Abstract
Movement ecologists have witnessed a rapid increase in the amount of animal position data collected over the past few decades, as well as a concomitant increase in the availability of ecologically relevant remotely sensed data. Many researchers, however, lack the computing resources necessary to incorporate the vast spatiotemporal aspects of datasets available, especially in countries with less economic resources, limiting the scope of ecological inquiry. We developed an R coding workflow that bridges the gap between R and the multi-petabyte catalogue of remotely sensed data available in Google Earth Engine (GEE) to efficiently extract raster pixel values that best match the spatiotemporal aspects (i.e., spatial location and time) of each animal’s GPS position. We tested our approach using movement data freely available on Movebank (movebank.org). In a first case study, we extracted Normalized Difference Vegetation Index information from the MOD13Q1 data product for 12,344 GPS animal locations by matching the closest MODIS image in the time series to each GPS fix. Data extractions were completed in approximately 3 min. In a second case study, we extracted hourly air temperature from the ERA5-Land dataset for 33,074 GPS fixes from 12 different wildebeest (Connochaetes taurinus) in approximately 34 min. We then investigated the relationship between step length (i.e., the net distance between sequential GPS locations) and temperature and found that animals move less as temperature increases. These case studies illustrate the potential to explore novel questions in animal movement research using high-temporal-resolution, remotely sensed data products. The workflow we present is efficient and customizable, with data extractions occurring over relatively short time periods. While computing times to extract remotely sensed data from GEE will vary depending on internet speed, the approach described has the potential to facilitate access to computationally demanding processes for a greater variety of researchers and may lead to increased use of remotely sensed data in the field of movement ecology. We present a step-by-step tutorial on how to use the code and adapt it to other data products that are available in GEE.
1. Introduction
The science of movement ecology has advanced rapidly over the past few decades [1], thanks in part to technological innovations that have decreased the size and weight of satellite tracking devices fitted on animals, broadening the diversity of species tracked and increasing the length of tracking periods [2]. Together with remotely sensed data products that are becoming increasingly (and freely) available, scientists are able to address a greater variety of scientific questions that harness the fine-scale spatiotemporal resolutions of each of these datasets [3], with elevation models and vegetation indices being great examples [3,4,5]. Similarly, new statistical methods to analyze and visualize movement data have become more accessible. For instance, there are at least 58 different packages developed for use in the R programming language (https://www.r-project.org; accessed date: 10 October 2021) [6,7], one of the most popular open-source programs for data analysis among ecologists [8]. With such an abundance in data and new methods, the limitation to address relevant scientific questions of interest frequently lies in the required computing power and the technological expertise to do so.
The launch of Google Earth Engine (GEE; https//earthengine.google.com; accessed data: 10 October 2021) in 2010 marked an important step toward improving accessibility of remotely sensed data and analysis tools for researchers globally. Google Earth Engine is a free, cloud-based spatial analysis platform that facilitates access to Google’s powerful computational infrastructure and a multi-petabyte catalogue of remotely sensed data and other spatial datasets [9]. One of the main limitations of using GEE for movement analyses is that it runs on an internet-accessible application programming interface (API) and an associated web-based interactive development environment (IDE), making it difficult to integrate remote sensing products from GEE directly into R. The recently launched rGEE package in R [10], however, has made bridging GEE with R more accessible for integrating data analysis workflows.
Here, we present R code that harnesses the strengths of GEE to extract remote sensing information matching the time at which the movement data was collected. We demonstrate with two case studies how to process high volumes of data on a personal computer in relatively short time periods. First, we extract the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) from NASA’s Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) that matches the closest image in time to the collection data for each GPS location across an entire year of tracking data for 10 animals of three different species: African buffalo (Syncerus caffer), African elephant (Loxodonta africana), and blue wildebeest (Connochaetes taurinus). Second, we extract surface temperature estimates from the ERA5-Land hourly data product and contrast the temperature between consecutive step lengths of 12 individual wildebeest across three Kenyan ecosystems. These two case studies exemplify the ease with which various remote sensing data products can be extracted. We present a step-by-step tutorial on how to use the code and adapt it to other data products that are available for extraction via GEE (Supplemental Materials or the GitHub repository).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Code Workflow
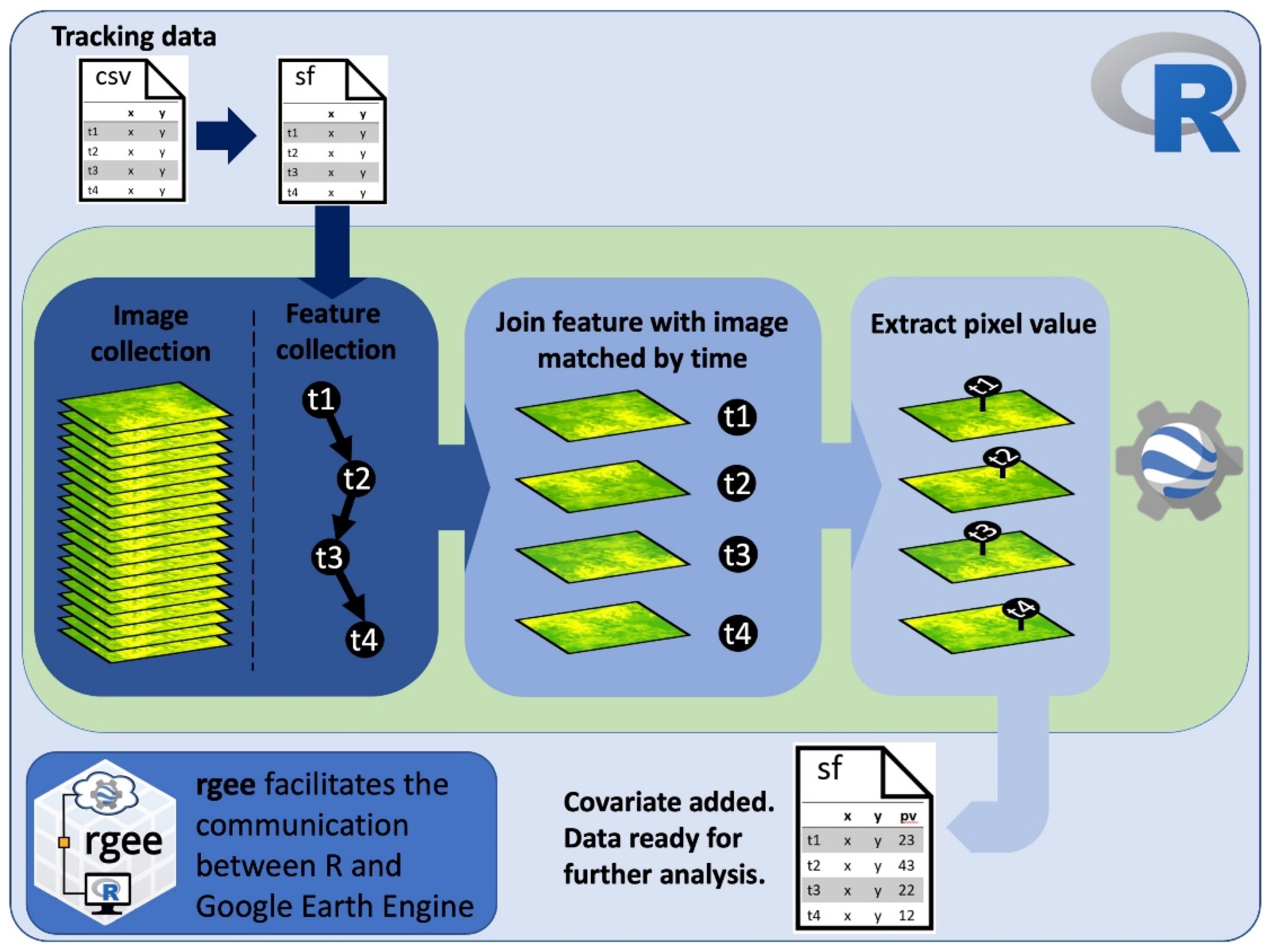
The code to extract remote sensing data that best match the time stamp of telemetry data is designed in a specific workflow that users can modify for their own interests (Figure 1). Once the telemetry data are loaded into R, the time stamp of the telemetry data needs to be converted into a factor with the format “YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SS” to then be converted into milliseconds since midnight on 1 January 1970, a format used in GEE to manage dates. The dataset is transformed into a simple feature (sf) object using the sf package [11], which in turn can be loaded into GEE as a feature collection using the sf_as_ee function from the rGEE package.
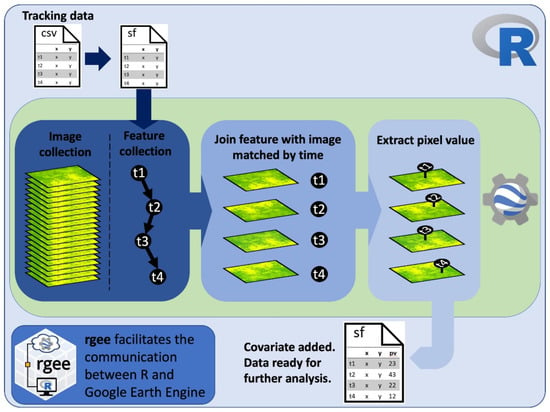
Figure 1.
Code workflow diagram showing the overall process to extract pixel values at animal-tracking locations from the most temporally proximate image in a time series using R and Google Earth Engine.
Using the join functions available in GEE allows elements from feature collections (e.g., collection of points in the tracking dataset) and image collections (e.g., all images of a remote sensing product) to be matched efficiently based on a filter. In our case, the filter finds all images in a time series within a certain time range from each point feature in the tracking dataset. We implemented the saveBest join, which saves the image closest in time to each GPS fix location. Each “best” matching image is then appended to each feature in the entire feature collection. We created an add_value function in GEE that first extracts the pixel value at the GPS location from a “best” matched image (or, optionally, an average from a specified radius around the GPS location) and then saves the pixel value as a new feature property. The ability of GEE to parallelize operations across a collection of features [9] makes this computationally expensive date-matching and raster data extraction process more efficient. The resulting feature collection with the extracted pixel values is then transformed back into an sf object using the ee_as_sf function from the rGEE package.
The ee_as_sf function allows to move the GEE feature collection into the R local environment as an sf object using one of two different methodologies, an intermediate container (Google Drive or Google Cloud Storage) or a direct call (getInfo) [10]. We implemented the getInfo method that is simple, direct, and fast. However, there are a maximum of 5000 features that can be converted at a time, after which a GEE memory limit is reached. To overcome this limitation, the code runs at 1000 points at a time using a loop in R for the length of the dataset. There is also a possibility for users to convert large feature collections into simple features through Google Drive or Google Cloud Storage. See the Supplemental Materials or the GitHub repository for a more detailed explanation of the code.
2.2. Animal-Tracking Data for Case Studies
To demonstrate the usefulness of the code workflow, we downloaded freely available movement data from Movebank (movebank.org accessed date: 10 October 2021) for the African buffalo [12], African elephant [13,14], and blue wildebeest [15,16]. For each species, we only included animals that contained an entire year of data. For case study 1 (NDVI extraction), our dataset consisted of 2 elephants, 1 buffalo, and 3 wildebeest (Table 1). For case study 2, (hourly temperature extraction), we incorporated 12 wildebeest (Table 1). All data were resampled to a 3 h temporal interval using the R package adehabitatLT [17].

Table 1.
Summary of species, telemetry data, remote sensing data product used, and processing time for extracting pixel values to each GPS location. For each GPS location, the closest remote sensing image in time was identified to extract pixel values.
2.3. Case Study 1—NDVI Extraction
The NDVI has been shown to be a strong predictor of herbivore movement and space use [5,18,19]. A common practice with the NDVI is to average raster images across years or seasons and extract values at animal locations to fit statistical models (e.g., [13,20]). However, herbivores often time their movements in concert with the progression of new plant growth to maximize nutrient intake [21,22,23], and there is evidence that some species have the capability to modify the wave of green vegetation as they move and graze [24]. As a result, obtaining vegetation productivity data from remotely sensed datasets that are temporally matched with the fine-scale movement of animals can be essential for understanding the effect of vegetation greenness on movement. The computational power necessary to extract this type of information is a main obstacle for many researchers, especially those working in countries or places where access to high computing power is limited. Beyond the computational power required, the process can also be time consuming. For instance, it might take hours, days, or weeks to download all the satellite data required to include the best temporal match for each observation in your movement dataset, especially if the study spans large spatial extents and/or long tracking periods.
The code workflow that we implemented in this example extracts the NDVI value from the 250 m, 16-day MODIS/Terra data product (MOD13Q1) that is closest in time to each GPS fix collected in an animal-tracking study. This means that the maximum time lag between each GPS point collected and the closest NDVI image composite date is 8 days. Note, however, that the difference between pixel dates and GPS fixes may be larger because in a MOD13Q1 16-day composite, the data values are not actually collected by the satellite on the nominal date of the composite image, so the actual observation dates for each pixel are unknown.
To showcase the potential benefits of pairing tracking data with the time at which images were acquired, we compared NDVI values extracted using the method described above with NDVI values extracted for all animal locations from an annual mean NDVI image calculated from all the MODIS images available for the year of each tracking dataset. We plotted the NDVI values against time for each animal and for each method (mean annual NDVI and time-matched NDVI) for a visual comparison.
2.4. Case Study 2—Temperature Extraction
In addition to ecological drivers such as vegetation greenness, the energetic cost of animal movement can influence the way in which animals behave and use resources [25,26,27]. For example, temperature is one of the main environmental drivers of animal habitat use [28]. In large herbivores, changes in environmental temperature can alter movement patterns and behavior, forcing animals to move closer to water, find shade, or increase the amount of time spent resting [29,30,31]. Similarly, snow cover can increase movement cost and restrict forage availability, altering habitat selection patterns [32,33]. The advances in telemetry technology and remotely sensed data products provide opportunities to better understand the effects of weather fluctuation on animal movement, with important implications for predicting animal responses to climate change [34].
To demonstrate the power of using GEE to associate climatic data with telemetry locations, we accessed the ERA5-Land dataset [35]. ERA5-Land consists of 50 climatic variables with an hourly temporal resolution and ~9 km spatial resolution. The data are available from 1981 to 3 months from the current time [35]. From the 50 variables available, our example demonstrates the use of air temperature at 2 m above the land surface, although other variables of the ERA5-Land dataset could be integrated (see code provided in the GitHub repository).
From the wildebeest dataset, we randomly chose 12 individuals from three different populations of wildebeest in Kenya: the Maasai Mara/Loita Plains population, the Athi-Kaputiei Plains population, and the Amboseli Basin population [15]. All individuals contained a full year of data for the year 2011. Similar to case study 1, we extracted temperature from the ERA5-Land dataset at the time at which each GPS fix was collected. In this example, we used a total time series of 8760 images. After extracting time-matched temperature values for each location, we inspected the relationship between step length and temperature by fitting a Gaussian linear mixed-effects model in a Bayesian framework. We log-transformed the step length and scaled the temperature to a mean of zero and one unit of standard deviation. We included individuals as random effects. We implemented the model using the JAGS program [36] through the jagsUI package in the R programming language [6]. We used un-informative priors for the random-level hyper-parameters. We ran three parallel Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) chains for 5000 iterations, discarding the first 1500 as burn-in. We thinned the remaining posterior samples at a rate of 1:5. We evaluated model convergence by visually inspecting chain outputs and by ensuring that the Gelman–Rubin diagnostic for all regression parameters was <1.01 [37]. We corroborated that variation in the remotely sensed temperature data was accurate in capturing the variation experienced by animals in our case study by correlating the remotely sensed values for air temperature at 2 m above the land surface, with external temperature recorded by the collar of animals for 1000 randomly selected fixes from the 12 individuals included in the analysis.
3. Results
3.1. Case Study 1—NDVI Extraction
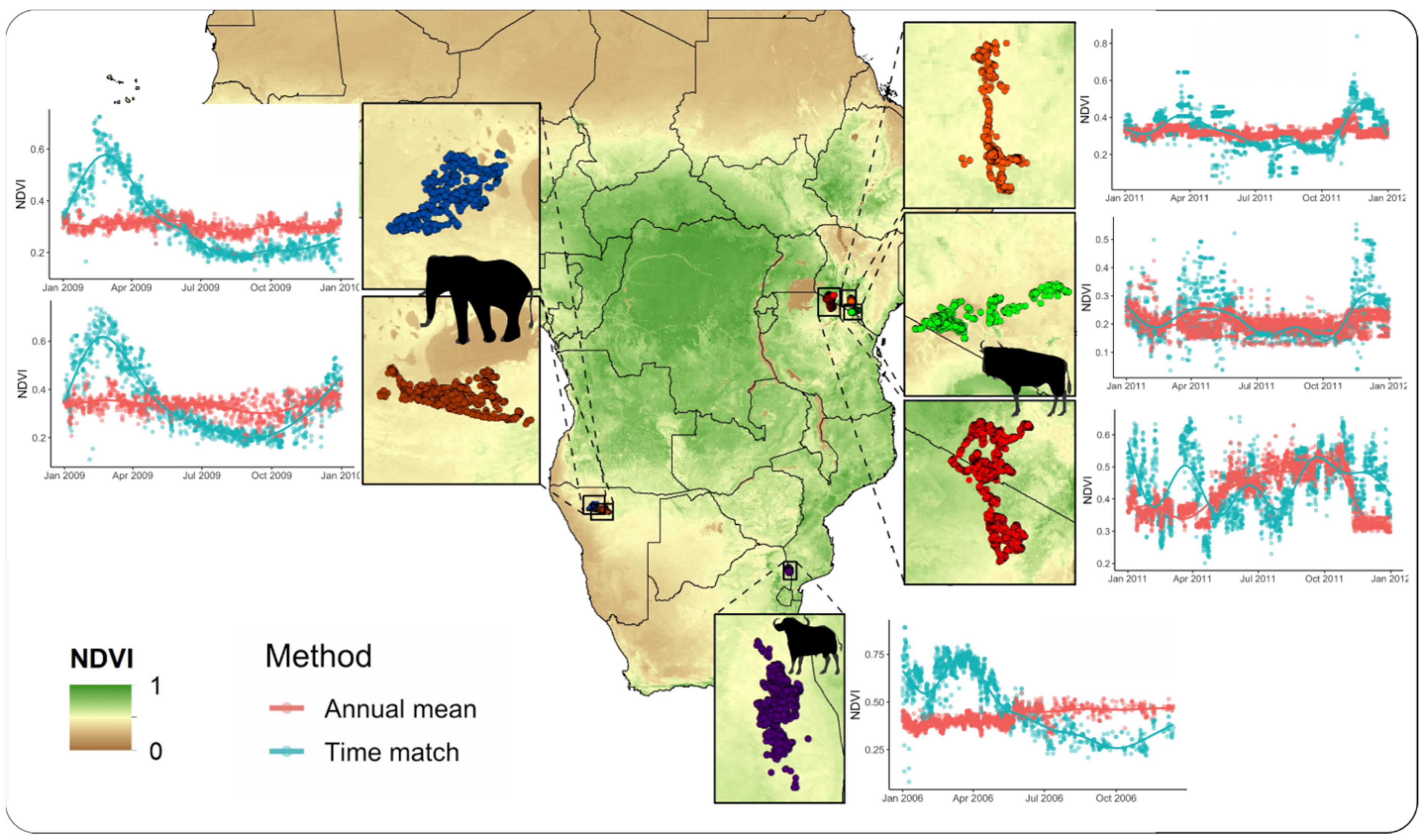
Extracting NDVI values matching the closest MODIS image to the time each GPS fix was collected was highly efficient. For the six animals included, it took approximately 3 min to process the 12,344 GPS locations (Table 1). A visual comparison between the time-matched NDVI and the mean annual NDVI (non-time-matched) shows that the mean annual NDVI fails to account for the seasonal variation in vegetation productivity experienced by animals. The severity of dissimilarity differs by species and region, with both overestimation and underestimation on the NDVI occurring depending on the time of year (Figure 2).
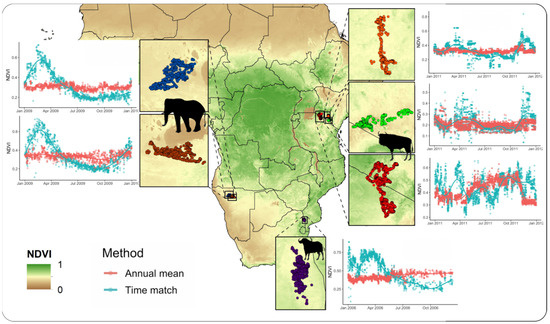
Figure 2.
MODIS NDVI values extracted across a year of data for the African buffalo (Syncerus caffer), African elephant (Loxodonta africana), and blue wildebeest (Connochaetes taurinus) tracked with GPS telemetry units. Results show widespread discrepancies between the annual mean NDVI (red) and the time-matched NDVI (blue) extracted at all animal locations across species and regions.
3.2. Case Study 2—Temperature Extraction
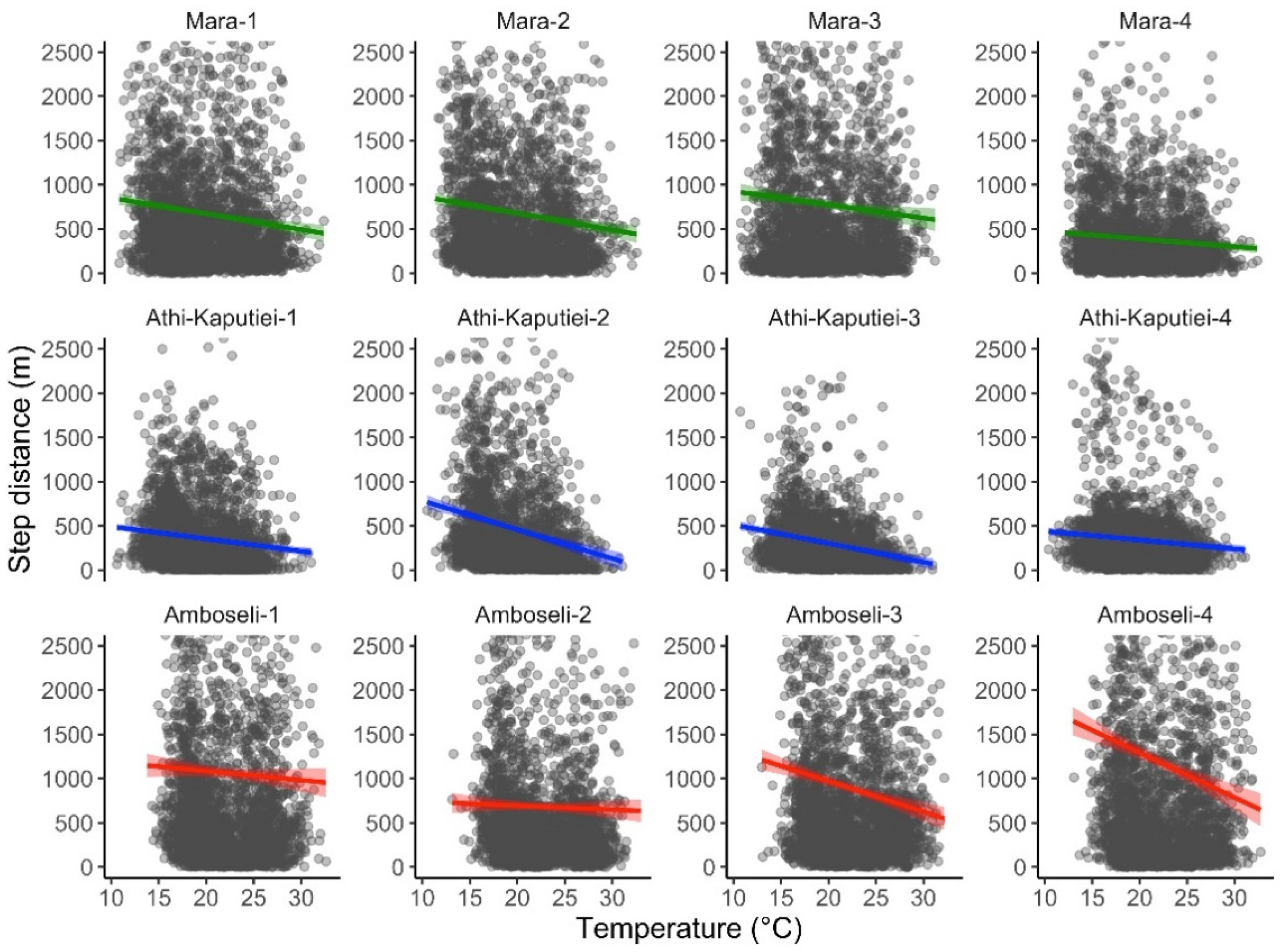
We extracted temperature data matching the hour of data collection for tracking data from 12 wildebeest. The ERA5-Land air temperature dataset was highly correlated with the temperature recorded by the animal collars (Pearson = 0.896). The total number of GPS point locations included in our analysis was 33,074. The total time required for data extraction was 33.83 min (0.06 s per data point extracted). We found high posterior support (100%) that wildebeest move less as temperature increases (slope = −0.169 (−0.168 to −0.081 95% credible intervals); Figure 3).
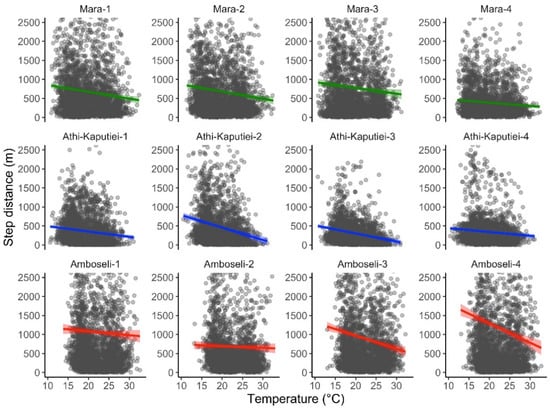
Figure 3.
Relationship between step length and air temperature for blue wildebeest. GPS tracking data were obtained from 12 individuals from three populations in Kenya: the Maasai Mara/Loita Plains (green), Athi-Kaputiei Plains (blue), and Amboseli Basin (red). Hourly air temperature at 2 m over the ground was obtained from the ERA5-Land dataset. All data are from 2011.
4. Discussion
The increasing availability of fine-scale spatiotemporal animal movement and remote sensing data has created new opportunities in animal movement research [3]. However, matching these data sources can be challenging and computationally intensive. Here we present a framework using GEE and R to rapidly match the time stamp of GPS telemetry data with that of remote sensing data products to improve the inference being made from animal movement datasets. The workflow is useful because it provides an approach to match the time stamp of movement data with remote sensing data products in real or near real time through GEE. This can provide unique opportunities to characterize animal space use and movement, which is especially important for species that are responding to seasonal changes in environmental productivity [21,22,23] anthropogenic disturbance [38] or changes in climate [34].
In this study, we present examples incorporating two environmental data layers that are recognized for their importance in explaining animal movement and behavior [5,18,28]. The code can be adapted to incorporate other data layers of interest. For instance, extracting snow cover or precipitation from the same ERA5-Land dataset can be accomplished by simply selecting different bands from the image collection. Alternatively, other image collections available via GEE, such as surface water availability [39] and other vegetation indices (e.g., VIIRS NASA Vegetation Index Product), can be substituted in the code. The step-by-step tutorial presented in the Supplemental Materials explains how to use the code and adapt it to other datasets. While clouds limit the possibility to use vegetation indexes with higher temporal resolution as they can result in images with large areas lacking information, novel advances for reconstructing daily MODIS NDVI products are opening new possibilities for incorporating these datasets into movement analysis in the near future [40]. Moreover, the flexibility of GEE makes it possible to incorporate information derived from multispectral imagery such as Landsat or Sentinel as potential covariates in models for animal movement data [41].
Our workflow is efficient in terms of time and its simplicity, with no need for downloading imagery or relying on powerful computer processors. Likewise, this workflow can be integrated into the most common analyses of movement data applicable in conservation and management of animals, such as resource selection [42] and step selection functions [43,44] to investigate questions related to how animals move and select habitat across space and time. Selecting the appropriate remotely sensed product, however, with temporal and spatial resolutions that are relevant to the specific research question and analysis methodology remains a central component of any movement analysis [3].
A recognized limitation of our methodology is that rGEE can be challenging to install and the learning curve for a new user may be steep. However, this new package is in constant development and the documentation provides many worked examples and helpful guidance to troubleshoot installation errors. Once rGEE is installed and running, the benefits of implementing GEE code directly in R are significant, as demonstrated by the efficiency of operating over large image collections of different remote sensing products in our study.
5. Conclusions
Making high computing power accessible to researchers who do not have access to high-computing infrastructure in their academic institutions can broaden the spectrum of possibilities for animal movement research. Here we introduced a coding workflow that uses R and GEE to rapidly extract remote sensing information matching the time at which the animal movement data were collected. We expect our code to facilitate the process of obtaining temporal-relevant predictor variables for animal movement analyses, promoting research that will increase our understanding of how animals respond to global changes.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/rs13204154/s1, A tutorial for spatiotemporal extraction of remotely sensed data using Google Earth Engine and R.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.D.C., J.A.S. and G.C.; methodology, R.D.C., M.M.M., J.A.S. and G.C.; formal analysis, R.D.C.; writing—original draft preparation, R.D.C.; writing—review and editing, R.D.C., M.M.M., J.A.S. and G.C.; visualization, R.D.C.; supervision, J.A.S. and G.C.; project administration, G.C.; funding acquisition, G.C. and J.A.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Smithsonian Conservation Commons Working Land & Seascapes Amplification and Innovation Award (grant no. WLS-2020-11) and the Smithsonian’s Movement of Life Initiative.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Code and data necessary to run the tutorial to obtain remote sensing data matching the time stamp of tracking data are available in the Supplemental Materials and in the GitHub repository: https://github.com/Smithsonian/SpatiotemporalMatchingOfAnimalPositionsWithRemotelySensedDataUsingGoogleEarthEngineAndR (accessed on 14 October 2021). The tutorial can be accessed at: https://smithsonian.github.io/SpatiotemporalMatchingOfAnimalPositionsWithRemotelySensedDataUsingGoogleEarthEngineAndR/ (accessed on 14 October 2021). All data used in this manuscript are freely available at www.movebank.org (accessed on 14 October 2021).
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the entire community at the SCBI GIS lab, with whom plenty of discussions have helped to shape the core ideas of this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Joo, R.; Picardi, S.; Boone, M.E.; Clay, T.A.; Patrick, S.C.; Romero-Romero, V.S.; Basille, M. A decade of movement ecology. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.00110. [Google Scholar]
- Kays, R.; Crofoot, M.C.; Jetz, W.; Wikelski, M. Terrestrial animal tracking as an eye on life and planet. Science 2015, 348, 2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neumann, W.; Martinuzzi, S.; Estes, A.B.; Pidgeon, A.M.; Dettki, H.; Ericsson, G.; Radeloff, V.C. Opportunities for the application of advanced remotely-sensed data in ecological studies of terrestrial animal movement. Mov. Ecol. 2015, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farr, T.G.T.G.; Rosen, P.A.P.A.; Caro, E.; Crippen, R.; Duren, R.; Hensley, S.; Kobrick, M.; Paller, M.; Rodriguez, E.; Roth, L.; et al. The shuttle radar topography mission. Rev. Geophys. 2007, 45, RG2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pettorelli, N.; Ryan, S.; Mueller, T.; Bunnefeld, N.; Jedrzejewska, B.; Lima, M.; Kausrud, K. The Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI): Unforeseen successes in animal ecology. Clim. Res. 2011, 46, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 6 May 2021).
- Joo, R.; Boone, M.E.; Clay, T.A.; Patrick, S.C.; Clusella-Trullas, S.; Basille, M. Navigating through the r packages for movement. J. Anim. Ecol. 2020, 89, 248–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lai, J.; Lortie, C.J.; Muenchen, R.A.; Yang, J.; Ma, K. Evaluating the popularity of R in ecology. Ecosphere 2019, 10, e02567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-scale geospatial analysis for everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aybar, C.; Wu, Q.; Bautista, L.; Yali, R.; Barja, A. rgee: An R package for interacting with Google Earth Engine. J. Open Source Softw. 2020, 5, 2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pebesma, E. Simple features for R: Standardized support for spatial vector data. R J. 2018, 10, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cross, P.; Bowers, J.; Hay, C.; Wolhuter, J.; Buss, P.; Hofmeyr, M.; du Toit, J.; Getz, W. Data from: Nonparameteric Kernel Methods for Constructing Home Ranges and Utilization Distributions. Movebank Data Repository. 2016. Available online: https://www.doi.org/10.5441/001/1.j900f88t (accessed on 6 May 2021).
- Tsalyuk, M.; Kilian, W.; Reineking, B.; Getz, W.M. Temporal variation in resource selection of African elephants follows long-term variability in resource availability. Ecol. Monogr. 2019, 89, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kilian, W.; Getz, W.; Zidon, R.; Tsalyuk, M. Data from: Temporal variation in resource selection of African elephants follows long term variability in resource availability. Movebank Data Repository. 2018. Available online: https://www.doi.org/10.5441/001/1.3nj3qj45 (accessed on 6 May 2021).
- Stabach, J.A. Movement, Resource Selection, And The Physiological Stress Response of White-Bearded Wildebeest. Ph.D. Thesis, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Stabach, J.; Hughey, L.; Reid, R.; Worden, J.; Leimgruber, P.; Boone, R. Data from: Comparison of Movement Strategies of Three Populations of White-Bearded Wildebeest. Movebank Data Repository. 2020. Available online: https://www.doi.org/10.5441/001/1.h0t27719 (accessed on 6 May 2021).
- Calenge, C. The package “adehabitat” for the R software: A tool for the analysis of space and habitat use by animals. Ecol. Model. 2006, 197, 516–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettorelli, N.; Laurance, W.F.; O’Brien, T.G.; Wegmann, M.; Nagendra, H.; Turner, W. Satellite remote sensing for applied ecologists: Opportunities and challenges. J. Appl. Ecol. 2014, 51, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boone, R.B.; Thirgood, S.J.; Hopcraft, J.G.C. Serengeti wildebeest migratory patterns modeled from rainfall and new vegetation growth. Ecology 2006, 87, 1987–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, N.J.; Grachev, I.A.; Bekenov, A.B.; Milner-Gulland, E.J. Saiga antelope calving site selection is increasingly driven by human disturbance. Biol. Conserv. 2010, 143, 1770–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkle, J.A.; Monteith, K.L.; Aikens, E.O.; Hayes, M.M.; Hersey, K.R.; Middleton, A.D.; Oates, B.A.; Sawyer, H.; Scurlock, B.M.; Kauffman, M.J. Large herbivores surf waves of green-up during spring. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 283, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aikens, E.O.; Mysterud, A.; Merkle, J.A.; Cagnacci, F.; Rivrud, I.M.; Hebblewhite, M.; Hurley, M.A.; Peters, W.; Bergen, S.; De Groeve, J.; et al. Wave-like Patterns of Plant Phenology Determine Ungulate Movement Tactics. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, 3444–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aikens, E.O.; Kauffman, M.J.; Merkle, J.A.; Dwinnell, S.P.H.; Fralick, G.L.; Monteith, K.L. The greenscape shapes surfing of resource waves in a large migratory herbivore. Ecol. Lett. 2017, 20, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geremia, C.; Merkle, J.A.; Eacker, D.R.; Wallen, R.L.; White, P.J.; Hebblewhite, M.; Kauffman, M.J. Migrating bison engineer the green wave. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 25707–25713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gibert, J.P.; Chelini, M.C.; Rosenthal, M.F.; Delong, J.P. Crossing regimes of temperature dependence in animal movement. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2016, 22, 1722–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryce, C.M.; Wilmers, C.C.; Williams, T.M. Energetics and evasion dynamics of large predators and prey: Pumas vs. hounds. PeerJ 2017, 2017, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scantlebury, D.M.; Mills, M.G.L.; Wilson, R.P.; Wilson, J.W.; Mills, M.E.J.; Durant, S.M.; Bennett, N.C.; Bradford, P.; Marks, N.J.; Speakman, J.R. Flexible energetics of cheetah hunting strategies provide resistance against kleptoparasitism. Science 2014, 346, 79–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, D.; Snelling, E.P.; Hetem, R.S.; Maloney, S.K.; Strauss, W.M.; Fuller, A. Revisiting concepts of thermal physiology: Predicting responses of mammals to climate change. J. Anim. Ecol. 2018, 87, 956–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alston, J.M.; Joyce, M.J.; Merkle, J.A.; Moen, R.A. Temperature shapes movement and habitat selection by a heat-sensitive ungulate. Landsc. Ecol. 2020, 35, 1961–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaker, M.; Gupte, P.R.; Prins, H.H.T.; Slotow, R.; Vanak, A.T. Fine-scale tracking of ambient temperature and movement reveals shuttling behavior of elephants to water. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mole, M.A.; DÁraujo, S.R.; van Aarde, R.J.; Mitchell, D.; Fuller, A. Coping with heat: Behavioural and physiological responses of savanna elephants in their natural habitat. Conserv. Physiol. 2016, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gilbert, S.L.; Hundertmark, K.J.; Person, D.K.; Lindberg, M.S.; Boyce, M.S. Behavioral plasticity in a variable environment: Snow depth and habitat interactions drive deer movement in winter. J. Mammal. 2017, 98, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, B.G.; Merrill, E.H. The influence of snow on the functional response of grazing ungulates. Oikos 2012, 121, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, S.C.; Bohrer, G.; Gurarie, E.; LaPoint, S.; Mahoney, P.J.; Boelman, N.T.; Eitel, J.U.H.; Prugh, L.R.; Vierling, L.A.; Jennewein, J.; et al. Ecological insights from three decades of animal movement tracking across a changing Arctic. Science 2020, 370, 712–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz Sabater, J. ERA5-Land hourly data from 1981 to present. Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) Climate Data Store (CDS). 2019. Available online: https://doi.org/10.24381/cds.e2161bac (accessed on 15 September 2021).
- Plummer, M. JAGS: A program for analysis of Bayesian graphical models using Gibbs sampling. (Version 4.2). In Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Distributed Statistical Computing (DSC 2003), Vienna, Austria, 20–22 March 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Gelman, A.; Rubin, D. Inference from iterative simulation using multiple sequences. Stat. Sci. 1992, 7, 457–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, M.A.; Böhning-gaese, K.; Fagan, W.F.; Fryxell, J.M.; Van Moorter, B.; Alberts, S.C.; Ali, A.H.; Allen, A.M.; Attias, N.; Avgar, T.; et al. Moving in the Anthropocene: Global reductions in terrestrial mammalian movements. Science 2018, 469, 466–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pekel, J.F.; Cottam, A.; Gorelick, N.; Belward, A.S. High-resolution mapping of global surface water and its long-term changes. Nature 2016, 540, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, L.; Wardlow, B.D.; Hu, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, G.; Peng, G.; Xiang, D.; Wang, R.; Meng, R.; Wu, W. A novel strategy to reconstruct NDVI time-series with high temporal resolution from MODIS multi-temporal composite products. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oeser, J.; Heurich, M.; Senf, C.; Pflugmacher, D.; Belotti, E.; Kuemmerle, T. Habitat metrics based on multi-temporal Landsat imagery for mapping large mammal habitat. Remote Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 6, 52–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manly, B.F.; McDonald, L.; Thomas, D.; McDonald, T.L.; Erickson, W.P. Resource Selection by Animals; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Thurfjell, H.; Ciuti, S.; Boyce, M.S. Applications of step-selection functions in ecology and conservation. Mov. Ecol. 2014, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Avgar, T.; Potts, J.R.; Lewis, M.A.; Boyce, M.S. Integrated step selection analysis: Bridging the gap between resource selection and animal movement. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2016, 7, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).