend until reaching the altitude of 4100 m, while Ec, Ei, and their ratios presented an opposite changing pattern to that of Es. Seasonal variation in daily ET components of highland barley displayed a parabolic pattern, peaked in August, while the temporal distributions differed considerably among different ET component ratios. The seasonal variations in ET components were correlated significantly with air temperature, relative humidity, and precipitation, while ET components ratios were more influenced by the environment, irrigation practice, and management rather than meteorological variables. Es and its ratio in highland barley decreased significantly during 2001–2020, while the Ec/ET ratio generally showed an opposite trend to the Es/ET ratio, and Ei and its ratio presented an insignificantly decreasing trend. The interannual variations in ET components were not correlated significantly with meteorological variables, while Ei was more influenced by meteorological variables, especially the precipitation characteristics.
1. Introduction
Terrestrial evapotranspiration (ET), comprising the transpiration from vegetation (Ec), the evaporation from soil (Es), and the evaporation of the intercepted precipitation by vegetation canopy (Ei) [1], is a critical process of water and carbon cycle, as well as the most important component of energy balance for soil–plant–atmosphere continuum [2]. ET and its components play key roles in linking ecosystem functioning, climate feedbacks, and water resources [3]. Crop water consumption by ET is a critical parameter for water and energy exchanges in the agriculture continuum [4]. Understanding the dynamic and characteristics of crop ET components is of great significance in the estimation of water requirements for agricultural irrigation [5], evaluation of water use efficiency [6], and development of optimal irrigation schedule [7].
Several techniques have been developed to measure ET components of crops. Many previous studies used the micro lysimeter and sap flow, respectively, to measure the Es and Ec of crops such as wheat [4], maize [8,9], and tomato [10], the results suggested that sap flow was a useful tool to measure Ec of crops at an instantaneous interval [8]. As far as short-stalk, closed-system planting crops such as wheat and rice were concerned, Ei was often measured with classic water wiping method [4], while it was usually calculated using the water balance method for maize, in which throughfall was collected with rainfall collectors, and stemflow was collected with collars attached around the maize stems, and then stemflow in collars was drained to collectors using a slot with a transfer hose [9]. Ma and Song [2] explored the isotope tracing technique coupled with the water balance method for partitioning ET of winter wheat under different irrigation and fertilization treatments during growing seasons. Some studies used the weighing lysimeter and eddy covariance system to measure the total ET, which was later partitioned into ET components using the energy balance method [10,11,12]. Zhou et al. [13] proposed a simple and practical method to estimate Es and Ec of crops; this method combined with an eddy covariance system was later used by Wang et al. [14] to separate Es and Ec of maize cropland in a dry, semihumid climate regime.
However, these techniques were not widely applied mainly due to the limitations of being time consuming, having costly equipment, and being prone to measuring manipulation [10]. Therefore, great efforts have been made for partitioning ET by means of modeling approaches, with the main focus on the improvements of the surface conductance model based on the Penman–Monteith (PM) model. Shuttleworth and Wallace [15] modified the PM model and developed the Shuttleworth–Wallace (SW) model based on the energy balance theory and the physical process of Es and Ec. Hu et al. [16,17] introduced Ball–Berry stomatal conductance model to modify the SW model and suggested an improved SW model. Leuning et al. [18] and Zhang et al. [19] used a surface conductance model to modify the PM model and proposed the Penman–Monteith–Leuning (PML) model. Introducing a water carbon coupled canopy conductance model, Gan et al. [20] revised the PML model and developed the PML-V2 model, which can estimate ET components and gross primary productivity (GPP) simultaneously. This model was further improved by Zhang et al. [1,21] by incorporating the vapor pressure deficit constraint to GPP. Rosa et al. [22] considered Es and Ec as a function of crop coefficient and reference evapotranspiration and presented a dual crop coefficient model. Gong et al. [10] reported a modified Priestley–Taylor model considering the effects of leaf senescence and plant temperature constraint on transpiration to estimate Es and Ec of tomato.
Due to the difference in climate, geomorphology, soil, hydrological regimes, and agricultural management practices, ET components and the proportion of components for crop varied greatly from site to site [3]. Generally, the ET, Ec, and the Ec/ET ratio in hot and humid areas were higher than those in arid and semiarid areas [23]. For example, ET, Ec and the Ec/ET ratio of wheat in eastern China [2] with humid climate were higher than those in western China with arid climate [4], and ET, Ec, and Ec/ET ratio of crops in southern China with hot temperature [24] were higher than those in northern China with cold temperature [25]. Previous studies revealed that Ec generally accounted for a large proportion of ET [6,26], while Es became a major component in arid and semiarid areas [27,28]. Compared with Ec and Es, Ei was not a major component of ET, while it was an important ET component of the soil–vegetation–atmosphere continuum, regulating the reallocation of rainfall reaching the canopy [26]. However, this component was often neglected in many studies on ET partitioning [4,29]. Ei was significantly affected by the structure of the canopy and by precipitation; the crop with higher leaf area and vegetation cover generally yielded higher Ei [30].
Featured as a unique germplasm resource and occupying 70% of cropland in Tibet Autonomous Region, China [31], highland barley plays a critical role in guaranteeing the livelihood and promoting social stability of herdsmen in Tibet. Tibetan highland barley has the characteristics of a short-stalk, closed-system planting crop, and it is usually sown between March and April. The growth, development, traits, and yield of highland barley are dramatically affected by hydrological regimes in the Tibetan Plateau. However, limited rainfall, coupled with higher ET, resulted in a severe shortage of available water resources [32], which significantly affected the yield of highland barley in this area. Therefore, it became an important alternative to irrigate highland barley using the available water resources for maintaining the yield of highland barley [33]. Irrigation management was based on the available water at the beginning of the growing season, while no detailed knowledge of water deficit and irrigation demand was taken into account due to the lack of relevant studies. In fact, water depth and the number of irrigations initially proposed can be modified according to rainfall. ET is a critical process and the most important component of the water cycle in Tibet; therefore, quantifying ET components of highland barley and understanding their dynamic can help in the better and more efficient management of the limited water resources and in developing an optimal irrigation schedule. However, the changes and characteristics of ET components for highland barley are still not clear and need to be investigated. Therefore, this study was carried out to fill this knowledge gap; the main objectives of this study were to (1) investigate the characteristics and variations in ET components and their proportions with regard to highland barley and (2) explore the meteorological factors affecting the variations in ET components.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The Tibet Autonomous Region (Figure 1) is located in the southern part of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and stands at the southwestern border of China, to the north of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region and Qinghai Province, and to the west of Sichuan and Yunnan Provinces, bordering northern Myanmar, India, Bhutan, and Nepal. It covers an area of 1.22 × 106 km2, occupying about 12.7% area of mainland China. Grassland dominates the whole region and accounts for approximately up to 67% and 26% area of Tibet and China, respectively, while cropland accounts for only 0.18% area of Tibet, and highland barley occupies 70% area of cropland, which plays a critical role in guaranteeing the livelihood and promoting social stability of herdsmen in Tibet. Tibet has unique plateau climate features, characterized by a large air temperature range between daytime and nighttime, and low-level precipitation with a highly pronounced spring and summer peak, which differs significantly from other regions at the same latitude dominated by the Mediterranean and semidesert/desert climates [34]. The annual mean air temperature varies between −2.4 °C and 12.1 °C, and the annual mean precipitation varies between 66.3 mm and 894.5mm [35].
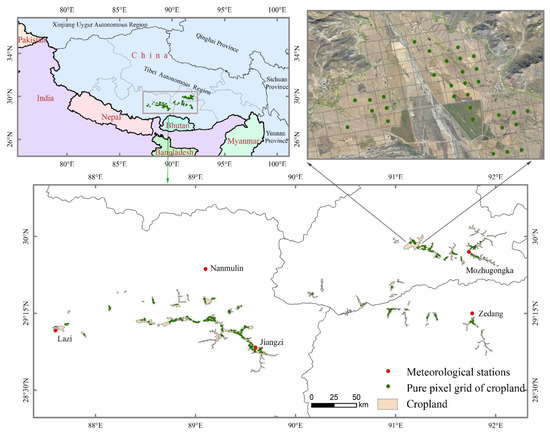
Figure 1.
Location of the study area and the distribution of meteorological stations and cropland of highland barley.
2.2. Data Collection
PML-V2 ET components product was used to investigate the characteristics and variations in ET components of highland barley in this study. This product was based on the PML-V2 model, which was initially developed by Leuning et al. [18] and Zhang et al. [19] and further revised by Gan et al. [20] and Zhang et al. [1,21] through the improvements in the surface conductance model. Coupled with MODIS data, including land use, albedo, leaf area index, surface-specific emissivity, and GLDAS meteorological data, including solar radiation, air temperature, precipitation, and water vapor pressure, a PML-V2 algorithm was employed to generate global ET components product with 500 m and 8-day resolution. These product data were evaluated using the measurements at 95 widely distributed flux towers globally, with the RMSE of 0.69 mm/day [1]. It was also validated across different regions in China and proved to be reliable data for investigating the variations in ET components across different ecosystems [36,37,38]. In this study, the PML-V2 ET product from 2001 to 2020 covering the study area was obtained from the Google Earth Engine (https://developers.google.com/earth-engine/datasets, accessed on 27 July 2021).
The land use data of Tibet in 2015 were collected from the Resource and Environment Science and Data Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences (https://www.resdc.cn, accessed on 27 July 2021). These data were interpreted from the Landsat images, with 30 m resolution. Meteorological data, including sunshine duration (SD), air temperature (T), precipitation (P), and air pressure (AP), water vapor (WP), and relative humidity (RH) were obtained from the China Meteorological Data Service Center at 5 meteorological stations during the same period with ET product. The distribution of meteorological stations is shown in Figure 1, and detailed information on these stations is listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Detailed information on meteorological stations.
2.3. The Selection of Pure Pixels of Cropland
The cropland mainly lies on the narrow alluvial plain along the main stream in Tibet. The limited area, coupled with its fragmented landscape, resulted in a limited number of pure pixels of highland barley ET obtained from the PML-V2 product with 500 m resolution. In order to retrieve a series of ET components’ data from the pure pixels of highland barley, the cropland selected from land-use data of Tibet was overlaid with the grid of the PML-V2 ET product and high-resolution satellite images from Google Earth. A total of 687 pure pixels of PML-V2 ET product for highland barley were identified, as shown in Figure 1.
2.4. Analysis Method
- (1)
- PML-V2 Model
The PML-V2 model used total primary productivity and atmospheric CO2 concentration to estimate canopy conductance, thereby realizing a joint estimation of ET and total primary productivity. ET was divided into three main components: vegetation transpiration (Ec), soil evaporation (Es), and canopy interception evaporation (Ei) [1,21].
where ε = s/γ, in which γ is the psychrometric constant (kPa/°C), and s is the slope of the curve relating saturation water vapor pressure to temperature (kPa/°C); A is the available energy absorbed by the surface (MJ/(m2·day))—that is, net absorbed radiation minus soil heat flux; As and Ac are the available energy of the soil and vegetation canopy, respectively; is the density of air (g/m3); is the specific heat of air at constant pressure (MJ/(g·°C)); is the water vapor pressure deficit of the air (kPa); is the aerodynamic conductance (m/s); Gc (m/s) is the canopy conductance; f is a dimensionless variable that determines the water availability for soil evaporation; is canopy leaf area; P is the daily precipitation (mm/d); Pwet is the threshold of precipitation when the canopy is enough wet.
ET = Ec + Es + Ei
- (2)
- Unitary Linear Regression Model
A unitary linear regression model was used to describe the interannual change trend in ET components of highland barley, and the trend rate (k) was calculated as
where is the ET components of highland barley for the ith year, and n is the number of years.
F-test was used to measure the significance of the linear trend as follows:
where U and Q are the sum of regression squares and the sum of residual squares, respectively; n is the sample size; is the ET components of highland barley from PML product; is the estimated ET components by the linear regression model; is the average ET components of highland barley. Python was used to calculate k and F values for the three components.
- (3)
- Pearson Correlation Analysis
Pearson correlation coefficient (R) was used to explore the relationship between the variations in ET components and meteorological variables. It was calculated using the following equation:
where xi and yi are the ET components and meteorological variables, respectively, and n is the sample size. The metric R varying between −1 and 1 was adopted to measure the degree of linear correlation between two variables; a higher absolute value of R suggests a stronger correlation. The Pearson correlation between ET components and meteorological variables was calculated by SPSS software.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. ET Components of Highland Barley in Tibet
The annual mean ET of highland barley was 506.9 mm in Tibet, and the Es, Ec, and Ei were 391.9 mm, 107.6 mm, and 7.4 mm, respectively, which accounted for 77.3%, 21.2%, and 1.5% of total ET, respectively. This result suggests that Es was the most important ET component for highland barley in Tibet, and most of the water was lost through soil evaporation, which was similar to the results in arid climate regions [5,26,39]. The ET of highland barley was similar to that of spring maize [40] and winter wheat [4] in northern China, yet higher than that of corn under microirrigation systems in a semiarid environment [28]. However, large differences in the ET components varied widely among different crops and regions. Observations showed that Es, Ec, and Ei ranged from 82.9 mm and 98 mm, from 217.2 mm to 304.1 mm, and from 11 mm to 16 mm for wheat in northern China, respectively [4]. The measured Es and Ec were approximately 183 mm-205 mm and 172–185 mm for winter wheat in Syria, respectively [25]. The Ec was up to 469–475 mm in a mulched agriculture ecosystem [40]. These results suggest that highland barley generally had much lower Ec and Ei but much higher Es than those of other crops such as wheat and corn, which was similar to the results observed in arid climate regions [5,28].
Numerous studies showed that the proportion of ET components differed greatly across different crops and from region to region. Previous studies reported that Ec accounted for 20–80% of ET for row crops [41,42]. Wei et al. [43] found that the Ec/ET ratio varied substantially between 0.2 and 1.0 for a rice paddy field during the growing season in Mase, Tsukuba. Aouade et al. [27] observed the ET components of winter wheat in a semiarid region in Morocco, with the average Ec/ET ratio of 0.69–0.8. Many observations also revealed obvious differences in Ec/ET ratios across China [44]. For example, the Ec/ET ratio varied widely from 0.52 to 0.96 for maize in northwestern China [45,46], which was very similar to the range between 0.51 and 0.98 for winter wheat in Beijing [2], and slightly higher than the Ec/ET ratio from 0.46 to 0.74 for winter wheat in North China Plain [47]. The Ec/ET ratios of these crops were much higher than that for highland barley in Tibet, generally indicating that highland barley has a relatively low transpiration rate in Tibet properly due to the stress from the extreme climate. Compared with Ec and Es, Ei accounted for only 1.5% of highland barley ET in Tibet, while Ei was an important component of the agricultural soil–plant–atmosphere continuum, regulating the reallocation of rainfall reaching the crop canopy [26]. Some observations and simulations demonstrated that Ei can account for a large proportion of ET [6]. For example, Ma et al. [4] found that Ei can amount to 14–15% of ET for wheat in northern China, which was much higher than that of highland barley in Tibet. However, many studies on ET partitioning often neglected this component [4,29].
ET components varied obviously over the altitude. As shown in Figure 2, ET generally decreased with the increase in altitude, with higher ET observed at 3700–3800 m altitude zone (Figure 2g). Es and Es/ET ratio showed a decreasing trend with the increase in altitude from 3500 m to 3800 m and then changed to an increasing trend until reaching the altitude of 4100 m (Figure 2c,d), while Ec, Ei, and their ratios presented an opposite changing pattern to Es (Figure 2a,b,e,f).
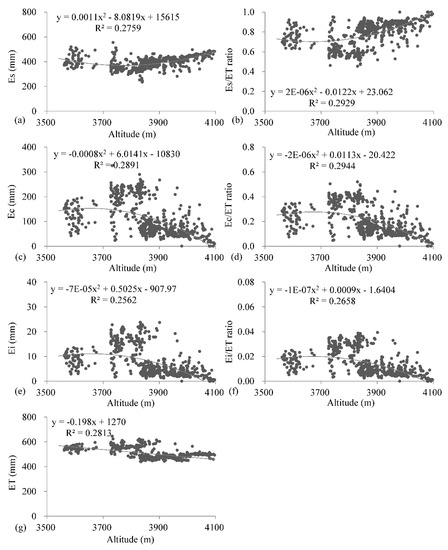
Figure 2.
Relationship between altitude and Es (a), Es/ET (b), Ec (c), Ec/ET (d), Ei (e), Ei/ET (f), and ET (g).
3.2. Seasonal Variations in ET Components
The temporal distributions of the daily ET components are presented in Figure 3. ET components of highland barley showed similar seasonal variation patterns at different altitude zones; they increased progressively from the beginning of the year and reached the maximum in August, and then they declined dramatically to the end of the year, while the peak time for Ei (Figure 3e) was slightly later than that for ET (Figure 3g) and Ec (Figure 3c). The peak time for Es differed greatly across different altitude zones (Figure 3a); Es at 3700–3800 m altitude zone reached the maximum on the 161st day in June, which was much earlier than those for other altitude zones. The maximum Es at 3900–4100 m altitude zone occurred on the 217th day, which was consistent with ET and Ec, and the maximum Es was observed on the 185th day in early July for other altitude zones.
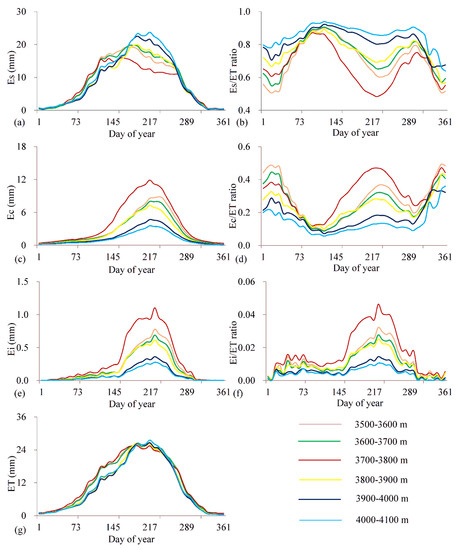
Figure 3.
Temporal trends of Es (a), Es/ET (b), Ec (c), Ec/ET (d), Ei (e), Ei/ET (f), and ET (g) of highland barley at different altitude zones.
The seasonal variations in ET components for highland barley were similar to that of other crops such as wheat, corn, and rice [9,23,48,49]. For example, Gao et al. [50] found that the ET components of spring maize presented a parabolic trend with the peak in the canopy-increasing stage in Loess Plateau in China. Four years of observations illustrated that ET, Ec, and Es showed similar seasonal variation patterns with the development of the canopy for maize in dry, semihumid climate regimes [14]. Both the observed and simulated ET exhibited similar temporal distributions for drylands in the arid regions of northwestern China [51].
The temporal distributions differed considerably among different ET component ratios. Ei/ET ratio (Figure 3f) generally presented a similar changing pattern to ET components. The Es/ET ratio (Figure 3b) increased progressively from the beginning of the year and reached the maximum in later April, and then it declined to the valley in the middle of August, and it subsequently increased, reaching the secondary maximum in early November, then it decreased till the end of the year. This was different from the result from Dehghanisanij et al. [28], who found that Es decreased with the increase in leaf area index (LAI) and time. The intra-annual variation in the Es/ET ratio was mainly related to the growing season of highland barley. From April to August, highland barley reaches its peak growth period. With the increase in vegetation canopy coverage, the shielding effect reduced the radiation energy reaching the surface, thus reducing the soil evaporation rate, and ultimately leading to the decrease in Es/ET. The Ec/ET ratio (Figure 3d) generally exhibited an opposite changing pattern to the Es/ET ratio, with two valleys corresponding to the two peaks of Es ratio, and a peak corresponding to the valley of Es ratio, which was consistent with the seasonal change in the Ec/ET ratio for dryland in northwestern China [51]. Ma and Song [2] also found that the Ec/ET ratio did not vary significantly among the seasons for winter wheat in Beijing. The opposite trend between the season variation in Ec/ET and Es/ET ratios was also observed for maize in northwestern China [9]. Many studies reported different temporal distributions of the Ec/ET ratio of crops from that of highland barley in Tibet [14]. Gao et al. [50] found that the Ec/ET ratio showed a parabolic trend for spring maize in the Loess Plateau. Zheng et al. [9] observed a strong seasonal pattern in the Ec/ET ratio, which increased continuously with the vegetation growth and then declined after grain filling for maize in northwestern China. A similar trend was also reported by Wei et al. [24] for rice and corn in Tsukuba, Japan.
ET components were greatly affected by meteorological variables; the correlation coefficients between the seasonal variation in ET components and meteorological variables are listed in Table 2. ET components were positively correlated significantly with air temperature (p < 0.01), relative humidity (p < 0.01), and precipitation (p < 0.01). ET and Es had the strongest correlations with air temperature, followed by relative humidity and precipitation. Previous studies showed that the meteorological variables had an important effect on seasonal variations in ET components [5,23,52,53]. Moreover, Ec and Es were greatly affected by soil moisture [2,54]; higher relative humidity and precipitation can increase the availability of soil moisture, which can promote the process of soil evaporation and vegetation transpiration [55]. Observation showed that the Ec rate had a linear relationship with air temperature for maize in arid regions [23,56]. The significant influence of air temperature on Ec was also reported by Zhang et al. [57] and Feng et al. [58]. These results were consistent with the strong correlations between Ec, Es, and air temperature, relative humidity, and precipitation. Ei correlated most significantly with relative humidity (p < 0.01) and precipitation (p < 0.01). The result agreed well with that from Zheng et al. [9] who found that Ei increased with the increase in precipitation for maize in northwestern China. Previous studies showed that Ei increased slowly with the increase in precipitation, while it gradually stabilized at maximum evaporation from the canopy, conforming well to a power function relationship [59,60]. However, the ratio of Ei to the gross precipitation decreased with the increase in precipitation, generally implying that higher Ei would occur during small precipitation yet with a longer duration [30]. ET components were negatively correlated with sunshine duration, while they correlated poorly with water vapor.

Table 2.
Correlation coefficients between the seasonal variations in ET components and meteorological variables.
Es/ET and Ec/ET ratios were not correlated with all the meteorological variables (Table 2), generally indicating that their seasonal variations were affected by the environment (such as sowing time, highland barley varieties), irrigation practice, and management rather than meteorological variables, which was reported by many studies [24,61]. For example, Ma and Song [2] revealed that seasonal changes in the Ec/ET ratio could be well described as a function of LAI for winter wheat in Beijing, implying that crop development plays a critical role in allocating the ET components. Yang et al. [44] also found a stronger correlation between the LAI and Ec/ET ratio of winter wheat. It is commonly reported that Es/ET and Ec/ET ratios varied exponentially and logarithmically with the increase in LAI for most crops, respectively [2,62,63]. This relationship was confirmed by many observations at field scale and model simulations at regional scales [24,41,46,64], while Ei/ET ratio correlated most significantly with relative humidity (p < 0.01), followed by precipitation (p < 0.01), air temperature (p < 0.01), and sunshine duration (p < 0.01).
3.3. Changing Trend of ET Components during 2001–2020
The variations in ET components and their ratios during 2001–2020 are shown in Figure 4. On average, ET of highland barley presented a decreasing trend with the rate of −3.79 mm/y (Figure 4g), while it increased significantly (p < 0.05) from 2001 to 2013 with the rate of 8.03 mm/y, and then sharply decreased (p < 0.01) until 2020, with the rate of −25.61 mm/y. ET did not have a universal trend at different altitude zones; it increased slightly at 3500–3600 and 3700–3800 m altitude zones, and a decreasing trend was observed for other altitude zones, with the most prominent changes at the 4000–4100 m altitude zone. Es decreased significantly (p < 0.05) with the rate of −4.88 mm/y (Figure 4a), while it increased significantly (p < 0.05) from 2001 to 2013 with the rate of 5.36 mm/y, and then sharply decreased (p < 0.01) until 2020, with the rate of −26.39 mm/y. The changing trend was similar to that of ET. Ec at different altitude zones presented a similar increasing trend during 2001–2020 (Figure 4c), with larger fluctuation occurring at 3700–3800 m and 3500–3600 m altitude zones, while Ei (Figure 4e) generally exhibited a similar trend to Ec.
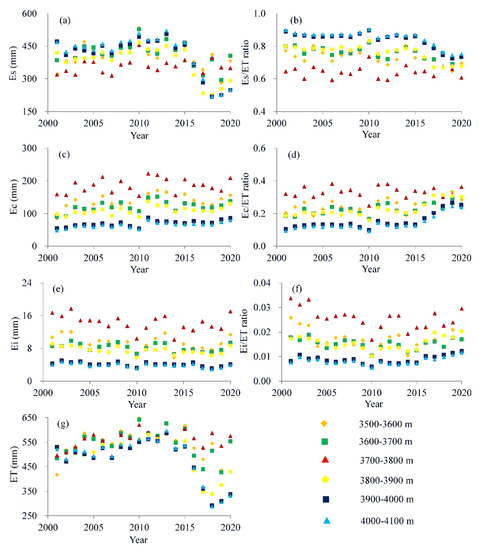
Figure 4.
Variations in Es (a), Es/ET (b), Ec (c), Ec/ET (d), Ei (e), Ei/ET (f), and ET (g) of highland barley during 2001–2020.
The Es/ET ratio decreased significantly (p < 0.05) with the rate of −0.44%/y during 2001–2020 (Figure 4b), resulting in an 8.34% decrease in the Es/ET ratio. The decreasing trend was more pronounced after 2010. The Ec/ET ratio (Figure 4d) generally showed an opposite trend to the Es/ET ratio. It increased significantly (p < 0.05) with the rate of 0.43%/y, resulting in an 8.08% increase in the Ec/ET ratio; a sharply increased trend (p < 0.01) was observed during 2010–2020. The Ei/ET ratio (Figure 4f) at different altitude zones had a similar changing trend, i.e., it slightly decreased during 2001–2010 and then changed to a slightly increasing trend during 2010–2020.
Many studies have been conducted to investigate the interannual variations in ET components over regional scales. Jiang et al. [65] used the improved SWH model to partition ET and analyzed the temporal variations in ET components in the Yellow River Basin. The results suggested that ET, Ec, and Es were significantly elevated during 1981–2010, and the air temperature was the most important factor affecting the variations. This was consistent with previous findings [66,67]. The increasing trend in ET components was also reported for the other regions [50,68]. Some studies revealed the increase in ET over the Tibet Plateau consequent to global warming [69,70]. For example, Wang et al. [36] estimated the ET components using the PML model and found that Es, Ec, and Ei exhibited an increasing trend during 1982–2012. The ET estimated from the water balance model also presented an increasing trend for 16 catchments [71,72]. This phenomenon of increasing trends had also been observed in Mediterranean-climate regions during almost the same period [73]. Additionally, the effect of temperature on the ET in the alpine region was more pronounced than that in other regions [74]. However, due to the lack of time-series datasets for the observations of ET components, few studies have been conducted for crops.
ET components were not correlated significantly with meteorological variables (Table 3); this was most likely due to the fact that Tibet has a unique plateau climate with an average precipitation of less than 480 mm [35], which is much lower than the ET demand, resulting in a severe water shortage for cropland. Under these conditions, it has been a common practice to irrigate cropland using the available water, making it important for influencing the soil moisture and crucial for affecting the interannual changes of Es and Ec for highland barley in Tibet. Previous studies also revealed the response of crop ET components to irrigation [44,75]. Compared with Es and Ec, the interannual variation in Ei was more influenced by meteorological variables, especially the precipitation characteristics. As can be seen from Table 3, Ei/ET ratio correlated significantly with precipitation (p < 0.05), which is consistent with the result from Wang et al. [36], who found that Ei was correlated significantly with precipitation in eastern Tibet.

Table 3.
Correlation coefficients between the interannual variations in ET components and meteorological variables.
3.4. Limitations
This study mainly dealt with seasonal and interannual variations in ET components and their ratio in highland barley in regions with different altitudes and then analyzed the correlation between the ET components and meteorological factors. However, there are still some limitations. In fact, the ET components of highland barley were affected by climate change, as well as by soil properties and barley varieties. Moreover, the meteorological factors affecting ET components were sunshine duration, air temperature, precipitation, air pressure, water vapor, and relative humidity used in this paper, as well as other meteorological variables such as wind speed, maximum air temperature, minimum air temperature, and water vapor deficit, all of which have an impact on ET component variations and need further research in future studies.
4. Conclusions
This study investigated the characteristics and variations in ET components and their proportions of highland barley in Tibet using the PML ET product during 2001–2020 and explored the relations between the variation in ET components and meteorological factors. The results showed that Es was the most predominant ET component and accounted for 77.3% of the total ET of highland barley in Tibet. ET components varied obviously over the altitude; ET generally decreased with the increase in altitude, with higher ET observed at 3700–3800 m altitude zone. Es and the Es/ET ratio showed a decreasing trend with the increase in altitude from 3500 m to 3800 m and then changed to an increasing trend until reaching the altitude of 4100 m, while Ec, Ei and their ratios presented an opposite varying pattern to ES. Seasonal variations in daily ET components of highland barley displayed a parabolic pattern peaked in August, while the temporal distributions differed considerably among different ET component ratios. The Ei/ET ratio generally presented a similar changing pattern to ET components. The Es/ET ratio showed a dual parabolic pattern with two peaks in April and November and a valley in August, while the Ec/ET ratio generally exhibited an opposite changing pattern to the Es/ET ratio. Seasonal variations in ET components were greatly affected by meteorological variables. ET components were correlated significantly with air temperature, relative humidity, and precipitation, while the seasonal variations in Es/ET and Ec/ET ratios were more influenced by the environment (such as sowing time, highland barley varieties), irrigation practices, and management rather than meteorological variables. Es and its ratio in highland barley decreased significantly during 2001–2020, while the Ec/ET ratio generally showed an opposite trend to the Es/ET ratio; Ei and its ratio presented an insignificantly decreasing trend. The interannual variations in ET components were not significantly correlated significantly with meteorological variables, while the Ei was more influenced by meteorological variables, especially precipitation characteristics.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, visualization, and writing—original draft preparation, J.C.; funding acquisition, review, and validation, H.T.; conceptualization, validation, and writing—review and editing, Y.J.; software, methodology, Q.T.; formal analysis, L.Y.; review and validation, Q.C.; review, supervision, funding acquisition, and writing—review and editing, D.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Youth Innovation Promotion Association (No. 2018417 and 2021385), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41901130 and 42061015), Chongqing Science and Technology project (No. cstc2021jcyj-msxmX0187), Chongqing Municipal Bureau of Water Resources (No. 5000002021BF40001), Institute of Agricultural Resources and Environment, Tibet Academy of Agricultural and Animal Husbandry Science (No. 2020ZZKT-01), and Rikaze City Science and Technology Plan Project (No. RKZ2020KJ01).
Data Availability Statement
PML-V2 ET and its components used in this paper can be downloaded from Google Earth Engine. The land use data of Tibet in 2015 can be collected from Resource and Environment Science and Data Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences (https://www.resdc.cn, accessed on 27 July 2021). Meteorological data are applicable.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the research environment provided by Chongqing Institute of Green and Intelligent Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Institute of Agricultural Resources and Environment, Tibet Academy of Agricultural and Animal Husbandry Science.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhang, Y.; Kong, D.; Gan, R.; Chiew, F.H.S.; McVicar, T.R.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y. Coupled estimation of 500 m and 8-day resolution global evapotranspiration and gross primary production in 2002–2017. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 222, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Song, X. Applying stable isotopes to determine seasonal variability in evapotranspiration partitioning of winter wheat for optimizing agricultural management practices. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Tang, Q.; Yan, L.; Wu, S.; Yan, L.; Tan, D.; Chen, J.; Chen, Q. Spatiotemporal Variations and Influencing Factors of Terrestrial Evapotranspiration and Its Components during Different Impoundment Periods in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. Water 2021, 13, 2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Li, Y.; Wu, P.; Zhao, X.; Chen, X.; Gao, X. Coupling evapotranspiration partitioning with water migration to identify the water consumption characteristics of wheat and maize in an intercropping system. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 290, 108034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentín, F.; Nortes, P.A.; Domínguez, A.; Sánchez, J.M.; Intrigliolo, D.S.; Alarcón, J.J.; López-Urrea, R. Comparing evapotranspiration and yield performance of maize under sprinkler, superficial and subsurface drip irrigation in a semi-arid environment. Irrig. Sci. 2020, 38, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Lu, N.; Fu, B.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Fang, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L. Evapotranspiration partitioning and its implications for plant water use strategy: Evidence from a black locust plantation in the semi-arid Loess Plateau, China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 424, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes, P.; Rodrigues, G.C.; Alves, I.; Pereira, L.S. Partitioning evapotranspiration, yield prediction and economic returns of maize under various irrigation management strategies. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 135, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhao, W. Canopy transpiration obtained from leaf transpiration, sap flow and FAO-56 dual crop coefficient method. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 2983–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Fan, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhuang, Q. Evapotranspiration partitioning and water productivity of rainfed maize under contrasting mulching conditions in Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 243, 106473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Qiu, R.; Ge, J.; Bo, G.; Ping, Y.; Xin, Q.; Wang, S. Evapotranspiration partitioning of greenhouse grown tomato using a modified Priestley–Taylor model. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 247, 106709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Mei, X.; Gu, F.; Hao, W.; Gong, D.; Li, H. Evapotranspiration partitioning and energy budget in a rainfed spring maize field on the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2018, 166, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, Y.; Xu, D.; Zhao, N.; Lei, B.; Rosa, R.D.; Paredes, P.; Paço, T.A.; Pereira, L.S. The dual crop coefficient approach to estimate and partitioning evapotranspiration of the winter wheat–summer maize crop sequence in North China Plain. Irrig. Sci. 2013, 31, 1303–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Yu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, G. Partitioning evapotranspiration based on the concept of underlying water use efficiency. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 1160–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cai, H.; Yu, L.; Peng, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, X. Evapotranspiration partitioning and crop coefficient of maize in dry semi-humid climate regime. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 236, 106164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuttleworth, W.J.; Wallace, J.S. Evaporation from sparse crops-an energy combination theory. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 111, 839–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Yu, G.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, X.; Li, Y.; Shi, P.; Wang, Y.; Song, X.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, L.; et al. Partitioning of evapotranspiration and its controls in four grassland ecosystems: Application of a two-source model. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2009, 149, 1410–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Li, S.; Yu, G.; Sun, X.; Zhang, L.; Han, S.; Li, Y. Modeling evapotranspiration by combing a two-source model, a leaf stomatal model, and a light-use efficiency model. J. Hydrol. 2013, 501, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuning, R.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Rajaud, A.; Cleugh, H.; Tu, K. A simple surface conductance model to estimate regional evaporation using MODIS leaf area index and the Penman-Monteith equation. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Leuning, R.; Hutley, L.B.; Beringer, J.; McHugh, I.; Walker, J.P. Using long-term water balances to parameterize surface conductances and calculate evaporation at 0.05° spatial resolution. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, R.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, H.; Yang, Y.; Eamus, D.; Cheng, L.; Chiew, F.H.S.; Yu, Q. Use of satellite leaf area index estimating evapotranspiration and gross assimilation for Australian ecosystems. Ecohydrology 2018, 11, e1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Peña-Arancibia, J.L.; McVicar, T.R.; Chiew, F.H.S.; Vaze, J.; Liu, C.; Lu, X.; Zheng, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. Multi-decadal trends in global terrestrial evapotranspiration and its components. Sci. Rep. UK 2016, 6, 19124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, R.D.; Paredes, P.; Rodrigues, G.C.; Alves, I.; Fernando, R.M.; Pereira, L.S.; Allen, R.G. Implementing the dual crop coefficient approach in interactive software. 1. Background and computational strategy. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 103, 8–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Kang, S.; Li, F.; Du, T.; Tong, L.; Comas, L. Evapotranspiration partitioning and variation of sap flow in female and male parents of maize for hybrid seed production in arid region. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 176, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Lee, X.; Wen, X.; Xiao, W. Evapotranspiration partitioning for three agro-ecosystems with contrasting moisture conditions: A comparison of an isotope method and a two-source model calculation. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 252, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberbach, P.; Pala, M. Crop row spacing and its influence on the partitioning of evapotranspiration by winter-grown wheat in Northern Syria. Plant Soil 2005, 268, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drastig, K.; Suárez Quiñones, T.; Zare, M.; Dammer, K.-H.; Prochnow, A. Rainfall interception by winter rapeseed in Brandenburg (Germany) under various nitrogen fertilization treatments. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 268, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouade, G.; Ezzahar, J.; Amenzou, N.; Er-Raki, S.; Benkaddour, A.; Khabba, S.; Jarlan, L. Combining stable isotopes, Eddy Covariance system and meteorological measurements for partitioning evapotranspiration, of winter wheat, into soil evaporation and plant transpiration in a semi-arid region. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 177, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DehghaniSanij, H.; Kanani, E.; Akhavan, S. Evapotranspiration and components of corn (Zea mays L.) under micro irrigation systems in a semi-arid environment. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2020, 18, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, P.; Zhao, X.; Gao, Y.; Chen, X. Water use and crop coefficient of the wheat–maize strip intercropping system for an arid region in northwestern China. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 161, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, R.; Pan, Y.; Paradeloc, M. Rainfall partitioning into throughfall, stemflow and interception loss by two xerophytic shrubs within a rain-fed re-vegetated desert ecosystem, northwestern China. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 1084–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Shen, Z.; Fu, G. Response of soil respiration to experimental warming in a highland barley of the Tibet. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Feng, W.; Lu, H.; Yao, T.; Yu, Q. Drought characteristics and its elevation dependence in the Qinghai–Tibet plateau during the last half-century. Sci. Rep.-UK 2020, 10, 14323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yao, Z.; Yu, C.; Zhong, Z. Assessing crop water demand and deficit for the growth of spring highland barley in Tibet, China. J. Integr. Agric. 2013, 12, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ge, Y.; Chang, J.; Jiang, B.; Jiang, H.; Peng, C.; Zhu, J.; Yuan, W.; Qi, L.; Yu, S. Carbon storage by ecological service forests in Zhejiang Province, subtropical China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2007, 245, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Y.; Li, X.; Cheng, G. Climate warming over the past half century has led to thermal degradation of permafrost on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Cryosphere 2018, 12, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, J.; Yu, Z.; Ding, Y.; Xing, W.; Lu, W. Satellite retrieval of actual evapotranspiration in the Tibetan Plateau: Components partitioning, multidecadal trends and dominated factors identifying. J. Hydrol. 2018, 559, 471–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Kong, D.; Zhou, X. LUCC-driven changes in gross primary production and actual evapotranspiration in northern China. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2020, 125, e2019JD031705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, L.; Zhang, K.; Wang, J.; Feng, J.; Zhang, M. A Comprehensive Evaluation of Five Evapotranspiration Datasets Based on Ground and GRACE Satellite Observations: Implications for Improvement of Evapotranspiration Retrieval Algorithm. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, T.; Paredes, P.; Duan, L.; Pereira, L.S. Water use by a groundwater dependent maize in a semi-arid region of Inner Mongolia: Evapotranspiration partitioning and capillary rise. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 152, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Deng, Y.; Li, X.Y.; Wei, Z.; Hu, X.; Tian, F.; Wu, X.; Huang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, C.; et al. Dynamical effects of plastic mulch on evapotranspiration partitioning in a mulched agriculture ecosystem: Measurement with numerical modeling. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 268, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Liang, L.L.; Wang, L.; Jenerette, G.D.; McCabe, M.F.; Grantz, D.A. Partitioning of evapotranspiration using a stable isotope technique in an arid and high temperature agricultural production system. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 179, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kool, D.; Agam, N.; Lazarovitch, N.; Heitman, J.L.; Sauer, T.J.; Ben-Gal, A. A review of approaches for evapotranspiration partitioning. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 184, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Yoshimura, K.; Okazaki, A.; Kim, W.; Liu, Z.; Yokoi, M. Partitioning of evapotranspiration using high-frequency water vapor isotopic measurement over a rice paddy field. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 3716–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wang, P.; You, D.; Liu, W. Coupling evapotranspiration partitioning with root water uptake to identify the water consumption characteristics of winter wheat: A case study in the North China Plain. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 259, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Yang, B.; Sun, X.; Lee, X. Evapotranspiration partitioning through in-situ oxygen isotope measurements in an oasis cropland. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 230, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Du, T.; Ding, R.; Tong, L.; Li, S.; Wang, L. Multiple methods to partition evapotranspiration in a maize field. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Song, X.; Han, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B. Determination of evaporation, transpiration and deep percolation of summer corn and winter wheat after irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 105, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Kang, S.; Tong, L.; Li, S.; Ding, R.; Du, T. Modeling evapotranspiration and its components of maize for seed production in an arid region of northwest China using a dual crop coefficient and multisource models. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 222, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafi, Z.; Merlin, O.; Le Dantec, V.; Khabba, S.; Mordelet, P.; Er-Raki, S.; Amazirh, A.; Olivera-Guerra, L.; Hssaine, B.A.; Simonneaux, V.; et al. Partitioning evapotranspiration of a drip-irrigated wheat crop: Inter-comparing eddy covariance-, sap flow-, lysimeter-and FAO-based methods. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 265, 310–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Sun, M.; Zhao, Q.; Wu, P.; Zhao, X.; Pan, W.; Wang, Y. Actual ET modelling based on the Budyko framework and the sustainability of vegetation water use in the loess plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1550–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Ma, M. Evapotranspiration components and water use efficiency from desert to alpine ecosystems in drylands. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 298, 108283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, W.; He, J.; Zhang, K. Energy exchange and evapotranspiration over irrigated seed maize agroecosystems in a desert-oasis region, northwest China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 223, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberto, M.C.R.; Quilty, J.R.; Buresh, R.J.; Wassmann, R.; Haidar, S.; Correa, T.Q., Jr.; Sandro, J.M. Actual evapotranspiration and dual crop coefficients for dry-seeded rice and hybrid maize grown with overhead sprinkler irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 136, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Song, X. Using stable isotopes to determine seasonal variations in water uptake of summer maize under different fertilization treatments. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 550, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiemuerbieke, B.; Min, X.J.; Zang, Y.X.; Xing, P.; Ma, J.Y.; Sun, W. Water use patterns of co-occurring C3 and C4 shrubs in the Gurbantonggut desert in northwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragoni, D.; Lakso, A.N.; Piccioni, R.M.; Tarara, J.M. Transpiration of grapevines in the humid northeastern United States. Am. J. Enol. Viticult. 2006, 57, 460–467. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Xu, D.; Liu, Y.; Li, F.; Cai, J.; Du, L. Multi-scale evapotranspiration of summer maize and the controlling meteorological factors in north China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 216, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Cui, N.; Du, T.; Gong, D.; Hu, X.; Zhao, L. Response of sap flux and evapotranspiration to deficit irrigation of greenhouse pear-jujube trees in semi-arid northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 194, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Chen, S.; Tian, D.; Kang, W. Contribution of Cinnamomum camphora (L.) presl plantation to precipitation redistribution. Bull. Soil Water Consery. 2005, 25, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Ren, D.; Wang, G.; Hu, H.; Li, T.; Liu, G. Analysis of artificial precipitation interception over two meadow species on Qinghai Tibet Plateau. Adv. Water Sci. 2009, 20, 769–774. [Google Scholar]
- Sutanto, S.J.; van den Hurk, B.J.J.M.; Dirmeyer, P.A.; Seneviratne, S.I.; Röckmann, T.; Trenberth, K.E.; Blyth, E.M.; Wenninger, J.; Hoffmann, G. HESS Opinions “A perspective on isotope versus non-isotope approaches to determine the contribution of transpiration to total evaporation”. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sc. 2014, 18, 2815–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Kimura, R.; Kamichika, M. Estimation of evapotranspiration, transpiration ratio and water-use efficiency from a sparse canopy using a compartment model. Agric. Water Manag. 2004, 65, 173–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Huang, G.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, M. Experimental investigation of soil evaporation and evapotranspiration of winter wheat under sprinkler irrigation. Agric. Sci. China 2009, 8, 1360–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Good, S.P.; Caylor, K.K. Global synthesis of vegetation control on evapotranspiration partitioning. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 6753–6757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Liao, C.; Hu, Z.; Cao, R.; Wu, H. Revealing the spatio-temporal variability of evapotranspiration and its components based on an improved Shuttleworth-Wallace model in the Yellow River Basin. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 262, 110310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, T.; Wu, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, F.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, C. Seasonal divergence in the sensitivity of evapotranspiration to climate and vegetation growth in the Yellow River Basin, China. J. Geophys. Res.-Biogeo. 2017, 122, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liang, W.; Fu, B.; Lü, Y.; Fu, S.; Wang, S.; Su, H. Vegetation changes in recent large-scale ecological restoration projects and subsequent impact on water resources in China’s Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, M.; Mo, X.; Liu, S.; Hu, S. Contributions of climate change and vegetation greening to evapotranspiration trend in a typical hilly-gully basin on the Loess Plateau, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 657, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, F.; You, Q.; Xue, X.; Guo, J.; Wang, T. Evapotranspiration and its source components change under experimental warming in alpine meadow ecosystem on the Qinghai-Tibet plateau. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 84, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Piao, S.; Jeong, S.J.; Zhou, L.; Zeng, Z.; Ciais, P.; Chen, D.; Huang, M.; Jin, C.; Li, L.Z.X.; et al. Evaporative cooling over the Tibetan Plateau induced by vegetation growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 9299–9304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Tang, Y.; Yang, Y. Trends in pan evaporation and reference and actual evapotranspiration across the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, D.M.; Thornton, P.E.; Oleson, K.W.; Bonan, G.B. The Partitioning of Evapotranspiration into Transpiration, Soil Evaporation, and Canopy Evaporation in a GCM: Impacts on Land–Atmosphere Interaction. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 862–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriadou, S.; Nikolakopoulos, K.G. Evapotranspiration Trends and Interactions in Light of the Anthropogenic Footprint and the Climate Crisis: A Review. Hydrology 2021, 8, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, L.; Yang, X.; Wu, X.; Wang, P.; Lin, H.; Zhang, G.; Miao, C. Evapotranspiration and its dominant controls along an elevation gradient in the Qinghai Lake watershed, northeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2019, 575, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wen, X.; Sun, X. Irrigation depth far exceeds water uptake depth in an oasis cropland in the middle reaches of Heihe River Basin. Sci. Rep. UK 2015, 5, 15206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).