Abstract
This study evaluated evapotranspiration (ET) estimated using the Earth Engine Evapotranspiration Flux (EEFlux), an automated version of the widely used Mapping Evapotranspiration at High Spatial Resolution with Internalized Calibration (METRIC) model, via comparison with ET measured using eddy covariance flux towers at two U.S. sites (St. John, WA, USA and Genesee, ID, USA) and for two years (2018 and 2019). Crops included spring wheat, winter pea, and winter wheat, all grown under rainfed conditions. The performance indices for daily EEFlux ET estimations combined for all sites and years dramatically improved when the cold pixel alfalfa reference ET fraction (ETrF) in METRIC was reduced from 1.05 (typically used for irrigated crops) to 0.85, with further improvement when the periods of early growth and canopy senescence were excluded. Large EEFlux ET overestimation during crop senescence was consistent in all sites and years. The seasonal absolute departure error was 51% (cold pixel ETrF = 1.05) and 23% (cold pixel ETrF = 0.85), the latter reduced to 12% when the early growth and canopy senescence periods were excluded. Departures of 10% are a reasonable expectation for methods of ET estimation, which EEFlux could achieve with more frequent satellite images, better daily weather data sources, automated adjustment of daily ETrF values during crop senescence, and a better understanding of the selection of adequate cold pixel ETrF values for rainfed crops.
1. Introduction
The estimation of actual evapotranspiration (ET) is important in both irrigated and rainfed agriculture. Experimentally, ET can be estimated with lysimeters, Bowen ratio, eddy covariance, and scintillometer systems [1,2,3,4]. These methods measure ET over relatively small areas and are difficult to extrapolate in time and space given heterogeneous land surfaces [5] and crop, soil and weather variations [1]. These limitations can be overcome by using methods based on remote sensing data.
Several remote sensing-based models and algorithms have been developed and used to estimate crop ET (e.g., [6,7,8,9,10]). Most of them are based on the surface energy balance [11], including the Two-Source Energy Balance (TSEB) [7], the Atmosphere-Land Exchange Inverse (ALEXI) [12], Surface Energy Balance Algorithm for Land (SEBAL) [8,9], Simplified Surface Energy Balance Index (S-SEBI) [13], Surface Energy Balance System (SEBS) [14], the North American Land and Data Assimilation System (NLDAS) [15], the disaggregated ALEXI model (DisALEXI) [16], and Mapping Evapotranspiration at High Spatial Resolution with Internalized Calibration (METRIC) [17].
Due to its internalized calibration, METRIC is widely used in the US to estimate regional and field crop ET, although it requires a significant amount of time for preprocessing satellite images and manual calibration of the model [18]. With mixed results, previous studies have evaluated the performance of the METRIC model compared to weighing lysimeters [19], soil water balance [20], Bowen Ratio Energy Balance Systems [21,22,23,24], and Eddy Covariance Flux Towers [25,26,27,28], mostly for irrigated crops, e.g., [10,20,29,30] and a few rainfed crops, e.g., [31,32]. Estimation errors typically arise from current technology limitations including low frequency of satellite passes (Landsat: 16 days, reduced to 8 days when Landsat 7 and 8 images are combined), cloud interference rendering images useless, insufficient spatial resolution (Landsat: 30 × 30 m) affecting situations of sparse canopies and high soil exposure, and daily weather data availability.
More recently, EEFlux, a fully automated evapotranspiration mapping tool that operates on the Google Earth Engine (GEE) platform (http://eeflux-level1.appspot.com/, accessed on 26 July 2020), was developed. Because of its automated nature and reliance on cloud data, EEFlux has the potential to assess water use and improve irrigation management in farm fields as well as large regions at extremely low cost. However, while METRIC results are influenced by users and their choices during manual calibration for specific applications [18], EEFlux automated processes reduce these choices to some adjustments at the time of products download. Thus, although many evaluations of METRIC have been performed, the automated ETa estimation process of EEFlux should be carefully evaluated on its own. Foolad et al. compared EEFlux with standard manually calibrated METRIC for agricultural and non-agricultural areas in the western and central United States and found that EEFlux ET estimates were comparable to METRIC for agricultural areas, but substantially underestimated ET in non-agricultural areas [18]; Duijndam reported 4% to 176% errors in cumulative ET from EEFlux compared to flux tower measurements at eighteen different flux tower sites (USA, NLD, ZAF, AUS, BRA, and TUN) and land covers (corn, wheat, onion, alfalfa, maize, soybean, scot pine, pasture, grapes, sugarcane, tropical rain forest, mango, and caatinga) in semi-arid regions [33].
Out of a few EEFlux evaluation studies conducted, only one compared EEFlux with EC for satellite overpass days, mostly for irrigated crops except for 2 of the 13 crop sites reported [33]. The aim of this study was to evaluate the quality of daily EEFlux ET estimates throughout the growing season via comparison with measurements obtained using eddy covariance (EC) flux towers in rainfed crops at two sites of the dryland region of the Pacific Northwest.
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Study Sites
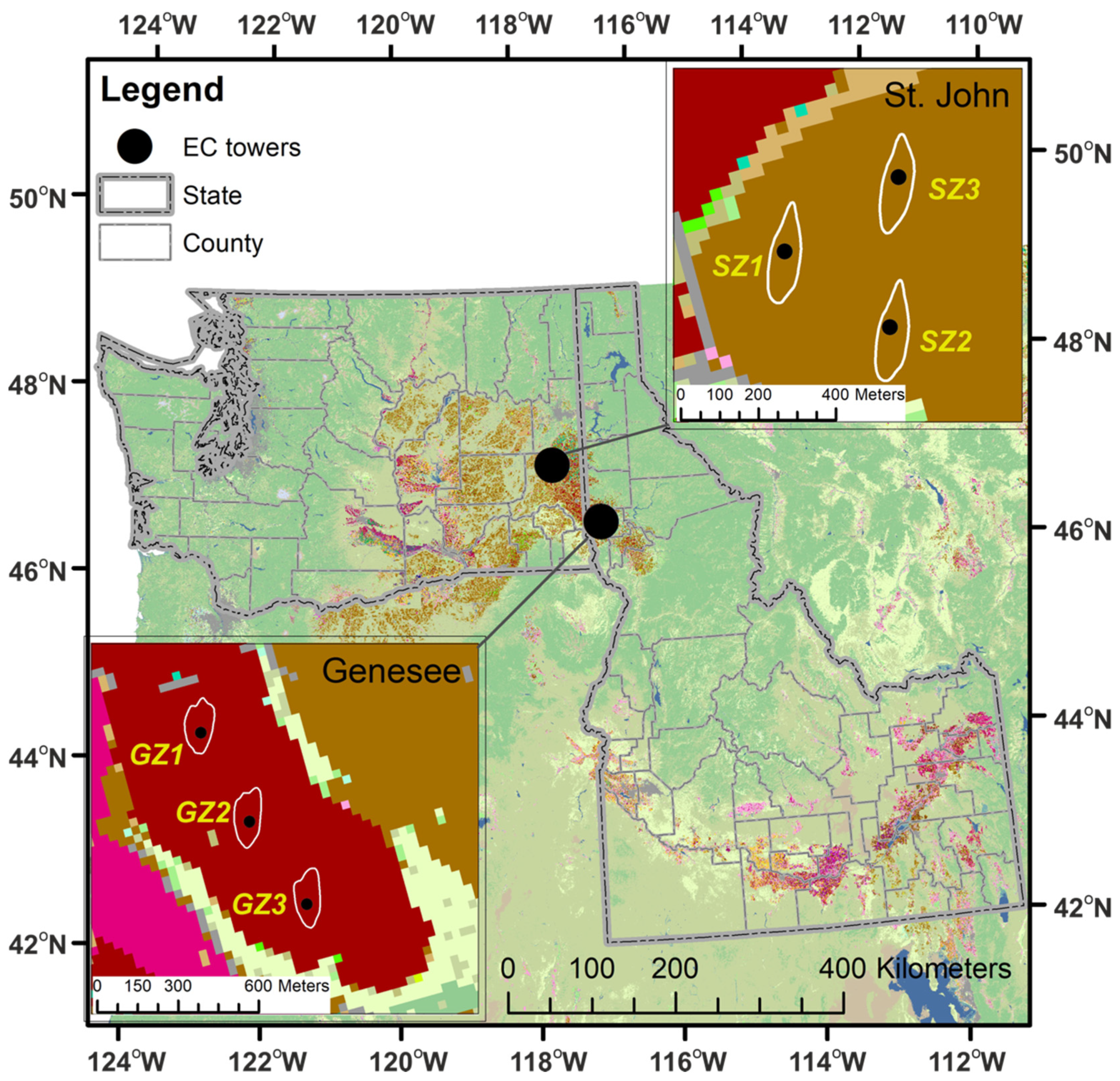
ET measurements were conducted at two dry farming sites, one in St. John, WA, USA and another in Genesee, ID, USA (Figure 1) during 2018 and 2019. Each site contains three EC flux towers on the same field. The fields were managed for fertilizer, herbicide, and pesticide using the common practices in this region. The cropping details at St. John and Genesee are presented in Table 1.
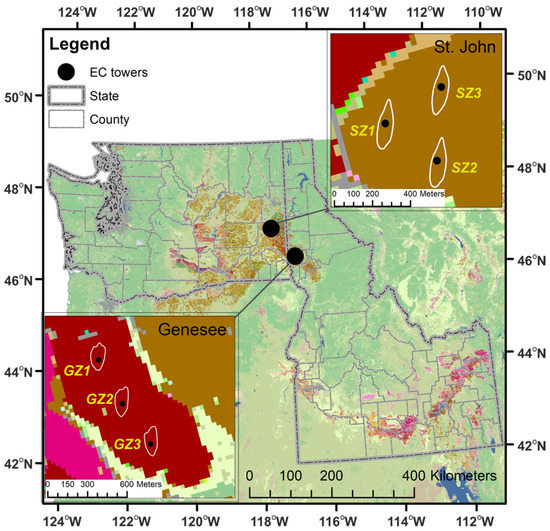
Figure 1.
Study area and locations of the eddy covariance flux towers (black circles) at St. John and Genesee (The background is USDA Crop Data Layer (CDL) in 2018, https://www.nass.usda.gov/Research_and_Science/Cropland/docs/US_2018_CDL_legend.jpg, accessed on 26 July 2020). The white lines around the tower locations represent the mean footprint climatology (90% contour lines).

Table 1.
Cropping details at St. John and Genesee during the 2017–2018 and 2018–2019 growing seasons.
2.2. Satellite Data
Eighteen clear-sky images (9 images in both 2018 and 2019) were available for St. John and twenty-nine images (14 in 2018 and 15 in 2019) were available for Genesee. These images were selected based on the acquisition dates and cloud-free conditions and they were processed on the EEFlux platform.
2.3. Field Data Collection
2.3.1. Eddy Covariance ET (EC ET)
The locations of eddy covariance flux towers are: SZ1: N47°7′28″/W117°31′50″, SZ2: N47°7′21″/W117°31′38″, SZ3: N47°7′34″/W117°31′34″ at St. John; and GZ1: N46°30′3″/W116°48′24″, GZ2: N46°29′52″/W116°48′17″, GZ3: N46°29′42″/W116°48′8″ at Genesee (Figure 1).
Each EC tower consisted of an integrated system of open-path CO2/H2O gas analyzer and three-dimensional sonic anemometer (IRGASON, Campbell Scientific, Logan, UT, USA) except the GZ1 tower, which was equipped with a CO2/H2O open-path gas analyzer (EC150, Campbell Scientific, Logan, UT, USA) and a three-dimensional sonic anemometer (CSAT3A, Campbell Scientific, Logan, UT, USA). The EC systems were mounted at a height of 2 m above the ground level (a.g.l.), and data were collected at 10 Hz by a datalogger (CR3000, Campbell Scientific, Logan, UT, USA). Other measurements included net radiation (Rn, NR-Lite2, Kipp and Zonen, Delft, The Netherlands), air temperature and relative humidity (HMP155A, Vaisala, Finland), soil heat flux (HFP01SC, Hukseflux, The Netherlands), and soil temperature and volumetric water content (TDR310, Acclima, Merifian, ID, USA). These data were sampled at 0.5 Hz and logged by the CR3000 datalogger.
The raw 10-Hz EC data were processed using the EddyPro® software (version 7.06, LI-COR Biosciences, Lincoln, NE, USA) to calculate the 30-min average fluxes of sensible and latent heat (H and LE). The data processing procedures include: (1) removing physically impossible values and spikes; (2) double rotation applied to sonic anemometer data [34]; (3) block averaging to determine the turbulent fluctuations for each 30-min interval; (4) corrections for the effects of high- and low-pass filtering [35,36,37] and air density fluctuations [38], respectively; and (5) quality check [39]. The 30-min flux data with low quality were removed for further analysis, and the gaps in the 30-min data of LE were filled using the “REddyProc” R package [40]. The gap-filled 30-min LE data were averaged to compute ET at daily intervals. The footprints of EC measurements were determined using the two-dimensional parameterization footprint model [41].
The ground heat flux (G) was estimated using the calorimetric method [42,43], which combines the measured soil heat flux at 10 cm depth and the change in heat storage in the layer above the heat flux plate (0–10 cm) at all six flux tower sites.
2.3.2. Weather Data
Daily weather data were obtained from gridMet [44] for the nearest grid cells in the tower locations for St. John and Genesee. The gridMet grids correspond to the centroid of the 1/24th degree (~4 km × 4 km) pixel. The data include daily maximum and minimum temperature, maximum and minimum relative humidity, wind speed, shortwave solar radiation, and precipitation. These data were used to calculate alfalfa-reference evapotranspiration (ETr) with the ASCE Penman-Monteith method [45]. The average meteorological conditions over the study area during the growing seasons of 2018 and 2019 at St. John and Genesee are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Average temperature, relative humidity, solar radiation, wind speed (at 10 m height), and ETr during the growing seasons of 2018 and 2019. Annual precipitation is also included for reference.
2.4. Methods
2.4.1. EEFlux
EEFlux is a fully automated version of METRIC that operates on the Google Earth Engine (METRIC-EEFlux (https://eeflux-level1.appspot.com, accessed on 26 July 2020)) using a variety of sources for weather, soil, and land use data, and digital elevation models. It uses NLDAS hourly data and gridMET daily gridded weather data to estimate alfalfa reference evapotranspiration, STASGO soil data to produce time series of bare soil evaporation, and the NCLD database for land use for the continental United States [46].
The actual ET is estimated as a residual of the surface energy balance [10,47], according to Equation (1).
where LE is latent heat flux (W/m2), Rn is net radiation (W/m2), H is sensible heat flux (W/m2), and G is ground heat flux (W/m2)
ET at the instant of the satellite image (ETinst) is calculated by EEFlux for each pixel according to Equation (2).
ETinst is in mm/h, 3600 converts seconds to hours, is the calculated latent heat flux at the time of the satellite pass, λ is the latent heat of vaporization (J/kg); and ρw is the density of water (~1000 kg/m3).
The alfalfa-reference ET fraction (ETrF) in Equation (3) is calculated as the ratio of the computed instantaneous ET (ETinst) for each pixel to hourly alfalfa-reference ET (ETrh) [47] calculated using the standardized ASCE Penman–Monteith equation.
Values of ETrF for each pixel and dates of the available images were calculated by the automated processing in EEFlux. Finally, the daily ET is calculated pixel by pixel based on daily ETr as in Equation (4)
where ETrF are daily values obtained by interpolation of the values for each day of satellite pass. For a complete description of the calculations embedded in EEFlux ET estimation from satellite data, readers are referred to reference [10].
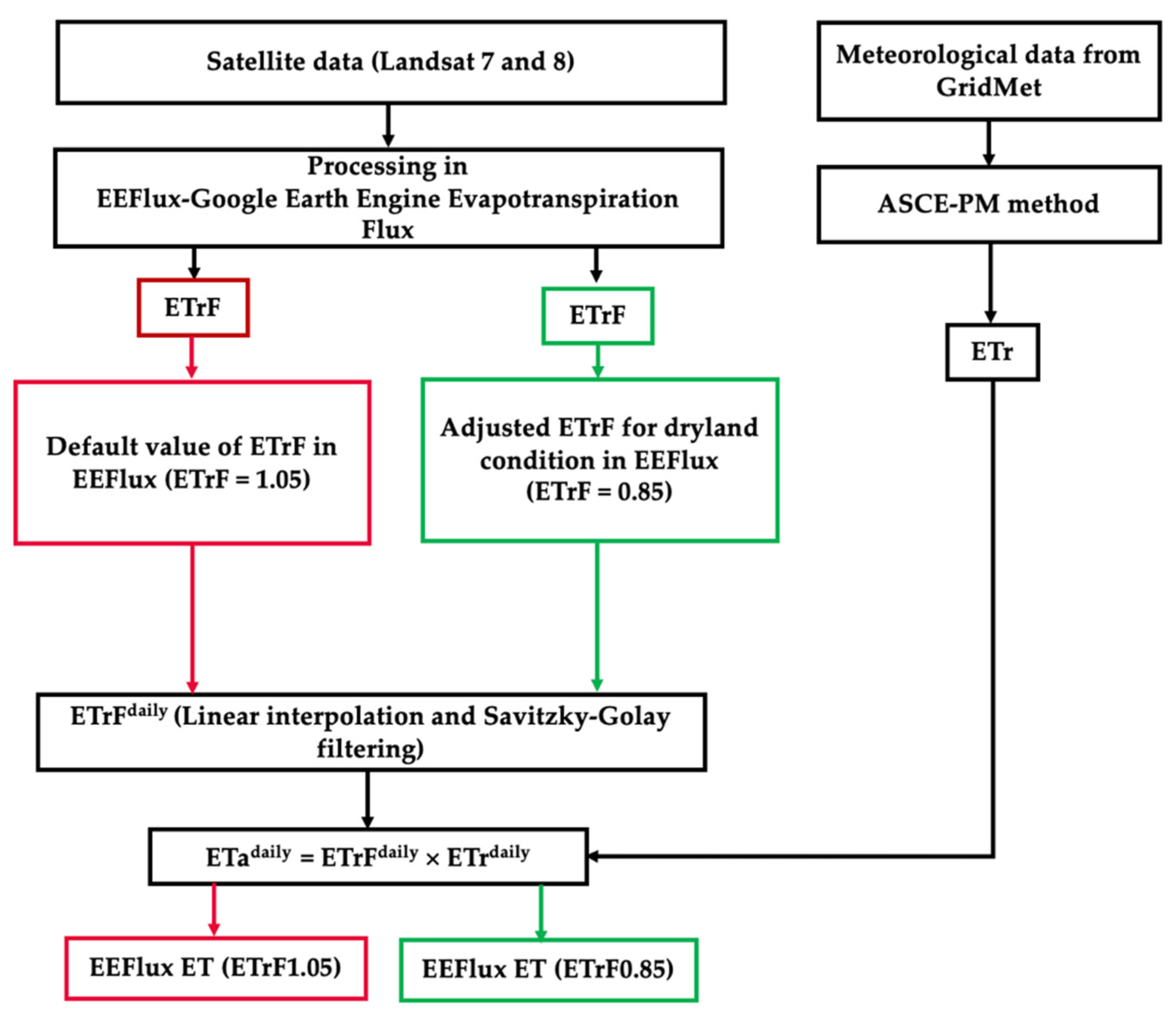
The Landsat images in this study were processed with METRIC-EEFlux version 0.20.2 (https://eeflux-level1.appspot.com, accessed on 26 July 2020) and the standard ETrF products were downloaded for further processing and analysis. In METRIC, the cold pixel is usually selected from a well-irrigated and non-stressed cropped field, with ETrFcold pixel = 1.05 representing maximum ET [10]. These standard values were termed ETrF1.05. However, it was found that ETrFcold pixel = 1.05 may not be adequate for rainfed conditions, leading to ET overestimation. In this study, we downloaded EEFlux adjusted ETrF values using ETrFcold pixel = 0.85, which is considered more adequate for rainfed conditions [31,48,49] and termed as ETrF0.85. The detailed flowchart of the methodology adopted is presented in Figure 2.
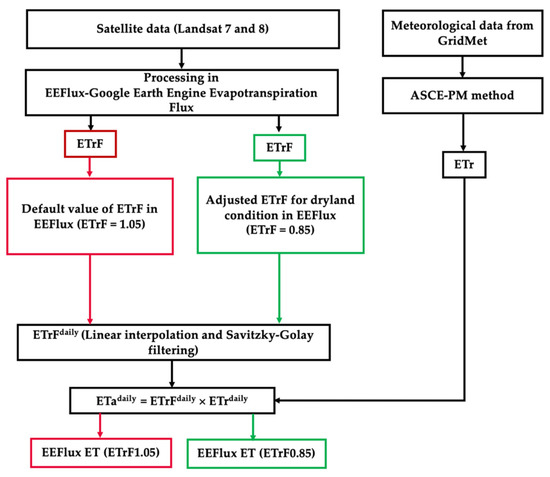
Figure 2.
Methodology flowchart of actual evapotranspiration (ETa) estimation using EEFlux Google Earth Engine Evapotranspiration Flux.
Downloaded ETrF values for days of satellite overpass were interpolated to obtain daily ETrF values during the growing season. The linear interpolation and smoothening were performed with Savitzky–Golay filtering based on Gram polynomials (window size = 15 days and Polynomial Order = 2) (courtesy of Benjamin Navarro; https://gite.lirmm.fr/rpc/signal-processing/gram-savitzky-golay, accessed on 26 July 2020).
An area matching the footprint area of the EC measurements was identified to calculate the average EEFlux ET for each EC tower. These footprints were determined with the mean footprint climatology (90% contour lines) estimated from a two-dimensional parameterization footprint model [41] around the eddy covariance flux tower. Pixel ET values in this footprint area were averaged to determine outputs of daily EEFlux ET and compared graphically and statistically with EC ET values.
2.4.2. Evaluation of EEFlux Performance
The following statistical indices were used to evaluate the agreement between EEFlux, and EC ET estimated values.
(a) The root mean square error (RMSE) calculated as:
where n is the number of ET values, Oi is the measured ET values, and Pi is the estimated ET value.
(b) The normalized root mean square error (NRMSE) is calculated as:
where is the average measured ET value. The lower limit of RMSE and NRMSE is 0, indicating perfect agreement between estimated and measured values.
(c) The Willmott (1982) index of agreement (d) [50] calculated as:
The index of agreement ranges between 0 and 1, where a value of 1 indicates perfect agreement and 0 indicates no agreement at all.
(d) Departure error (DE)
DE is expressed in percent.
3. Results
3.1. Eddy Covariance Flux Tower ET
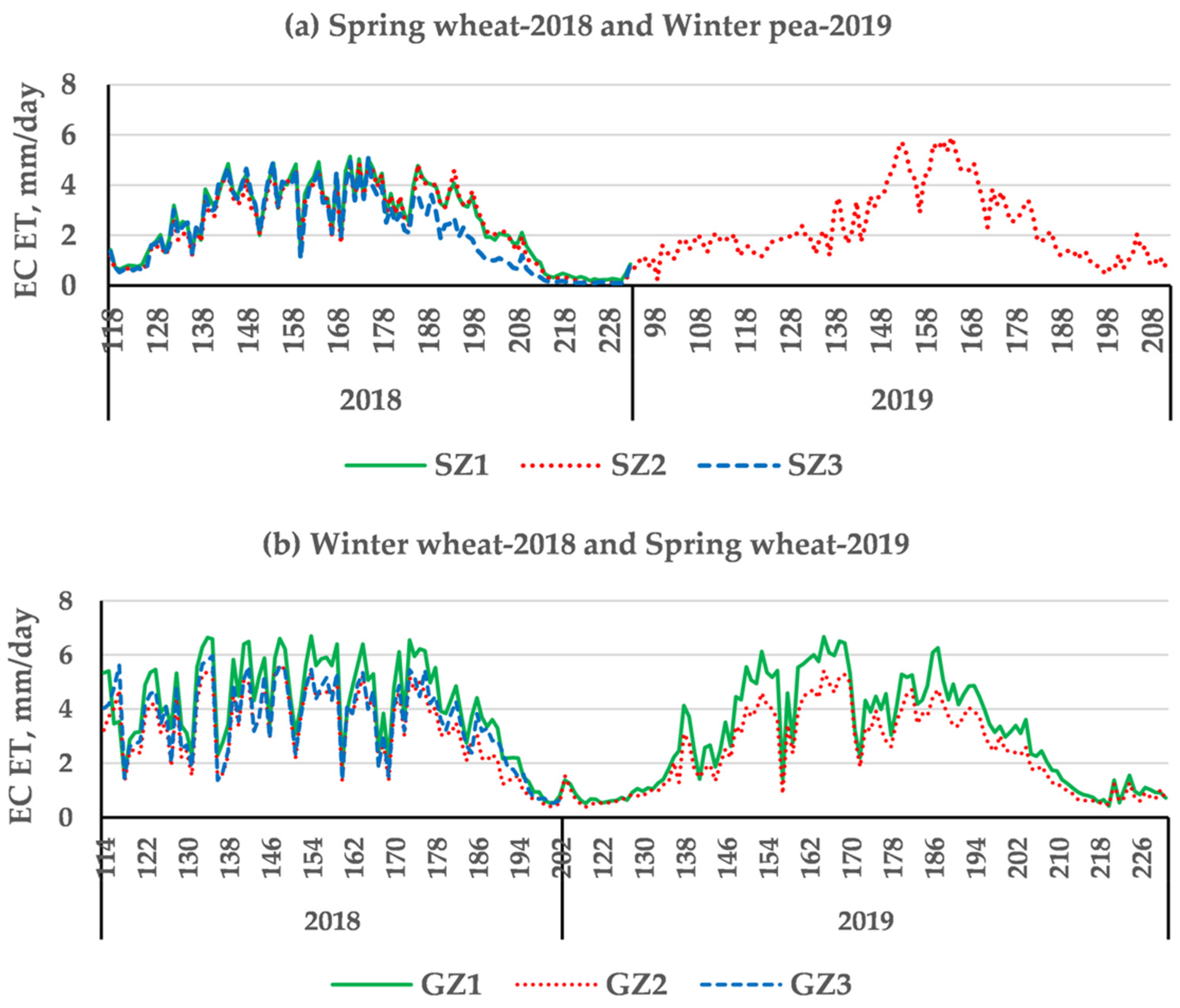
Figure 3 displays the EC ET measured at St. John (WA, USA) and Genesee (ID, USA) during the 2018 and 2019 growing seasons, and the statistics of the daily observations are listed in Table 3.
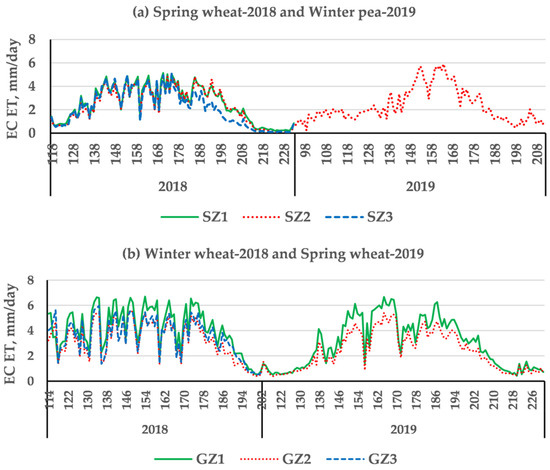
Figure 3.
Eddy-covariance measured ET (EC ET) with flux towers at St. John (a) and Genesee sites (b) during the 2018 and 2019 growing seasons. SZ1, SZ2, SZ3, and GZ1, GZ2, GZ3 indicates the eddy covariance flux towers at St. John and Genesee, respectively.

Table 3.
Summary of daily EC ET measured during the 2018 and 2019 growing seasons at St. John, WA, USA and Genesee, ID, USA.
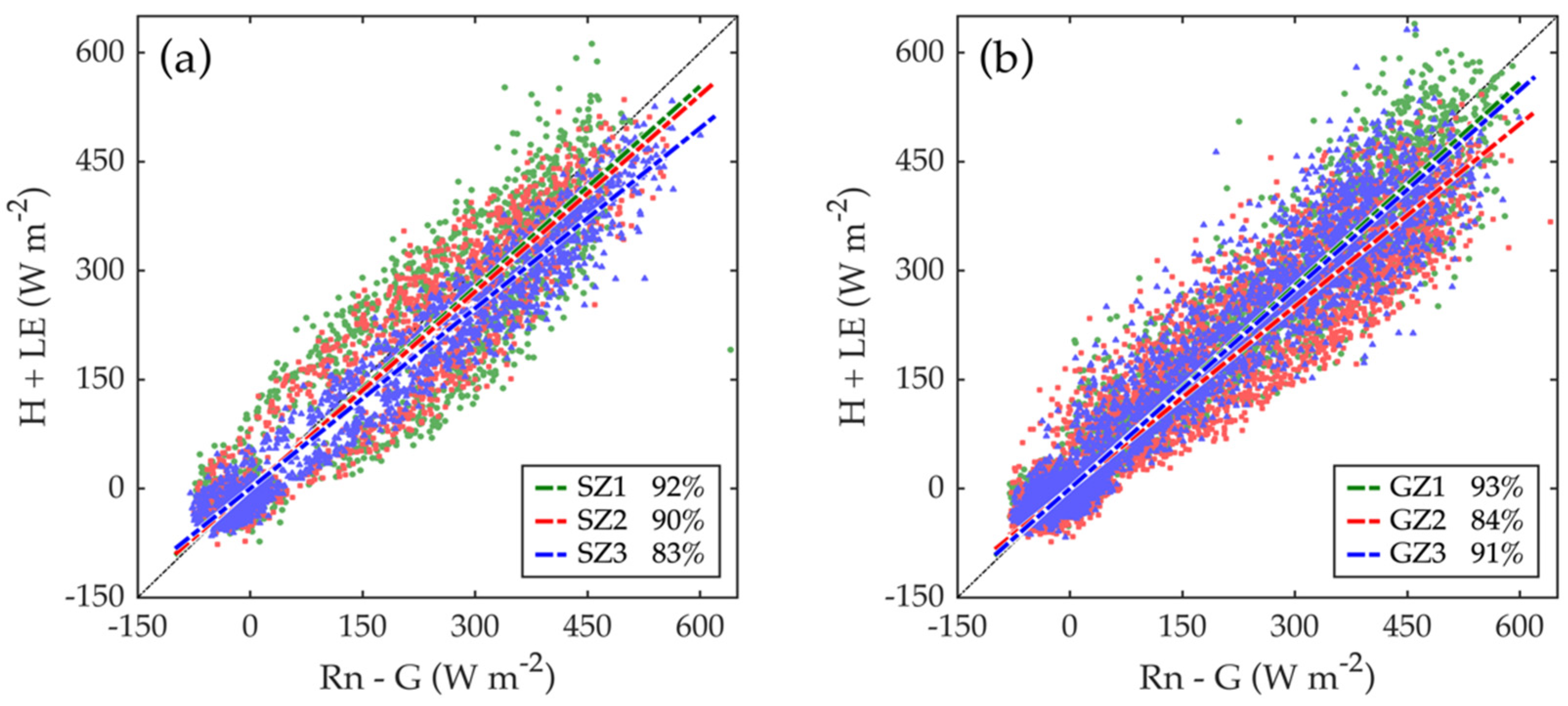
The three flux towers on the same field showed differences in daily ET patterns during the growing seasons (Figure 3 and Table 3). These differences could be attributed to variations of topography and soil depth, but also to the lack of energy balance closure of the EC measurements. The ratios of the energy balance closure varied within a site and from site to site (Figure 4). For the three flux towers at St. John, the ratios were 92%, 90%, and 83% for SZ1, SZ2, and SZ3, respectively, whereas for the three towers at Genesee they were 93%, 84%, and 91% for GZ1, GZ2, and GZ3, respectively. Reasons for the non-closure of the surface energy balance may include violations in the assumptions of homogeneous landscapes for the EC method, measurement errors in each component of the energy budget, mismatch of the sensor footprints, advection, and impacts of large-scale turbulent eddies [39,43,51,52]. However, the EC ET values could not be adjusted without a detailed analysis of the causes for the non-closure.
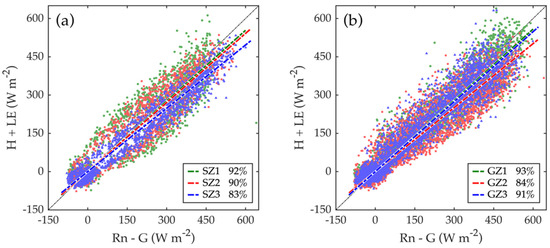
Figure 4.
Scatter plots comparing the available energy (Rn–G) to the turbulent energy fluxes (H + LE) for three flux towers at St. John (a) and Genesee (b). Rn, G, H, and LE denote the net radiation, ground heat flux, sensible and latent heat fluxes, respectively. The percentage refers to the overall ratio of energy balance closure for each tower.
3.2. Comparison of EEFlux and EC ET
3.2.1. Daily Patterns
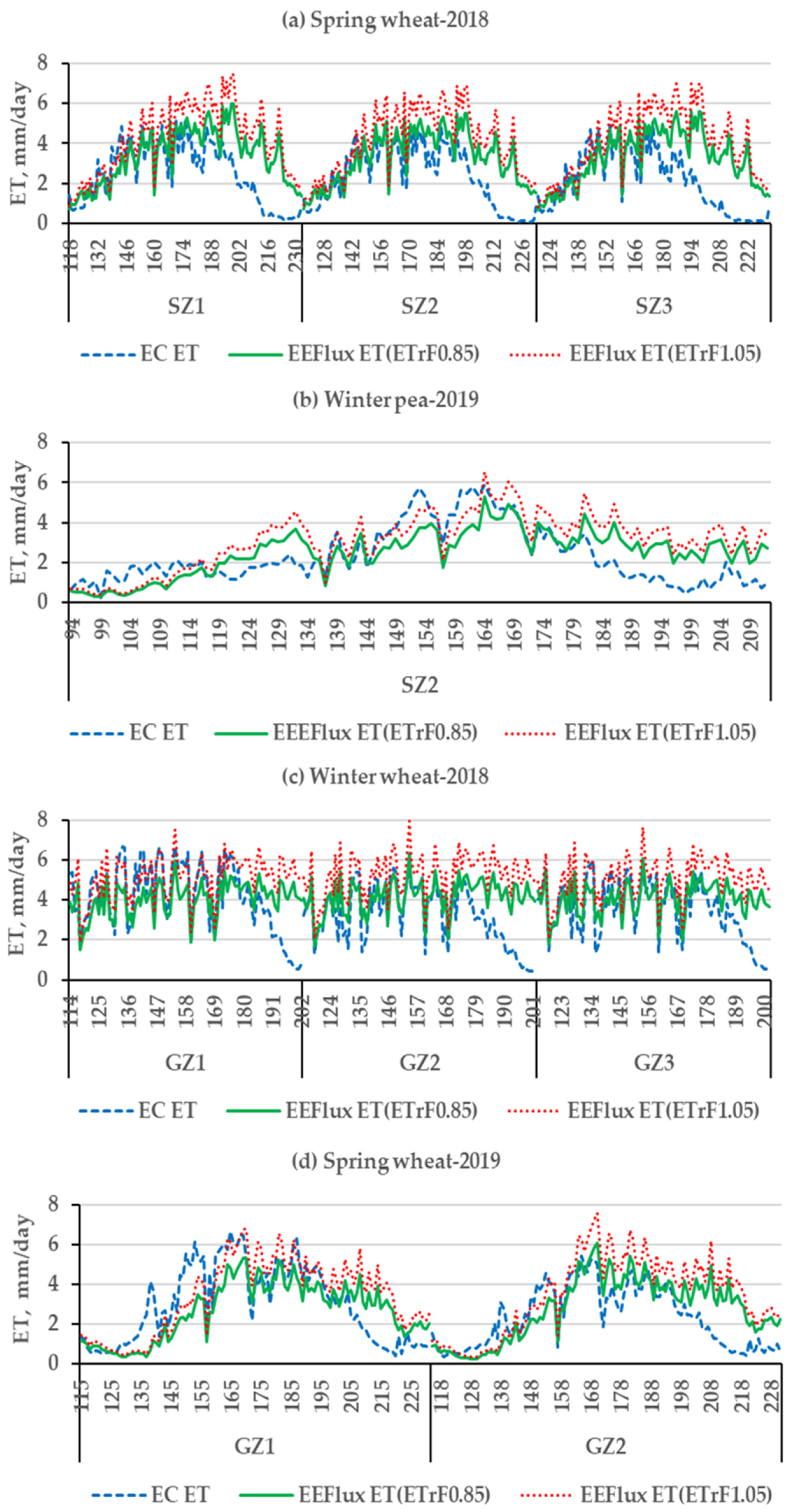
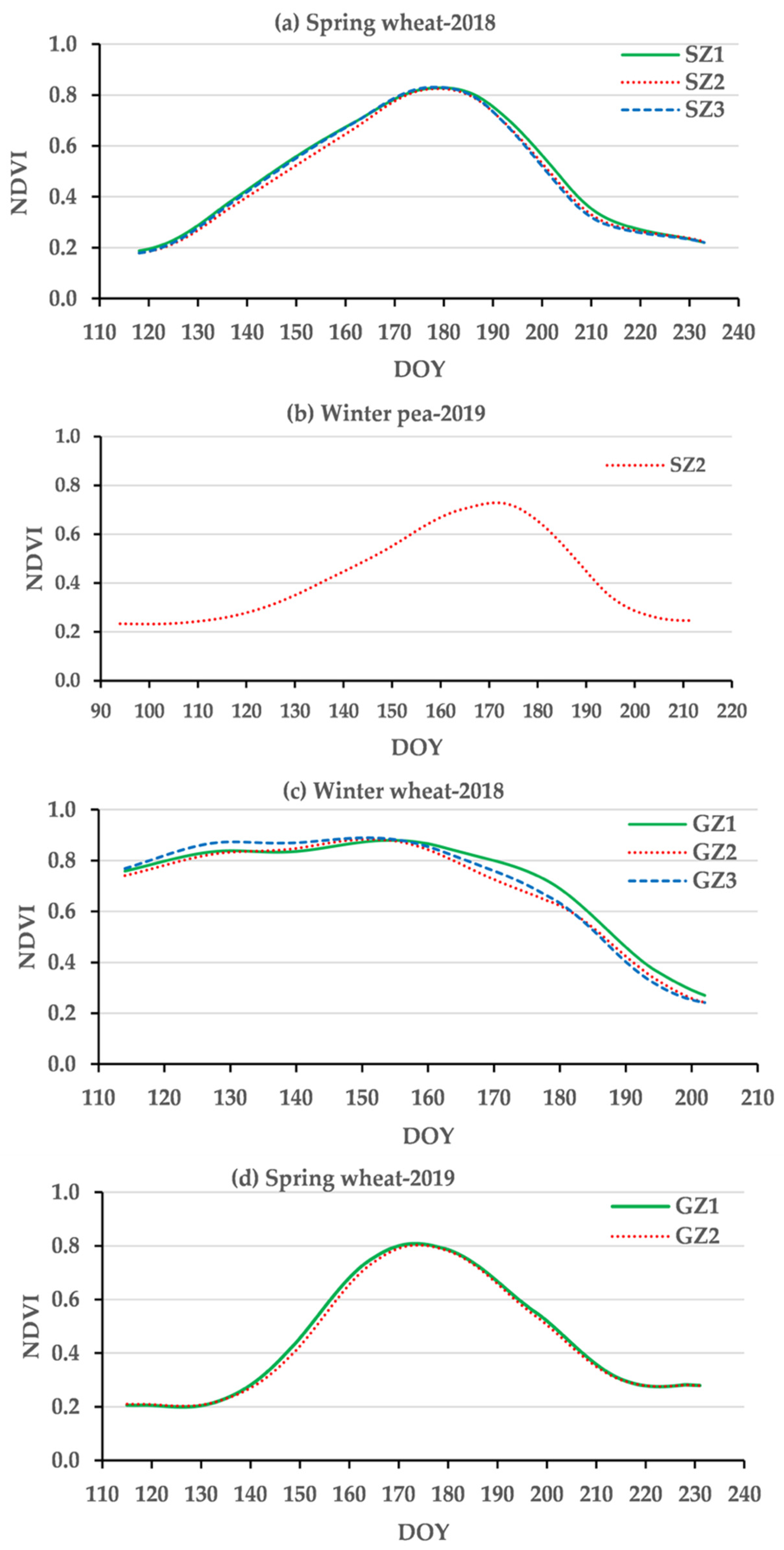
Figure 5 presents the comparison between daily EEFlux and EC ET at St. John and Genesee during the 2018 and 2019 growing seasons. The results show that EEFlux ET: (a) tracked most of the daily variations of EC ET albeit with over and underestimations, (b) the use of ETrFcold pixel = 1.05 resulted mostly in overestimations while ETrFcold pixel = 0.85 tended to agree better with EC ET, (c) departures early in the season were common for spring wheat, (d) fluctuating periods of over and underprediction alternated for winter peas, and (e) important and consistent overestimation with both cold pixel ETrF values were evident towards the end of the season (canopy senescence) in all cases. Figure 6 presents NDVI values, a close indicator of the fraction of canopy cover, showing spring wheat crops with low NDVI at the start of the EC measurements, and a similar pattern for winter pea that additionally had the lowest canopy development at midseason. Sparse canopies at the beginning of the EC measurements or relatively smaller canopy development (winter peas) incorporate a mix of soil and vegetation into the 30 m × 30 m pixels and the remotely sensed surface temperature, a likely source of error. During canopy senescence greenness and crop transpiration are reduced, becoming eventually zero, a dynamic not fully captured by EEFlux. The vegetation index NDVI is used in EEFlux as part of the calculation of the energy balance but is possible that EEFlux could be improved by using EVI, an index that showed a better correlation with regional ET in a recent paper [53].
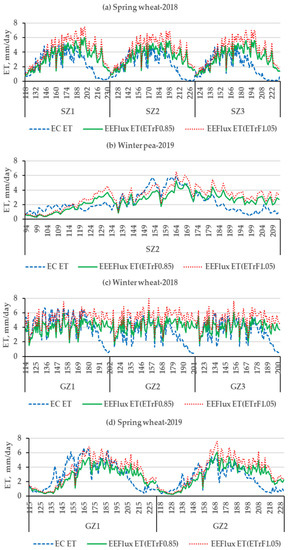
Figure 5.
Comparisons of daily EEFlux and EC ET at St. John (SZ) (a,b) and Genesee (GZ) (c,d) and two growing seasons. (a) spring wheat-2018 (b) winter pea-2019 (c) winter wheat-2018; and (d) spring wheat-2019.
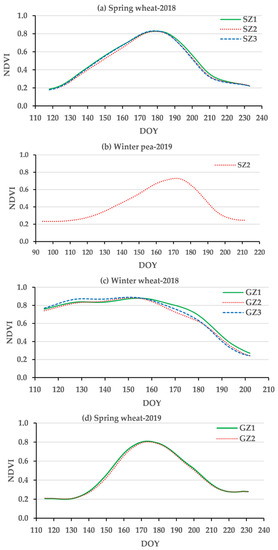
Figure 6.
NDVI values during the four growing seasons used for EEFlux evaluation. (a) spring wheat-2018; (b) winter pea-2019; (c) winter wheat-2018; and (d) spring wheat-2019.
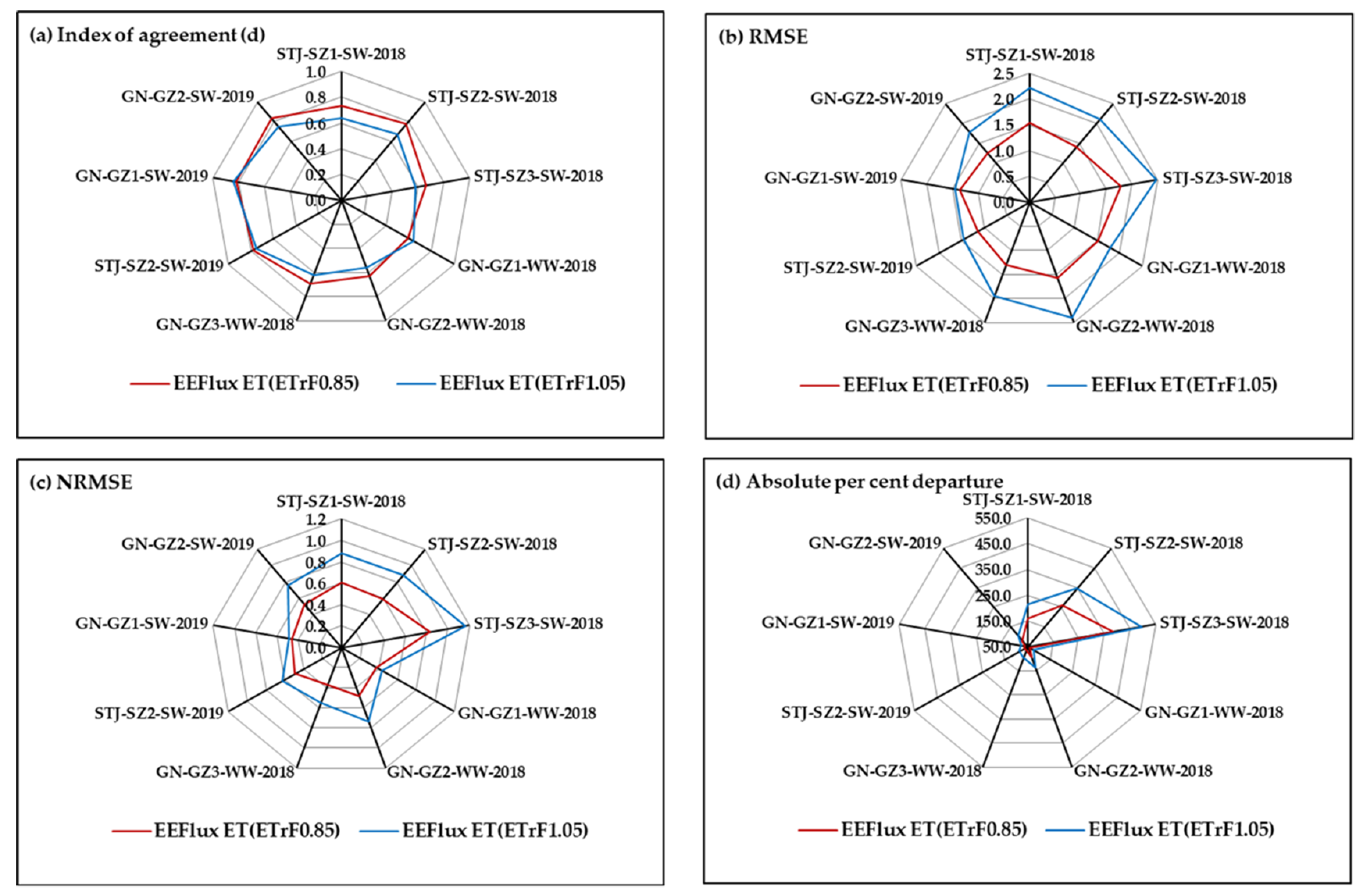
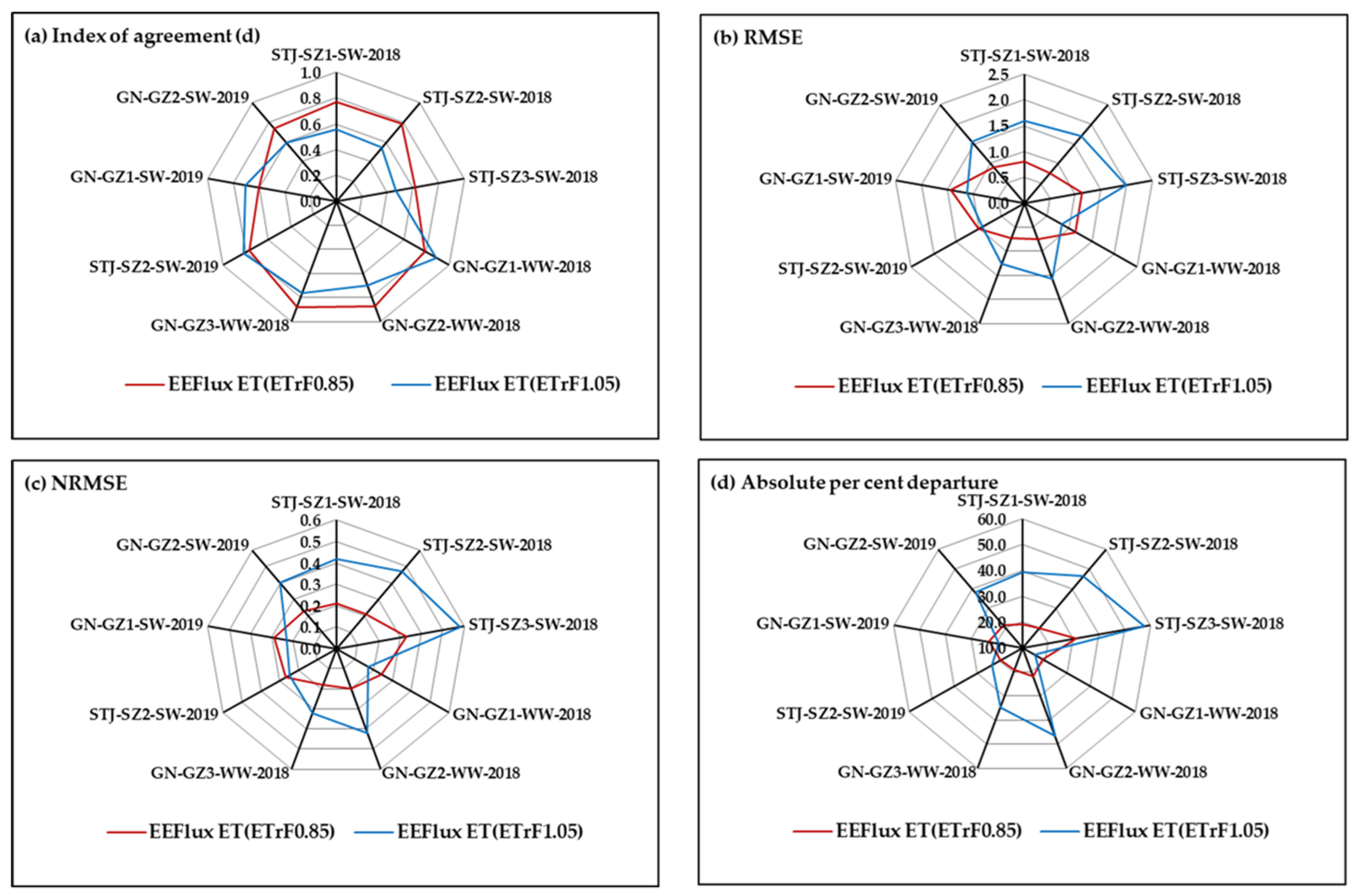
The statistical comparison of EEFlux and EC daily ET is presented in Figure 7. Overall, the index of agreement (d) was greater (with two exceptions), and RMSE and NRMSE were lower with ETrFcold pixel = 0.85. For towers with the lowest ratio of energy balance closure (SZ3 and GZ2), NRMSE was higher than other flux towers for the same site and year. Except for the GZ2 tower in 2019, EEFlux performance was also poor for these towers as indicated by d and RMSE values (Figure 7). Given the large and consistent EEFlux ET overestimation during senescence, and variable response during early growth (sparse canopy with a mix of soil and vegetation), performance indices were also evaluated excluding these two periods (Figure 8). All performance indices improved dramatically.
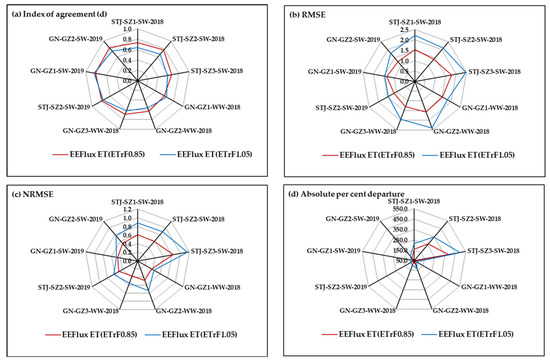
Figure 7.
Statistical comparison of EC and EEFlux ET for different crops and flux tower sites including early growth and crop senescence period. (a) Index of agreement; (b) RMSE; (c) NRMSE; and (d) Absolute percent departure.
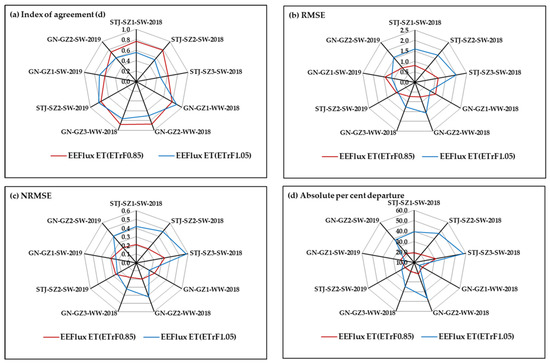
Figure 8.
Statistical comparison of EC and EEFlux ET for different crops and flux tower sites excluding early growth and crop senescence period. (a) Index of agreement; (b) RMSE; (c) NRMSE; and (d) Absolute percent departure.
3.2.2. Cumulative Measured and Estimated ET in the Growing Season
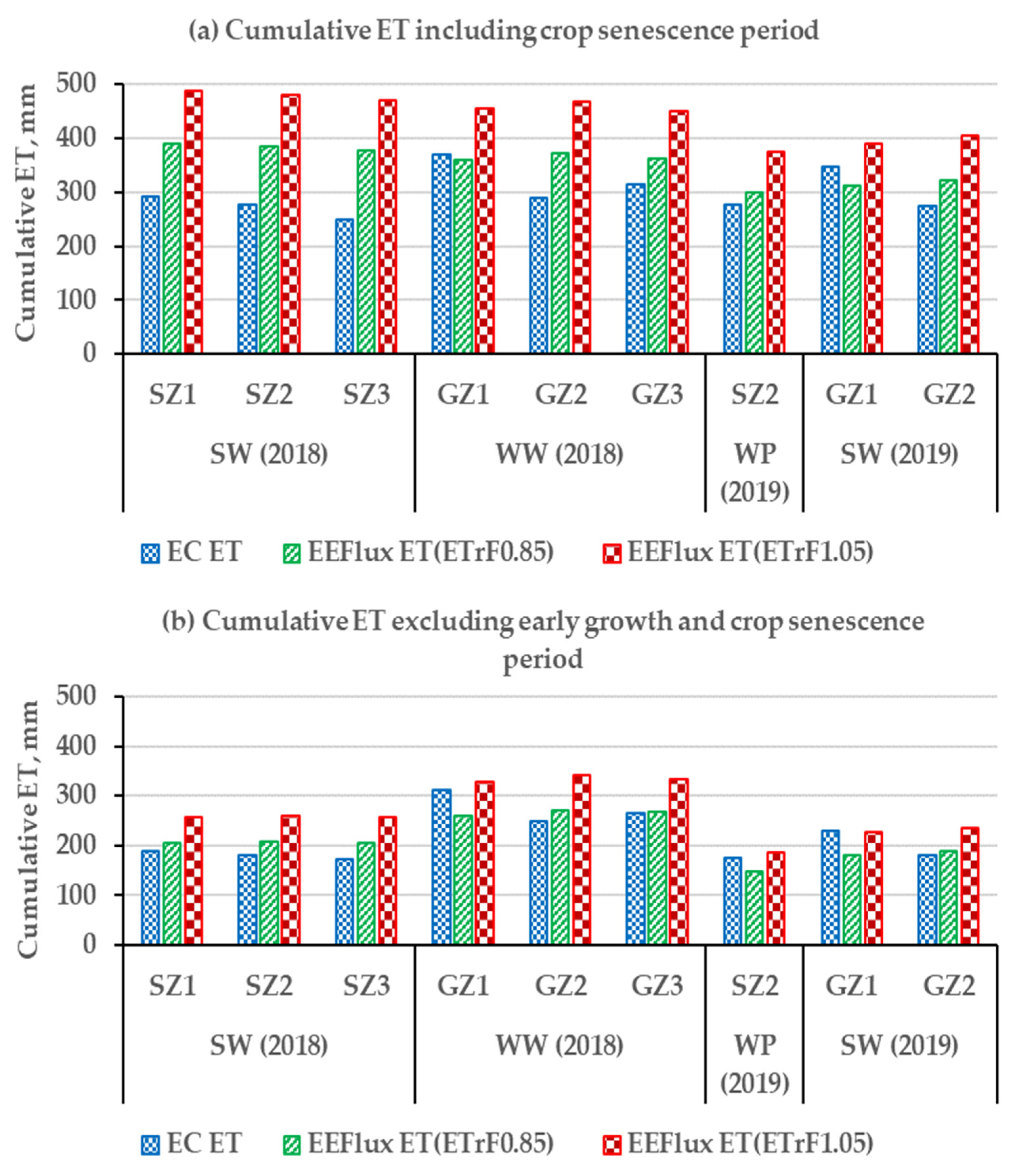
The cumulative value of daily ET estimates from EEFlux and EC are presented in Figure 9. The cumulative values are the sum of daily ET over the days of EC measurements and cannot be treated as crop cumulative ET for the entire growing season.
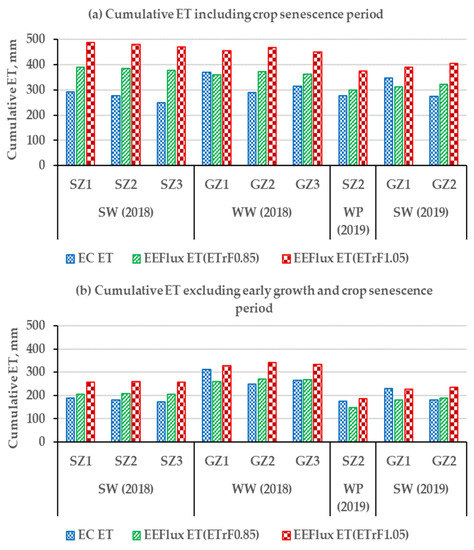
Figure 9.
Cumulative EEFlux and EC ET comparison for each site-year (SW: Spring wheat, WW: Winter wheat, WP: Winter pea): (a) during the entire period of EC measurements; and (b) excluding early growth and senescence periods.
The number of days included in the cumulative ET totals and the percent departure ((EEFlux-EC)/EC) × 100) are listed in Table 4. The highest departure was found for towers SZ3 and GZ2 during both years, probably due to their lower ratios of the energy balance closure. The towers with the highest ratio of the energy balance closure (GZ1 and SZ1) showed the lowest departures in each site, and even negative departures (EEFlux ET lower than EC ET). The cumulative percent departures were lower for EEFlux ET (ETrF0.85) during both years and at all tower sites compared to EEFlux ET(ETrF1.05). Again, excluding the period of early growth and crop senescence, the overall departures were reduced substantially (Table 5).

Table 4.
Percent departures for cumulative ET.

Table 5.
Percent departures for cumulative ET excluding early growth and crop senescence period.
4. Discussion
EEFlux is a version of METRIC implemented on the GEE platform, automating all the processing required to calculate pixel ET so that users can download ET, ETrF, ETr, and other products for the available images. In this study, we evaluated the performance of EEFlux in the estimation of daily ET of rainfed crops using EC ET as a reference, but as shown in Figure 3, one difficulty is that EC ET is not a perfect reference due to lack of closure of the energy balance (Figure 4) and uncertainties in the estimation of the footprint or ground area represented by the measured water vapor exchange. The ratio of the energy balance closure fluctuated between 83% and 93% and, for the purpose of this discussion, we will focus on two towers in each site with a ratio of 90% or more. Although some ET underprediction is likely, these towers offer reasonably low uncertainty to be helpful for this evaluation.
- ET overprediction during canopy senescence
The large and consistent overestimation of ET by EEFlux during crop senescence (Figure 5) increased the magnitude of errors (Figure 7 and Figure 8), indicating the need to investigate possible corrections to this problem. Similar overpredictions can be gleaned from figures presented in published METRIC evaluations [30,54], but the cause of this problem has not been addressed. The greenness fraction of the senescing crop canopy starts declining during senescence, eventually becoming zero, and the stomatal conductance of green portions often decreases dramatically due to terminal water stress, both factors reducing transpiration (and therefore ET) and increasing canopy temperature. In principle, this should be picked up by EEFlux, but it does only partially. Perhaps one issue is that senescence starts with the oldest (lowest) leaves, so that the top greener portion of the canopy may have a proportionally larger contribution to satellite-measured surface temperature, making it cooler and overestimating ET. However, some overestimation persists even when the entire canopy is senesced, perhaps implying that the bare and dry soil temperature of the hot pixel, assumed to have ET~0, is likely greater than the temperature of the non-transpiring senesced canopy that covers most of the pixel during senescence.
- Choice of cold pixel ETrF
Another important factor affecting the agreement between EC and EEFlux ET is the choice of cold pixel ETrF value. In addition to rainfed agriculture, the satellite images used for this study include irrigated areas that produce many different crops (annual, perennial, and fruit tree crops), with pixels in this area contributing the bulk and likely all the selected cold pixels. However, the use of an ETrF value of 1.05 to estimate ET from cold pixels in irrigated agriculture may not be adequate when applied in rainfed agriculture. Rainfed crops may suffer episodes of water deficit and fluctuating diurnal and day-to-day stomatal closure events as precipitation amount and distribution tend to limit crop transpiration, thus changing the proportion of sensible to latent heat fluxes. Although the METRIC energy balance has been shown to be able to estimate ET in response to water deficit [55], the water deficit in these studies is imposed by varying applied water amounts within the same experimental site in an irrigated region.
The fact remains that the use of a cold pixel ETrF of 1.05 led to significant ET overestimation in the rainfed conditions of this study (Figure 5), which has been previously reported [31,48,49]. The empirical solution to this problem has been to reduce cold pixel ETrF (from 1.05 to 0.85 in this and other studies), but this adjustment may be variable depending on environmental conditions. Not including towers SZ3 and GZ2, the seasonal average EEFlux ET departure was 26.5% and 1% with ETrF = 1.05 and 0.85 at Genesee, and 58.5% and 26.8% at St. John (Figure 8). This difference in overestimation between these two sites persists if the period of crop senescence is excluded (Table 5): departure was 10.1% and −12.2% (i.e., underestimation) with ETrF = 1.05 and 0.85 at Genesee, and 30.5% and 3.6% at St. John. The annual precipitation in St. John was 405 mm (2018) and 396 mm (2019), and 500 mm (2018) and 511 mm (2019) at Genesee, which is 26% higher than St. John over these two years. Differences in amount and distribution of precipitation and their effect on crop development and plant–water relations (canopy cover, canopy conductance to water vapor transfer, root depth, distribution of fractional root density with root depth, and others) are likely to impact the choice of cold pixel ETrF adjustment for rainfed conditions. Considering the results excluding the early growth and canopy senescence periods, agreement between EEFlux and EC ET would likely improve by choosing a cold pixel ETrF somewhat higher than 0.85 at Genesee.
- EEFlux performance
Considering cold pixel ETrF = 0.85, and not including the two towers with the lowest ratio of energy balance closure, the average performance indicators for St. John and Genesee were d = 0.76, RMSE = 1.36 mm/day, NRMSE = 0.56, average absolute daily departure = 161%, and d = 0.7, RMSE = 1.39 mm/day, NRMSE = 0.43, average absolute daily departure = 62%, respectively. When the early growth and crop senescence periods were excluded, the indicators improved dramatically: d = 0.77, RMSE = 0.86 mm/day, NRMSE = 0.23, average absolute daily departure = 19.6% (St. John) and d = 0.76, RMSE = 1.1 mm/day, NRMSE = 0.24, average absolute daily departure = 20.5% (Genesee). Working in the same rainfed region of this study, Khan et al. reported standard errors (SSE; similar to RMSE) of METRIC ET estimations of 0.34 mm/day for satellite overpass days at 4 sites (one EC tower per site) over three years, fluctuating between 0.49 and 0.83 mm/day among sites during growing seasons [31]. These METRIC estimates were obtained using manual calibration and weather stations located at each site, resulting in better agreement than the EEFlux estimates obtained in this study using gridMet weather data.
Based on comparisons with lysimeter ET, which is expected to be a more reliable measurement than EC, Allen et al. reported departures between lysimeter and METRIC ET for a sugar crop at Kimberly, ID, USA for 8 days of available images ranging from −26% to 34%, with one day of very low lysimeter ET (0.73 mm/day) resulting in a departure of 139% [10]. Average absolute daily departures for alfalfa at Rocky Ford, CO, USA was 15% (range: −5.1% to −25%) [56], and 12% (range: −17% to 21%) for sorghum at Apodi, Brazil [57], calculated for days of satellite pass only.
With random errors tending to cancel out with longer periods of comparison, Allen et al. reported departures for weekly periods ranging from −14% to 28% and ranging from −18% to 22% for monthly periods for forage crops near Montpellier, ID [10]. The same authors reported a departure of −0.6% for the period April 1-Sept 30, 1989 compared to the departure ranging from −26% to 34% for 8 individual satellite pass days. In this study, the mean absolute departure for cumulative ET fluctuated from 8.2% to 39.1% at St. John and 2.3% to 15.1% at Genesee (ETrF = 0.85 and excluding towers SZ3 and GZ2), and 8.3% to 14.7% at St. John and 0.6% to 20.7% at Genesee when the early growth and crop senescence periods were excluded. The overall cumulative ET average absolute departure with all sites and towers included was 22.9%, reduced to 11.9% when the early growth and crop senescence periods were excluded.
It is hard to reach definitive conclusions regarding EEFlux performance. Evaluations of METRIC using lysimeters in irrigated areas are scarce, often limited to a few days of the satellite overpass. A recent study evaluated hourly METRIC ET estimates on days of satellite overpass using lysimeters at Bushland, TX for the period 2001–2010 obtaining NRMSE of 0.5 for dryland lysimeters and 0.37 for irrigated lysimeters [58]. The authors attributed the lower performance for dryland lysimeters to lower overall ET and greater sensible heat flux, but how the figures of this study would translate to daily ET estimates during entire seasons is unclear.
Comparisons of EEFlux ET with lysimeters are currently nonexistent to the best of our knowledge. Foolad et al. compared METRIC and EEFlux in five locations in the US and found similarity in the energy balance, with high agreement for ETrF values (R2 and slope close to 1 and low RMSE of 0.03) but large departures for ET (~10% EEFlux ET overestimation), attributed to differences in weather sources—gridded weather used in automated EEFlux and ground-based weather in the manually calibrated METRIC estimations – that affect the calculated ETr [18]. Overall, for agricultural sites, mostly irrigated, EEFlux calculated ET values comparable to those obtained by trained METRIC users.
Applications for water management in irrigated agriculture and water productivity for rainfed and irrigated cropping systems would benefit from ET estimations within 10% of actual values, so improvements are needed. With improvements in technology, and mitigation of known sources of error, EEFlux automated implementation of METRIC has potential as a tool to greatly facilitate ET estimation, and eventually to offer near real-time ET estimates with reasonable accuracy.
5. Conclusions
Although well-installed and maintained lysimeters are arguably the best reference to evaluate the performance of ET estimation methods, EC flux towers are commonly used. In this study, the use of three EC towers in each field revealed differences in energy balance closure and ET values. At each site, two towers had closure ratios equal or greater than 90%, and one 84% or less, with the latter towers showing lower values of ET compared to the former. Although the towers with the larger ratios are still likely to under measure actual ET values, the uncertainty was considered small enough to serve as adequate reference.
Although the cold pixel ETrF is typically set at a value of 1.05 in irrigated agriculture, we found that a value of 0.85 resulted in better agreement and avoided large ET overprediction, but this value may need to be adjusted for specific rainfed agriculture conditions. We also found a large and consistent EEFlux ET overprediction during the period of crop senescence that greatly affected performance. The performance indices for daily ET estimations combined for all sites and years (d = 0.67, RMSE = 1.96 mm/day, NRMSE = 0.75, Absolute Departure Error = 181%) dramatically improved when cold pixel ETrF was reduced from 1.05 to 0.85 and the periods of early growth and canopy senescence were excluded (d = 0.76, RMSE = 0.97 mm/day, NRMSE = 0.24, Absolute Departure Error = 21.6%).
The absolute departure error determined on a seasonal basis resulted in errors of 11.9% with cold pixel ETrF = 0.85 and excluding the early growth and canopy senescence periods. Departures of 10% are a reasonable expectation for methods of ET estimation, which EEFlux could achieve with more frequent satellite images and better daily weather data sources. However, more work will be needed to develop adjustment methods of ETrF values during crop senescence and better understanding of the selection of adequate cold pixel ETrF for rainfed crops.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.O.S., S.A.K. and M.L.; methodology, C.O.S., S.A.K. and M.L.; software, M.L. and S.A.K.; validation, S.A.K.; formal analysis, S.A.K.; investigation, S.A.K., C.O.S. and M.L.; resources, C.O.S., S.A.K., E.S.R., Z.G. and E.S.R.; data curation, S.A.K. and Z.G.; writing—original draft preparation, S.A.K.; writing—review and editing, S.A.K., C.O.S., M.L., Z.G. and E.S.R.; visualization, S.A.K. and M.L.; supervision, C.O.S.; project administration, C.O.S.; funding acquisition, C.O.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Water for Agriculture grant no.1016467 from the USDA National Institute of Food and Agriculture and the Landscapes in Transition grant funded through award #2017-68002-26819 from the National Institute of Food and Agriculture. This work is not formally reviewed by USDA. The views expressed in this document are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of the agency.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author through the Email.
Acknowledgments
We thank the LIT project team at Washington State University, Pullman, WA, USA and University of Idaho, Moscow, ID, USA.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
References
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Howell, T.A.; Jensen, M.E. Evapotranspiration Information Reporting: I. Factors Governing Measurement Accuracy. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 23, 899–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rana, G.; Nader, K. Measurement and Estimation of Actual Evapotranspiration in the Field under Mediterranean Climate: A Review. Eur. J. Agron. 2000, 13, 125–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chávez, J.L.; Gowda, P.H.; Howell, T.A.; Copeland, K.S. Radiometric Surface Temperature Calibration Effects on Satellite Based Evapotranspiration Estimation. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 2337–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drexler, J.Z.; Snyder, R.L.; Spano, D.; Paw, U.K.T. A review of models and micrometeorological methods used to estimate wetland evapotranspiration. Hydro. Process. 2004, 18, 2071–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, M.S.; Jackson, R.D. Assessing the Spatial Distribution of Evapotranspiration Using Remotely Sensed Inputs. J. Environ. Qual. 1991, 20, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courault, D.; Seguin, B.; Olioso, A. Review on Estimation of Evapotranspiration from Remote Sensing Data: From Empirical to Numerical Modeling Approaches. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2005, 19, 223–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutas, W.P.; Norman, J.M. Use of Remote Sensing for Evapotranspiration Monitoring over Land Surfaces. Hydrol. Sci. J. 1996, 41, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Menenti, M.; Feddes, R.A.; Holtslag, A.A.M. A Remote Sensing Surface Energy Balance Algorithm for Land (SEBAL). 1. Formulation. J. Hydrol. 1998, 212–213, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Noordman, E.J.M.; Pelgrum, H.; Davids, G.; Thoreson, B.P.; Allen, R.G. SEBAL Model with Remotely Sensed Data to Improve Water-Resources Management under Actual Field Conditions. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2005, 131, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Tasumi, M.; Morse, A.; Trezza, R.; Wright, J.L.; Bastiaanssen, W.; Kramber, W.; Lorite, I.; Robison, C.W. Satellite-Based Energy Balance for Mapping Evapotranspiration with Internalized Calibration (METRIC)—Applications. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2007, 133, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Kimball, J.S. A review of remote sensing based actual evapotranspiration estimation. WIREs Water 2016, 3, 834–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.C.; Norman, J.M.; Diak, G.R.; Kustas, W.P.; Mecikalski, J.R. A Two-Source Time-Integrated Model for Estimating Surface Fluxes Using Thermal Infrared Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 60, 195–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roerink, G.J.; Su, Z.; Menenti, M. S-SEBI: A Simple Remote Sensing Algorithm to Estimate the Surface Energy Balance. Phys. Chem. Earth Part B Hydrol. Ocean. Atmos. 2000, 25, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z. The Surface Energy Balance System (SEBS) for Estimation of Turbulent Heat Fluxes. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2002, 6, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosgrove, B.A.; Lohmann, D.; Mitchell, K.E.; Houser, P.R.; Wood, E.F.; Schaake, J.C.; Robock, A.; Marshall, C.; Sheffield, J.; Duan, Q.; et al. Real-Time and Retrospective Forcing in the North American Land Data Assimilation System (NLDAS) Project. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Norman, J.M.; Anderson, M.C.; Kustas, W.P.; French, A.N.; Mecikalski, J.; Torn, R.; Diak, G.R.; Schmugge, T.J.; Tanner, B.C.W. Remote Sensing of Surface Energy Fluxes at 101-m Pixel Resolutions. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allen, R.; Tasumi, M.; Trezza, R. Satellite-Based Energy Balance for Mapping Evapotranspiration With Internalized Calibration (METRIC)-Model. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2007, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foolad, F.; Blankenau, P.; Kilic, A.; Allen, R.G.; Huntington, J.L.; Erickson, T.A.; Ozturk, D.; Morton, C.G.; Ortega, S.; Ratcliffe, I.; et al. Comparison of the Automatically Calibrated Google Evapotranspiration Application—EEFlux and the Manually Calibrated METRIC Application. Prepr. Eng. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.; Morton, C.; Kamble, B.; Kilic, A.; Huntington, J.; Thau, D.; Erickson, T.; Moore, R.; Trezza, R.; Ratcliffe, I.; et al. EEFlux: A Landsat-Based Evapotranspiration Mapping Tool on the Google Earth Engine. In 2015 ASABE/IA Irrigation Symposium: Emerging Technologies for Sustainable Irrigation-A Tribute to the Career of Terry Howell, Sr. Conference Proceedings; American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineer: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2015; Volume 12, pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Chávez, J.L.; Gowda, P.H.; Howell, T.A.; Copeland, K.S. Evaluating Three Evapotranspiration Mapping Algorithms with Lysimetric Data in the Semi-Arid Texas High Plains. In Proceedings of the 28th Annual International Irrigation Show, San Diego, CA, USA, 9–11 December 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hankerson, B.; Kjaersgaard, J.; Hay, C. Estimation of Evapotranspiration from Fields with and without Cover Crops Using Remote Sensing and in Situ Methods. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 3796–3812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Healey, N.C.; Irmak, A.; Arkebauer, T.J.; Billesbach, D.P.; Lenters, J.D.; Hubbard, K.G.; Allen, R.G.; Kjaersgaard, J. Remote Sensing and in Situ-Based Estimates of Evapotranspiration for Subirrigated Meadow, Dry Valley, and Upland Dune Ecosystems in the Semi-Arid Sand Hills of Nebraska, USA. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2011, 25, 151–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Kilic, A. Treatment of Anchor Pixels in the METRIC Model for Improved Estimation of Sensible and Latent Heat Fluxes. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2011, 56, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco-Benavides, M.; Ortega-Farías, S.; Lagos, L.; Kleissl, J.; Morales-Salinas, L.; Kilic, A. Parameterization of the Satellite-Based Model (METRIC) for the Estimation of Instantaneous Surface Energy Balance Components over a Drip-Irrigated Vineyard. Remote Sens. Basel Switz. 2014, 6, 11342–11371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Folhes, M.T.; Rennó, C.D.; Soares, J.V. Remote Sensing for Irrigation Water Management in the Semi-Arid Northeast of Brazil. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 1398–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebert, R.; Huntington, J.; Morton, C.; Sueki, S.; Acharya, K. Reduced Evapotranspiration from Leaf Beetle Induced Tamarisk Defoliation in the Lower Virgin River Using Satellite-Based Energy Balance: Reduced ET from Tamarisk Defoliation in the Lower Virgin River. Ecohydrology 2015, 9, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madugundu, R.; Al-Gaadi, K.A.; Abdalhaleem, E.T.; Hassaballa, A.; Patil, V.C. Performance of the METRIC Model in Estimating Evapotranspiration Fluxes over an Irrigated Field in Saudi Arabia Using Landsat-8 Images. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 6135–6151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niza, Z.; Khan, M.Z.; Govind, A.; Marchetti, M.; Lasserre, B.; Magliulo, E.; Manco, A. Evaluation of SEBS, METRIC-EEFlux, and QWaterModel Actual Evapotranspiration for a Mediterranean Cropping System in Southern Italy. Agronomy 2021, 11, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Tasumi, M.; Morse, A.; Trezza, R. A Landsat-Based Energy Balance and Evapotranspiration Model in Western US Water Rights Regulation and Planning. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2005, 19, 251–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Liu, S.; Tieszen, L.L.; Suyker, A.E.; Verma, S.B. Estimating Seasonal Evapotranspiration from Temporal Satellite Images. Irrig. Sci. 2011, 30, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, A.; Stöckle, C.O.; Nelson, R.L.; Peters, T.; Adam, J.C.; Lamb, B.; Chi, J.; Waldo, S. Estimating Biomass and Yield Using METRIC Evapotranspiration and Simple Growth Algorithms. Agron. J. 2019, 111, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khand, K.; Bhattarai, N.; Taghvaeian, S.; Wagle, P.; Gowda, P.H.; Alderman, P.D. Modeling Evapotranspiration of Winter Wheat Using Contextual and Pixel-Based Surface Energy Balance Models. Trans. ASABE 2021, 64, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duijndam, L.M. Evaluation of Two Automated Remote Sensing- Based Surface Energy Balance Models for Estimating Daily Evapotranspiration. Master’s Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands, October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wilczak, J.M.; Oncley, S.P.; Stage, S.A. Sonic Anemometer Tilt Correction Algorithms. Bound. Layer. Meteorol. 2001, 99, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massman, W.J. A Simple Method for Estimating Frequency Response Corrections for Eddy Covariance Systems. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2000, 104, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massman, W.J. Reply to Comment by Rannik on ‘A Simple Method for Estimating Frequency Response Corrections for Eddy Covariance Systems. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2001, 107, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncrieff, J.; Clement, R.; Finnigan, J.; Meyers, T. Averaging, Detrending, and Filtering of Eddy Covariance Time Series. In Handbook of Micrometeorology; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 7–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, E.K.; Pearman, G.I.; Leuning, R. Correction of Flux Measurements for Density Effects Due to Heat and Water Vapour Transfer. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1980, 106, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauder, M.; Foken, T. Documentation and Instruction Manual of the Eddy Covariance Software Package TK2. Bayreuth Abt. Mikrometeorol. 2004, 26, 26–42. [Google Scholar]
- Wutzler, T.; Lucas-Moffat, A.; Migliavacca, M.; Knauer, J.; Sickel, K.; Šigut, L.; Menzer, O.; Reichstein, M. Basic and Extensible Post-Processing of Eddy Covariance Flux Data with REddyProc. Biogeosciences 2018, 15, 5015–5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kljun, N.; Calanca, P.; Rotach, M.W.; Schmid, H.P. A simple two-dimensional parameterisation for Flux Footprint Prediction (FFP). Geosc. Model Dev. 2015, 8, 3695–3713. Available online: http://www.geosci-model-dev.net/8/3695/2015/gmd-8-3695-2015.html (accessed on 26 July 2020). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russell, E.S.; Liu, H.; Gao, Z.; Finn, D.; Lamb, B. Impacts of soil heat flux calculation methods on the surface energy balance closure. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 214–215, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Russell, E.S.; Missik, J.E.C.; Huang, M.; Chen, X.; Strickland, C.E.; Clayton, R.; Arntzen, E.; Ma, Y.; Liu, H. A Novel Approach to Evaluate Soil Heat Flux Calculation: An Analytical Review of Nine Methods. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 6934–6949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abatzoglou, J.T. Development of Gridded Surface Meteorological Data for Ecological Applications and Modelling. Int. J. Climatol. 2013, 33, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Technical Committee on Standardization of Reference Evapotranspiration. The ASCE Standardized Reference Evapotranspiration Equation; Ivan AWalter Elliott, R.L., Howell, T.A., Itenfisu, D., Jensen, M.E., Snyder, R.L., Eds.; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, A.; Allen, R. Google Earth Engine Evapotranspiration Flux—EEFlux. INOVAGRI 2015, 1, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Irmak, A.; Allen, R.G.; Jeppe, K.; Justin, H.; Kamble, B.; Ricardo, T.; Ian, R. Operational Remote Sensing of ET and Challenges. In Evapotranspiration—Remote Sensing and Modeling; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012; pp. 467–492. [Google Scholar]
- Conrad, C.; Dech, S.W.; Hafeez, M.; Lamers, J.; Martius, C.; Strunz, G. Mapping and assessing water use in a Central Asian irrigation system by utilizing MODIS remote sensing products. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2007, 21, 197–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liaqat, U.W.; Choi, M. Surface Energy Fluxes in the Northeast Asia Ecosystem: SEBS and METRIC Models Using Landsat Satellite Images. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 214–215, 60–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, C.J. Some comments on the evaluation of model performance. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1982, 63, 1309–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, K.; Goldstein, A.; Falge, E.; Aubinet, M.; Baldocchi, D.; Berbigier, P.; Bernhofer, C.; Ceulemans, R.; Dolman, H.; Field, C.; et al. Energy Balance Closure at FLUXNET Sites. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2002, 113, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oncley, S.; Foken, T.; Vogt, R.; Kohsiek, W.; DeBruin, H.A.R.; Bernhofer, C.; Christen, A.; Van Gorsel, E.; Grantz, D.; Feigenwinter, C.; et al. The energy balance experiment ebex-2000. Part I: Overview and energy balance. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2007, 123, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, N.; Srivastava, A.; Dumka, U.C. A Long-Term Spatiotemporal Analysis of Vegetation Greenness over the Himalayan Region Using Google Earth Engine. Climate 2021, 9, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Senay, G.B. Comparison of Four Different Energy Balance Models for Estimating Evapotranspiration in the Midwestern United States. Water 2016, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chandel, A.K.; Khot, L.R.; Molaei, B.; Peters, R.T.; Stöckle, C.O.; Jacoby, P.W. High-Resolution Spatiotemporal Water Use Mapping of Surface and Direct-Root-Zone Drip-Irrigated Grapevines Using UAS-Based Thermal and Multispectral Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkhwanazi, M.M.; Chávez, J.L. Mapping evapotranspiration with the remote sensing ET algorithms METRIC and SEBAL under advective and non-advective conditions: Accuracy determination with weighing lysimeters. Hydrol. Days 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, J.G.; Sánchez, J.M.; Piqueras, J.G.; Espínola, J.; Viana, P.C.; Alves, A.D.S. Evapotranspiration of Sorghum from the Energy Balance by METRIC and STSEB. Rev. Bras. Eng. Agric. Ambient. 2020, 24, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, A.A.; Engel, B.A.; Bralts, V.F.; Marek, G.W.; Moorhead, J.E.; Radwan, S.A.; Gowda, P.H. Assessment of Landsat-Based Evapotranspiration Using Weighing Lysimeters in the Texas High Plains. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).