Impacts of Orbital and Constellation Parameters on the Number and Spatiotemporal Coverage of LEO-LEO Occultation Events
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Brief Review of Previous Occultation Mission and Orbit Design Studies
3. LEO-LEO Occultation Simulation and Assessment Methods
3.1. LEO-LEO Occultation Geometry Simulation Model
3.2. Global Coverage Fraction of Occultation Events
4. Experimental Results and Analysis
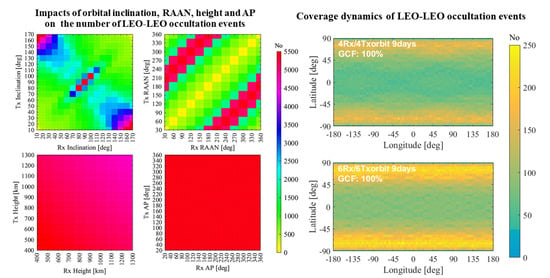
4.1. Impacts of the Orbital Parameters on LEO-LEO Occultation Events
4.1.1. Orbital Parameter Setup for the Two-Satellite Experimental Demonstration Mission
4.1.2. Overall Simulation Results
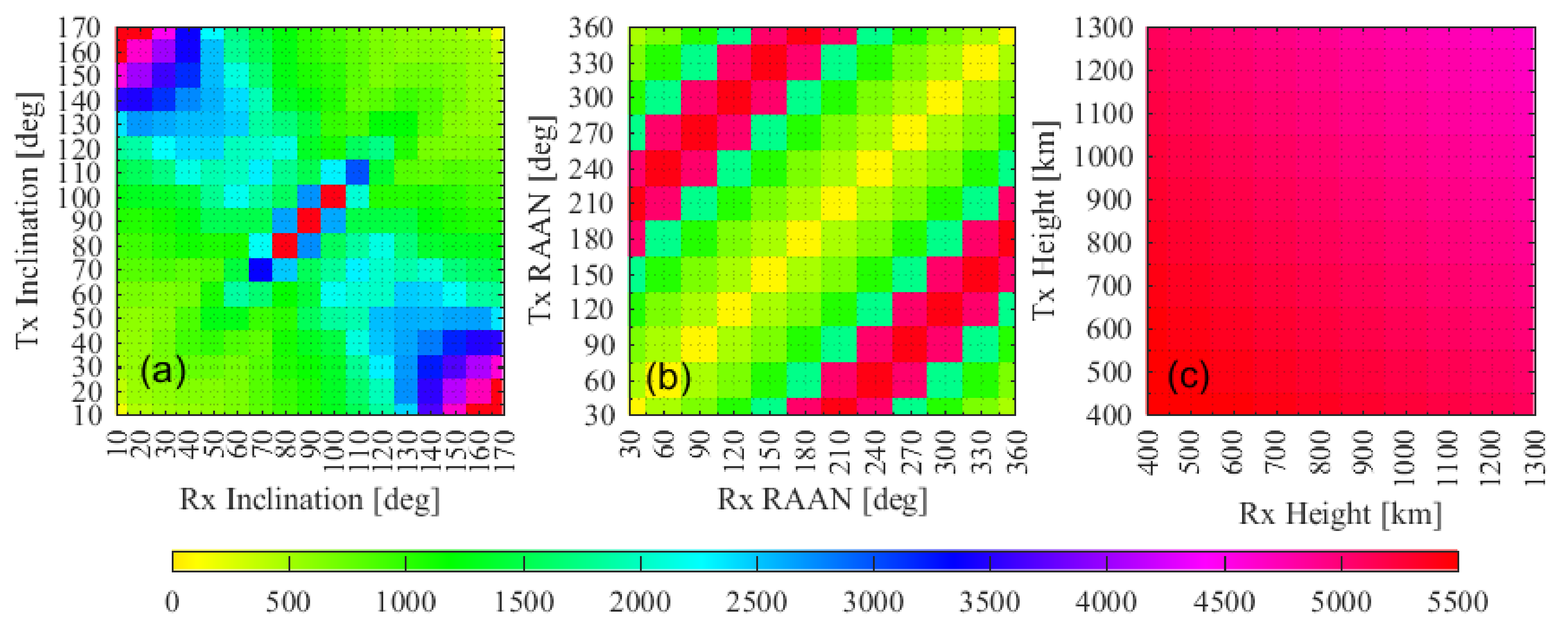
4.1.3. Impact of the Inclination
4.1.4. Impact of the RAAN
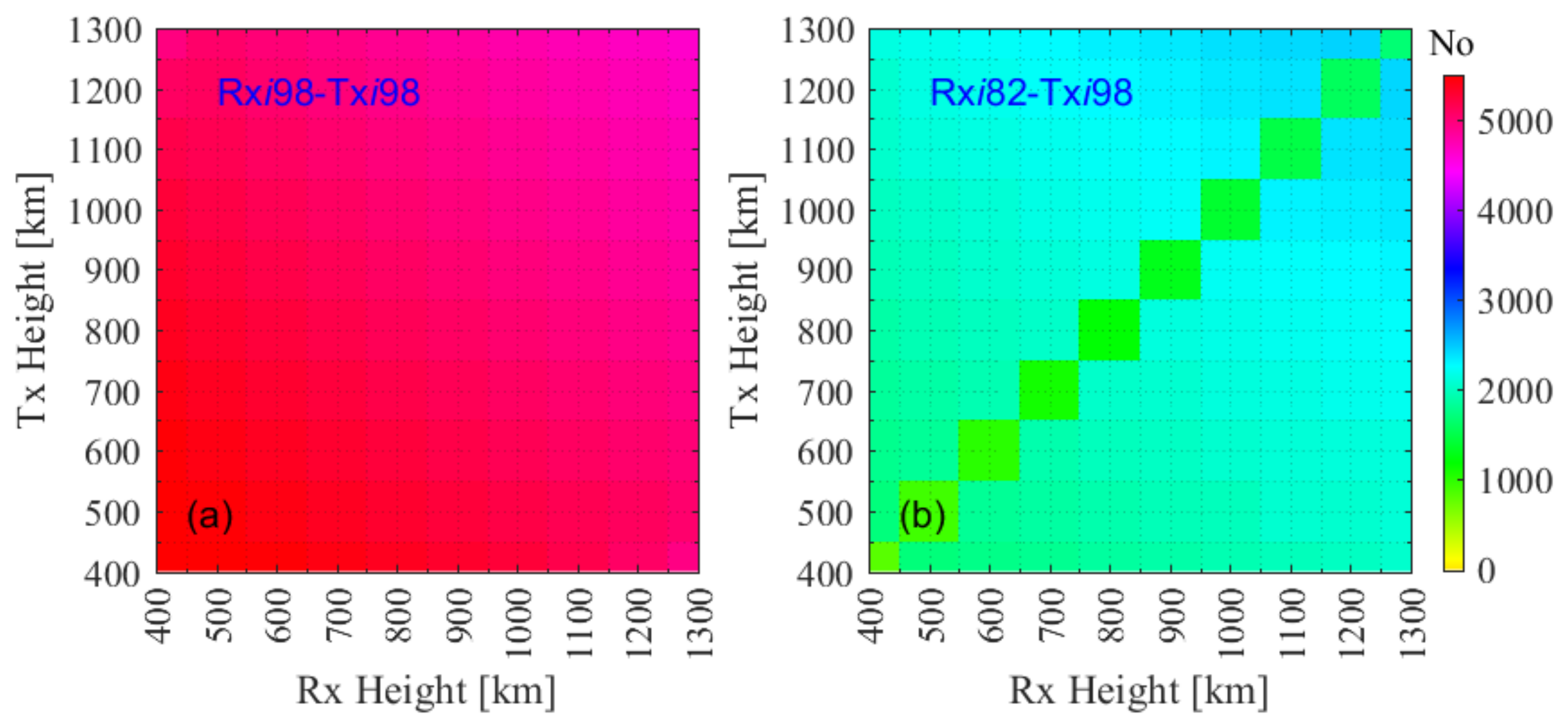
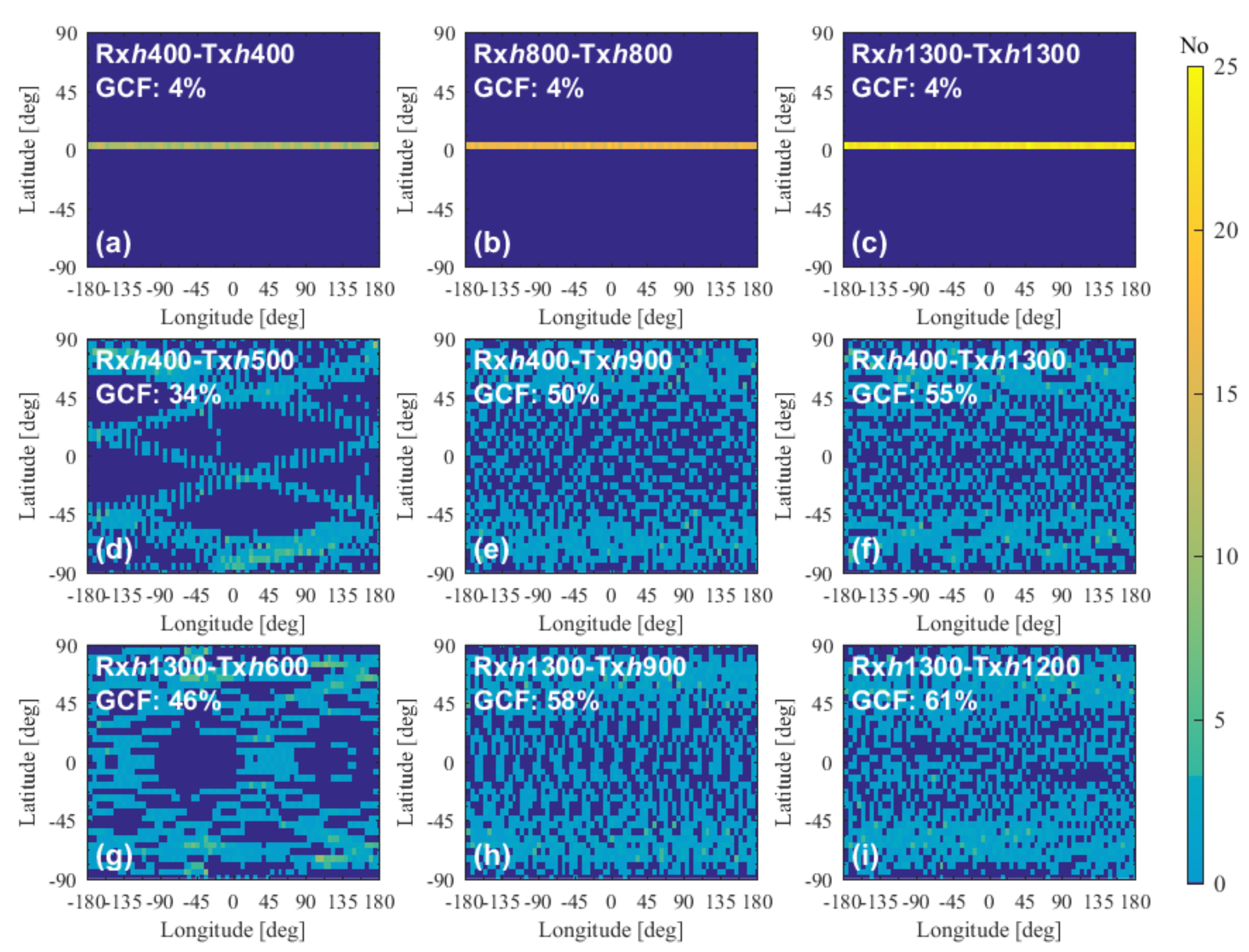
4.1.5. Impact of the Height
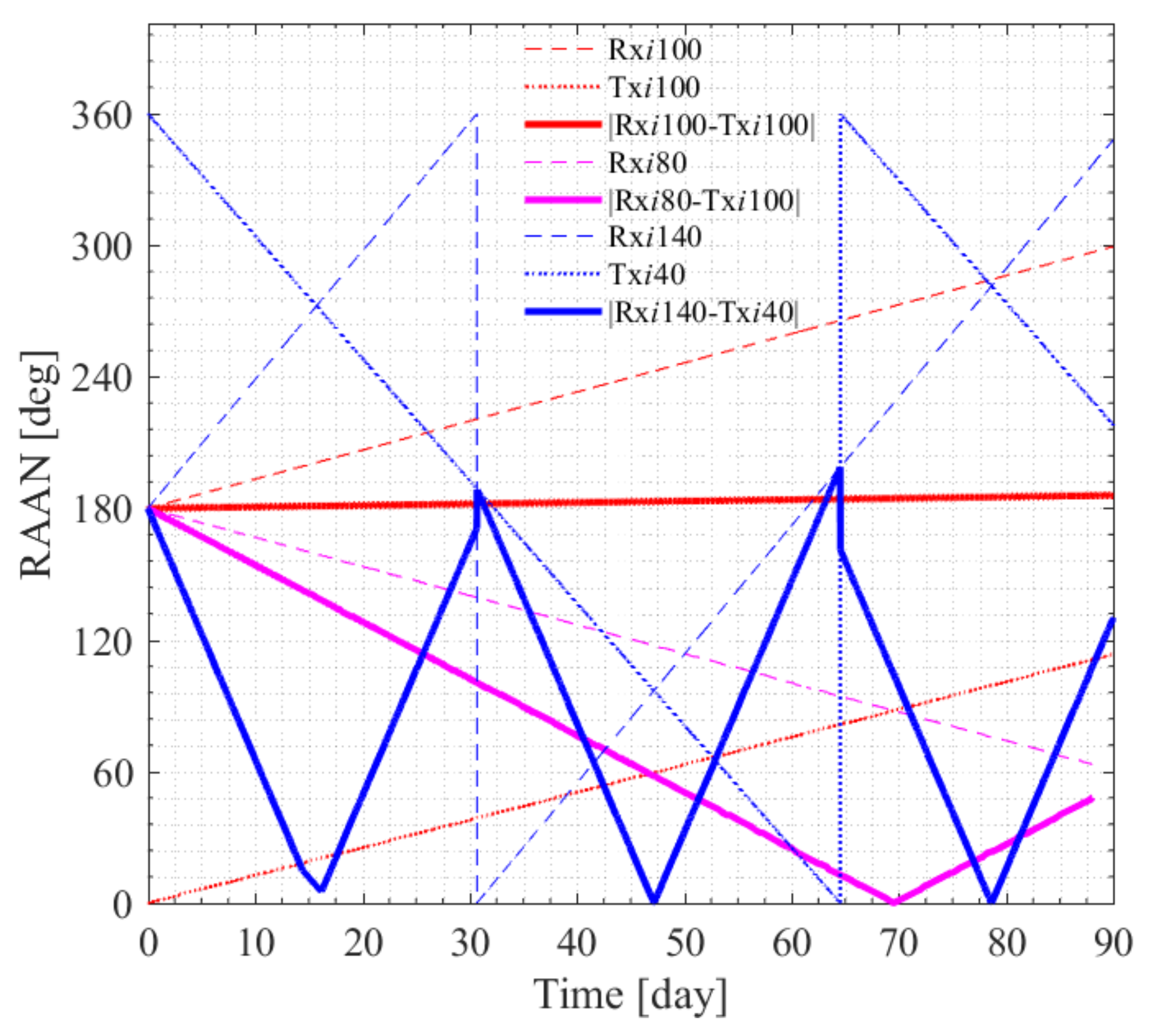
4.2. Impact of the RAAN Precession on the LEO-LEO Occultation Events
4.2.1. RAAN Precession Impact Analysis
4.2.2. Impacts of the Height on the Near-Polar Orbit Constellation Occultation Events
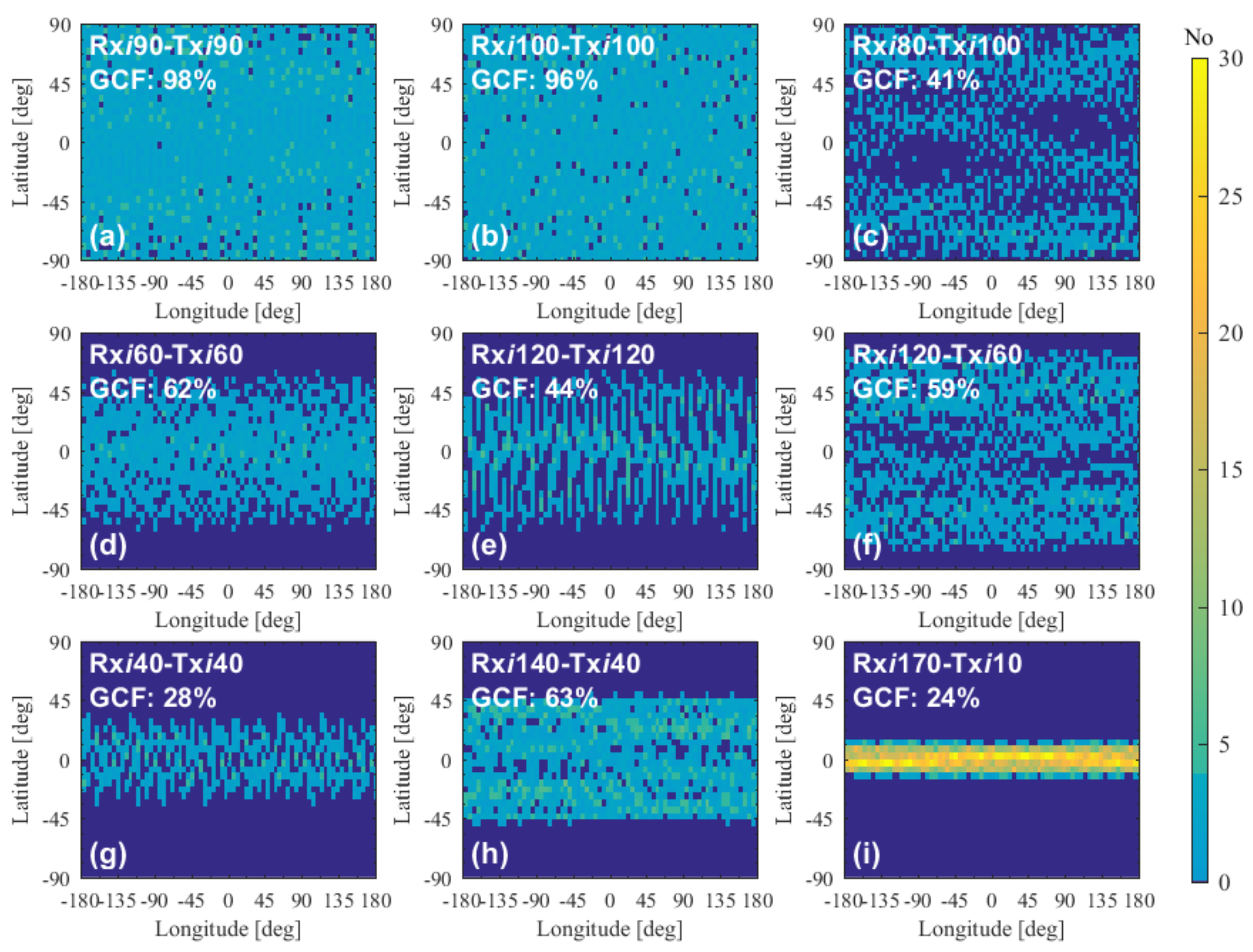
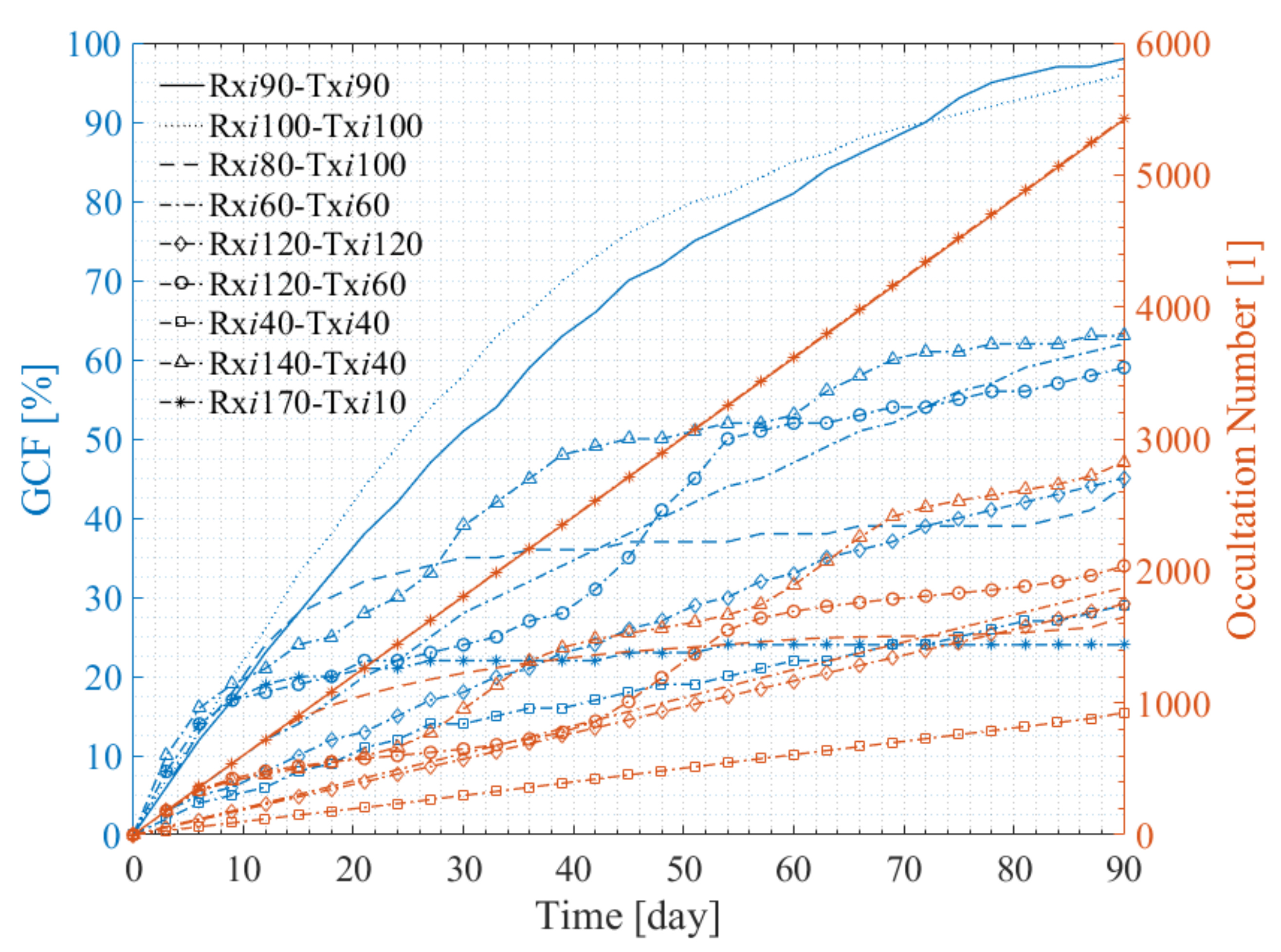
4.3. Assessment of Multi-Rx and Multi-Tx LEO-LEO Occultation Constellation Performance
4.3.1. Orbital Parameter Setup for Multi-Satellite Experimental Constellations
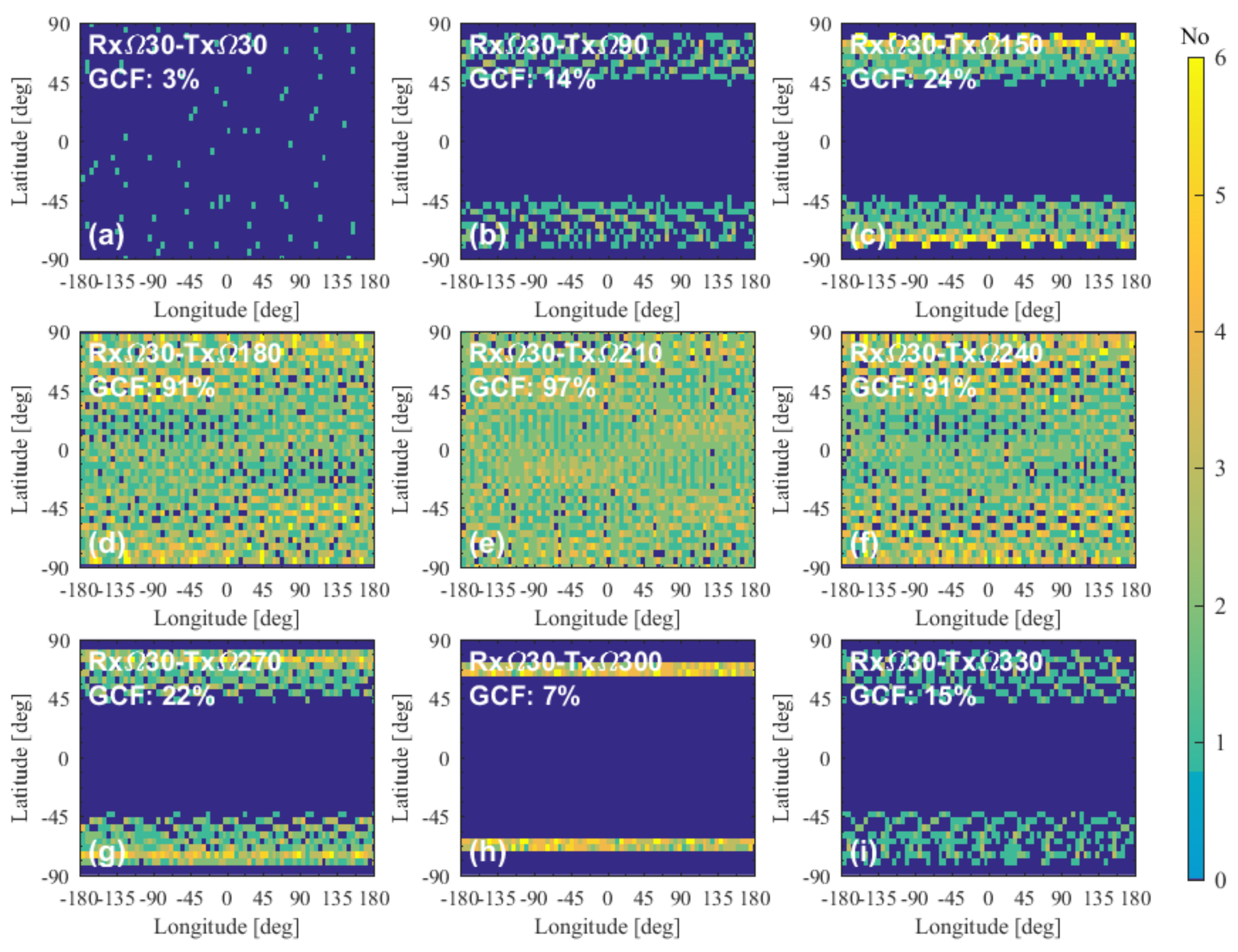
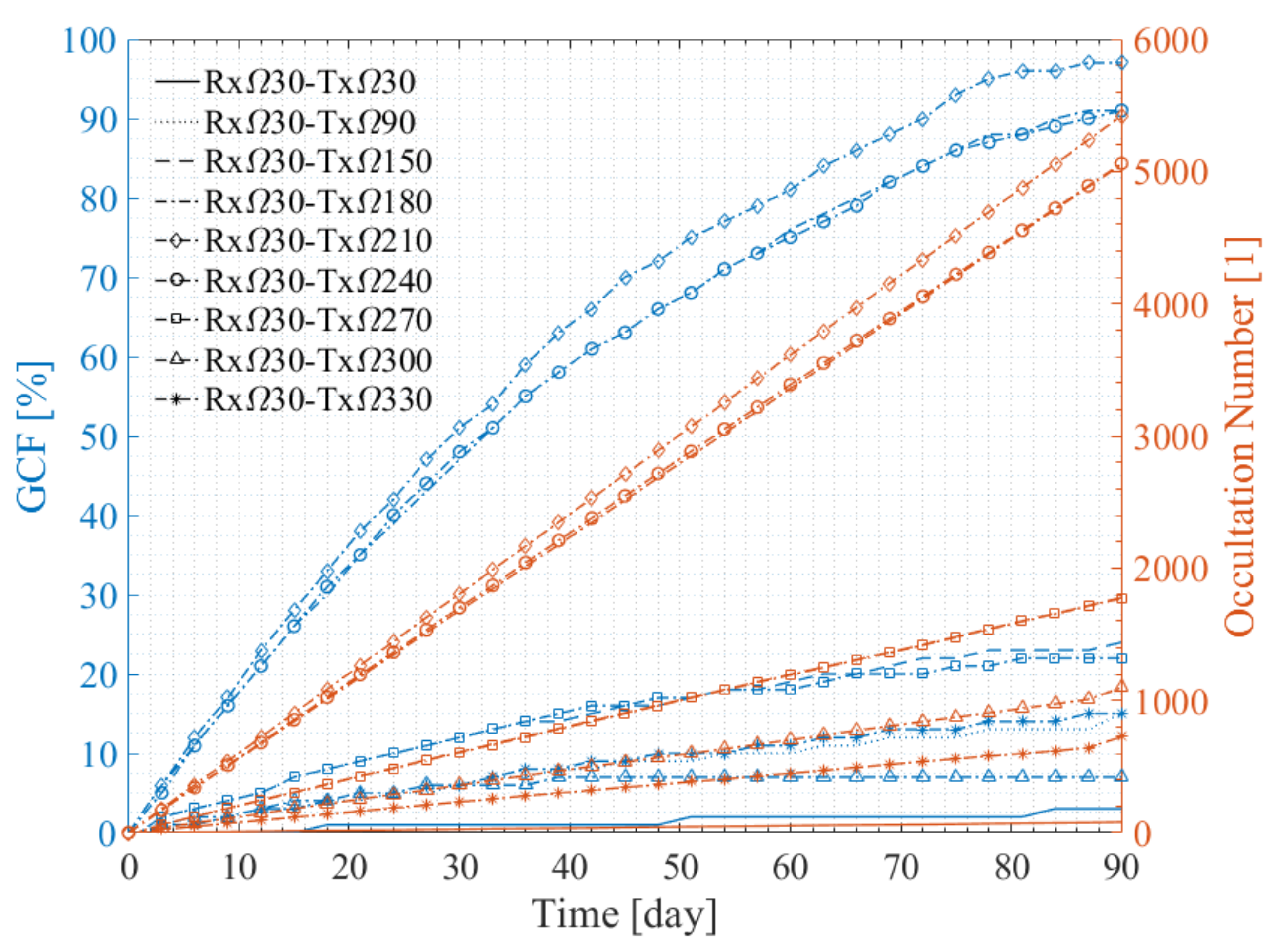
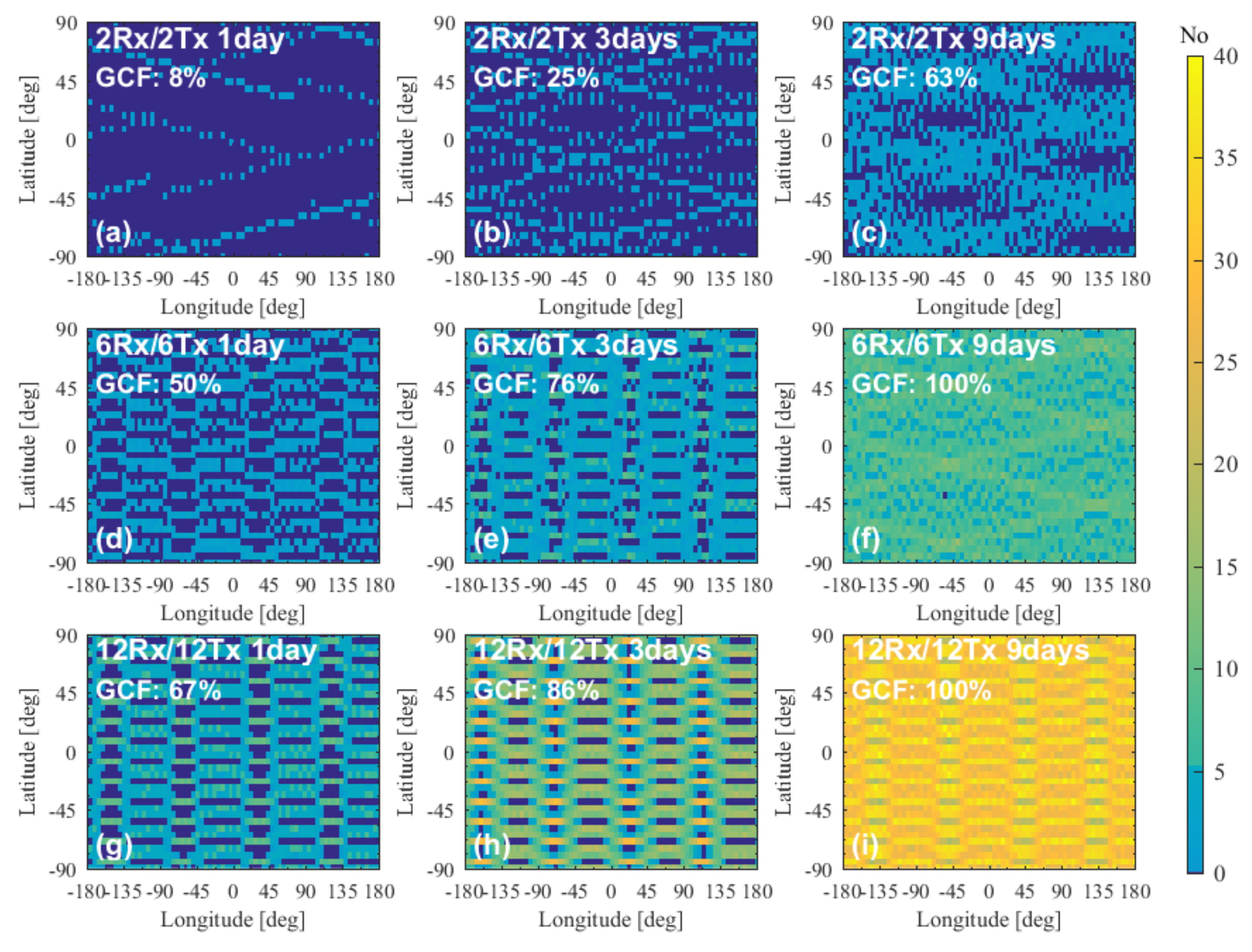
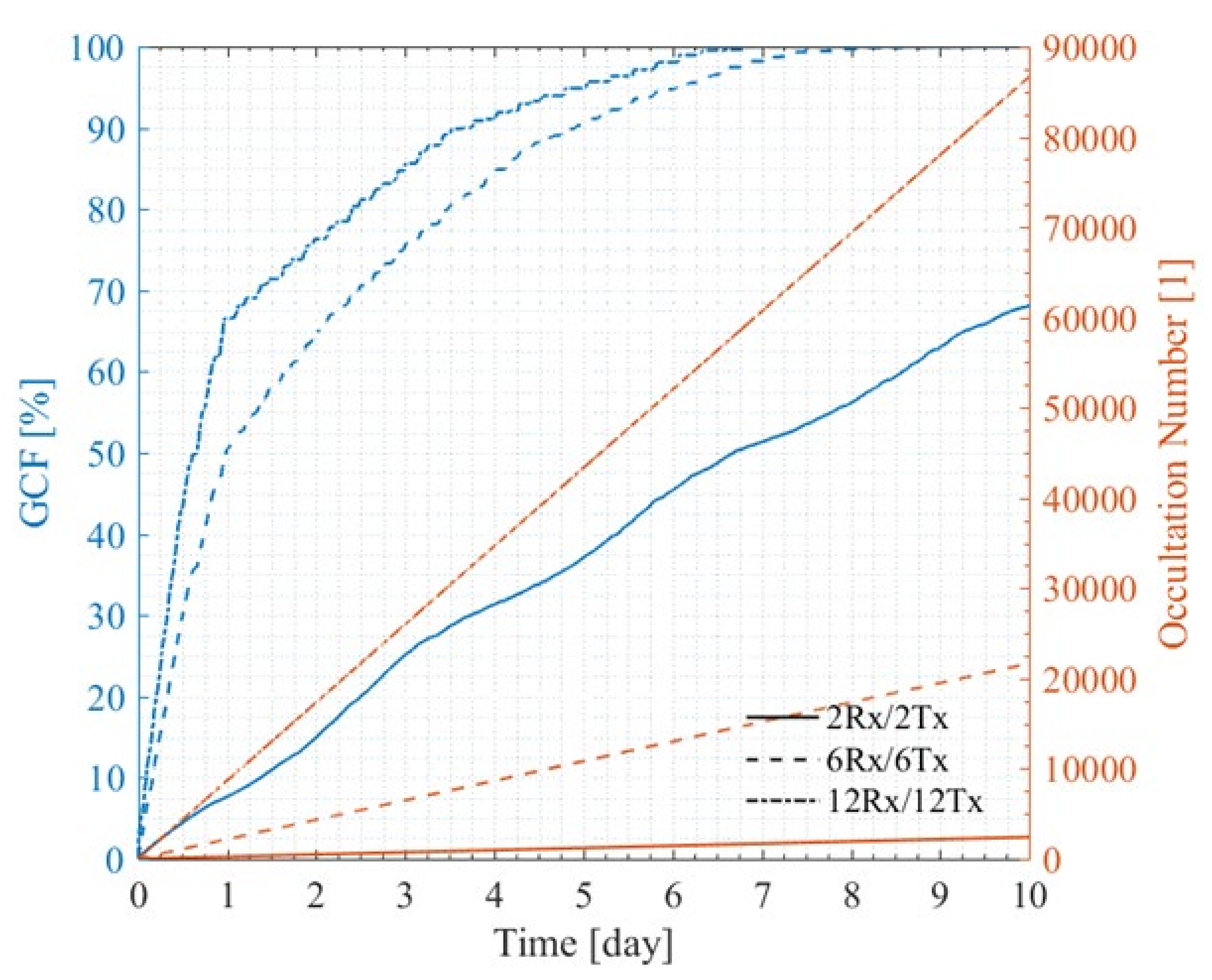
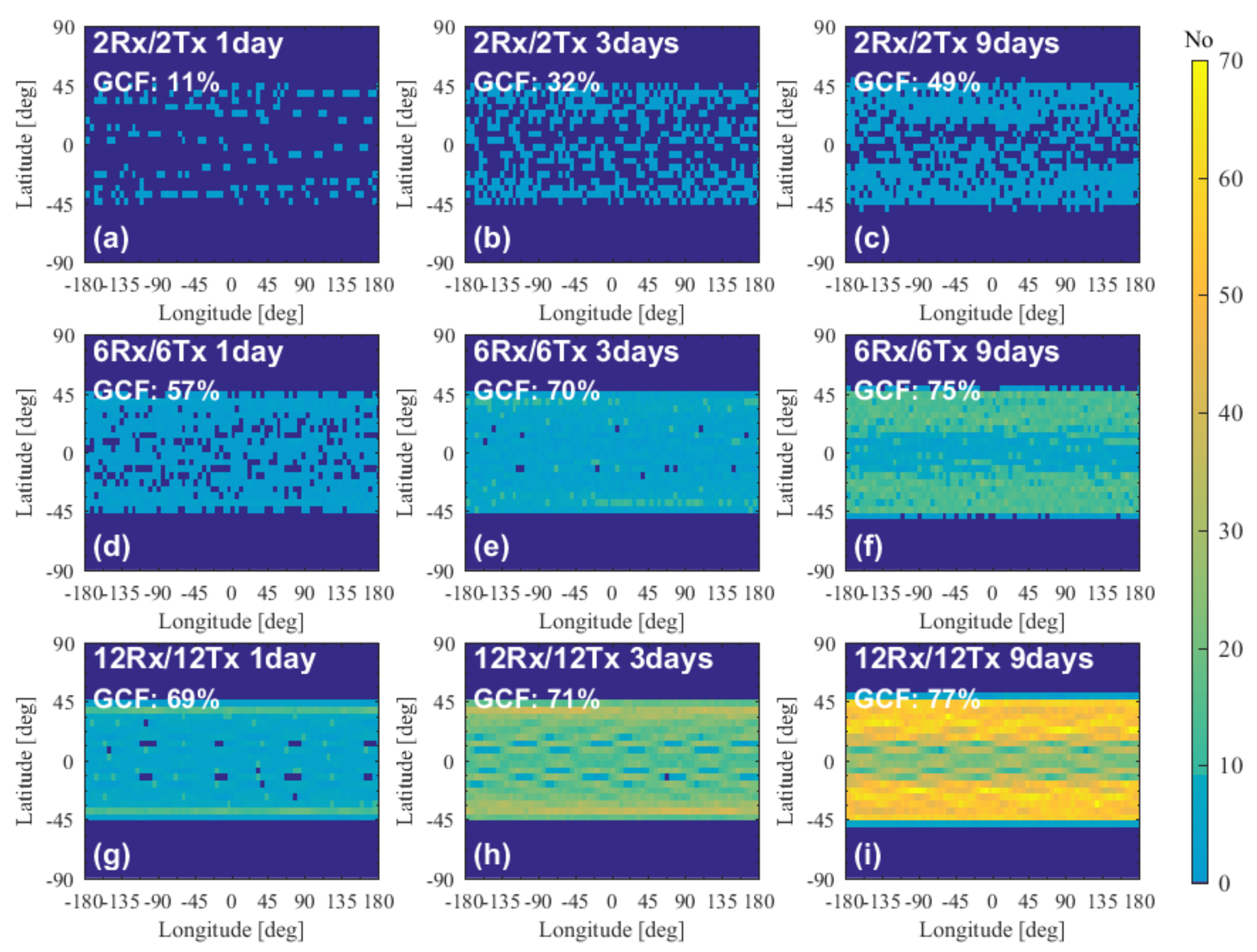
4.3.2. Performance of Two-Orbit Constellations
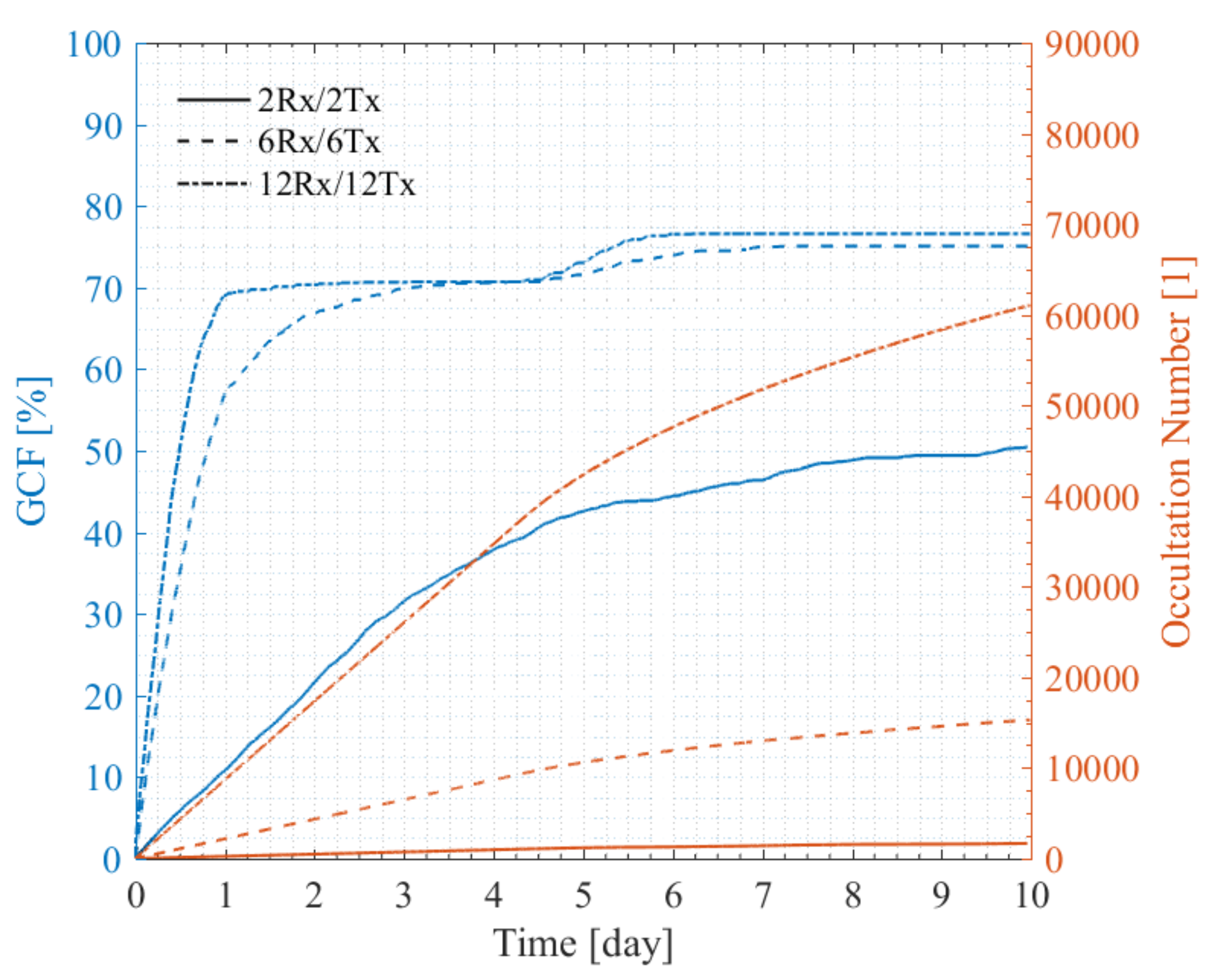
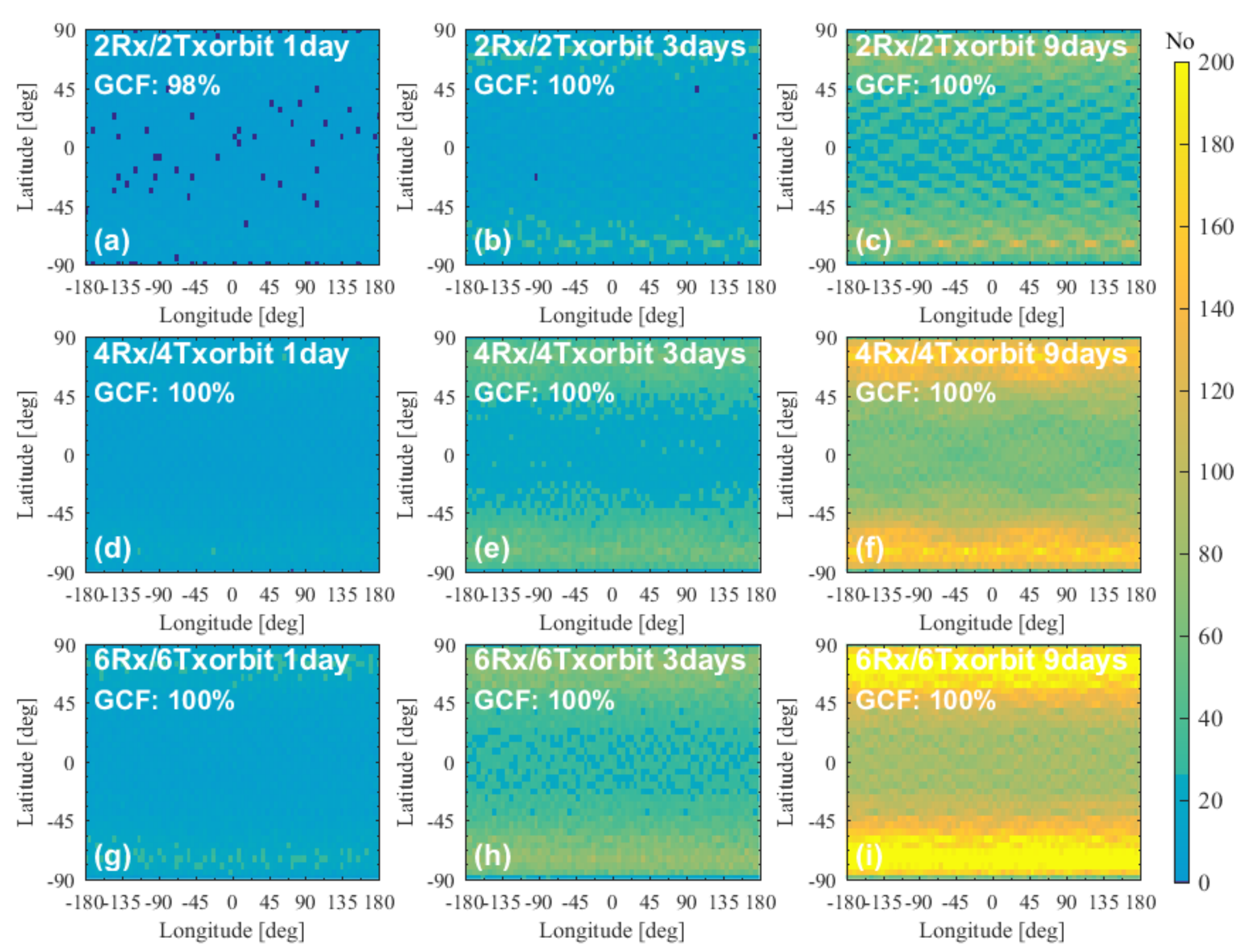
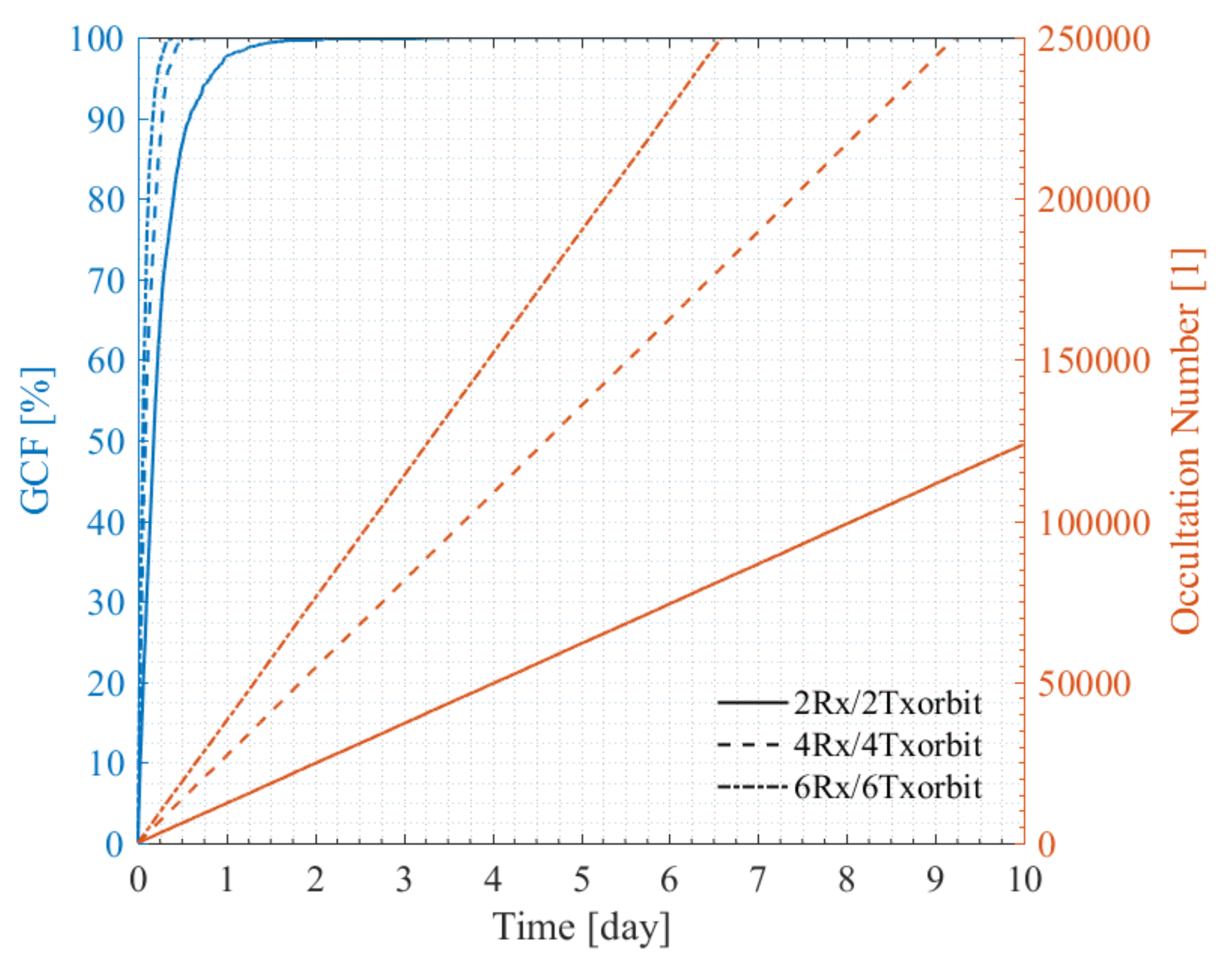
4.3.3. Performance of Multiple-Orbit Constellations
5. Discussions
5.1. Summary of the Impacts of the Orbital Parameters on the LEO-LEO Occultation Events
5.2. Summary of the Performances of the Multi-Rx and Multi-Tx Constellations
5.3. Outlook on the Potential for LEO-LEO Occultation Demonstration and Operational Constellations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Melbourne, W.G.; Davis, E.S.; Duncan, C.B.; Hajj, G.A.; Hardy, K.R.; Kursinski, E.R.; Meehan, T.K.; Yong, L.E.; Yunck, T.P. The application of spaceborne GPS to atmospheric limb sounding and global monitoring. JPL Publ. 1994, 147, 94-18. [Google Scholar]
- Kursinski, E.R.; Hajj, G.A.; Bertiger, W.I.; Leroy, S.S.; Meehan, T.K.; Romans, L.J.; Schofield, J.T.; McCleese, D.J.; Melbourne, W.G.; Thornton, C.L.; et al. Initial results of radio occultation observations of Earth’s atmosphere using the Global Positioning System. Science 1996, 271, 1107–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, A.K.; Kirchengast, G.; Ladreiter, H.-P. Inversion, error analysis, and validation of GPS/MET occultaiton data. Ann. Geophys. 1999, 17, 122–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunck, T.P.; Hajj, G.A.; Kursinski, E.R.; LaBrecque, J.A.; Lowe, S.T.; Watkins, M.M.; McCormick, C. AMORE: An autonomous constellation concept for atmospheric and ocean observation. Acta Astronaut. 2000, 46, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchengast, G.; Hoeg, P. The ACE+ mission: An atmosphere and climate explorer based on GPS, Galileo, and LEO-LEO radio occultation. In Occultations for Probing Atmosphere and Climate; Kirchengast, G., Foelsche, U., Steiner, A.K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 201–220. [Google Scholar]
- Kursinski, E.R.; Feng, D.; Flittner, D.; Hajj, G.; Herman, B.; Romberg, F.; Syndergaard, S.; Ward, D.; Yunck, T. An active microwave limb sounder for profiling water vapor, ozone, temperature, geopotential, clouds, isotopes and stratospheric winds. In Occultations for Probing Atmosphere and Climate; Kirchengast, G., Foelsche, U., Steiner, A.K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 173–187. [Google Scholar]
- Kirchengast, G.; Schweitzer, S. Climate benchmark profiling of greenhouse gases and thermodynamic structure and wind from space. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proschek, V.; Kirchengast, G.; Schweitzer, S. Greenhouse gas profiling by infrared-laser and microwave occultation: Retrieval algorithm and demonstration results from end-to-end simulations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2011, 4, 2035–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitzer, S.; Kirchengast, G.; Proschek, V. Atmospheric influences on infrared-laser signals used for occultation measurements between low Earth orbit satellites. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2011, 4, 2273–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooke, J.S.A.; Bernath, P.F.; Kirchengast, G.; Thomas, C.B.; Wang, J.G.; Tereszchuk, K.A.; González Abad, G.; Hargreaves, R.J.; Beale, C.A.; Harrison, J.J.; et al. Greenhouse gas measurements over a 144 km open path in the Canary Islands. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 2309–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurvich, A.S.; Gorbunov, M.E.; Fedorova, O.V.; Kirchengast, G.; Proschek, V.; Gonzalez Abad, G.; Tereszchuk, K.A. Spatiotemporal structure of a laser beam over 144 km in a Canary Islands experiment. Appl. Opt. 2012, 51, 7374–7383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syndergaard, S.; Kirchengast, G. An Abel transform for deriving line-of-sight wind profiles from LEO-LEO infrared laser occultation measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 2525–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthes, R.A. Exploring Earth’s atmosphere with radio occultation: Contributions to weather, climate and space weather. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2011, 4, 1077–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Han, Y.; Luo, J.; Wickert, J.; Asgarimehr, M. Seeking optimal GNSS radio occultation constellations using evolutionary algorithms. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kursinski, E.R.; Ward, D.; Otarola, A.; Frehlich, R.; Groppi, C.; Albanna, S.; Shein, M.; Bertiger, W.; Pickett, H.; Ross, M. The active temperature, ozone and moisture microwave spectrometer (ATOMMS). In New Horizons in Occultation Research: Studies in Atmosphere and Climate; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 295–313. [Google Scholar]
- Kursinski, E.R.; Young, A.; Otarola, A.; Stovern, M.; Wheelwright, B.; Ward, D.; Sammler, K.; Stickney, R.; Groppi, C.; Banna, S.A.; et al. Laboratory and ground testing results from ATOMMS: The active temperature, ozone and moisture microwave spectrometer. In Proceedings of the 21st International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology, Oxford, UK, 23–25 March 2010; pp. 155–163. [Google Scholar]
- Kursinski, E.R.; Ward, D.; Stovern, M.; Otarola, A.C.; Young, A.; Wheelwright, B.; Stickney, R.; Albanna, S.; Duffy, B.; Groppi, C.; et al. Development and testing of the active temperature, ozone and moisture microwave spectrometer (ATOMMS) cm and mm wavelength occultation instrument. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 439–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.L.; Kirchengast, G.; Syndergaard, S.; Kursinski, E.R.; Sun, Y.Q.; Bai, W.H.; Du, Q.F. A review of low Earth orbit occultation using microwave and infrared-laser signals for monitoring the atmosphere and climate. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 60, 2776–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Kirchengast, G.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Lu, D.; Bai, W.; Du, Q.; Loscher, A.; Syndergaard, S.; Tian, L.; et al. Exploring greenhouse gases water and climate changes: Scientific opportunities for the climate and atmospheric composition exploring satellites mission. Chin. J. Space Sci. 2021, 40, 151–168. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, J.J.; Bernath, P.F.; Kirchengast, G. Spectroscopic requirements for ACCURATE, a microwave and infrared-laser occultation satellite mission. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2011, 112, 2347–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackner, B.C.; Steiner, A.K.; Hegerl, G.C.; Kirchengast, G. Atmospheric climate change detection by radio occultation data using a fingerprinting method. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 5275–5291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurvich, A.S.; Gorbunov, M.E.; Fedorova, O.V.; Fortus, M.I.; Kirchengast, G.; Proschek, V.; Tereszchuk, K.A. Spatiotemporal structure of a laser beam at a path length of 144 km: Comparative analysis of spatial and temporal spectra. Appl. Opt. 2014, 53, 2625–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proschek, V.; Kirchengast, G.; Schweitzer, S.; Brooke, J.S.A.; Bernath, P.F.; Thomas, C.B.; Wang, J.G.; Tereszchuk, K.A.; González Abad, G.; Hargreaves, R.J.; et al. Retrieval and validation of carbon dioxide, methane and water vapor for the Canary Islands ir-laser occultation experiment. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 3315–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fjeldbo, G.; Kliore, A.J. The neutral atmosphere of Venus as studied with the Marriner V radio occultation experiments. Astron. J. 1971, 76, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.S. On the determination and investigation of the terrestrial ionospheric refractive indices using GEO-3/ATS-6 satellite-to-satellite tracking data. Radio Sci. 1978, 13, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kursinski, E.R.; Hajj, G.A.; Schofield, J.T.; Linfield, R.P.; Hardy, K.R. Observing Earth’s atmosphere with radio occultation measurements using the global positioning system. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 23429–23465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickert, J.; Reigber, C.; Beyerle, G.; Konig, R.; Marquardt, C.; Schmidt, T.; Grunwaldt, L.; Galas, R.; Meehan, T.K.; Melbourne, W.G.; et al. Atmosphere sounding by GPS radio occultation: First results from CHAMP. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 3263–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foelsche, U.; Kirchengast, G.; Steiner, A.K. Global climate monitoring based on CHAMP/GPS radio occultation data. In First CHAMP Mission Results for Gravity, Magnetic and Atmospheric Studies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 397–407. [Google Scholar]
- Foelsche, U.; Pirscher, B.; Borsche, M.; Kirchengast, G.; Wickert, J. Assessing the climate monitoring utility of radio occultation data: From CHAMP to Formosat-3/COSMIC. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2009, 20, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Beyerle, G. GPS radio occultation with GRACE: Atmospheric profiling utilizing the zero difference technique. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L13806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickert, J.; Schmidt, T.; Michalak, G.; Heise, S.; Arras, C.; Beyerle, G.; Falck, C.; König, R.; Pingel, D.; Rothacher, M. GPS radio occultation with CHAMP, GRACE-A, SAC-C, TerraSar-X, and Formosat-3/COSMIC: Brief review of results from GFZ. In New Horizons in Occultation Research; Steiner, A., Pirscher, B., Foelsche, U., Kirchengast, G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luntama, J.P.; Kirchengast, G.; Borsche, M.; Foelsche, U.; Steiner, A.; Healy, S.; von Engeln, A.; O’Clerigh, E.; Marquardt, C. Prospects of the EPS GRAS mission for operational atmospheric applications. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2008, 89, 1863–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucurull, L.; Kuo, Y.H.; Barker, D.; Rizvi, S.R.H. Assessing the impact of simulated COSMIC GPS radio occultation data on weather analysis over the antarctic: A case study. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2006, 134, 3283–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiner, W.; Rocken, C.; Sokolovskiy, S.; Syndergaard, S.; Hunt, D. Estimates of the precision of GPS radio occultations from the COSMIC/Formosat-3 mission. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, 545–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthes, R.A.; Ector, D.; Hunt, D.C.; Kuo, Y.H.; Rocken, C.; Schreiner, W.S.; Sokolovskiy, S.V.; Syndergaard, S.; Wee, T.K.; Zeng, Z.; et al. The COSMIC/Formosat-3 mission: Early results. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2008, 89, 313–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.H.; Liu, C.L.; Meng, X.G.; Sun, Y.Q.; Kirchengast, G.; Du, Q.F.; Wang, X.Y.; Yang, G.L.; Liao, M.; Yang, Z.D.; et al. Evaluation of atmospheric profiles derived from single- and zero-difference excess phase processing of BeiDou radio occultation data from the FY-3C GNOS mission. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 819–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.Q.; Bai, W.H.; Liu, C.L.; Liu, Y.; Du, Q.F.; Wang, X.Y.; Yang, G.L.; Liao, M.; Yang, Z.D.; Zhang, X.X.; et al. The FengYun-3C radio occultation sounder GNOS: A review of the mission and its early results and science applications. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 5797–5811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, L.; Ho, S.-P.; Zhou, X. Inverting COSMIC-2 phase data to bending angle and refractivity profiles using the full spectrum inversion method. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, J.-C.; Tsai, Y.-F.; Chu, C.-H. On constellation design of multi-GNSS radio occultation mission. Acta Astronaut. 2013, 82, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, P.; Radnóti, G.; Healy, S.; Cardinali, C. GNSS radio occultation constellation observing system experiments. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2014, 142, 555–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, A.; Aoyama, Y.; Tsuda, T. A simulation analysis to optimize orbits for a tropical GPS radio occultation mission. Earth Planets Space 2006, 58, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgarimehr, M.; Hossainali, M.M. GPS radio occultation constellation design with the optimal performance in Asia Pacific region. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 519–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoniem, I.; Mousa, A.E.-K.; El-Fiky, G. Distribution of the GNSS-LEO occultation events over Egypt. NRIAG J. Astron. Geophys. 2019, 6, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoniem, I.F.; Mousa, A.E.-K.; El-Fiky, G. GNSS-RO LEO satellite orbit optimization for Egypt and the middle east region. Alex. Eng. J. 2020, 59, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WATS–water vapor and temperature in the troposphere and stratosphere (3rd Report of Reports for mission selection, the five candidate Earth Explorer core missions). ESA Spec. Publ. 2001, 1257, 98.
- Mimoun, D.; Abbondanza, S. The genesis of the ACE+ anti-rotating satellites concept. In Occultations for Probing Atmosphere and Climate; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 245–258. [Google Scholar]
- Kirchengast, G.; Ramsauer, J. Impact of an Atmospheric Profiling Mission on NWP: Assessment of Mission Scenarios and Definition of OSSE Study Test Missions. IMG/UoG Technical Report for ESA/ESTEC No. 3; 1999; 16p. Available online: https://wegcwww.uni-graz.at/publ/users/gki/web/1999/gkandjr-imgtechrepfesa-16p-n3y1999.pdf (accessed on 23 November 2021).
- Kornblueh, L.; Bengtsson, L.; Kirchengast, G.; Huang, X.-Y.; Hoeg, P.; Larsen, G.B. Impact of an Atmospheric Profiling Mission on Numerical Weather Prediction. 2000. Available online: https://wegcwww.uni-graz.at/publ/users/gki/web/arsclisys/publications/publ2000/LKornbluehetal-ESAStudyRep-110p-y2000.pdf (accessed on 23 November 2021).
- Kirchengast, G.; Bernath, P.; Buehler, S. ACCURATE─climate benchmark profiling of greenhouse gases and thermodynamic variables and wind from space (ESA Earth Explorer opportunity mission EE-8 proposal). Sci. Rep. 2010. Available online: https://wegccon.uni-graz.at/opac2010/pdf_presentation/opac_2010_kirchengast_gottfried_presentation57.pdf (accessed on 23 November 2021).
- Kirchengast, G.; Zwanziger, C.; Larsen, G.B. Scientific Impact of an ACCURATE Mission and Synergies and Complementarities with Other Missions and GHG Observations; Technical Report for ESA-ESTEC No. 1/2010; 51p. Available online: https://wegcwww.uni-graz.at/publ/wegcpubl/arsclisys/2010/wegc_gkirchengastetal-wegctechrepfesa-no1-2010.pdf (accessed on 23 November 2021).
- Kursinski, E.R.; Folkner, W.; Zuffada, C.; Walker, C.; Hinson, D.; Ingersoll, A.; Gurwell, M.A.; Schofield, J.T.; Limaye, S.; Stern, A.; et al. The Mars atmospheric constellation observatory (MACO) concept. In Occultations for Probing Atmosphere and Climate; Kirchengast, G., Foelsche, U., Steiner, A.K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Mortari, D. 2-D lattice flower constellations for radio occultation missions. Front. Aerosp. Eng. 2013, 2, 79–90. [Google Scholar]
- Vallado, D.; Crawford, P.; Huisak, R.; Kelso, T.S. Revisiting Spacetrack Report #3. In Proceedings of the AIAA/AAS Astrodynamics Specialist Conference & Exhibit, Keystone, CO, USA, 21−24 August 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann-Wellenhof, B.; Lichtenegger, H.; Wasle, E. GNSS—Global Navigation Satellite Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]


| Orbit Elements (Rx/Tx) | Experimental Groups | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| i | raan | h | |
| I (°) | 10:10:170/10:10:170 | 90/90 | 90/90 |
| RAAN (°) | 180/0 | 30:30:360/30:30:360 | 180/0 |
| H (km) | 500/600 | 500/600 | 400:100:1300/400:100:1300 |
| AP (°) | 80/80 | 80/80 | 80/80 |
| M0 (°) | 210/30 | 210/30 | 210/30 |
| E | 0.0001/0.0001 | 0.0001/0.0001 | 0.0001/0.0001 |
| Orbit Elements (Rx/Tx) | Experimental Groups | |
|---|---|---|
| Rxi98-Txi98 | Rxi98-Txi82 | |
| I (°) | 98/98 | 98/82 |
| RAAN (°) | 180/0 | 180/0 |
| H (km) | 400:100:1300/400:100:1300 | 400:100:1300/400:100:1300 |
| AP (°) | 80/80 | 80/80 |
| M0 (°) | 210/30 | 210/30 |
| E | 0.0001/0.0001 | 0.0001/0.0001 |
| Experiment Groups | Orbit Elements (Rx/Tx) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I (°) | RAAN (°) | M0 (°) | ||
| Rxi98-Txi98 | 2Rx/2Tx | 98/98 | 180/0 | 30, 120/150, 240 |
| 6Rx/6Tx | 98/98 | 180/0 | 30:60:360/30:60:360 | |
| 12Rx/12Tx | 98/98 | 180/0 | 30:30:360/30:30:360 | |
| Rxi140-Txi40 | 2Rx/2Tx | 140/40 | 180/0 | 30, 120/150, 240 |
| 6Rx/6Tx | 140/40 | 180/0 | 30:60:360/30:60:360 | |
| 12Rx/12Tx | 140/40 | 180/0 | 30:30:360/30:30:360 | |
| Multiple orbits of Rxi98-Txi98 | 2Rx/2Txorbit | 98/98 | 0, 90/180, 270 | 30:60:360/30:60:360 |
| 4Rx/4Txorbit | 98/98 | 30:30:120/210:30:300 | 30:60:360/30:60:360 | |
| 6Rx/6Txorbit | 98/98 | 0:30:150/180:30:330 | 30:60:360/30:60:360 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Kirchengast, G.; Sun, Y.; Proschek, V.; Wang, X.; Tian, L.; Du, Q.; Bai, W.; Wu, C.; Hu, P.; et al. Impacts of Orbital and Constellation Parameters on the Number and Spatiotemporal Coverage of LEO-LEO Occultation Events. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4849. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13234849
Liu C, Kirchengast G, Sun Y, Proschek V, Wang X, Tian L, Du Q, Bai W, Wu C, Hu P, et al. Impacts of Orbital and Constellation Parameters on the Number and Spatiotemporal Coverage of LEO-LEO Occultation Events. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(23):4849. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13234849
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Congliang, Gottfried Kirchengast, Yueqiang Sun, Veronika Proschek, Xin Wang, Longfei Tian, Qifei Du, Weihua Bai, Chunjun Wu, Peng Hu, and et al. 2021. "Impacts of Orbital and Constellation Parameters on the Number and Spatiotemporal Coverage of LEO-LEO Occultation Events" Remote Sensing 13, no. 23: 4849. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13234849
APA StyleLiu, C., Kirchengast, G., Sun, Y., Proschek, V., Wang, X., Tian, L., Du, Q., Bai, W., Wu, C., Hu, P., & Tan, G. (2021). Impacts of Orbital and Constellation Parameters on the Number and Spatiotemporal Coverage of LEO-LEO Occultation Events. Remote Sensing, 13(23), 4849. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13234849