Abstract
Building instances extraction is an essential task for surveying and mapping. Challenges still exist in extracting building instances from high-resolution remote sensing imagery mainly because of complex structures, variety of scales, and interconnected buildings. This study proposes a coarse-to-fine contour optimization network to improve the performance of building instance extraction. Specifically, the network contains two special sub-networks: attention-based feature pyramid sub-network (AFPN) and coarse-to-fine contour sub-network. The former sub-network introduces channel attention into each layer of the original feature pyramid network (FPN) to improve the identification of small buildings, and the latter is designed to accurately extract building contours via two cascaded contour optimization learning. Furthermore, the whole network is jointly optimized by multiple losses, that is, a contour loss, a classification loss, a box regression loss and a general mask loss. Experimental results on three challenging building extraction datasets demonstrated that the proposed method outperformed the state-of-the-art methods’ accuracy and quality of building contours.
1. Introduction
Automatic extraction of building instances from remote sensing imagery is significant in urban planning, environmental management, change detection, map making, and updating [1,2,3,4]. A large number of high-resolution satellite imagery with finer spectral and texture features can extract more precise building instances. However, due to the complex and heterogeneous appearance of buildings in mixed backgrounds [3], accurately building instance extraction from high-resolution satellite imagery is still a highly challenging task, such as finer building contours generation especially for small buildings.
The building instance extraction aims to detect all buildings and precisely segment each individual building, which can be treated as an image instance segmentation task that performs instantiation and then segmentation [4]. Inspired by the Mask R-CNN [5], advanced models derived from instance segmentation approaches have been explored to extract building instances from remote sensing imagery, and have achieved promising results in the last four years [4,6,7]. However, existing methods still have two limitations. First, the remote sensing imagery with complex background has much noise, which dramatically affects the extraction of building contours with mask regression-based methods. More specifically, it leads to a deviation between ground truth and prediction. Second, some small building instances cannot be identified because scale differences of high-resolution remote sensing images are not fully considered. Figure 1 presents an example of the two issues, blurred contours and undetected small buildings, in the results of a classical instance segmentation model. The red boxes represent buildings with blurring contours and the yellow boxes represent undetected small buildings.

Figure 1.
Visualization examples with classical instance segmentation model-Mask R-CNN. Note: the red boxes represent buildings with blurring contours, the yellow boxes represent undetected small buildings and the green boxes are generated by Mask R-CNN.
This study proposes a coarse-to-fine contour optimization network to extract building instances accurately from high-resolution remote sensing imagery and alleviate the above two limitations. The network contains two sub-networks, an attention-based feature pyramid (AFPN) sub-network and a coarse-to-fine contour sub-network.
The main contributions of this study are the following:
- A coarse-to-fine contour sub-network is developed for better-capturing building contour, which employs a significant loss in an iteration learning way and achieves great improvement in the refinement of building contour;
- An AFPN sub-network is designed to introduce an attention mechanism into the feature pyramid network (FPN [8]) and improve the ability to detect small buildings;
- A new metric index contour score (CS) is derived from the differences between predicted contours and ground truths to evaluate model performance further. The CS provides a new exploration in assessing the performance of image instance segmentation models;
- Experiments on three diverse building extraction datasets, two public datasets (WHU aerial image dataset [3] and CrowdAI mapping challenge dataset [CrowdAI] [9]) and a self-annotated dataset are conducted. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method shows advantages over existing state-of-the-art instance segmentation methods.
This study is organized as follows. Section 2 reviews related works. Section 3 provides details on the proposed network. Section 4 describes datasets, implementation details, evaluation metrics, and baseline models. Section 5 presents experimental results. Section 6 elaborates the ablation study and discusses the effects of edge detection operators, loss functions, and hyperparameters. Finally, Section 7 concludes this study.
2. Related Work
The building extraction methods can be classified into three categories [10,11,12]: pixel-based, object-oriented, and deep-leaning methods. The pixel-based method mainly emphasizes the spectral characteristic [13,14], while ignoring features such as geometry [15,16], texture [17] and context information [18]. Hence, most pixel-based methods result in irregular building shapes and require further processing such as shape refinement and vectorization [19]. The object-oriented method identifies the building as a whole, which can extract regular buildings but cannot segment complex masks. In recent years, deep learning-based methods, such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks, have shown effective and superior performance in automatically learning high-level and discriminative features in extracting buildings [2,20,21,22]. Related studies can be further grouped into building extraction based on semantic segmentation and building extraction based on instance segmentation, which are discussed in the following two subsections.
2.1. Building Extraction Based on Semantic Segmentation
Building extraction can be considered a binary pixel classification task. Pixel-based semantic segmentation methods have been adopted to extract buildings from remote sensing imagery, making significant progress. Many studies have explored different CNN-based semantic segmentation methods for improving the accuracy of building extraction. For example, Alshehhi et al. [20] proposed a single patch-based CNN architecture to extract roads and buildings. Low-level features of roads and buildings (e.g., asymmetry and compactness) of adjacent regions are integrated with CNN features during the post-processing stage to improve the performance. Xu et al. [23] designed an image segmentation neural network, based on the deep residual networks, and used a guided filter to extract buildings.
With the advent of the fully convolutional network (FCN) [24] that performs image segmentation and pixel-wise labeling synchronously via an end-to-end encode-decoder framework, numerous variants of FCNs were successfully employed to building extraction. Shrestha et al. [2] presented an enhanced FCN framework for building extraction by applying conditional random fields. Ye et al. [21] proposed an attention-based re-weighting FCN to extract buildings from aerial imagery. Ji et al. [3] proposed a Siamese FCN model to obtain better segmentation accuracy.
Apart from FCN, more encoder–decoder-based models that fuse different levels of features more comprehensively, such as U-Net [25], are also preferred in building extraction. Li et al. [26] designed and combined several strategies (i.e., data augmentation, post-processing, and integration of the GIS map data and satellite images) with the U-Net–based semantic segmentation model to extract building footprints. Duan et al. [22] inserted identity skip connection into the U-net network for samples training to improve the accuracy of building extraction. Furthermore, the Deeplab series [27,28] has been widely exploited to extract buildings, employing atrous spatial pyramid pooling to aggregate multi-scale contextual information with a larger field of view. Chen et al. [29] proposed a dense residual neural network, which used a deeplabv3+net encoder–decoder backbone, in combination with a densely connected CNN and residual network (ResNet [30]) structure.
Benefiting from the rapid growth of available remote sensing data and computing power, the semantic segmentation technology on building extraction has achieved a breakthrough. However, this kind of method cannot distinguish inter-connected objects of the same category. That is, it may fail to separate adjacent building instances and cause errors in building contours.
2.2. Building Instances Extraction Based on Instance Segmentation
With the arrival of the instance segmentation method pioneered by Mask R-CNN, studies on building instance extraction have been advanced. For example, Zhao et al. [4] presented a method combining Mask R-CNN with building boundary regularization to produce better-regularized polygons. Wen et al. [6] proposed an improved Mask R-CNN method to detect the rotated bounding boxes of buildings and segment them from complex backgrounds simultaneously. Liu et al. [7] designed a multi-scale U-shaped CNN building instance extraction framework with edge constraint to extract precise building masks. Wu et al. [31] proposed an improved anchor-free instance segmentation method based on CenterMask [32] with spatial and channel attention-guided mechanisms to achieve balanced performance in terms of speed and accuracy.
Although the above approaches have facilitated the progress of building instance extraction, they are still insufficient in the accurate extraction of buildings, resulting from the lack of consideration for the optimization of building contours and the identification of small buildings.
3. Methodology
This study proposes a coarse-to-fine contour optimization network to enhance the performance of building instance extraction from high-resolution remote sensing imagery. The architecture of the proposed network is illustrated in Figure 2. The following subsections will describe the two main components of the network: the attention-based FPN (AFPN) sub-network and the coarse-to-fine contour sub-network. The AFPN introduces channel attention into each layer of the original feature pyramid network (FPN) to improve the identification of small buildings, and the coarse-to-fine contour sub-network is designed to accurately extract building contours via two-cascaded contour optimization learning.
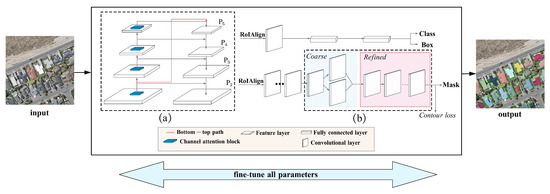
Figure 2.
Overview of the proposed network for building instance extraction: (a) AFPN sub-network, (b) coarse-to-fine contour sub-network.
3.1. AFPN Sub-Network
In the proposed network, the AFPN sub-network is designed to improve the identification of small buildings, introducing channel attention into each layer of the classical FPN, as shown in Figure 2a. The sub-network captures foreground information of small and big buildings in each layer of the pyramid network via foreground channel attention learning.
The detailed structure of the attention component is illustrated in Figure 3. The module consists of a global average pooling (GAP), a 1D convolution, a Sigmoid operation, and an element-wise multiplication.
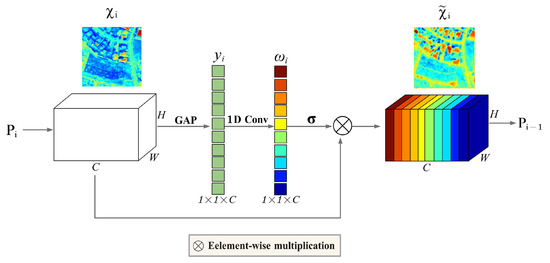
Figure 3.
Structure of AFPN. is the i-th layer of FPN.
First, at the i-th layer of AFPN, a GAP is used to aggregate the features of the pyramid with the dimension of into a channel descriptor with the dimension of , similar to [33], where C is the number of the channels at each layer.
Then, a convolution is used to learn the attention weights representing the importance of foreground information in each channel. It drives the network’s preference to focus on the foreground information of small buildings at each layer of AFPN. The attention weights can be calculated as follows:
where indicates convolution, and denotes a Sigmoid function. The attention weight is used to weigh the importance of features for achieving building foreground information. It enforces a high weight for building foreground features and a low weight for complex background features.
Finally, the foreground attention features can be calculated by an element-wise multiplication operation as follows:
where denotes element-wise multiplication.
A bottom-up connection is added from the low-layer to the top layer of the pyramid (presented by the red line in Figure 2a) to reduce further information loss of small buildings in the FPN’s top layer, following [34]. With this connection, the AFPN can retain features of small buildings without any additional model complexity, guaranteeing the effectiveness of the sub-network.
3.2. Coarse-to-Fine Contour Sub-Network
After obtaining the foreground attention features, a two-stage coarse-to-fine contour sub-network is designed to extract building instance contours in an end-to-end manner. Specifically, a coarse-to-fine contour sub-network consists of a coarse contour branch and a refined contour branch. The structure of the coarse-to-fine contour sub-network is illustrated in Figure 4.
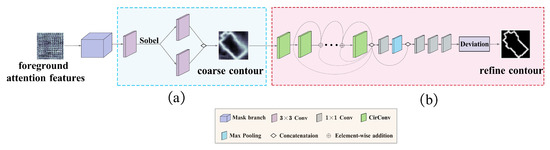
Figure 4.
Structure of coarse-to-fine contour sub-network: (a) coarse contour branch, (b) refined contour branch.
3.2.1. Coarse Contour Branch
Given the learned attention features as the input, the coarse contour branch first uses a de-convolutional layer as the mask branch. It then employs a Sobel operator [35] and two simple convolution operations to identify coarse building contours, as shown in Figure 4a.
Specifically, the Sobel operator is used to extract two-channel building contour positions in horizontal and vertical directions. Then, two convolutions further learn building contour representation from the extracted coarse contour positions. The coarse contour of building can be modeled as follows:
where denotes convolution, represents the Sobel operator, and denotes mask features from the mask branch.
Once the coarse contours are achieved, they will be fed into the next branch to guide more precise contour extraction.
3.2.2. Refined Contour Branch
Although the rough building contours are extracted by the above coarse contour branch and closer to the ground truth, the deviation between the coarse and true contours still exists. A refined contour branch is introduced into our model to reduce the deviation, as shown in Figure 4b. Following the idea of Deepsnake [36], the refined contour branch consists of three parts: circular convolution block, fusion block, and a deviation prediction head.
The circular convolution block includes eight circular convolution layers with residual skip connections for further adjusting the contour deviation in all layers of this branch. The is defined as follows:
where S is the ground truth of the building contours. To fuse the information across all contour points at multiple scales, the fusion block concatenates features from all circular convolution layers and feeds them into a convolution layer followed by max pooling. Followed by the fused block, the prediction head applies three convolution layers to the fused features and outputs the vertex-wise deviation.
The objective of the refined contour branch is to learn a nonlinear regression from the coarse contours to the minimum of the deviation . The final learned deviation adjusts and refines final contours by filling and merging operations.
3.2.3. Loss Function
A contour loss [37] is introduced into the general mask regression loss in Mask R-CNN, which is additional supervision information to optimize the contour learning, minimize the deviation, and achieve more precise contours for building extraction. The overall training objective is the combination of the following four losses:
where classification loss , regression loss and mask loss are inherited from Mask R-CNN. The classification loss is given as follows:
where is the number of classes, and is the class label, is the predicted class. The mask loss is written as follows:
where is the mask label and y is the predicted mask. The regression loss is given as follows:
where is the box label and is the predicted box.
The contour loss function is defined as follows:
where and denote the predicted contour and the corresponding ground truth contour, respectively; and are pixel loss [38] and binary cross-entropy loss, respectively; and is a hyper-parameter that is used to adjust the proportion of each loss in the loss function. The contour loss encourages the predicted contours to match the ground truth contours according to the predicted deviation adaptively. Furthermore, to avoid a zero in the denominator of Equation (10), the default value of the is set as 1.
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets
The proposed method was evaluated on three building segmentation datasets: the WHU aerial image dataset, CrowdAI, and the self-annotated dataset.
4.1.1. WHU Aerial Image Dataset
The WHU aerial image dataset is proposed by Ji et al. [3]. The dataset has a large variation in image characteristics, including different lighting and atmospheric, sensor qualities, scales and building architectures. Some samples are illustrated in Figure 5. The spatial resolution of the images is 0.3 m. The dataset covers approximately 450 km and more than 187,000 buildings with different sizes and appearances in Christchurch, New Zealand. Aerial images and corresponding ground truth images are provided in the dataset containing 8188 RGB images with 512 × 512 pixels. The dataset is divided into the training set with 4736 images, a validation set with 1036 images and a test set with 2416 images.
Figure 5.
Samples of the WHU aerial imagery dataset. The ground truth of the buildings is in cyan.
4.1.2. CrowdAI
CrowdAI consists of 280,000 satellite images for training and 60,000 images for testing. The image samples are provided in JPEG format with an image resolution of 300 × 300 pixels, and their annotations are provided in the MS-COCO format. Some samples from the CrowdAI are demonstrated in Figure 6. The dataset has a wide variety of buildings with different sizes and shapes.
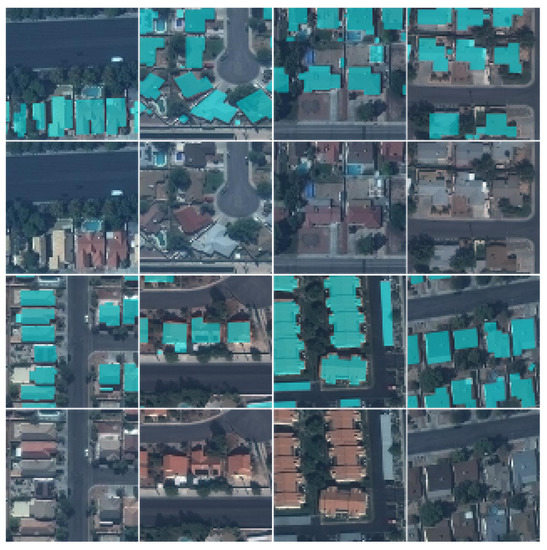

Figure 6.
Samples of CrowdAI. The ground truth of buildings is in cyan.
4.1.3. Self-Annotated Building Instance Segmentation Dataset
The self-annotated building instance dataset [39] images are acquired from Google Earth (Google Inc., Mountain View, CA, USA.) and are manually annotated. As shown in Figure 7, the dataset consists of 7260 tiles, and 63,886 building instances in four Chinese cities: Beijing, Shanghai, Shenzhen and Wuhan. Each image has a size of 500 × 500 pixels with a resolution of 0.29 m/pixel. The dataset contains a large number of non-orthophoto images. Some samples from the self-annotated building instance segmentation dataset are shown in Figure 8. A total of 7260 labeled images are split into 5985 images for training and 1275 for testing.
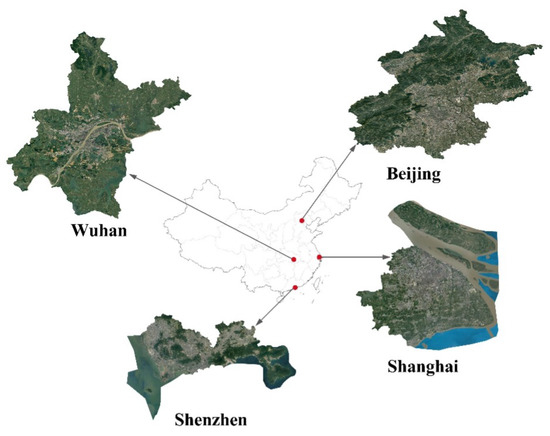
Figure 7.
Distribution of the self-annotated building instance segmentation dataset.
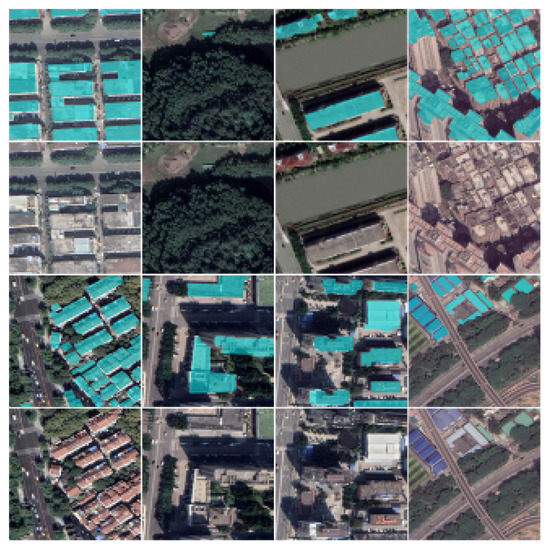

Figure 8.
Samples of the self-annotated building instance segmentation dataset. The ground truth of the buildings is in cyan.
4.2. Implementation Details
All the experiments were implemented in the Pytorch framework and were carried out on a 2080 GPU. A stochastic gradient descent (SGD [40]) with a learning rate of 0.0025 was adopted as an optimizer. The shared convolutional layers were initialized with the released pre-trained ResNet-50 [30] model. The weight decay rate was set to 0.0001 with a momentum value of 0.9.
To increase the diversity of training samples, rotate, flip, noise, blur and brightness operations were applied to each remote sensing image, which enlarged the volume of the datasets about six times.
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
In this study, the standard MS COCO metrics [41] were employed for evaluating the task, including the mean average precision (), and mean average recall () over multiple intersection over union () values. is given in Equation (12) below:
where and denote the predicted mask and the corresponding ground truth, respectively.
Specifically, and are computed at 10 overlap thresholds ranging from 0.50 to 0.95 in steps of 0.05 following [41]. is calculated as Equation (13), and is given in Equation (14).
Furthermore, is used to measure further the performance of the methods on detecting small buildings with an pixels.
IoU is mainly used to evaluate model performances by quantifying the size of the common region between predicted results and ground truths, which cannot yet directly and finely evaluate the performance of predicted contour lines. To further measure the quality of the extracted building contours, a new measure indicator called contour scores () was proposed. The CS is defined as follows:
As shown in Figure 9, and denote the length and the length between the real contour and the predicted contour in the same direction, respectively. That is, the closer the two contours are, the closer the is to 1, and vice versa. Compared with , is better for examining the performance of predicted contours.
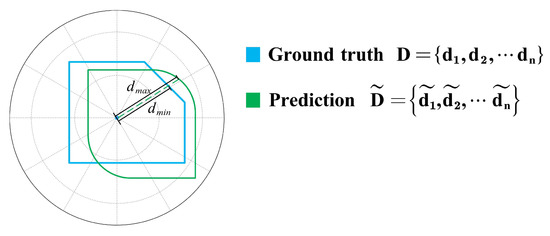
Figure 9.
Schematic diagram of CS.
In the equation, the contour is calculated as a whole, and evaluating the quality of building contours accurately is easy, especially that of small buildings. Meanwhile, is more robust regardless of the shape of the building.
4.4. Baselines
In this study, the proposed method was compared with four baselines, including Mask R-CNN, Hybrid Task Cascade(HTC), CenterMask and SOLOv2 on three datasets. Mask R-CNN [5] is the most popular for building instance extraction, which adds a network branch to the original Faster R-CNN [42] for predicting segmentation masks on each Region of Interest (RoI). HTC [43] effectively integrates cascade into instance segmentation by interweaving detection and segmentation features together for joint multi-stage processing. CenterMask [32] is a simple and efficient anchor-free instance segmentation method that achieves significant performance at real-time speed. SOLOv2 [44] takes one step further by dynamically learning the mask head of the object segmenter such that the mask head is conditioned on the location. It can dynamically segment each instance in the image without resorting to bounding box detection. All the methods adopted the same settings, except Centermask which used Vovnet-39 [32] as a backbone.
5. Results
5.1. Evaluation with the WHU Aerial Image Dataset
Table 1 shows the comparison results on the WHU aerial image dataset. Our method achieves the best results of the five methods, reaching and values of 69.8% and 79.5%, respectively. In terms of AP of small (), the proposed method exceeds 10.1%, 6.3%, 6.0% and 12.0% compared with Mask R-CNN, HTC, CenterMask and SOLOv2, respectively. It suggests that our method effectively extracts building instances because it can produce more accurate building contours and is more effective for small-scale buildings detection.

Table 1.
Comparison of different network extraction methods on the WHU aerial image dataset. The best results are highlighted in bold.
To further observe the results, some samples are illustrated in Figure 10. As the red boxes from column(b) to column(e) in the first and second rows show, the buildings are not well segmented with precise contours in the results of the comparison models. In contrast, as the red box in column(f) shows, the proposed model generates clearer contours of individual buildings. In the third row, some small-scale buildings are overlooked by the baseline methods, but are successfully detected by our method. These results indicate that the proposed method has superior performance compared with the baseline methods.
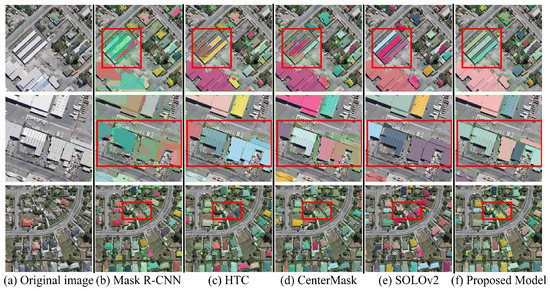
Figure 10.
Visualized results of building instance extraction using the WHU aerial image dataset: (a) the original remote sensing imagery, (b) Mask R-CNN, (c) HTC, (d) CenterMask, (e) SOLOv2, (f) Proposed model.
5.2. Evaluation with CrowdAI
The experimental results on CrowdAI are listed in Table 2. The proposed method achieves a higher of 64.9%, compared with baselines. The of small () outperforms that of Mask R-CNN, HTC, CenterMask and SOLOv2 by 4.0%, 1.3%, 3.9% and 3.0%, respectively. Furthermore, the values of indicate that the extracted contours of our method are more precise than those of the four baselines.

Table 2.
Comparison of different network extraction methods on CrowdAI. The best results are highlighted in bold.
As shown in Figure 11, the proposed method still generates more accurate building contours than those of the baselines on CrowdAI.
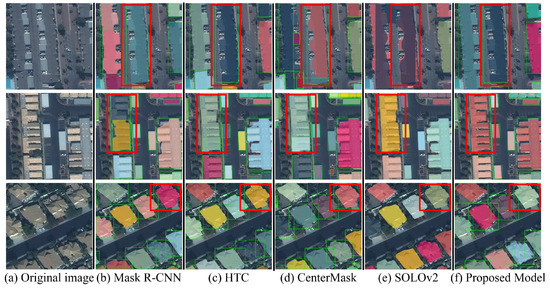
Figure 11.
Visualized results of building instance extraction using CrowdAI: (a) the original remote sensing imagery, (b) Mask R-CNN, (c) HTC, (d) CenterMask, (e) SOLOv2, (f) Proposed model.
5.3. Evaluation with the Self-Annotated Building Instance Segmentation Dataset
To demonstrate the performance of the proposed method, the proposed method was examined using the self-annotated building instance segmentation dataset. The dataset contains non-orthophoto images with complex backgrounds, which makes building instance extraction challenging. As shown in Table 3, the values of evaluation metrics of all models are lower than those of the two above datasets. The proposed method obtains more precise results than the four baselines, reaching and values of 68.3% and 54.6%, respectively. Experimental results on this dataset show that our method is still promising.

Table 3.
Comparison of different network extraction methods on the self-annotated building instance segmentation dataset.The best results are highlighted in bold.
Figure 12 shows the comparison results for the dataset. For some challenging building scenes (such as the one represented in the first row of Figure 12), shadow interference (the second row of Figure 12), and dense distribution of small-scale buildings (the third row of Figure 12), the proposed method achieves the best performance.

Figure 12.
Visualized results of building instance extraction using the self-annotated building instance segmentation Dataset: (a) the original remote sensing imagery, (b) Mask R-CNN, (c) HTC, (d) CenterMask, (e) SOLOv2, (f) Proposed model.
6. Discussion
6.1. Ablation Study
In this section, the ablation study is reported to examine the effectiveness of two key components in the proposed model. The ablation analysis was performed on the WHU aerial image dataset. The Mask R-CNN was adopted as the baseline model, and then each component was added progressively.
As shown in Table 4, the integration of the channel attention block improved the baseline from 60.1% to 64.7% in terms of . In particular, the AP value of small () has been promoted from 47.3% to 53.6%. The promotion demonstrates that introducing an attention block is effective, especially for small buildings. The addition of the coarse contour branch improves the and from 64.7% to 66.3% and 76.3% to 77.1%, respectively, implying that the coarse branch can help learn more building contour features. Finally, the refined contour branch brings and further improvements of 69.8% and 79.5%, respectively, demonstrating that more accurate contours can be obtained by adding the refined contour branch.

Table 4.
Ablation study with different components combinations on the WHU aerial image dataset. The best results are in bold.
The feature representations of without and with attention module in different convolution layers are visualized to understand how the channel attention module improves the extraction results. By using the channel attention module, the learned features obtain more foreground information and ignore background information. Therefore, the building regions can get more attention. As shown in Figure 13, the feature values in the building area become higher, which means the network can focus more on the foreground features of buildings. Furthermore, the small building features can also be reinforced during feature processing. To sum up, with the introduction of the attention module, the proposed model has superior performance in building instance extraction.
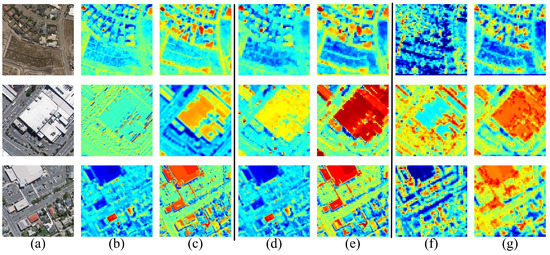
Figure 13.
Visualization of features in different convolution layers: (a) the original remote sensing imagery, (b) feature maps in conv1 without attention module, (c) feature maps in conv1 with attention module, (d) feature maps in conv2 without attention module, (e) feature maps in conv2 with attention module, (f) feature maps in conv3 without attention module, (g) feature maps in conv3 with attention module.
6.2. Effect of Edge Detection Operators
Taking the WHU aerial image dataset as an example, the performance of several edge detection operators is discussed, including Sobel [35], Laplace [45] and Canny [46]. As shown in Table 5, the best and are obtained when applying the Sobel operator. It can be explained by the fact that the Sobel operator affects smoothing and suppressing noise [47].

Table 5.
Comparison results of edge detection operators on the WHU aerial image dataset. The best results are in bold.
6.3. Effect of Contour Loss
In this section, the effect of different contour loss functions on optimized contour learning is discussed. The comparison experiments are still conducted with the WHU aerial image dataset [3] as an example. The selected loss functions include dice loss [37,38] (shown in Equation (10)), binary cross-entropy loss (shown in Equation (11)), and dice loss and binary cross-entropy loss (shown in Equation (9)), respectively.
As shown in Table 6, when and losses are adopted, the values are 2.7% and 0.7% higher than only and only , respectively. The values are also higher than only loss and only loss. Comparison with only loss, negative loss shows higher values of major metrics including precision, , , and . Replacing both and losses with only loss or only leads to a weaker performance in all metrics. These results demonstrate that our proposed contour loss is a critical factor for improving the performance of building extraction. Meanwhile, both and losses together also have a better convergence than only loss or only loss. Moreover, to examine the sensitivity of the hyper-parameter in Equation (9), two experiments are conducted. As the results show, various have little effect on the performance. The best performance is observed when and losses are used and is set to 1.

Table 6.
Comparison results on different loss functions on WHU aerial image dataset. The best results are in bold.
6.4. More Experiments with Different Thresholds
is used to measure how much our predicted contour overlaps with the ground truth (the real object contour). Considering that the obtained accuracy is different using different thresholds, this section uses more thresholds to observe the performance of the proposed model. As shown in Table 7, the proposed method performs better than the baselines, and the of the proposed method exceeds that of Mask R-CNN, HTC, CenterMask and SOLOV2 by 9.8%, 5.6%, 4.1%, and 8.5%, respectively. The value of the is also higher than those of the four baselines. Furthermore, the of our method can always obtain the best results no matter the being 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8 or 0.9. The higher the value is, the more distinct an advantage the proposed method has. For example, the value of of our method is 2.0% higher than that of Mask R-CNN with an of 0.5, whereas the gap between the two methods increases to 31.9% with an of 0.9. These experimental results further suggest that the model is robust and excellent.

Table 7.
Comparison results with different IoU thresholds. The best results are in bold.
The precision-recall curves generated from different methods are shown in Figure 14. All the curves of the proposed methods are located above the other baseline methods in different thresholds, demonstrating that the proposed method is more appropriate for extraction building instance and has strong robustness and good stability.
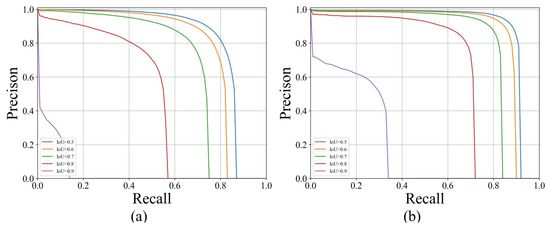
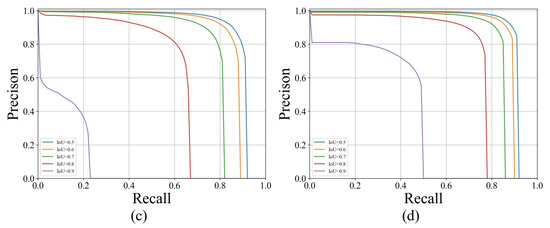
Figure 14.
Precision-recall curve with different IoU thresholds: (a) Mask R-CNN, (b) Hybrid Task Cascade, (c) SOLOv2, (d) Proposed model.
7. Conclusions
This study has proposed a coarse-to-fine contour optimization network to extract building instances accurately from high-resolution remote sensing images. An attention-based pyramid sub-network has been introduced to improve the identification of small buildings, and a two-stage coarse-to-fine contour sub-network has been designed to refine building instance contours. The proposed method has been evaluated on three challenging building extraction datasets. The experimental results have indicated that the proposed model outperforms the state-of-the-art models with higher accuracy and more precise contours. This study has suggested that introducing the inherent features of buildings into the model can enhance the ability to generate refined contours of building instances. This method should provide a reference for applications extracting other objects from remote sensing images.
Author Contributions
Conceived the foundation, F.F.; designed the methods, F.F. and K.W.; preformed the experiments, K.W.; interpretation of results, F.F. and K.W.; writing-original draft preparation, F.F. and K.W.; writing-review and editing, F.F., Y.L., S.L. and B.W.; data curation, D.Z. and Y.C.; supervision, Y.L.; funding acquisition, F.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Open Research Fund of National Earth Observation Data Center (No. NODAOP2020015), the National Natural Science Foundation of China grant (62076227) and the Wuhan Applied Fundamental Frontier Project under Grant (2020010601012166).
Data Availability Statement
The self-annotated dataset presented in this study is available on request from Science Data Bank. This data can be found here: https://doi.org/10.11922/sciencedb.00620, accessed on 25 March 2021.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mayer, H. Automatic object extraction from aerial imagery—A survey focusing on buildings. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 1999, 74, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shrestha, S.; Vanneschi, L. Improved fully convolutional network with conditional random fields for building extraction. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, S.; Wei, S.; Lu, M. Fully convolutional networks for multisource building extraction from an open aerial and satellite imagery data set. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 57, 574–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Kang, J.; Jung, J.; Sohn, G. Building extraction from satellite images using mask R-CNN with building boundary regularization. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 247–251. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask R-CNN. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2961–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Q.; Jiang, K.; Wang, W.; Liu, Q.; Guo, Q.; Li, L.; Wang, P. Automatic building extraction from Google Earth images under complex backgrounds based on deep instance segmentation network. Sensors 2019, 19, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, D.; Ma, A.; Zhong, Y.; Fang, F.; Xu, K. Multiscale U-Shaped CNN Building Instance Extraction Framework With Edge Constraint for High-Spatial-Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 6106–6120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty, S.P.; Czakon, J.; Kaczmarek, K.A.; Pyskir, A.; Tarasiewicz, P.; Kunwar, S.; Rohrbach, J.; Luo, D.; Prasad, M.; Fleer, S.; et al. Crowdai Mapping Challenge 2018: Baseline with Maskrcnn. Front. Artif. Intell. 2020, 3. Available online: https://www.crowdai.org/challenges/mapping-challenge/dataset_files (accessed on 26 July 2021).
- Shao, Z.; Tang, P.; Wang, Z.; Saleem, N.; Yam, S.; Sommai, C. BRRNet: A fully convolutional neural network for automatic building extraction from high-resolution remote sensing images. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, W.; Wan, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, S.; Wang, M. An automatic morphological attribute building extraction approach for satellite high spatial resolution imagery. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagner, F.H.; Dalagnol, R.; Tarabalka, Y.; Segantine, T.Y.; Thomé, R.; Hirye, M.C. U-net-id, an instance segmentation model for building extraction from satellite images—Case study in the Joanopolis City, Brazil. Remote Sen. 2020, 12, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, G. EANet: Edge-aware network for the extraction of buildings from aerial images. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Y. An improved snake model for building detection from urban aerial images. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2005, 26, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackelford, A.K.; Davis, C.H.; Wang, X. Automated 2-D building footprint extraction from high-resolution satellite multispectral imagery. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Anchorage, AK, USA, 20–24 September 2004; Volume 3, pp. 1996–1999. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Huang, X.; Zhang, G. Urban area extraction by regional and line segment feature fusion and urban morphology analysis. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Cui, S.; Yan, Q. Building extraction from high resolution satellite imagery based on multi-scale image segmentation and model matching. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Earth Observation and Remote Sensing Applications (EORSA), Beijing, China, 30 June–2 July 2008; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Huang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, H.; Tang, X.; Gong, J. Automatic extraction of built-up area from ZY3 multi-view satellite imagery: Analysis of 45 global cities. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 226, 51–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wu, L.; Xie, Z.; Chen, Z. Building extraction in very high resolution remote sensing imagery using deep learning and guided filters. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alshehhi, R.; Marpu, P.R.; Woon, W.L.; Mura, M.D. Simultaneous extraction of roads and buildings in remote sensing imagery with convolutional neural networks. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 130, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Fu, Y.; Gan, M.; Deng, J.; Comber, A.; Wang, K. Building extraction from very high resolution aerial imagery using joint attention deep neural network. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, Y.; Sun, L. Buildings Extraction from Remote Sensing Data Using Deep Learning Method Based on Improved U-Net Network. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2019—2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 3959–3961. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Liu, X.; Liu, M.; Shi, Q.; Yang, J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y. Building footprint extraction from high-resolution images via spatial residual inception convolutional neural network. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics). Volume 9351, pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; He, C.; Fang, J.; Zheng, J.; Fu, H.; Yu, L. Semantic segmentation-based building footprint extraction using very high-resolution satellite images and multi-source GIS data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Wu, J.; Liu, L.; Zhao, W.; Tian, F.; Shen, Q.; Zhao, B.; Du, R. Dr-net: An improved network for building extraction from high resolution remote sensing image. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.; Hu, Y.; Peng, L.; Chen, R. Improved anchor-free instance segmentation for building extraction from high-resolution remote sensing images. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Park, J. Centermask: Real-time anchor-free instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 13906–13915. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Qi, L.; Qin, H.; Shi, J.; Jia, J. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 8759–8768. [Google Scholar]
- Kittler, J. On the accuracy of the Sobel edge detector. Image Vis. Comput. 1983, 1, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Jiang, W.; Pi, H.; Li, X.; Bao, H.; Zhou, X. Deep snake for real-time instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 8530–8539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Wang, X.; Huang, L.; Liu, W. Boundary-preserving mask R-CNN. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 660–676. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, R.; Shen, C.; Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Liu, X. Learning to predict crisp boundaries. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 562–578. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, F.; Wu, K.; Zheng, D. A dataset of building instances of typical cities in China [DB/OL]. Sci. Data Bank 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, H.; Monro, S. A stochastic approximation method. Ann. Math. Stat. 1951, 22, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft COCO: Common objects in context. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, K.; Pang, J.; Wang, J.; Xiong, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, S.; Feng, W.; Liu, Z.; Shi, J.; Ouyang, W.; et al. Hybrid task cascade for instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 4974–4983. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, R.; Kong, T.; Li, L.; Shen, C. SOLOv2: Dynamic, faster and stronger. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.10152. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X. Laplacian operator-based edge detectors. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2007, 29, 886–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Goshtasby, A. On the Canny edge detector. Pattern Recognit. 2001, 34, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.C.; Fang, J.D.; Atlantis, P. Edge Detection Based on Improved Sobel Operator. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Computer Engineering and Information Systems, Gdansk, Poland, 11–14 September 2016; Volume 52, pp. 129–132. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).