Abstract
Microwave land surface emissivity (MLSE) is an important geophysical parameter to determine the microwave radiative transfer over land and has broad applications in satellite remote sensing of atmospheric parameters (e.g., precipitation, cloud properties), land surface parameters (e.g., soil moisture, vegetation properties), and the parameters of interactions between atmosphere and terrestrial ecosystem (e.g., evapotranspiration rate, gross primary production rate). In this study, MLSE in China under both clear and cloudy sky conditions was retrieved using satellite passive microwave measurements from Aqua Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer-Earth Observing System (AMSR-E), combined with visible/infrared observations from Aqua Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS), and the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) atmosphere reanalysis dataset of ERA-20C. Attenuations from atmospheric oxygen and water vapor, as well as the emissions and scatterings from cloud particles are taken into account using a microwave radiation transfer model to do atmosphere corrections. All cloud parameters needed are derived from MODIS visible and infrared instantaneous measurements. Ancillary surface skin temperature as well as atmospheric temperature-humidity profiles are collected from ECMWF reanalysis data. Quality control and sensitivity analyses were conducted for the input variables of surface skin temperature, air temperature, and atmospheric humidity. The ground-based validations show acceptable biases of primary input parameters (skin temperature, 2 m air temperature, near surface relative humidity, rain flag) for retrieving using. The subsequent sensitivity tests suggest that 10 K bias of skin temperature or observed brightness temperature may result in a 4% (~0.04) or 7% (0.07) retrieving error in MLSE at 23.5 GHz. A nonlinear sensitivity in the same magnitude is found for air temperature perturbation, while the sensitivity is less than 1% for 300 g/m2 error in cloud water path. Results show that our algorithm can successfully retrieve MLSE over 90% of the satellite detected land surface area in a typical cloudy day (cloud fraction of 64%), which is considerably higher than that of the 29% area by the clear-sky only algorithms. The spatial distribution of MLSE in China is highly dependent on the land surface types and topography. The retrieved MLSE is assessed by compared with other existing clear-sky AMSR-E emissivity products and the vegetation optical depth (VOD) product. Overall, high consistencies are shown for the MLSE retrieved in this study with other AMSR-E emissivity products across China though noticeable discrepancies are observed in Tibetan Plateau and Qinling-Taihang Mountains due to different sources of input skin temperature. In addition, the retrieved MLSE exhibits strong positive correlations in spatial patterns with microwave vegetation optical depth reported in the literature.
1. Introduction
Satellite passive microwave remote sensing has great potential in detecting surface/atmospheric hydrological conditions, ecosystem monitoring, and numerical weather predictions (NWP) [1,2,3,4], due to its strong capability in penetrating vegetation canopy and cloud, and being less affected by atmosphere. The assimilation of passive microwave remote sensing over land is significantly inferior compared to that over ocean, generally because of the highly varied surface properties (e.g., types, roughness, moisture, soil texture etc.) and the difficulty in separating the surface radiation from that of atmosphere compositions [5,6,7]. As an essential surface property, microwave land surface emissivity (MLSE) is independent of atmosphere and surface temperature, and provides information of water abundance in soil and vegetation canopy. A high time-efficient estimate of MLSE is critical and will benefit at least two kinds of applications. First, MLSE largely determines the background brightness temperature in the over-land emission-based retrievals of precipitation [8,9,10]. Second, MLSE has wide applications in monitoring/estimating surface properties and processes, including but not limited to soil moisture, surface evapotranspiration, and forest carbon uptake [11,12,13,14,15,16,17], assessment of wildfire risk [18,19], determination of vegetation physiology activity (respiration and photosynthesis), and the estimation of gross primary production and above ground biomass [20,21,22].
To date, many studies have retrieved MLSE under both clear and cloudy skies using data from various sensors. Retrievals under clear sky have been more intensively implemented than under cloudy conditions. Since the 1990s, MLSE was retrieved from the Special Sensor Microwave Imagers (SSM/I), Advanced Microwave Sounding Unit (AMSU), and the Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer-Earth Observing System (AMSR-E) etc. [6,23,24,25,26]. For example, Moncet et al. [6] retrieved MLSEs from AMSR-E observations at frequencies higher than 10.65 GHz under cloud-free conditions. In their study, MODIS observations were used to provide cloud mask, land surface temperature, and atmospheric temperature, and water vapor profiles were derived from the 1° × 1° National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP) Global Data Assimilation System (GDAS) analysis [27]. Norouzi et al. [26] further retrieved MLSE from all AMSR-E frequencies and used it to study the surface properties. In their study, the atmospheric profiles information was provided by the TIROS Operational Vertical Sounder (TOVS) dataset available with International Satellite Cloud Climatology Project (ISCCP) [28]; cloud flag and land surface temperatures were taken from ISCCP-DX [29]. These studies are generally carried out under clear sky, retrieving MLSE from direct satellite observation with correction of atmosphere contributions from vapor and gases. However, in this case, the great advantage of microwave over the infrared (IR) spectrum in minimizing “cloud bias” is eliminated [6]. The measures of systematically excluding cloudy areas usually lead to remarkable gaps and sample loss in the final data records. It is worthwhile to understand the characteristics of instantaneous MLSE under all weather conditions.
Compared to clear sky, direct retrieval of MLSE under cloudy skies still remains limited. Even so, efforts have been made by a few researchers to achieve more progress in this aspect. Lin and Minnis [24] used SSM/I measurements of brightness temperatures (Tbs) combined with ground-based measurements of cloud to retrieve MLSE at one site. Baordo and Geer [7] retrieved all-sky MLSE using SSM/I channels above 18 GHz at large scale. In their work, cloud properties were taken from European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) model simulations. Aires et al. [30] used neural network approach to retrieve atmospheric water vapor, cloud liquid water path, surface temperature and multi-band emissivity simultaneously. This method can achieve high consistencies among emissivity and associated environmental parameters. In their study, a pre-calculated monthly MLSE [23] under clear sky was used as first-guess to train their network. Such works were usually conducted under the assumption of no significant difference of MLSE between clear and cloudy skies, which may be improper because clouds may affect MLSE significantly by changing the incoming solar radiation, soil moisture, and potentially the vegetation water content. Thus, direct retrieval using instantaneous cloud observation is of particular importance.
The aim of this study is to retrieve MLSE across China using combined satellite passive microwave radiation observation, optical observation of cloud properties, and the reanalysis data of ancillary atmospheric states. Compared with previous studies, the MLSE product is available under both clear and cloudy skies without relying on any other emissivity atlas or historic records. Since the lack of in situ measurement of MLSE poses a great challenge to direct validation, the MLSE is evaluated with Moncet’s [6] and Norouzi’s [25] MLSE products. The retrieval quality is also assured by validating the primary input (near) surface parameters and rainfall against observations of metrological sites and conducting sensitivity tests in corresponding error ranges. Because one of the main purposes of this study is to further obtain land-atmosphere interaction parameters such as evapotranspiration rate, carbon exchange rate, and vegetation biochemical emission in terrestrial ecosystem [15,17], we selected the eight ChinaFlux sites that can provide in situ measurements of these parameters for validation study.
In this paper, we introduce all associated datasets in Section 2. Then, we describe our retrieval algorithm, validations analysis, and sensitivity tests in Section 3. Section 4 shows the spatial distribution and temporal variations of MLSE in China, and the inter-comparison with two clear-sky only MLSE products as well as a VOD dataset. Section 5 presents the discussion. Finally, we conclude our work in Section 6.
2. Datasets
2.1. Input Data
In our study, the top of atmosphere (TOA) microwave brightness temperatures are adopted from the AMSR-E/Aqua L2A (AE_L2A) Global Swath Spatially-Resampled Brightness Temperatures, Version 3 [31]. This dataset has 5 different resampled resolutions with respect to the effective field of view (EFOV) ranging from 5.4 to 56 km. At each resampled resolution, all higher microwave frequencies are spatially averaged to meet the footprint of the lowest one using the Backus–Gilbert method [32]. We take Tbs from resampled “Resolution 1”, which includes all 6 dual polarized frequencies centered at 6.925, 10.65, 18.7, 23.8, 36.5, and 89.0 GHz with an EFOV of 56 km and a 10 km spatial gap on the ground between two adjacent EFOVs. This dataset also provides land/ocean flags for waterbody screening. In addition, because rainfall may essentially change the surface properties, all identified rainy pixels are excluded prior to retrieval using the surface rain rate data from AMSR-E/Aqua Level-2B precipitation product (AE_Rain) [33].
We adopt surface skin temperature and the atmospheric humidity-temperature profiles from the ECMWF reanalysis dataset ERA-20C [34]. The profiles have 37 layers, from the surface to the 1 mb pressure layer with a spatial resolution of 0.125° and a temporal resolution of 3 h. When matching them to the AMSR-E observation, the two 3-h ERA-20C estimations which bracket the overpass time of AMSR-E are weighted and averaged. Spatially, these two ERA estimations are taken from the nearest gird to the center of AMSR-E footprint.
The cloud properties including cloud water path (CWP), cloud phase index (CPI), cloud top temperature (CTT), and cloud top pressure (CTP) are taken from MODIS level 2 cloud product MYD06_L2 [35] which is derived from Aqua/MODIS VIS-IR observations. The dataset provides cloud properties at 1 and 5 km resolutions. To fuse AMSR-E Tbs observation with MODIS cloud properties, we averaged all cloud observations located within a given AMSR-E footprint.
2.2. Validation Data
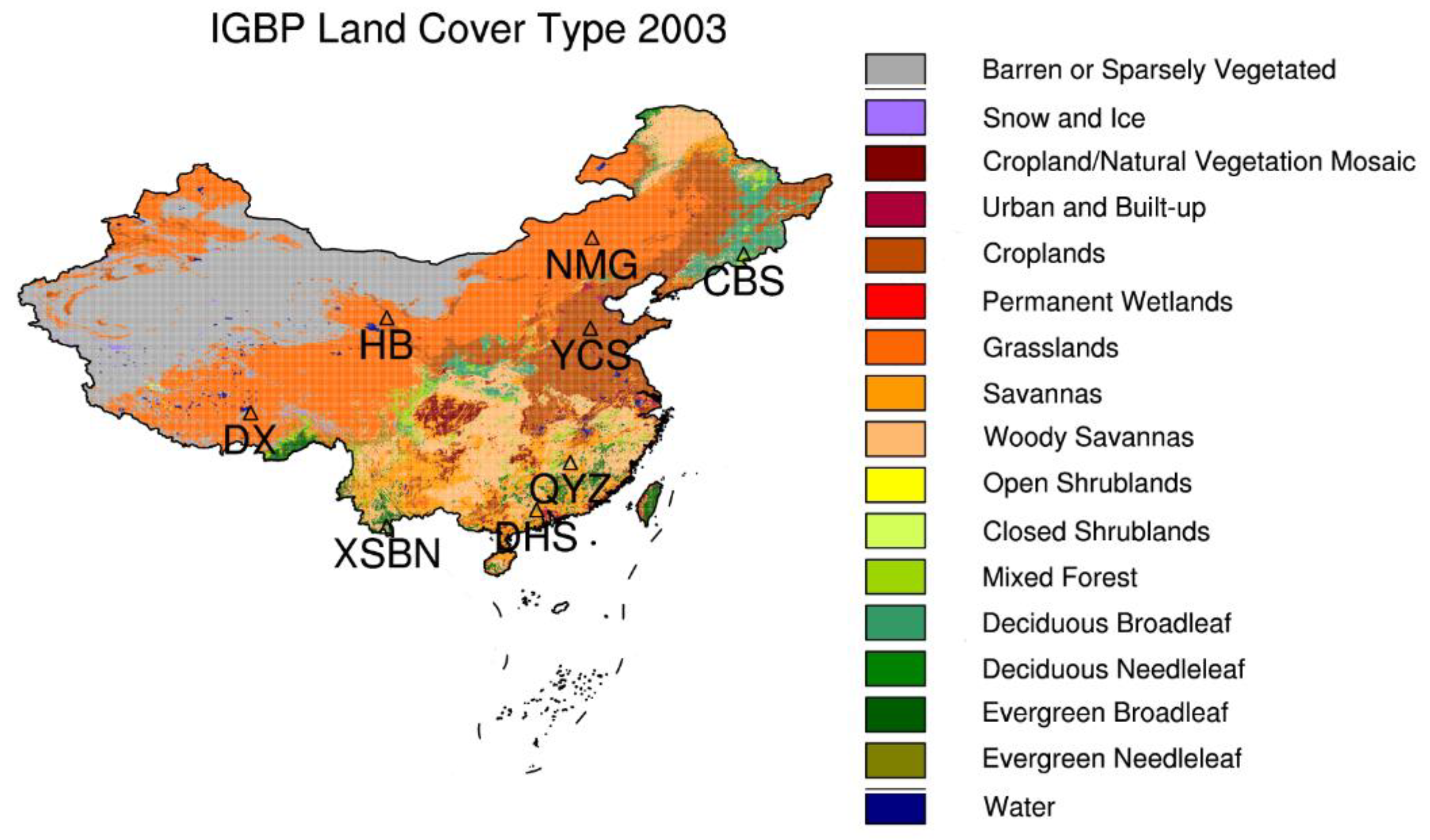
To validate the input parameters from the reanalysis dataset ERA-20C, we collect the in-situ measurements of skin temperatures, the 2 m surface temperatures and near surface relative humidity from 8 ChinaFlux sites (Table 1, http://www.cnern.org.cn/index.jsp, accessed on 14 August 2021) for validation analysis. Meanwhile, we also evaluate the AE_Rain rainfall estimates used in our algorithm by comparing them with rainfall data from the hourly precipitation database [36] developed based on historical records from the meteorological stations in China. Figure 1 shows International Geosphere-Biosphere Programme (IGBP) land cover types of 2003 in the study area China and the locations of the 8 ChinaFlux sites. The IGBP land cover types are extracted from MODIS Terra + Aqua Combined Land Cover product (MCD12C1) [37].

Table 1.
Basic information of the 8 ChinaFlux sites for inputs evaluation.
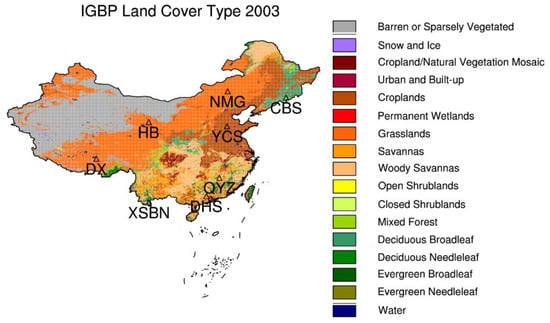
Figure 1.
IGBP land cover types in 2003 in the study area China, along with the geolocations of 8 ChinaFlux sites.
To assess the performance of the retrieval algorithm, we compare our MLSE with two previous AMSR-E emissivity products (Table 2) derived under cloud-free conditions. Norouzi et al. [26] developed a MLSE product under cloud-free conditions (hereafter Norouzi_MLSE) based on the microwave brightness temperature product AE_L2A (version 2) at resampled “Resolution 1” (56 km EFOV) (https://nsidc.org/data/NSIDC-0543/, accessed on 14 August 2021). As reported, their work was the first study that retrieved MLSE to the lowest microwave frequency (6.925 GHz) from AMSR-E. Moncet et al. [6] derived another emissivity product based on the AE_L2A (version 2) dataset at the resampled “Resolution 2” (38 km EFOV) (https://www.aer.com/science-research/atmosphere/remote-sensing/environmental-monitoring/microwave-surface-emissivity-dat/, accessed on 14 August 2021). In their work, the microwave observations from AMSR-E with frequencies ≥10.65 GHz were used for the retrieval. We conducted MLSE retrieval under both “Resolution 1” and “Resolution 2”. We took the sub-dataset “1a” from Moncet’s product, which was derived directly from AMSR-E observation under clear sky, hereinafter called Moncet_MLSE. To compare with Moncet_MLSE at the same resolution, we retrieve another MLSE dataset from AE_L2A Tbs resampled at “Resolution 2”, referred as MLSE_Res2. Table 2 lists the primary input variables and corresponding data sources for these two MLSE products and the ones that derived in our study.

Table 2.
Data sources of three AMSR-E emissivity products discussed in this study.
The global long-term microwave vegetation optical depth (VOD) climate archive (VODCA) [38] is obtained to provide surface VOD in comparison with our MLSE. The data archive merged VOD retrievals that had been derived from multiple sensors in the Ku-band, X-band, and C-band.
2.3. Ancillary Data
We obtained the monthly vegetation index from Aqua MODIS products MODIS/Aqua Vegetation Indices Monthly L3 Global 0.05Deg CMG (MYD13C2) dataset [39] to provide Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) information on monthly basis. In addition, Global Precipitation Climatology Centre (GPCC) gauge measurements-based 0.5° monthly precipitation dataset [40] was obtained to indicate the surface moisture state. MODIS/Aqua Snow Cover Monthly L3 Global 0.05Deg CMG (MYD10CM), Version 6 [41] was obtained to provide the surface snow cover extent.
3. Methods of MLSE Retrieval
The retrieving algorithm was modified from the one in Lin and Minnis [24] and Min et al. [4], with substantial modifications made as follows. First, we substituted the coarse monthly mean static temperature-humidity profiles with the finer dynamic ones and extended the retrieval to all AMSR-E channels. Second, we replaced the forward microwave radiative transfer model (MWRT) of Lin et al. [42] with a 4-stream MWRT model of Liu [43] to simulate the upwelling microwave radiation at TOA from temperature-humidity profiles. Third, we adopted the latest MODIS observations of cloud properties and reconfigured a cloud vertical hydrometeor profile with the help of vertical coordinates of ERA-20C reanalysis dataset so as to simulate the cloud contributions through Liu’s MWRT.
3.1. Radiative Transfer Model
In the core of the retrieving algorithm, we adopted a 4-stream MWRT model developed by Liu [43] to simulate the upwelling microwave radiation emitted from surface to the TOA. This model is widely used to calculate the radiative contributions from atmosphere compositions such as rain droplets, oxygen, vapor, cloud liquid hydrometeors, and the spherical/non-spherical ice particles [15,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54]. In the forward simulation, fundamental inputs are derived from the above-introduced data sources, majorly, surface skin temperature, humidity-temperature profiles and cloud hydrometeor profiles. In Liu’s MWRT, cloud water and cloud ice are modelled as spherical particles using Mie theory and following the general three-parameter gamma particle size distribution [55]. Contributions from cloud particles can be quantified for a given cloudy footprint of AMSR-E. After correcting the effects from water vapor and gases, we can derive the upwelling TOA Tbs.
3.2. Descriptions of Retrieval Algorithm of MLSE
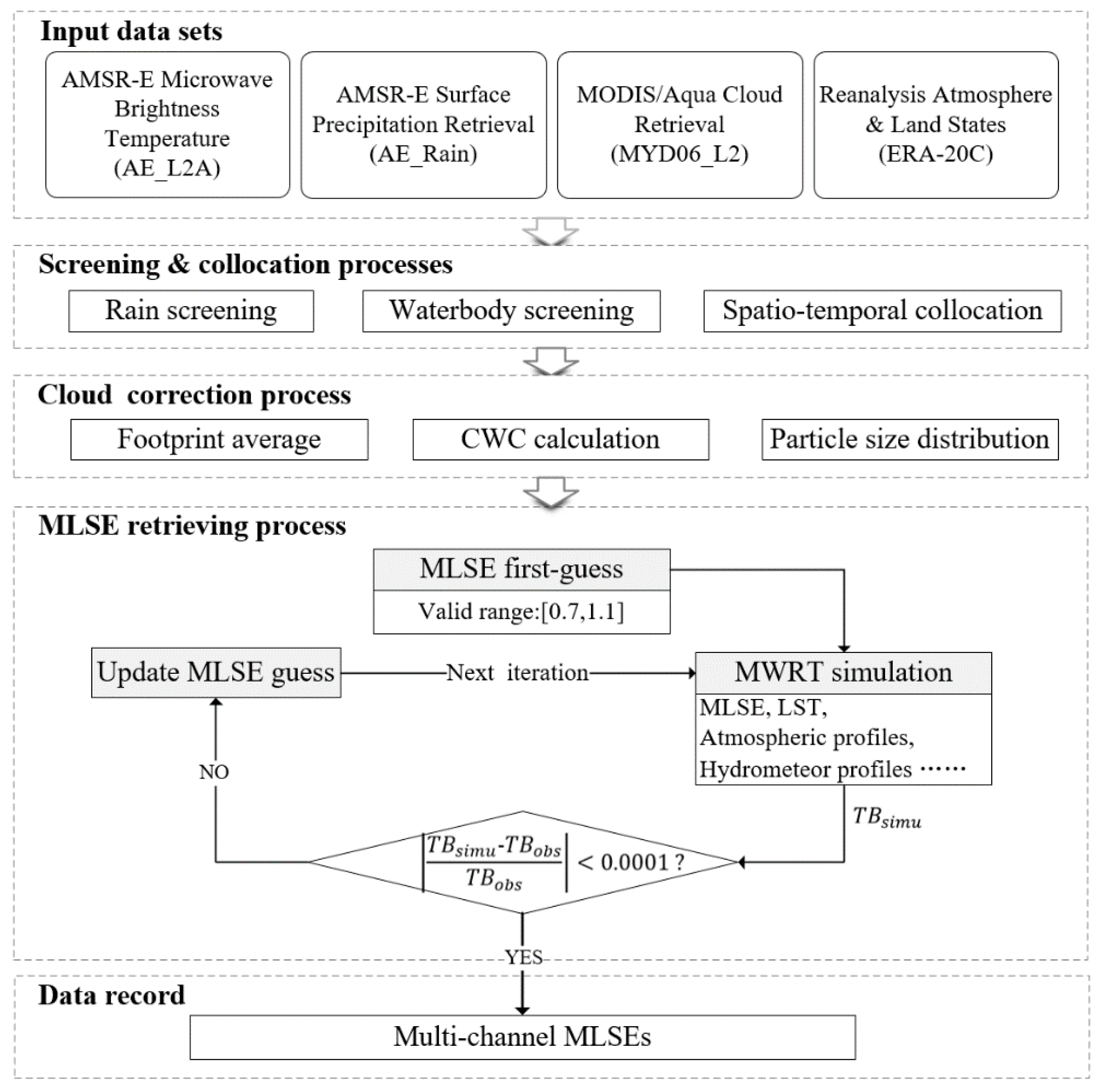
There are three main steps in the retrieval algorithm, as shown in Figure 2. First, those multi-source datasets are preprocessed in terms of spatiotemporal collocation and raining/water pixel screening. In this step, MODIS cloud observations located within a given AMSR-E footprint are averaged and the two 3-h ERA-20C estimations that bracket the overpass time of AMSR-E from the nearest gird are weighted averaged to the same spatiotemporal resolution. Second, cloud properties inside the AMSR-E footprints are converted to microwave radiative properties required in the MWRT simulation. Finally, multi-channel MLSEs are retrieved using an iterative retrieving core.
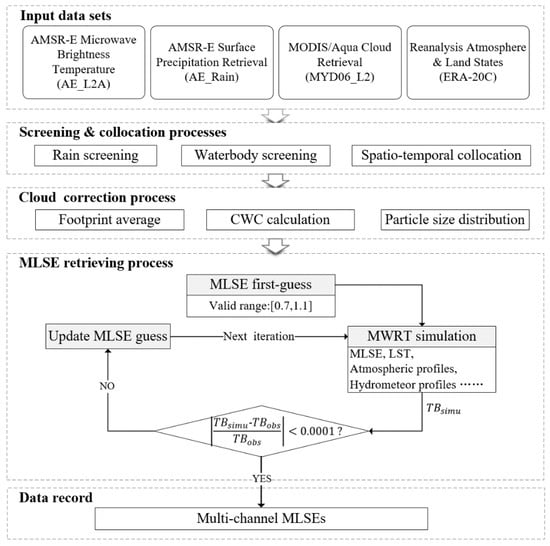
Figure 2.
The flow chart of MLSE retrieval in this study.
The visible and infrared observations of MODIS do not provide vertical resolution on cloud water distribution. In the MODIS cloud product, CWP is a column integral of cloud water content, CTP and CTT give cloud top information, and CPI indicates the thermal-dynamic phase of the cloud particles. In the preprocessing, we reconfigured a vertical cloud structure by virtue of ERA-20C layers assuming that cloud is located only at one single ERA layer determined with CTT (or CTP). In addition, this single layer was filled with homogeneous cloud water content (CWC) whose column integral was identical to the observed CWP. Hence, the CWC can be derived by CWCi = CWP/ΔHi, where CWCi and ΔHi are the cloud water content and thickness at ith ERA layer, respectively. CWCs of different phases (CPI) were calculated independently and seen as different clouds, which may be located at different layers even if coming from the same observation.
In the iterative core, assuming all Tb-controlling factors but the MLSE are known, the retrieving algorithm iteratively adjusts the approximation of MLSE until the forward simulated TOA Tb matches the real satellite measurement (with a precision 0.0001). For those satellite-observed TOA Tb that are greater (less) than the simulated Tb when MLSE guess is set to 1.1 (0.7), the retrieval is flagged as failed and is abandoned. Throughout the flow, retrieval is conducted individually upon different satellite footprints and channels. The final instantaneous retrieval record temporally spans from 1 January 2003 to 31 December 2010, and spatially covers the area 10°–55°N and 70°–145°E.
3.3. Validations of Inputs
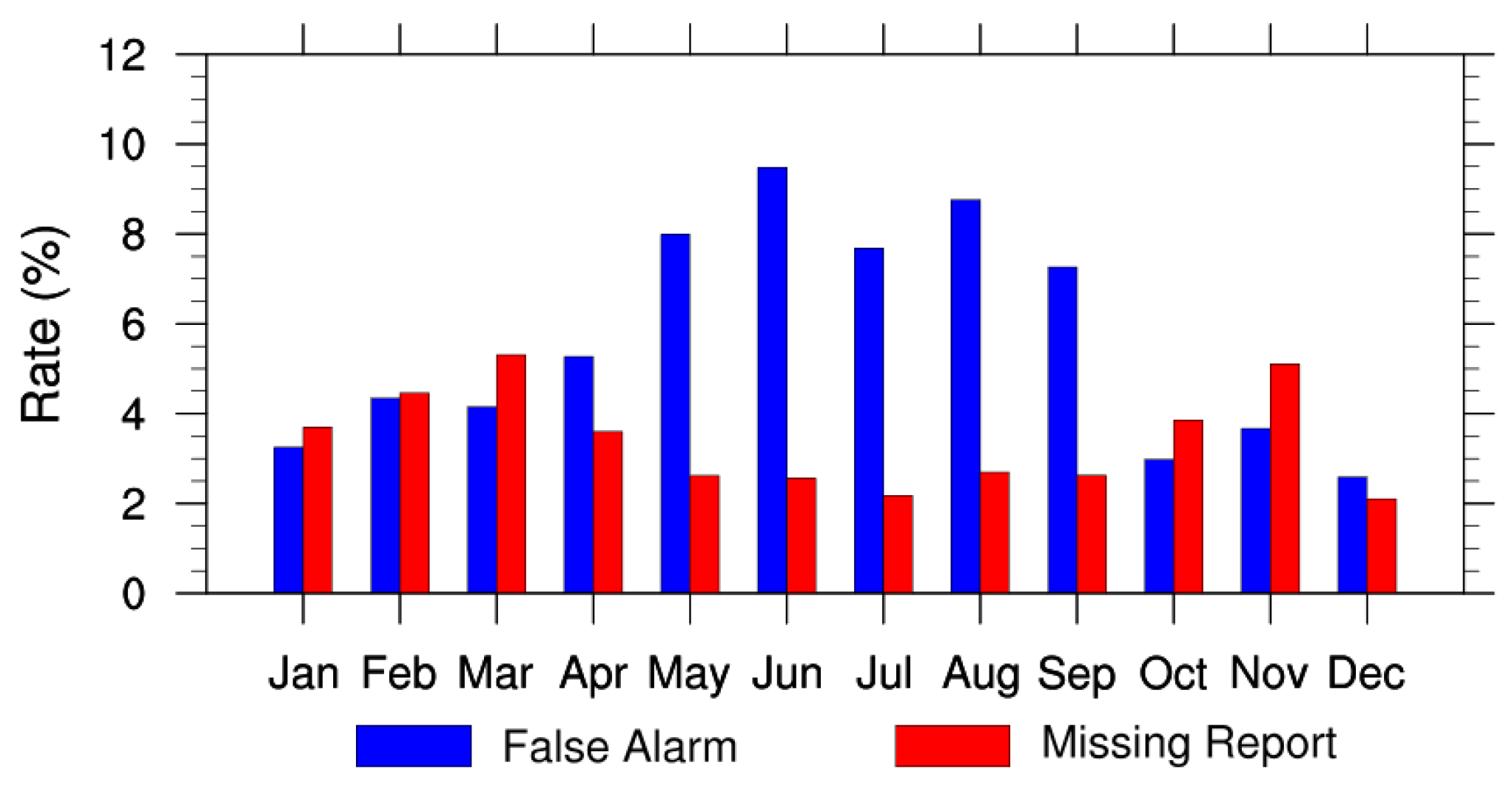
The AE_Rain rain flag used in the algorithm to filter out rainy pixels can directly impact the retrieval of MLSE because of the false alarm error and missing report in the product. The false alarm error causes sample loss but does no harm to final retrieval quality, while missing report may introduce samples contaminated by surface precipitation. To evaluate the data quality of AE_Rain, we calculated the false alarm rate (FAR) and missing report rate (MRR) as follows:
where NP is the number of matched pairs of the AE_Rain rain data and the in situ measurements. The box size for matching is 0.25° × 0.25°. We investigated the FAR and MRR of AE_Rain rain flag versus ground-based hourly precipitation [36] over meteorological stations throughout China in 2004. Results are shown in Figure 3. In summer, with more contiguous and persistent rainfalls, MRR reaches the lowest level; on the contrary, FAR reaches the highest. As for the whole year of 2004, MRR and FAR are lower than 6% and 10%, respectively.
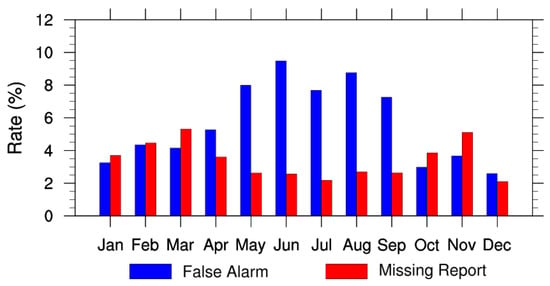
Figure 3.
The false alarm rate (FAR) and missing report rate (MRR) of the AE_Rain rainfall in 2004 using the in-situ measurements of rainfall data [36] as reference.
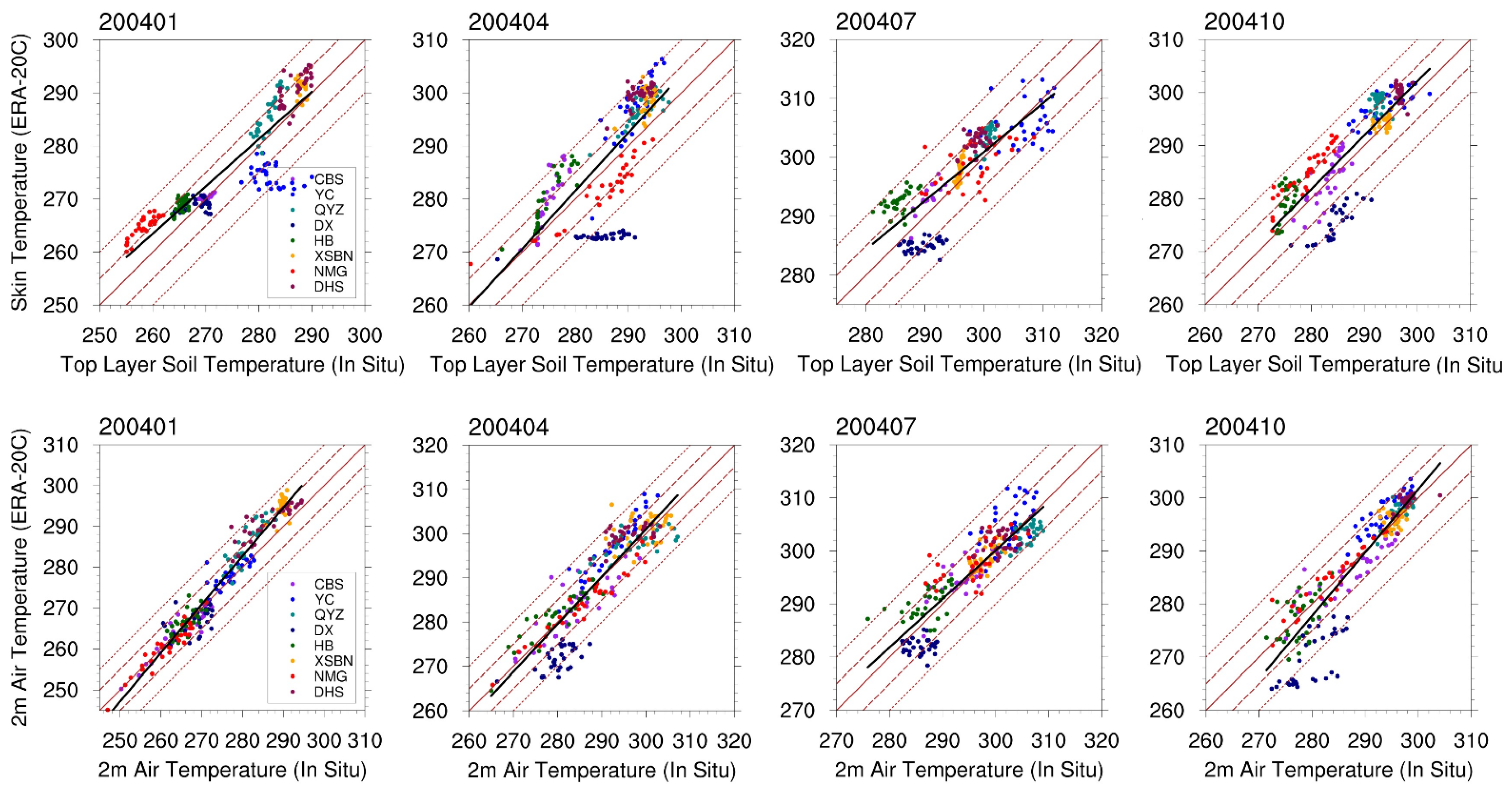
We also evaluated the data quality of the skin temperature, 2 m air temperature, and the near surface relative humidity from the ERA-20C reanalysis dataset against the in situ measurements from the 8 selected ChinaFlux sites (Table 1). We adopted the in situ measured topmost layer soil temperature to evaluate ERA skin temperature, and conducted comparisons of the 2 m air temperature and near surface relative humidity between the in situ measurements and the reanalysis estimations to indirectly evaluate the ERA-20C air temperature and humidity profiles. Comparisons were conducted during January, April, July, and October in 2004, and the root-mean-square error (RMSE), mean bias (MB), mean absolute error (MAE), and Pearson correlation coefficient (R) were examined for validation.
The results are shown in Figure 4, with the major statistical metrics summarized in Table 3. The surface skin temperature from ERA-20C generally shows high correlation and overall small difference with the ground observations from the 8 ChinaFlux sites. In the four inspected months, most of the samples lie within the ±10 K error lines, with the reported Pearson R ranging from 0.796 to 0.907, RMSE ranging from 4.01 to 6.83 K, and MAE ranging from 3.77 to 6.17 K, respectively. For the 2 m air temperatures, R values are higher than 0.88, and RMSE (2.91~5.04 K) and MAE (2.87~4.05 K) values are smaller than those of the skin temperatures in the four months. As for the near surface relative humidity, relatively lower correlation (R = 0.42~0.68) and larger difference (RMSE = 15.21~17.44%, MAE = 12.92~16.20%) are observed compared to those of the surface skin temperature and the 2 m air temperatures (Table 3). Previous studies reported that the uncertainty of the atmospheric water vapor profile can be as high as 20–25% [56,57,58]. However, such error caused less than 1% uncertainty for the retrieval of MLSE according to our sensitivity test (shown in Section 3.4). These results suggest that the reanalysis data of ERA-20C are accurate enough as model inputs for the retrieval of MLSE.
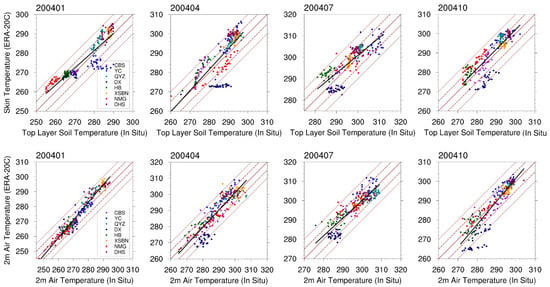
Figure 4.
Scatterplots of the skin temperature, 2 m air temperature from ERA-20C against data from the 8 ChinaFlux sites. Overlapped are biases of the ±5 K and ±10 K lines (red dashed), the 1:1 line (red solid), and the linear regression line (black solid).

Table 3.
Validation of skin temperature, 2 m air temperature, and near surface relative humidity from ERA-20C against in situ measurements at the 8 ChinaFlux sites.
3.4. Sensitivity Tests
We designed a series of tests to examine the sensitivities of MLSE retrieval to those key inputs, from which both the performances of MWRT and the impacts of input biases can be informed. These tests were conducted by introducing biases into these parameters individually and determining their impacts on the emissivity retrieval. TOA brightness temperature (Tb), surface skin temperature (SKT), air temperature (Ta) profile, and relative humidity (RH) profile were tested.
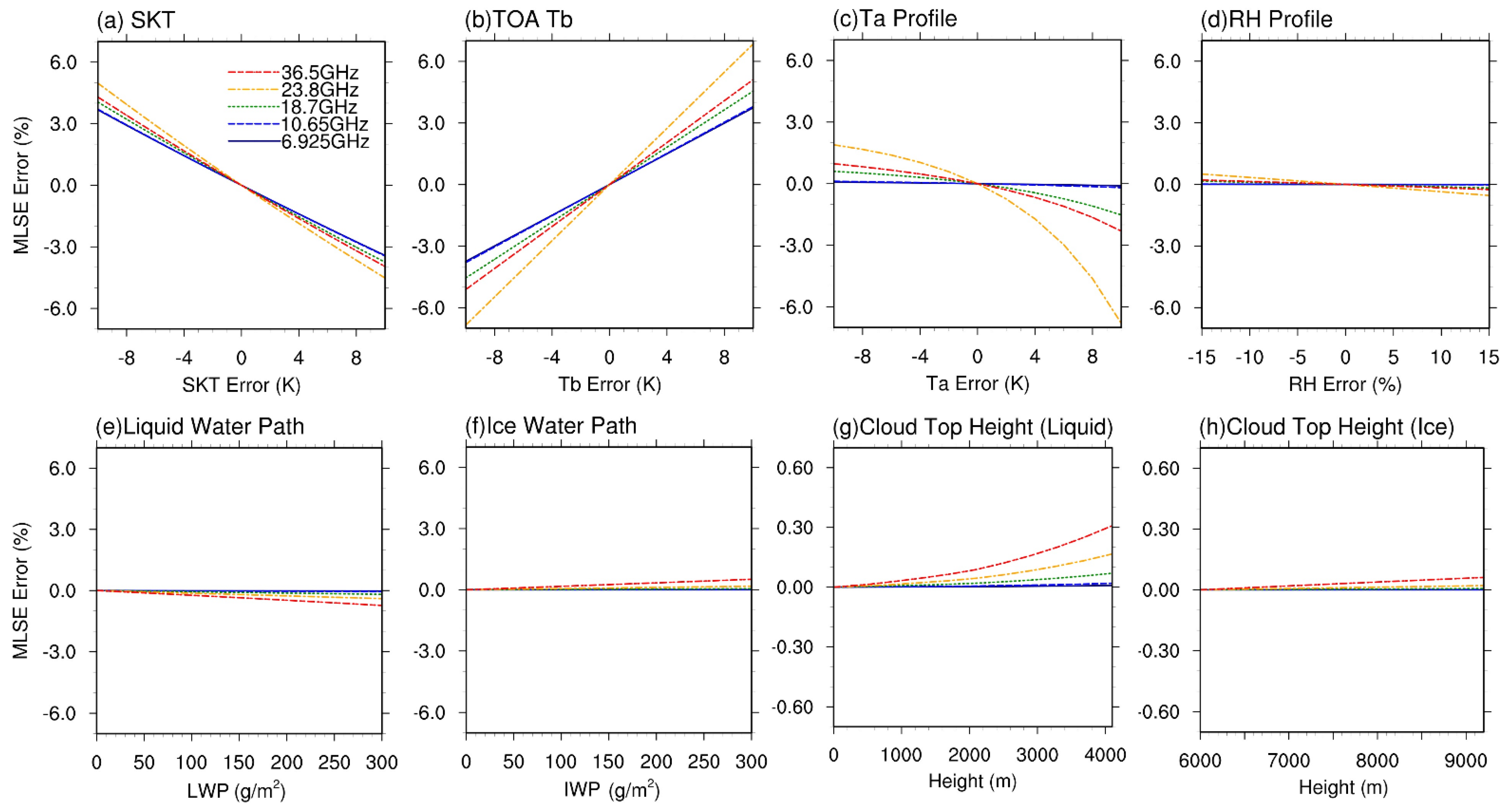
A series of perturbations from −10 to +10 K with an increment of 2 K were introduced into SKT and TOA Tb. Biases from −5 to +5 K with an increment of 1 K were introduced into the air temperature profile. Bias ranging from −15% to +15% with an increment of 3% was applied to relative humidity profile. All the emissivity retrievals with biased inputs were compared with the retrievals with unbiased inputs. Due to high sensitivity of MWRT to vapor and cloud water at 89.0 GHz, this frequency is not included in the present study. The results of sensitivity analysis are presented in Figure 5a–d.
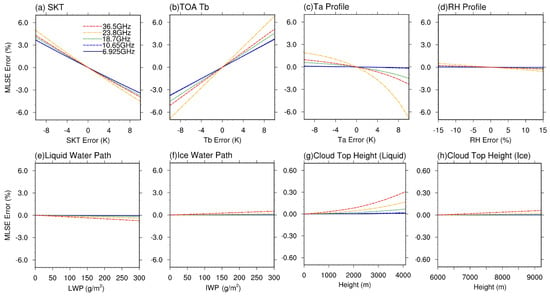
Figure 5.
Sensitivity analysis of MLSE to the error introduced by primary inputs: (a) skin temperature (SKT), (b) TOA brightness temperature (Tb), (c) air temperature (Ta) profile, (d) relative humidity (RH) profile, (e) liquid water path (LWP), (f) ice water path (IWP), and cloud top height ((g): liquid phase, (h): ice phase).
MLSE retrieval shows a linear response to the errors of SKT (TOA Tb) with a negative (positive) slope. A 10 K error (based on the validation study in Section 3.3) of SKT and TOA Tb will cause 3–7% error in MLSE depending on the frequencies. Except for MLSE at the water vapor absorption frequency of 23.8 GHz, MLSEs only show 1–2% error to 10% bias of air temperature (Figure 5c). A nonlinear sensitivity of MLSE at 23.8 GHz from −8% to 2% was found for the air temperature perturbation of 10%. Meanwhile, very low sensitivity (less 1%) of MLSE to 15% perturbation RH was found.
The emissivity sensitivity to cloud properties was tested by introducing biases to initial cloud water path and cloud height for the liquid and ice clouds, respectively. The initial cloud water path was set as 0 g/m2 for both liquid and ice clouds, and the initial cloud heights were set as 0 and 6 km for liquid and ice phase, respectively.
As Figure 5e–f shows, retrieved MLSE generally decreases with the cloud liquid water and increases with the cloud ice water. For example, a cloud liquid water path of 300 g/m2 will cause a negative error of −0.7% (~−0.007) and −0.2% (~−0.002) for MLSE at 36.5 and 18.7 GHz, respectively. On the other hand, such a value for the cloud ice water path will cause a positive error of 0.5% (~0.005) and 0.05% (~0.0005) for MLSE at the two frequencies, respectively. The MLSE nonlinearly increases with the increasing liquid cloud top height (Figure 5g); this is because the radiative contribution (absorption) of cloud liquid water is mainly controlled by cloud/air temperature, which is anti-correlated to the cloud top height. Comparatively, ice cloud top height (Figure 5h) exerts very weak influence on MLSE estimation.
4. Results
4.1. Retrieval of Instantaneous MLSE
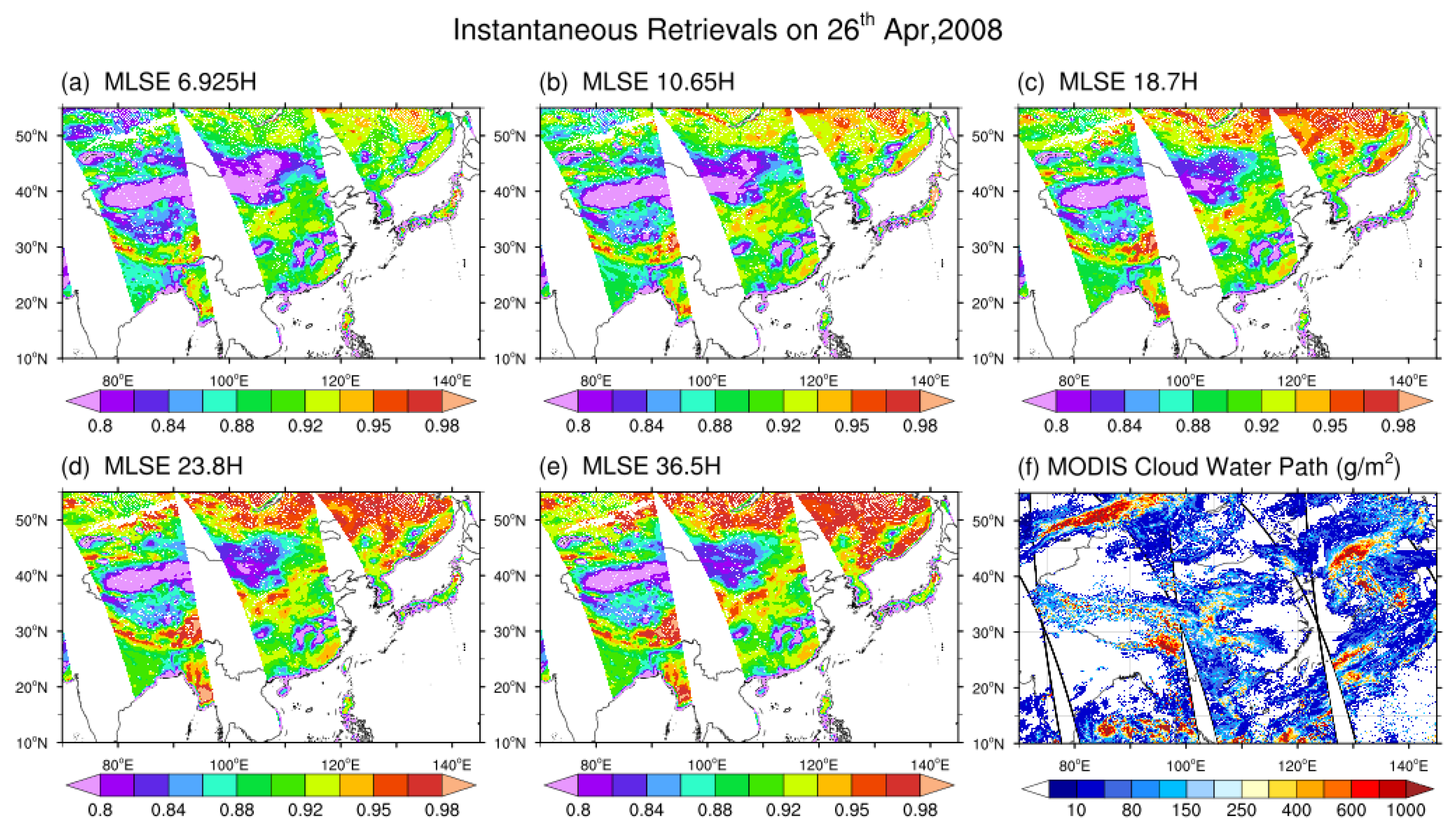
Figure 6 shows a case for the retrieval of MLSE using the instantaneous satellite observation on 26 April 2008 in the study area along with the instantaneous MODIS CWP. We mainly focus on the horizontal polarization composition for its stronger sensitivity to the surface soil moisture and vegetation water content [38]. In this case, 64.12% of the land area within the Aqua AMSR-E swaths is covered by clouds, and we successfully retrieved MLSEs under both clear and cloudy skies covering 90.04% of the total land area in the Aqua AMSR-E swaths. If we exclude all cloudy pixels, we can only retrieve MLSE over 28.79% of the land area.
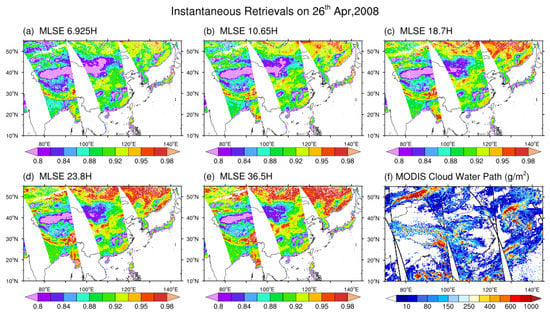
Figure 6.
Instantaneous multi-channel MLSE (horizontal polarization) retrieval on 26 April 2008, and the simultaneous MODIS cloud water path (CWP) retrieval in the studying area. (a) MLSE, (b) MLSE, (c) MLSE, (d) MLSE, (e) MLSE, (f) MODIS.
There is no significant residue of cloud texture from the instantaneous retrieval pattern in this case when MLSE shows smooth transition from the edge of the cloud (Figure 6f) to the neighboring cloudy-free areas, which indicates that the contribution from the cloud to the upwelling radiation has been properly corrected in our algorithm.
4.2. Spatial Distribution of MLSE
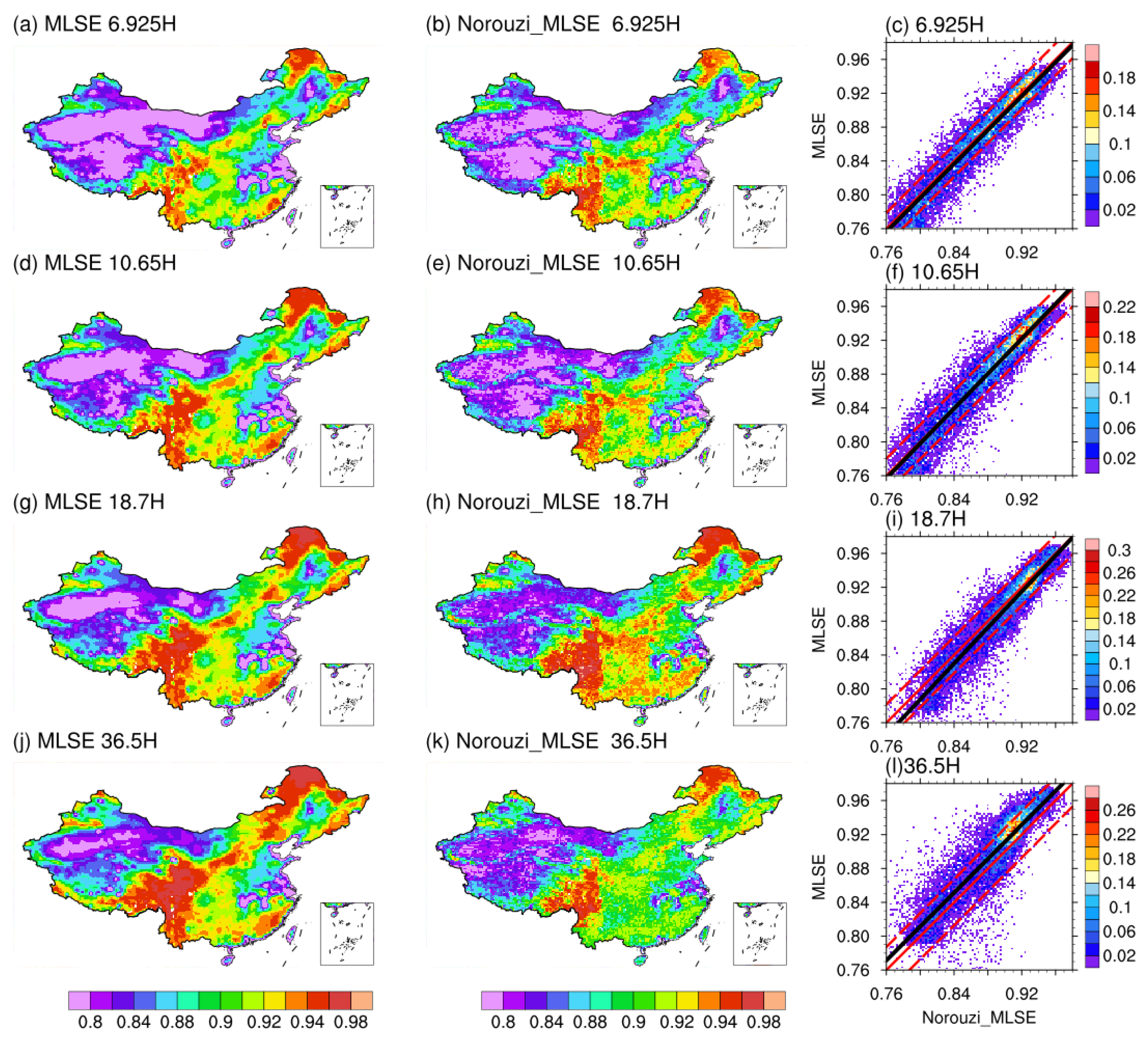
We evaluated our MLSE retrieved in this study by comparing its spatial distribution with AMSR-E MLSE product of Norouzi_MLSE during summer (JJA) in 2003. As shown in Figure 7, the spatial distributions of MLSE at the four frequencies of 6.925, 10.65, 18.7, and 36.5 GHz are highly consistent between the two products over China. Specifically, in southeastern China, MLSE is generally higher than in northwestern China, and considerably high MLSE is shown along the Qinling-Taihang Mountains and the eastern edge of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. On the contrary, low MLSE (i.e., <0.9) is observed in desert areas such as in the Taklimakan desert and the western Inner Mongolian desert, while river basins, agricultural areas, and coastal areas feature low to moderate MLSEs. Moderate to high MLSEs usually appear over regions that are densely vegetated, for example, in the southeast and northeast parts of China. Similar spatial patterns of microwave emissivity are also presented in the work of Prigent et al. [59], where emissivity features were investigated in typical surface types globally. Quantitative analyses further show that the spatial correlation coefficients (Rs) between our MLSE and the Norouzi_MLSE are 0.85~0.95 for the horizontal polarization and 0.67~0.73 for the vertical polarization, with low RMSEs ranging between 0.019–0.027 and between 0.017–0.02, respectively (Table 4). Corresponding scatter plots between the two products (Figure 7) show that most of the samples converge around the 1:1 line, with the mean absolute errors (MAEs) less than 0.022 for both the horizontal and vertical polarizations. Similar high consistency between the two products is also found during winter (DJF) in 2003 (Figure S1 and Table S1 in Supplementary file).
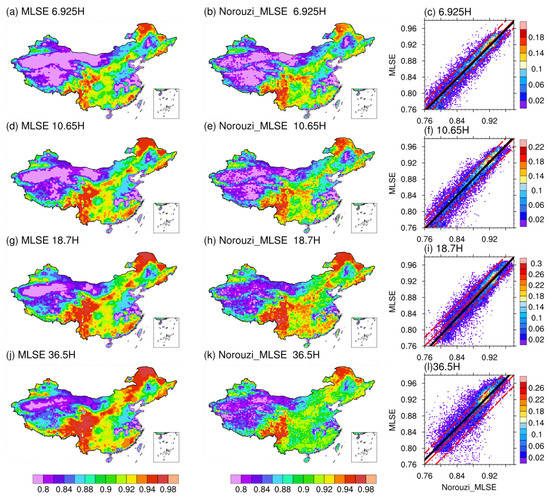
Figure 7.
Spatial distributions (0.25° × 0.25°) of mean MLSE retrieved in this study (a,d,g,j) and those from the No-rouzi_MLSE product (b,e,h,k) during summer in 2003, and the corresponding scatter plots between them (c,f,i,l). From top to bottom: the spatial distributions of MLSE at 6.925 H, 10.65 H, 18.7 H, and 36.5 H, respectively. Overlapped in the scatter plots are the RMSE lines (red dashed), 1:1 line (red solid), and the linear regression line (black solid).

Table 4.
Statistical metrics of comparison of MLSE derived in our study with those from Norouzi_MLSE in China during summer (JJA) in 2003.
However, discrepancies are noticeable for the absolute values of MLSE between the two products. For example, MLSE derived in our study is generally higher in western Tibetan Plateau but is lower in Qinling Mountains compared to the Norouzi_MLSE product. In addition, our MLSEs are systematic higher than those in Norouzi_MLSE at 36.5 GHz, which is found to be due to the ~2 K bias of atmosphere brightness temperatures between the two version datasets of AE_L2A that are used in the MLSE retrieval (Figure S4). The sensitivity test (Figure 5b) and the scatterplot at 36.5 GHz (Figure 7l) showed that such a bias can cause a difference of ~0.007 of MLSE between them.
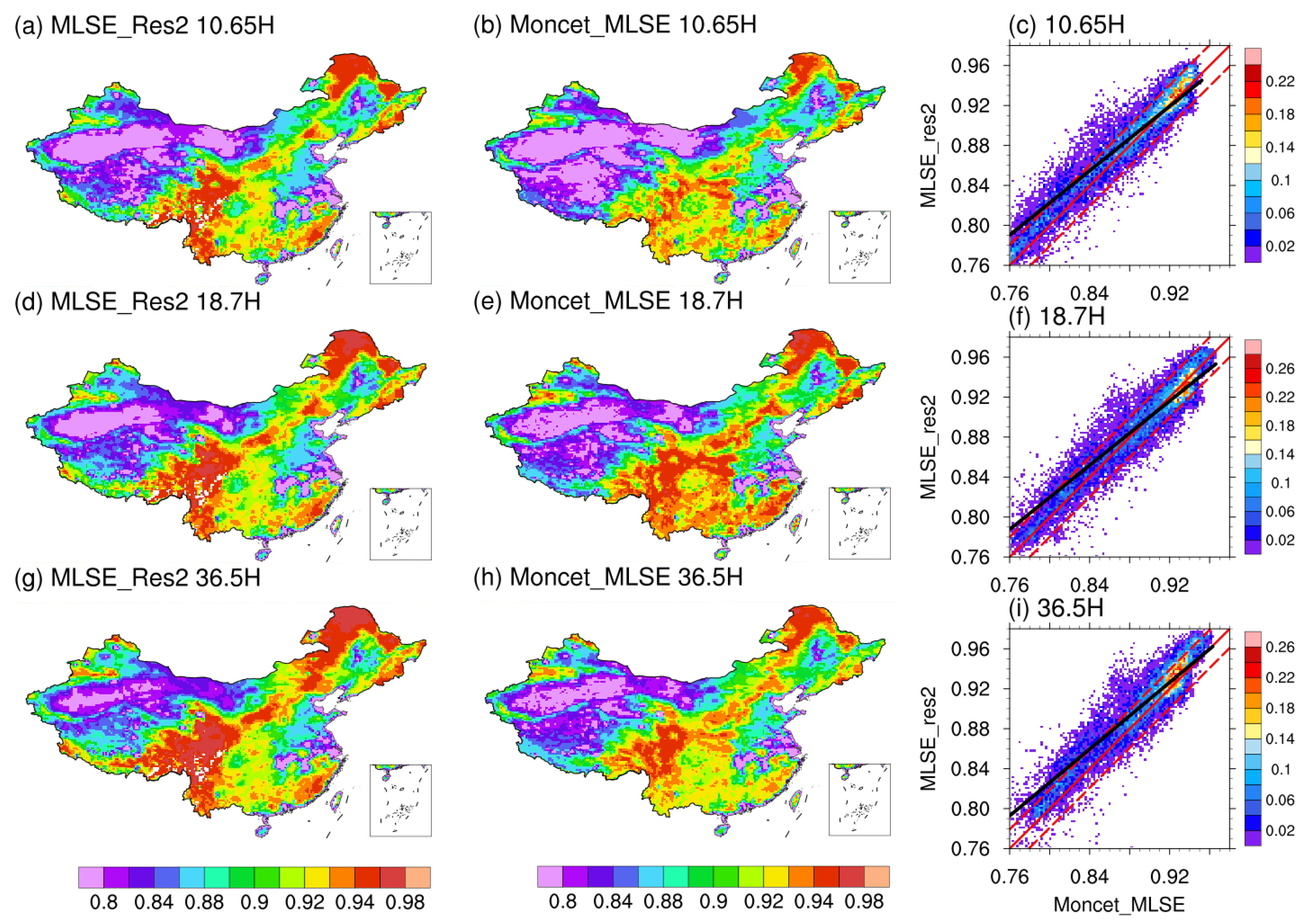
We also evaluated our MLSE by comparing MLSE_Res2 with Moncet_MLSE at three frequencies of 10.65, 18.7, and 36.5 GHz in our study region. Similar to the correlation with Norouzi_MLSE, our MLSE showed high consistency with the Moncet_MLSE product in spatial distribution during the summer in 2003, and high spatial correlations of R ≥ 0.838/0.935 and low values of MAE ≤ 0.017/0.016 were observed for the vertical/horizontal component of MLSE (Figure 8 and Table 5). As for the comparison with Moncet_MLSE during winter in 2003, the results are similar to those during the summer in 2003 (Figure S2 and Table S2).
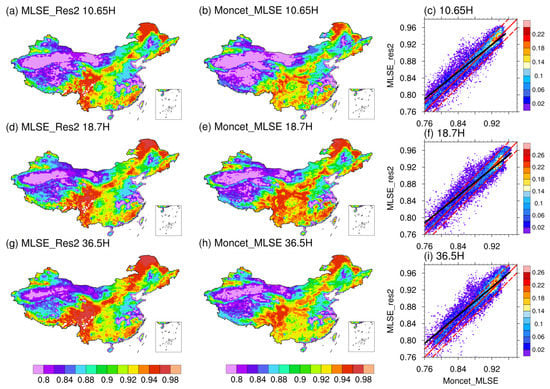
Figure 8.
The same as Figure 7, but for comparison between MLSE_Res2 and Moncet_MLSE at 10.65 H (a,d,g), 18.7 H (b,e,h), and 36.5 H (c,f,i).

Table 5.
Statistical metrics of comparison of MLSE between MLSE_Res2 and Moncet_MLSE in China during summer 2003.
4.3. Seasonal Variation and Potential Controlling Factors of MLSE
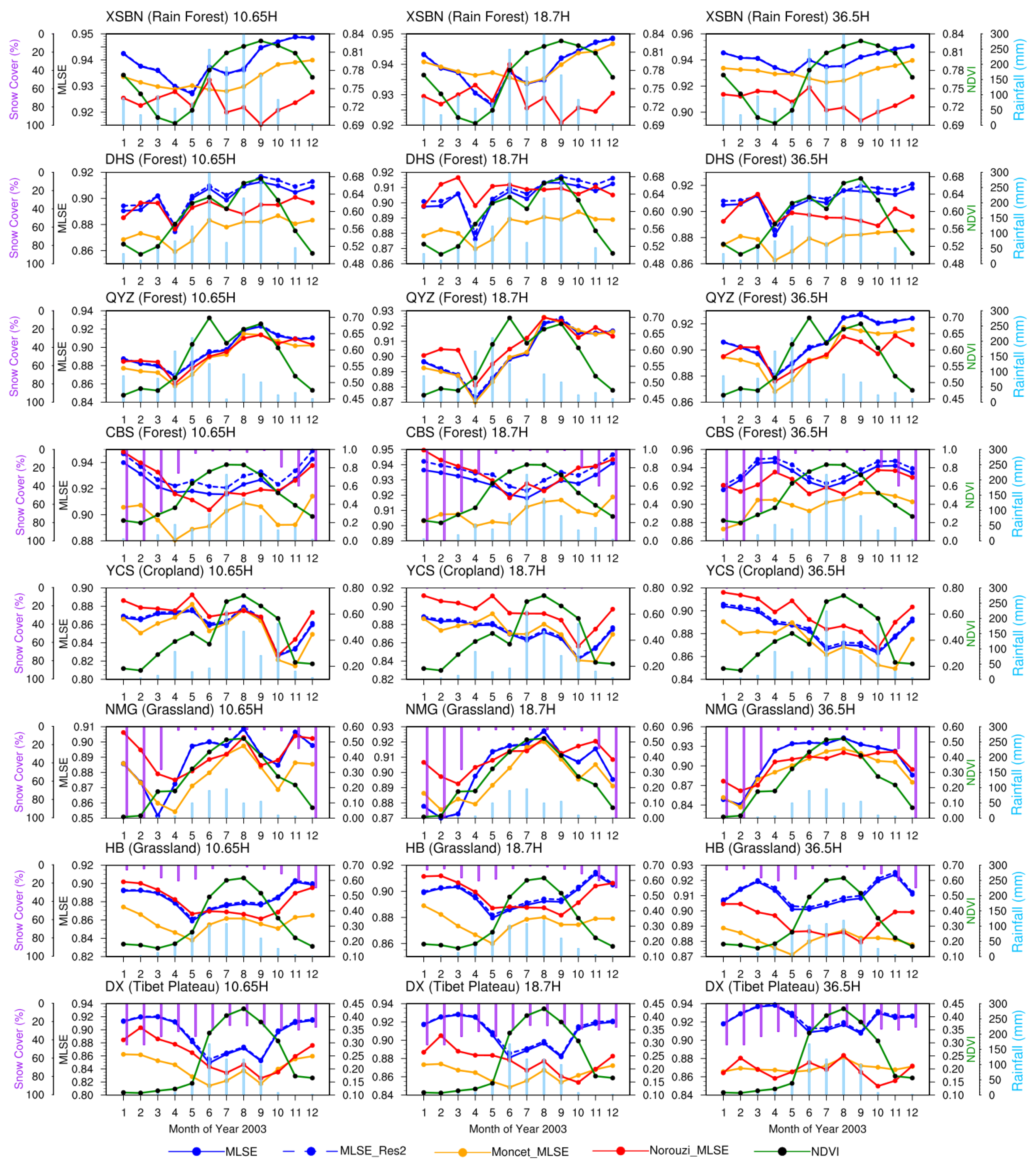
Figure 9 shows the seasonal variations of MLSE from the three emissivity products (along with MLSE_Res2) in 2003 at 8 ChinaFlux sites (see Table 1). To examine the potential influence of vegetation, rainfall, and snow on MLSE at those sites, we also showed the time series of MODIS NDVI, GPCC surface rainfall, and MODIS snow cover in Figure 9 and the correlations in Table 6. Overall, similar seasonal trends are presented among all of the three MLSE products, though MLSE from Moncet_MLSE is overall lower than that retrieved in this study and in the Norouzi_MLSE product. Different MLSE products of similar land types exhibit comparable dynamic ranges.
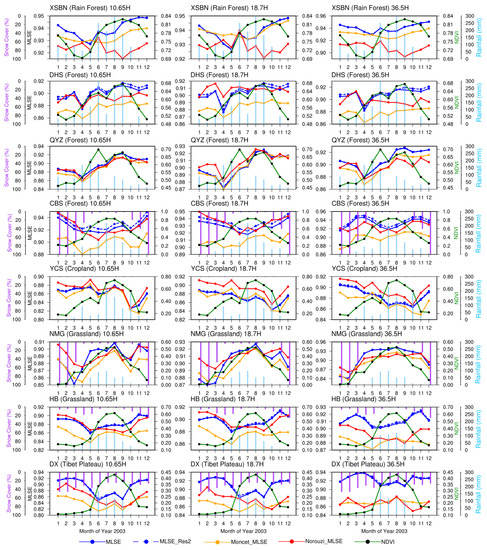
Figure 9.
Seasonal variations of four AMSR-E emissivity products (horizontal polarization): MLSE (blue solid line) in this study, MLSE_Res2 in this study (blue dashed line), Moncet’s MLSE (orange solid line), and Norouzi’s MLSE (red solid line) at the 8 ChinaFlux sites in 2003, along with the MODIS NDVI (black dotted green solid line), GPCC rainfall (sky blue bars) and MODIS snow cover (purple bars).

Table 6.
Temporal correlation coefficient (R) of MLSE with MODIS NDVI and GPCC rainfall.
The XSBN is the only tropical site in the 8 ChinaFlux sites where a rainforest type dominates. At this site (the first row in Figure 9), our MLSEs exhibit a weak seasonal amplitude (<0.025) at all three frequencies. The minimum values occur in spring when NDVI is relatively low and rainfall is becoming more and more frequent. For the discrepancies, our MLSEs are closer to Moncet_MLSE (difference < 0.03) at lower frequencies. The differences between our MLSE and Norouzi_MLSE are the greatest in autumn. The DHS and QYZ sites are both subtropical sites that feature an evergreen broad-leaf forest type. Generally, medium seasonal variations and amplitude (<0.05) are found in these two sites. Moncet_MLSE is found systematically to be lower than the other two products in the DHS site. The MLSE variations at the three southern forest-type sites above are mainly dominated by the seasonal growth and decline of vegetation. As shown in Table 6, the correlations of MLSE and NDVI at these three sites are high, especially for 10.65 GHz. As for rainfall, its influence at the DHS site is very weak, while at the XSBN and QYZ sites, the significant negative Rs (MLSE-Rainfall) indicate evident suppression effects on MLSE. For example, MLSEs are lower in spring and summer when rainfall is frequent; that rainfall acts as a perturbation in the MLSE seasonal variations.
The CBS is a mixed forest site at relatively high latitude (41.40° N, see Table 1). At this site, the seasonal variations and magnitudes of MLSEs in our product agree very well with Norouzi_MLSE (the fourth row in Figure 9). At 10.65 and 18.7 GHz, the minimal MLSE appears in summer, during which rainfall and NDVI reach their peak values, and high MLSE is shown in winter due to the relatively dry surface condition. The remarkable negative Rs in Table 6 also prove the point that rainfall exerts a key impact on MLSE at this site. At 36.5 GHz, decreases in MLSE are pronounced before April and after October; this likely correlates with the occurrence of snow in these months. The snow cover over land scatters and weakens the upwelling Tbs at 36.5 GHz in winter, while at lower frequencies, this effect is weaker [59,60,61]. Similar phenomena can also be seen in the other snow-impacted sites.
At the crop site of YCS, the peak values of MLSEs in the three products appear in May and August, when NDVI reaches its peak values as well, and this is exactly one month delayed from the peaks of rainfall. The minimum values of MLSE appear in October/November, followed by an increase until January when NDVI and rainfall are minimal. At that time, the MLSE is more related to the dry bare soil. Those temporal variations could be related to anthropogenic activities such as irrigation and harvest. For example, the sharp decline of NDVI and MLSEs from May to June coincides with the winter wheat harvest practiced in this region.
The NMG site is located in a semiarid area in northern China and is dominated by grass. At this site, MLSEs from the three products agree well in terms of magnitudes and seasonal variations (Figure 9). Significant positive correlations are observed with the NDVI and rainfall in spring, summer, and fall seasons, which implies that the impact is dominated by vegetation rather than soil moisture. As the vegetation declines quickly in fall, the end of rainy season leads to a dry surface condition, thus the emissivity increases in this period. In winter, all frequencies are impacted by snowfall, leading to a decrease of MLSEs.
The HB and DX sites are located in the Tibetan Plateau, and the dominant land cover type is grassland. These two sites witness the most remarkable discrepancies among three products. At the HB site, in months where snow is present, the MLSEs are evidently lower than in the surrounding months even at lower frequencies. This may happen due to heavy snow, since impact of snow is highly related to the relative grain size with respect to wavelength and the metamorphism [59]. At the DX site, MLSE values retrieved in this study are higher than those from the Moncet_MLSE and Norouzi_MLSE products.
4.4. Comparison with Microwave Vegetation Optical Depth (VOD)
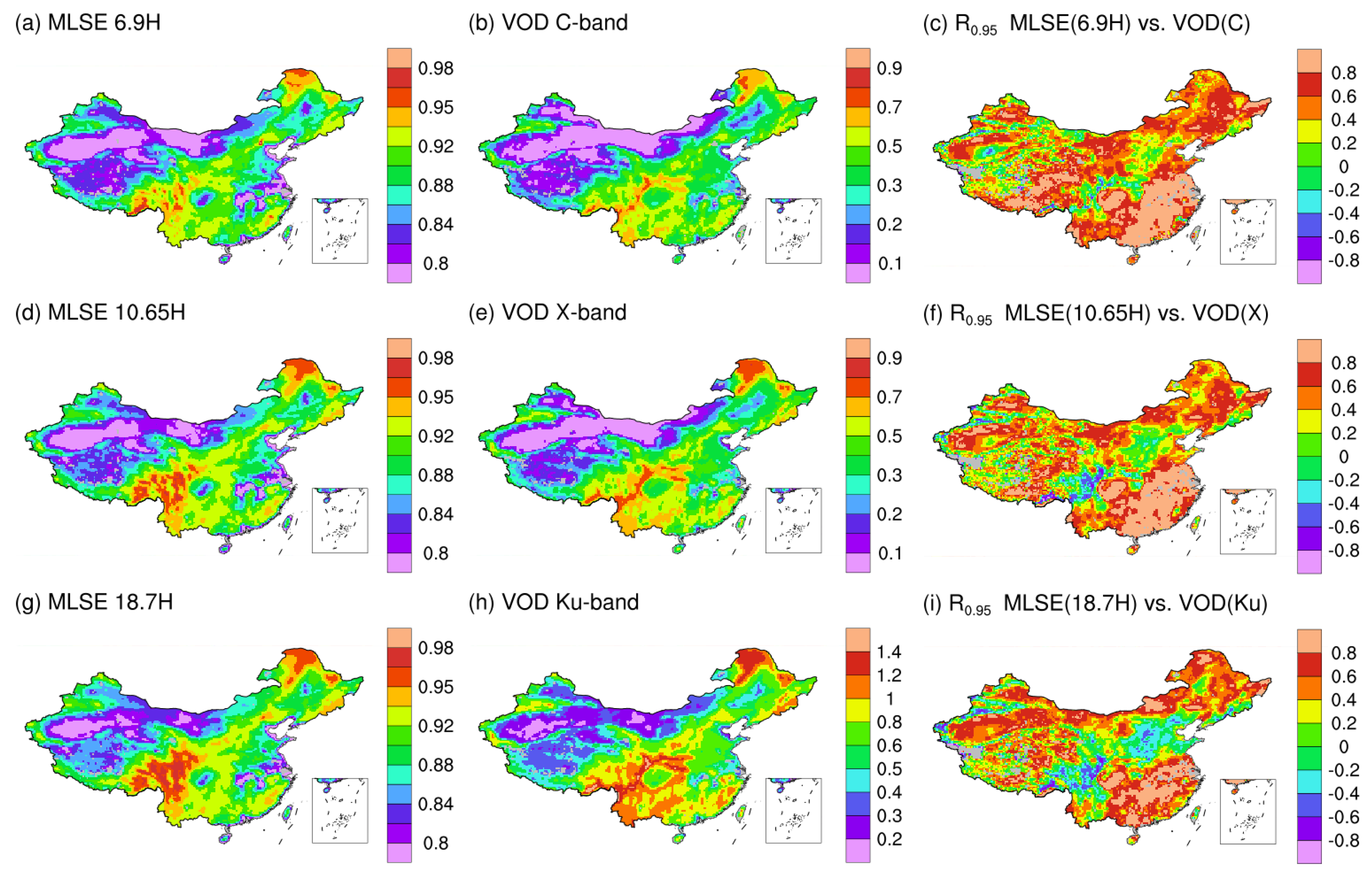
To investigate the performance of our MLSE under all-weather conditions, we compared it with the newly released dataset vegetation optical depth (VOD) climate archive (VODCA) [38] on a monthly scale. Figure 10 shows the spatial distributions of mean MLSE and mean VOD during 2003–2010. As the figure shows, the spatial distributions of MLSEs at 6.9H, 10.65H, and 18.7H are highly consistent with that of the VOD at C-, X-, and Ku-bands, respectively. This agree well with the findings of Owe et al. [62]. High MLSE and VOD are found in forests distributed in areas in the south and northeast China, while low MLSE and VOD are found in the deserts and sparsely vegetated areas in northwestern China. As for areas with abundant wetlands and agricultural lands, low to moderate MLSE and VOD are observed.
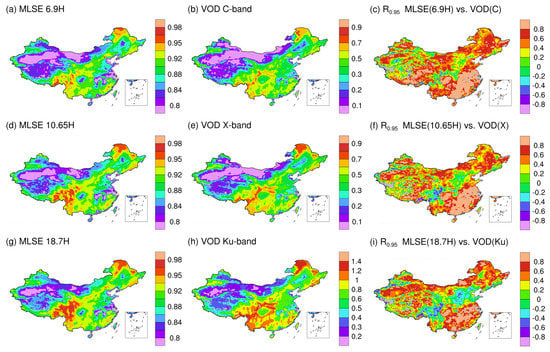
Figure 10.
Spatial distributions of mean MLSEs at 6.9, 10.65 and 18.7 GHz (horizontal polarizations, (a,d,g), and mean VODCA VOD at C-, X- and Ku-bands (b,e,h), and corresponding correlation coefficients (c,f,i) between the monthly mean MLSEs and VOD during 2003–2010.
Correlation analysis further shows that strong positive correlations are found between MLSEs and VODs, with Pearson R generally larger than 0.6 in most areas except for those along the Qinling-Taihang Mountains and in the eastern edge of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Specifically, the Pearson R is high in southeast and northeast China where vegetation is very dense and climate is moist, and in western China where vegetation is sparse and the climate is dry. However, in transition areas between the moist and arid regions (the Qinling-Taihang Mountains), correlation between MLSE and VOD is weak. This can be explained as follows. First, the VOD is retrieved using the satellite-derived surface temperature at Ka-band (37.5 GHz) [38]. By using a single channel in the retrieval, VOD may have very large uncertainties over barren and sparsely vegetated areas, especially when the surface roughness is high [63]. Second, VOD is retrieved at night to minimize surface temperature-related errors, while our MLSE is retrieved during daytime, and this may also cause some discrepancies between MLSE and VODCA VOD.
5. Discussion
The comparison between our MLSE and the other two AMSR-E products of Norouzi_MLSE and Moncet_MLSE achieve favorable agreements on spatial correlations and seasonal variations. Nevertheless, noticeable discrepancies are found. In this section, we compare our results with previous works and attempt to explain the remarkable differences by taking into account error sources.
5.1. Comparing with Similar Works in the Literature
In this study, we compare our MLSE with Norouzi_MLSE and Moncet_MLSE in Section 4.2; our MLSEs show good consistencies in terms of spatial correlations with both reference datasets. As for the “bias”, the comparison with Norouzi_MLSE shows RMSE of up to 0.027 in summer and 0.032 in winter. The RMSE between our MLSE and Moncet_MLSE is less than 0.021 in summer and 0.022 in winter. For different surface types, Figure 9 shows differences of up to 0.03 between our MLSE and any others over forest types (i.e., XSBN, DHS, QYZ, and CBS) at lower frequencies, and differences less than 0.04 over short vegetated types (i.e., YCS, NMG) on a monthly scale. Ferraro et al. [8] studied several MLSEs estimated from various sensors to investigate the consistencies among existing retrieving schemes. They found that estimates of MLSE vary by as much as 3% (~0.03) on a monthly mean scale and are even greater for any instantaneous estimation. For the 36.5 GHz, the differences among the techniques can be up to 5% (~0.05). In a quantitative study, Tian et al. [64] reported that emissivity retrieved from various sensors agree better at lower frequencies, with differences ranging 1~7% over rainforest. In a similar study, Norouzi et al. [65] found that the standard deviation of various emissivity products is lowest (less than 0.01) in rain forest types and highest at northern latitudes; the deviations are above 0.04 for AMSR-E and SSM/I and around 0.03 for WindSat. All the differences reported in these literatures are quite close to our results. This demonstrate a reasonable quality of our estimations in terms of comparing with similar works.
5.2. Error Sources
Surface skin temperature. As seen in the input evaluations and sensitivity analysis in Section 3, the skin temperature is the biggest error source in our retrieval algorithm. As reported, 10 K error in SKT may result in ~4% (~0.04) at lower frequencies. This is comparable to Yang and Weng [66], who studied the sensitivities of surface emissivity to the errors of brightness temperature, atmospheric transmittance, and surface temperature. In this study, uncertainty of SKT is responsible for the noticeable discrepancies with Norouzi_MLSE and Moncet_MLSE. For example, MLSE derived in our study is generally higher in the western Tibetan Plateau but is lower in the Qinling Mountains compared to the other two products. This is mainly because of the discrepancies among skin temperatures of ISCCP (used in the retrieval of Norouzi_MLSE), MODIS (used in the retrieval of Moncet_MLSE), and ERA-20C (used in this study) over the above two regions (Figure S3), as the differences of SKT between the two products can be up to 20 K and low to −6 K in the two regions, respectively. It is hard to tell which temperature source is more accurate, but SKT from ISCCP and MODIS are available only under clear sky, thus tend to be warmer than ERA-20C. The big SKT difference in the Tibetan plateau also accounts for the large discrepancies between our MLSE and the other two at the DX and HB sites (Figure 9).
Brightness temperature. TOA Tb is another big error source reported in our sensitivity analysis. Tb error is responsible for the remarkable differences found at 36.5 GHz in spatial patterns (Figure 7 and Figure 8) and magnitudes (Figure 9) between our MLSE and the other twos. The version difference is presented in Figure S4, where version 3 of AE_L2A Tb was adopted in our algorithm while version 2 (no longer public available) was used in Norouzi and Moncet’s works. The newer version 3 is up to 2 K higher at 36.5 GHz than the older one over forest regions. According to above sensitivity test, such bias can lead to ~+0.007 difference bias to the MLSE estimation.
Topography effect. Noticeably high values are found in the belt along the Qinling-Taihang mountains, the eastern edge of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and the Daxing’an Mountains. Such continuous high values along mountains are widely found elsewhere in other works [59,67]. The potential reason for this is the relief effect, which causes an increase at H polarization as well as the view angle variations [68]. The relevant investigations are ongoing in our team.
5.3. Potential Applications
The potential applications of the results of this study are reflected in at least two aspects. First, the study of passive microwave remote sensing of precipitation over land can be improved [8,10]. At present, the study is generally based on Bayesian inversion framework (e.g., Kummerow et al. [69]), and the influence of land surface emission is completely ignored in the calculation of conditional probability. With the improvement in the accuracy of MLSE retrieval, it is possible to take the influence of surface microwave emission into consideration, thereby improving the accuracy of precipitation retrieval over land. As rains are inevitably accompanied by clouds, the MLSE retrievals under cloud conditions in this study are expected have good applications. Second, the inversion of key parameters of land and its interaction with the atmosphere can be improved. The rate of water vapor exchange and carbon exchange processes between the land and the atmosphere strongly depends on the characteristics of the vegetation water content. The MLSE results in this study were successfully used in the retrieval of vegetation water content [70], the estimation of water vapor evapotranspiration rate in mid-latitude forests [15,16,71], and the volatile organic gas emissions [17]. The influence of clouds on the evapotranspiration process has also been studied using MLSE-based products [72]. The above studies have proved that the all-weather MLSE obtained by this research has great application prospects in the field of vegetation-atmosphere interaction research.
6. Summary and Conclusions
In this study, we developed an algorithm to retrieve satellite microwave land surface emissivity (MLSE) in China using passive microwave measurements from Aqua AMSR-E, cloud observations from Aqua MODIS, and atmosphere profiles from ERA-20C reanalysis. Compared with previous studies, our algorithm is able to directly retrieve MLSE under a cloudy sky by using simultaneous satellite observations of cloud, without relying on any other emissivity atlas or historic records. The introduction of MODIS cloud properties in our algorithm gives us the ability to estimate the cloud contributions to the upwelling microwave radiation.
The evaluations of skin temperature and air temperature as well as the near surface humidity are performed using the in-situ measurements from 8 ChinaFlux sites. High correlations (R) of 0.796, 0.886, and 0.420 are identified for the surface skin temperature, 2 m air temperature, and the relative humidity, respectively, corresponding with a mean bias of 6.17 K, 4.05 K, 16.2%. Rain flag from AE_Rain is assessed using the in situ rainfall measurements, and reports a low false alarm rate (<10%) and missing report rate (<5%).
The sensitivity studies show that the retrieval of MLSE is greatly affected by the SKT (or Tbs at TOA) and air temperature, but is slightly affected by the cloud properties. Specifically, MLSE is linearly related to the bias of SKT (Tbs at TOA), with a negative (positive) slope found. A 10 K bias of SKT or Tbs at TOA can result in 4% (~0.04) or 7% (0.07) errors of MLSE at 23.5 GHz. For air temperature, a nonlinear increase of MLSE from −8% to 2% is found when the air temperature bias increases from −10% to 10%. The change in MLSE due to bias/uncertainty of cloud water path and cloud top temperature is less than 1%.
On a typical cloudy day with cloud fraction of 64%, our algorithm successfully retrieves MLSE over 90% of the satellite detected land area, while this is only 29% for the clear-sky algorithms. Based on the MLSE retrieved by our algorithm, the MLSE is high in southeast China and low in northwest China; and the highest MLSE is found in the Qinling-Taihang Mountains and the eastern edge of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau while the lowest MLSE (e.g., less than 0.9) are shown in the Xinjiang province (e.g., the Taklimakan Desert), western Inner Mongolia, and the Yangtze River delta. High heterogeneity of MLSE is revealed across China with moderate values in vegetated areas and low values in river basins, coast, and croplands such as the Yangtze River basin, Sichuan basin, and the northeast plain. For seasonal variations, MLSE is highly related to the seasonality of vegetation growth, rainfall, and snow cover.
The spatial distribution and seasonal cycle of MLSE retrieved in this study are generally consistent with the products developed by Norouzi et al. [26] and Moncet et al. [6]. The spatial correlation coefficients of our MLSE with the above two products range from 0.71 to 0.95, corresponding with the root mean square errors between 0.014 and 0.027, and the mean absolute errors between 0.012 and 0.02. The largest discrepancies of MLSE among those products are found to be contributed by the different land skin temperature data used in the algorithm. This issue is particularly serious in sparsely populated areas such as the Tibetan Plateau where few in situ measurements are available to validate reanalysis data or satellite estimation of surface temperature. In addition, our MLSE shows good agreement with the VODCA VOD [38] in moist and arid-semiarid regions.
This MLSE retrieving algorithm and the associated product are crucial complements to the previous techniques, which are unable to provide instantaneous MLSE retrievals under a cloudy sky. MLSE provides extended and successive perspectives on monitoring critical surface properties such as soil moisture and vegetation water content, and it has great potential for use in various applications. For example, used as dynamic surface background, MLSE can improve the accuracy of the physical algorithm in retrieving precipitation over land [8,10]. Additionally, this MLSE product can be used for forward model evaluations [9,73,74] and for ecological remote sensing, land-atmosphere energy exchange, and water cycle studies, as well as wildfire risk assessment.
However, some uncertainties still exist in the retrieval algorithm. Measures are expected in the future to improve this product, including the accuracy of land surface temperature and mitigating relief effects. Using in situ measurements of land surface temperature in densely populated areas and more research on collaborated modelling of topography effects may help to largely reduce those errors for the retrieval of MLSE, and this is undergoing in our lab.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/rs13193980/s1, Table S1: Statistical metrics of comparison of our MLSE with Norouzi_MLSE in China during winter (DJF) in 2003, Table S2: Statistical metrics of comparison of MLSE with MLSE_Res2 and Moncet_MLSE in China during winter (DJF) in 2003, Figure S1: The same as Figure 7, but for the comparisons during winter (DJF) in 2003, Figure S2: The same as Figure 8, but for the comparisons during winter (DJF) in 2003, Figure S3: Distributions of seasonal (summer, 2003) mean surface skin temperatures from ERA-20C reanalysis, ISCCP-DX estimations, MODS/Aqua satellite LST observations, Figure S4: Comparisons of the brightness temperatures at the top of atmosphere (TBTOA) from AE_L2A version 2 and version 3 on 26 April 2008.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.L. and Q.M.; data curation, J.H. and Y.F.; formal analysis, J.H. and R.L.; investigation, J.H. and Y.F.; methodology, R.L. and J.H.; resources, R.L. and Q.M.; software, J.H. and Y.F.; supervision, R.L.; visualization, J.H.; writing—original draft, J.H.; writing—review and editing, R.L., P.Z., Z.G. and S.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grants 2017YFC1501402 and 2018YFC1507401), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (Grants 41830104, 41675022, 41661144007), and the Jiangsu Provincial 2011 Pro-gram (Collaborative Innovation Center of Climate Change).
Data Availability Statement
Research data are available online (at http://rse.ustc.edu.cn, accessed on 14 August 2021).
Acknowledgments
The authors thank editors and anonymous reviewers for their critical and constructive suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Weng, F.; Yan, B.; Grody, N.C. A microwave land emissivity model. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2001, 106, 20115–20123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njoku, E.; Jackson, T.; Lakshmi, V.; Chan, T.; Nghiem, S. Soil moisture retrieval from AMSR-E. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.A.; Kimball, J.S.; McDonald, K.C.; Chan, S.T.K.; Njoku, E.G.; Oechel, W. Satellite Microwave Remote Sensing of Boreal and Arctic Soil Temperatures From AMSR-E. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 2004–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Q.; Lin, B.; Li, R. Remote Sensing Vegetation Hydrological States Using Passive Microwave Measurements. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2010, 3, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaby, F.T.; Moore, R.K.; Fung, A.K. Microwave Remote Sensing Active and Passive-Volume III: From Theory to Applications; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Moncet, J.-L.; Liang, P.; Galantowicz, J.F.; Lipton, A.E.; Uymin, G.; Prigent, C.; Grassotti, C. Land surface microwave emissivities derived from AMSR-E and MODIS measurements with advanced quality control. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2011, 116, D16104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baordo, F.; Geer, A.J. Assimilation of SSMIS humidity-sounding channels in all-sky conditions over land using a dynamic emissivity retrieval. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 142, 2854–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, R.; Peters-Lidard, C.; Hernandez, C.; Turk, F.J.; Aires, F.; Prigent, C.; Lin, X.; Boukabara, S.A.; Furuzawa, F.A.; Gopalan, K.; et al. An Evaluation of Microwave Land Surface Emissivities Over the Continental United States to Benefit GPM-Era Precipitation Algorithms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 51, 378–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, K.W.; Tian, Y.; Peters-Lidard, C.; Ringerud, S.; Kumar, S. Calibration to Improve Forward Model Simulation of Microwave Emissivity at GPM Frequencies Over the U.S. Southern Great Plains. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 1103–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, F.J.; Ringerud, S.E.; You, Y.; Camplani, A.; Casella, D.; Panegrossi, G.; Sanò, P.; Ebtehaj, A.; Guilloteau, C.; Utsumi, N.; et al. Adapting Passive Microwave-Based Precipitation Algorithms to Variable Microwave Land Surface Emissivity to Improve Precipitation Estimation from the GPM Constellation. J. Hydrometeorol. 2021, 22, 1755–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Q.; Lin, B. Determination of spring onset and growing season leaf development using satellite measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 104, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Q.; Lin, B. Remote sensing of evapotranspiration and carbon uptake at Harvard Forest. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owe, M.; De Jeu, R.; Holmes, T. Multisensor historical climatology of satellite-derived global land surface moisture. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2008, 113, F01002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigneron, J.-P.; Jackson, T.; O’Neill, P.; De Lannoy, G.; de Rosnay, P.; Walker, J.; Ferrazzoli, P.; Mironov, V.; Bircher, S.; Grant, J.; et al. Modelling the passive microwave signature from land surfaces: A review of recent results and application to the L-band SMOS & SMAP soil moisture retrieval algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 192, 238–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, R.; Min, Q.; Fu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, L.; Fu, Y. A three-source satellite algorithm for retrieving all-sky evapotranspiration rate using combined optical and microwave vegetation index at twenty AsiaFlux sites. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 235, 111463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, R.; Min, Q.; Zhang, L.; Yu, G.; Bergeron, Y. Estimation of Vegetation Latent Heat Flux over Three Forest Sites in ChinaFLUX using Satellite Microwave Vegetation Water Content Index. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, R.; Min, Q.; Bo, H.; Fu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Z. The Controlling Factors of Atmospheric Formaldehyde (HCHO) in Amazon as Seen from Satellite. Earth Space Sci. 2019, 6, 959–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forkel, M.; Dorigo, W.; Lasslop, G.; Teubner, I.; Chuvieco, E.; Thonicke, K. A data-driven approach to identify controls on global fire activity from satellite and climate observations (SOFIA V1). Geosci. Model Dev. 2017, 10, 4443–4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Wigneron, J.-P.; Xiao, Q.; Al-Yaari, A.; Wen, J.; Martin-StPaul, N.; Dupuy, J.-L.; Pimont, F.; Al Bitar, A.; Moran, R.F.; et al. Evaluation of microwave remote sensing for monitoring live fuel moisture content in the Mediterranean region. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 205, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigneron, J.-P.; Chanzy, A.; Calvet, J.-C.; Bruguier, N. A simple algorithm to retrieve soil moisture and vegetation biomass using passive microwave measurements over crop fields. Remote Sens. Environ. 1995, 51, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Van Dijk, A.; De Jeu, R.A.M.; Canadell, J.; McCabe, M.; Evans, J.; Wang, G. Recent reversal in loss of global terrestrial biomass. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2015, 5, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, M.; Wigneron, J.-P.; Chave, J.; Tagesson, T.; Penuelas, J.; Ciais, P.; Rasmussen, K.; Tian, F.; Mbow, C.; Al-Yaari, A.; et al. Satellite passive microwaves reveal recent climate-induced carbon losses in African drylands. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prigent, C.; Rossow, W.B.; Matthews, E. Microwave land surface emissivities estimated from SSM/I observations. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1997, 102, 21867–21890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Minnis, P. Temporal Variations of Land Surface Microwave Emissivities over the Atmospheric Radiation Measurement Program Southern Great Plains Site. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2000, 39, 1103–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbou, F.; Prigent, C.; Eymard, L.; Pardo, J.R. Microwave land emissivity calculations using AMSU measurements. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 948–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norouzi, H.; Temimi, M.; Rossow, W.B.; Pearl, C.; Azar, M.; Khanbilvardi, R. The sensitivity of land emissivity estimates from AMSR-E at C and X bands to surface properties. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 3577–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E.; Kanamitsu, M.; Baker, W.E. Global Numerical Weather Prediction at the National Meteorological Center. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1990, 71, 1410–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossow, W.B.; Schiffer, R.A. ISCCP Cloud Data Products. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1991, 72, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossow, W.B.; Schiffer, R.A. Advances in understanding clouds from ISCCP. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1999, 80, 2261–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aires, F.; Prigent, C.; Rossow, W.B.; Rothstein, M. A new neural network approach including first guess for retrieval of atmospheric water vapor, cloud liquid water path, surface temperature, and emissivities over land from satellite microwave observations. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2001, 106, 14887–14907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashcroft, P.; Wentz, F.J. AMSR-E/Aqua L2A Global Swath Spatially-Resampled Brightness Temperatures; Version 3; NASA National Snow and Ice Data Center Distributed Active Archive Center: Boulder, CO, USA, 2013. [CrossRef]
- Ashcroft, P.; Wentz, F.J. Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document (ATBD) AMSR Level 2A Algorithm; Remote Sensing Systems: Santa Rosa, CA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Kummerow, C.; Ferraro, R.; Randel, D. AMSR-E/Aqua L2B Global Swath Surface Precipitation GSFC Profiling Algorithm; Version 3; NASA National Snow and Ice Data Center Distributed Active Archive Center: Boulder, CO, USA, 2015. [CrossRef]
- Poli, P.; Hersbach, H.; Dee, D.; Berrisford, P.; Simmons, A.J.; Vitart, F.; Laloyaux, P.; Tan, D.G.H.; Peubey, C.; Thépaut, J.-N.; et al. ERA-20C: An Atmospheric Reanalysis of the Twentieth Century. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 4083–4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platnick, S.; Ackerman, S.A.; King, M.D.; Meyer, K.; Menzel, W.P.; Holz, R.E.; Baum, B.A.; Yang, P. MODIS Atmosphere L2 Cloud Product (06_L2), NASA MODIS Adaptive Processing System; Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, S. Development of hourly precipitation datasets for national meteorological stations in China. Torrential Rain Disasters 2016, 35, 182–186. [Google Scholar]
- Friedl, M.; Sulla-Menashe, D. MCD12C1 MODIS/Terra + Aqua Land Cover Type Yearly L3 Global 0.05Deg CMG V006; NASA EOSDIS Land Processes DAAC: Sioux Falls, SD, USA, 2015.
- Moesinger, L.; Dorigo, W.; de Jeu, R.; van der Schalie, R.; Scanlon, T.; Teubner, I.; Forkel, M. The global long-term microwave Vegetation Optical Depth Climate Archive (VODCA). Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2020, 12, 177–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didan, K. MYD13C2 MODIS/Aqua Vegetation Indices Monthly L3 Global 0.05Deg CMG V006; NASA EOSDIS Land Processes DAAC: Sioux Falls, SD, USA, 2015. [CrossRef]
- Schneider, U.; Becker, A.; Finger, P.; Meyer-Christoffer, A.; Rudolf, B.; Ziese, M. GPCC Full Data Reanalysis Version 7.0 at 0.5°: Monthly Land-Surface Precipitation from Rain-Gauges built on GTS-based and Historic Data; Global Precipitation Climatology Centre: Offenbach, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.K.; Riggs, G.A.; Solomonson, V.; Sips, N.M. MODIS/Aqua Snow Cover Monthly L3 Global 0.05Deg CMG, Version 6; NASA National Snow and Ice Data Center Distributed Active Archive Center: Boulder, CO, USA, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Wielicki, B.; Minnis, P.; Rossow, W. Estimation of water cloud properties from satellite microwave, infrared and visible measurements in oceanic environments: 1. Microwave brightness temperature simulations. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1998, 103, 3873–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G. A Fast and Accurate Model for Microwave Radiance Calculations. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 1998, 76, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G. Approximation of Single Scattering Properties of Ice and Snow Particles for High Microwave Frequencies. J. Atmos. Sci. 2004, 61, 2441–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, Y.-J.; Liu, G.; Seo, E.-K.; Wang, J.R.; Aonashi, K. Development of a snowfall retrieval algorithm at high microwave frequencies. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2006, 111, D22216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aonashi, K.; Awaka, J.; Hirose, M.; Kozu, T.; Kubota, T.; Liu, G.; Shige, S.; Kida, S.; Seto, S.; Takahashi, N.; et al. GSMaP Passive Microwave Precipitation Retrieval Algorithm: Algorithm Description and Validation. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2009, 87, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, H.; Koike, T.; Imaoka, K. Improvement of the AMSR-E Algorithm for Soil Moisture Estimation by Introducing a Fractional Vegetation Coverage Dataset Derived from MODIS Data. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 29, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, Y.-J.; Liu, G.; Jones, A.S.; Haar, T.H.V. Toward snowfall retrieval over land by combining satellite and in situ measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2009, 114, D24205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shige, S.; Yamamoto, T.; Tsukiyama, T.; Kida, S.; Ashiwake, H.; Kubota, T.; Seto, S.; Aonashi, K.; Okamoto, K. The GSMaP Precipitation Retrieval Algorithm for Microwave Sounders—Part I: Over-Ocean Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 3084–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Liu, G.; Liu, Q.; Sun, L. A new water vapor algorithm for TRMM Microwave Imager (TMI) measurements based on a log linear relationship. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2009, 114, D21304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shige, S.; Kida, S.; Ashiwake, H.; Kubota, T.; Aonashi, K. Improvement of TMI Rain Retrievals in Mountainous Areas. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2013, 52, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, A.; Shige, S.; Yamamoto, M.; Mega, T.; Kida, S.; Kubota, T.; Kachi, M.; Ushio, T.; Aonashi, K. Improvement of High-Resolution Satellite Rainfall Product for Typhoon Morakot (2009) over Taiwan. J. Hydrometeorol. 2013, 14, 1859–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeoung, H.; Liu, G.; Kim, K.; Lee, G.; Seo, E.-K. Microphysical properties of three types of snow clouds: Implication for satellite snowfall retrievals. Atmospheric Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2020, 20, 14491–14507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, T.; Aonashi, K.; Ushio, T.; Shige, S.; Takayabu, Y.N.; Kachi, M.; Arai, Y.; Tashima, T.; Masaki, T.; Kawamoto, N.; et al. Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation (GSMaP) Products in the GPM Era. In Satellite Precipitation Measurement; Springer: Richmond, VA, USA, 2020; pp. 355–373. [Google Scholar]
- Ackerman, S.A.; Stephens, G.L. The Absorption of Solar Radiation by Cloud Droplets: An Application of Anomalous Diffraction Theory. J. Atmos. Sci. 1987, 44, 1574–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lin, B.; Rossow, W.B. Observations of cloud liquid water path over oceans: Optical and microwave remote sensing methods. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1994, 99, 20907–20927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- English, S.J. Airborne radiometric observations of cloud liquid-water emission at 89 and 157 GHz: Application to retrieval of liquid-water path. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1995, 121, 1501–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Rossow, W.B.; Stackhouse, P.W. Comparison of different global information sources used in surface radiative flux calculation: Radiative properties of the near-surface atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2006, 111, D13106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prigent, C.; Aires, F.; Rossow, W.B. Land Surface Microwave Emissivities over the Globe for a Decade. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2006, 87, 1573–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, S.; Grody, N. Anomalous microwave spectra of snow cover observed from Special Sensor Microwave/Imager measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2000, 105, 14913–14925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongoli, C.; Grody, N.C.; Ferraro, R.R. Interpretation of AMSU microwave measurements for the retrievals of snow water equivalent and snow depth. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2004, 109, D24111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owe, M.; De Jeu, R.; Walker, J. A methodology for surface soil moisture and vegetation optical depth retrieval using the microwave polarization difference index. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 1643–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, T.R.H.; De Jeu, R.A.M.; Owe, M.; Dolman, A. Land surface temperature from Ka band (37 GHz) passive microwave observations. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2009, 114, D04113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Peters-Lidard, C.; Harrison, K.W.; Prigent, C.; Norouzi, H.; Aires, F.; Boukabara, S.A.; Furuzawa, F.A.; Masunaga, H. Quantifying Uncertainties in Land-Surface Microwave Emissivity Retrievals. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 52, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norouzi, H.; Temimi, M.; Prigent, C.; Turk, J.; Khanbilvardi, R.; Tian, Y.; Furuzawa, F.A.; Masunaga, H. Assessment of the consistency among global microwave land surface emissivity products. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Weng, F. Error Sources in Remote Sensing of Microwave Land Surface Emissivity. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3437–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Weihermüller, L.; Jiang, L.; Vereecken, H. Measurement and Simulation of Topographic Effects on Passive Microwave Remote Sensing Over Mountain Areas: A Case Study from the Tibetan Plateau. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 52, 1489–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulvirenti, L.; Pierdicca, N.; Marzano, F.S. Prediction of the Error Induced by Topography in Satellite Microwave Radiometric Observations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3180–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummerow, C.; Hong, Y.; Olson, W.S.; Yang, S.; Adler, R.F.; Mccollum, J.; Ferraro, R.; Petty, G.; Shin, D.-B.; Wilheit, T.T. The Evolution of the Goddard Profiling Algorithm (GPROF) for Rainfall Estimation from Passive Microwave Sensors. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2001, 40, 1801–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; Min, Q.; Bergeron, Y.; Valeria, O.; Gao, Z.; Liu, J.; Fu, Y. Spatiotemporal Variations of Satellite Microwave Emissivity Difference Vegetation Index in China Under Clear and Cloudy Skies. Earth Space Sci. 2020, 7, e2020EA001145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Min, Q.; Lin, B. Estimation of evapotranspiration in a mid-latitude forest using the Microwave Emissivity Difference Vegetation Index (EDVI). Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2011–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, R.; Hu, J.; Wang, X.; Kabeja, C.; Min, Q.; Wang, Y. Evaluations of MODIS and microwave based satellite evapotranspiration products under varied cloud conditions over East Asia forests. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 264, 112606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringerud, S.; Kummerow, C.; Peters-Lidard, C.; Tian, Y.; Harrison, K. A Comparison of Microwave Window Channel Retrieved and Forward-Modeled Emissivities Over the U.S. Southern Great Plains. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 2395–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prigent, C.; Liang, P.; Tian, Y.; Aires, F.; Moncet, J.-L.; Boukabara, S.A. Evaluation of modeled microwave land surface emissivities with satellite-based estimates. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 2706–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).