IAS: A New Novel Phase-Based Filter for Detection of Unexploded Ordnances
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodological Background
3. IAS: A New Detection Filter
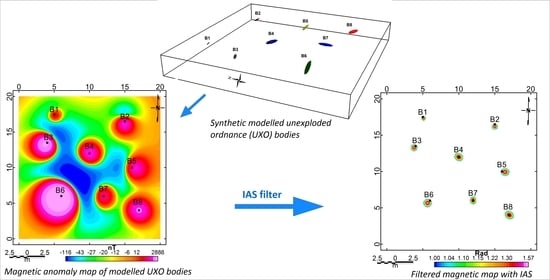
4. Datasets for Filter Analysis
4.1. Magnetic Surveying
4.2. Synthetic Data
4.3. Magnetic Data Collected from a Test Site
4.4. Real Magnetic Data Collected at the Field
5. Results
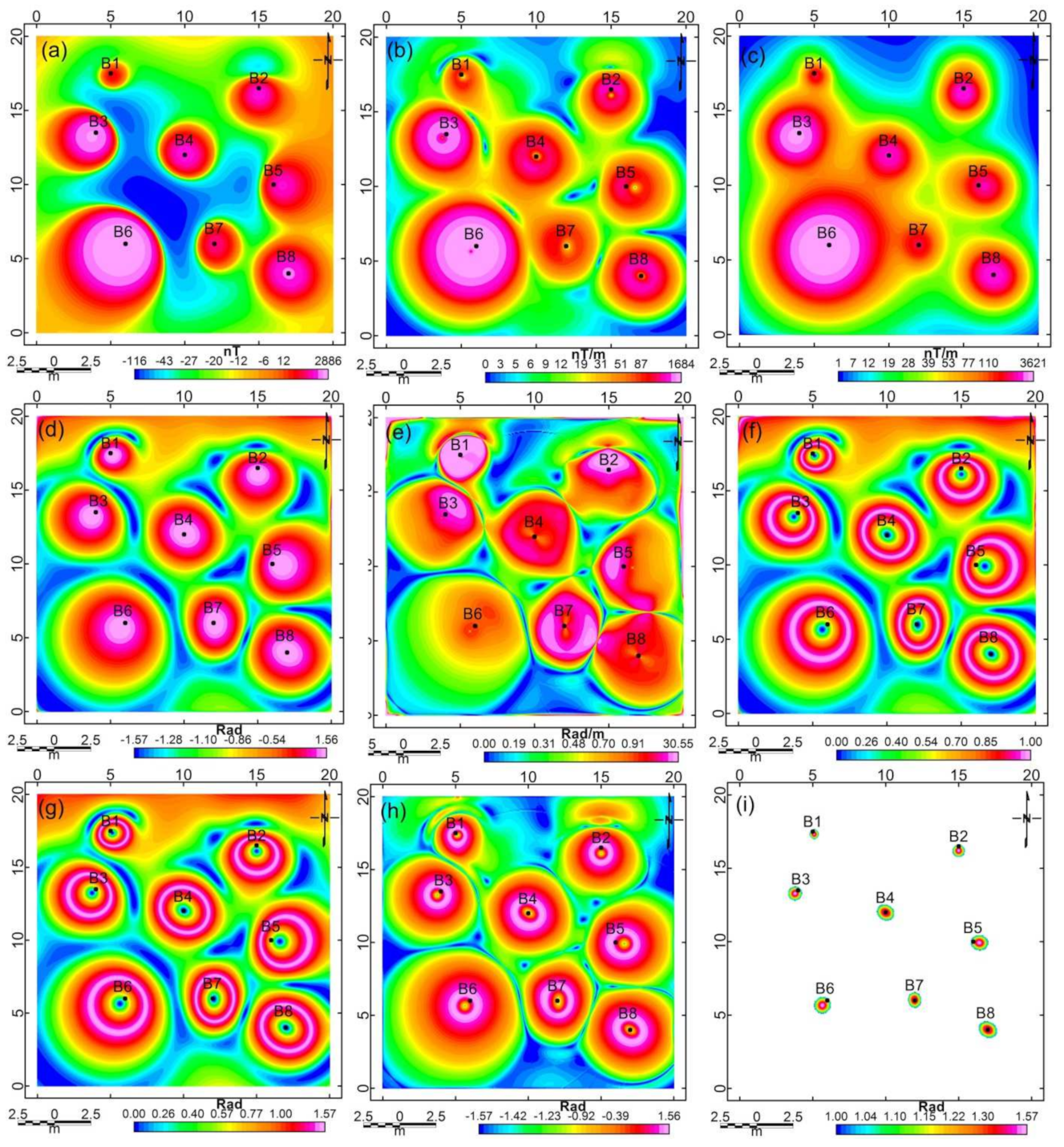
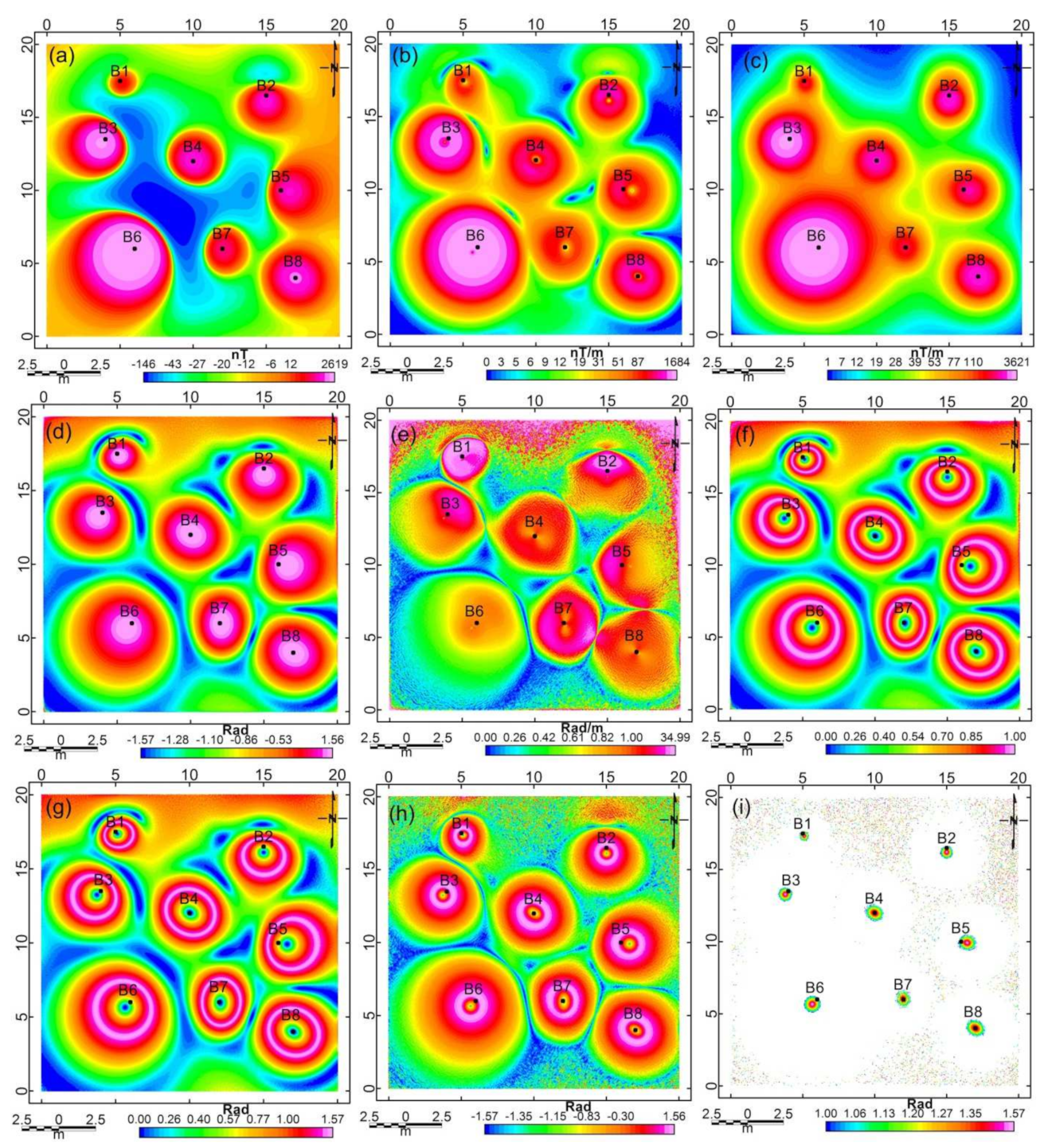
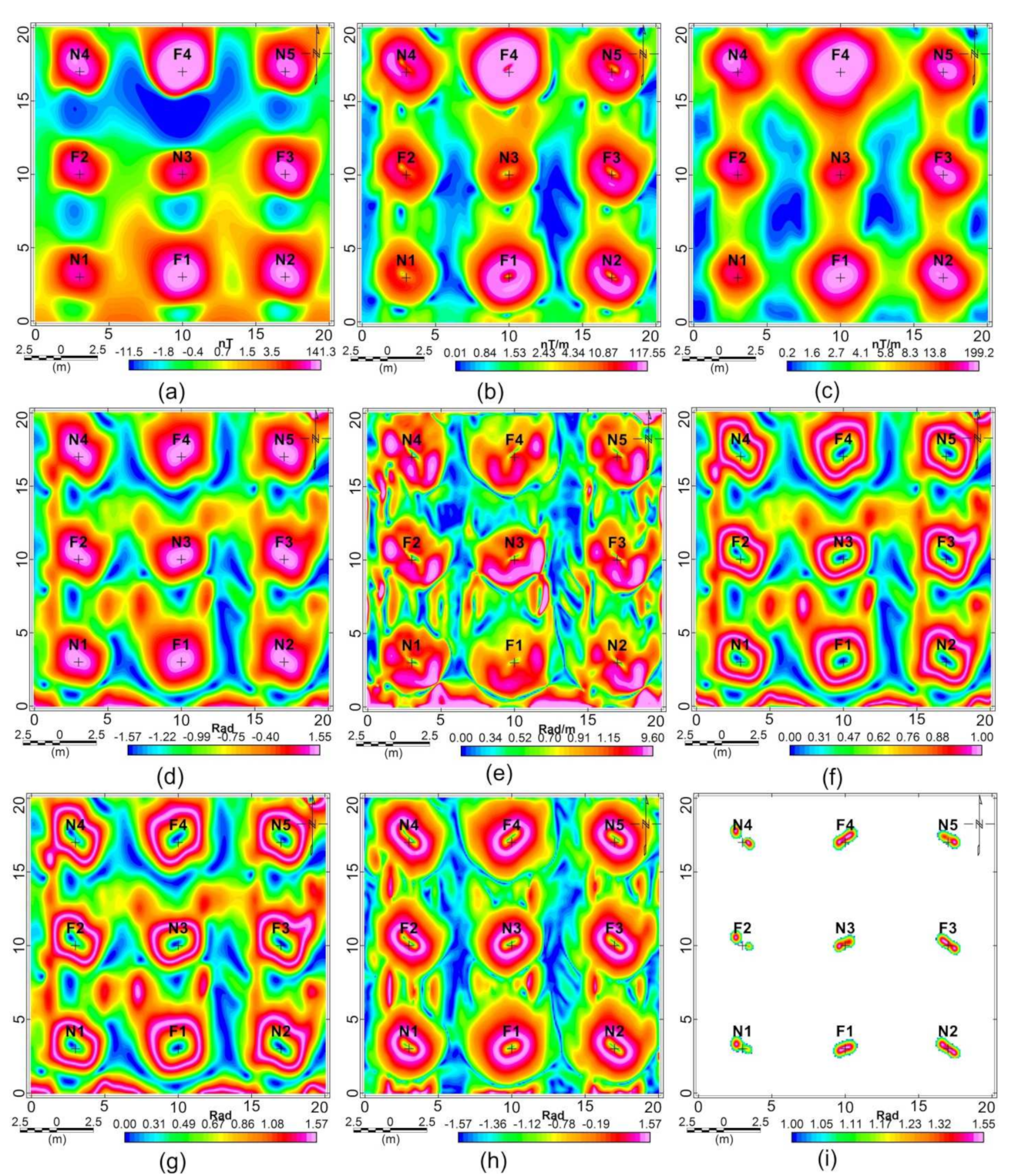
5.1. Synthetic Data
5.2. Test Site Data
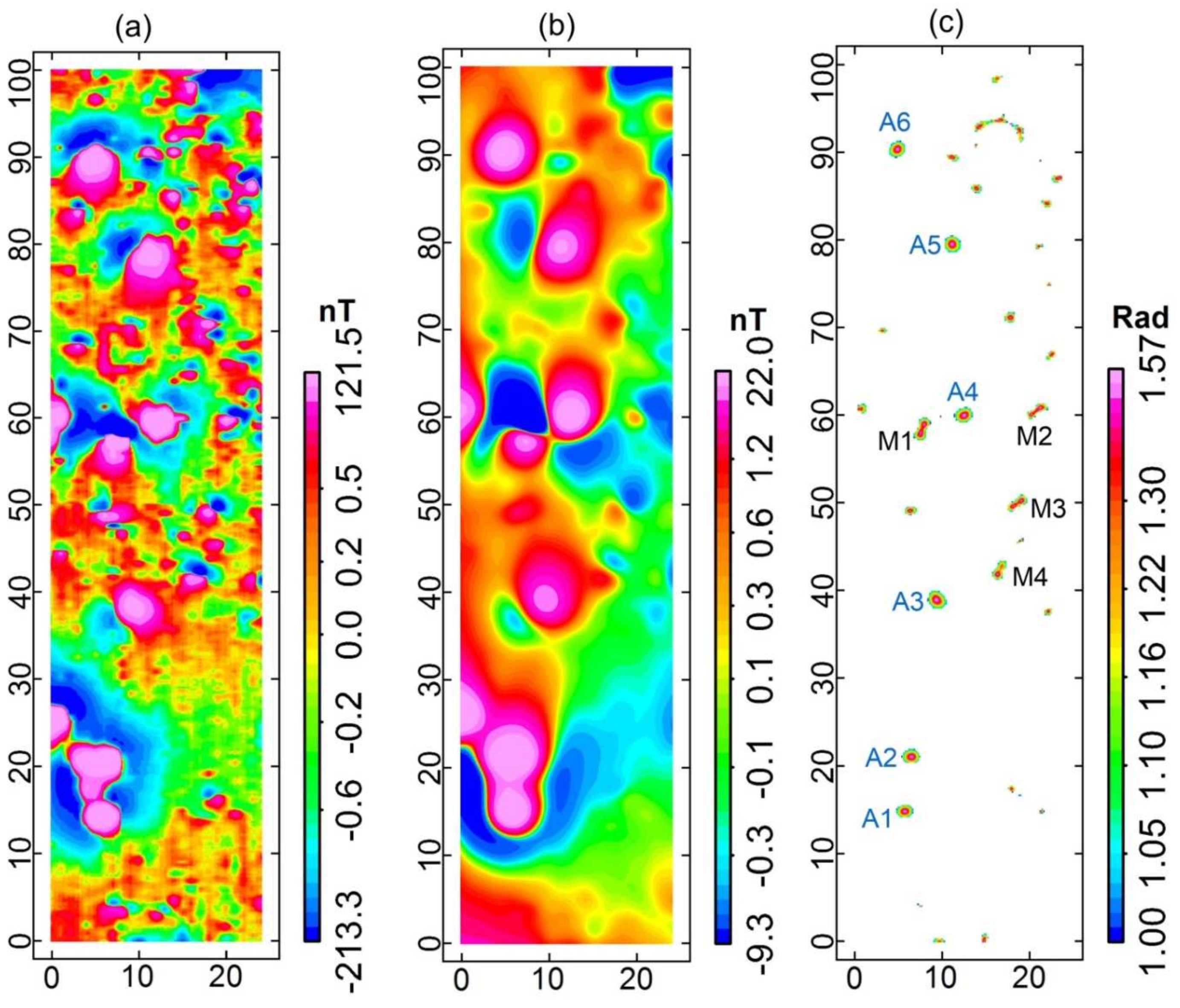
5.3. Real Field Data
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- SNHR. Syrian Network for Human Rights Report. 2020, p. 17. Available online: https://sn4hr.org/wp-content/pdf/english/Syria_Is_Among_the_Worlds_Worst_Countries_for_the_Number_of_Mines_Planted_Since_2011_en.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2021).
- Czub, M.; Kotwicki, L.; Lang, T.; Sanderson, H.; Klusek, Z.; Grabowski, M.; Szubska, M.; Jakacki, J.; Andrzejewski, J.; Rak, D.; et al. Deep Sea habitats in the chemical warfare dumping areas of the Baltic Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616-617, 1485–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klammler, H.; Sheremet, A.; Calantoni, J. Seafloor Burial of Surrogate Unexploded Ordnance by Wave-Induced Sediment Instability. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2020, 45, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, A.; Hamada, T.; Asahina, J.K.; Ushijima, K. Detection of unexploded ordnance (UXO) using marine magnetic gradiometer data. Explor. Geophys. 2005, 36, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billings, S.D.; Li, Y.; Goodrich, W. Advanced UXO Discrimination Using Magnetometry—Understanding Remanent Magnetization: Final Report SERDP Project MM-1380; Strategic Environmental Research and Development Program; Sky Research, Inc.: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2009; Available online: https://serdp-estcp.org/index.php//Program-Areas/Munitions-Response/Land/Modeling-and-Signal-Processing/MR-1380.
- Billings, S.; Youmans, C. Experiences with unexploded ordnance discrimination using magnetometry at a live-site in Montana. J. Appl. Geophys. 2007, 61, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.; Li, Y.; Nabighian, M. Automatic detection of UXO magnetic anomalies using extended Euler deconvolution. SEG Tech. Program. Expanded Abstr. 2005, 1133–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wigh, M.; Hansen, T.M.; Døssing, A. Inference of Unexploded Ordnance (UXO) by Probabilistic Inversion of Magnetic Data. Geophys. J. Int. 2020, 220, 37–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reynolds, R.; Barrowes, B.; Shubitidze, T.; Hartshorn, C.; Quinn, B.; Shubitidze, F. Electromagnetic induction sensing of unexploded ordinance and soil properties from unmanned aerial systems. In Proceedings of the SPIE 11750, Detection and Sensing of Mines, Explosive Objects, and Obscured Targets XXVI, Online, 12–17 April 2021; p. 1175002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, K.; Fernández, J.B. Electromagnetic Methods for UXO Discrimination. In Unexploded Ordnance Detection and Mitigation; Byrnes, J., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 197–221. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, F.; Liu, J. Transient electromagnetic detection of unexploded ordnance buried in underwater sediments. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2018 MTS/IEEE Charleston, Charleston, SC, USA, 22–25 October 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito-da-Costa, A.M.; Martins, D.; Rodrigues, D.; Fernandes, L.; Moura, R.; Madureira-Carvalho, Á. Ground Penetrating Radar for Buried Explosive Devices Detection: A Case Studies Review. Aust. J. Forensic Sci. 2021, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, D.J. Ground Penetrating Radar for Buried Landmine and IED Detection. In Unexploded Ordnance Detection and Mitigation; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 89–111. [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths, H.; McAslan, A. Low Frequency Radar for Buried Target Detection. In Unexploded Ordnance Detection and Mitigation; Byrnes, J., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 125–140. [Google Scholar]
- Núñez-Nieto, X.; Solla, M.; Gómez-Pérez, P.; Lorenzo, H. GPR Signal Characterization for Automated Landmine and UXO Detection Based on Machine Learning Techniques. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 9729–9748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beran, L.; Zelt, B.; Billings, S.D. Detecting and classifying UXO. J. ERW Mine Action 2013, 17, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Butler, D.K.; Simms, J.E.; Furey, J.S.; Bennett, H.H. Review of Magnetic Modeling for UXO and Applications to Small Items and Close Distances. J. Environ. Eng. Geophys. 2012, 17, 53–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, J.M.A. Introduction to Applied and Environmental Geophysics, 2nd ed.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.; Huang, D.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, Y. Detection of UXO magnetic anomaly in Jinshan area. Glob. Geology 2015, 18, 54–58. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, H.H.; Altshuler, T.W.; Rosen, E.M.; McDonald, J.R.; Barrow, B.; Khadr, N. Magnetic modeling of UXO and UXO-like targets and comparison with signatures measured by MTADS. In Proceedings of the UXO Forum, Anaheim, CA, USA, 19 May 1998; pp. 282–291. [Google Scholar]
- Butler, D.K. Potential fields methods for location of unexploded ordnance. Leading Edge 2001, 20, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billings, S.; Pasion, L.; Oldenburg, D. Discrimination and Identification of UXO by Geophysical Inversion of Total-Field Magnetic Data: ERDC/GSL TR-02-16; US Army Engineer Research and Development Center: Vicksburg, MS, USA, 2002.
- Paoletti, V.; Buggi, A.; Pašteka, R. UXO Detection by Multiscale Potential Field Methods. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2019, 176, 4363–4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appiah, I.; Wemegah, D.D.; Asare, V.-D.S.; Danuor, S.K.; Forson, E.D. Integrated geophysical characterisation of Sunyani Municipal solid waste disposal site using magnetic gradiometry, magnetic susceptibility survey and electrical resistivity tomography. J. Appl. Geophys. 2018, 153, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, R.; Glaccum, R.A.; Noel, M.R. Geophysical Techniques for Sensing Buried Wastes and Waste Migration; National Ground Water Association: Westerville, OH, USA, 1982; pp. 163–188. [Google Scholar]
- Dumont, G.; Robert, T.; Mark, N.; Nguyen, F. Assessment of multiple geophysical techniques for the characterization of municipal waste deposit sites. J. Appl. Geophys. 2017, 145, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibraheem, I.M.; Tezkan, B.; Bergers, R. Integrated interpretation of magnetic and ERT data to characterize a landfill in the north-west of Cologne, Germany. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2021, 178, 2127–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soupios, P.; Ntarlagiannis, D. Characterization and monitoring of solid waste disposal sites using geophysical methods: Current applications and novel trends. In Modelling Trends in Solid and Hazardous Waste Management; Sengupta, D., Agrahari, S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 75–103. [Google Scholar]
- Wemegah, D.D.; Fiandaca, G.; Auken, E.; Menyeh, A.; Danour, S.K. Spectral time-domain induced polarization and magnetics surveying– an efficient tool for characterisation of solid waste deposits in developing countries. Near Surf. Geophys. 2017, 15, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibraheem, I.M.; Gurk, M.; Tougiannidis, N.; Tezkan, B. Subsurface imaging of the Neogene Mygdonian basin, Greece using magnetic data. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2018, 175, 2955–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibraheem, I.M.; Haggag, M.; Tezkan, B. Edge Detectors as Structural Imaging Tools Using Aeromagnetic Data: A Case Study of Sohag Area, Egypt. Geosciences 2019, 9, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cordell, L.; Grauch, V.J.S. Mapping basement magnetization zones from aeromagnetic data in the San Juan basin, New Mexico. In The Utility of Regional Gravity and Magnetic Anomaly Maps; Hinzc, W.J., Ed.; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1985; pp. 181–197. [Google Scholar]
- Roest, W.R.; Verhoef, J.; Pilkington, M. Magnetic interpretation using the 3-D analytic signal. Geophysics 1992, 57, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, H.G.; Singh, V. Potential field tilt—A new concept for location of potential field sources. J. Appl. Geophys. 1994, 32, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verduzco, B.; Fairhead, J.D.; Green, C.M.; MacKenzie, C. New insights into magnetic derivatives for structural mapping. Lead. Edge 2004, 23, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijns, C.; Perez, C.; Kowalczyk, P. Theta map: Edge detection in magnetic data. Geophysics 2005, 70, L39–L43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, G.R.J.; Cowan, D.R. Enhancing potential field data using filters based on the local phase. Comp. Geosci. 2006, 32, 1585–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, F.; De Souza, J.; Bongiolo, A.D.B.E.S.; De Castro, L.G. Enhancement of the total horizontal gradient of magnetic anomalies using the tilt angle. Geophysics 2013, 78, J33–J41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabighian, M.N. The analytic signal of two-dimensional magnetic bodies with polygonal cross-section: Its properties and use for automated anomaly interpretation. Geophysics 1972, 37, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X. Understanding 3D analytic signal amplitude. Geophysics 2006, 71, L13–L16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pašteka, R.; Mikuška, J.; Karcol, R. New Methods in Ammunition Detection; Report PPZ-VTR-69-015/2010, MS; G-trend Ltd.: Bratislava, Slovakia, 2008; pp. 1–14. (In Slovak) [Google Scholar]
- Mikuška, J.; Pašteka, R.; Hajach, M.; Kadeckŷ, J.; Appel, J. Pyrotechnical Exploration along Planned Seismic Reflection Profile trough the Military Site Zahorie; Technical Report; G-trend Ltd. and Pyra Ltd.: Bratislava, Slovakia, 2006; pp. 1–2. (In Slovak) [Google Scholar]
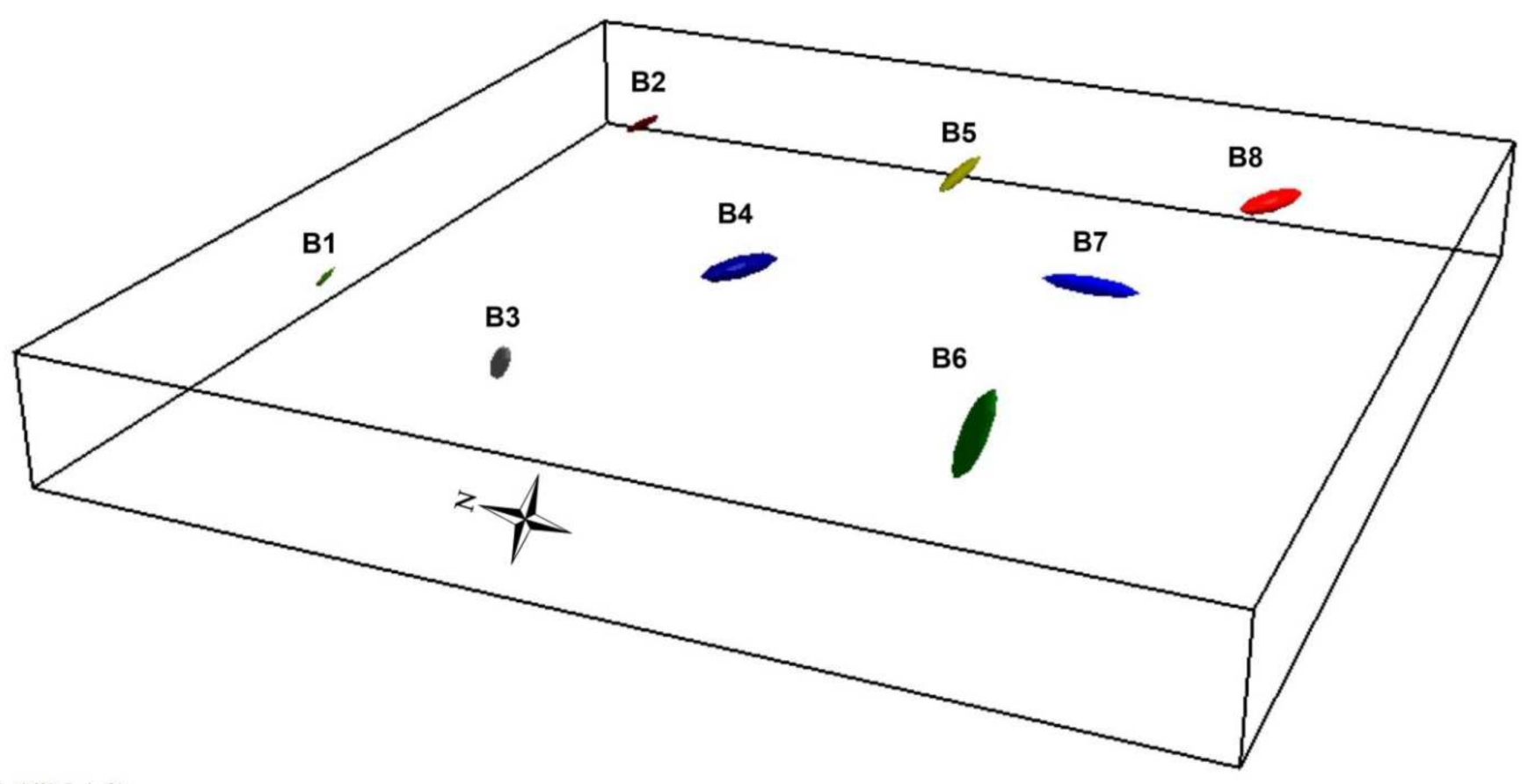



| UXO Body | X (m) | Y (m) | Depth (m) | Length/2 (m) | Diameter/2 (m) | Azimuth | Plunge | Susc. (SI) | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 | 17.5 | 0.35 | 0.24 | 0.052 | 330 | 45 | 250 | 105 mm projectile |
| 2 | 15 | 16.5 | 0.55 | 0.435 | 0.087 | 0 | 30 | 250 | 175 mm projectile |
| 3 | 4 | 13.5 | 0.80 | 0.605 | 0.152 | 45 | 45 | 250 | 12 in projectile |
| 4 | 10 | 12 | 1.10 | 0.845 | 0.203 | 300 | 0 | 250 | 16 in projectile |
| 5 | 16 | 10 | 1.00 | 0.795 | 0.133 | 280 | 10 | 250 | 500 lb bomb |
| 6 | 6 | 6 | 1.50 | 1.250 | 0.229 | 45 | 60 | 250 | 1000 lb bomb |
| 7 | 12 | 6 | 1.20 | 0.920 | 0.170 | 0 | 0 | 250 | 2000 lb bomb |
| 8 | 17 | 4 | 1 | 0.845 | 0.203 | 300 | 0 | 250 | 16 in projectile |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ibraheem, I.M.; Aladad, H.; Alnaser, M.F.; Stephenson, R. IAS: A New Novel Phase-Based Filter for Detection of Unexploded Ordnances. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4345. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13214345
Ibraheem IM, Aladad H, Alnaser MF, Stephenson R. IAS: A New Novel Phase-Based Filter for Detection of Unexploded Ordnances. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(21):4345. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13214345
Chicago/Turabian StyleIbraheem, Ismael M., Hasan Aladad, Mohamad Faek Alnaser, and Randell Stephenson. 2021. "IAS: A New Novel Phase-Based Filter for Detection of Unexploded Ordnances" Remote Sensing 13, no. 21: 4345. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13214345
APA StyleIbraheem, I. M., Aladad, H., Alnaser, M. F., & Stephenson, R. (2021). IAS: A New Novel Phase-Based Filter for Detection of Unexploded Ordnances. Remote Sensing, 13(21), 4345. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13214345