Evaluation of Satellite-Derived Products for the Daily Average and Extreme Rainfall in the Mearim River Drainage Basin (Maranhão, Brazil)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Databases
2.2.1. Reference Data
2.2.2. Precipitation Data from Remote Sensing
Climate Hazards Group Infrared Precipitation with Station Data
Multi-Source Weighted-Ensemble Precipitation Version 2
| Name | Source | Spatial Res. | Temporal Res. | Temporal Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMORPH [47,50] | Satellite | 0.07 degrees | 30 min | 1998–present |
| Station daily data [47,51] | Station (GHCN-D and GSOD, other sources) | – – | Daily | 1979–2017 |
| ERA-Iterim [52] | Reanalysis | ~80 km | 3 h | 1979–present |
| GPCC FDR [49,53,54] | Station | 0.5/1 degrees | Monthly | 1951–present |
| GridSat [55] | Satellite | 0.1 degrees | 3 h | 1980–2016 |
| GPSMAP [56] | Satellite | 0.1 degrees | 1 h | 2000–present |
| JRA-55 [57] | Reanalysis | ~60 km | 3 h | 1959–present |
| TMPA 3B42RT [58] | Satellite | 0.25 degrees | 3 h | 2000–present |
| WorldClim [59] | Stations | ~1 km | Monthly | Climate |
Precipitation Estimation from Remotely Sensed Information Using Artificial Neural Networks Climate Data Records
2.3. Analysis
2.3.1. Mean and Extreme Indices
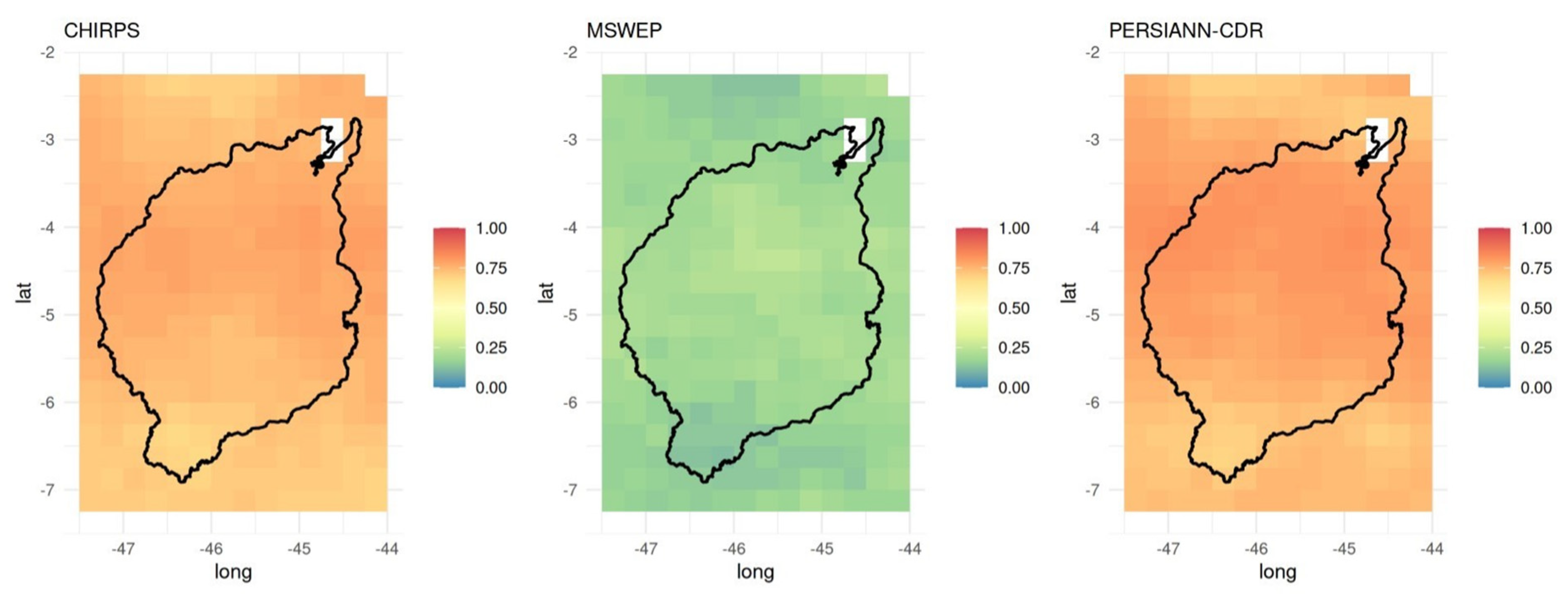
2.3.2. Evaluation of RES Products Versus gridBR
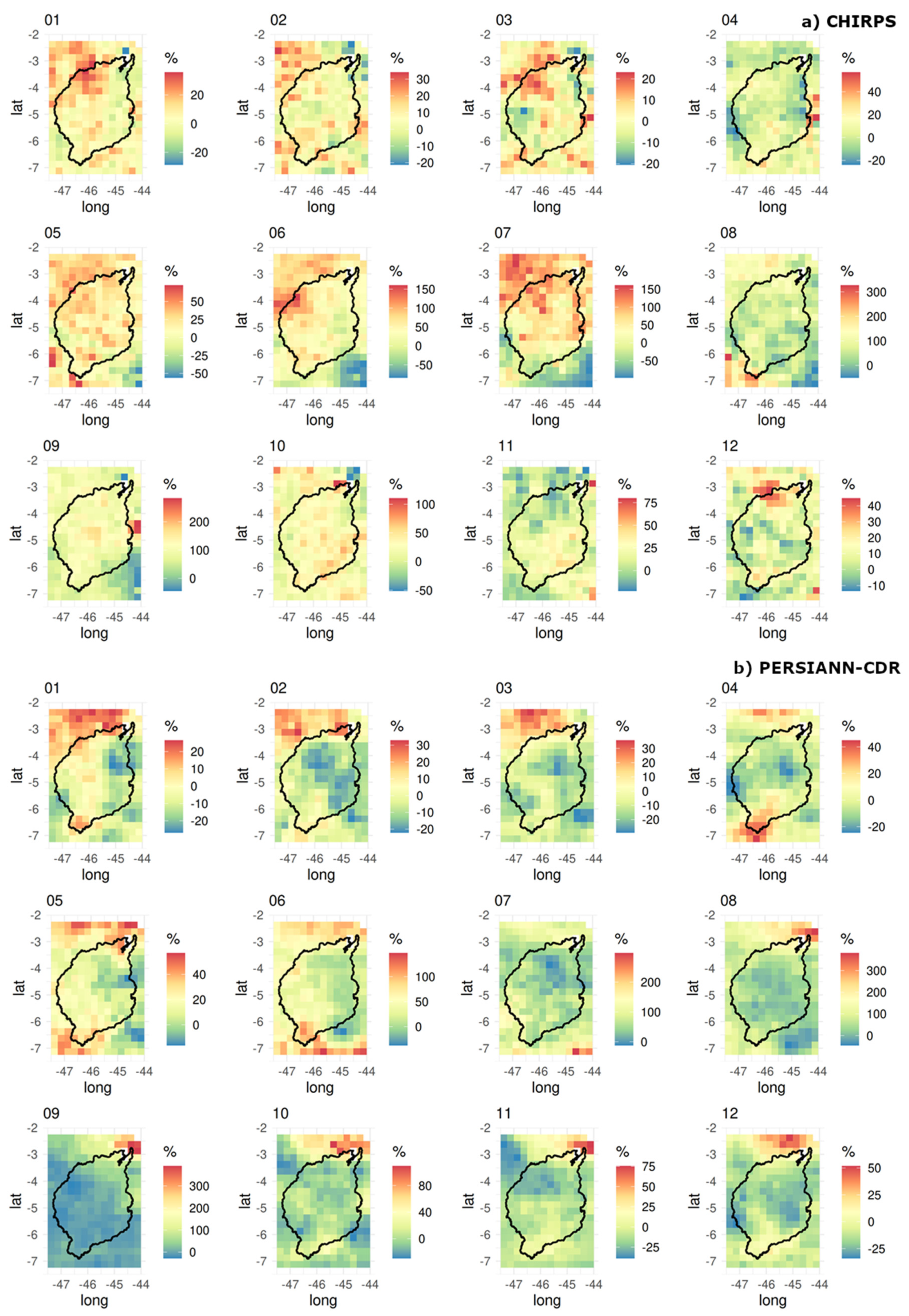
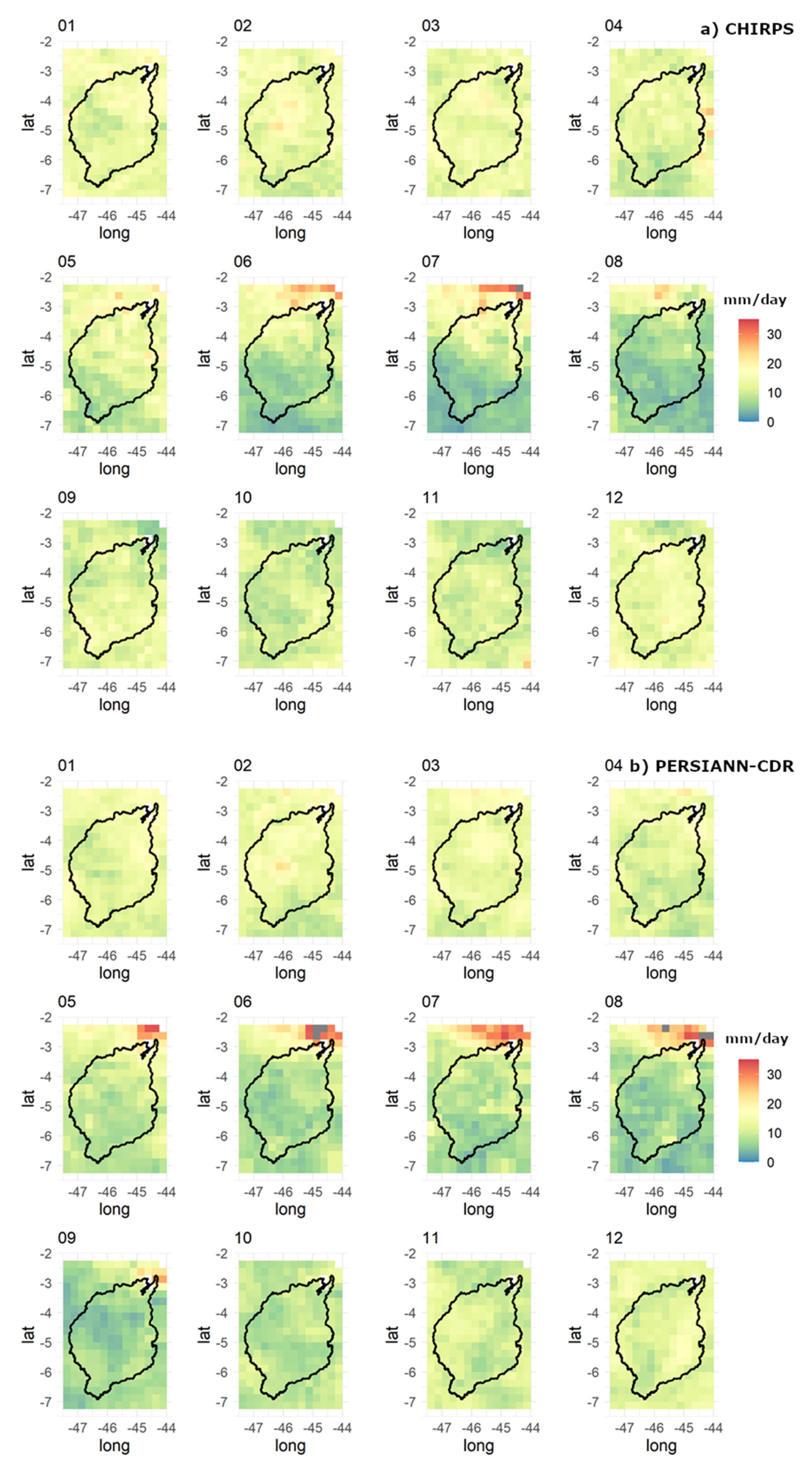
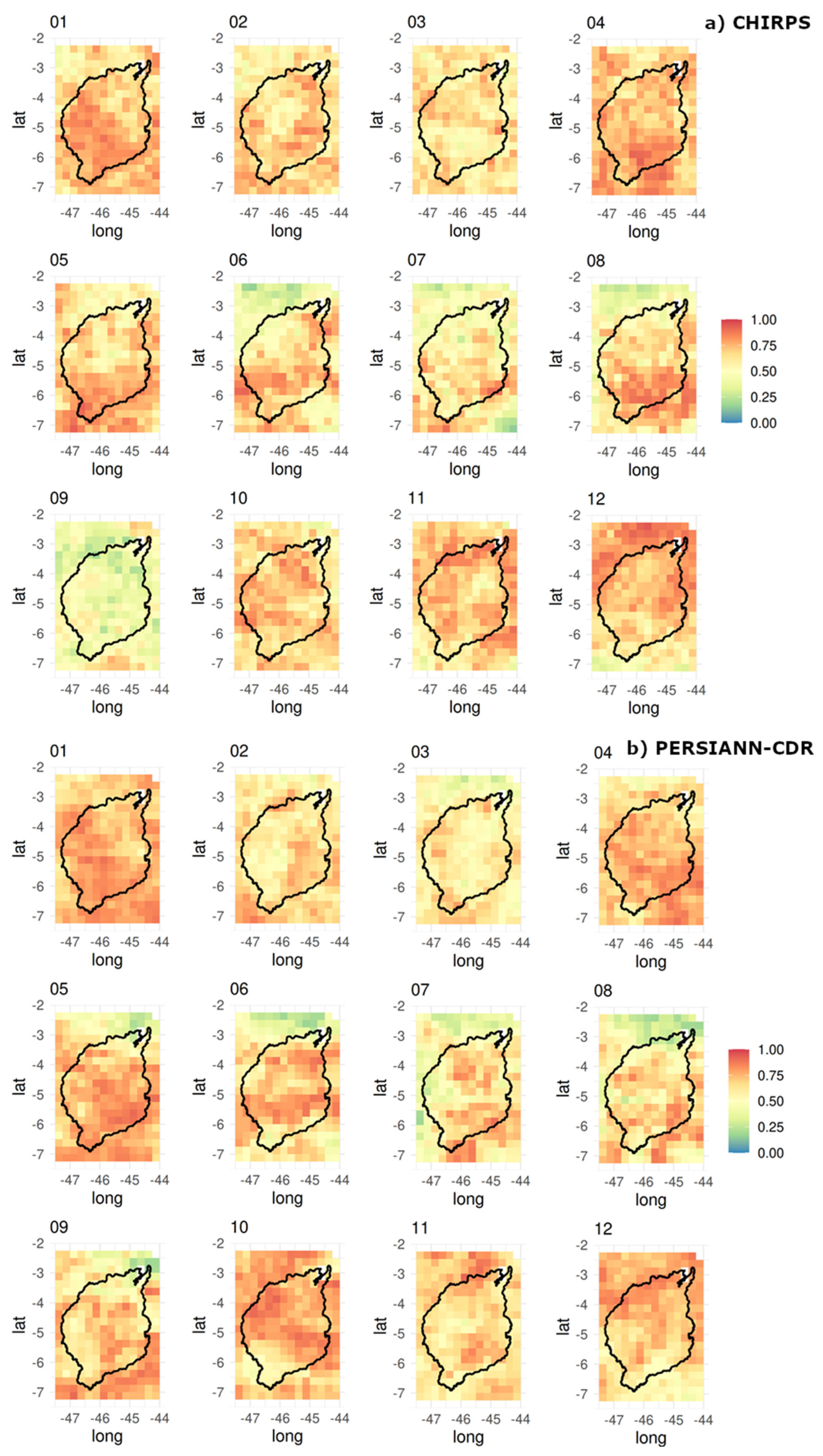
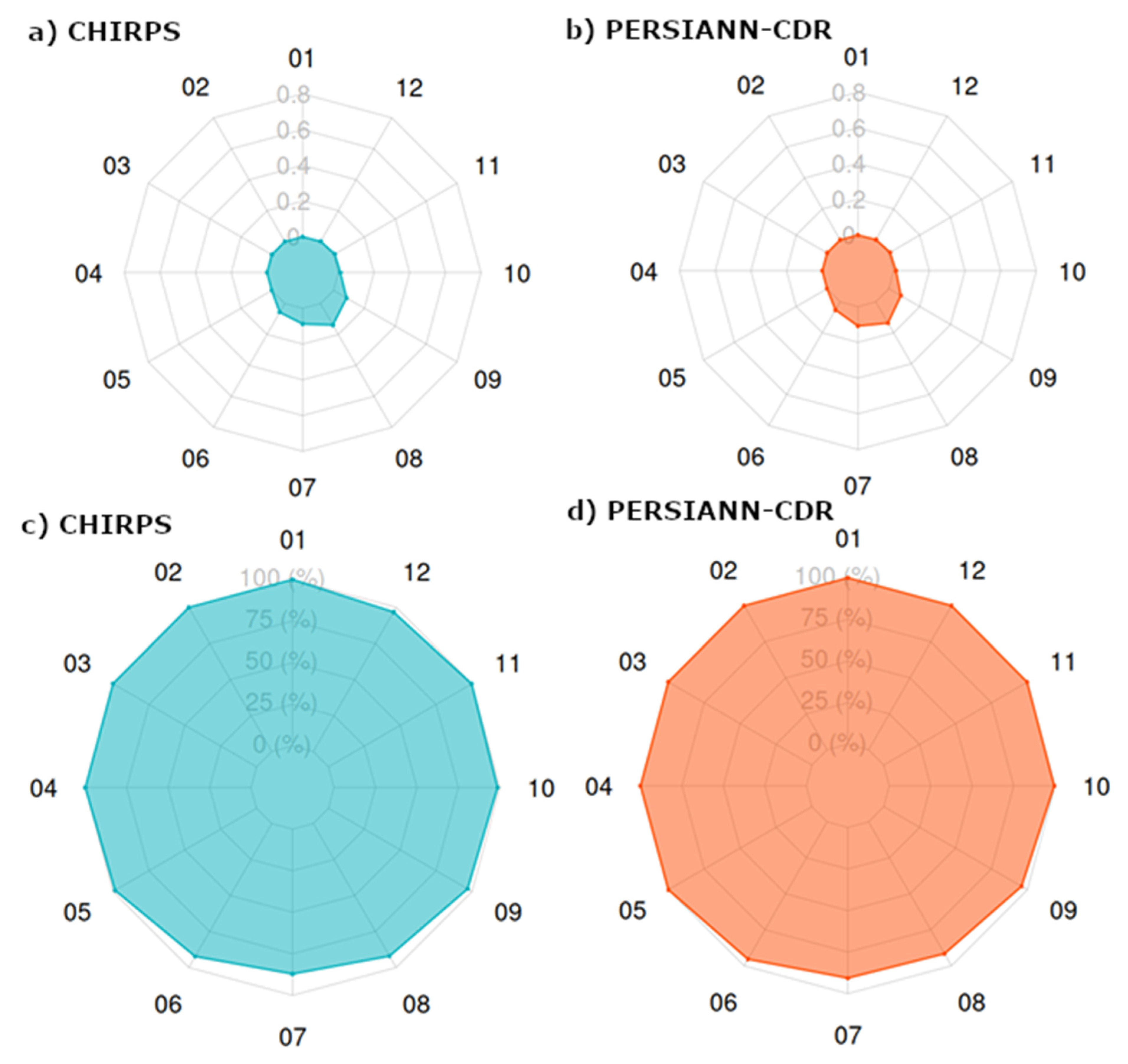
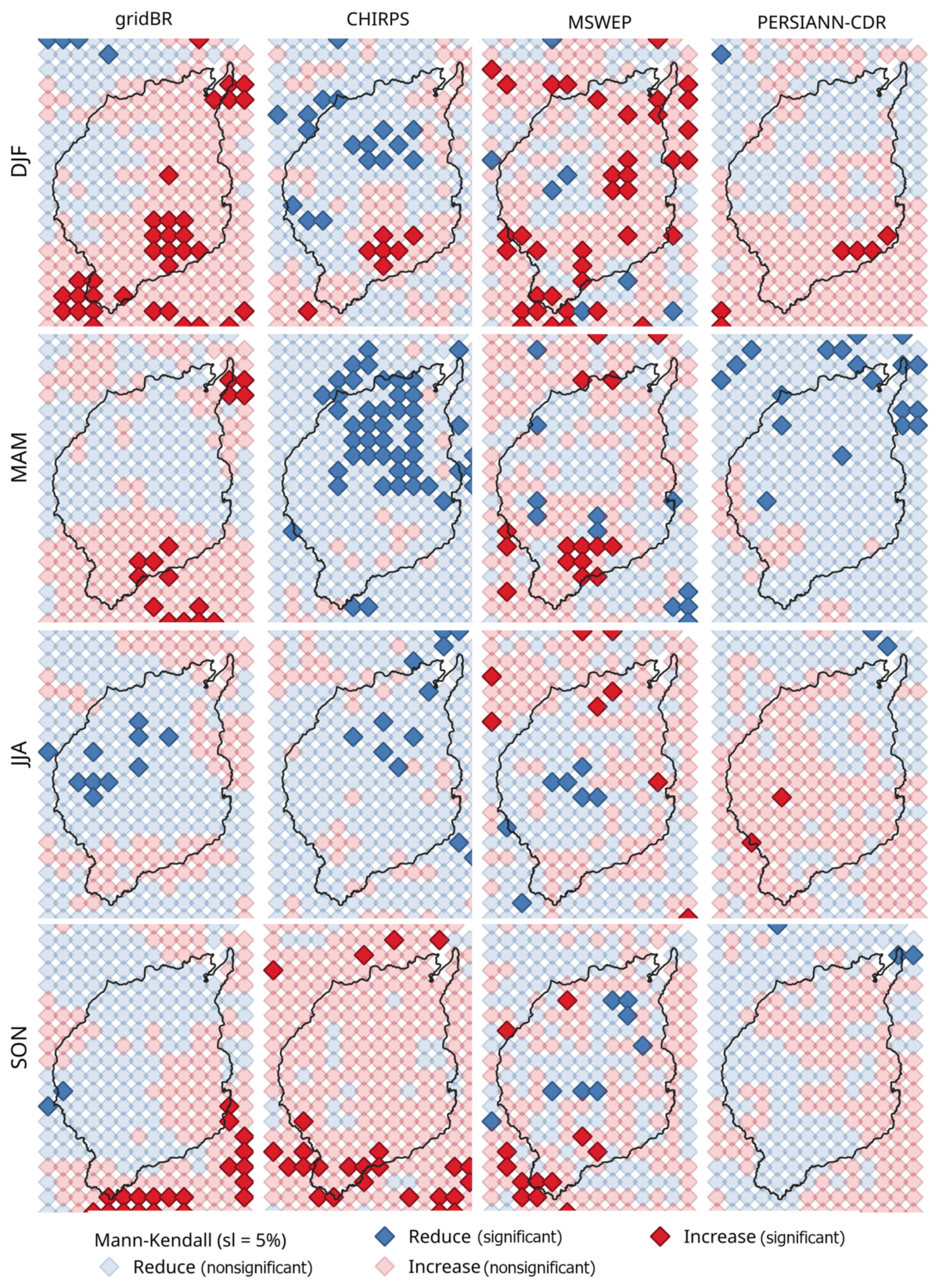
3. Results
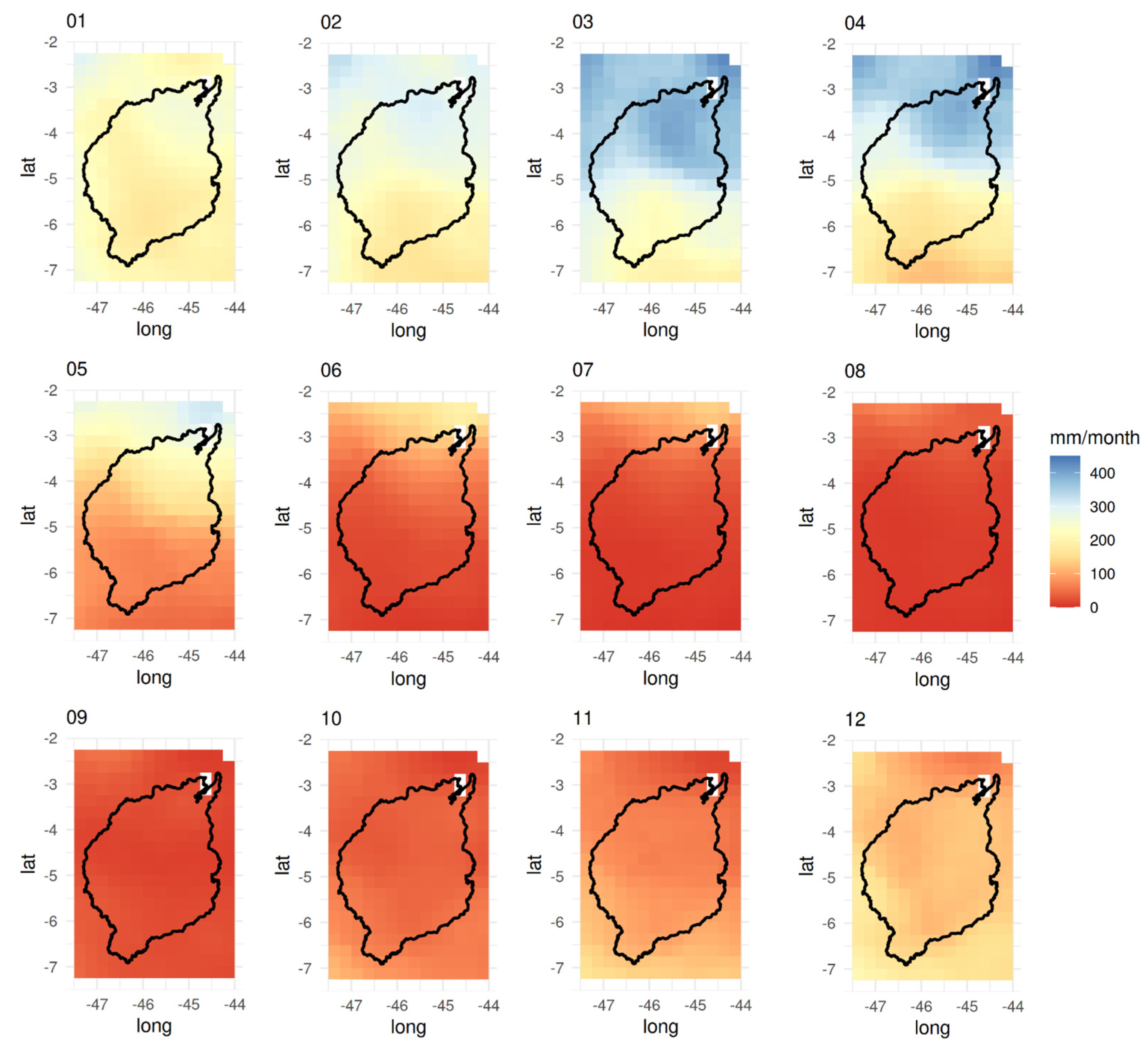
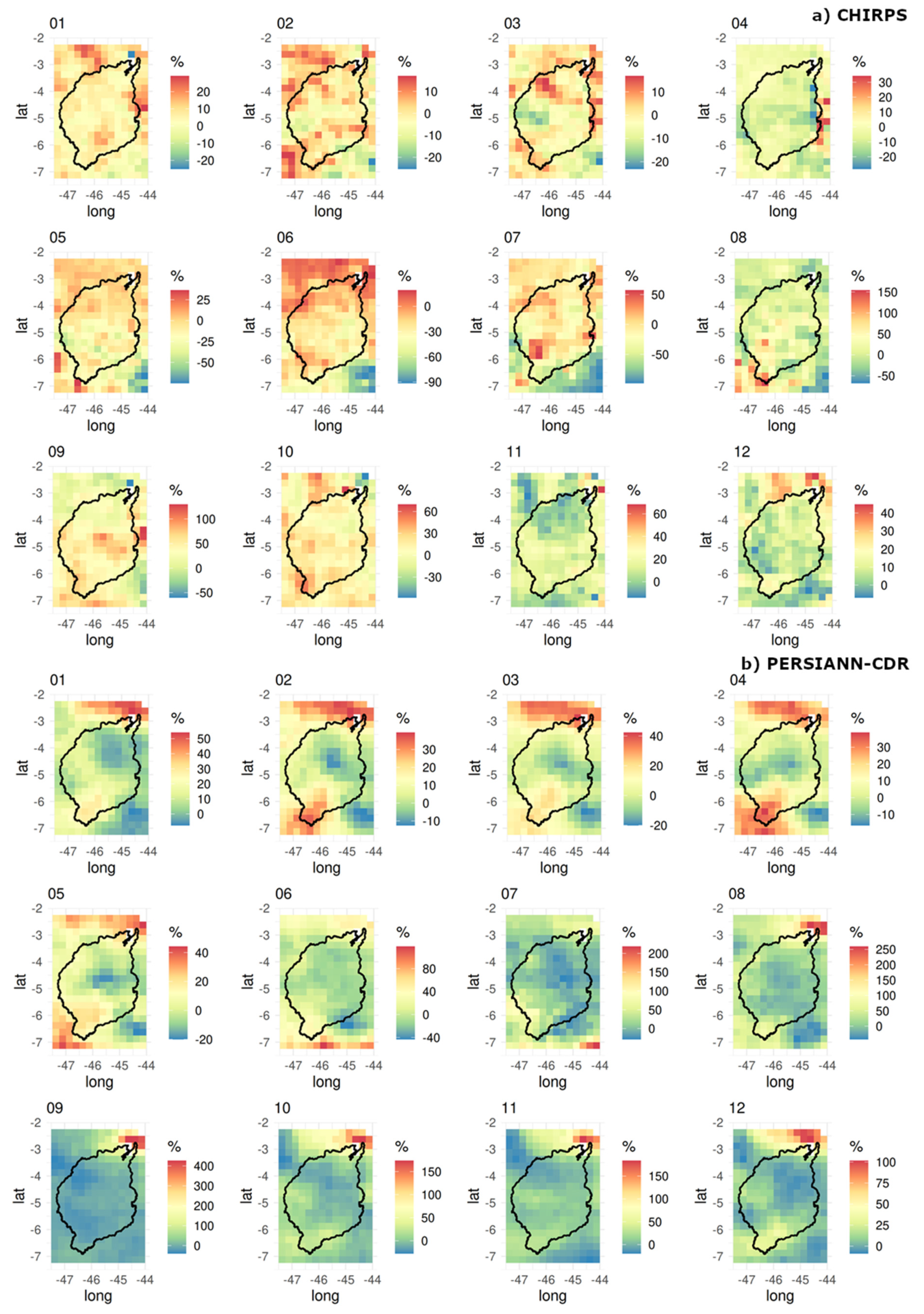
3.1. Climatological Mean
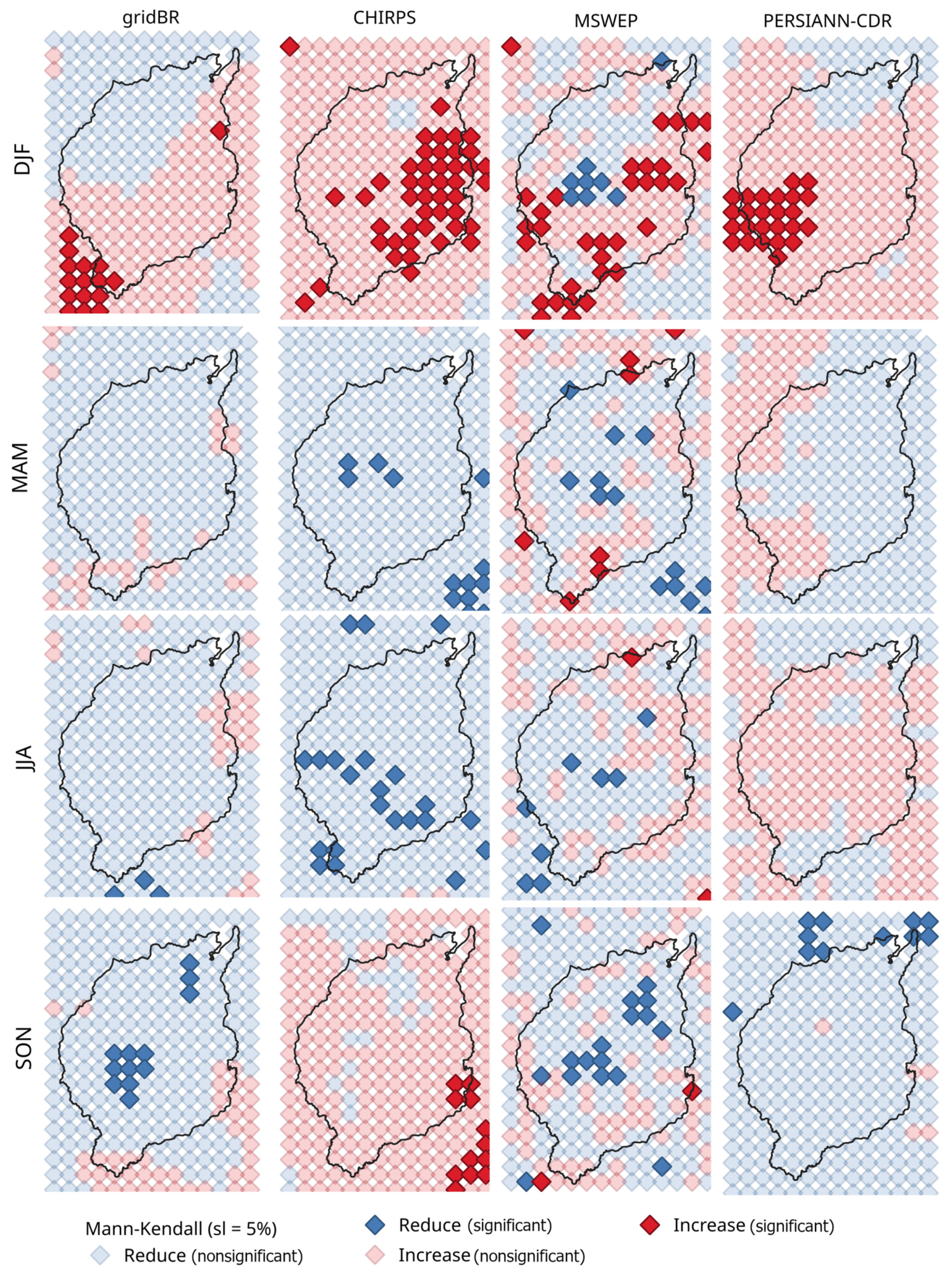
3.2. Extremes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Filho, W.L.F.C.; De Oliveira-Júnior, J.F.; Santiago, D.D.B.; Terassi, P.M.D.B.; Teodoro, P.E.; De Gois, G.; Blanco, C.J.C.; Souza, P.H.D.A.; da Silva Costa, M.; Gomes, H.B.; et al. Rainfall Variability in the Brazilian Northeast Biomes and Their Interactions with Meteorological Systems and ENSO via CHELSA Product. Big Earth Data 2019, 3, 315–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.E.; Vergopolan, N.; Pan, M.; Levizzani, V.; van Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Weedon, G.P.; Brocca, L.; Pappenberger, F.; Huffman, G.J.; Wood, E.F. Global-Scale Evaluation of 22 Precipitation Datasets Using Gauge Observations and Hydrological Modeling. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 6201–6217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontes, P.R.M.; Cavalcante, R.; Sahoo, P.; da Silva Júnior, R.O.; da Silva, M.S.; Dall’Agnol, R.; Siqueira, J.O. The Role of Protected and Deforested Areas in the Hydrological Processes of Itacaiúnas River Basin, Eastern Amazonia. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 235, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira Serrão, E.A.; Silva, M.T.; Ferreira, T.R.; de Paulo Rodrigues da Silva, V.; de Salviano de Sousa, F.; de Lima, A.M.M.; de Ataide, L.C.P.; Wanzeler, R.T.S. Land Use Change Scenarios and Their Effects on Hydropower Energy in the Amazon. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De BodasTerassi, P.M.; de Oliveira-Júnior, J.F.; de Gois, G.; Júnior, A.C.O.; Sobral, B.; Biffi, V.H.R.; Blanco, C.J.C.; Filho, W.L.F.C.; Vijith, H. Rainfall and Erosivity in the Municipality of Rio de Janeiro—Brazil. Urban Clim. 2020, 33, 100637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante, R.B.L.; da SilvaFerreira, D.B.; Pontes, P.R.; Tedeschi, R.G.; da Costa, C.P.W.; de Souza, E. Evaluation of Extreme Rainfall Indices from CHIRPS Precipitation Estimates over the Brazilian Amazonia. Atmos. Res. 2020, 238, 104879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, C.; Becker, A.; Huffman, G.J.; Muller, C.L.; Joe, P.; Skofronick-Jackson, G.; Kirschbaum, D.B. So, How Much of the Earth’s Surface Is Covered by Rain Gauges? Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 98, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, A.C.; King, C.W.; Scanlon, B.R. Daily Gridded Meteorological Variables in Brazil (1980–2013). Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 2644–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, A.C.F.; Rudke, A.P.; Fujita, T.; Blain, G.C.; De Morais, M.V.B.; De Almeida, D.S.; Rafee, S.A.A.; Martins, L.D.; De Souza, R.A.F.; De Freitas, E.D.; et al. Stationary and Non-Stationary Detection of Extreme Precipitation Events and Trends of Average Precipitation from 1980 to 2010 in the Paraná River Basin, Brazil. Int. J. Climatol. 2020, 40, 1197–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, A.C.F.; Martins, L.L.; Rudke, A.P.; de Morais, M.V.B.; Martins, J.A.; Blain, G.C. Evaluation of Quantile Delta Mapping as a Bias-Correction Method in Maximum Rainfall Dataset from Downscaled Models in São Paulo State (Brazil). Int. J. Climatol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Miao, C.; Duan, Q.; Ashouri, H.; Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K.L. A Review of Global Precipitation Data Sets: Data Sources, Estimation, and Intercomparisons. Rev. Geophys. 2018, 56, 79–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salio, P.; Hobouchian, M.P.; Skabar, Y.G.; Vila, D. Evaluation of High-Resolution Satellite Precipitation Estimates over Southern South America Using a Dense Rain Gauge Network. Atmos. Res. 2015, 163, 146–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobouchian, M.P.; Salio, P.; Skabar, Y.G.; Vila, D.; Garreaud, R. Assessment of Satellite Precipitation Estimates over the Slopes of the Subtropical Andes. Atmos. Res. 2017, 190, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANA Agência Nacional de Águas e Saneamento Básico: Rede Hidrometeorológica Nacional. Available online: https://dadosabertos.ana.gov.br/datasets/8014bf6e92144a9b871bb4136390f732_0/explore?filters=eyJFc3RhZG8iOlsiTUEiXSwiVGlwbyI6WyJQbHV2aW9t6XRyaWNhIl19&location=2.373885%2C-31.799803%2C4.94 (accessed on 10 July 2021).
- World Meteorological Organization. Guide to Hydrological Practices, Data Acquisition and Processing, Analysis, Forecasting and Other Applications; WMO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1994; p. 770. [Google Scholar]
- Gadelha, A.N.; Coelho, V.H.R.; Xavier, A.C.; Barbosa, L.R.; Melo, D.C.; Xuan, Y.; Huffman, G.J.; Petersen, W.A.; Almeida, d.N. Grid Box-Level Evaluation of IMERG over Brazil at Various Space and Time Scales. Atmos. Res. 2019, 218, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolfe, É.L.; Victória, D.C.; Contini, E.; Bayma-Silva, G.; Spinelli-Araujo, L.; Gomes, D. Matopiba Em Crescimento Agrícola Aspectos Territoriais e Socioeconômicos. Rev. Política Agrícola 2017, 25, 38–62. [Google Scholar]
- Maranhão, G. do Estado do Lei Ordinária no 9.957, de 21 de Novembro de 2013; Palácio do Governo do Estado do Maranhão: São Luís, Brazil, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Vale, S.A. Relato Int.egrado, Vale, Brazil. 2020. Available online: http://www.vale.com/brasil/pt/business/reports/siteassets/relato-integrado-2020/assets/docs/vale_relato_integrado_2020.pdf (accessed on 12 July 2021).
- IBGE Censo Demográfico. 2017. Available online: https://cidades.ibge.gov.br/brasil/ma/panorama (accessed on 31 May 2021).
- CODEVASF. Plano Nascente Mearim: Plano de Preservação e Recuperação de Nascentes da Bacia do rio Mearim; Evolução do Conhecimento Científico na Engenharia Ambiental e Sanitária: Brasília, Brazil, 2019; p. 190. [Google Scholar]
- IBGE Censo. 2010. Available online: https://cidades.ibge.gov.br/brasil/ma/pesquisa/48/48986?tipo=ranking&indicador=48986 (accessed on 12 July 2021).
- Mearim, P.N. Plano de Recuperação de Nascentes Do Rio Mearim; Codevasf Sede: Brasília, Brazil, 2019; p. 190. [Google Scholar]
- Castells-Quintana, D.; del PilarLopez-Uribe, M.; McDermott, T.K. Adaptation to Climate Change: A Review through a Development Economics Lens. World Dev. 2018, 104, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.-C.; Wei, Y.-M.; Wang, B.; Mi, Z. Risk Management of Extreme Events under Climate Change. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 166, 1169–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, M.O.; Campos, C.C.; Carneiro, P.B.M.; Barroso, H.S.; Marins, R.V.; Teixeira, C.E.P.; Menezes, M.O.B.; Pinheiro, L.S.; Viana, M.B.; Feitosa, C.V.; et al. Challenges and Perspectives for the Brazilian Semi-Arid Coast under Global Environmental Changes. Perspect. Ecol. Conserv. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBGE Downloads: Geociências, Organização Territorial. Available online: https://www.ibge.gov.br/geociencias/downloads-geociencias.html (accessed on 9 June 2021).
- Alvares, C.A.; Stape, J.L.; Sentelhas, P.C.; Gonçalves, J.L.D.M.; Sparovek, G. Köppen’s Climate Classification Map for Brazil. Meteorol. Z. 2013, 22, 711–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, D.T.; Gonçalves, W.A.; Spyrides, M.H.C.; Silva, C.M.S. e Spatial and Temporal Assessment of the Extreme and Daily Precipitation of the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission Satellite in Northeast Brazil. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 549–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante, R.B.L.; Pontes, P.R.M.; Souza-Filho, P.W.M.; de Souza, E. Opposite Effects of Climate and Land Use Changes on the Annual Water Balance in the Amazon Arc of Deforestation. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 3092–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastenrath, S.; Heller, L. Dynamics of Climatic Hazards in Northeast Brazil. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1977, 103, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombardi, R.J.; Trenary, L.; Pegion, K.; Cash, B.; Delsole, T.; Kinter, J.L., III. Seasonal Predictability of Summer Rainfall over South America Seasonal Predictability of Summer Rainfall over South America. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 8181–8195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorova, N.; dos Santos, D.M.B.; Segundo, M.M.L.; Levit, V. Middle Tropospheric Cyclonic Vortex in Northeastern Brazil and the Tropical Atlantic. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2017, 174, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorova, N.; Levit, V.; Campos, A.M.V. Brazilian Northeast Jet Stream: Association with Synoptic-scale Systems. Meteorol. Appl. 2018, 25, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kousky, V.E.; Kagano, M.T.; Cavalcanti, I.F.A. A Review of the Southern Oscillation: Oceanic-atmospheric Circulation Changes and Related Rainfall Anomalies. Tellus 1984, 36A, 490–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.T.; Alcântara, C.R.; de Souza, E.P.; de Olinda, R.A.; Gonçalves, W.A. Influência Da Temperatura Da Superfície Do Mar Na Ocorrência de Linhas de Instabilidade Na Costa Norte e Nordeste Do Brasil. Rev. Bras. Meteorol. 2017, 32, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, N.S.-N. Spatial Interpolation Methods: A Review. Am. Cartogr. 1983, 10, 129–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grain, I.K. Computer Interpolation and Contouring of Two-Dimensional Data: A Review. Geoexploration 1970, 8, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes-Trejo, F.J.; Barbosa, H.A.; Kumar, T.V.L. Validating CHIRPS-Based Satellite Precipitation Estimates in Northeast Brazil. J. Arid. Environ. 2017, 139, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almagro, A.; Oliveira, P.T.S.; Nearing, M.A.; Hagemann, S. Projected Climate Change Impacts in Rainfall Erosivity over Brazil. Sci. Rep.-UK 2017, 7, 8130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pousa, R.; Costa, M.H.; Pimenta, F.; Fontes, V.C.; de Brito, V.F.A.; Castro, M. Climate Change and Intense Irrigation Growth in Western Bahia, Brazil: The Urgent Need for Hydroclimatic Monitoring. Water-Sui 2019, 11, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila-Diaz, A.; Abrahão, G.; Justino, F.; Torres, R.; Wilson, A. Extreme Climate Indices in Brazil: Evaluation of Downscaled Earth System Models at High Horizontal Resolution. Clim. Dynam. 2020, 54, 5065–5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila-Diaz, A.; Benezoli, V.; Justino, F.; Torres, R.; Wilson, A. Assessing Current and Future Trends of Climate Extremes across Brazil Based on Reanalyses and Earth System Model Projections. Clim. Dynam. 2020, 55, 1403–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, E.W.M.; de Assis Salviano de Souza, F.; Daneil, F.; Júnior, R.; Duarte, D.; de Paulo Rodrigues da Silva, V. Trends in Climate Extreme Indices Assessed in the Xingu River Basin—Brazilian Amazon. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2021, 31, 100306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijmans, R.J. Raster: Geographic Data Analysis and Modeling [R package raster version 3.4-10]. 2021. Available online: http://cran.stat.unipd.it/web/packages/raster/ (accessed on 9 June 2021).
- Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Landsfeld, M.; Pedreros, D.; Verdin, J.; Shukla, S.; Husak, G.; Rowland, J.; Harrison, L.; Hoell, A.; et al. The Climate Hazards Infrared Precipitation with Stations—a New Environmental Record for Monitoring Extremes. Sci. Data 2015, 2, 150066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.E.; Wood, E.F.; Pan, M.; Fisher, C.K.; Miralles, D.G.; Van Dijk, A.; McVicar, T.R.; Adler, R.F. MSWep v2 Global 3-Hourly 0.1° Precipitation: Methodology and Quantitative Assessment. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 100, 473–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Dirmeyer, P.A.; Tawfik, A.; Lawrence, D.M. Sensitivities of Land Cover–Precipitation Feedback to Convective Triggering. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 2265–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Dirmeyer, P.A. Impacts of Land-Use/Land-Cover Change on Afternoon Precipitation over North America. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 2121–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, R.J.; Janowiak, J.E.; Arkin, P.A.; Xie, P. CMORPH: A Method That Produces Global Precipitation Estimates from Passive Microwave and Infrared Data at High Spatial and Temporal Resolution. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.L.; de Mello Baptista, G.M.; Gomes, H.B.; dos Santos Silva, F.D.; da Rocha Júnior, R.L.; de Araújo Salvador, M.; Herdies, D.L. Analysis of Climate Extremes Indices over Northeast Brazil from 1961 to 2014. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2020, 28, 100254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P.; et al. The ERA-Interim Reanalysis: Configuration and Performance of the Data Assimilation System. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, U.; Finger, P.; Meyer-Christoffer, A.; Rustemeier, E.; Ziese, M.; Becker, A. Evaluating the Hydrological Cycle over Land Using the Newly-Corrected Precipitation Climatology from the Global Precipitation Climatology Centre (GPCC). Atmosphere 2017, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, U.; Becker, A.; Finger, P.; Meyer-Christoffer, A.; Ziese, M.; Rudolf, B. GPCC’s New Land Surface Precipitation Climatology Based on Quality-Controlled in Situ Data and Its Role in Quantifying the Global Water Cycle. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 115, 15–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, K.R.; Ansari, S.; Bain, C.L.; Bourassa, M.A.; Dickinson, M.J.; Funk, C.; Helms, C.N.; Hennon, C.C.; Holmes, C.D.; Huffman, G.J.; et al. Globally Gridded Satellite Observations for Climate Studies. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 92, 893–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushio, T.; Sasashige, K.; Kubota, T.; Shige, S.; Okamoto, K.; Aonashi, K.; Inoue, T.; Takahashi, N.; Iguchi, T.; Kachi, M.; et al. A Kalman Filter Approach to the Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation (GSMaP) from Combined Passive Microwave and Infrared Radiometric Data. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. Ser. II 2009, 87A, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Ota, Y.; Harada, Y.; Ebita, A.; Moriya, M.; Onoda, H.; Onogi, K.; Kamahori, H.; Kobayashi, C.; Endo, H.; et al. The JRA-55 Reanalysis: General Specifications and Basic Characteristics. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. Ser. II 2015, 93, 5–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J.; Wolff, D.B.; Adler, R.F.; Gu, G.; Hong, Y.; Bowman, K.P.; Stocker, E.F. The TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA): Quasi-Global, Multiyear, Combined-Sensor Precipitation Estimates at Fine Scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fick, S.E.; Hijmans, R.J. WorldClim 2: New 1-km Spatial Resolution Climate Surfaces for Global Land Areas. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 4302–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashouri, H.; Hsu, K.-L.; Sorooshian, S.; Braithwaite, D.K.; Knapp, K.R.; Cecil, L.D.; Nelson, B.R.; Prat, O.P. PERSIANN-CDR: Daily Precipitation Climate Data Record from Multisatellite Observations for Hydrological and Climate Studies. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K.-L.; Gao, X.; Gupta, H.V.; Imam, B.; Braithwaite, D. Evaluation of PERSIANN System Satellite–Based Estimates of Tropical Rainfall. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2000, 81, 2035–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uvo, C.B.; Foster, K.; Olsson, J. The Spatio-Temporal Influence of Atmospheric Teleconnection Patterns on Hydrology in Sweden. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2021, 34, 100782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, T. Overview. In Weather and Climate Extremes; Karl, T.R., Nicholls, N., Ghazi, A., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das Amorim, J.; Viola, M.; Junqueira, R.; Oliveira, V.; Mello, C. Evaluation of Satellite Precipitation Products for Hydrological Modeling in the Brazilian Cerrado Biome. Water 2020, 12, 2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnitou, G.T.; Tan, G.; Niu, R.; Nooni, I.K. Assessing Past Climate Biases and the Added Value of CORDEX-CORE Precipitation Simulations over Africa. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rougé, C.; Ge, Y.; Cai, X. Detecting Gradual and Abrupt Changes in Hydrological Records. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 53, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schellander, H.; Lieb, A.; Hell, T. Error Structure of Metastatistical and Generalized Extreme Value Distributions for Modeling Extreme Rainfall in Austria. Earth Space Sci. 2019, 6, 1616–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, J.G.; Althoff, D.; Bazame, H.C.; Neale, C.M.U.; Duarte, S.N.; Ruhoff, A.L.; Gonçalves, I.Z. Evaluating the Latest Imerg Products in a Subtropical Climate: The Case of Paraná State, Brazil. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Falahi, A.H.; Saddique, N.; Spank, U.; Gebrechorkos, S.H.; Bernhofer, C. Evaluation the Performance of Several Gridded Precipitation Products over the Highland Region of Yemen for Water Resources Management. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilks, D.S. Statistical Methods in the Atmospheric Sciences, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; Volume 10, ISBN 978-0-12-385022-5. [Google Scholar]
- AghaKouchak, A.; Behrangi, A.; Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K.; Amitai, E. Evaluation of Satellite-retrieved Extreme Precipitation Rates across the Central United States. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AghaKouchak, A.; Mehran, A. Extended Contingency Table: Performance Metrics for Satellite Observations and Climate Model Simulations. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 7144–7149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A. Statistical Comparison of Satellite-Retrieved Precipitation Products with Rain Gauge Observations over Bangladesh. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 2906–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, K.H.; Rao, A.R. A Modified Mann-Kendall Trend Test for Autocorrelated Data. J. Hydrol. 1998, 204, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, K.H. Trend Detection in Hydrologic Data: The Mann-Kendall Trend Test under the Scaling Hypothesis. J. Hydrol. 2008, 349, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagbasan, O.; Demir, V.; Yazicigil, H. Trend Analyses of Meteorological Variables and Lake Levels for Two Shallow Lakes in Central Turkey. Water 2020, 12, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Reis, L.C.; Santos e Silva, C.M.; Bezerra, B.; Mutti, P.R.; Spyrides, M.H.C.; da Silva, P.E. Analysis of Climate Extreme Indices in the MATOPIBA Region, Brazil. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2020, 177, 4457–4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regoto, P.; Dereczynski, C.; Chou, S.C.; Bazzanela, A.C. Observed Changes in Air Temperature and Precipitation Extremes over Brazil. Int. J. Climatol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, P.M.; Trigo, R.M.; Aizpurua, P.; Nieto, R.; Gimeno, L. Trends and Extremes of Drought Indices throughout the 20th Century in the Mediterranean. Nat. Hazard. Earth Sys. 2011, 11, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Biggs, T.; Shen, S.S.P. Satellite-Based Precipitation Estimates Using a Dense Rain Gauge Network over the Southwestern Brazilian Amazon: Implication for Identifying Trends in Dry Season Rainfall. Atmos. Res. 2021, 105741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.; Ombadi, M.; Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K.; AghaKouchak, A.; Brathwaite, D.; Ashouri, H.; Thorstensen, A.R. The PERSIANN Family of Global Satellite Precipitation Data: A Review and Evaluation of Products. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2018, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifroth, U.; Mueller, R.; Ahrens, B. Evaluation of Satellite-Based and Reanalysis Precipitation Data in the Tropical Pacific. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2013, 52, 634–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahi, N.; Hsu, K.; Sorooshian, S. An Artificial Neural Network Model to Reduce False Alarms in Satellite Precipitation Products Using MODIS and CloudSat Observations. J. Hydrometeorol. 2013, 14, 1872–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alijanian, M.; Rakhshandehroo, G.R.; Mishra, A.K.; Dehghani, M. Evaluation of Satellite Rainfall Climatology Using CMORPH, PERSIANN-CDR, PERSIANN, TRMM, MSWEP over Iran. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 4896–4914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, E.; Chapman, L. The Impacts of Climate Change on National Road and Rail Networks. In Transport and Climate Change; Transport and Sustainability; Europe Union: Luxembourg, 2012; pp. 105–136. ISBN 9781780524405. [Google Scholar]
- Ilalokhoin, O.; Pant, R.; Hall, J.W. A Multi-Track Rail Model for Estimating Journey Impacts from Extreme Weather Events: A Case Study of Great Britain’s Rail Network. Int. J. Rail Transp. 2021, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinks, C.; Hiete, M.; Comes, T.; Schultmann, F. Extreme Weather Events and Road and Rail Transportation in Germany. Int. J. Emerg. Manag. 2012, 8, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klenzendorf, J.B.; Barrett, M.E.; Charbeneau, R.J. Impact of Bridge Rail Geometry on Floodplain Analysis. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2010, 15, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izaguirre, C.; Losada, I.J.; Camus, P.; Vigh, J.L.; Stenek, V. Climate Change Risk to Global Port Operations. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2021, 11, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourlay, M.R. Wave Set-Up. In Encyclopedia of Earth Sciences Series; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; p. 1144. ISBN 978-90-481-2639-2. [Google Scholar]
- Konisky, D.M.; Hughes, L.; Kaylor, C.H. Extreme Weather Events and Climate Change Concern. Clim. Chang. 2016, 134, 533–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W. Extreme Weather and Climate Events in China under Changing Climate. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 938–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubiello, F.N.; Soussana, J.-F.; Howden, S.M. Crop and Pasture Response to Climate Change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19686–19690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, J.; Medvigy, D.; Fueglistaler, S.; Walko, R. Regional Dry-Season Climate Changes Due to Three Decades of Amazonian Deforestation. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2017, 7, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales, F.D.; Santiago, T.; Biggs, T.W.; Mullan, K.; Sills, E.O.; Monteverde, C. Impacts of Protected Area Deforestation on Dry-Season Regional Climate in the Brazilian Amazon. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeidizand, R.; Sabetghadam, S.; Tarnavsky, E.; Pierleoni, A. Evaluation of CHIRPS Rainfall Estimates over Iran. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 144, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AghaKouchak, A.; Nakhjiri, N. A near Real-Time Satellite-Based Global Drought Climate Data Record. Environ. Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 044037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derin, Y.; Yilmaz, K.K. Evaluation of Multiple Satellite-Based Precipitation Products over Complex Topography. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 1498–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moraes Cordeiro, A.L.; Blanco, C.J.C. Assessment of Satellite Products for Filling Rainfall Data Gaps in the Amazon Region. Nat. Resour. Model. 2021, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xavier, A.C.F.; Rudke, A.P.; Serrão, E.A.d.O.; Terassi, P.M.d.B.; Pontes, P.R.M. Evaluation of Satellite-Derived Products for the Daily Average and Extreme Rainfall in the Mearim River Drainage Basin (Maranhão, Brazil). Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4393. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13214393
Xavier ACF, Rudke AP, Serrão EAdO, Terassi PMdB, Pontes PRM. Evaluation of Satellite-Derived Products for the Daily Average and Extreme Rainfall in the Mearim River Drainage Basin (Maranhão, Brazil). Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(21):4393. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13214393
Chicago/Turabian StyleXavier, Ana Carolina Freitas, Anderson Paulo Rudke, Edivaldo Afonso de Oliveira Serrão, Paulo Miguel de Bodas Terassi, and Paulo Rógenes Monteiro Pontes. 2021. "Evaluation of Satellite-Derived Products for the Daily Average and Extreme Rainfall in the Mearim River Drainage Basin (Maranhão, Brazil)" Remote Sensing 13, no. 21: 4393. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13214393
APA StyleXavier, A. C. F., Rudke, A. P., Serrão, E. A. d. O., Terassi, P. M. d. B., & Pontes, P. R. M. (2021). Evaluation of Satellite-Derived Products for the Daily Average and Extreme Rainfall in the Mearim River Drainage Basin (Maranhão, Brazil). Remote Sensing, 13(21), 4393. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13214393








