Desertification Extraction Based on a Microwave Backscattering Contribution Decomposition Model at the Dry Bottom of the Aral Sea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
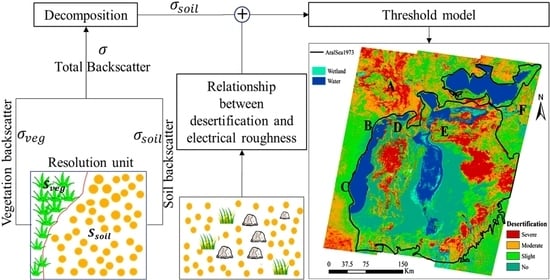
- The variation trend of the roughness and electrical roughness of the topsoil in the process of desertification, the evaluation of the effects of soil moisture and soil salinity on backscatter in arid and semi-arid regions, and whether the backscattering coefficient can be used to describe the degree of desertification.
- Developing a model for decomposing the backscattering contribution of vegetation and soil within a resolution unit and estimating the backscattering coefficient of soil within this resolution unit.
- Use the backscattering coefficient of soil to assess the severity of desertification at the dry bottom of the Aral Sea.
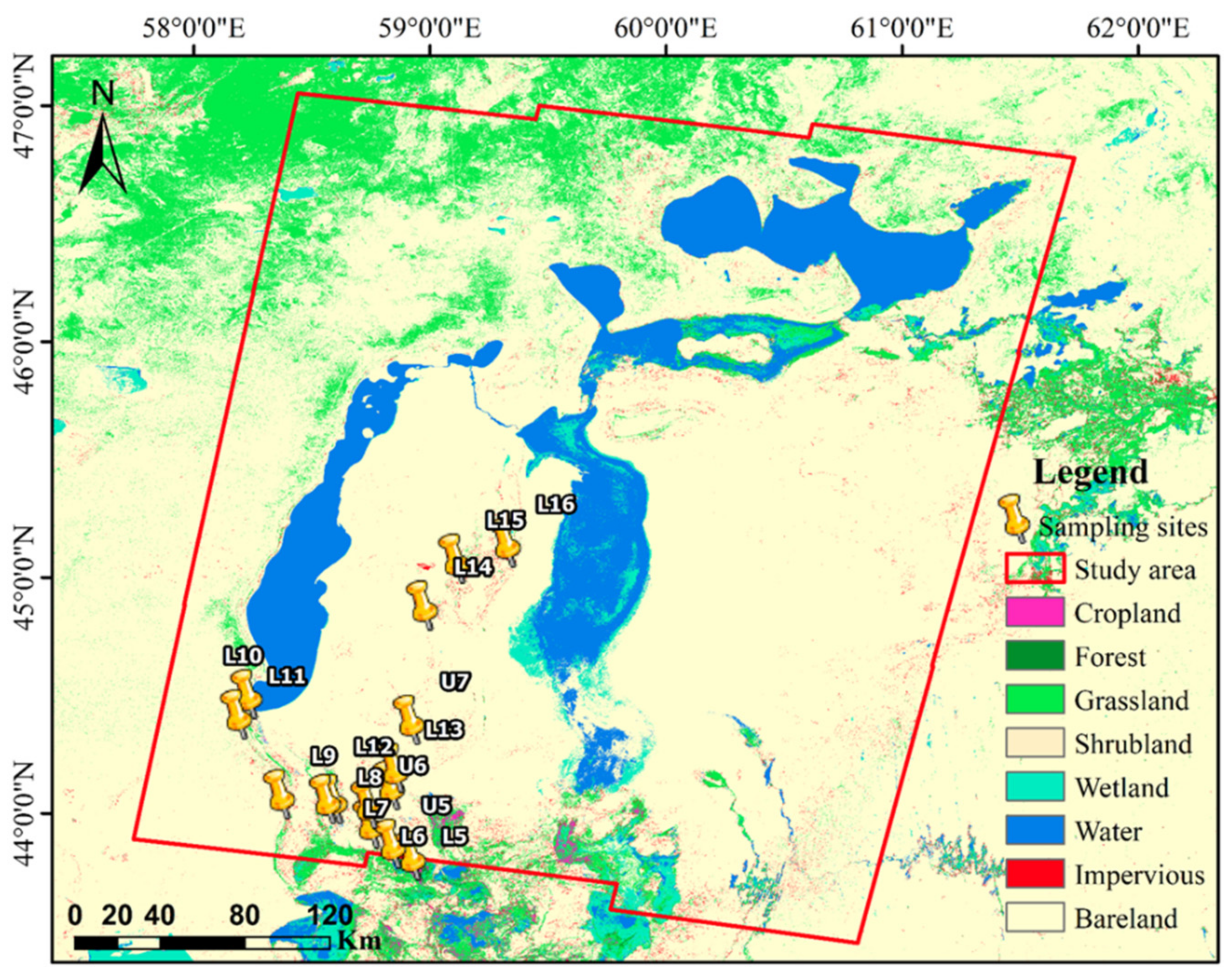
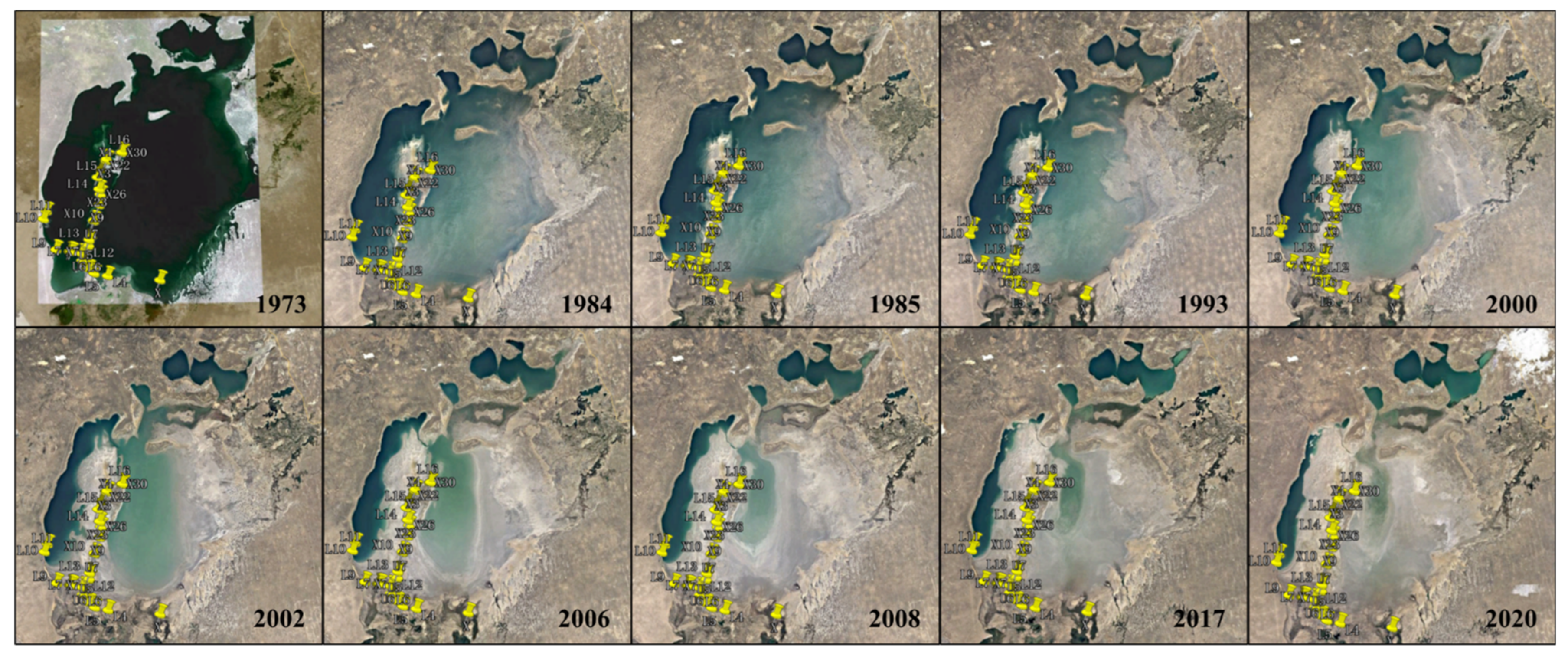
2. Research Area
3. Data and Method
3.1. Data
3.1.1. Remote Sensing Data
3.1.2. Field Sampling Data
3.2. Methods
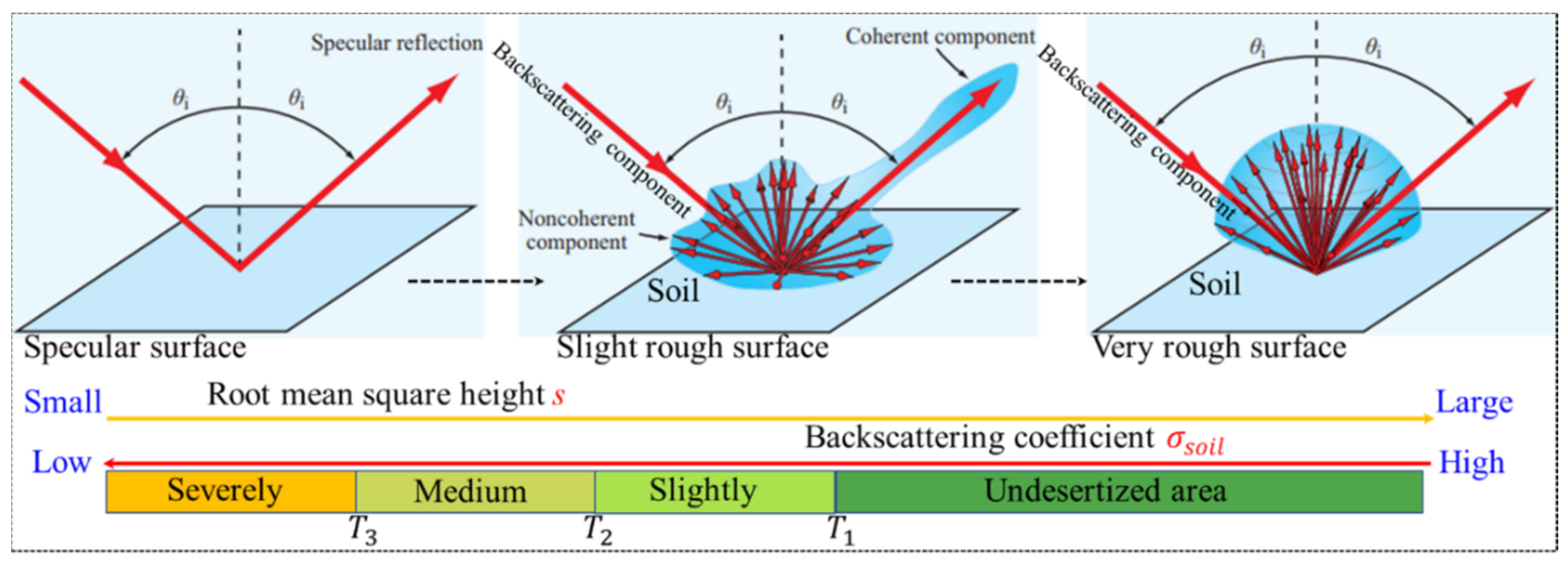
3.2.1. Simple Microwave Backscattering Threshold (SMSBT) Model
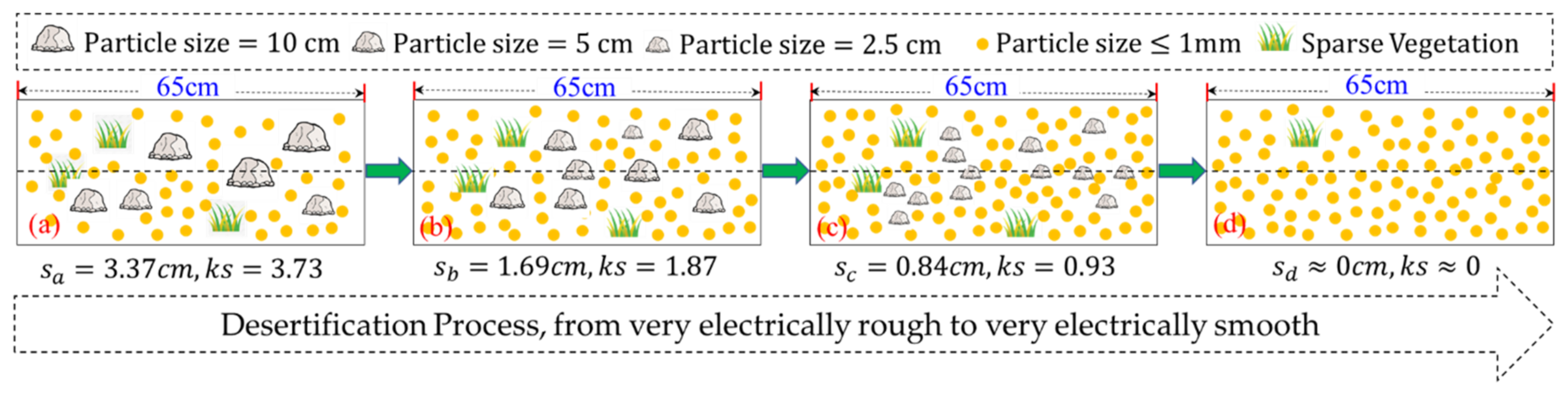
3.2.2. Influence of Soil Moisture and Salinity on the Uncertainty of the SMSBT Model
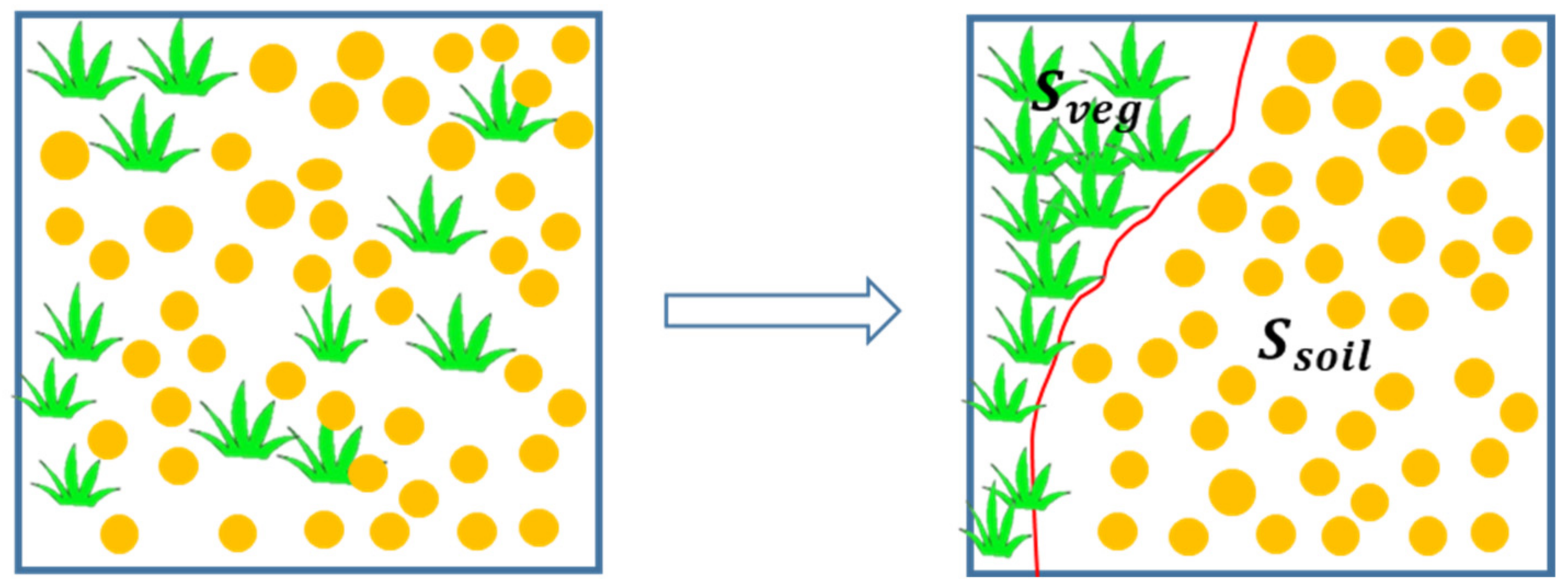
3.2.3. Microwave Backscattering Contribution Decomposition (MBCD) Model
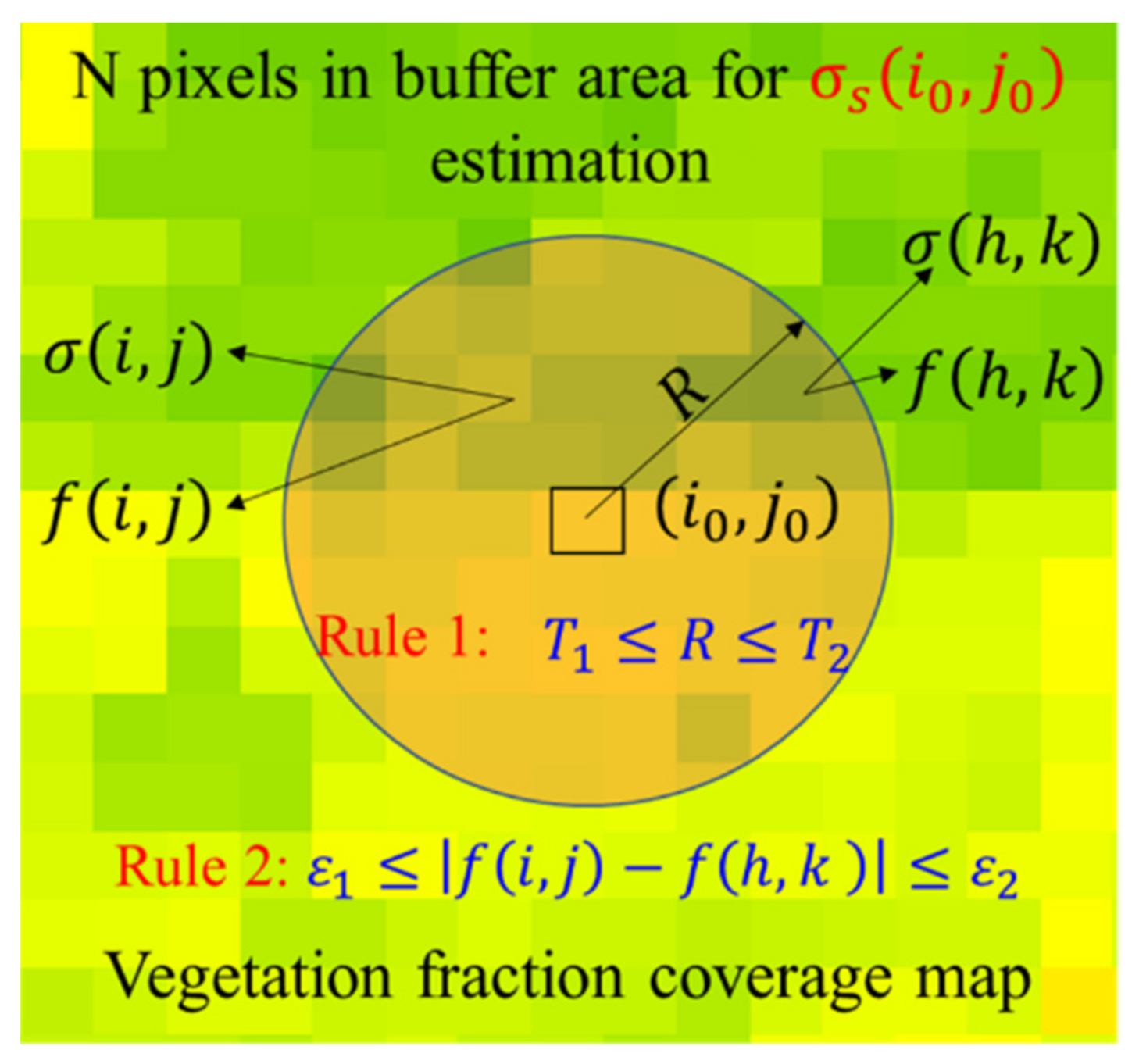
3.2.4. MBC Estimation Based on Least-Squares Method
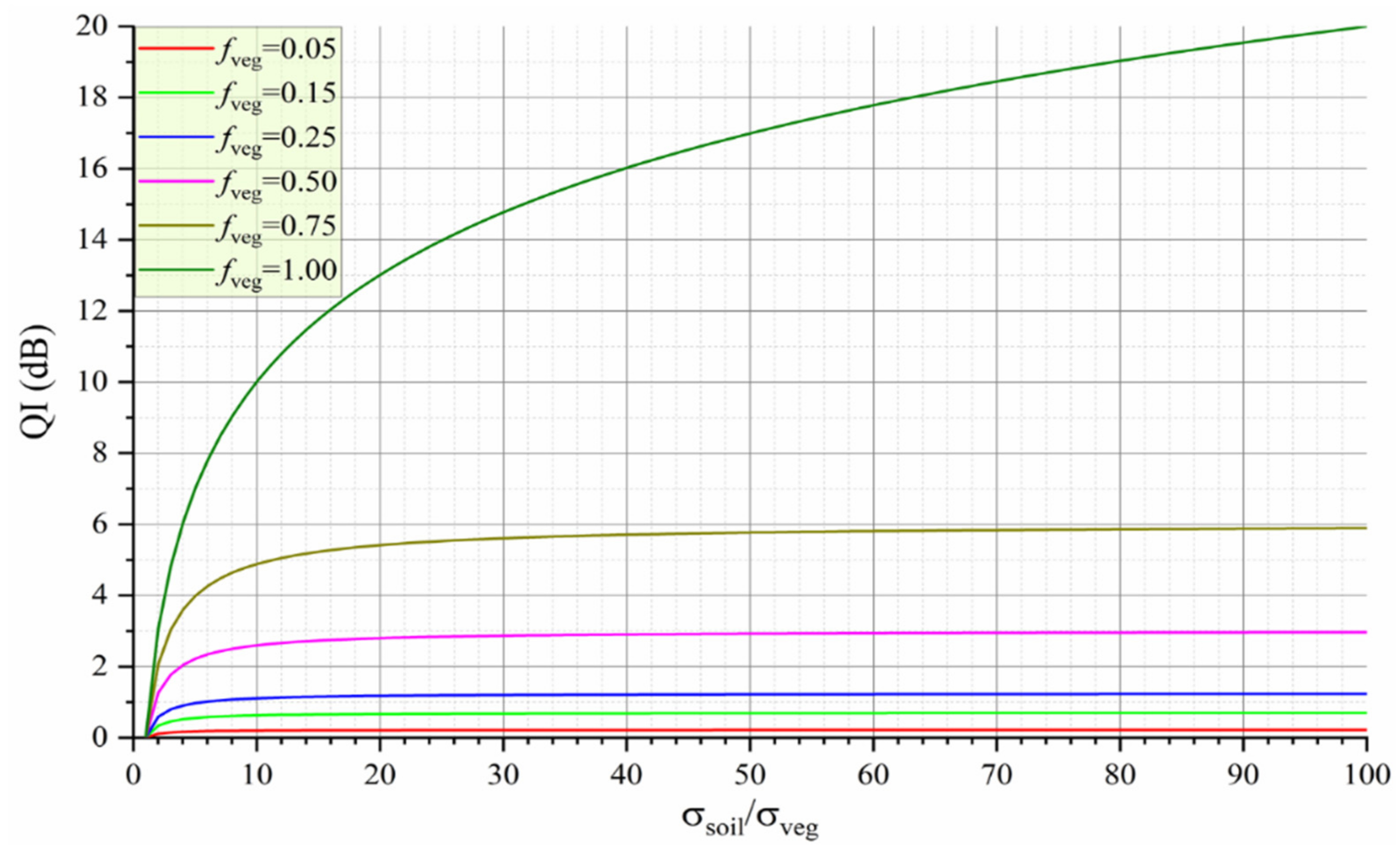
3.2.5. Tips about Soil MBC Estimation
4. Results
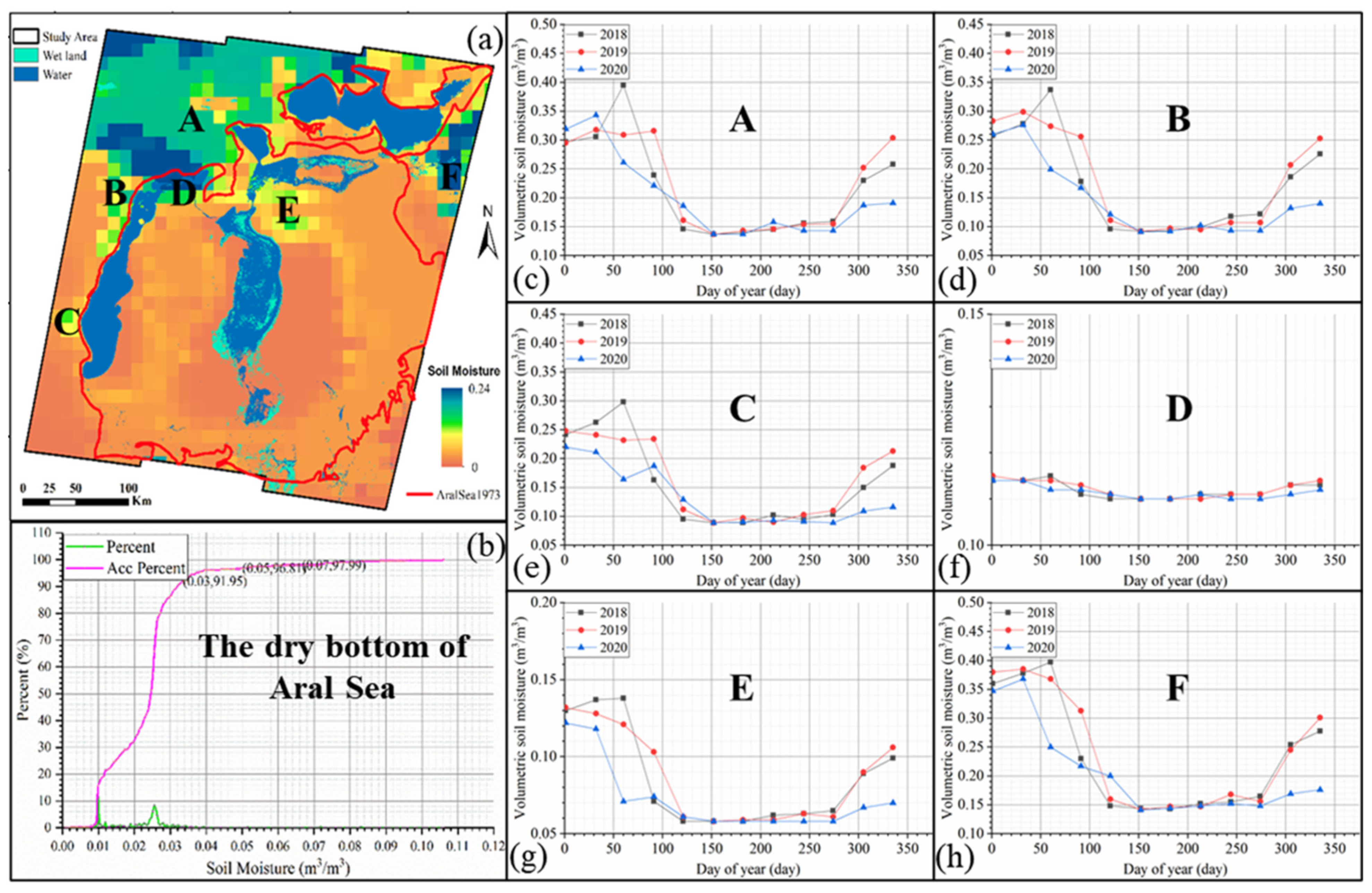
4.1. The Spatial Distribution of Soil Moisture and Salt-Rich Soil in Study Area
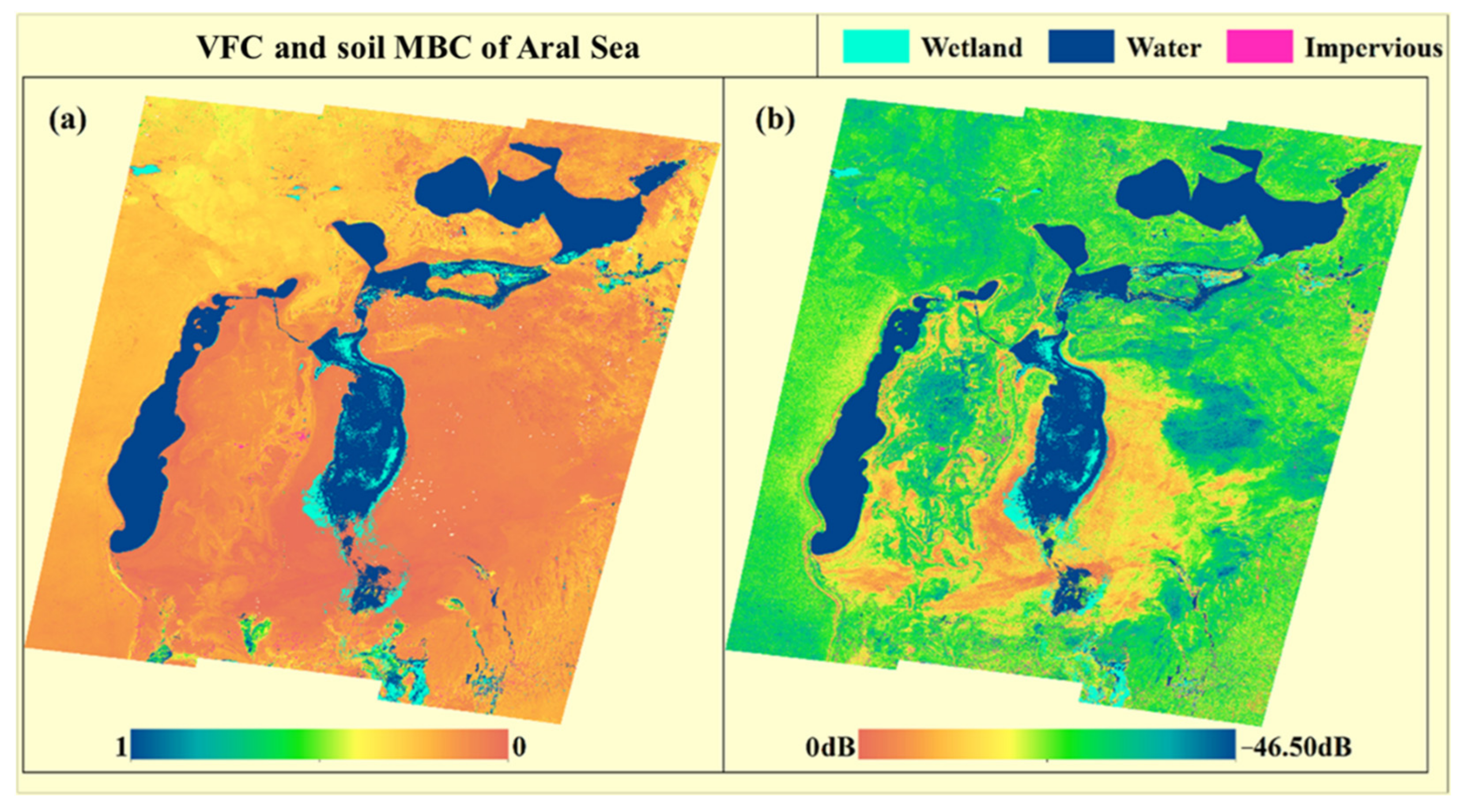
4.2. Backscattering Coefficient and VFC in the Aral Sea
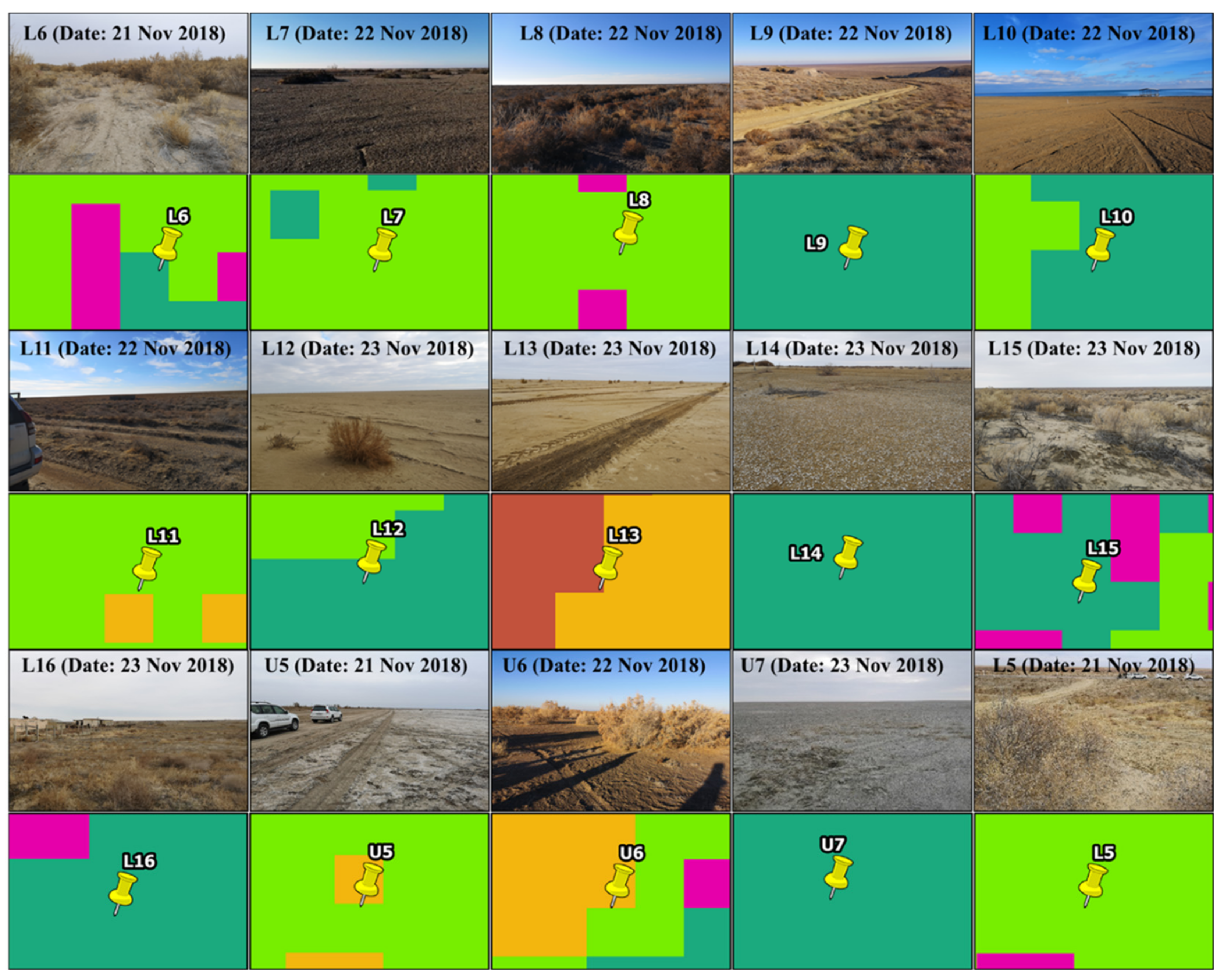
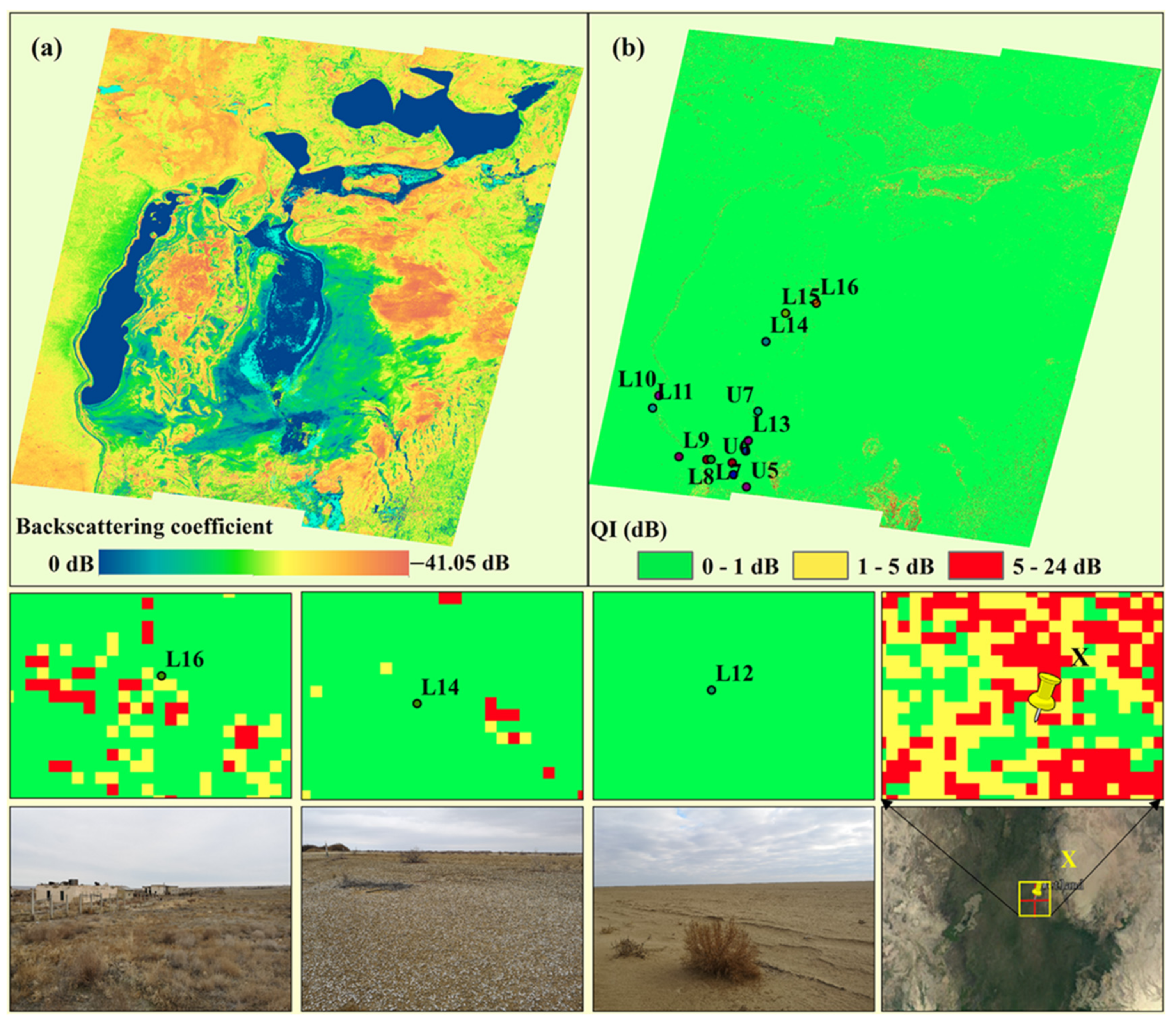
4.3. Backscattering Coefficient of Soil and the Landscape Photos of Sampling Sites
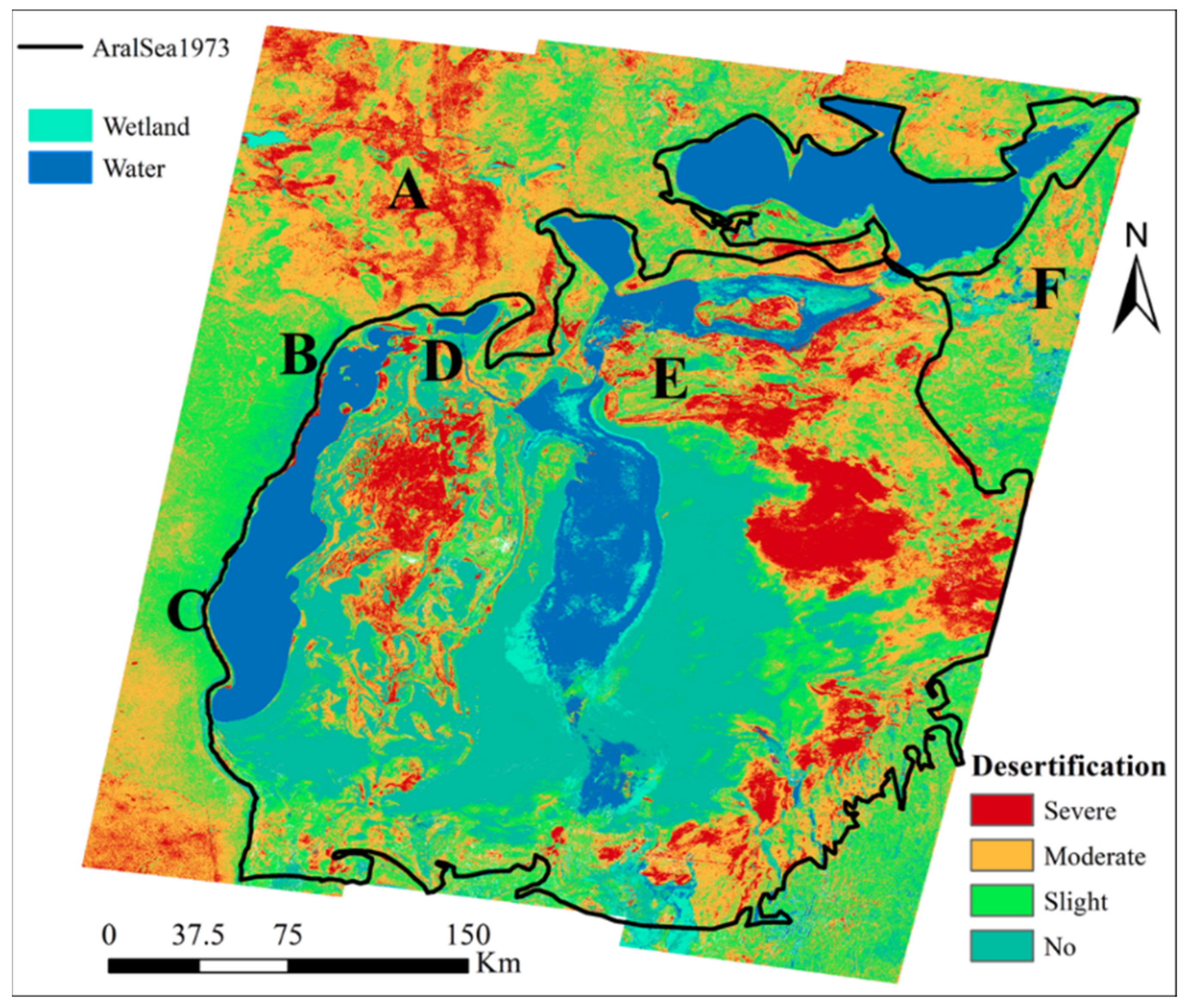
4.4. Results of Desertification Classification and Landscape Photos of Sampling Sites
5. Discussion
5.1. The Influence of Soil Moisture and Soil Salinity on the SMSBT Model in the Study Area
5.1.1. The Influence of Soil Moisture on the SMSBT Model
5.1.2. The Influence of Soil Salinity on the SMSBT Model
5.2. Assessment of the Estimation Results of the Soil MBC within a Resolution Unit
- 2.
- ,
- 3.
- ,
- 4.
- ,
5.3. Evaluation of the Results of the Desertification Classification
5.4. Spatial Distribution of Desertification with Different Severity at the Dry Bottom of Aral Sea
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zha, Y.; Gao, J. Characteristics of desertification and its rehabilitation in China. J. Arid Environ. 1997, 37, 419–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepehr, A.; Hassanli, A.M.; Ekhtesasi, M.R.; Jamali, J.B. Quantitative assessment of desertification in south of Iran using MEDALUS method. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 134, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, B.; Luo, X.; Guan, Y.; Guo, S.; Nie, Y. Land desertification monitoring and assessment in Yulin of Northwest China using remote sensing and geographic information systems (GIS). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 147, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, E.S. Spatial assessment of desertification in north Sinai using modified MEDLAUS model. Arab. J. Geosci. 2013, 6, 4647–4659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Qin, Z.; Li, H.; Ding, G.; Meng, X. Evaluation of aeolian desertification from 1975 to 2010 and its causes in northwest Shanxi Province, China. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2013, 107, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symeonakis, E.; Karathanasis, N.; Koukoulas, S.; Panagopoulos, G. Monitoring Sensitivity to Land Degradation and Desertification with the Environmentally Sensitive Area Index: The Case of Lesvos Island. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 1562–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Q.; Fu, B.; Shi, P.; Cudahy, T.; Zhang, J.; Xu, H. Satellite Monitoring the Spatial-Temporal Dynamics of Desertification in Response to Climate Change and Human Activities across the Ordos Plateau, China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.-L.; Li, Q.; Shen, Y.-P.; Zhou, N.; Wang, X.-S.; Li, J.; Jia, W.-R. Monitoring of aeolian desertification on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau from the 1970s to 2015 using Landsat images. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619, 1648–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Gong, S.L.; Zhao, T.L.; Arimoto, R.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhou, Z.J. Sources of Asian dust and role of climate change versus desertification in Asian dust emission. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Indoitu, R.; Kozhoridze, G.; Batyrbaeva, M.; Vitkovskaya, I.; Orlovsky, N.; Blumberg, D.; Orlovsky, L. Dust emission and environmental changes in the dried bottom of the Aral Sea. Aeolian Res. 2015, 17, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aili, A.; Abuduwaili, J.; Xu, H.; Zhao, X.; Liu, X. A Cluster Analysis of Forward Trajectory to Identify the Transport Pathway of Salt-Dust Particles from Dried Bottom of Aral Sea, Central Asia. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, F.; Choudhury, B.J. Relative sensitivity of normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) and microwave polarization difference index (MPDI) for vegetation and desertification monitoring. Remote Sens. Environ. 1988, 24, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Griend, A.A.; De Jeu, R.; Seyhan, E. Desertification/aridification monitoring of the Iberian Peninsula by passive microwave remote sensing. In Proceedings of the NATO Advanced Research Workshop on Environmental Reconstruction in Headwater Areas, Prague, Czech Republic, 21–26 November 2000; pp. 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Tripathy, G.K.; Ghosh, T.K.; Shah, S.D. Monitoring of desertification process in Karnataka state of India using multi-temporal remote sensing and ancillary information using GIS. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 2243–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladisa, G.; Todorovic, M.; Liuzzi, G.T. A GIS-based approach for desertification risk assessment in Apulia region, SE Italy. Phys. Chem. Earth 2012, 49, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collado, A.D.; Chuvieco, E.; Camarasa, A. Satellite remote sensing analysis to monitor desertification processes in the crop-rangeland boundary of Argentina. J. Arid Environ. 2002, 52, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, X.; Jin, Y.; Yang, Z.; Huang, W.; Zhao, L.; Gao, T.; Yu, H.; Ma, H.; Qin, Z.; et al. Monitoring and analysis of grassland desertification dynamics using Landsat images in Ningxia, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 138, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asner, G.P.; Heidebrecht, K.B. Imaging spectroscopy for desertification studies: Comparing AVIRIS and EO-1 Hyperion in Argentina drylands. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1283–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symeonakis, E.; Drake, N. Monitoring desertification and land degradation over sub-Saharan Africa. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 573–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Siegert, F. Land cover classification optimized to detect areas at risk of desertification in North China based on SPOT VEGETATION imagery. J. Arid Environ. 2006, 67, 308–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Dawson, R.; Li, H.; Wei, R.; Li, B. A landscape connectivity index for assessing desertification: A case study of Minqin County, China. Landsc. Ecol. 2007, 22, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.-L.; Chen, C.-W.; Wang, Q.-B.; Cao, Y.; Shih, J.-Y.; Lee, Y.-T.; Chen, C.-Y.; Wang, S. Fuzzy model-based assessment and monitoring of desertification using MODIS satellite imagery. Eng. Comput. 2009, 26, 745–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, P.; Zhang, J.; Lin, Z. An Artificial Neural Network Method for the Information of Desertification Extraction. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2004, 33, 58–62. [Google Scholar]
- Shuhai, J.I.A.; Zhigen, H.A.N.; Monan, L.V.; Jing, W.; Dongqi, X.I.E. Extraction of desertification information based on decision tree in northern Liaoning province. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2011, 20, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, H.S.; Wang, J.L.; Cheng, K.; Li, G.; Ochir, A.; Davaasuren, D.; Chonokhuu, S. Desertification Information Extraction Based on Feature Space Combinations on the Mongolian Plateau. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, Y.; Zheng, D.; Zhi, C.; Yao, A.; Gao, Z. Desertification Land Information Extraction Based on Object-Oriented Classification Method. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2013, 49, 126–133. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Li, W. Primary study on the multi-layer remote sensing information extraction of desertification land types by using decision tree technology. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS 2002)/24th Canadian Symposium on Remote Sensing, Toronto, ON, Canada, 24–28 June 2002; pp. 2513–2515. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, H.S.; Wang, J.L.; Han, B.M. Desertification Information Extraction Along the China-Mongolia Railway Supported by Multisource Feature Space and Geographical Zoning Modeling. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.R.; Castro, F.S.P.; Centeno, J.A.S. The use of images CBERS 2 and CBERS 2b in identification of areas affected by desertification. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Digital Image Processing, Singapore, 26–28 February 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Owe, M.; Van de Griend, A.A.; de Jeu, R.; de Vries, J.; Seyhan, E. Satellite microwave estimates of soil moisture and their application for desertification studies. In Proceedings of the Conference on Remote Sensing for Agriculture, Ecosystems, and Hydrology, Barcelona, Spain, 22–24 September 1998; pp. 30–40. [Google Scholar]
- Semenov, O.E. Dust Storms and Sandstorms and Aerosol Long-Distance Transport. In Aralkum-a Man-Made Desert: The Desiccated Floor of the Aral Sea (Central Asia); Breckle, S.-W., Wucherer, W., Dimeyeva, L.A., Ogar, N.P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegmuller, U.; Strozzi, T.; Farr, T.; Werner, C.L. Arid land surface characterization with repeat-pass SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 776–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wu, B.; Yan, C.; Zhou, W. Estimation of Vegetation Fraction in the Upper Basin of Miyun Reservoir by Remote Sensing. Resour. Sci. 2004, 26, 153–159. [Google Scholar]
- Nashashibi, A.Y.; Sarabandi, K.; Al-Zaid, F.A.; Alhumaidi, S. Characterization of Radar Backscatter Response of Sand-Covered Surfaces at Millimeter-Wave Frequencies. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 2345–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nashashibi, A.; Ulaby, F.T.; Sarabandi, K. Measurement and modeling of the millimeter-wave backscatter response of soil surfaces. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1996, 34, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.; Sarabandi, K.; Ulaby, F.T. An empirical-model and an inversion technique for radar scattering from bare soil surfaces. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaby, F.T.; Long, D.G.; Blackwell, W.; Elachi, C.; Zebker, H. Microwave Radar and Radiometric Remote Sensing; University of Michigan Press: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hallikainen, M.T.; Ulaby, F.T.; Dobson, M.C.; Elrayes, M.A.; Wu, L.K. Microwave dielectric behavior of wet soil-part 1: Empirical-models and experimental-observations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1985, 23, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenivas, K.; Venkataratnam, L.; Rao, P.V.N. Dielectric-properties of salt-affect soils. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1995, 16, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.N.; Dong, Z.B.; Li, Z.S.; Yang, Z.T. Wind tunnel test of the influence of moisture on the erodibility of loessial sandy loam soils by wind. J. Arid Environ. 1996, 34, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, Z.; Chen, C.; Cui, Y.; Wang, J. Wind tunnel experimental study on desert surface of Kubuqi desert, Inner Mongolia. China Environ. Sci. 2017, 37, 2888–2895. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dijk, P.M.; Stroosnijder, L.; de Lima, J. The influence of rainfall on transport of beach sand by wind. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1996, 21, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisal, F.; Hsieh, J. Influence of moisture on erodibility of soil by wind. Soil Sci. 1966, 102, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Site | Sample | Date | Soil Depth (cm) | Conductivity (µs/cm) | Total Salt (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U5 | us19 | 22 November 2018 | 0–5 | 39.875 | 119.275 |
| us20 | 5–10 | 20.300 | 61.400 | ||
| U6 | us23 | 0–5 | 18.770 | 54.350 | |
| us24 | 5–10 | 13.490 | 38.075 | ||
| U7 | us30 | 23 November 2018 | 0–5 | 20.300 | 63.800 |
| us31 | 5–10 | 5.275 | 15.950 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Y.; Zheng, H.; Chen, X.; Bao, A.; Lei, J.; Xu, W.; Luo, G.; Guan, Q. Desertification Extraction Based on a Microwave Backscattering Contribution Decomposition Model at the Dry Bottom of the Aral Sea. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4850. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13234850
Song Y, Zheng H, Chen X, Bao A, Lei J, Xu W, Luo G, Guan Q. Desertification Extraction Based on a Microwave Backscattering Contribution Decomposition Model at the Dry Bottom of the Aral Sea. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(23):4850. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13234850
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Yubin, Hongwei Zheng, Xi Chen, Anming Bao, Jiaqiang Lei, Wenqiang Xu, Geping Luo, and Qing Guan. 2021. "Desertification Extraction Based on a Microwave Backscattering Contribution Decomposition Model at the Dry Bottom of the Aral Sea" Remote Sensing 13, no. 23: 4850. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13234850
APA StyleSong, Y., Zheng, H., Chen, X., Bao, A., Lei, J., Xu, W., Luo, G., & Guan, Q. (2021). Desertification Extraction Based on a Microwave Backscattering Contribution Decomposition Model at the Dry Bottom of the Aral Sea. Remote Sensing, 13(23), 4850. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13234850