Cross-Comparison of Global Surface Albedo Operational Products-MODIS, GLASS, and CGLS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
2.1. Data
2.1.1. Ground Measurements
2.1.2. MODIS
2.1.3. GLASS
2.1.4. CGLS
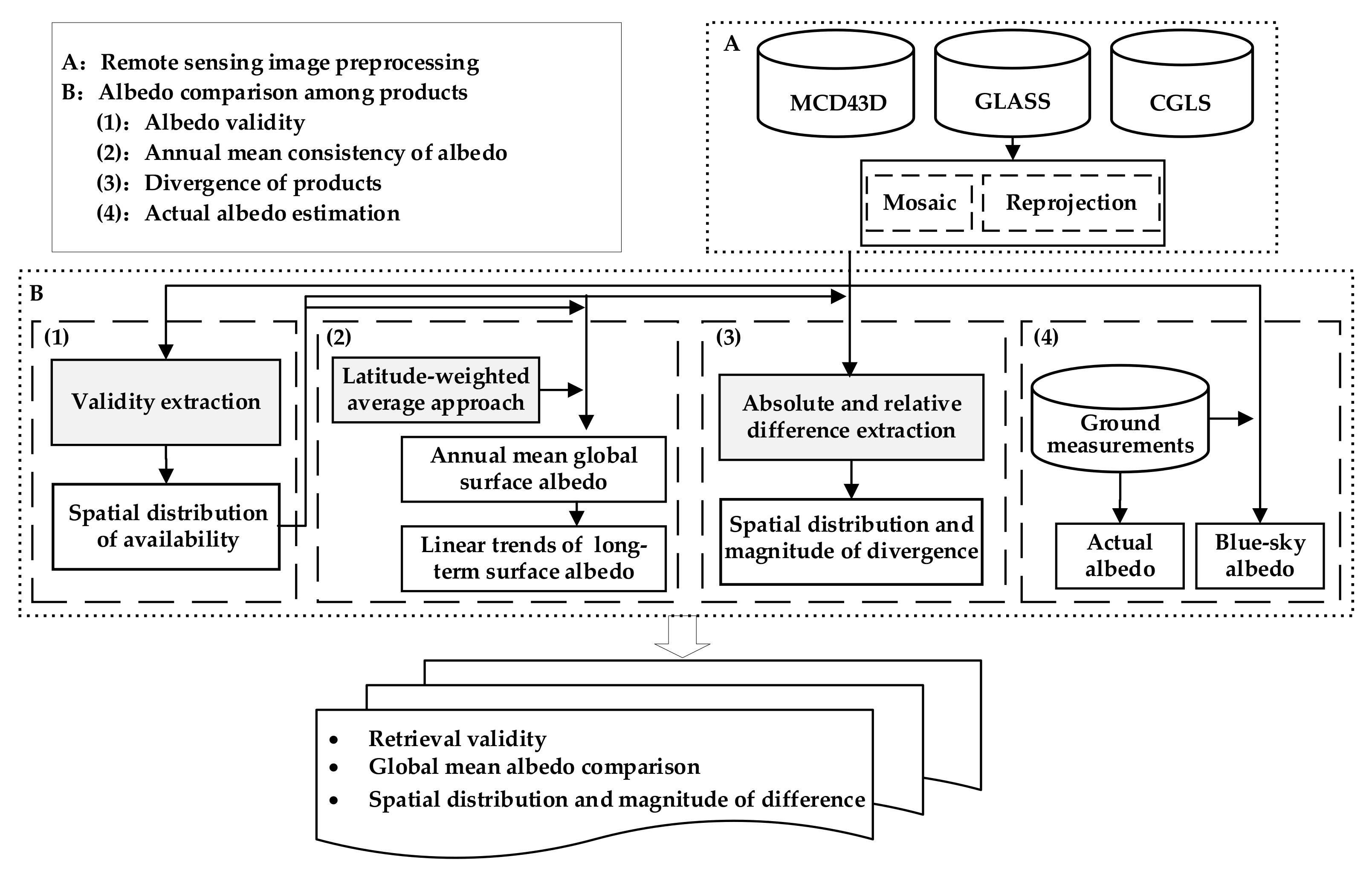
2.2. Methodology
3. Result
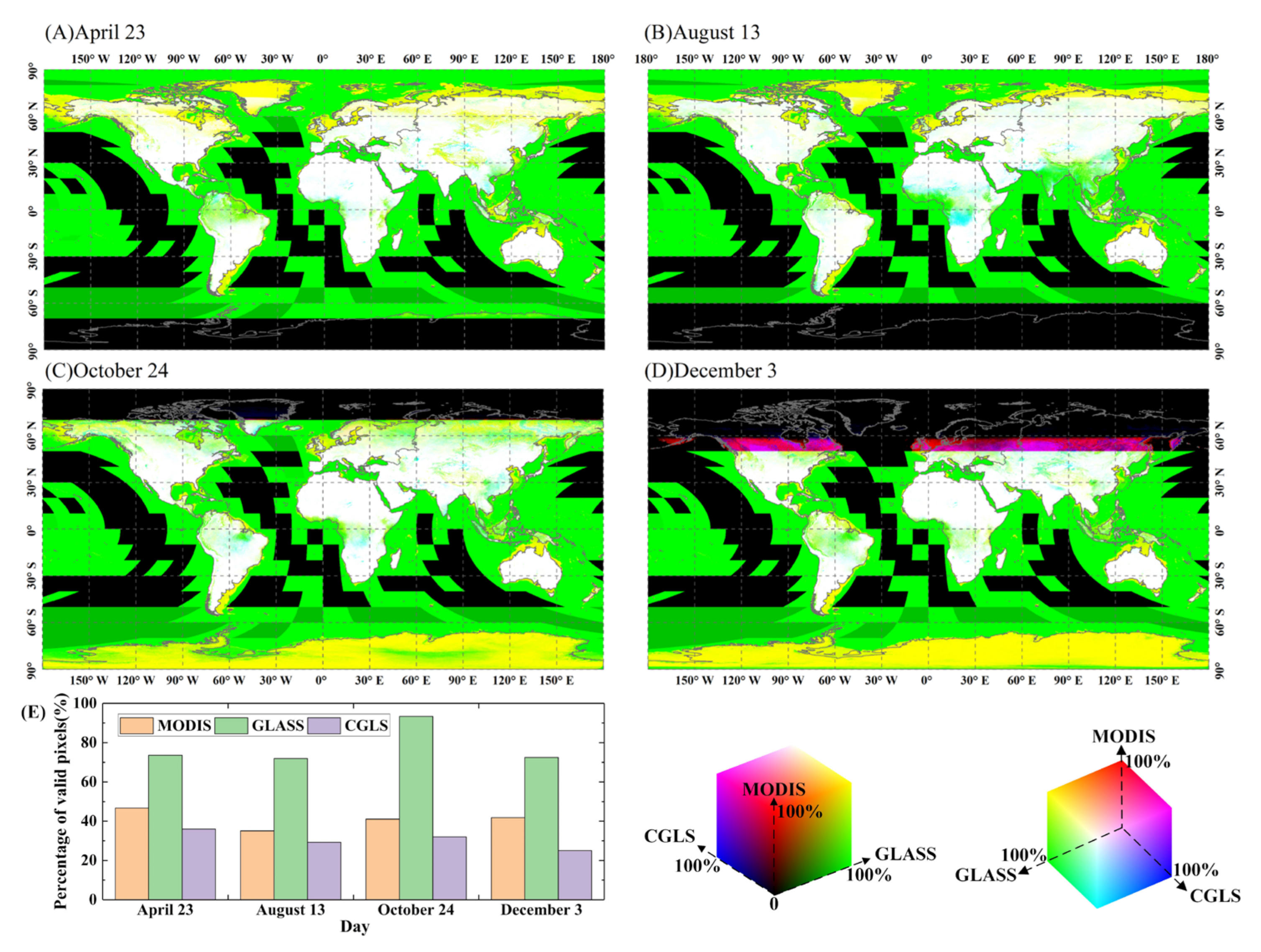
3.1. Retrieval Validity
3.2. Global Mean Albedo Comparison
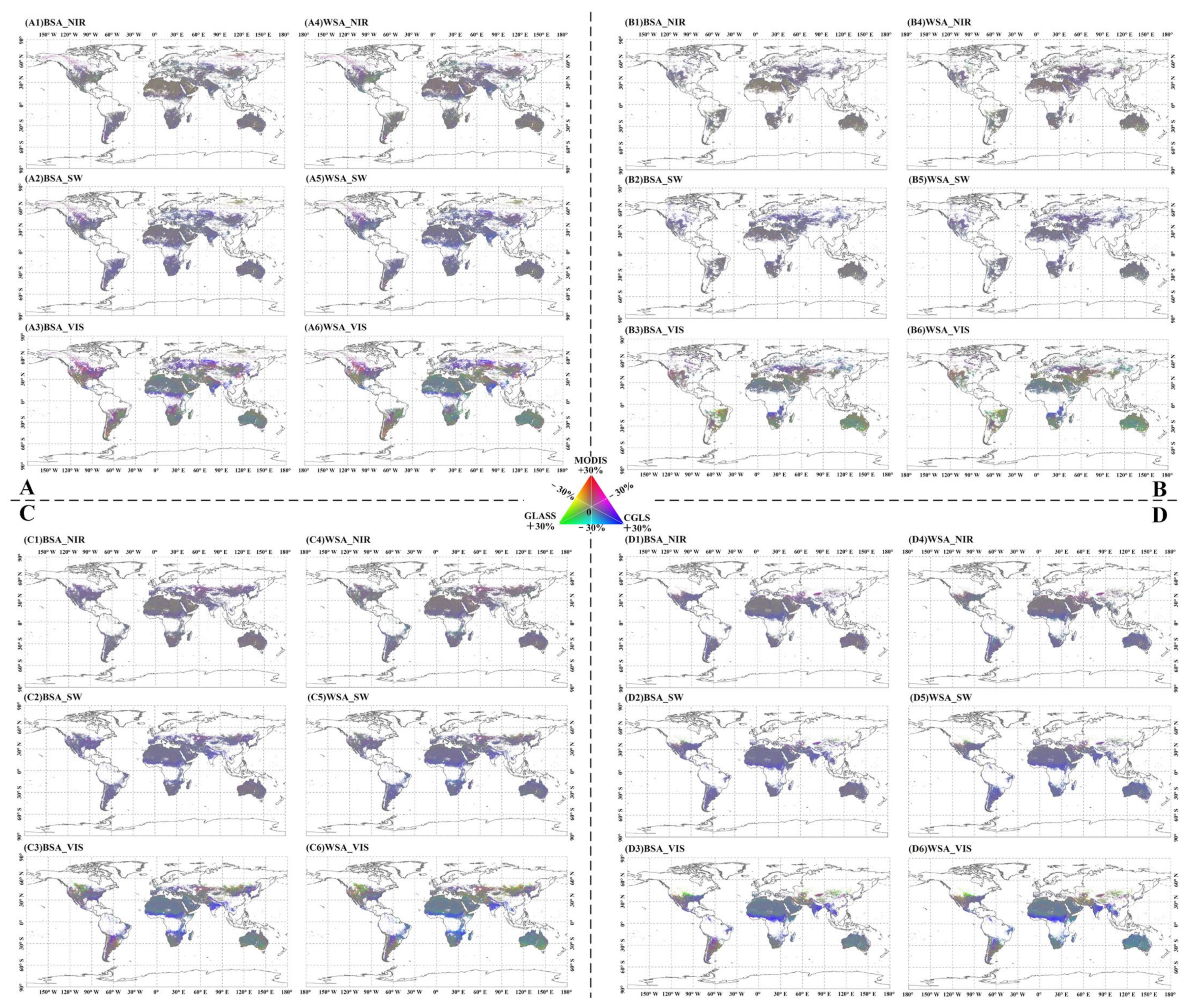
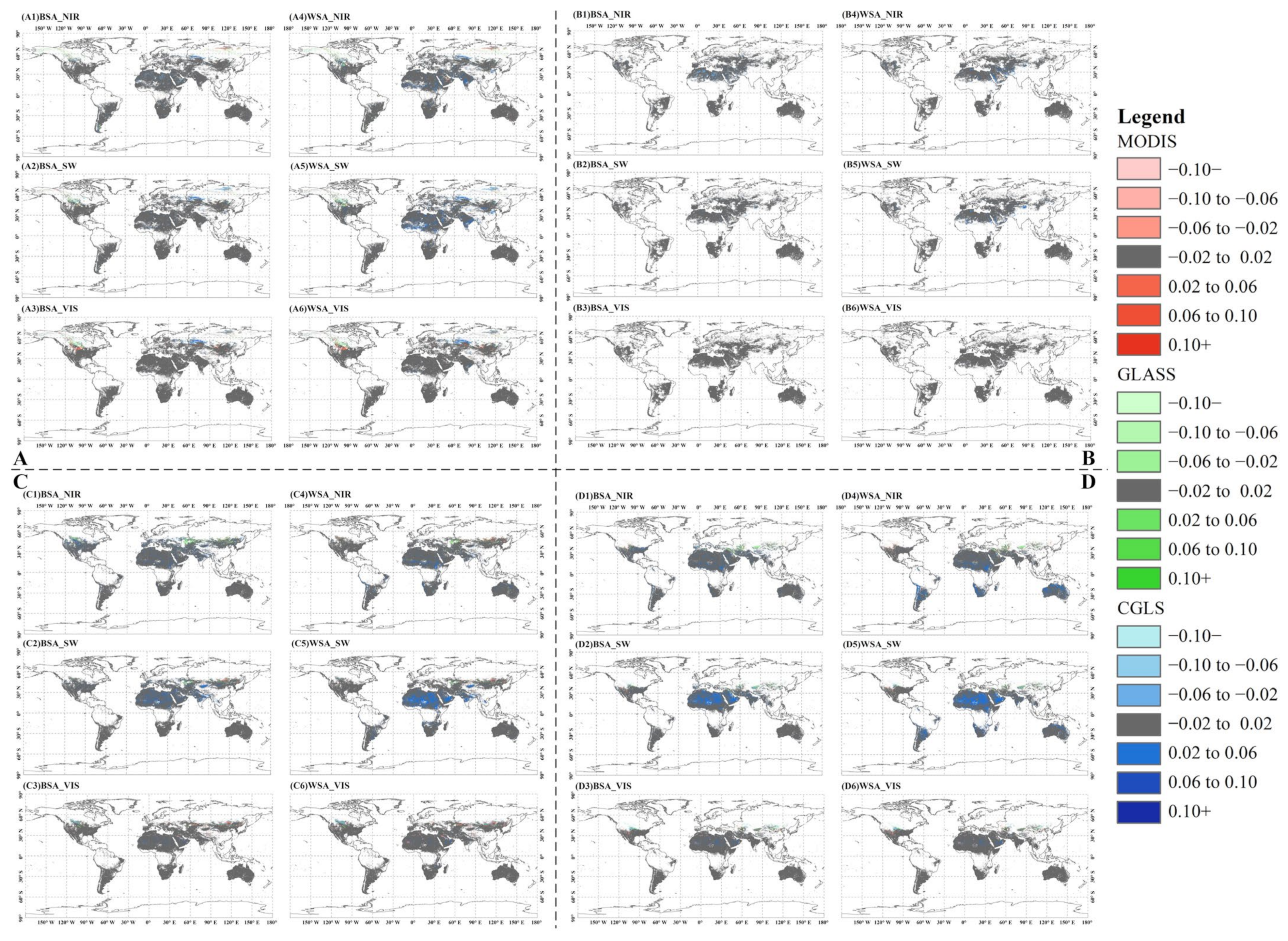
3.3. Differences among Albedo Products
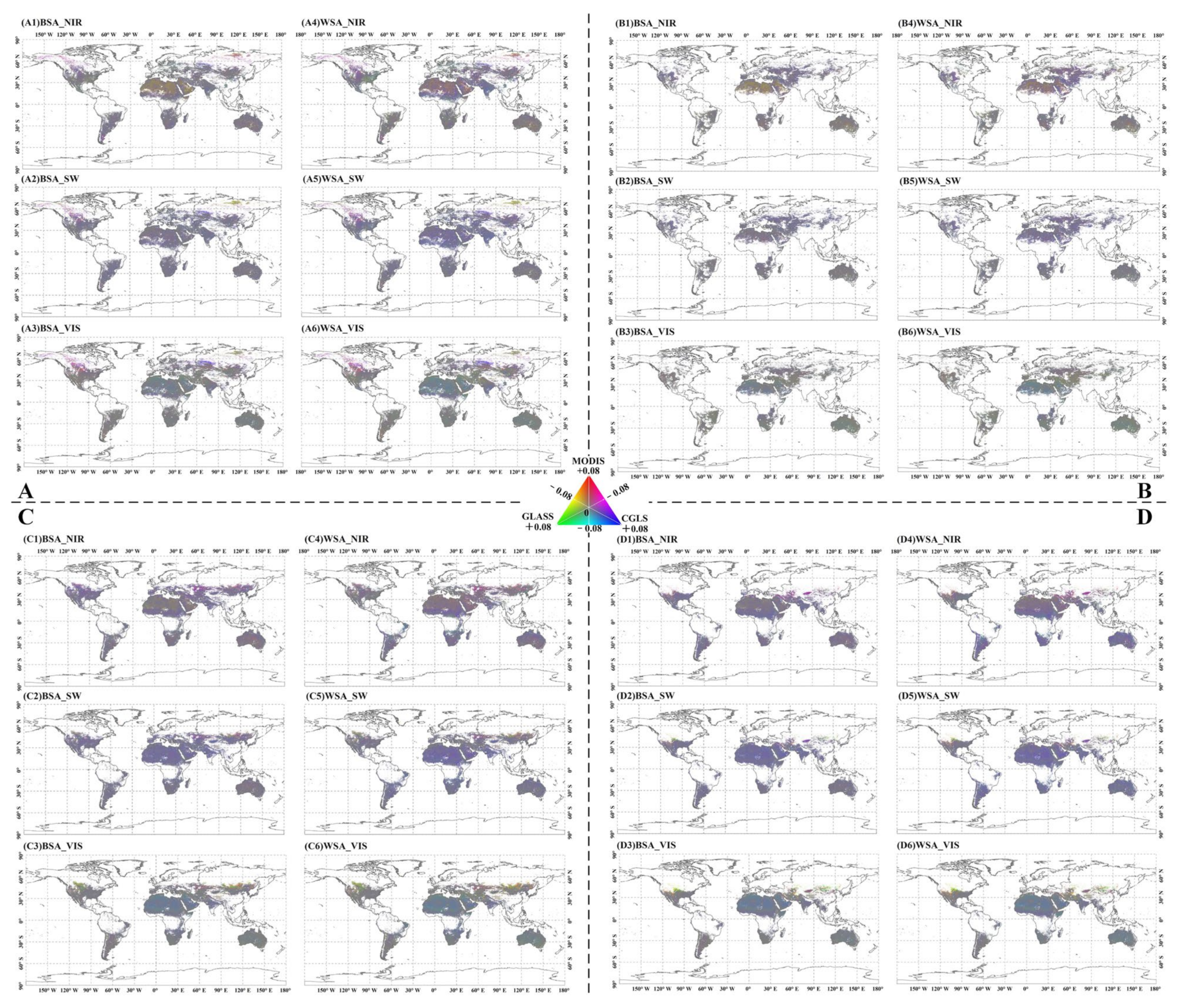
3.3.1. Spatial Distribution of Difference
3.3.2. Magnitude of Apparent Difference
3.4. Comparison with Ground Measurements
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dickinson, R.E. Land surface processes and climate—Surface albedos and energy balance. In Advances in Geophysics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1983; Volume 25, pp. 305–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.L.; Wang, D.D.; He, T.; Yu, Y.Y. Remote sensing of earth’s energy budget: Synthesis and review. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2019, 12, 737–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, C.L.; Zhang, B.Q.; Cheng, L.Y.; Hu, L.Q.; Chen, F.H. Vegetation dynamics and their effects on surface water-energy balance over the Three-North Region of China. Agric. Meteorol. 2019, 275, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.H.; Hou, M.T.; Zhao, C.L.; Zhen, X.J.; Yao, L.; Xu, Y.H. Human-induced changes of surface albedo in Northern China from 1992–2012. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 79, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Lan, X.; Li, W.; Li, T. Influence of Land Use Change on the Surface Albedo and Climate Change in the Qinling-Daba Mountains. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charney, J.; Stone, P.H.; Quirk, W.J. Drought in the Sahara: A biogeophysical feedback mechanism. Science 1975, 187, 434–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veraverbeke, S.; Verstraeten, W.W.; Lhermitte, S.; Van De Kerchove, R.; Goossens, R. Assessment of post-fire changes in land surface temperature and surface albedo, and their relation with fire–burn severity using multitemporal MODIS imagery. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2012, 21, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyons, E.A.; Jin, Y.F.; Randerson, J.T. Changes in surface albedo after fire in boreal forest ecosystems of interior Alaska assessed using MODIS satellite observations. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bright, B.C.; Hudak, A.T.; Kennedy, R.E.; Braaten, J.D.; Khalyani, A.H. Examining post-fire vegetation recovery with Landsat time series analysis in three western North American forest types. Fire Ecol. 2019, 15, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Wei, Y.; Fu, B.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Moran, E.F. Evolution and effects of the social-ecological system over a millennium in China’s Loess Plateau. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Liang, S.L.; Liu, Q.; He, T.; Liu, S.H.; Li, X.W. Mapping Surface Broadband Albedo from Satellite Observations: A Review of Literatures on Algorithms and Products. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 990–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaaf, C.B.; Gao, F.; Strahler, A.H.; Lucht, W.; Li, X.W.; Tsang, T.; Strugnell, N.C.; Zhang, X.Y.; Jin, Y.F.; Muller, J.P.; et al. First operational BRDF, albedo nadir reflectance products from MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Q.; Erb, A.M.; Li, Z.; Schaaf, C.B.; Zhang, X.; Roman, M.O.; Scott, R.L.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Evaluation of the VIIRS BRDF, Albedo and NBAR products suite and an assessment of continuity with the long term MODIS record. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 201, 256–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrer, D.; Smets, B.; Ceamanos, X.; Roujean, J.-L. SPOT/VEGETATION and PROBA-V Surface Albedo Products—1 Km Version 1; Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document (ATBD), Issue 2.11. Copernicus Global Land Operations CGLOPS-1 (Framework Service Contract N° 199494-JRC). Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/global/sites/cgls.vito.be/files/products/CGLOPS1_ATBD_SA1km-V1_I2.11.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- Liu, N.F.; Liu, Q.; Wang, L.Z.; Liang, S.L.; Wen, J.G.; Qu, Y.; Liu, S.H. A statistics-based temporal filter algorithm to map spatiotemporally continuous shortwave albedo from MODIS data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 2121–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Liang, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, N.; Liu, S. Direct-estimation algorithm for mapping daily land-surface broadband albedo from MODIS data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 52, 907–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diner, D.J.; Martonchik, J.V.; Borel, C.; Gerstl, S.A.W.; Gordon, H.R.; Knyazikhin, Y.; Myneni, R.; Pinty, B.; Verstraete, M.M. Multi-Angle Imaging Spectro-Radiometer: Level 2 Surface Retrieval Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document; Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2008. Available online: https://eospso.gsfc.nasa.gov/sites/default/files/atbd/ATB_L2Surface43.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- Shuai, Y.M.; Masek, J.G.; Gao, F.; Schaaf, C.B. An algorithm for the retrieval of 30-m snow-free albedo from Landsat surface reflectance and MODIS BRDF. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2204–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, Y.M.; Masek, J.G.; Gao, F.; Schaaf, C.B.; He, T. An approach for the long-term 30-m land surface snow-free albedo retrieval from historic Landsat surface reflectance and MODIS-based a priori anisotropy knowledge. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, O.; Pinnock, P.; Mulle, J.-P.; Kennedy, T.; Lewis, P.; Kharbouche, S.; Fisher, D.; North, P.; Fisher, J.; Preusker, R.; et al. GlobAlbedo: Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document. European Space Agency. Available online: http://www.globalbedo.org/docs/ (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- Schroeder, T.; Fischer, J.; Preusker, R.; Schaale, M.; Regner, P. Retrieval of surface reflectances in the framework of the MERIS GLOBAL LAND SURFACE ALBEDO MAPS Project. In Proceedings of the MERIS (A) ATSR Workshop 2005 (ESA SP-597), Frascati, Italy, 26–30 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, J.P.; Preusker, R.; Fischer, J.; Zuhlke, M.; Brockmann, C.; Regner, P. ALBEDOMAP: MERIS land surface albedo retrieval using data fusion with MODIS BRDF and its validation using contemporaneous EO and in situ data products. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS 2007), Barcelona, Spain, 23–28 June 2007; pp. 2404–2407. [Google Scholar]
- Carrer, D.; Roujean, J.-L.; Meurey, C. Comparing operational MSG/SEVIRI land surface albedo products from Land SAF with ground measurements and MODIS. IEEE Trans Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 48, 1714–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kati, A.; Jääskeläinen, E.; Riihelä, A.; Manninen, T.; Andersson, K. Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document–CM SAF Cloud, Albedo, Radiation Data Record, AVHRR-based, Edition 2 (CLARA-A2) –Surface Albedo. EUMETSAT Satellite Application Facility on Climate Monitoring. Available online: https://www.cmsaf.eu/SharedDocs/Literatur/document/2016/saf_cm_fmi_atbd_gac_sal_2_3_pdf.pdf?__blob=publicationFile (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- Maignan, F.; Breon, F.M.; Lacaze, R. Bidirectional reflectance of Earth targets: Evaluation of analytical models using a large set of spaceborne measurements with emphasis on the Hot Spot. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 90, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacaze, R.; Maignan, F. POLDER-3/PARASOL Land Surface Algorithms Description. Available online: https://www.theia-land.fr/wp-content-theia/uploads/sites/2/2018/12/PARASOL_TE_AlgorithmDescription_I3.11.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- Shuai, Y.; Tuerhanjiang, L.; Shao, C.; Gao, F.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, D.; Liu, T.; Liang, J.; Chu, N. Re-understanding of land surface albedo and related terms in satellite-based retrievals. Big Earth Data 2020, 4, 45–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roujean, J.L.; Leroy, M.; Deschamps, P.Y. A bidirectional reflectance model of the Earth’s surface for the correction of remote sensing data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1992, 97, 20455–20468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucht, W.; Schaaf, C.B.; Strahler, A.H. An algorithm for the retrieval of albedo from space using semiempirical BRDF models. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 977–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Houspanossian, J.; Gimenez, R.; Jobbagy, E.; Nosetto, M. Surface albedo raise in the South American Chaco: Combined effects of deforestation and agricultural changes. Agric. Meteorol. 2017, 232, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hovi, A.; Lindberg, E.; Lang, M.; Arumae, T.; Peuhkurinen, J.; Sirparanta, S.; Pyankov, S.; Rautiainen, M. Seasonal dynamics of albedo across European boreal forests: Analysis of MODIS albedo and structural metrics from airborne LiDAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 224, 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planque, C.; Carrer, D.; Roujean, J.L. Analysis of MODIS albedo changes over steady woody covers in France during the period of 2001–2013. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 191, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riihelä, A.; King, M.D.; Anttila, K. The surface albedo of the Greenland Ice Sheet between 1982 and 2015 from the CLARA-A2 dataset and its relationship to the ice sheet’s surface mass balance. Cryosphere 2019, 13, 2597–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Möllera, R.; Dagsson-Waldhauserova, P.; Mller, M.; Möller, R.; Dagsson-Waldhauserova, P.; Möller, M.; Kukla, P.A.; Schneider, C.; Gudmundsson, M.T. Persistent albedo reduction on southern Icelandic glaciers due to ashfall from the 2010 Eyjafjallajökull eruption. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 233, 111396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.S.; Dong, J.W.; Cui, Y.P.; Liu, J.Y.; Zhai, J.; He, T.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Xiao, X.M. Evapotranspiration-dominated biogeophysical warming effect of urbanization in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 52, 1231–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Liang, S.L.; Song, D.X. Analysis of global land surface albedo climatology and spatial-temporal variation during 1981–2010 from multiple satellite products. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 10281–10298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Muller, J.P.; Kharbouche, S.; Woodgate, W. Intercomparison of Surface Albedo Retrievals from MISR, MODIS, CGLS Using Tower and Upscaled Tower Measurements. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mota, B.; Gobron, N.; Cappucci, F.; Morgan, O. Burned area and surface albedo products: Assessment of change consistency at global scale. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 225, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abera, T.A.; Heiskanen, J.; Pellikka, P.K.; Maeda, E.E. Impact of rainfall extremes on energy exchange and surface temperature anomalies across biomes in the Horn of Africa. Agric. Meteorol. 2020, 280, 107779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomon, J.G.; Schaaf, C.B.; Strahler, A.H.; Gao, F.; Jin, Y.F. Validation of the MODIS Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function and Albedo retrievals using combined observations from the Aqua and Terra platforms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 1555–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.C.; Schaaf, C.; Strahler, A.; Jiao, Z.T.; Shuai, Y.M.; Zhang, Q.L.; Roman, M.; Augustine, J.A.; Dutton, E.G. Validation of Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) albedo retrieval algorithm: Dependence of albedo on solar zenith angle. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, L.Z.; Qu, Y.; Liu, N.F.; Liu, S.H.; Tang, H.R.; Liang, S.L. Preliminary evaluation of the long-term GLASS albedo product. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2013, 6, 69–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Zapero, J.; de la Madrid, L.; Camacho, F. Validation Report of Surface Albedo (SA) from PROBA-V Collection 1 km Version 1.5 (Issue I2.21). Copernicus Global Land Operations CGLOPS-1 (Framework Service Contract N° 199494-JRC). Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/global/sites/cgls.vito.be/files/products/CGLOPS1_VR_SA1km-PROBAV-V1.5_I2.21.pdf (accessed on 9 April 2020).
- Driemel, A.; Augustine, J.; Behrens, K.; Colle, S.; Cox, C.; Cuevas-Agulló, E.; Denn, F.M.; Duprat, T.; Fukuda, M.; Grobe, H.; et al. Baseline Surface Radiation Network (BSRN): Structure and data description (1992–2017). Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2018, 10, 1491–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Augustine, J.A.; Hodges, G.B.; Cornwall, C.R.; Michalsky, J.J.; Medina, C.I.; Augustine, J.A.; Hodges, G.B.; Cornwall, C.R.; Michalsky, J.J.; Medina, C.I. An update on SURFRAD–the GCOS Surface Radiation Budget Network for the Continental United States. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2005, 22, 1460–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.S.; Schaaf, C.B.; Sun, Q.S.; Shuai, Y.M.; Roman, M.O. Capturing rapid land surface dynamics with Collection V006 MODIS BRDF/NBAR/Albedo (MCD43) products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 207, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Meteorological Organization. Guide to Instruments and Methods of Observation: Volume I—Measurement of Meteorological Variables; WMO-No.8; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 256–267. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Q.; Wang, Z.S.; Zhan, L.; Román, M.O.; Crystal, S. VIIRS BRDF, Albedo, and NBAR Product Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document. Available online: https://www.umb.edu/editor_uploads/images/school_for_the_environment_cs/Viirs/VIIRS_ATBD_Apr_Jul2017_final.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- Shuai, Y. Tracking Daily Land Surface Albedo and Reflectance Anisotropy with MODerate-Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS). Ph.D. Thesis, Boston University, Boston, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Shuai, Y.M.; Schaaf, C.B.; Strahler, A.H.; Liu, J.C.; Jiao, Z.T. Quality assessment of BRDF/albedo retrievals in MODIS operational system. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, Z.; Cheng, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, X. Global Land Surface Satellite (GLASS) Products: Algorithms, Validation and Analysis; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Zapero, J. Scientific Quality Evaluation (SQE) of PROBA-V Surface Albedo (SA) Collection 1 km Version 1 (Issue I1.00). Copernicus Global Land Operations CGLOPS-1 (Framework Service Contract N° 199494-JRC). Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/global/sites/cgls.vito.be/files/products/CGLOPS1_SQE2017_SA1km-V1_I1.00.pdf (accessed on 9 April 2020).
- Sanchez-Zapero, J. Quality Assessment Report of Surface Albedo (SA) -Version 1 SPOT/VEGETATION (Issue I1.10). Gio Global Land Component-Lot I (Framework Service Contract N° 388533-JRC). Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/global/sites/cgls.vito.be/files/products/CGLOPS1_SQE2017_SA1km-V1_I1.00.pdf (accessed on 9 April 2020).
- Zhang, X.T.; Liang, S.L.; Wang, K.C.; Li, L.; Gui, S. Analysis of Global Land Surface Shortwave Broadband Albedo From Multiple Data Sources. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2010, 3, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, P.; Barnsley, M. Influence of the Sky Radiance Distribution on Various Formulations of the Earth Surface Albedo. In Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on Physical Measurements and Signatures in Remote Sensing, Val d’Isère, France, 17–21 January 1994; pp. 707–715. [Google Scholar]
- Román, M.O.; Schaaf, C.B.; Lewis, P.; Gao, F.; Anderson, G.P.; Privette, J.L.; Strahler, A.H.; Woodcock, C.E.; Barnsley, M. Assessing the coupling between surface albedo derived from MODIS and the fraction of diffuse skylight over spatially-characterized landscapes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 738–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermote, E.; Vermeulen, A. Atmospheric correction algorithm: Spectral reflectances (MOD09). ATBD Version 1999, 4, 1–107. [Google Scholar]
- Carrer, D.; Smets, B.; Swinnen, E.; Ceamanos, X.; Roujean, J.-L. Top of canopy normalized reflectance (toc-r) Collection 1km Version 1.5; Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document (ATBD), Issue 2.11. Copernicus Global Land Operations CGLOPS-1 (Framework Service Contract N° 199494-JRC). Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/global/sites/cgls.vito.be/files/products/CGLOPS1_ATBD_TOCR1km-V1.5_I2.21.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- Gu, L.X.; Shuai, Y.M.; Shao, C.Y.; Xie, D.H.; Zhang, Q.L.; Li, Y.M.; Yang, J. Angle Effect on Typical Optical Remote Sensing Indices in Vegetation Monitoring. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Zapero, J.; Camacho, F.; Martínez-Sánchez, E.; Lacaze, R.; Carrer, D.; Pinault, F.; Benhadj, I.; Muñoz-Sabater, J. Quality Assessment of PROBA-V Surface Albedo V1 for the Continuity of the Copernicus Climate Change Service. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proud, S.R.; Fensholt, R.; Rasmussen, M.O.; Sandholt, I. A comparison of the effectiveness of 6S and SMAC in correcting for atmospheric interference of Meteosat Second Generation images. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toté, C.; Swinnen, E.; Sterckx, S.; Clarijs, D.; Quang, C.; Maes, R. Evaluation of the SPOT/VEGETATION Collection 3 reprocessed dataset: Surface reflectances and NDVI. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 201, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, A.X.; Jiao, Z.T.; Dong, Y.D.; Zhang, X.N.; He, D.D.; Cui, L.; Yin, S.Y.; Chang, Y.X. Performance assessment of the operational MODIS BRDF model for snow/ice cover type. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 23, 1147–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokhanovsky, A.A.; Breon, F.M. Validation of an Analytical Snow BRDF Model Using PARASOL Multi-Angular and Multispectral Observations. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 9, 928–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokrovsky, O.; Roujean, J.L. Land surface albedo retrieval via kernel-based BRDF modeling: II. An optimal design scheme for the angular sampling. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 84, 120–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.L. Narrowband to broadband conversions of land surface albedo I Algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 76, 213–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Leeuwen, W.J.; Roujean, J.-L. Land surface albedo from the synergistic use of polar (EPS) and geo-stationary (MSG) observing systems: An assessment of physical uncertainties. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 81, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
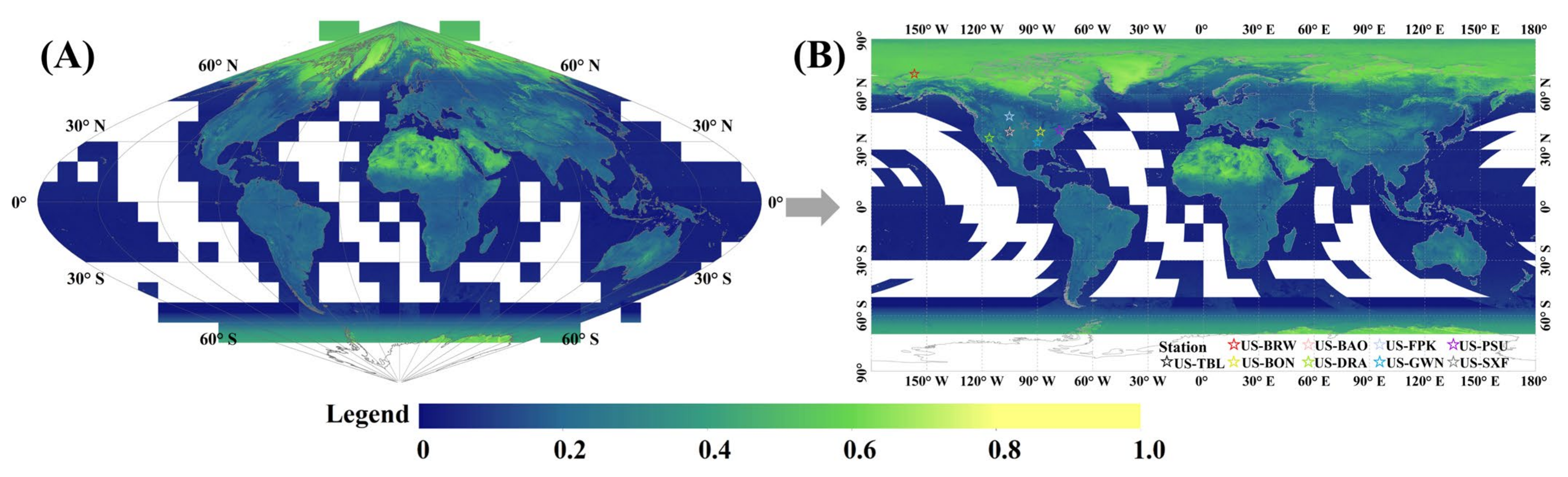


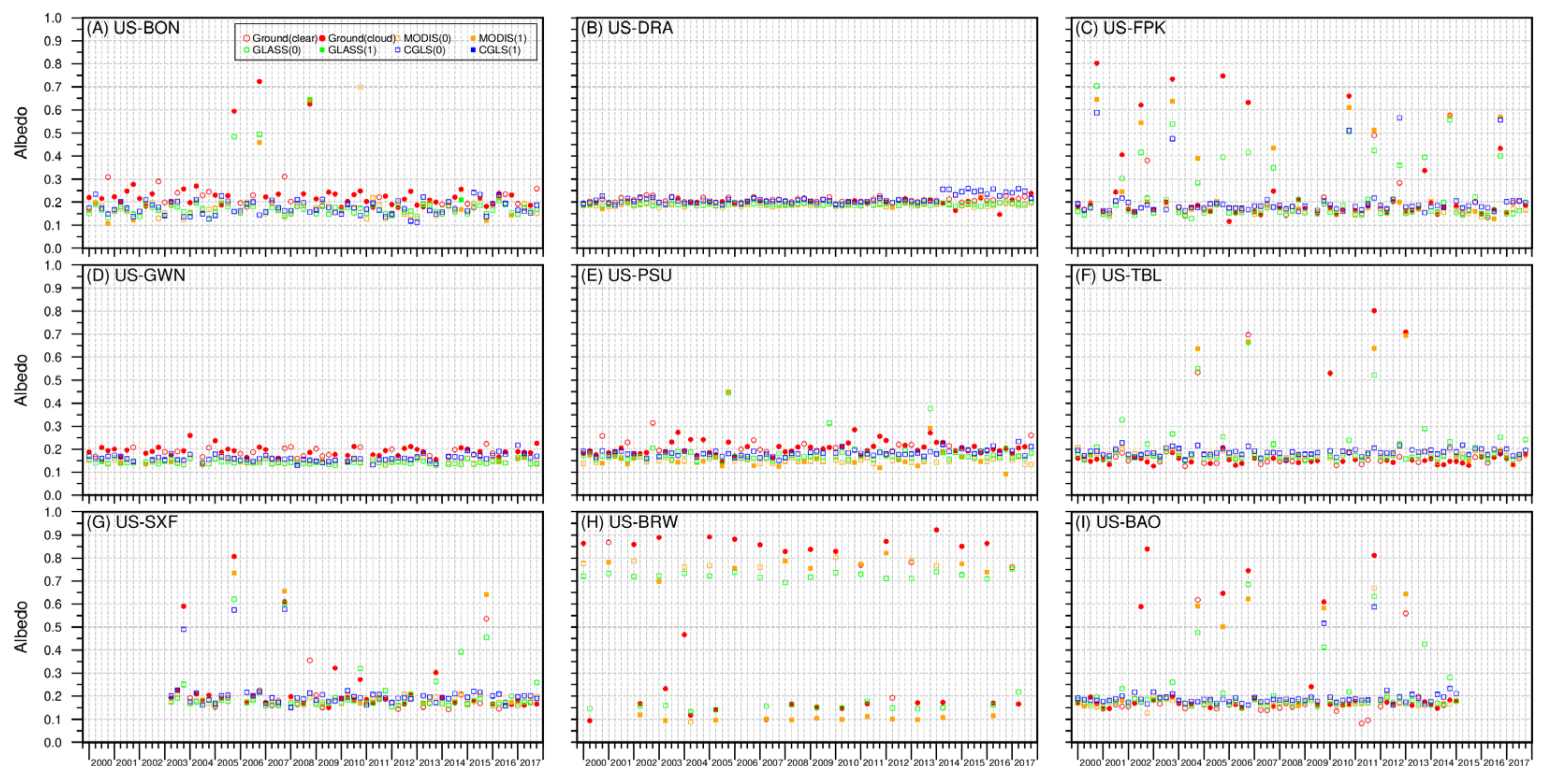
| Station Name | Latitude (°) | Longitude (°) | Network | Tower Height (m) | Land Classification (IGBP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bondville (US-BON) | 40.052 | −88.373 | SURFRAD | 10 | Croplands |
| Desert Rock (US-DRA) | 36.624 | −116.019 | SURFRAD | 10 | Open Shrublands |
| Fort Peck (US-FPK) | 48.308 | −105.102 | SURFRAD | 10 | Grasslands |
| Goodwin Creek (US-GWN) | 34.255 | −89.873 | SURFRAD | 10 | Deciduous Broadleaf |
| Penn State (US-PSU) | 40.720 | −77.931 | SURFRAD | 10 | Deciduous Broadleaf |
| Table Mountain (US-TBL) | 40.125 | −105.237 | SURFRAD | 10 | Bare soil and Rocks |
| Sioux Falls (US-SXF) | 43.730 | −96.620 | SURFRAD | 10 | Croplands |
| Barrow (US-BRW) | 71.323 | −156.607 | BSRN | 4 | Snow and Ice |
| Boulder (US-BAO) | 40.050 | −105.004 | BSRN | 300 | Cropland Mosaics |
| Result Station Name | MODIS | GLASS | CGLS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | Mean Error | RMSE | Mean Error | RMSE | Mean Error | |
| Bondville (US-BON) | 0.077 | −0.048 | 0.074 | −0.054 | 0.069 | −0.04 |
| Desert Rock (US-DRA) | 0.024 | −0.022 | 0.021 | −0.019 | 0.017 | 0.002 |
| Fort Peck (US-FPK) | 0.046 | −0.018 | 0.044 | −0.017 | 0.095 | 0.001 |
| Goodwin Creek (US-GWN) | 0.048 | −0.045 | 0.05 | −0.046 | 0.037 | −0.032 |
| Penn State (US-PSU) | 0.072 | −0.065 | 0.057 | −0.051 | 0.034 | −0.027 |
| Table Mountain (US-TBL) | 0.032 | 0.023 | 0.037 | 0.022 | 0.118 | −0.002 |
| Sioux Falls (US-SXF) | 0.044 | 0.003 | 0.054 | −0.003 | 0.045 | 0.013 |
| Barrow (US-BRW) | 0.056 | −0.032 | 0.073 | −0.06 | - | - |
| Boulder (US-BAO) | 0.033 | 0.016 | 0.09 | −0.002 | 0.123 | −0.005 |
| All sites | 0.047 | −0.018 | 0.055 | −0.02 | 0.075 | −0.009 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shao, C.; Shuai, Y.; Tuerhanjiang, L.; Ma, X.; Hu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, A.; Liu, T.; Tian, Y.; Wang, C.; et al. Cross-Comparison of Global Surface Albedo Operational Products-MODIS, GLASS, and CGLS. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4869. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13234869
Shao C, Shuai Y, Tuerhanjiang L, Ma X, Hu W, Zhang Q, Xu A, Liu T, Tian Y, Wang C, et al. Cross-Comparison of Global Surface Albedo Operational Products-MODIS, GLASS, and CGLS. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(23):4869. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13234869
Chicago/Turabian StyleShao, Congying, Yanmin Shuai, Latipa Tuerhanjiang, Xuexi Ma, Weijie Hu, Qingling Zhang, Aigong Xu, Tao Liu, Yuhang Tian, Chongyang Wang, and et al. 2021. "Cross-Comparison of Global Surface Albedo Operational Products-MODIS, GLASS, and CGLS" Remote Sensing 13, no. 23: 4869. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13234869
APA StyleShao, C., Shuai, Y., Tuerhanjiang, L., Ma, X., Hu, W., Zhang, Q., Xu, A., Liu, T., Tian, Y., Wang, C., & Ma, Y. (2021). Cross-Comparison of Global Surface Albedo Operational Products-MODIS, GLASS, and CGLS. Remote Sensing, 13(23), 4869. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13234869








