Morphometry and Debris-Flow Susceptibility Map in Mountain Drainage Basins of the Vallo di Diano, Southern Italy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Morphometric Parameters
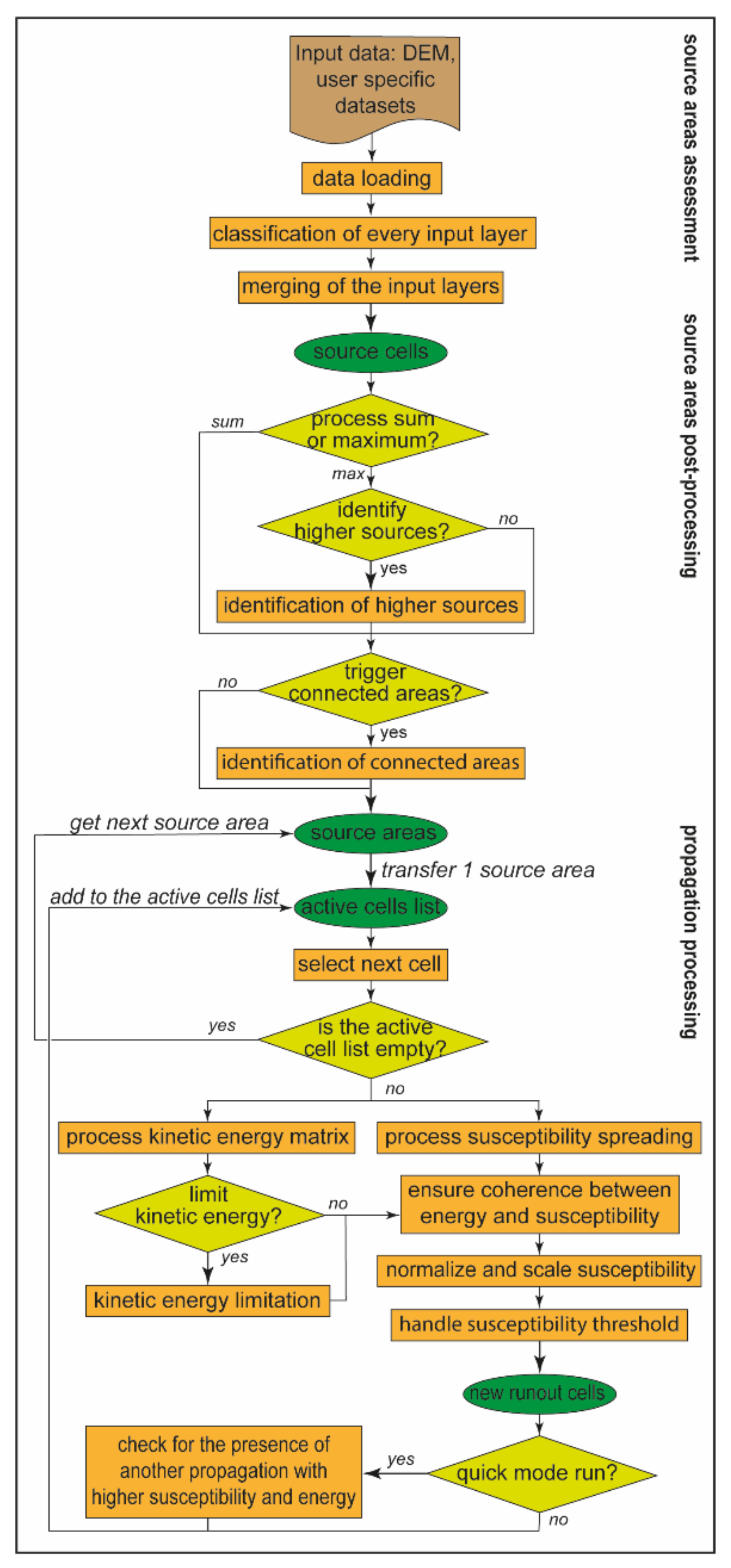
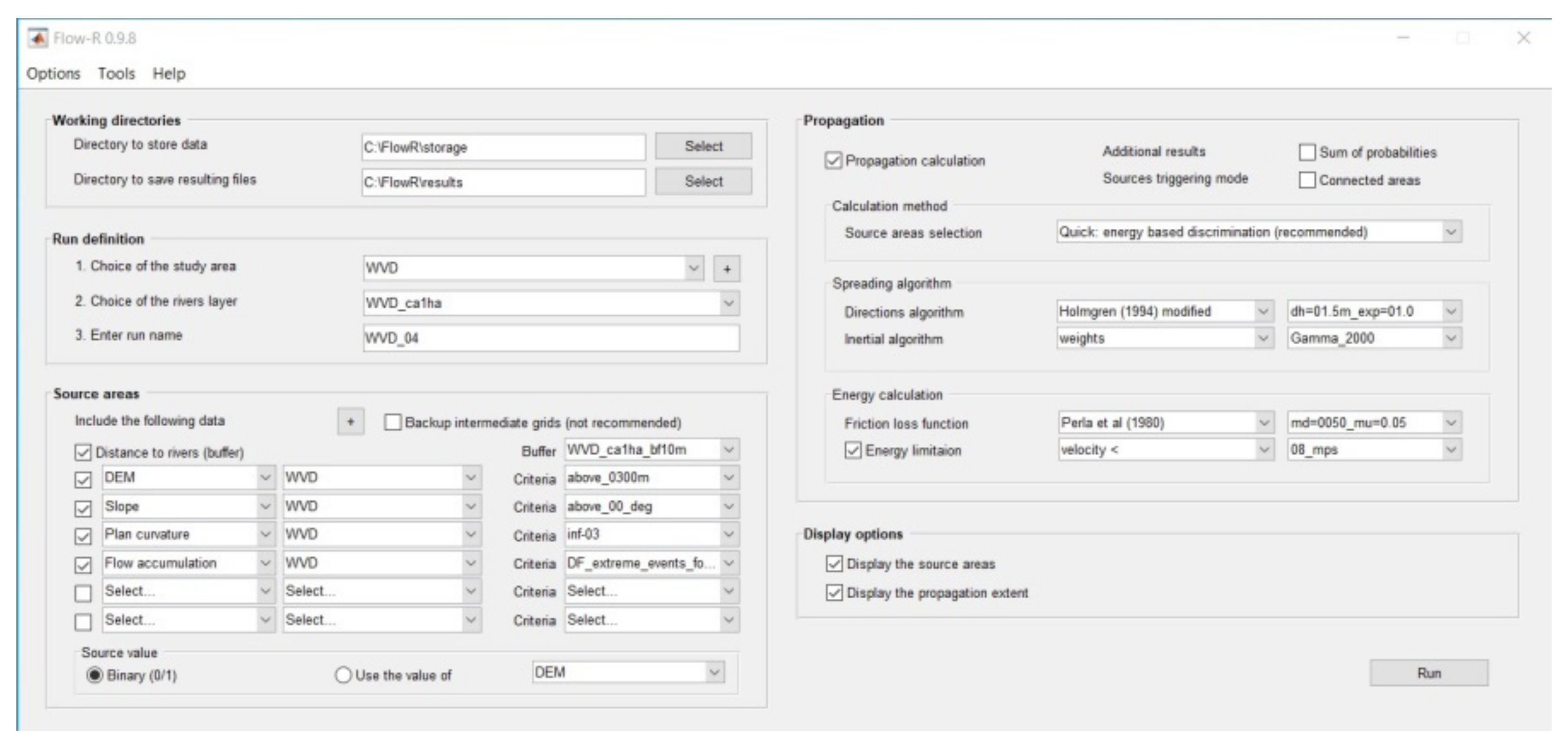
2.2. The Flow-R Model
2.3. Identification of Potential Source Areas
2.4. Assessment of Debris Flows Propagation
3. Geological and Geomorphological Settings
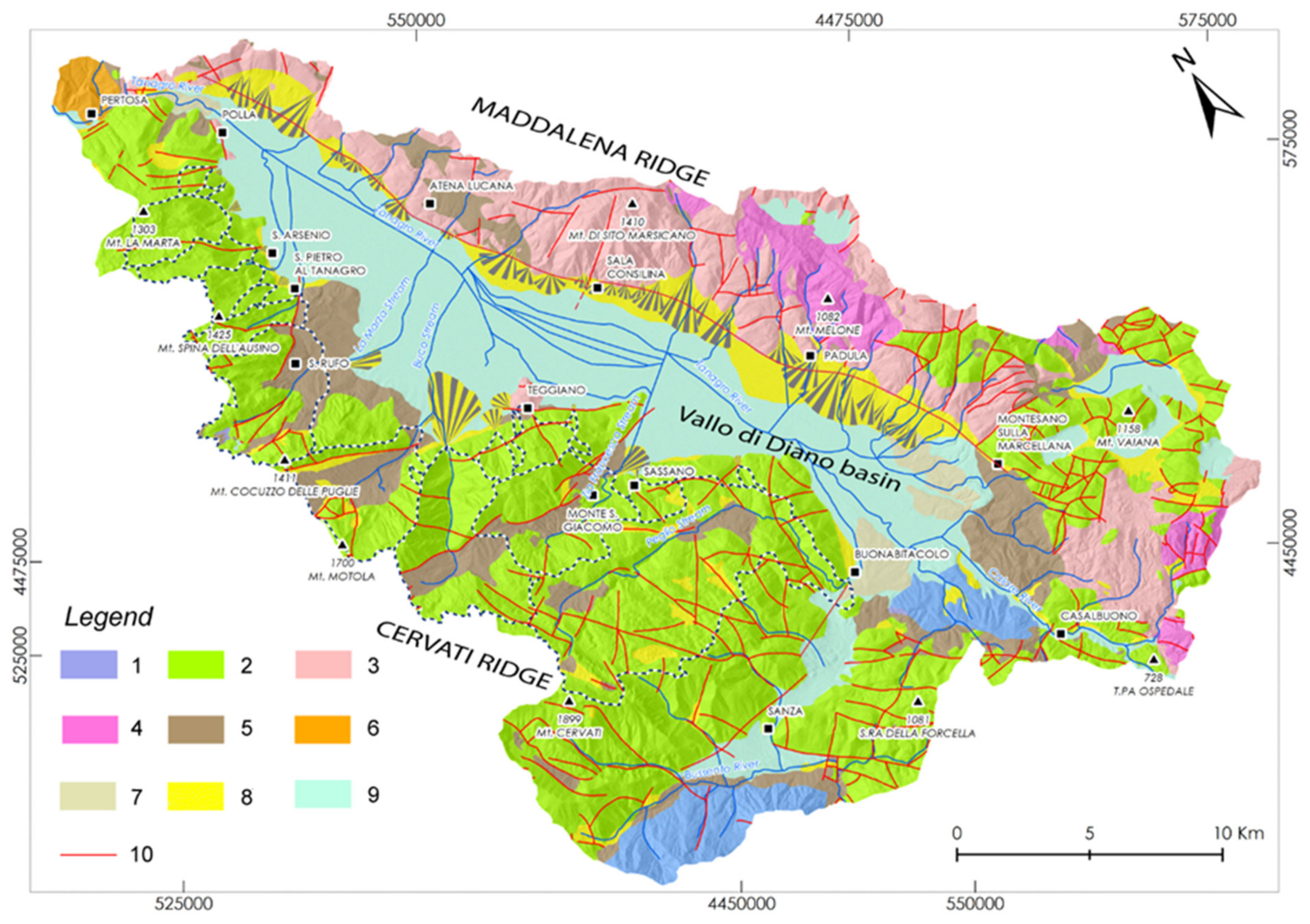
3.1. Regional Framework
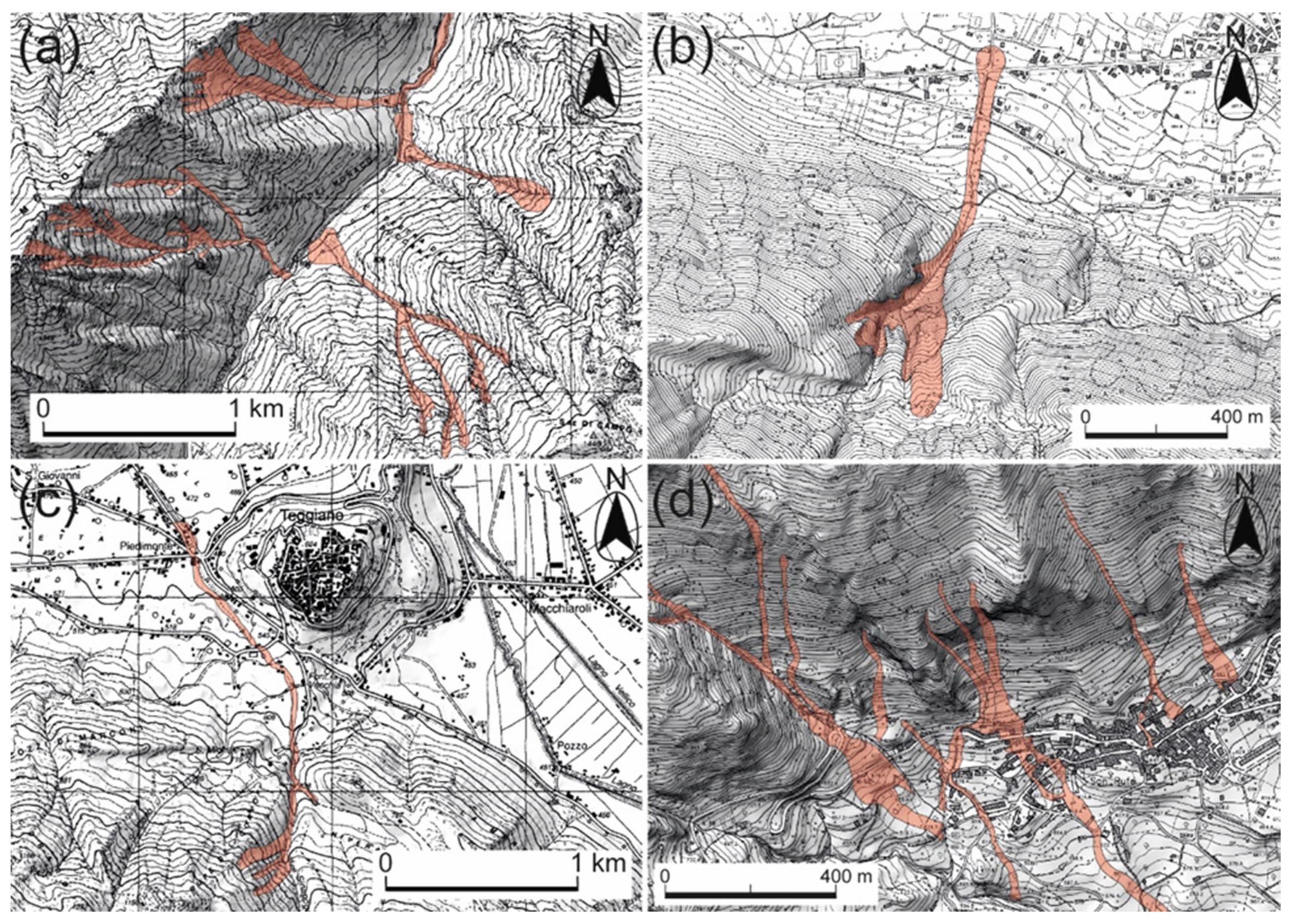
3.2. Geology and Geomorphology of the Vallo di Diano Basin
4. Results
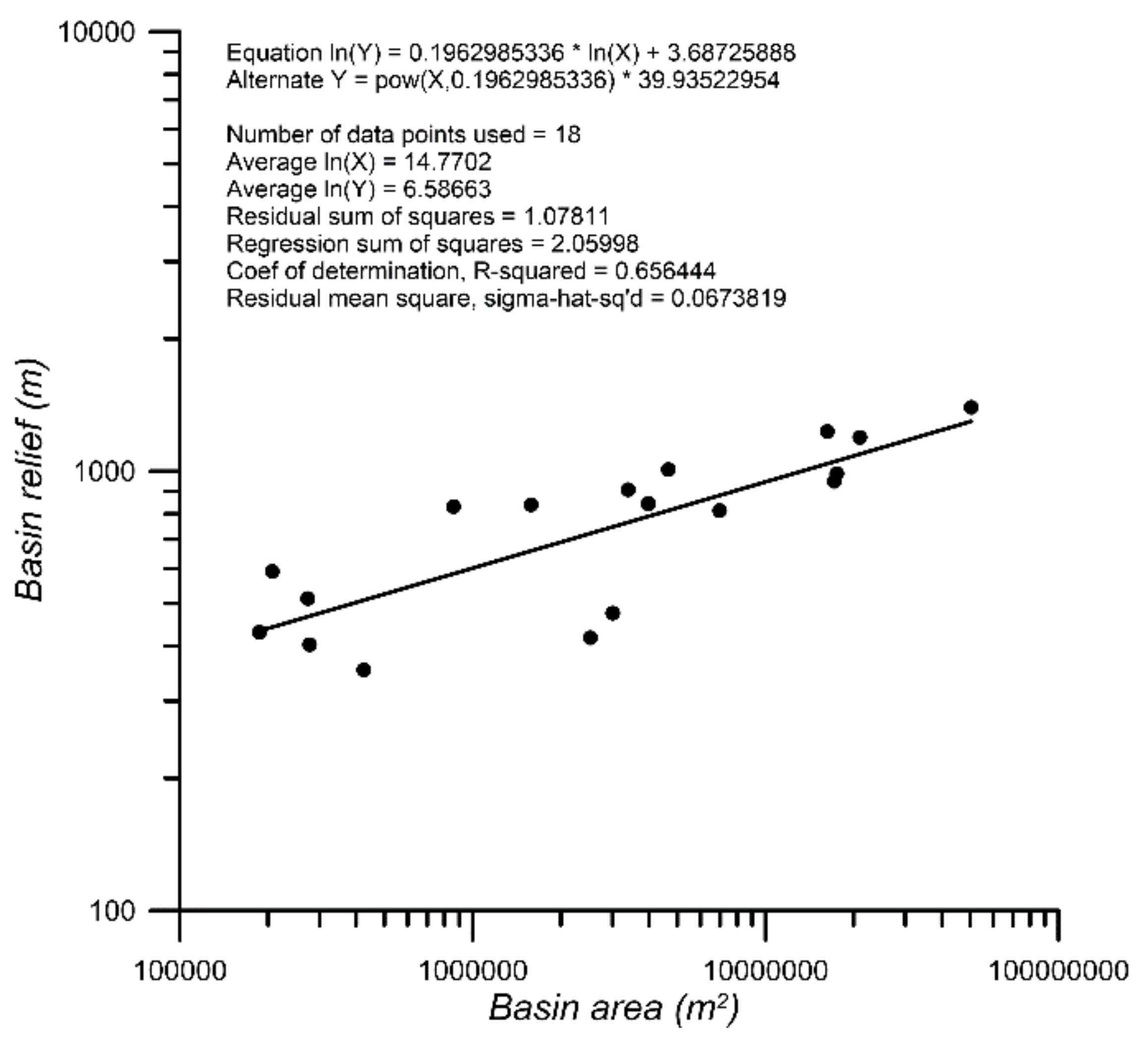
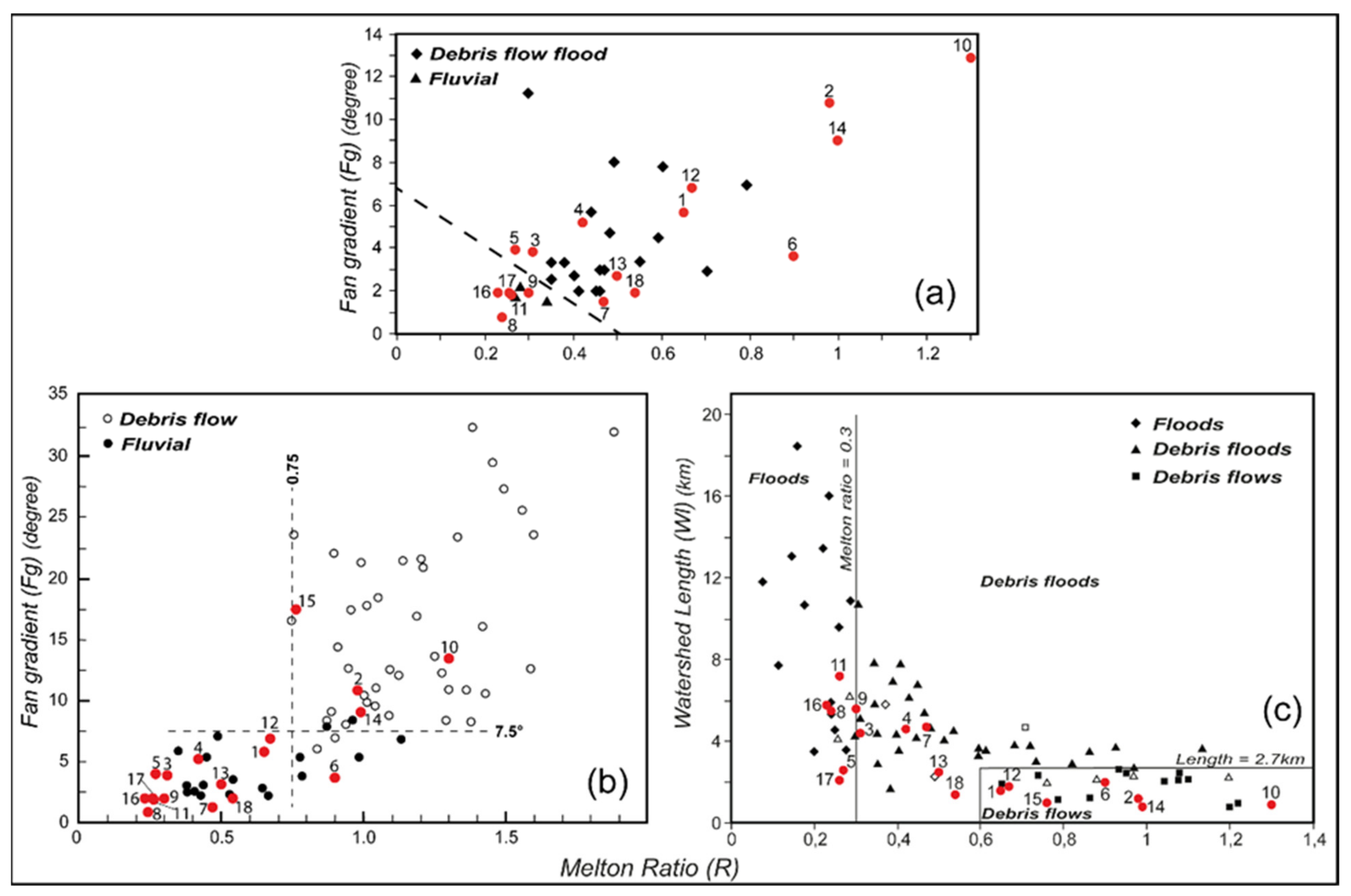
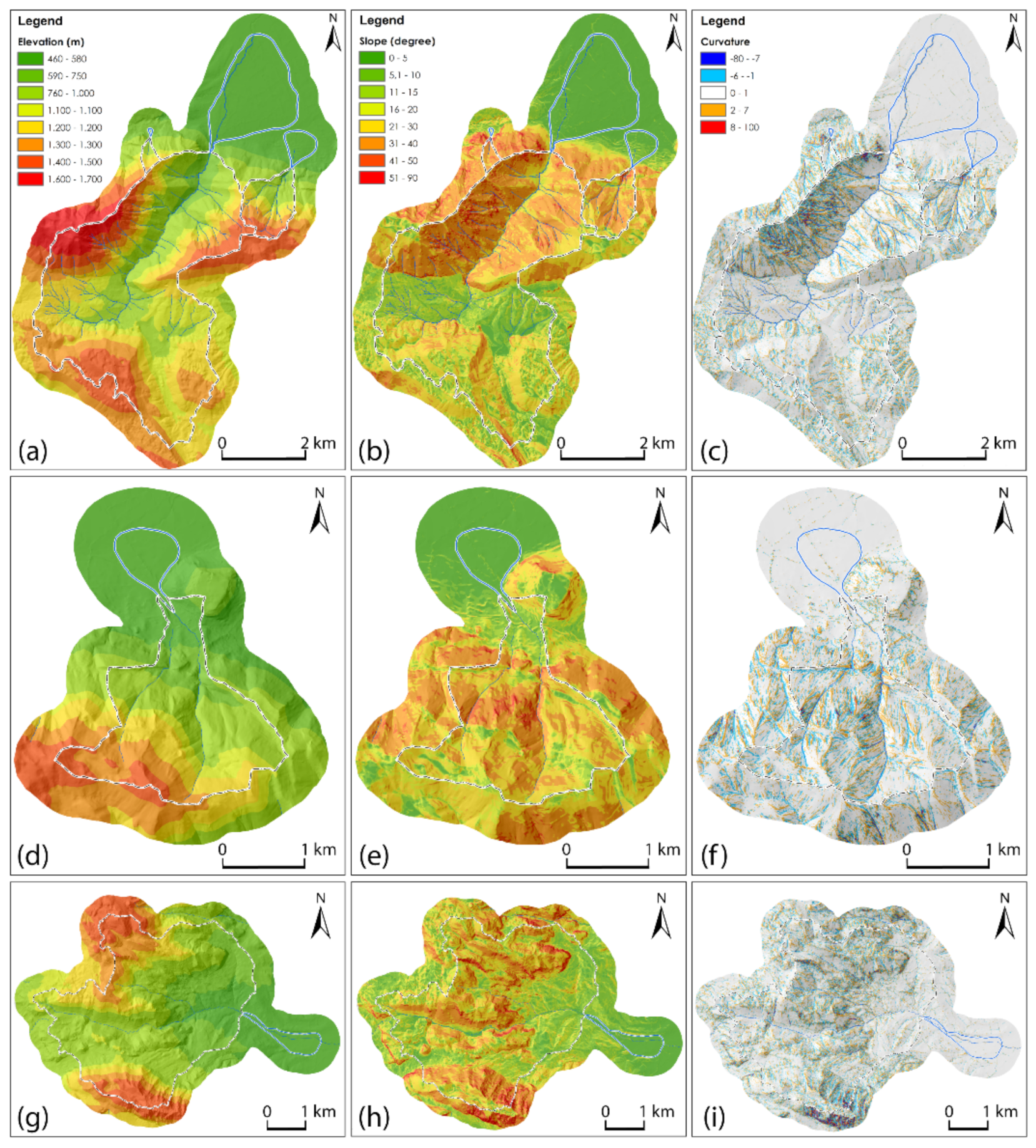
4.1. Morphometric Parameters
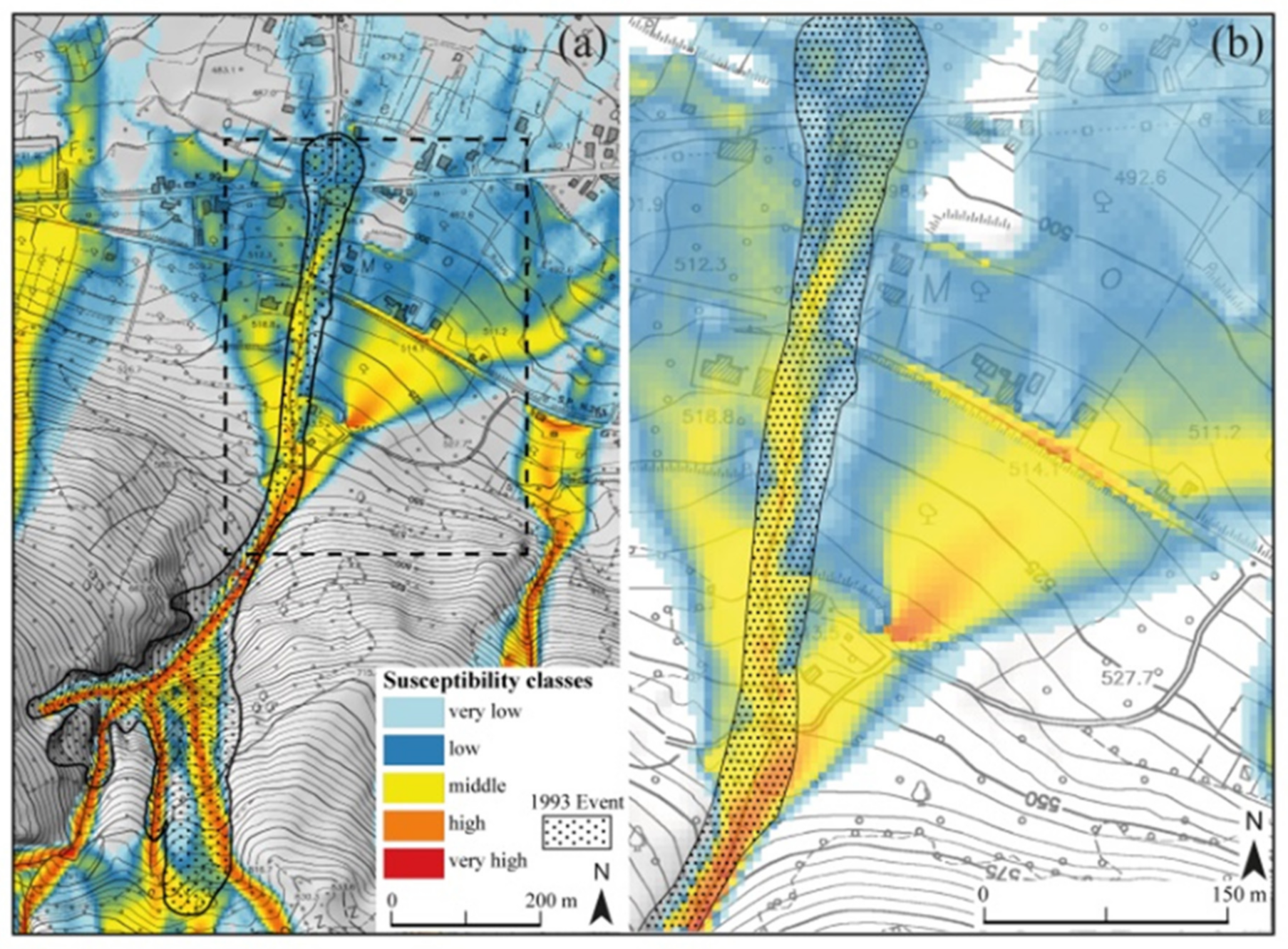
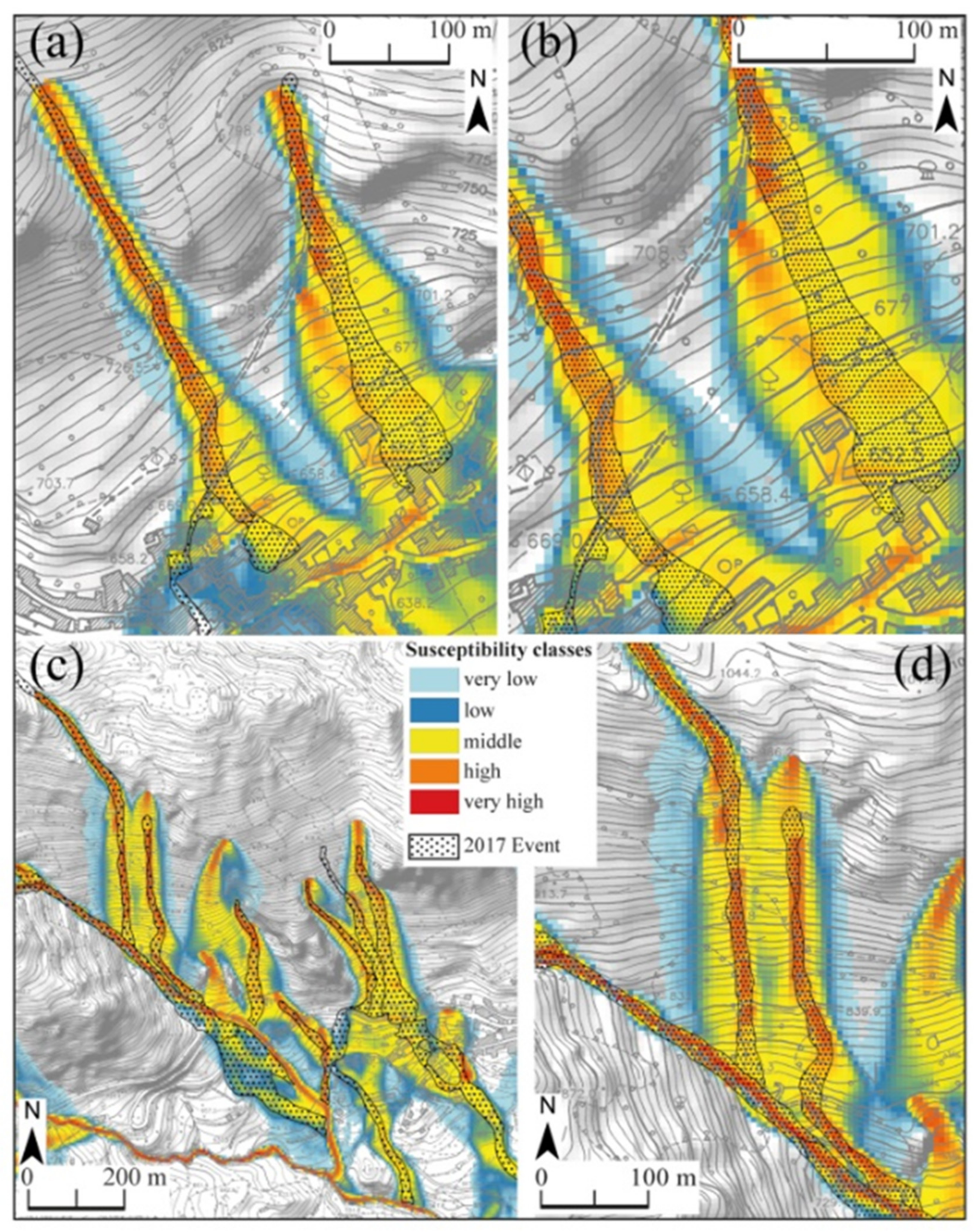
4.2. Calibration of the Flow-R Methodology
4.3. Flow-R Parameters
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kappes, M.S.; Malet, J.P.; Remaitre, A.; Horton, P.; Jaboyedoff, M.; Bell, R. Assessment of debris-flow susceptibility at medium-scale in the Barcelonnette Basin, France. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 11, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Steijn, H. Debri-flow maginitude-frequency relationships for mountainous regions of Central and Northwest Europe. Geomorphology 1996, 15, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmori, H.; Shimazu, H. Distribution of hazard types in a drainage basin and its relation to geomorphological setting. Geomorphology 1994, 10, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hungr, O. A model for the runout analysis of rapid flow slides, debris flows, and avalanches. Can. Geotech. J. 1995, 32, 610–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosta, G.B.; Imposimato, S.; Roddeman, D.G. Numerical modelling of large landslides stability and runout. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2003, 3, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Westen, C.J.; van Asch, T.W.J.; Soeters, R. Landslide hazard and risk zonation—Why is it so difficult? Eng. Geol. Environ. 2006, 65, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berti, M.; Simoni, A. Prediction of debris flow inundation areas using empirical mobility relationships. Geomorphology 2007, 90, 144–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.E. Rheologic, Geomorphic and Sedimentologic differentiation of water floods, hyperconcentrated flows, and debris flows. In Flood Geomorphology; Baker, R.R., Kochel, R.C., Patto, N.C., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1988; pp. 113–122. [Google Scholar]
- Hungr, O.; Morgan, G.C.; Kellerhals, R. Quantitative analysis of debris torrent hazards for design of remedial measures. Can. Geotech. J. 1984, 21, 663–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickenmann, D. Empirical Relationships for Debris Flows. Nat. Hazards 1999, 19, 47–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, P.; Jaboyedoff, M.; Rudaz, B.; Zimmermann, M. Flow-R, a model for susceptibility mapping of debris flows and other gravitational hazards at a regional scale. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 13, 869–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horton, P.; Jaboyedoff, M.; Bardou, E. Debris flow susceptibility mapping at a regional scale. In Proceedings of the 4th Canadian Conference on Geo-Hazards, Quebec, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2008; pp. 339–406. [Google Scholar]
- Blahut, J.; Horton, P.; Sterlacchini, S.; Jaboyedoff, M. Debris flow hazard modelling on medium scale: Valtellina di Tirano, Italy. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 10, 2379–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, V.; Wick, E.; Horton, P.; Jaboyedoff, M. Debris flow susceptibility mapping at a regional scale along the National Road N7, Argentina. In Proceedings of the 14th Pan-American Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2–6 October 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Horton, P.; Jaboyedoff, M.; Zimmermann, M.; Mazotti, B.; Longchamp, C. Flow-R, a model for debris flow susceptibility mapping at a regional scale—Some case studies. It. J. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2011, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lari, S.; Crosta, G.B.; Frattini, P.; Horton, P.; Jaboyedoff, M. Regional-scale debris-flow risk assessment for an alpine valley. It. J. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2011, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, L.; Rubensdotter, L.; Sletten, K.; Stalsberg, K.; Melchiorre, C.; Horton, P.; Jaboyedoff, M. Debris flow modeling for susceptibility mapping at regional to national scale in Norway. In Landslides and Engineered Slopes: Protecting Society through Improved Understanding; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2012; pp. 723–729. [Google Scholar]
- Jaboyedoff, M.; Choffet, C.; Derron, M.H.; Horton, P.; Loye, A.; Longchamp, C.; Mazotti, B.; Michoud, C.; Pedrazzini, A. Preliminary Slope Mass Movements Susceptibility Mapping Using DEM and LiDAR DEM. In Terrigenous Mass Movements: Detection, Modelling, Early Warning and Mitigation Using Geoinformation Technology; Pradhan, B., Buchroithner, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 109–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strahler, A.N. Quantitative analysis of watershed geomorphology. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1957, 38, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crosta, G.B.; Frattini, P. Controls on modern alluvial fan processes in the central Alps, northern Italy. Earth Surf. Proc. Land. 2004, 29, 267–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, A.J. Delineating Debris-Flow Hazards on Alluvial Fans in the Coromandel and Kaimai Regions, New Zealand, Using GIS. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Canterbury, Canterbury, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Santangelo, N.; Daunis-i Estadella, J.; Di Crescenzo, G.; Di Donato, V.; Faillace, P.I.; Martín-Fernández, J.A.; Romano, P.; Santo, A.; Scorpio, V. Topographic predictors of susceptibility to alluvial fan flooding, Southern Apennines. Earth Surf. Proc. Land. 2012, 37, 803–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogelis, M.C.; Werner, M. Regional debris flow susceptibility analysis in mountainous peri-urban areas through morphometric and land cover indicators. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 14, 3043–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Scally, F.; Owens, I. Morphometric controls and geomorphic responses on fans in the Southern Alps, New Zealand. Earth Surf. Proc. Land. 2004, 29, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowbotham, D.; De Scally, F.; Louis, J. The identification of debris torrent basins using morphometric measures derived within a GIS. Geografiska Annaler 2005, 87, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilford, D.J.; Sakals, M.E.; Innes, J.L.; Sidle, R.C.; Bergerud, W.A. Recognition of debris flow, debris flood and flood hazard through watershed morphometrics. Landslides 2004, 1, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santangelo, N.; Santo, A.; Faillace, P. Valutazione della pericolosità alluvionale delle conoidi del Vallo di Diano (Salerno, Italia meridionale). II Quaternario 2006, 19, 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand, M.; Liébault, F.; Piégay, H. Debris-flow susceptibility of upland catchments. Nat. Hazards 2013, 67, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’agostino, V. Analisi quantitativa e qualitativa del trasporto solido torrentizio nei bacini montani del Trentino Orientale. In Proceedings of the Convegno di Studio “I Problemi dei Grandi Comprensori Irrigui”, Novara, Italy, 6–7 June 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Iverson, R.M.; Schilling, S.P.; Vallance, J.W. Objective delineation of lahar inundation hazard zones. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1998, 110, 972–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hürlimann, M.; Rickenmann, D.; Medina, V.; Bateman, A. Evaluation of approaches to calculate debris-flow parameters for hazard assessment. Eng. Geol. 2008, 102, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iverson, R.M.; Denlinger, R.P. Mechanics of debris flows and debris-laden flash floods. In Proceedings of the Seventh Federal Interagency Sedimentation Conference, Reno, NV, USA, 25–29 March 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Rickenmann, D.; Zimmermann, M. The 1987 debris flows in Switzerland: Documentation and analysis. Geomorphology 1993, 8, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T. Estimation of potential debris flows and their hazardous zones: Soft counter measures for a disaster. J. Nat. Dis. Sci. 1981, 3, 57–89. [Google Scholar]
- Delmonaco, G.; Leoni, G.; Margottini, C.; Puglisi, C.; Spizzichino, D. Large scale debris-flow hazard assessment: A geotechnical approach and GIS modelling. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2003, 3, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wieczorek, G.F.; Mandrone, G.; DeCola, L. The Influence of Hillslope Shape on Debris-Flow Initiation. In Proceedings of the First International Conference Water Resources Engineering Division, San Antonio, TX, USA, 14–18 August 1995; pp. 21–31. [Google Scholar]
- Tarboton, D.G. A new method for the determination of flow di-rections and upslope areas in grid digital elevation models. Water Resour. Res. 1997, 33, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erskine, R.H.; Green, T.; Ramirez, J.; MacDonald, L. Comparison of grid-based algorithms for computing upslope contributing area. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heinimann, H.R. Methoden zur Analyse und Bewertung von Naturgefahren; Bundesamt für Umwelt, Wald und Landschaft, Federal Office for the Environment, Forests and Landscape (BUWAL): Bern, Switzerland, 1998; pp. 1–247.
- O’Callaghan, J.F.; Mark, D.M. The extraction of drainage networks from digital elevation data. Comput. Vision Graph. 1984, 28, 328–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenson, S.K.; Domingue, J.O. Extracting topographic structure from digital elevation data for geographic information system analysis. Photogr. Eng. Rem. Sens. 1988, 54, 1593–1600. [Google Scholar]
- Fairfield, J.; Laymarie, P. Drainage Networks from Grid Digital Elevation Models. Water Resour. Res. 1991, 30, 1681–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, P.; Beven, K.; Chevalier, P.; Planchon, O. The Prediction of Hillslope Flow Paths For Distributed Hydrological Modelling Using Digital Terrain Models. Hydrol. Process. 1991, 5, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, T.G. Calculating catchment area with divergent flow based on a regular grid. Comput. Geosci. 1991, 17, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmgren, P. Multiple flow direction algorithms for runoff modelling in grid based elevation models: An empirical evaluation. Hydrol. Process. 1994, 8, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamma, P. Dfwalk—Ein Murgang-Simulationsprogramm zur Gefahrenzonierung; Geographisches Institut der Universität Bern: Bern, Switzerland, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Perla, R.; Cheng, T.T.; McClung, D.M. A two-parameter model of snow-avalanche motion. J. Glaciol. 1980, 26, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patacca, E.; Scandone, P. Geology of the Southern Apennines. Boll. Soc. Geol. It. Spec. Issue 2007, 7, 75–119. [Google Scholar]
- Schiattarella, M.; Di Leo, P.; Beneduce, P.; Giano, S.I.; Martino, C. Tectonically driven exhumation of a young orogen: An example from southern Apennines, Italy. In Penrose Conference Series: Tectonics, Climate, and Landscape Evolution; Willett, S.D., Hovius, N., Brandon, M.T., Fisher, D., Eds.; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 2006; Special Paper 398; pp. 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavusi, M.; Chianese, D.; Giano, S.I.; Mucciarelli, M. Multi-disciplinary investigations on the Grumentum Roman acqueduct (Basilicata, Southern Italy). Ann. Geophyis. 2004, 47, 1791–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giano, S.I.; Pescatore, E.; Agosta, F.; Prosser, G. Geomorphic evidence of quaternary tectonics within an underlap fault zone of southern Apennines, Italy. Geomorphology 2018, 303, 172–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiattarella, M.; Giano, S.I.; Gioia, D. Long-term geo-morphological evolution of the axial zone of the Campania-Lucania Apennine, Southern Italy. Geol. Carpathica 2017, 68, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogniben, L. Schema introduttivo alla geologia del confine cala-bro-lucano. Mem. Soc. Geol. It. 1969, 8, 453–763. [Google Scholar]
- Mostardini, F.; Merlini, S. Appennino centro meridionale. Sezioni geologiche e proposta di modello strutturale. Mem. Soc. Geol. It. 1986, 35, 177–202. [Google Scholar]
- Di Leo, P.; Giano, S.I.; Gioia, D.; Mattei, M.; Pescatore, E.; Schiattarella, M. Evoluzione morfotettonica quaternaria del bacino intermontano di Sanza (Appennino meridionale). Alp. Mediterr. Quat. (II Quat.) 2009, 22, 189–206. [Google Scholar]
- Giano, S.I.; Gioia, D.; Schiattarella, M. Morphotectonic evolution of connected intermontane basins from the Southern Apennines, Italy: The legacy of the preexisting structurally controlled landscape. Rend. Lincei 2014, 25 (Suppl. S2), S241–S252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pescatore, T.; Renda, P.; Schiattarella, M.; Tramutoli, M. Stratigraphic and structural relationships between Meso-Cenozoic Lagonegro basin and coeval carbonate platforms in the southern Apennines, Italy. Tectonophysics 1999, 315, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giano, S.I.; Lapenna, V.; Piscitelli, S.; Schiattarella, M. Nuovi dati geologici e geofisici sull’assetto strutturale dei depositi continentali quaternari dell’alta Val d’Agri (Basilicata). Alp. Mediterr. Quat. (II Quat.) 1997, 10, 589–594. [Google Scholar]
- Schiattarella, M.; Giano, S.I.; Gioia, D.; Martino, C.; Nico, G. Age and statistical properties of the summit palaeosurface of southern Italy. Geogr. Fis. Din. Quat. 2013, 36, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancaccio, L.; Cinque, A.; Sgrosso, I. Forma e genesi di alcuni versanti di faglia in rocce carbonatiche: Il riscontro naturale di un modello teorico. Rend. Accad. Sci. Fis. Mat. 1979, 46, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Giano, S.I.; Schiattarella, M. Age constraints and denudation rate of a multistage fault line scarp: An example from Southern Italy. Geochronometria 2014, 41, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beneduce, P.; Giano, S.I. Osservazioni preliminari sull’assetto morfostrutturale dell’edificio vulcanico del Monte Vulture (Basilicata). Alp. Mediterr. Quat. (II Quat.) 1996, 9, 325–330. [Google Scholar]
- Giano, S.I.; Giannandrea, P. Late pleistocene differential uplift inferred from the analysis of fluvial terraces (Southern Apennines, Italy). Geomorphology 2014, 217, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascione, A.; Cinque, A.; Santangelo, N.; Tozzi, M. Il bacino del Vallo di Diano e la tettonica trascorrente plio-quaternaria: Nuovi vincoli cronologici e cinematici. Studi. Geol. Cam. 1992, 1992, 201–208. [Google Scholar]
- Sgrosso, I.; Bonardi, G.; Amore, F.O.; Ascione, A.; Castellano, M.C.; De Vita, P.; Di Donato, V.; Morabito, S.; Parente, M.; Pescatore, E.; et al. Note Illustrative Della Carta Geologica d’Italia Alla Scala 1:50.000; ISPRA-Servizio Geologico d’Italia: Roma, Italy, 2010; Foglio n. 504 Sala Consilina. (In Italian) [Google Scholar]
- Bentivenga, M.; Giano, S.I.; Piccarreta, M. Recent increase of flood frequency in the Ionian belt of Basilicata region, Southern Italy: Human or climatic changes? Water 2020, 12, 2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putignano, M.L.; Schiattarella, M. Struttura, esumazione ed evoluzione morfologica del nucleo mesozoico del Monte Motola (Cilento, Italia meridionale). Boll. Soc. Geol. It. 2008, 127, 477–493. [Google Scholar]
- Amicucci, L.; Barchi, M.R.; Montone, P.; Rubiliani, N. The Vallo di Diano and Auletta extensional basins in the southern Apennines (Italy): A simple model for a complex setting. Terra Nova 2008, 20, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancaccio, L.; Cinque, A.; Sgrosso, I. L’analisi morfolo-gica dei versanti come strumento per la ricostruzione degli eventi neotettonici. Mem. Soc. Geol. It. 1978, 19, 621–626. [Google Scholar]
- Marchi, L.; D’Agostino, V. Estimation of de-bris-flow magnitude in the Eastern Italian Alps. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2004, 29, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santangelo, N.; Santo, A.; Di Crescenzo, G.; Foscari, G.; Liuzza, V.; Sciarrotta, S.; Scorpio, V. Flood susceptibility assessment in a highly urbanized alluvial fan: The case study of Sala Consilina (southern Italy). Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 11, 2765–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Claessens, L.; Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Schoorl, J.M.; Veldkamp, A. DEM resolution effects on shallow landslide hazard and soil redistribution modelling. Earth Surf. Proc. Landf. 2005, 30, 461–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
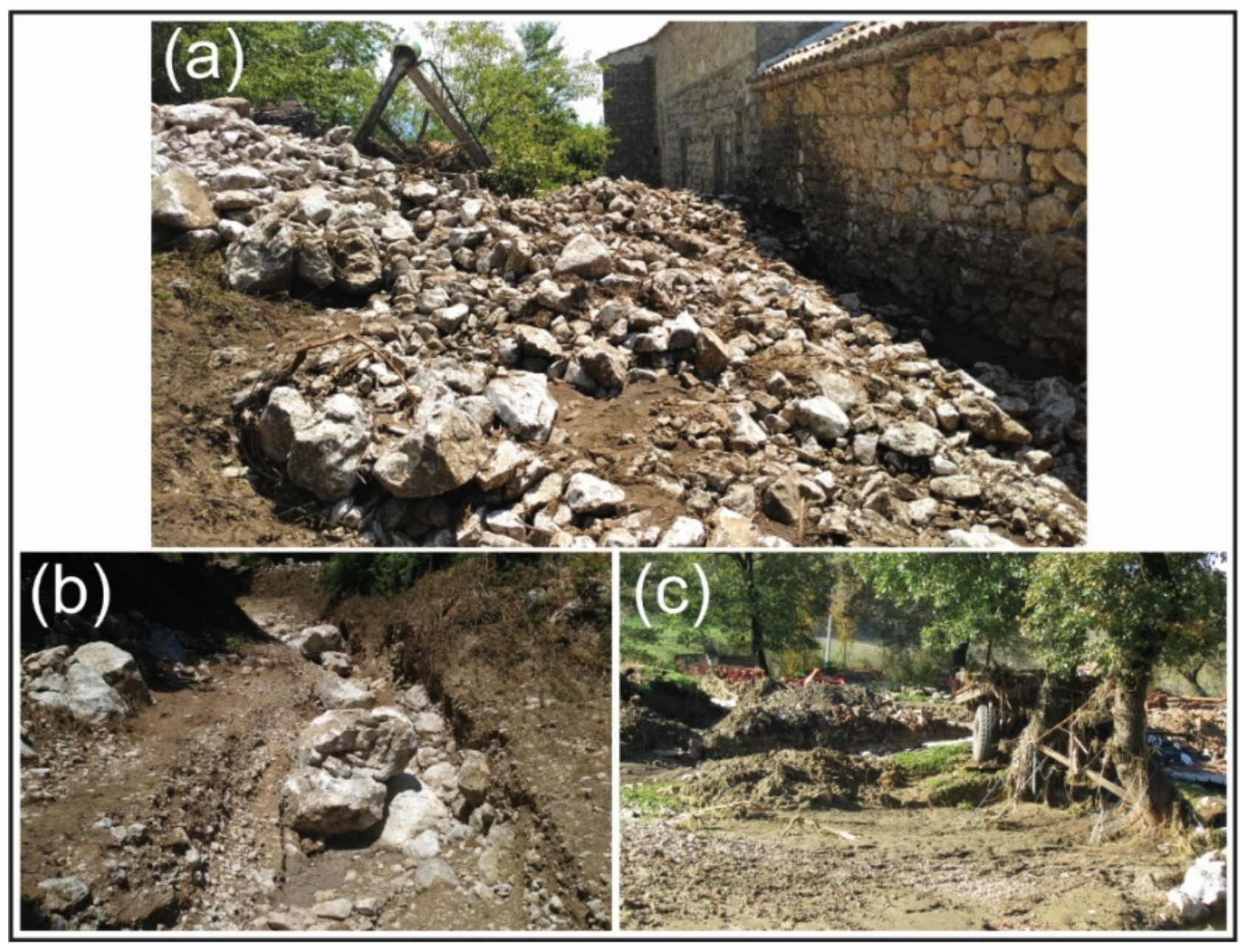



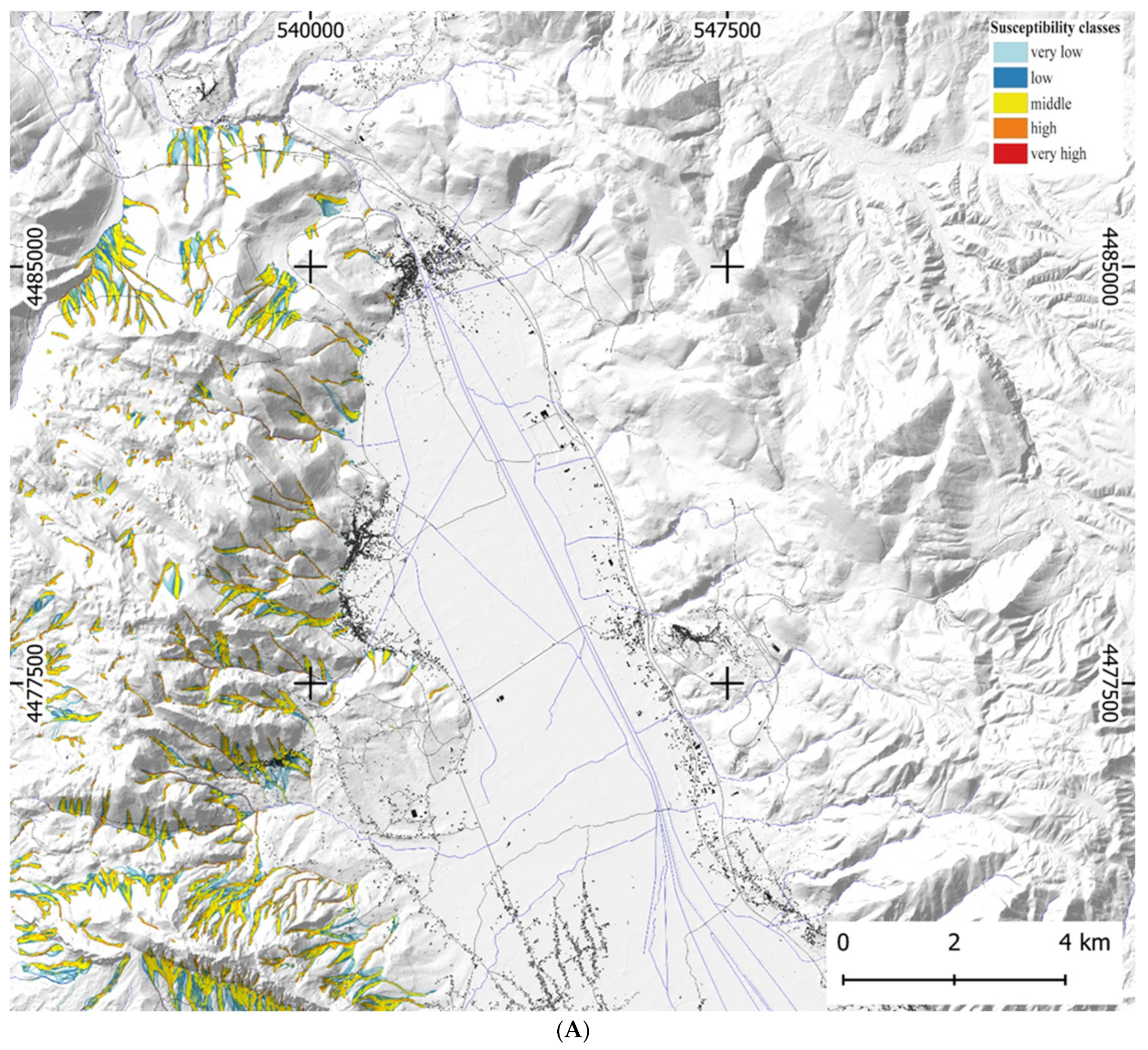
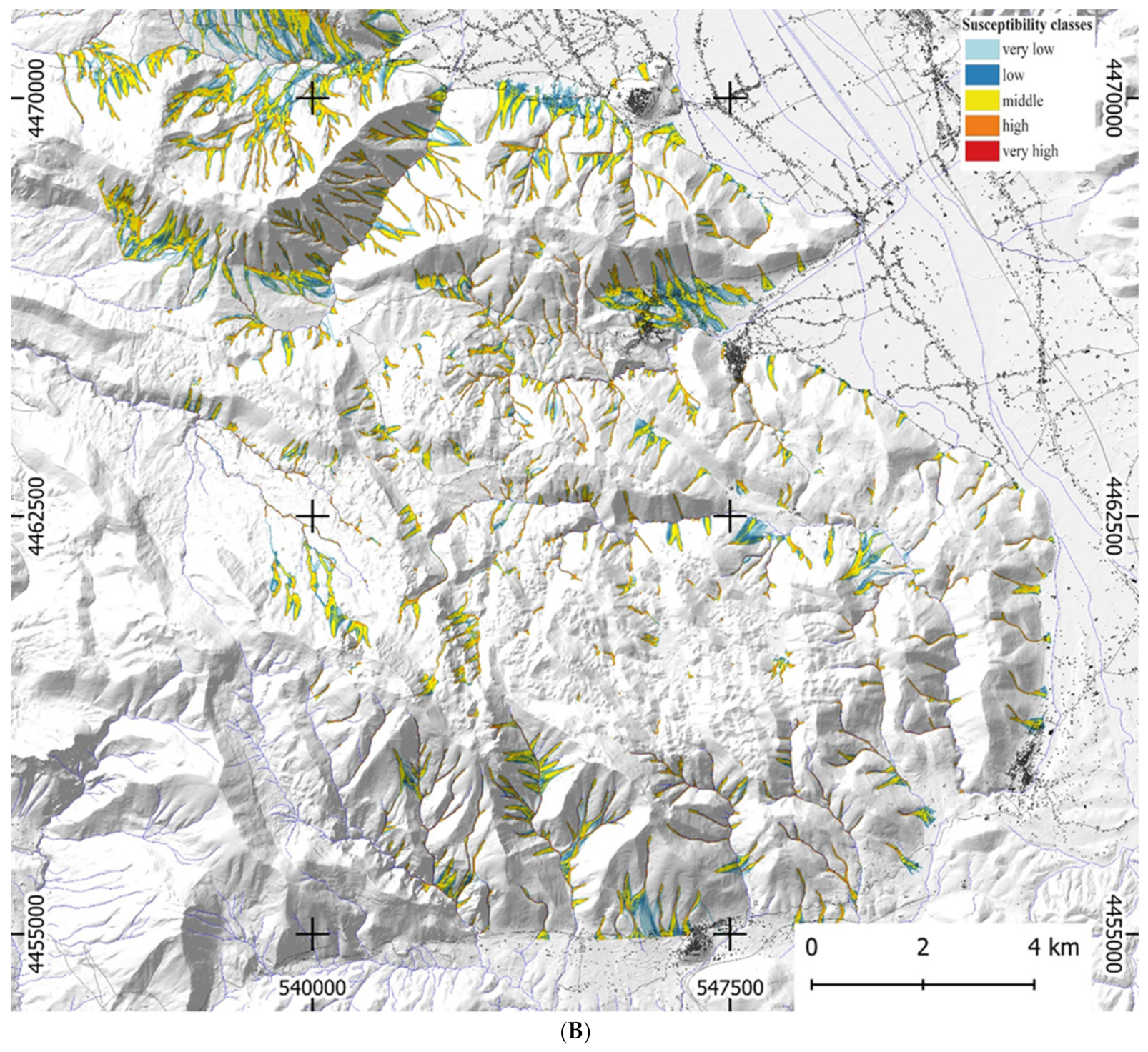
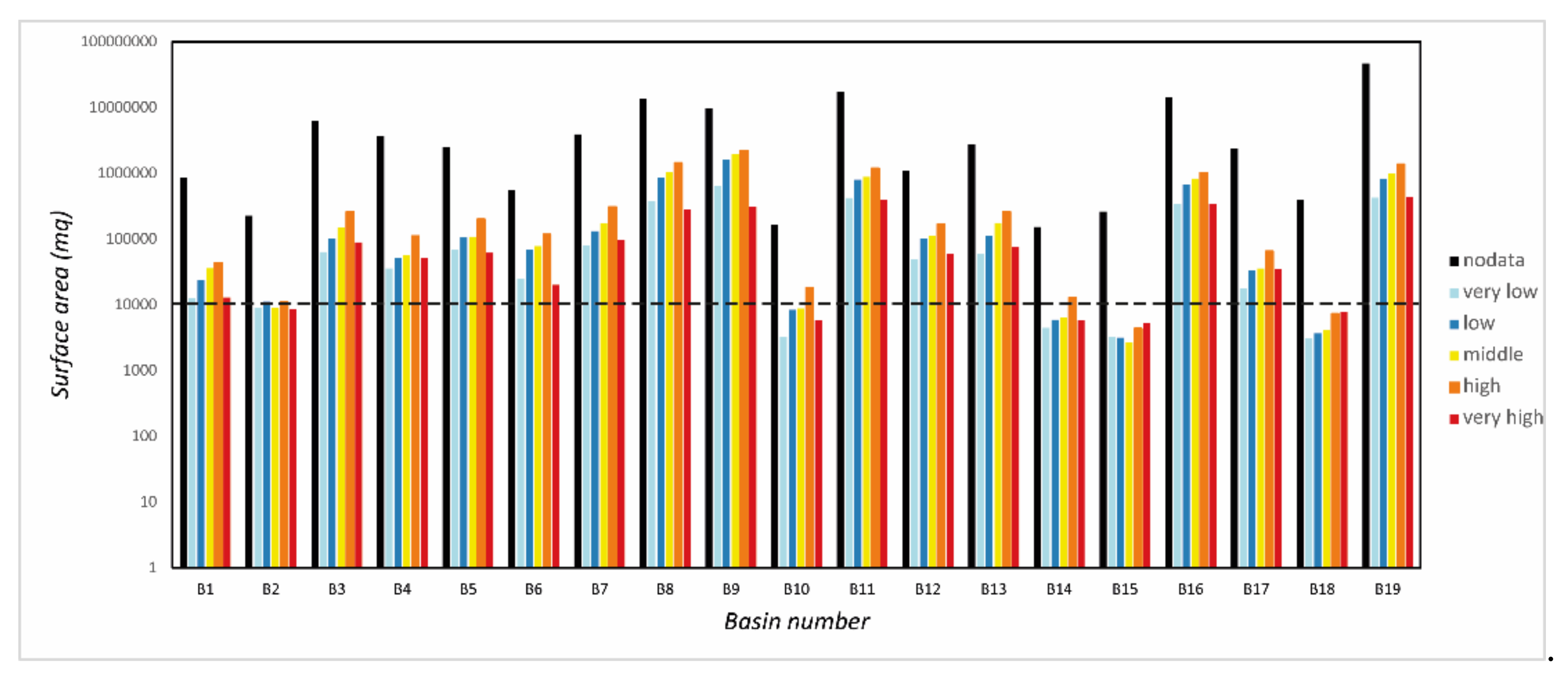
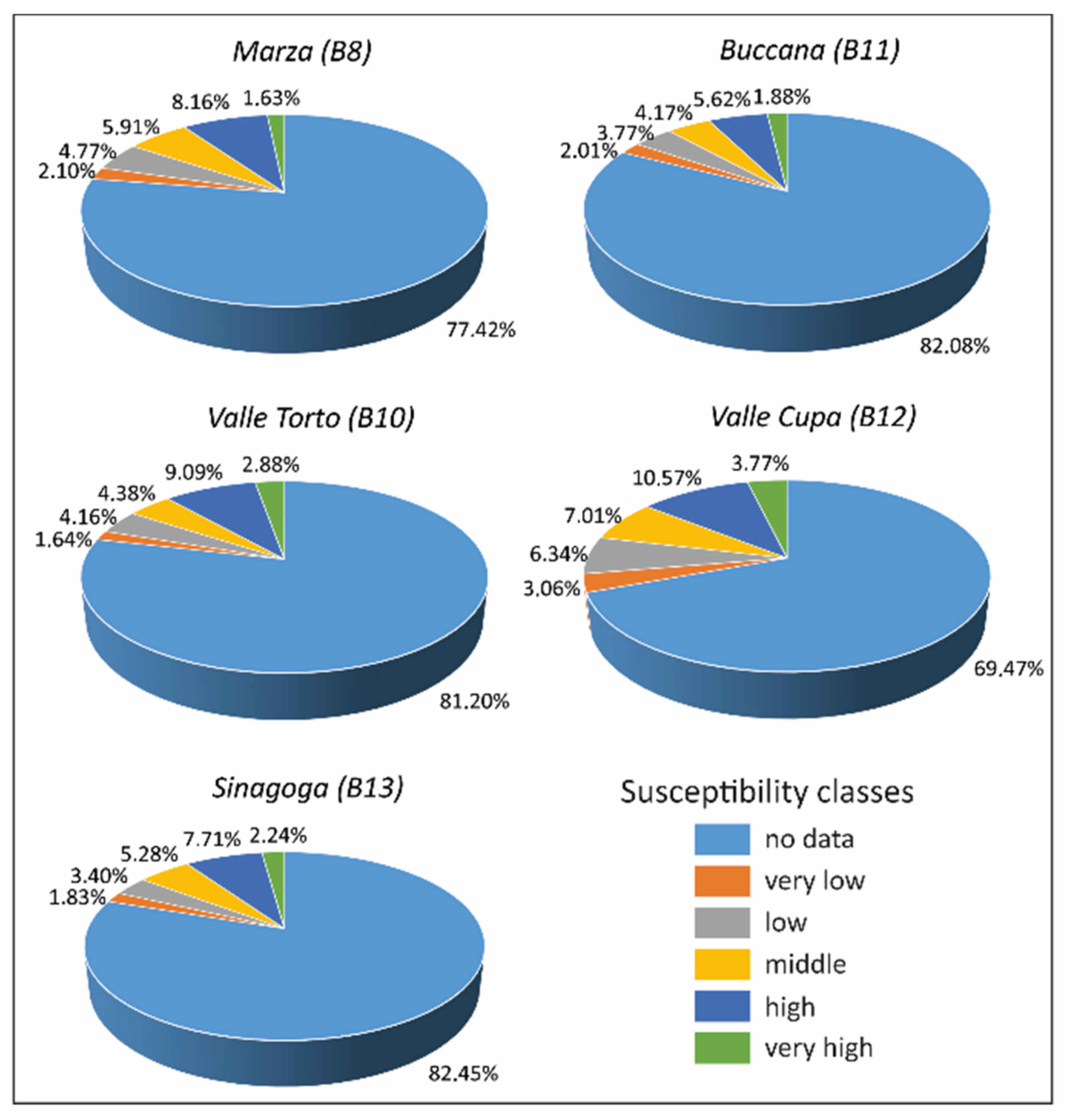

| Basin Area | Ba | Planimetric Area of the Basin Measured above the Fan Apex |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum elevation | Hmax | maximum elevation point measured at the crest of the basin |
| Minimum elevation | Hmin | minimum elevation point of the basin, measured up the fan apex |
| Mean elevation | Hmean | mean elevation point measured in the basin |
| Basin relief | Bf | vertical difference between the maximum and minimum elevation of the basin |
| Watershed length | Wl | length of the planimetric straight-line measured from the fan apex to the most distant point on the watershed boundary |
| Melton’s ruggedness number | R | index of the basin expressed by the following algorithm: where Hb is the basin relief and Ab is the planimetric area of the basin |
| Fan toe | Ft | elevation a.s.l. in meters of the fan toe |
| Fan gradient | Fg | average gradient measured along the longitudinal fan axes |
| Fan area | Fa | planimetric area of the fan measured below the fan apex |
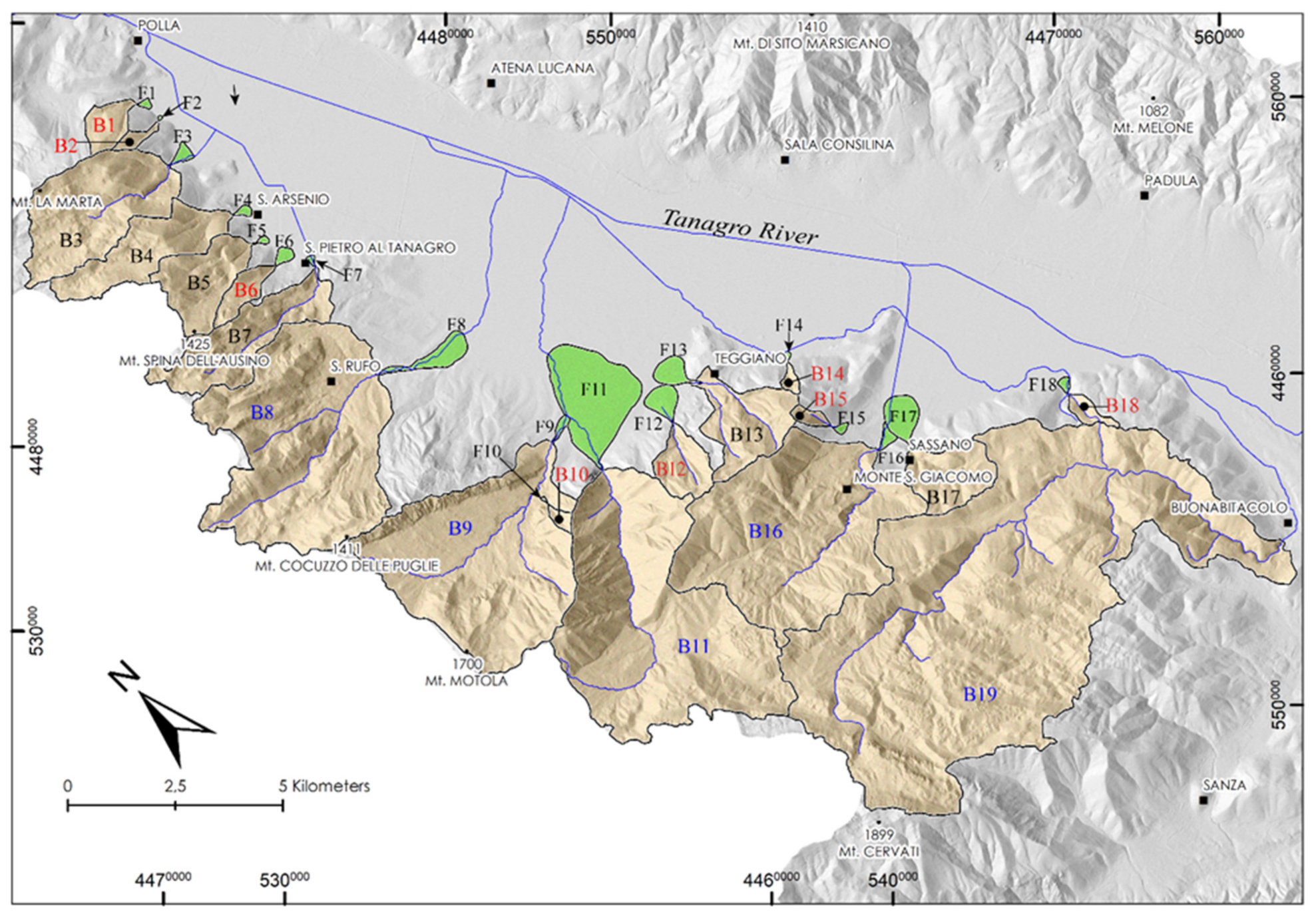
| Basin N. | Name | Hmax (m) | Hmin (m) | Hmean (m) | Br (m) | Ba (km2) | Wl (m) | R |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | V. Pastena | 1127.7 | 484.7 | 769.9 | 643 | 0.97 | 1611 | 0.65 |
| B2 | V. Petrosa | 992.9 | 479.8 | 785.6 | 513.1 | 0.27 | 1263 | 0.98 |
| B3 | V. Tuorchi | 1301.6 | 488 | 994.8 | 813.6 | 6.97 | 4416 | 0.31 |
| B4 | V. Tornaturi | 1332.4 | 489.7 | 1033.2 | 842.7 | 3.97 | 4569 | 0.42 |
| B5 | T. Futorella | 1426.9 | 951.6 | 1003.8 | 475.3 | 3.0 | 2664 | 0.27 |
| B6 | F.so della Torre | 1312.6 | 481.9 | 893.9 | 830.7 | 0.85 | 2051 | 0.9 |
| B7 | V. Setone | 1468.6 | 461 | 1042 | 1007.6 | 4.65 | 4725 | 0.47 |
| B8 | T. Marza | 1471.3 | 483.8 | 915.1 | 987.5 | 17.5 | 5491 | 0.24 |
| B9 | T. Buco | 1735.6 | 505.7 | 1053.6 | 1229.9 | 16.2 | 5660 | 0.3 |
| B10 | Valle Torto | 1273.2 | 681.5 | 1035.7 | 591.7 | 0.2 | 932 | 1.3 |
| B11 | T. Buccana | 1738.1 | 544.2 | 1101.7 | 1193.9 | 21.0 | 7203 | 0.26 |
| B12 | Valle Cupa | 1410.8 | 572.3 | 1068.1 | 838.5 | 1.58 | 1808 | 0.67 |
| B13 | V. Sinagoga | 1390.6 | 483.5 | 959.7 | 907.1 | 3.39 | 2555 | 0.5 |
| B14 | V. del Duca | 913.3 | 711 | 756.7 | 430.3 | 0.18 | 798 | 0.99 |
| B15 | V. Secco | 1114.1 | 404.3 | 959 | 403.1 | 0.27 | 999 | 0.76 |
| B16 | T. Zia Francesca | 1445.3 | 497.6 | 966.1 | 947.7 | 17.1 | 5773 | 0.23 |
| B17 | V. San Nicola | 924.3 | 506.9 | 741.5 | 417.4 | 2.52 | 2086 | 0.26 |
| B18 | T. Valla | 828 | 475.1 | 663.7 | 352.9 | 0.42 | 1429 | 0.54 |
| B19 | T. Peglio | 1896.6 | 500.3 | 1008 | 1396.3 | 50.30 | 12,134 | 0.19 |
| Fan N. | Fan Area (km2) | Fan Apex Elevation (m) | Fan Toe (m) | Fan Gradient (Degree) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 0.048220 | 484 | 448 | 5.6 |
| F2 | 0.009039 | 475 | 448 | 10.8 |
| F3 | 0.134259 | 487 | 450 | 3.8 |
| F4 | 0.074192 | 490 | 448 | 5.2 |
| F5 | 0.040244 | 476 | 448 | 3.9 |
| F6 | 0.128934 | 480 | 446 | 3.6 |
| F7 | 0.032508 | 465 | 457 | 1.5 |
| F8 | 0.655337 | 486 | 455 | 0.8 |
| F9 | 0.096612 | 508 | 487 | 1.9 |
| F10 | 0.010876 | 682 | 640 | 12.9 |
| F11 | 3.686782 | 560 | 465 | 1.8 |
| F12 | 0.432525 | 572 | 464 | 6.8 |
| F13 | 0.423579 | 505 | 455 | 2.7 |
| F14 | 0.026371 | 483 | 449 | 9.0 |
| F15 | 0.057295 | 707 | 593 | 17.5 |
| F16 | 0.124157 | 501 | 480 | 1.9 |
| F17 | 0.660485 | 508 | 465 | 1.9 |
| F18 | 0.071381 | 475 | 462 | 1.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giano, S.I.; Pescatore, E.; Siervo, V. Morphometry and Debris-Flow Susceptibility Map in Mountain Drainage Basins of the Vallo di Diano, Southern Italy. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3254. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163254
Giano SI, Pescatore E, Siervo V. Morphometry and Debris-Flow Susceptibility Map in Mountain Drainage Basins of the Vallo di Diano, Southern Italy. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(16):3254. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163254
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiano, Salvatore Ivo, Eva Pescatore, and Vincenzo Siervo. 2021. "Morphometry and Debris-Flow Susceptibility Map in Mountain Drainage Basins of the Vallo di Diano, Southern Italy" Remote Sensing 13, no. 16: 3254. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163254
APA StyleGiano, S. I., Pescatore, E., & Siervo, V. (2021). Morphometry and Debris-Flow Susceptibility Map in Mountain Drainage Basins of the Vallo di Diano, Southern Italy. Remote Sensing, 13(16), 3254. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163254








