MTRC-Tolerated Multi-Target Imaging Based on 3D Hough Transform and Non-Equal Sampling Sparse Solution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
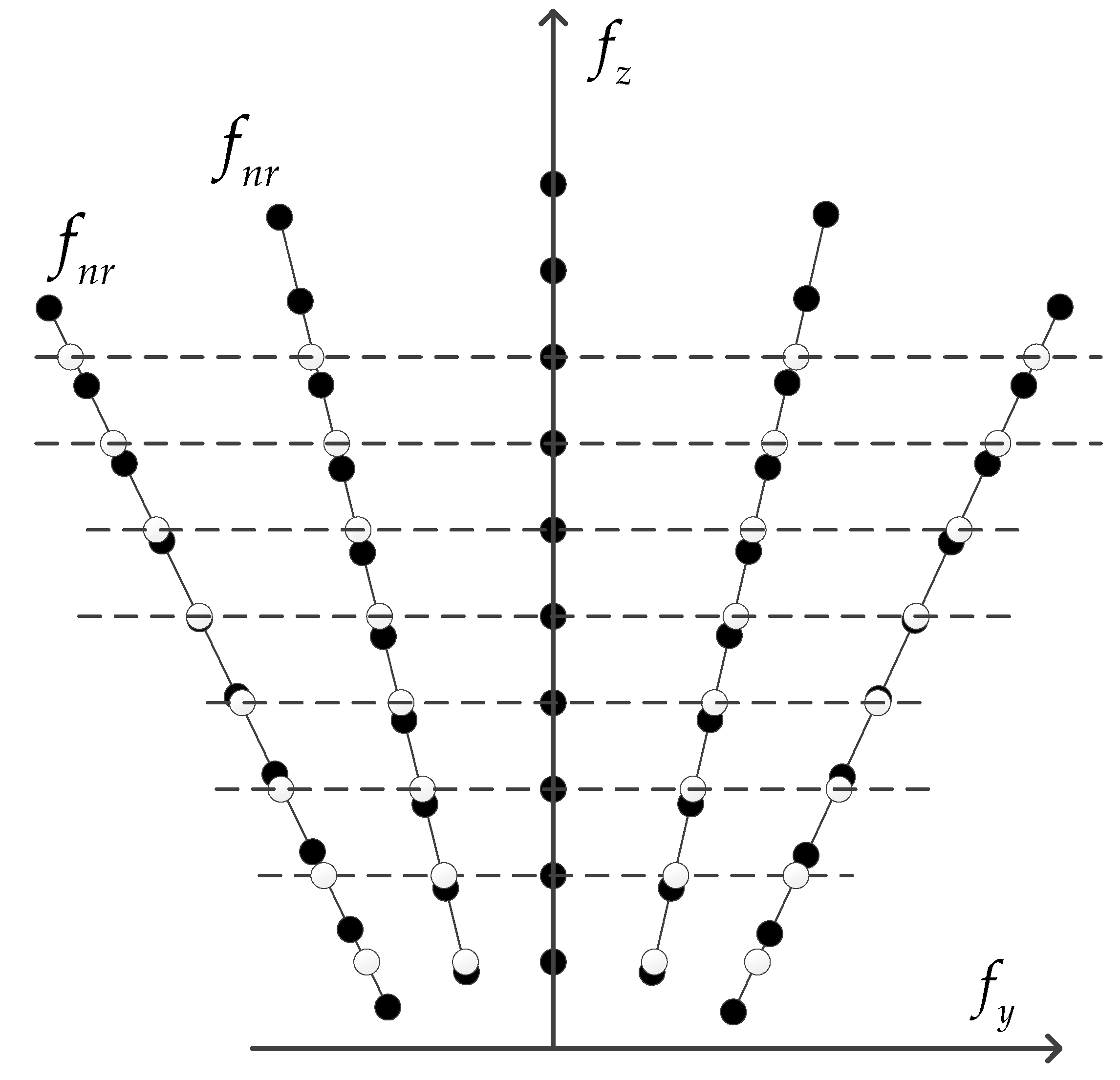
2. Multi-Target Echo Processing Based on 3D Hough Transform
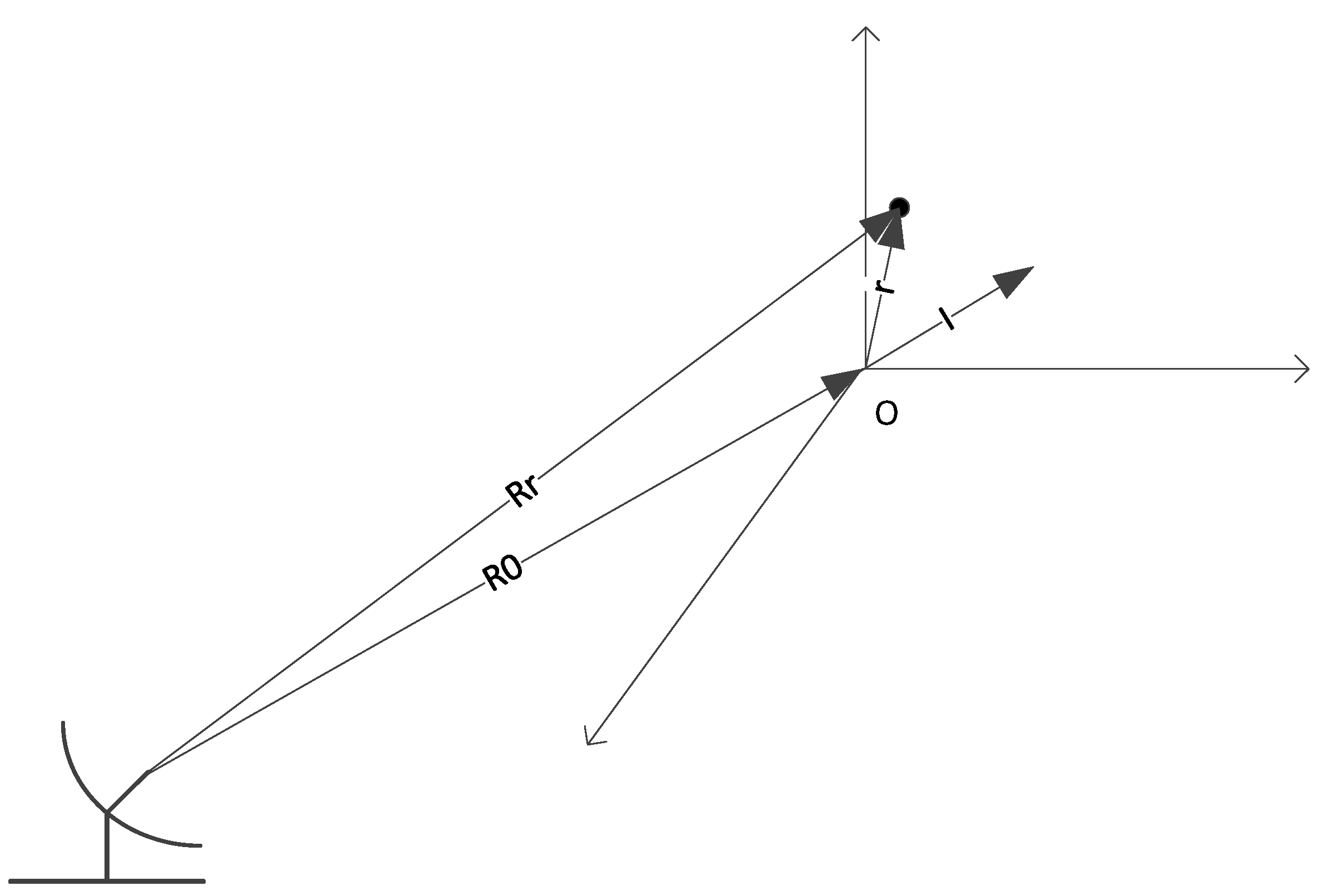
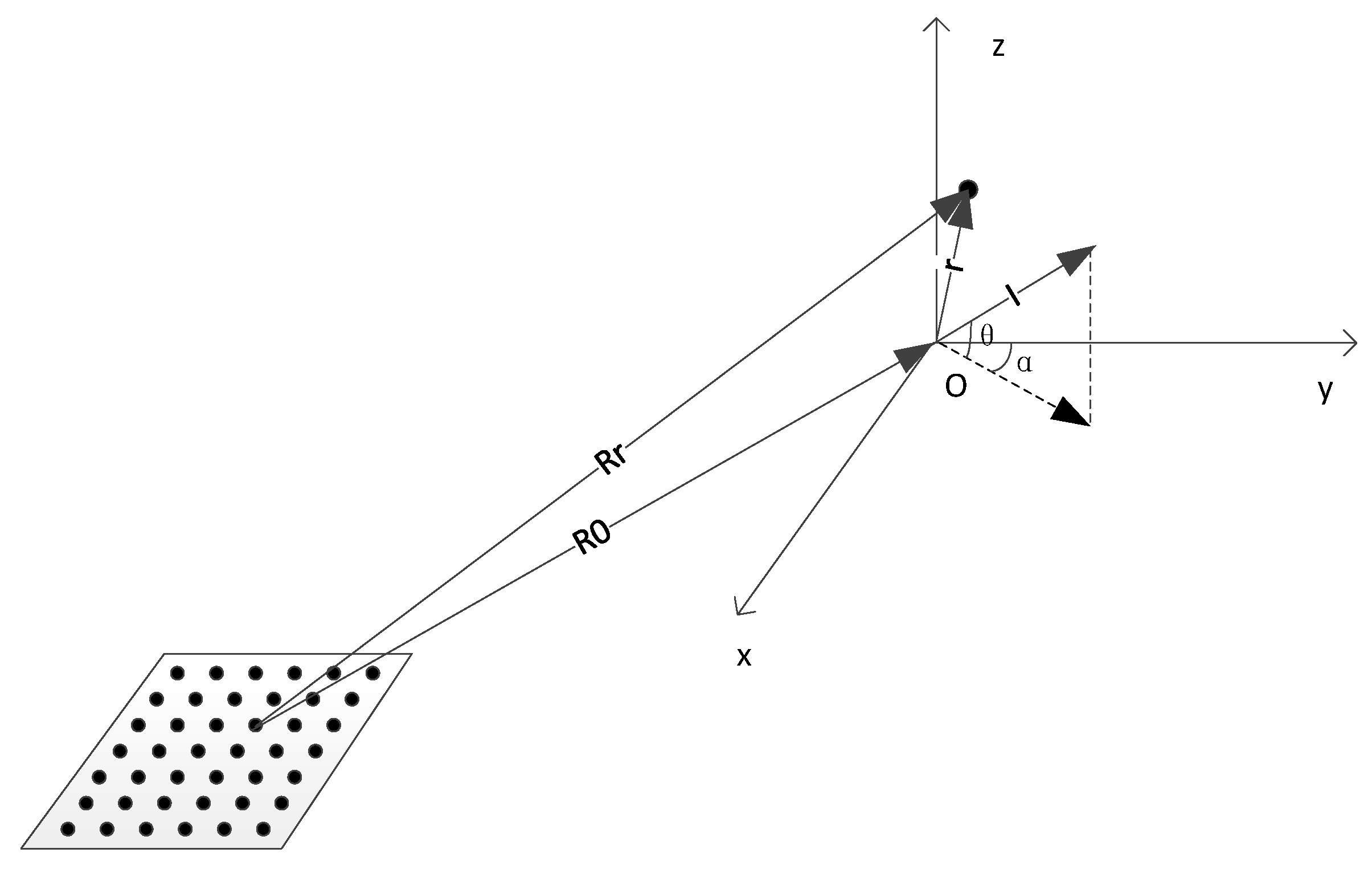
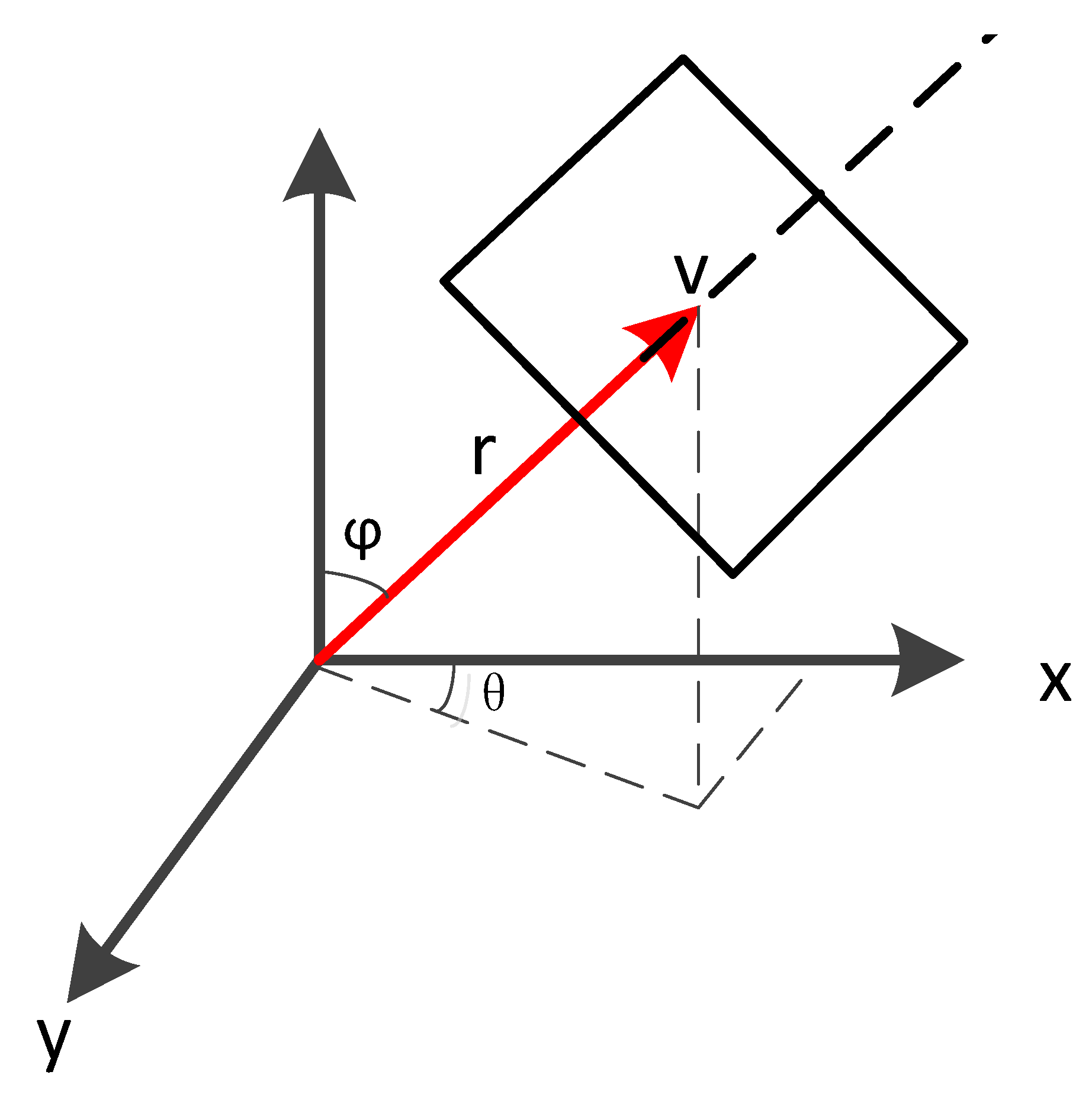
2.1. Signal Model
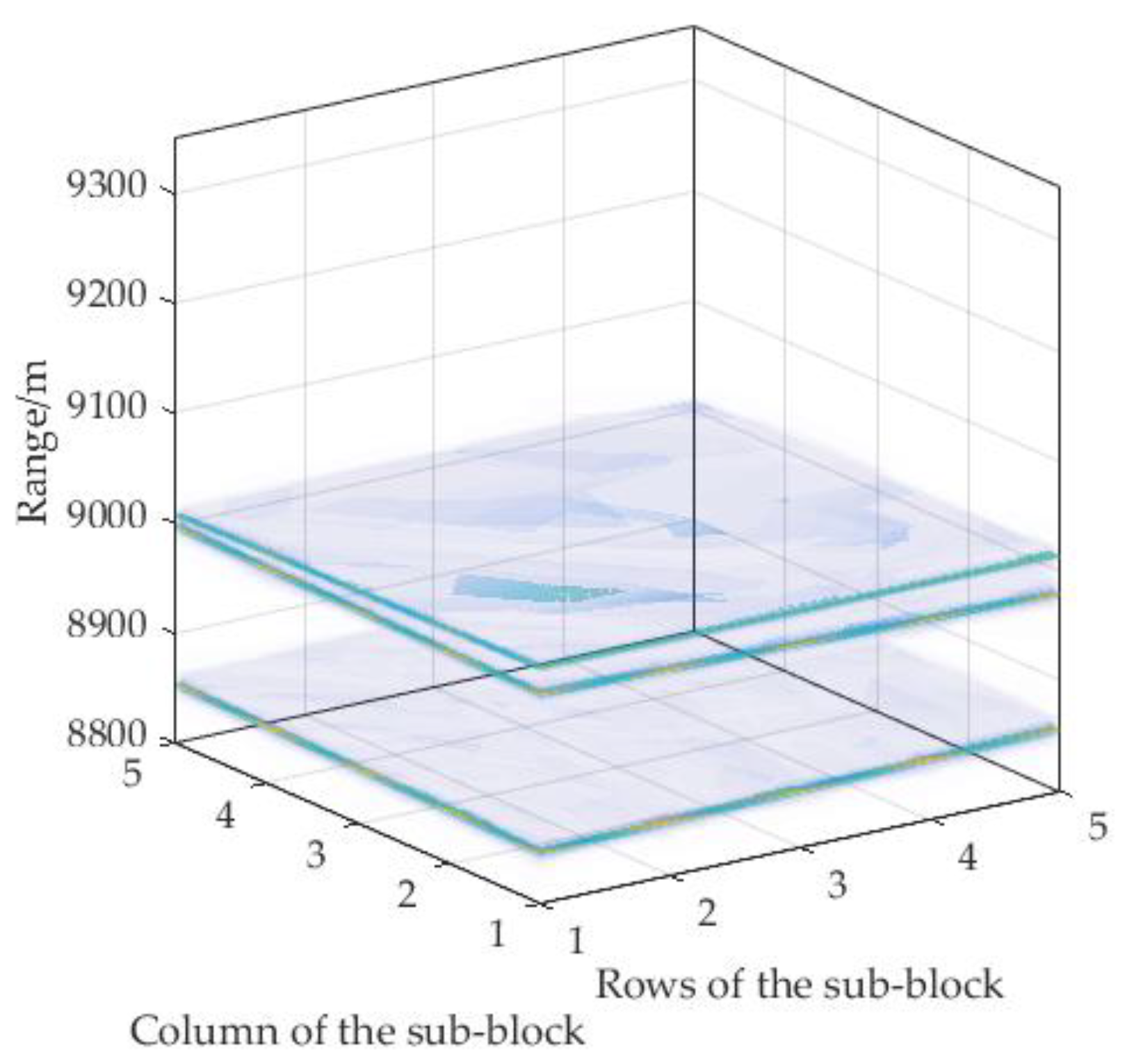
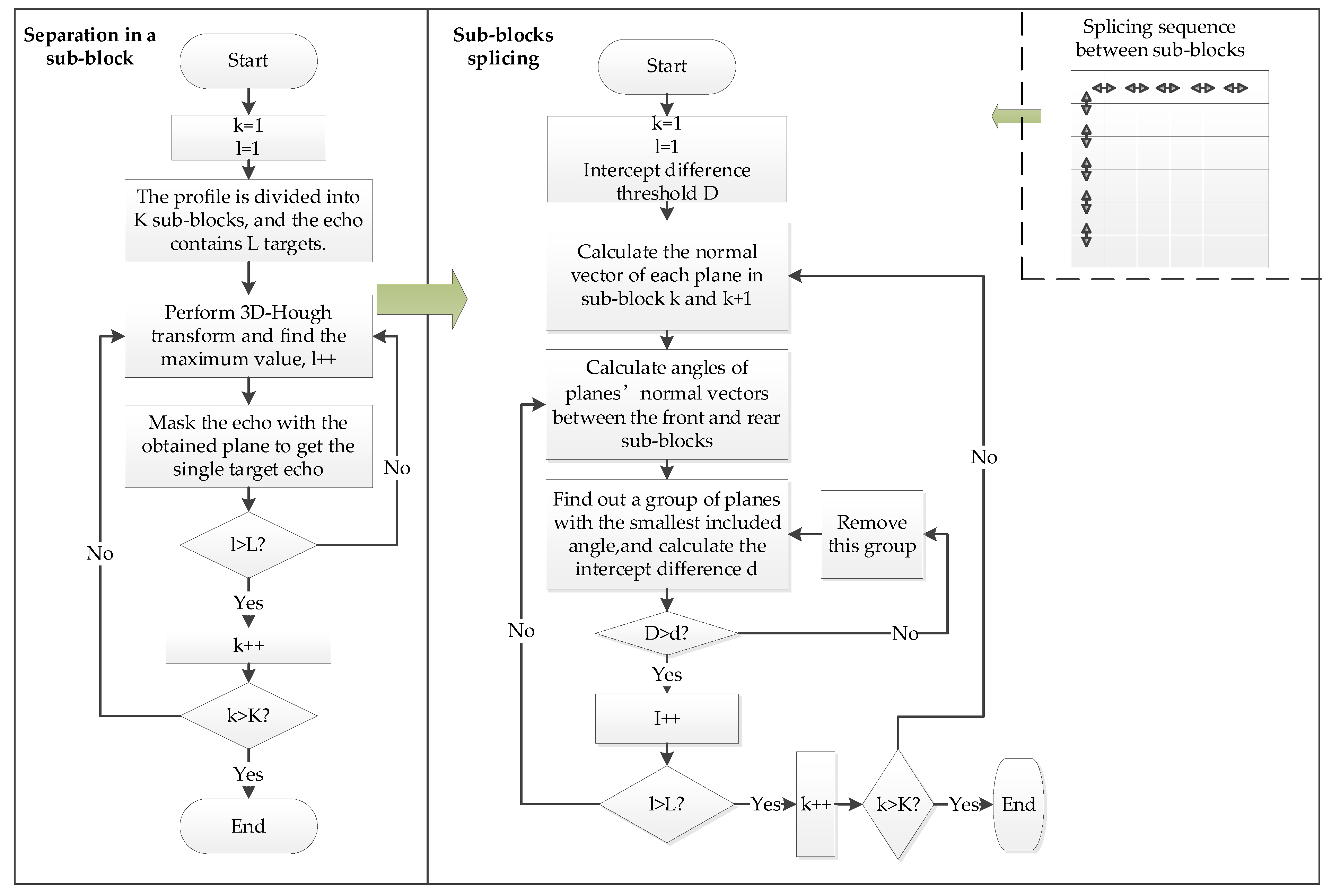
2.2. Multi-Target Echo Separation in the Sub-Block
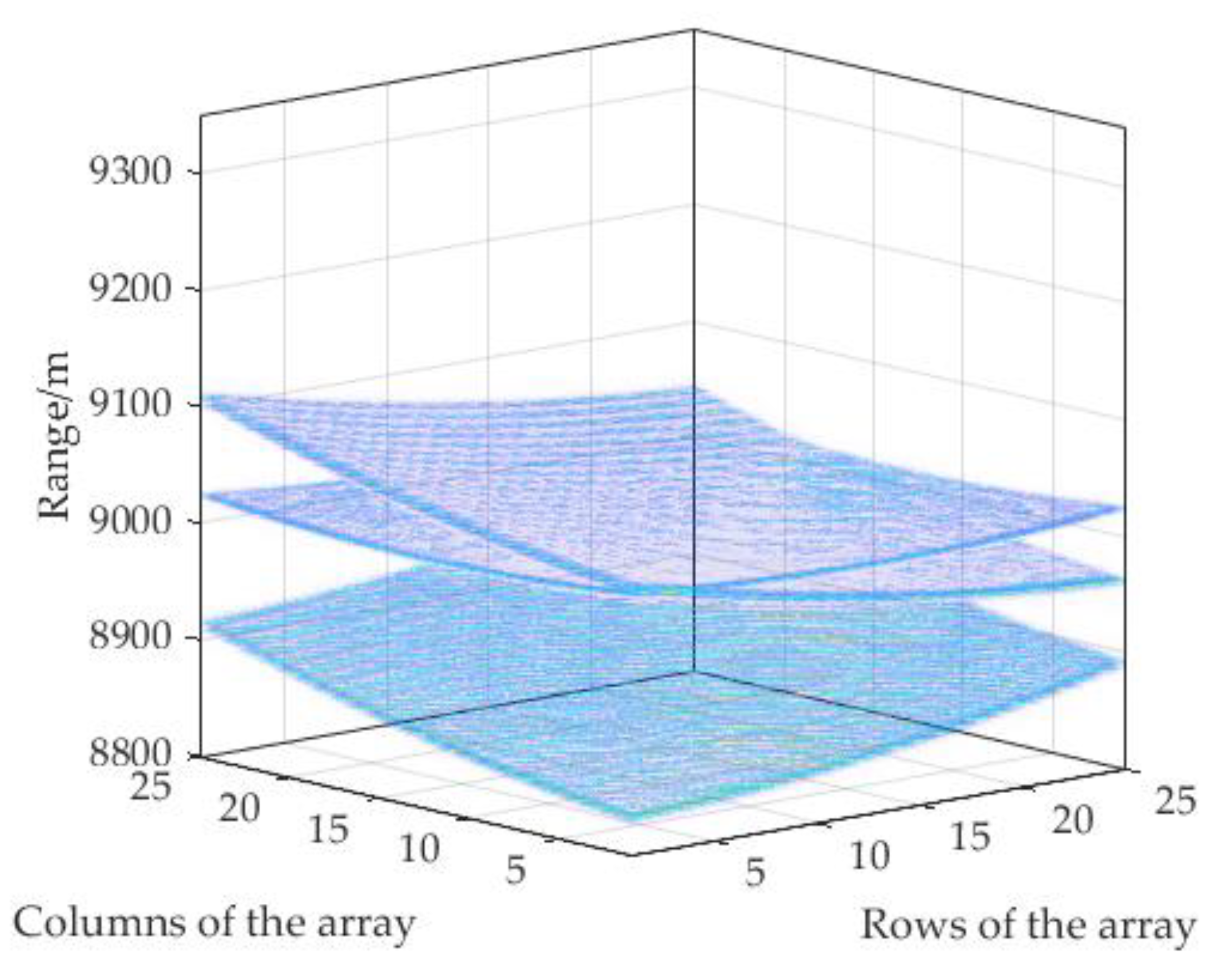
2.3. Sub-Block Splicing
3. MTRC-Tolerated Imaging Based on Compressed Sensing Imaging
3.1. Compressed Sensing Method
| Algorithm 1. The Orthogonal Matching Pursuit Algorithm | |
| Input: observation signal and measurement matrix A Output: sparse vector Step 1: Set the initial value of the residual as , the selected atomic as , and the number of iterations as Step 2: Find the atom in the set (each column in the measurement matrix) that best matches the signal, | |
| (17) | |
| Step 3: Solve the solution of minimizing noise according to the least square method, | |
| (18) | |
| Step 4: Update residual, | |
| (19) | |
| Step 5: Let k = k + 1, keep looping steps 2 through 4 before meeting the condition to end the loop. | |
| Step 6: Output the result | |
| (20) | |
3.2. Imaging Algorithm Based on Compressed Sensing
 ” is the received signal after interpolation, which is recorded as . in this way, imaging in azimuth direction can be performed for each , i.e.,
” is the received signal after interpolation, which is recorded as . in this way, imaging in azimuth direction can be performed for each , i.e.,
4. Experiment Simulations
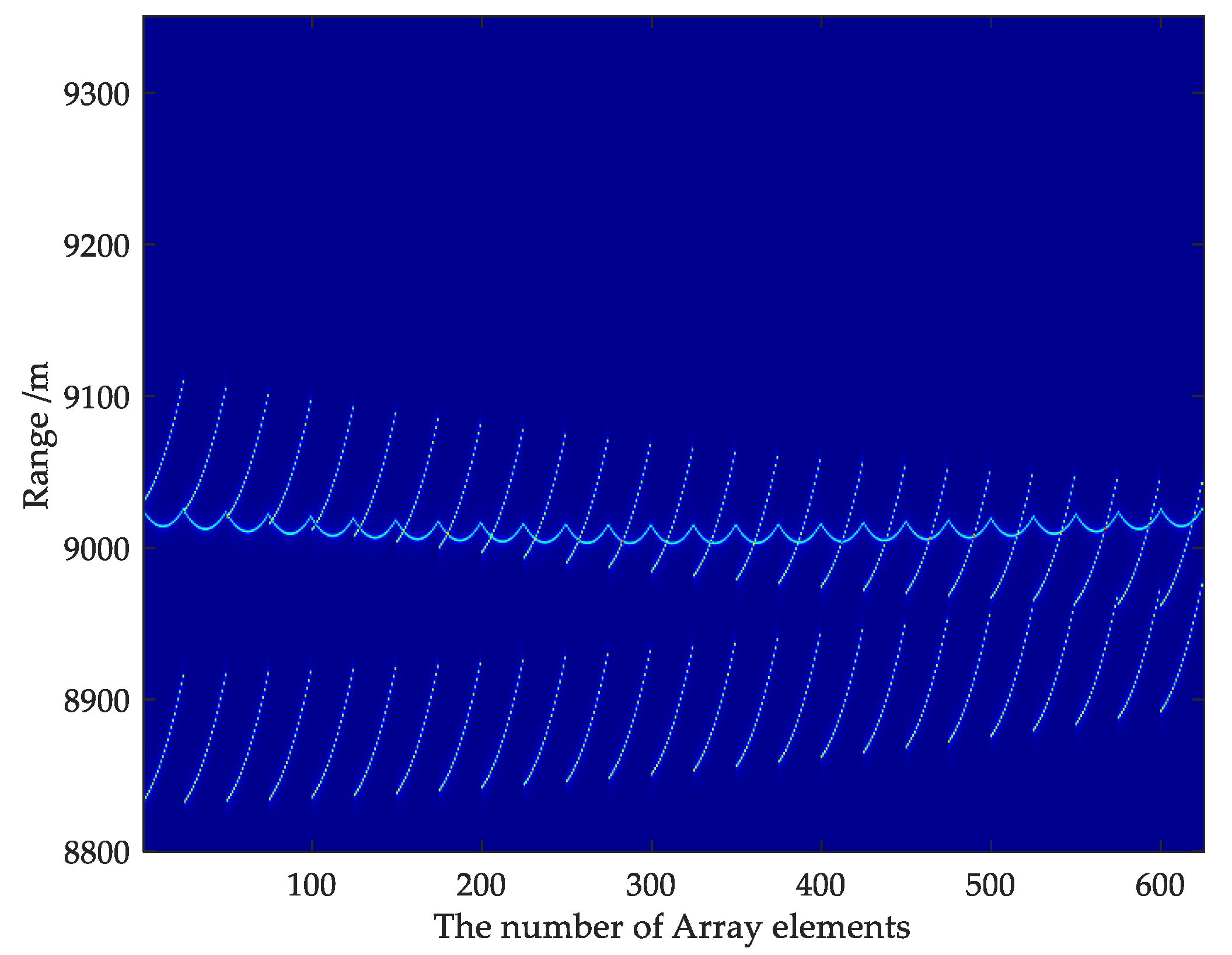
4.1. Multi-Target Echo Separation
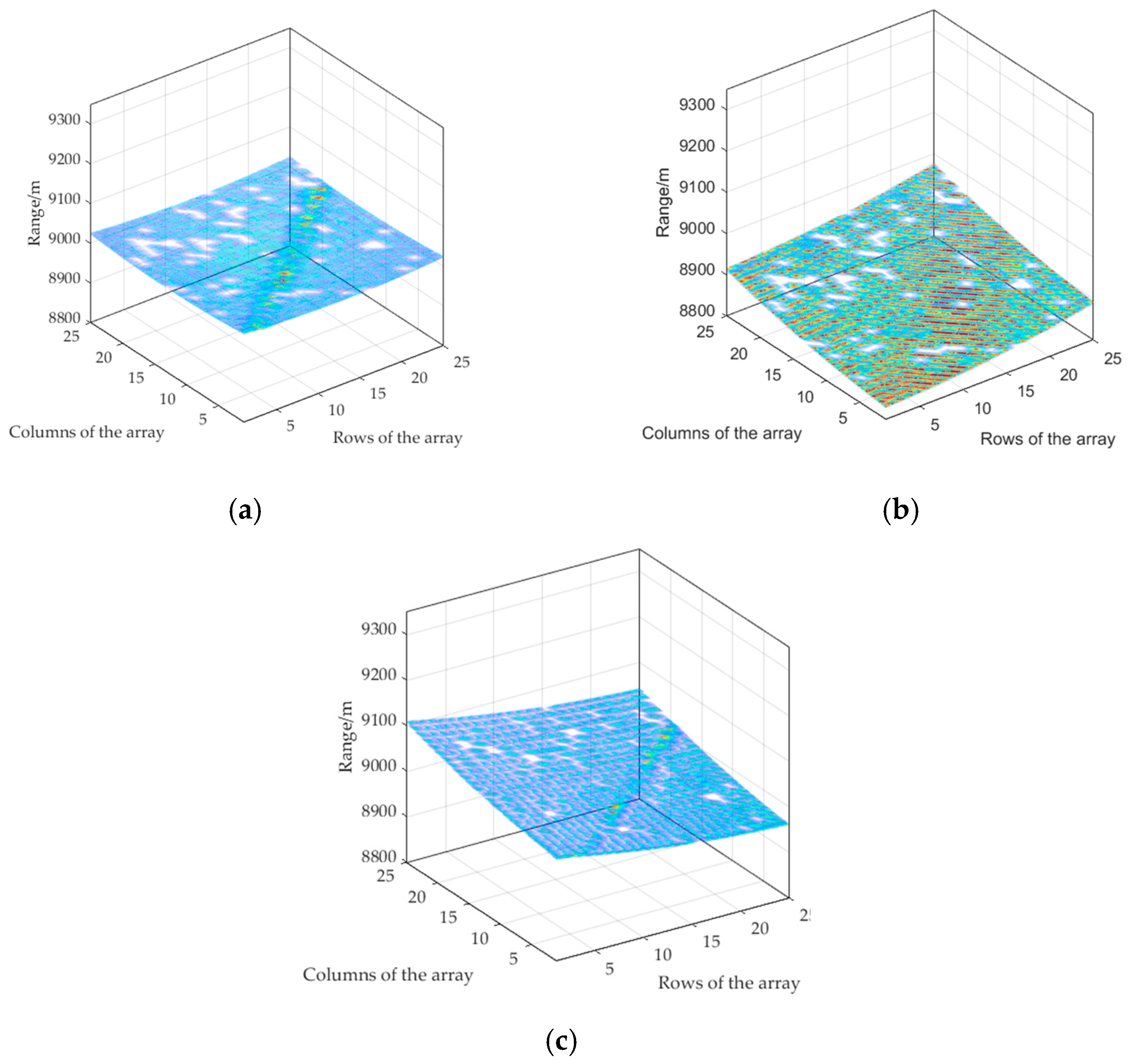
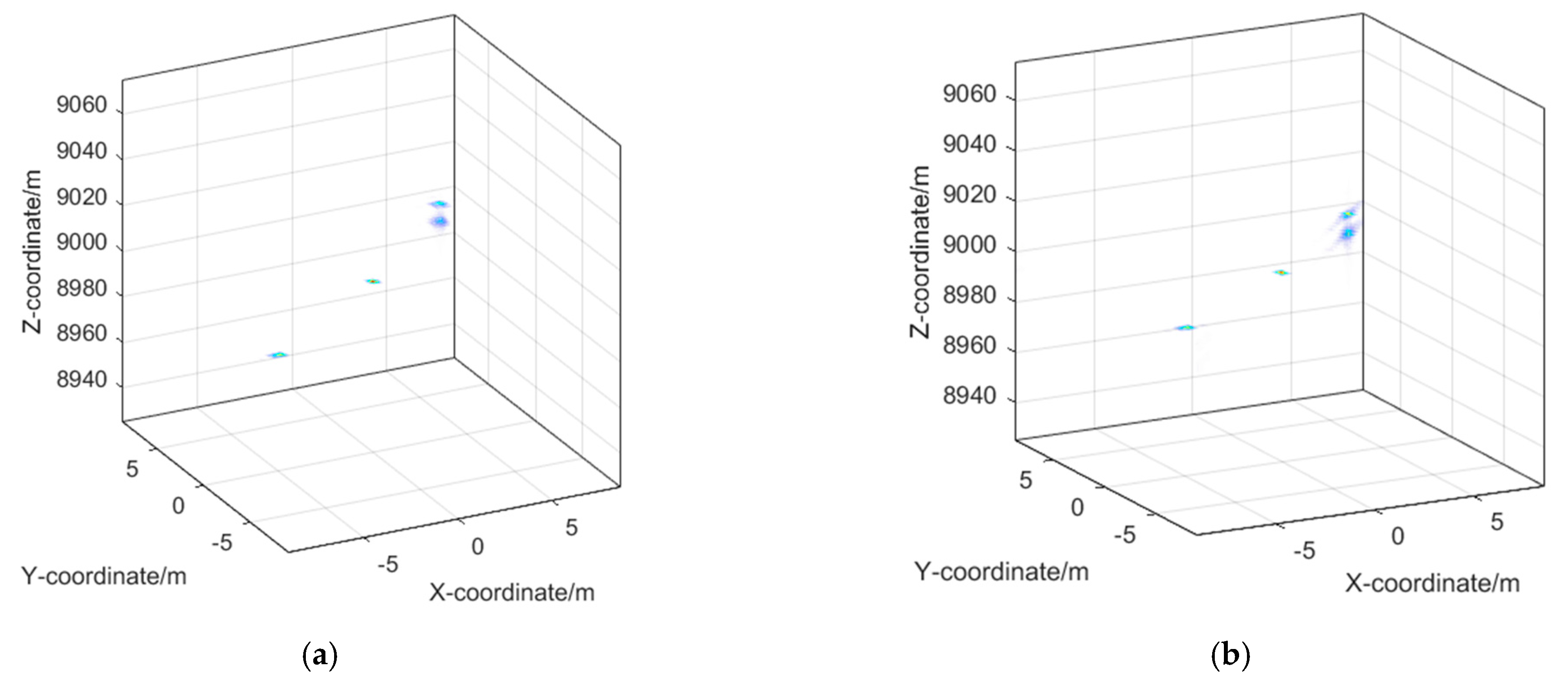
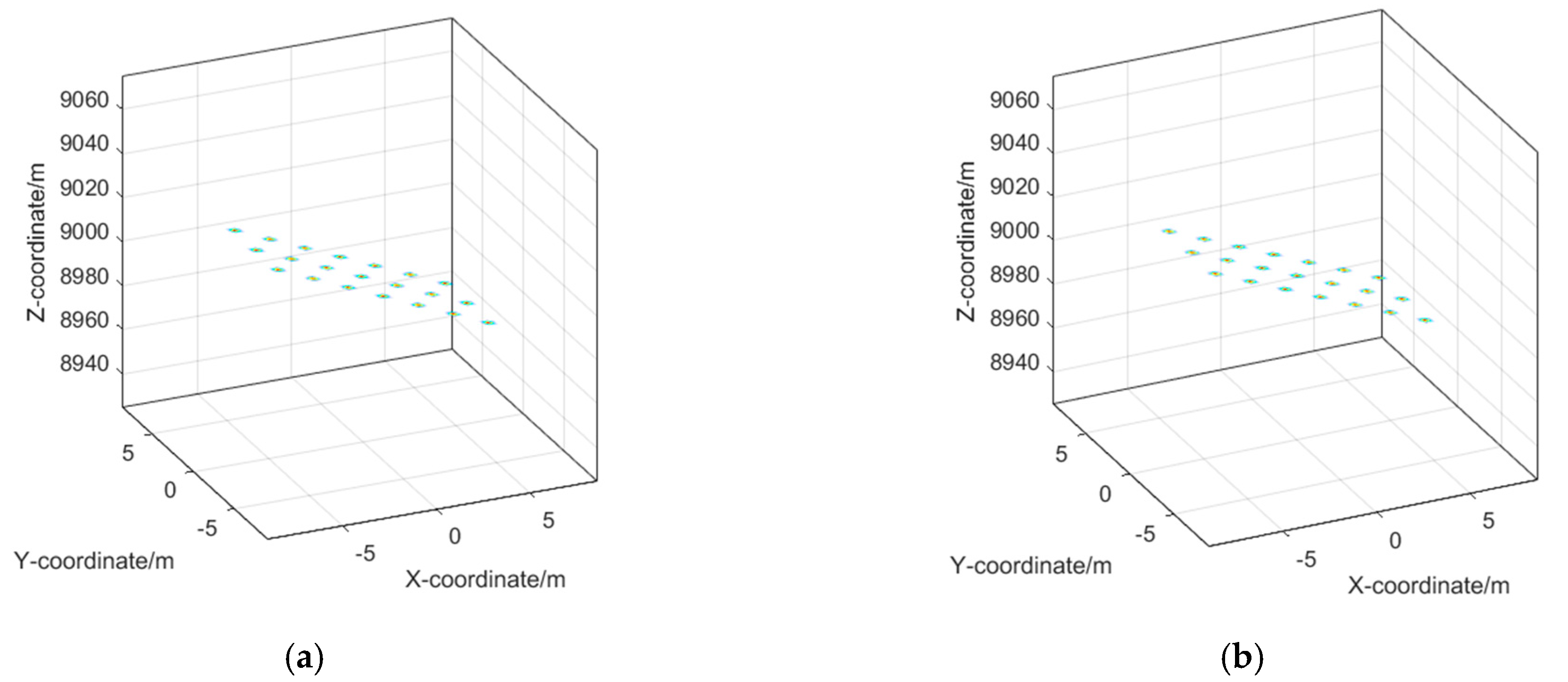
4.2. Compressed Sensing Imaging Algorithm
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sherwin, C.W.; Ruina, J.P.; Rawcliffe, R.D. Some Early Developments in Synthetic Aperture Radar Systems. IRE Trans. Mil. Electron. 1962, MIL-6, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skolnik, M.I. Fifty years of radar. IEEE Proc. 1985, 73, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soumekh, M. Synthetic Aperture Radar Signal Processing with Matlab Algorithms; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik, M.I. Radar in the twentieth century. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2000, 15, 27–46. [Google Scholar]
- Burgmann, R.; Rosen, P.A.; Fielding, E.J. Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry to Measure Earth’s Surface Topography and Its Deformation. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2000, 28, 169–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avent, R.K.; Shelton, J.D.; Brown, P. The ALCOR C-band imaging radar. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 1996, 38, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, W.; Ward, W. An Overview of the First Fifty Years; Radar Development at Lincoln Laboratory: Lexington, KY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Andrews, H.C. Target-Motion-Induced Radar Imaging. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1980, AES–16, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Song, H.; He, W. A Novel Method for Refocusing Moving Ships in SAR Images via ISAR Technique. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, X.; Chang, Y.; Liu, J.; Xiao, S. Estimation of Precession Parameters and Generation of ISAR Images of Ballistic Missile Targets. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2010, 46, 1983–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karine, A.; Toumi, A.; Khenchaf, A.; El Hassouni, M. Radar Target Recognition Using Salient Keypoint Descriptors and Multitask Sparse Representation. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhu, H. Interferometric ISAR 3D Imaging of Target Satellite in Low Earth Orbit. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Test and Measurement (ISTM), Beijing, China, 5–8 August 2007. [Google Scholar]
- McFadden, F.E. Three-dimensional reconstruction from ISAR sequences. In Radar Sensor Technology and Data Visualization; SPIE Press: Bellingham, DC, USA, 2002; SPIE 4744. [Google Scholar]
- Lord, R.; Nel, W.; Abdul, G. Investigation of 3-D RCS Image formation of ships using ISAR. Physics 2006, 5, 320–325. [Google Scholar]
- Suwa, K.; Wakayama, T.; Iwamoto, M. Three-Dimensional Target Geometry and Target Motion Estimation Method Using Multistatic ISAR Movies and Its Performance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 2361–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwa, K.; Wakayama, T.; Iwamoto, M. Estimation of target motion and 3D target geometry using multistatic ISAR movies. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Boston, MA, USA, 6–11 July 2008; Volume 5, pp. V-429–V-432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skolnik, M.I. Introduction to RADAR Systems; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Xia, X.-G.; Chen, V. Three-dimensional ISAR imaging of maneuvering targets using three receivers. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2001, 10, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Narayanan, R. Three-dimensional interferometric ISAR imaging for target scattering diagnosis and modeling. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2001, 10, 1094–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Yeo, T.S.; Guo, Q.; Wei, P. Bistatic ISAR Imaging Incorporating Interferometric 3-D Imaging Technique. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 3859–3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stagliano, D.; Martorella, M.; Casalini, E. Interferometric bistatic ISAR processing for 3D target reconstruction. In Proceedings of the 2014 11th European Radar Conference, Rome, Italy, 8–10 October 2014; pp. 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.; Ding, C.; Liang, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, F. Sparse Bayesian Learning Based Three-Dimensional Imaging Algorithm for Off-Grid Air Targets in MIMO Radar Array. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Del-Rey-Maestre, N.; Mata-Moya, D.; Jarabo-Amores, M.-P.; Gómez-Del-Hoyo, P.-J.; Bárcena-Humanes, J.-L.; Rosado-Sanz, J. Passive Radar Array Processing with Non-Uniform Linear Arrays for Ground Target’s Detection and Localization. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monteith, A.R.; Ulander, L.M.H.; Tebaldini, S. Calibration of a Ground-Based Array Radar for Tomographic Imaging of Natural Media. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rabideau, D.J.; Parker, P. Ubiquitous MIMO multifunction digital array radar. In Proceedings of the 37th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems & Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 9–12 November 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraniuk, R.; Steeghs, P. Compressive Radar Imaging. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Radar Conference, Boston, MA, USA, 17–20 April 2007; pp. 128–133. [Google Scholar]
- Uḡur, S.; Arıkan, O. SAR image reconstruction and autofocus by compressed sensing. Digit. Signal Process. 2012, 22, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haneche, H.; Ouahabi, A.; Boudraa, B. Compressed Sensing-Speech Coding Scheme for Mobile Communications. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 40, 5106–5126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ender, J.H. On compressive sensing applied to radar. Signal Process. 2010, 90, 1402–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, G.Q.; Wang, D.W.; Ma, X.Y.; Su, Y. Three-Dimensional Imaging via Wideband MIMO Radar System. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2010, 7, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Su, Y. A type of M 2-transmitter N 2-receiver MIMO radar array and 3D imaging theory. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2011, 54, 2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, F.; Chi, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, F.; Liang, Y. An imaging method for MIMO radar with sparse array based on Compressed Sensing. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing (ICSPCC), Xi’an, China, 14–16 September 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Natarajan, B.K. Sparse approximate solutions to linear systems. Siam J. Comput. 1995, 24, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.S.; Saunders, D. Atomic Decomposition by Basis Pursuit. Siam J. Comput. 2001, 43, 129–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donoho, D.L.; Elad, M. Optimally sparse representation in general (nonorthogonal) dictionaries via l~1 minimization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 2197–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tropp, J.A.; Gilbert, A.C. Signal Recovery From Random Measurements Via Orthogonal Matching Pursuit. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2007, 53, 4655–4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


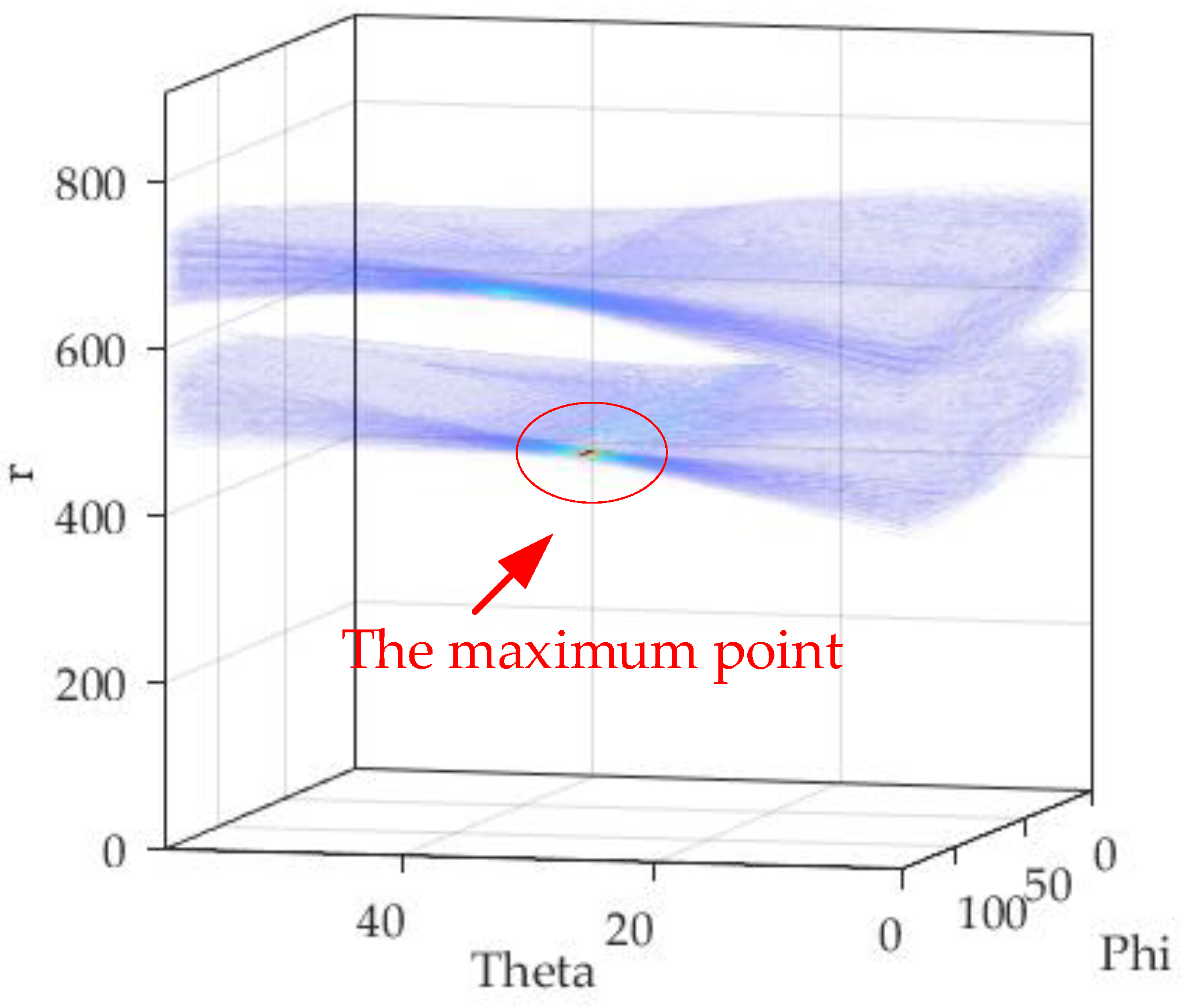
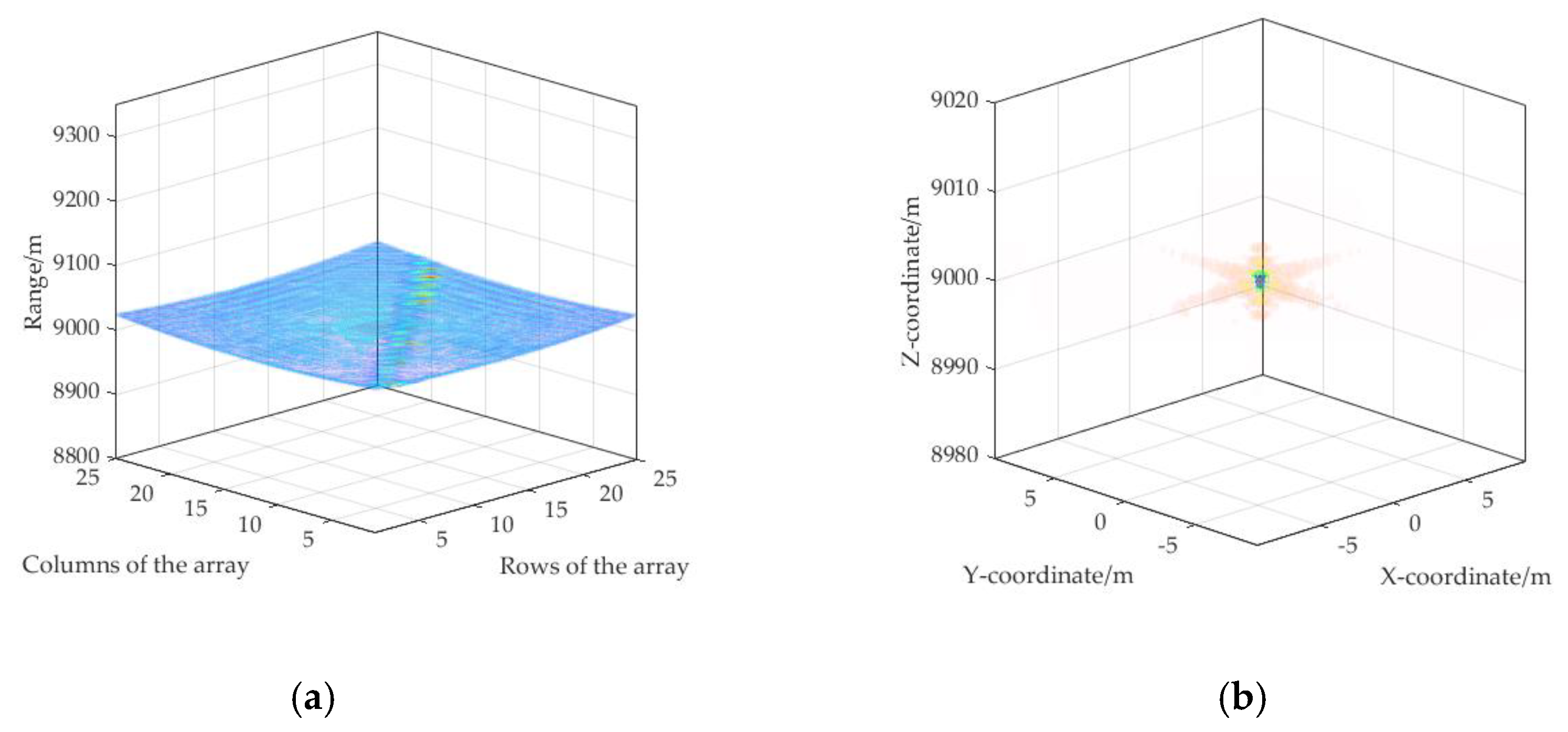
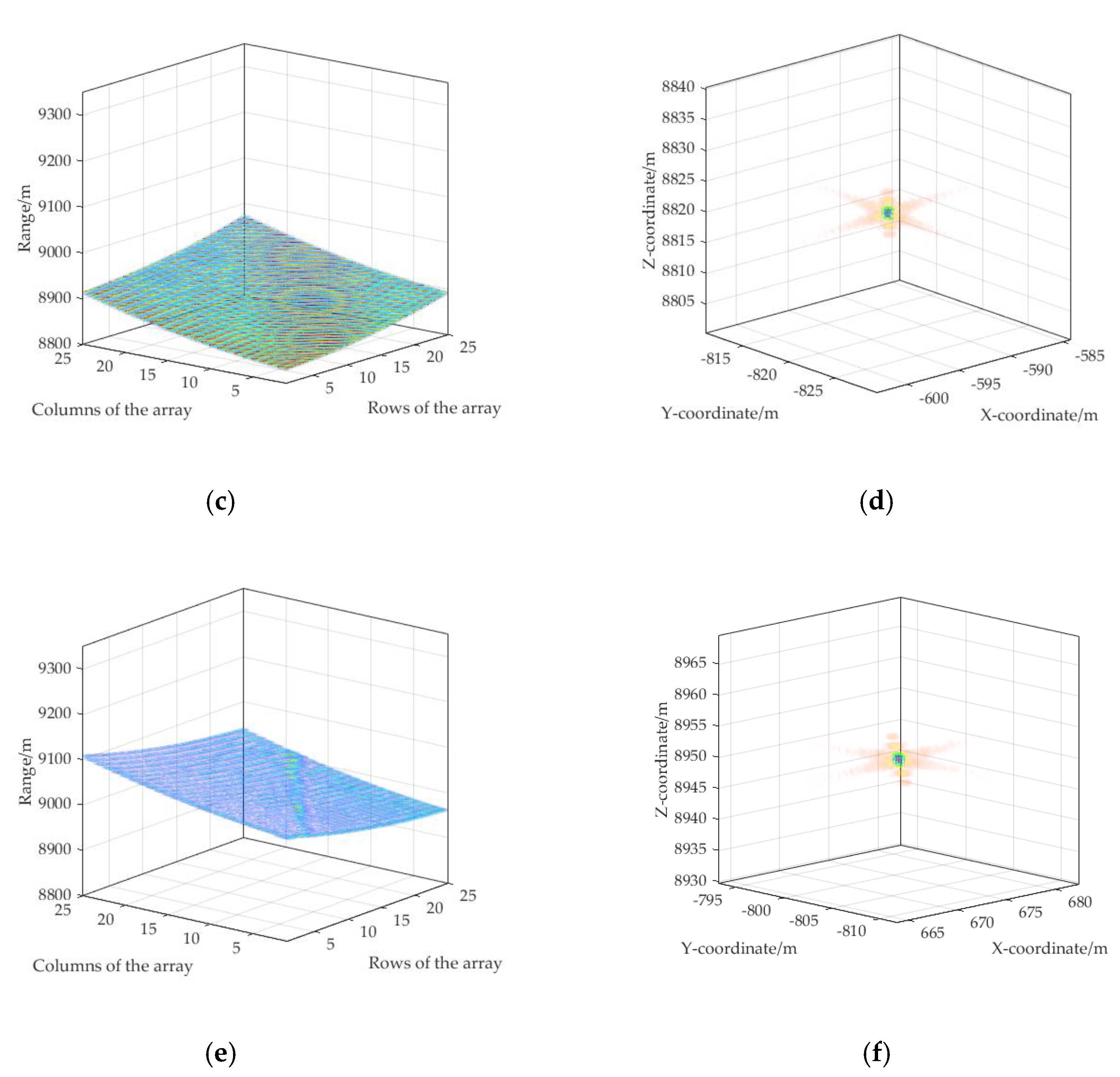



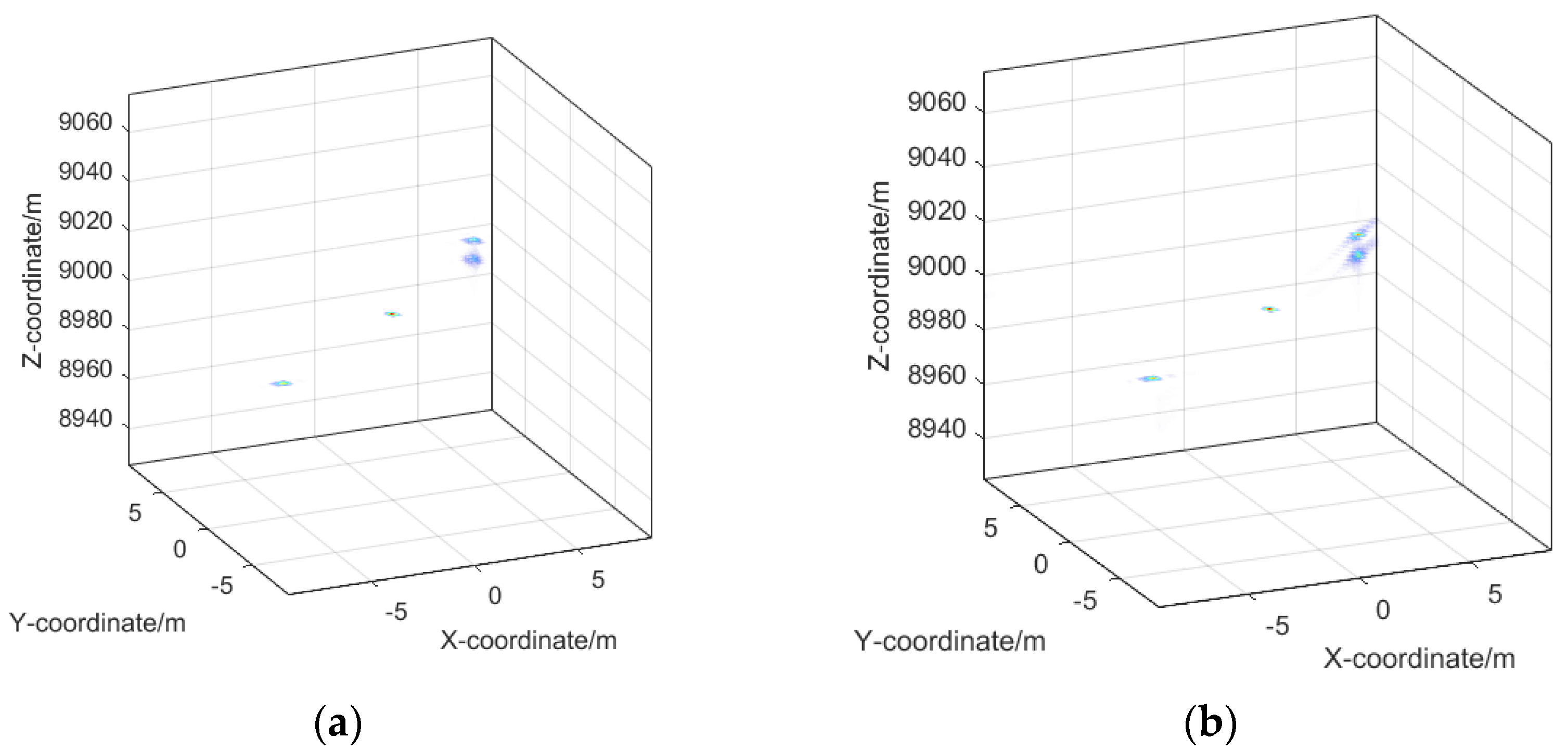
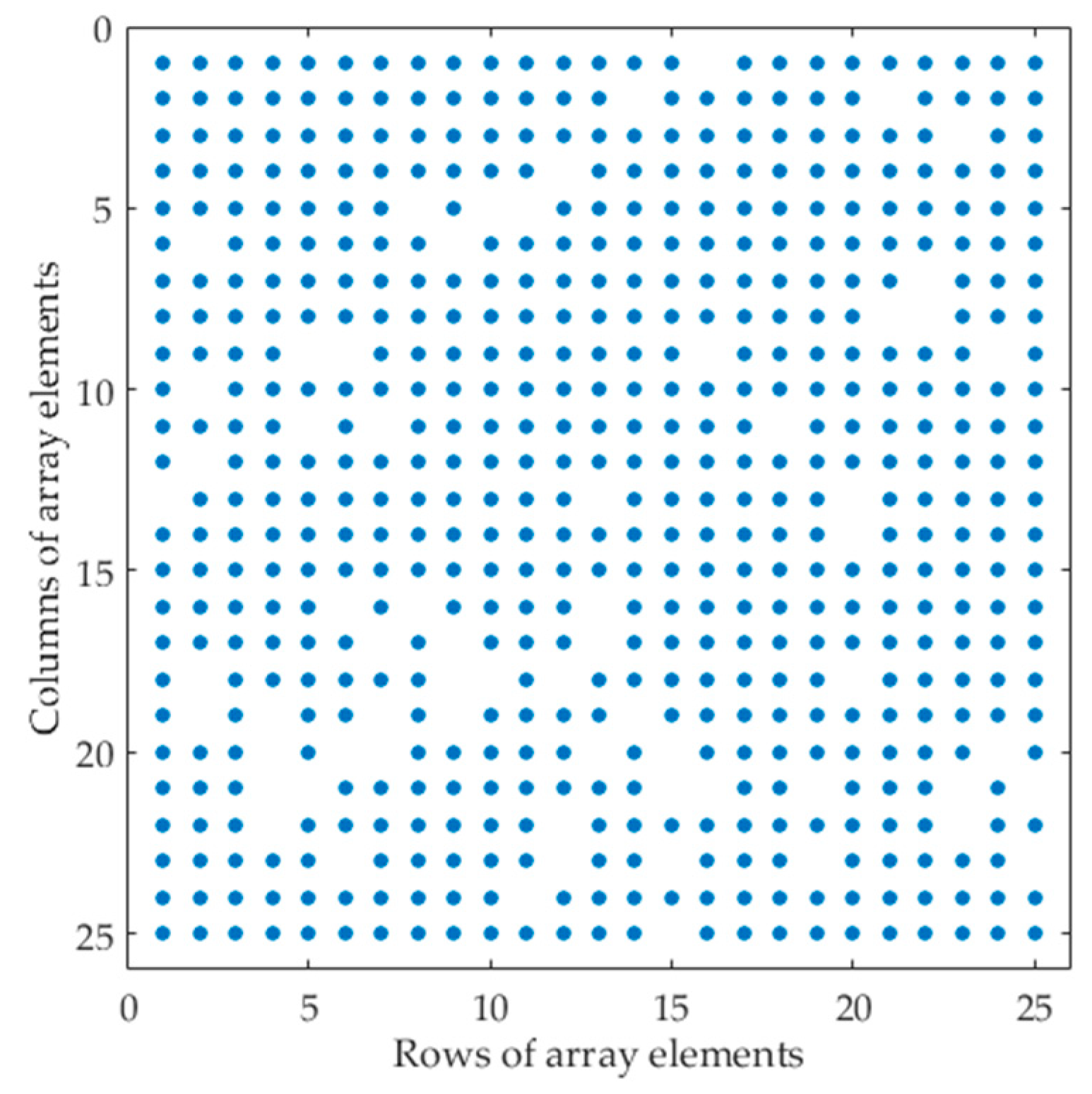

| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pulse duration | 10 | Sampling Frequency | 70 MHz |
| Bandwidth | 100 MHz | Wavelength | 0.15 m |
| Carrier Frequency | 2 GHz |
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Array Size | 25 × 25 | Target 1 Position | (0, 0, 0) m |
| Baseline Length | 900 m | Target 2 Position | (−593.5, −820.2, −179.7) m |
| Reference Point Position | (0, 0, 9000) m | Target 3 Position | (673.1, −802.5, −50.3) m |
| Scattering Points | Position | Scattering Points | Position | Scattering Points | Position |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | (0, −5.25, 0) m | T8 | (0, 0, 0) m | T15 | (0, 5.25, 0) m |
| T2 | (−3.75, −5.25, 8991) m | T9 | (−3.75, 0, 8991) m | T16 | (−3.75, 5.25, 8991) m |
| T3 | (−7.5, −5.25, 8982) m | T10 | (−7.5, 0, 8982) m | T17 | (−7.5, 5.25, 8982) m |
| T4 | (−11.25, −5.25, 8973) m | T11 | (−11.25, 0, 8973) m | T18 | (−11.25,5.25, 8973) m |
| T5 | (3.75, −5.25, 9009) m | T12 | (3.75, 0, 9009) m | T19 | (3.75, 5.25, 9009) m |
| T6 | (7.5, −5.25, 9018) m | T13 | (7.5, 0, 9018) m | T20 | (7.5, 5.25, 9018) m |
| T7 | (11.25, −5.25, 9027) m | T14 | (11.25, 0, 9027) m | T21 | (11.25, 5.25, 9027) m |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, Y.; Tian, J.; Jin, G.; Zhang, Y. MTRC-Tolerated Multi-Target Imaging Based on 3D Hough Transform and Non-Equal Sampling Sparse Solution. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3817. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13193817
Zou Y, Tian J, Jin G, Zhang Y. MTRC-Tolerated Multi-Target Imaging Based on 3D Hough Transform and Non-Equal Sampling Sparse Solution. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(19):3817. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13193817
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Yimeng, Jiahao Tian, Guanghu Jin, and Yongsheng Zhang. 2021. "MTRC-Tolerated Multi-Target Imaging Based on 3D Hough Transform and Non-Equal Sampling Sparse Solution" Remote Sensing 13, no. 19: 3817. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13193817
APA StyleZou, Y., Tian, J., Jin, G., & Zhang, Y. (2021). MTRC-Tolerated Multi-Target Imaging Based on 3D Hough Transform and Non-Equal Sampling Sparse Solution. Remote Sensing, 13(19), 3817. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13193817






