An Improved Smooth Variable Structure Filter for Robust Target Tracking
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The SVSF Strategies
2.1. The SVSF
2.2. Review of Combining SVSF with Other Estimation Strategies
3. Methodology for the Proposed ISVSF
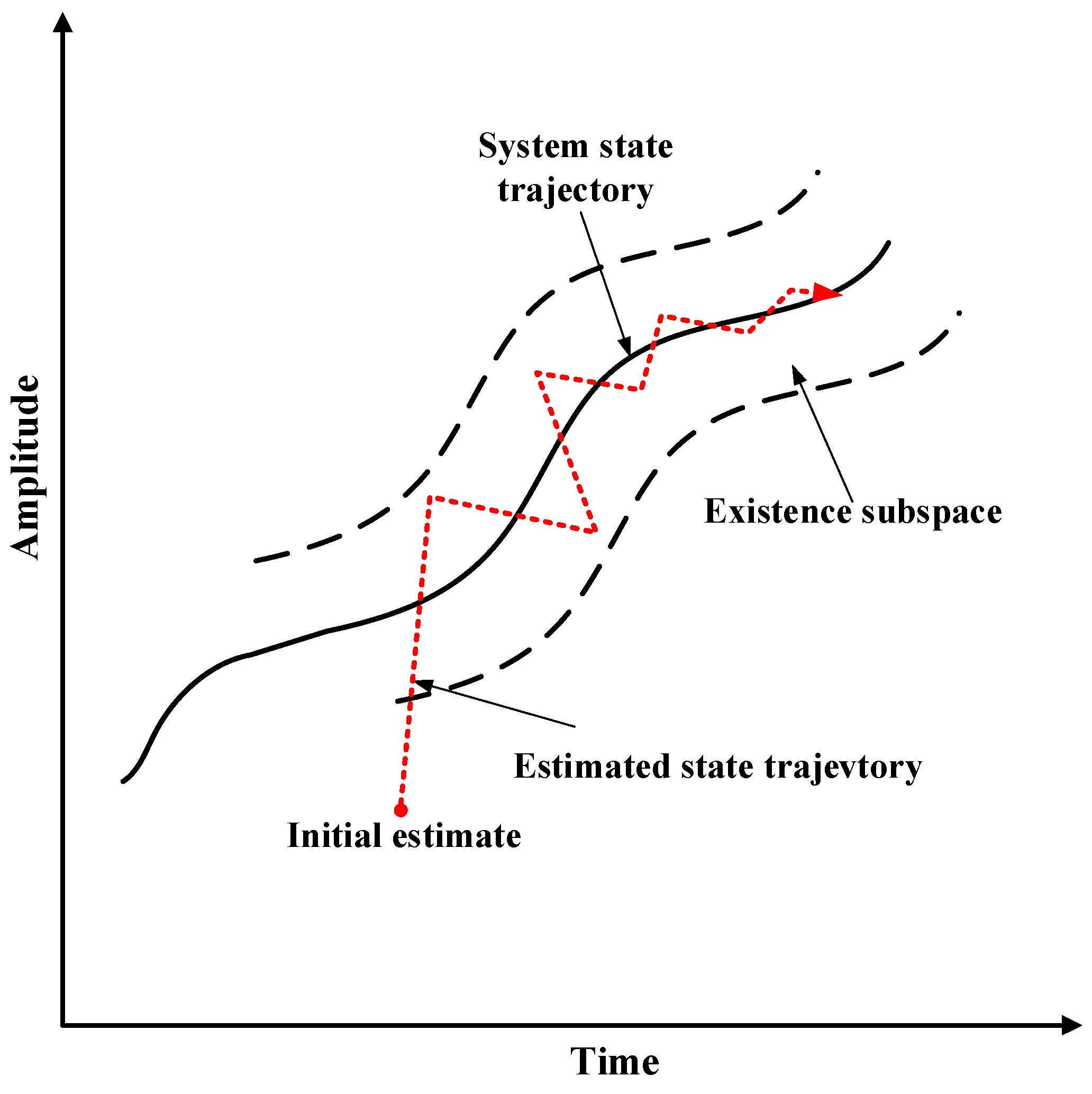
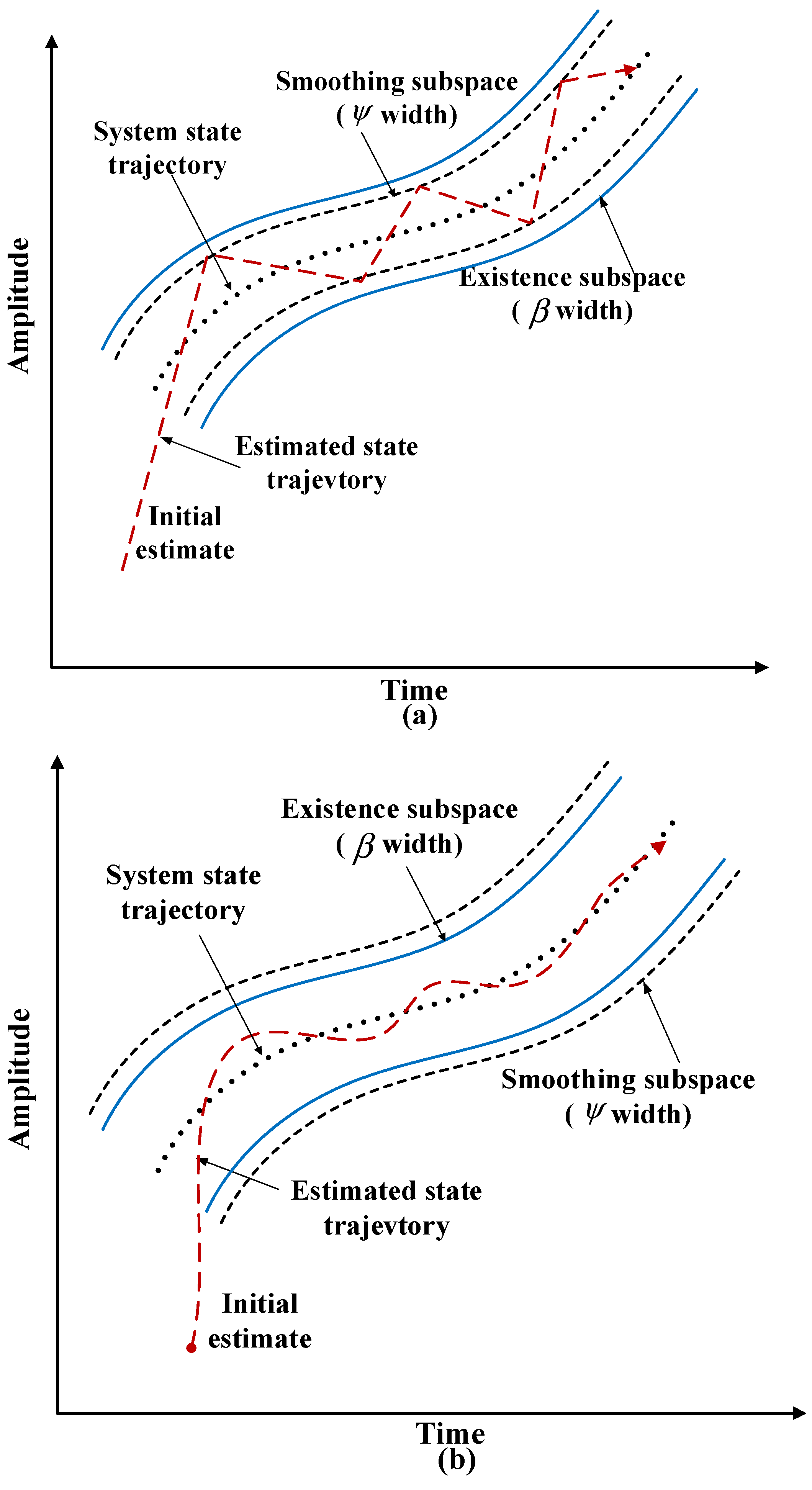
3.1. Motivation of This Work
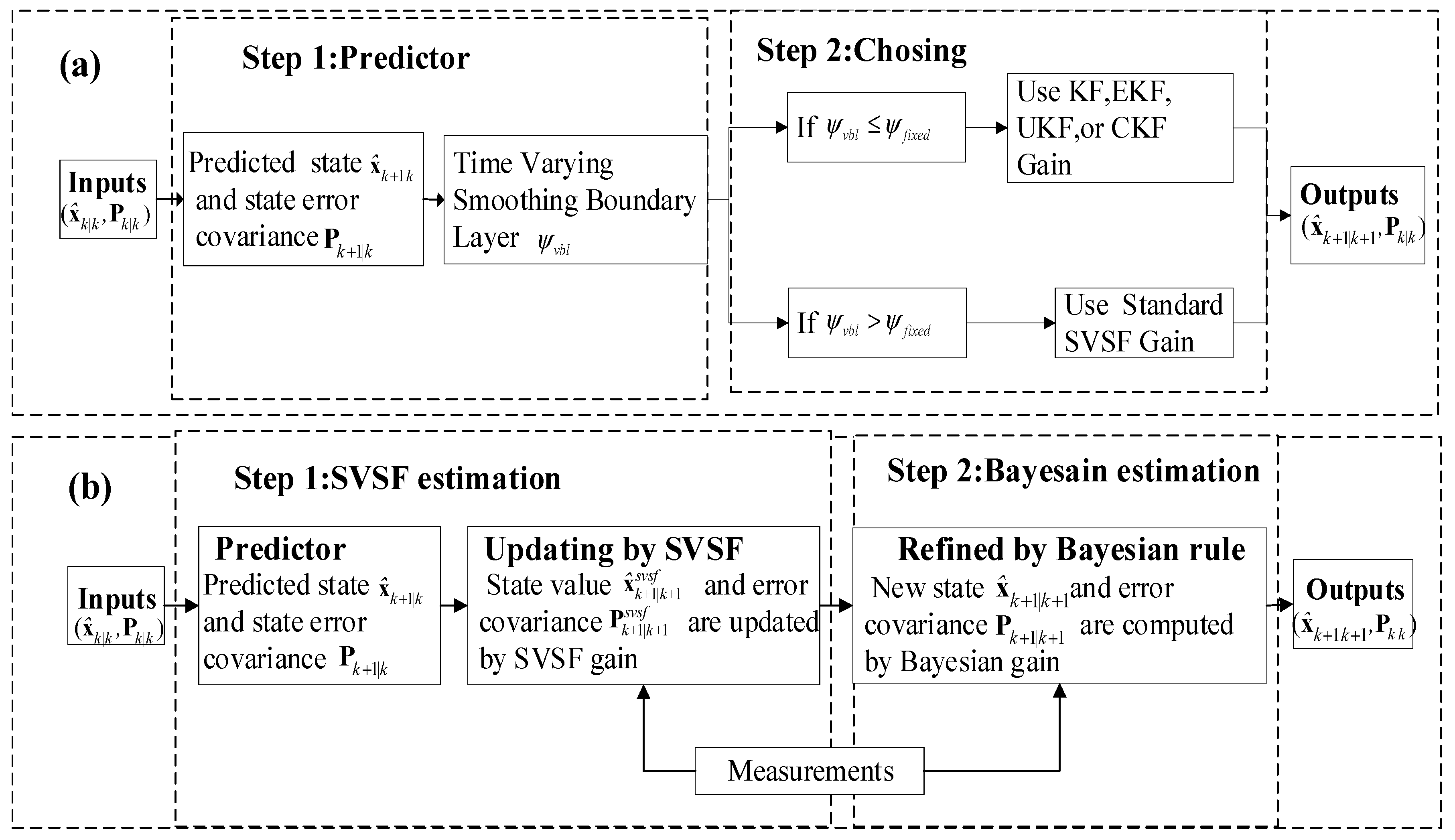
3.2. The Proposed ISVSF Derivation
3.2.1. Step 1: The SVSF Estimation Process
3.2.2. Step 2: Revised by Bayesian Estimation Method
| Algorithm 1: The ISVSF algorithm |
| Input {} and the sequence measurement {} For k = 1:N Step 1 SVSF estimation propagate the nominal state Propagate the error covariance Compute the SVSF gain Update the state Step 2 revised by Bayesian estimation: Compute the measurement error covariance Compute the Bayesian gain Update the a posteriori error state Compute the posteriori error covariance Output {, , } End for |
4. Simulation
4.1. A Classic Target Tracking Scenario
4.1.1. Simulation under Unknown Noise
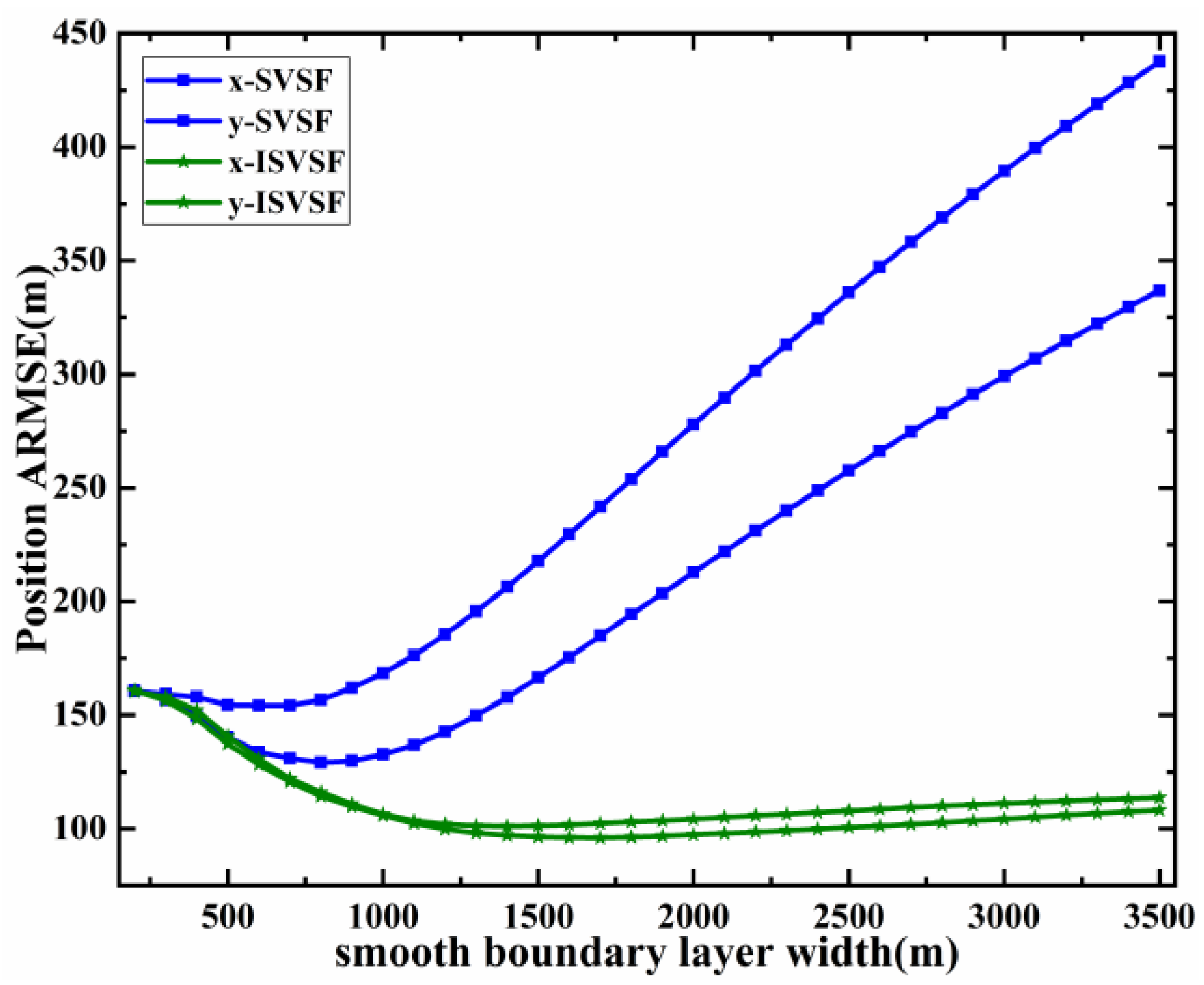
4.1.2. Results under the Condition of Different Smooth Boundary Layer Widths
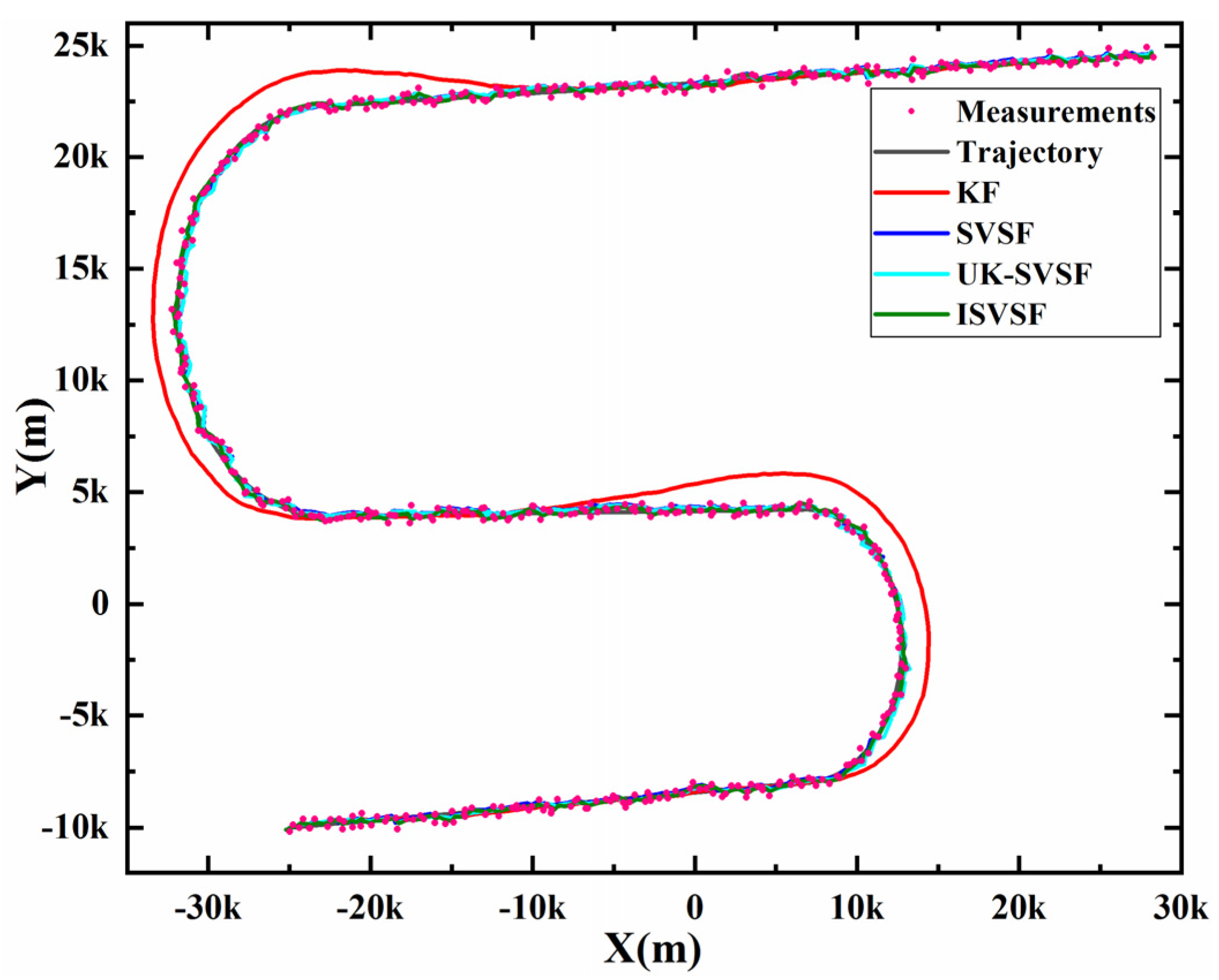
4.2. Simulation Results in Modeling Error
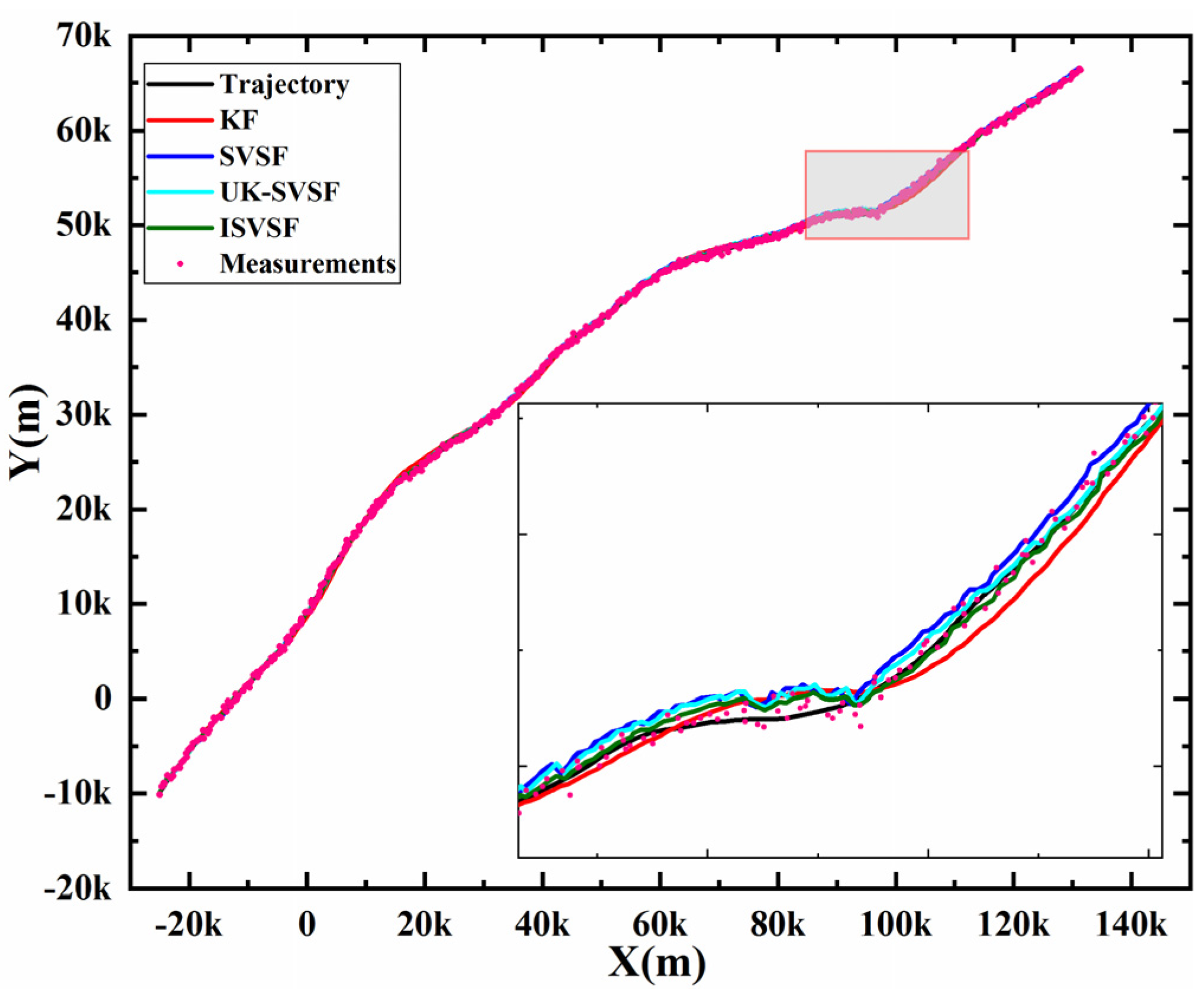
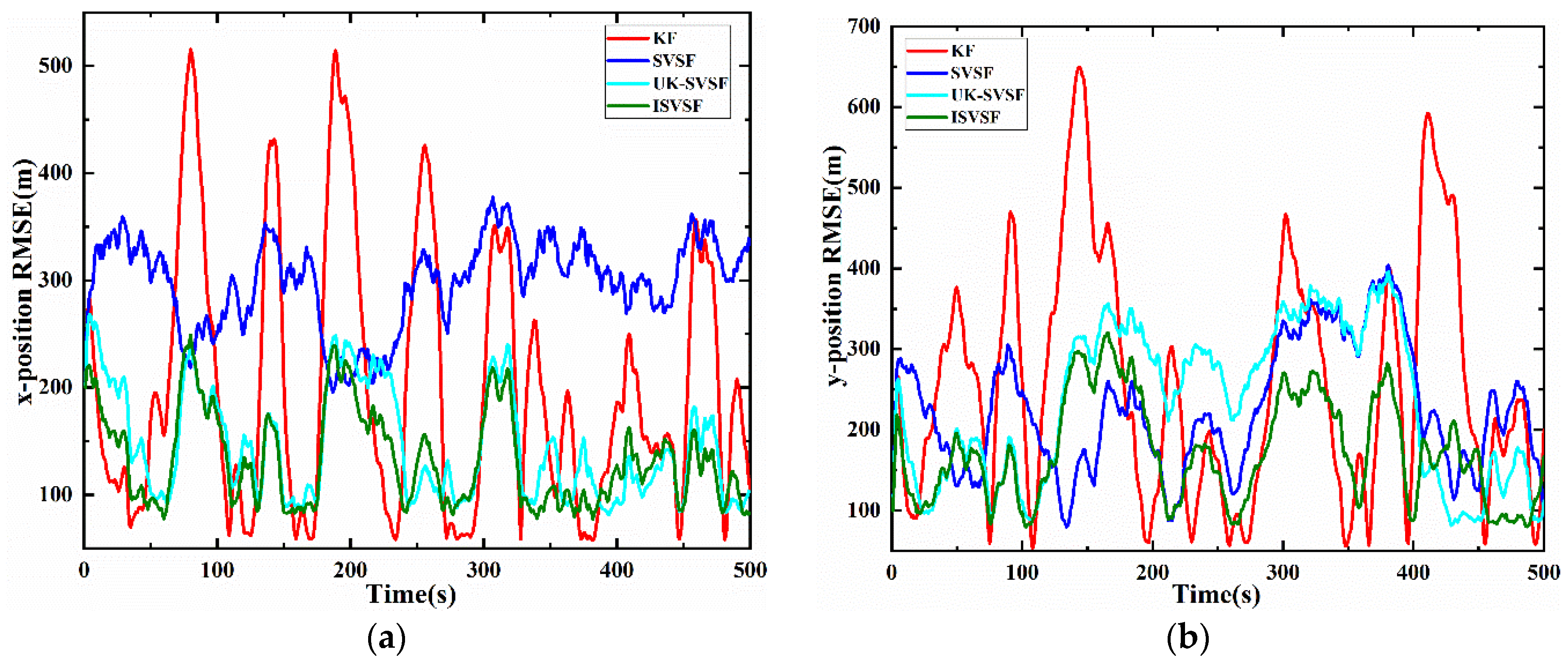
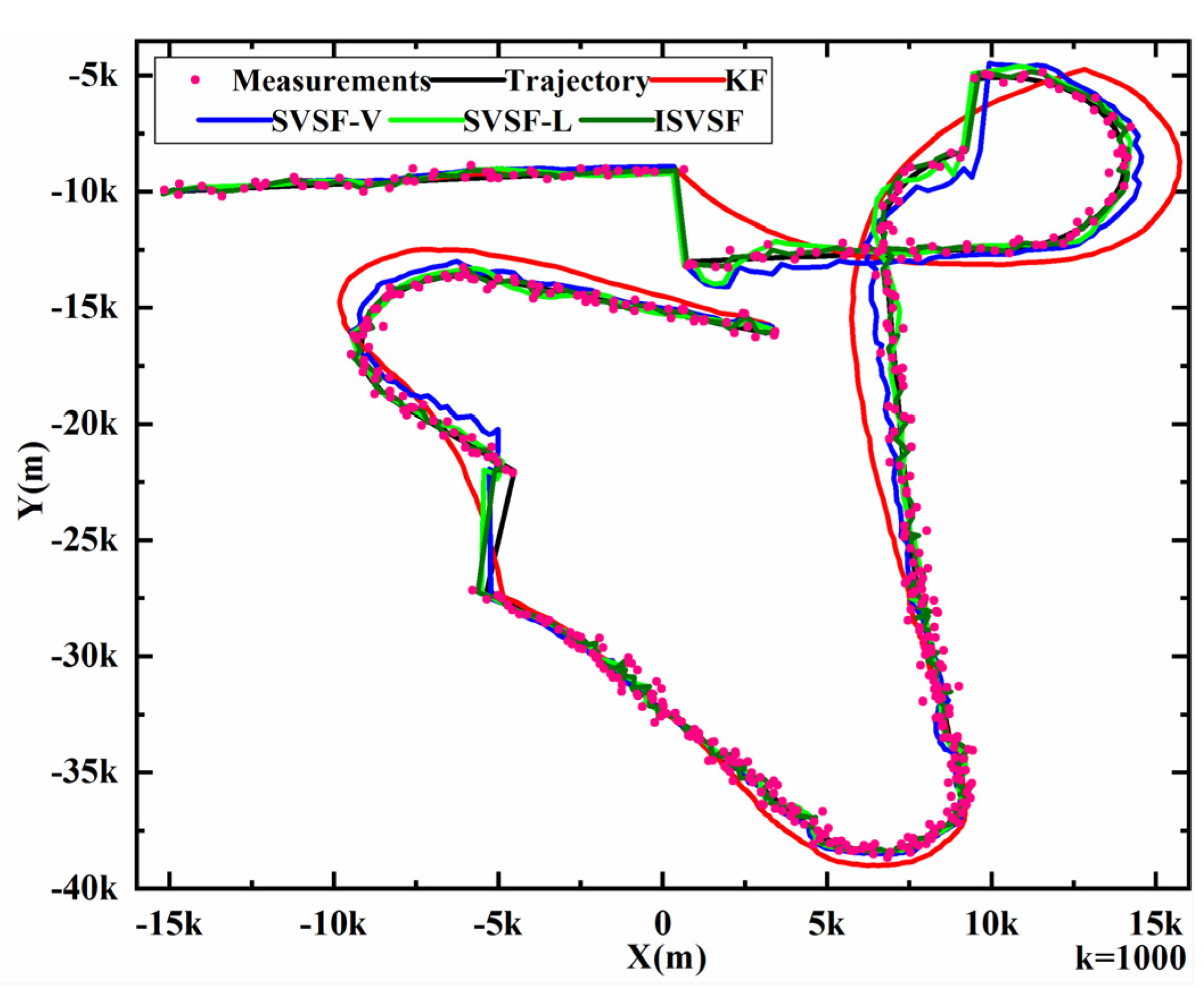
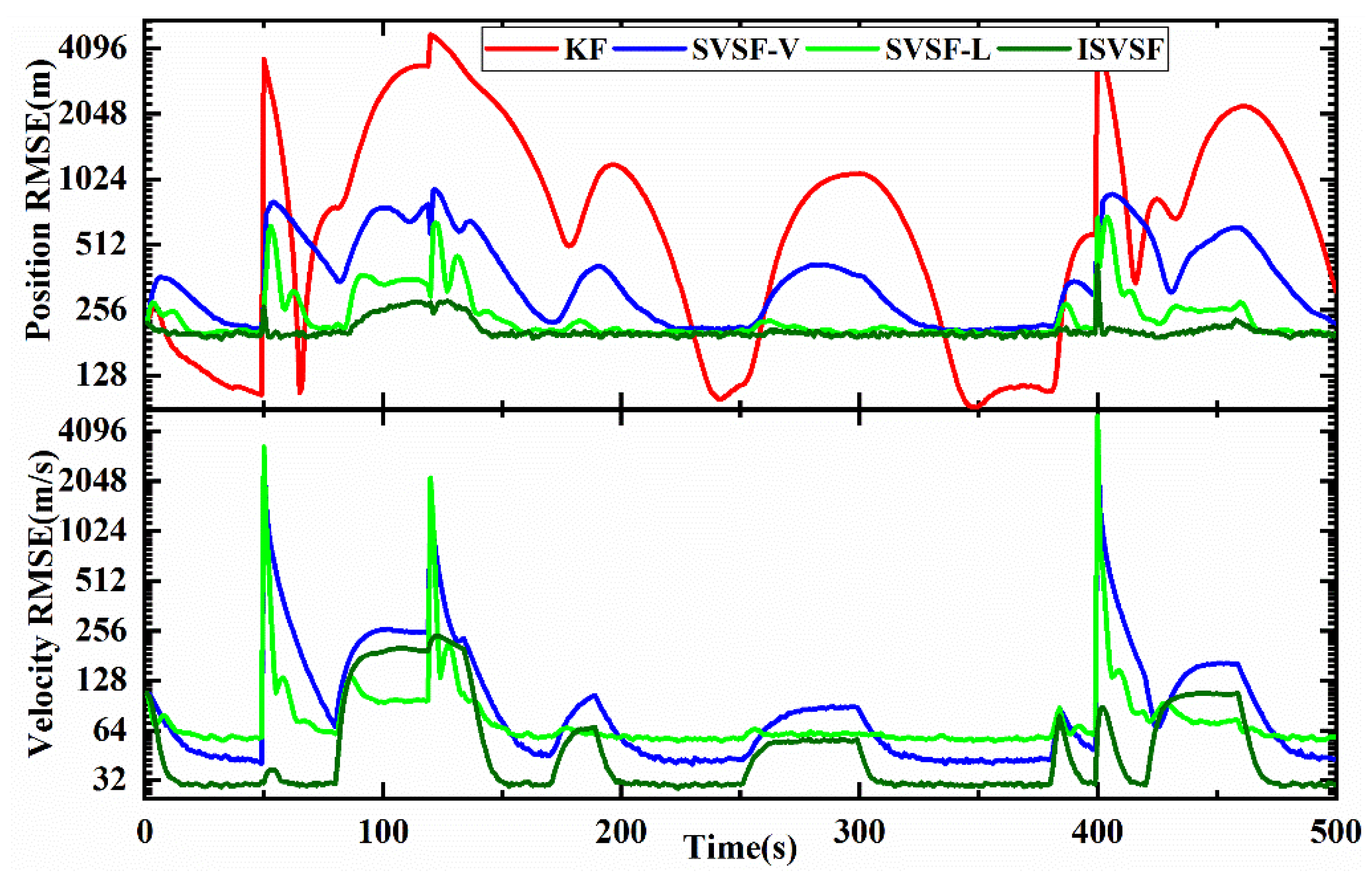
4.3. A Comprehensive Simulation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. The Application of ISVSF in a System with State Undergoing a Sudden Change
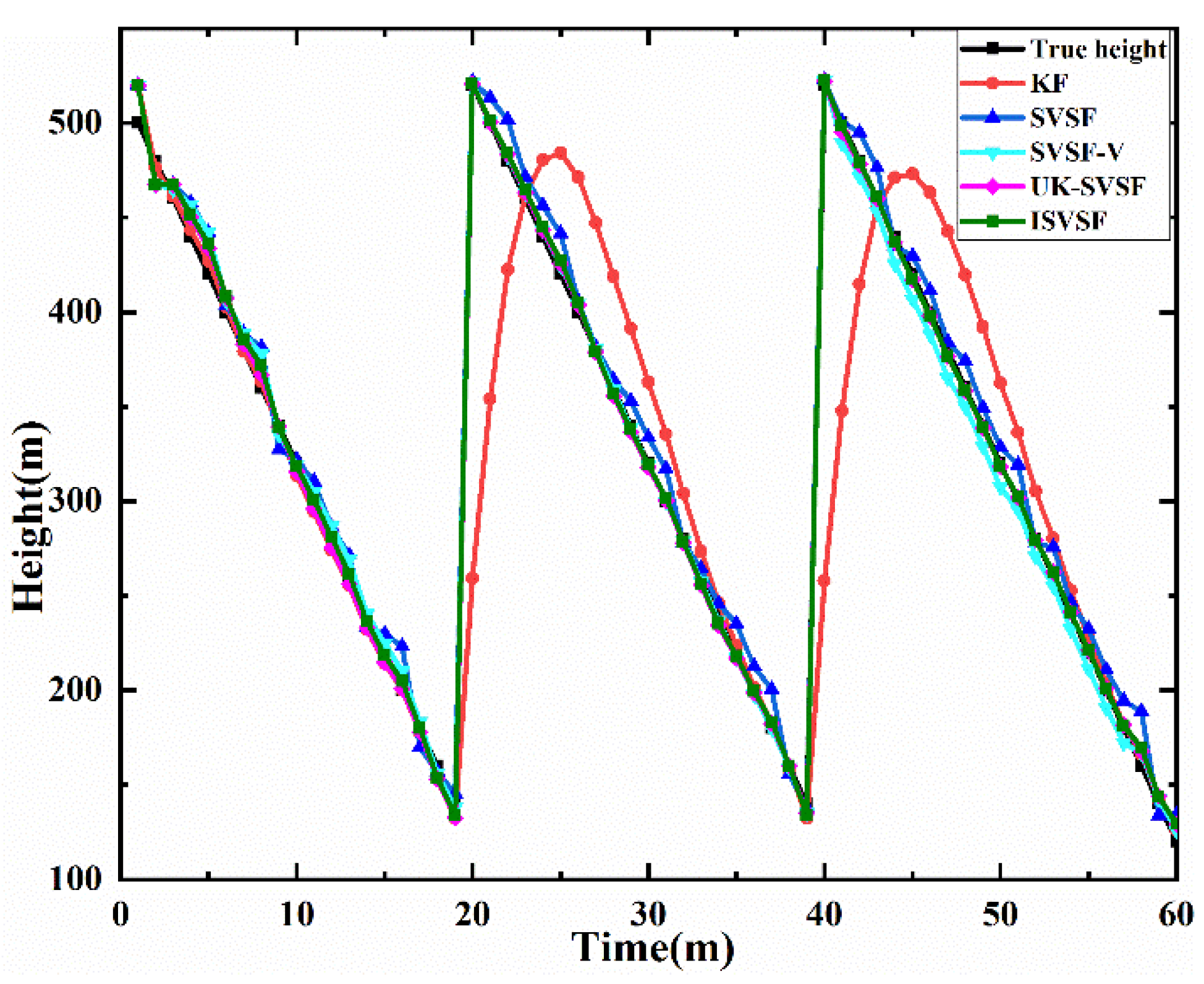
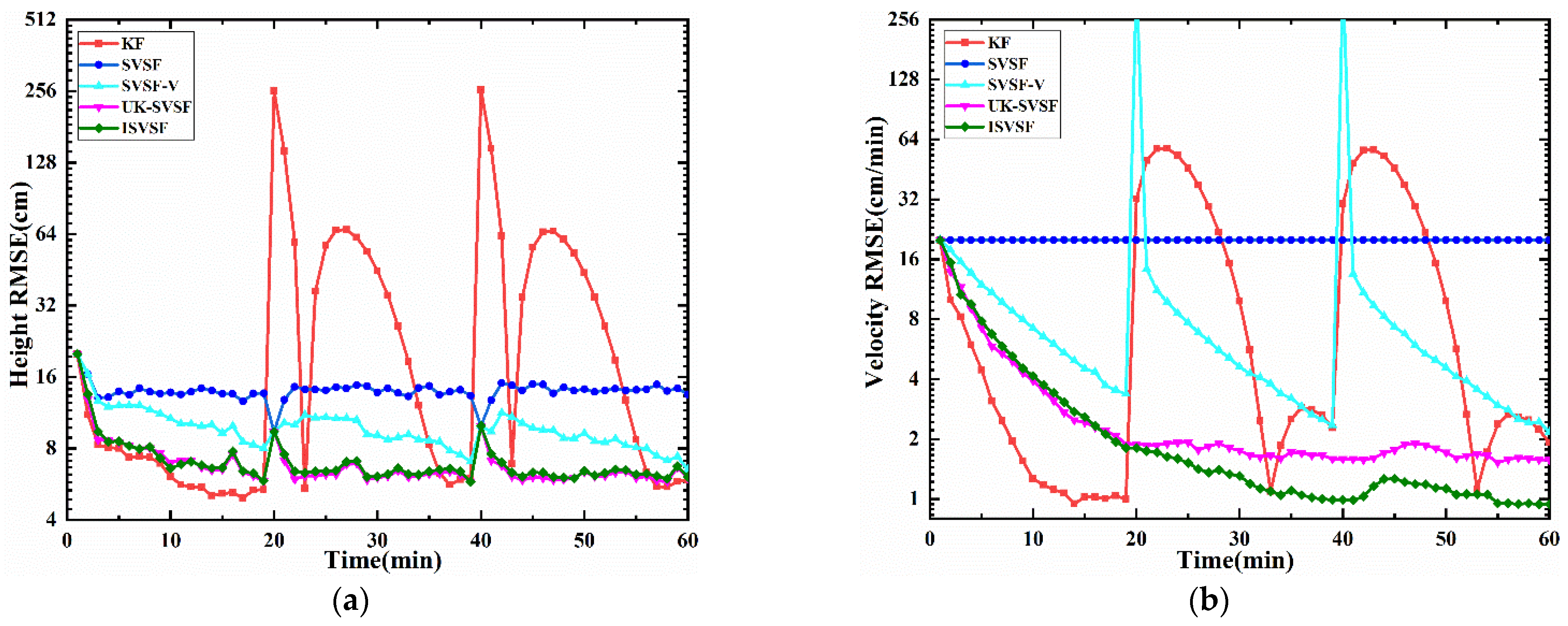
| Different Methods | KF | SVSF | SVSF-V | UK-SVSF | ISVSF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Height ARMSE (cm) | 35.0 | 14.0 | 9.8 | 6.9 | 7.1 |
| Velocity ARMSE (cm/min) | 15.5 | 20 | 19.7 | 2.5 | 2.2 |
References
- Li, X.R.; Jilkov, V.P. Survey of maneuvering target tracking. Part V. Multiple-model methods. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2005, 41, 1255–1321. [Google Scholar]
- Patwardhan, S.C.; Narasimhan, S.; Jagadeesan, P.; Gopaluni, B.; Shah, S.L. Nonlinear Bayesian state estimation: A review of recent developments. Control. Eng. Pr. 2012, 20, 933–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalman, R.E. A New Approach to Linear Filtering and Prediction Problems. J. Basic Eng. 1960, 82, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Tronarp, F.; Sarkka, S. Iterated Extended Kalman Smoother-Based Variable Splitting for L1-Regularized State Estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2019, 67, 5078–5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari, M.; Khaloozadeh, H. Robust extended Kalman filtering for non-linear systems with unknown input: A UBB model approach. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2020, 14, 1837–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Hu, B.; Li, A.; Qin, F. Transformed Unscented Kalman Filter. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 2013, 58, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadsden, S.; AlShabi, M.; Arasaratnam, I.; Habibi, S. Combined cubature Kalman and smooth variable structure filtering: A robust nonlinear estimation strategy. Signal Process. 2014, 96, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, J. Fault detection and diagnosis based on particle filters combined with interactive multiple-model estimation in dynamic process systems. ISA Trans. 2019, 85, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, H.; Xue, X.; Yang, Q. GNSS multipath estimation and mitigation based on particle filter. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2019, 13, 1588–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jondhale, S.R.; Deshpande, R.S. GRNN and KF framework based real time target tracking using PSOC BLE and smartphone. Ad Hoc Netw. 2019, 84, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jondhale, S.R.; Deshpande, R.S. Kalman Filtering Framework-Based Real Time Target Tracking in Wireless Sensor Networks Using Generalized Regression Neural Networks. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-R.; Bar-Shalom, Y. Multiple-model estimation with variable structure. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 1996, 41, 478–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Tang, J.; Zhang, B.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Song, X. A Novel Nonlinear Algorithm for Non-Gaussian Noises and Measurement Information Loss in Underwater Navigation. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 118472–118484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Sun, C.; Zhang, B.; Wang, P. Maximum Correntropy Square-Root Cubature Kalman Filter for Non-Gaussian Measurement Noise. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 70162–70170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chambers, J.A. A Novel Robust Gaussian–Student’s t Mixture Distribution Based Kalman Filter. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2019, 67, 3606–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, S. The Smooth Variable Structure Filter. Proc. IEEE 2007, 95, 1026–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadsden, S.A.; Habibi, S.; Kirubarajan, T. Kalman and smooth variable structure filters for robust estimation. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2014, 50, 1038–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadsden, S.A.; Habibi, S.R. A new form of the smooth variable structure filter with a covariance derivation. In Proceedings of the 49th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), Atlanta, GA, USA, 15–17 December 2010; pp. 7389–7394. [Google Scholar]
- Gadsden, S.A.; Habibi, S.R. A New Robust Filtering Strategy for Linear Systems. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control. 2013, 135, 014503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, A.; Ah, A.; Asb, C.; Sag, C. The smooth variable structure filter: A comprehensive review. Digit. Signal Process. 2020, 110, 102912. [Google Scholar]
- AlShabi, M.; Gadsden, S.; Habibi, S. Kalman filtering strategies utilizing the chattering effects of the smooth variable structure filter. Signal Process. 2013, 93, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiller, M.; Bakhshande, F.; Soeffker, D. The uncertainty learning filter: A revised smooth variable structure filter. Signal Process. 2018, 152, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshari, H.H.; Gadsden, S.A.; Habibi, S. A nonlinear second-order filtering strategy for state estimation of uncertain systems. Signal Process. 2019, 155, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Attari, M.; Habibi, S.; Von Mohrenschildt, M. Online Multiple Maneuvering Vehicle Tracking System Based on Multi-Model Smooth Variable Structure Filter. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 21, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, W.; Gadsden, S.A. Combined Quaternion-Based Error State Kalman Filtering and Smooth Variable Structure Filtering for Robust Attitude Estimation. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 148989–149004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attari, M.; Habibi, S.; Gadsden, S.A. Target Tracking Formulation of the SVSF With Data Association Techniques. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2017, 53, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attari, M.; Luo, Z.; Habibi, S. An SVSF-Based Generalized Robust Strategy for Target Tracking in Clutter. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2016, 17, 1381–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demim, F.; Nemra, A.; Boucheloukh, A.; Kobzili, E.; Hamerlain, M.; Bazoula, A. SLAM based on Adaptive SVSF for Cooperative Unmanned Vehicles in Dynamic environment. IFAC PapersOnLine 2019, 52, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, N.; Sadhu, S.; Ghoshal, T.K. Adaptive state estimation for tracking of civilian aircraft. IET Sci. Meas. Technol. 2018, 12, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demim, F.; Nemra, A.; Louadj, K.; Hamerlain, M.; Bazoula, A. Cooperative SLAM for multiple UGVs navigation using SVSF filter. Automatika 2017, 58, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H.-N.; Misra, A.K. Predictive Smooth Variable Structure Filter for Attitude Synchronization Estimation During Satellite Formation Flying. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2017, 53, 1375–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadsden, S.A.; Song, Y.; Habibi, S.R. Novel Model-Based Estimators for the Purposes of Fault Detection and Diagnosis. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2013, 18, 1237–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.; El Sayed, M.; Gadsden, S.A.; Tjong, J.; Habibi, S. Automotive Internal-Combustion-Engine Fault Detection and Classification Using Artificial Neural Network Techniques. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2015, 64, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.; El Sayed, M.; Arasaratnam, I.; Tjong, J.; Habibi, S. Reduced-Order Electrochemical Model Parameters Identification and State of Charge Estimation for Healthy and Aged Li-Ion Batteries—Part II: Aged Battery Model and State of Charge Estimation. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2014, 2, 678–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshabi, M.; Elnady, A. Recursive Smooth Variable Structure Filter for Estimation Processes in Direct Power Control Scheme Under Balanced and Unbalanced Power Grid. IEEE Syst. J. 2020, 14, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Lin, Y.; Wang, F.; Yang, S.; Zhou, Z. A hybrid observer for SOC estimation of lithium-ion battery based on a coupled electrochemical-thermal model. Int. J. Green Energy 2019, 16, 1527–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshari, H.H.; Attari, M.; Ahmed, R.; Delbari, A.; Habibi, S.; Shoa, T. Reliable state of charge and state of health estimation using the smooth variable structure filter. Control. Eng. Pr. 2018, 77, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Attari, M.; Habibi, S.; Ziada, S. Estimation theory and Neural Networks revisited: REKF and RSVSF as optimization techniques for Deep-Learning. Neural Netw. 2018, 108, 509–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.; El Sayed, M.; Gadsden, S.A.; Tjong, J.; Habibi, S. Artificial neural network training utilizing the smooth variable structure filter estimation strategy. Neural Comput. Appl. 2016, 27, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arasaratnam, I.; Haykin, S. Cubature kalman filters. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2009, 54, 1254–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, L.; Yan, B.; Li, C. A Novel Smooth Variable Structure Smoother for Robust Estimation. Sensors 2020, 20, 1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habibi, S.R.; Burton, R.M. The Variable Structure Filter. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control. 2003, 125, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shabi, M.; Hatamleh, K.S.; Gadsden, S.A.; Soudan, B.; El-Nady, A. Robust nonlinear control and estimation of a prrr robot system. Int. J. Robot. Autom. 2019, 34, 632–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avzayesh, M.; Abdel-Hafez, M.F.; Al-Masri, W.M.F.; Alshabi, M.; El-Hag, A.H. A Hybrid Estimation-Based Technique for Partial Discharge Localization. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 8744–8753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewal, M.; Andrews, A. Kalman Filtering: Theory and Practice with MATLAB, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]


| Symbol | Definition |
|---|---|
| ^ | Notation denoting an estimated variable, function, or model parameter |
| ~ | Notation denoting the error in an estimated variable, function, or model parameter |
| System model, mathematical modeling, and modeling error | |
| measurement (out) matrix | |
| System state, prior estimate state, state error | |
| The priori and posterior measurement innovation of SVSF | |
| A posterior error | |
| Diagonal of vector or matrix | |
| Saturation function | |
| System and measurement covariance matrix | |
| Absolute value of | |
| + | Pseudoinverse of some non-square matrix |
| Indication or Hadamard product | |
| Transpose of a vector or sample rate | |
| SVSF smoothing boundary layer | |
| Matrix dimension | |
| SVSF gain matrix | |
| Bayes’ rule gain | |
| Expectation | |
| Nonlinear function | |
| SVSF “memory” or convergence | |
| Probability density function | |
| Existence subspace layer | |
| State error covariance matrix | |
| Measurement (system output) matrix | |
| System noise and measurement noise vector |
| Different Methods | KF | SVSF | UK-SVSF | ISVSF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position ARMSE on x-axis (m) | 200 | 298 | 145 | 133 |
| Position ARMSE on y-axis (m) | 256 | 225 | 232 | 172 |
| Velocity ARMSE on x-axis (m) | 26 | 133 | 36 | 31 |
| Velocity ARMSE on y-axis (m) | 31 | 63 | 69 | 42 |
| Different Methods | KF | SVSF | UK-SVSF | ISVSF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position ARMSE (m) | 769 | 296 | 269 | 176 |
| Velocity ARMSE (m/s) | 86 | 253 | 245 | 55 |
| Maneuver | Duration | Maneuver | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| initial state [−15,000 m,320 m/s,−10,000 m,20 m/s] | 0 s | constant velocity | 190–250 s |
| constant velocity | 1–49 s | coordinated turn motion with | 251–299 s |
| a sudden change on the y-axis z = z-4000 m | 50 s | constant velocity | 300–380 s |
| constant velocity | 50–80 s | acceleration with x-axis a = −20 m/s2, y-axis a = 10 m/s2 | 381–384 s |
| coordinated turn motion with | 81–119 s | constant velocity | 385–399 s |
| a sudden change on the y-axis z = z-3000 m | 120 s | a sudden change, x-axis z = z-1000 m, y-axis z = z-5000 m, | 400 s |
| coordinated turn motion with | 121–134 s | constant velocity | 401–420 s |
| constant velocity | 135–170 s | coordinated turn motion with | 421–460 s |
| acceleration with x-axis a = −10 m/s2 | 171–189 | constant velocity | 461–500 s |
| Different Methods | KF | SVSF-V | SVSF-L | ISVSF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position ARMSE (m) | 1041 | 389 | 245 | 206 |
| Velocity ARMSE (m/s) | 113 | 135 | 102 | 59 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, G.; Yan, B.; Sun, J. An Improved Smooth Variable Structure Filter for Robust Target Tracking. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4612. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13224612
Chen Y, Xu L, Wang G, Yan B, Sun J. An Improved Smooth Variable Structure Filter for Robust Target Tracking. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(22):4612. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13224612
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yu, Luping Xu, Guangmin Wang, Bo Yan, and Jingrong Sun. 2021. "An Improved Smooth Variable Structure Filter for Robust Target Tracking" Remote Sensing 13, no. 22: 4612. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13224612
APA StyleChen, Y., Xu, L., Wang, G., Yan, B., & Sun, J. (2021). An Improved Smooth Variable Structure Filter for Robust Target Tracking. Remote Sensing, 13(22), 4612. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13224612






