Elevation Spatial Variation Error Compensation in Complex Scene and Elevation Inversion by Autofocus Method in GEO SAR
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Geometric Model
3. Analysis of the Elevation Spatial Variant Error
4. Elevation Spatial Variant Error Compensation and Elevation Inversion
4.1. Elevation Spatial Variant Error Compensation
4.2. Elevation Inversion and Estimation Accuracy Analysis
5. Simulations
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, D.; Wu, M.; Sun, Z.; He, F.; Dong, Z. Modelling and Processing of Two-Dimensional Spatial-Variant Geosynchronous SAR Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 3999–4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, D.; Hobbs, S.; Ottavianelli, G. Geosynchronous synthetic aperture radar. Acta Astronaut. 2006, 59, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Long, T.; Liu, Z.; Zeng, T.; Tian, Y. An Improved Frequency Domain Focusing Method in Geosynchronous SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 9, 5514–5528. [Google Scholar]
- Kempf, T.; Anglberger, H.; Suess, H. Depth-of-focus issues on spaceborne very high resolution SAR. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; pp. 7448–7451. [Google Scholar]
- Prats, P.; Scheiber, R.; Rodriguez-Cassola, M. On the Processing of Very High Resolution Spaceborne SAR Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 6003–6015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prats, P.; Macedo, K.; Reigber, A.; Scheiber, R.; Mallorqui, J. Comprasion of topography and aperture dependent motion compensation algorithms for airborne SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2007, 4, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peras, S.; Zamparelli, V.; Pauciullo, A.; Fornaro, G. Azimuth-to-frequency mapping in airborne SAR data corrupted by uncompensated motion errors. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 1493–1497. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, W.; Li, W.; Wu, J.; Huang, Y.; Yang, J.; Yang, H. An azimuth-variant autofocus scheme of bistatic forward-looking synthetic aperture radar. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 689–693. [Google Scholar]
- Prats, P.; Scheiber, R.; Mittermayer, J.; Meta, A.; Moreira, A. Processing of sliding spotlight and TOPS SAR data using baseband azimuth scaling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madsen, S. Motion compensation for ultra wide band SAR. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Sydney, Australia, 9–13 July 2015; pp. 1436–1438. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, F.G.; Li, D.X. Elevation Spatial variation Analysis and Compensation in GEO SAR Imaging. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, A.; Farris, P. Repeat-pass interferometry with airborne synthetic aperture radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1993, 31, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samczynski, P.; Kulpa, K. Coherent mapdrift techinique. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 1505–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, M.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, F. Robust Two-Dimensional Spatial-Variant Map-Drift Algorithm for UAV SAR Autofocusing. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calloway, T.; Donohoe, G. Subaperture Autofocus for Synthetic Aperture Radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1994, 30, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, D.; Eichel, P.; Ghiglia, D.; Jakowatz, C. Phase gradient autofocus a robust tool for high resolution SAR phase correction. IEEE Trans. Accept. Electron. Syst. 1994, 30, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, D.; Jiang, R.; Mao, X.; Zhu, Z. Multi-aubaperture PGA for SAR autofocusing. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2013, 49, 468–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, D.; Jakowatz, C. New approach to strip-map SAR autofocus. In Proceedings of the IEEE 6th Digital Signal Processing Workshop, Yosemite National Park, CA, USA, 2–5 October 1994; pp. 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, B.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yeo, T. Accurate slant range model and focusing method in geosynchronous SAR. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Milan, Italy, 26–31 July 2015; pp. 4464–4467. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B.; Qi, X.; Song, H.; Wang, R.; Mo, Y.; Zheng, S. An Accurate Range Model Based on the Fourth-Order Doppler Parameters for Geosynchronous SAR. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Lin, P.; Xiao, P.; Kang, L.; Li, C. Correcting spatial variance of RCM for GEO SAR imaging based on time-frequency scaling. Sensors 2016, 16, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duque, S.; Breit, H.; Balss, U.; Parizzi, A. Absolute height estimation using a single TerraSAR-X staring spotlight acquisition. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 1735–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kay, S. Fundamentals of Statistical Signal Processing: Estimation Theory; Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Bamler, R.; Eineder, M. Accuracy of differential shift estimation by correlation and split-bandwidth interferometry for wideband and delta-k SAR systems. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2005, 2, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

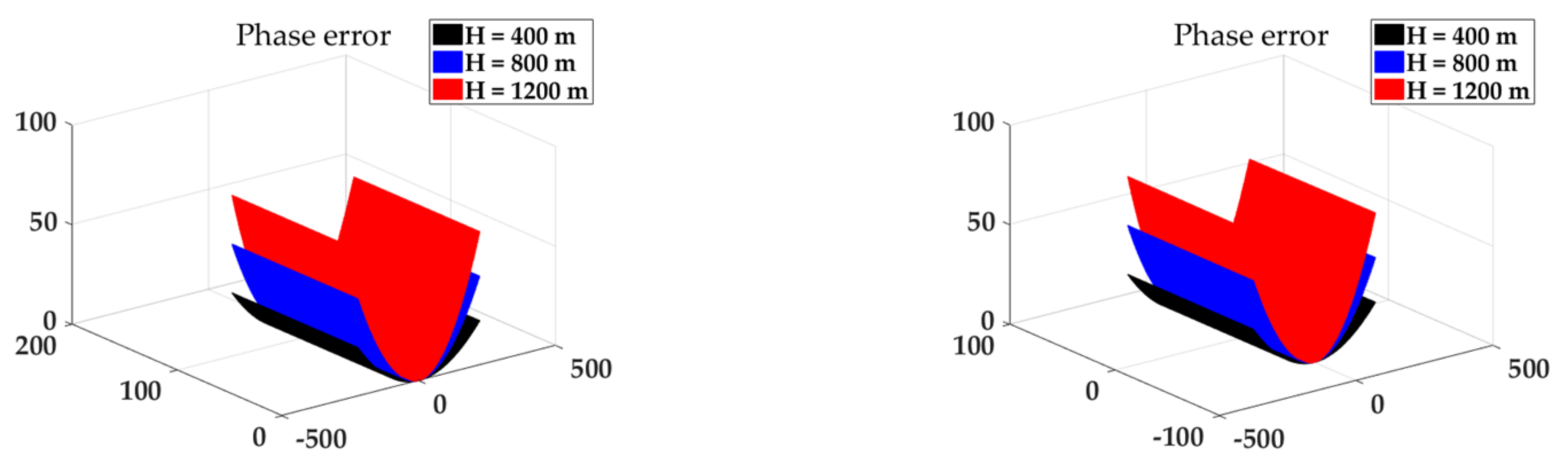
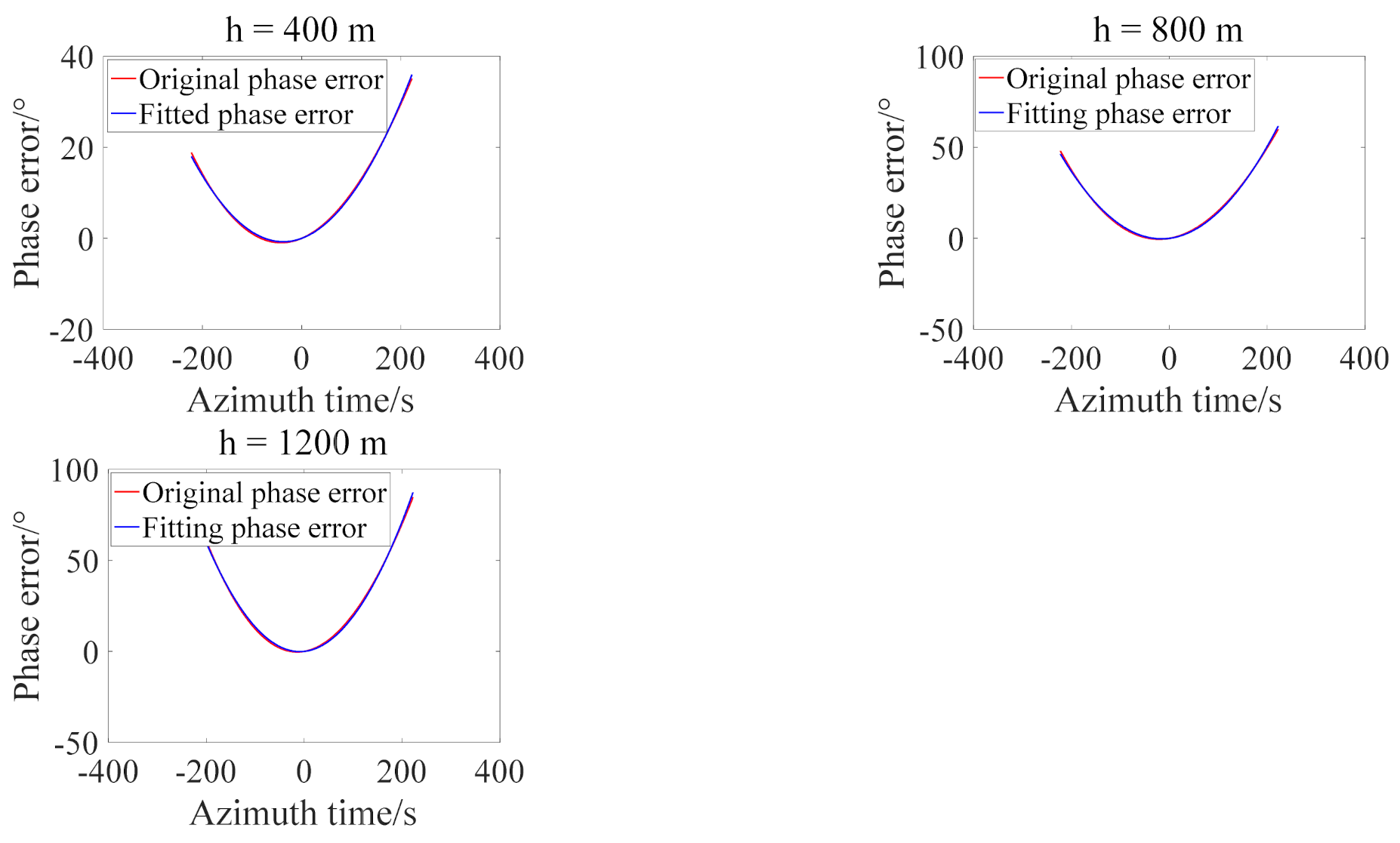
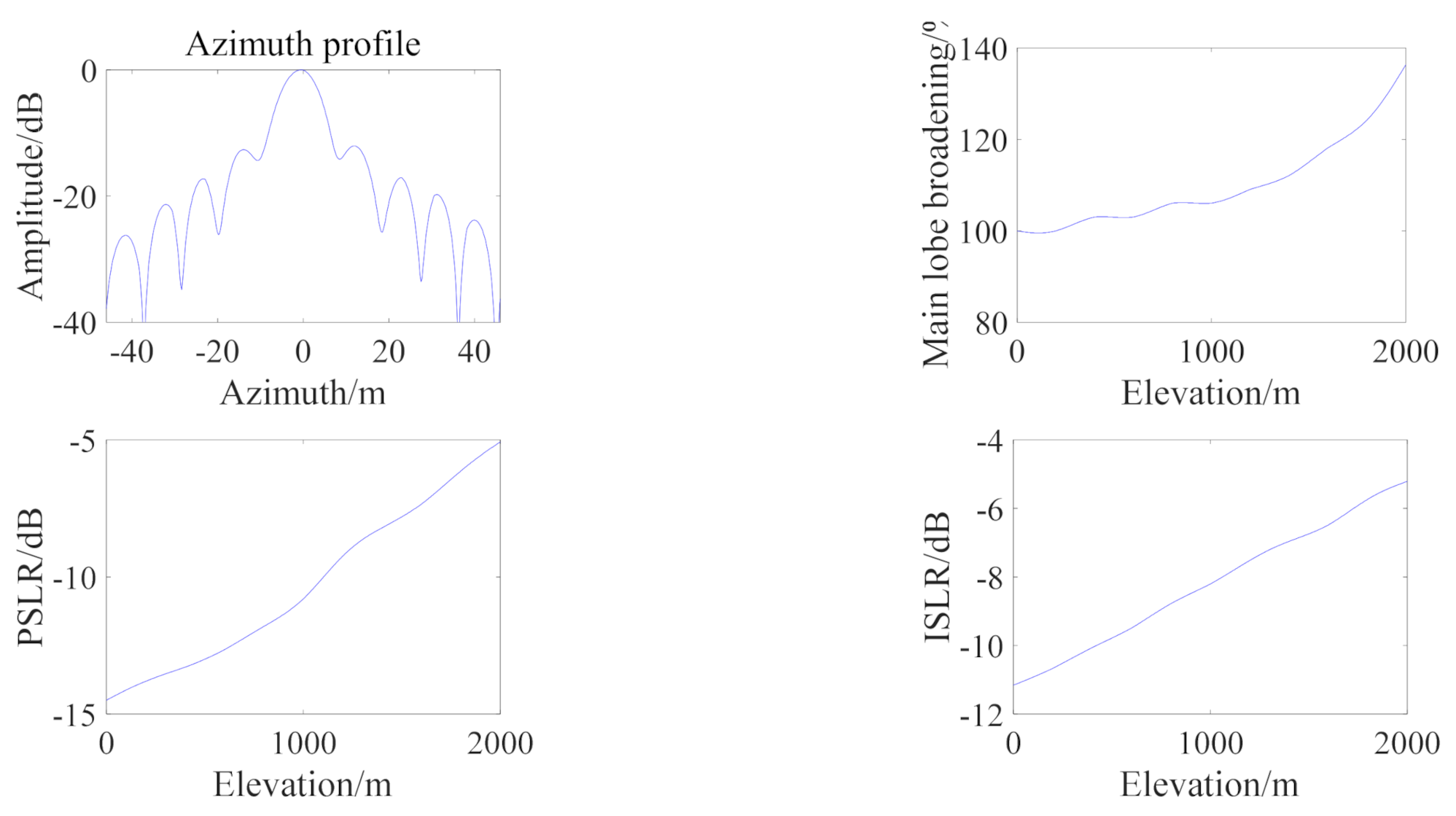

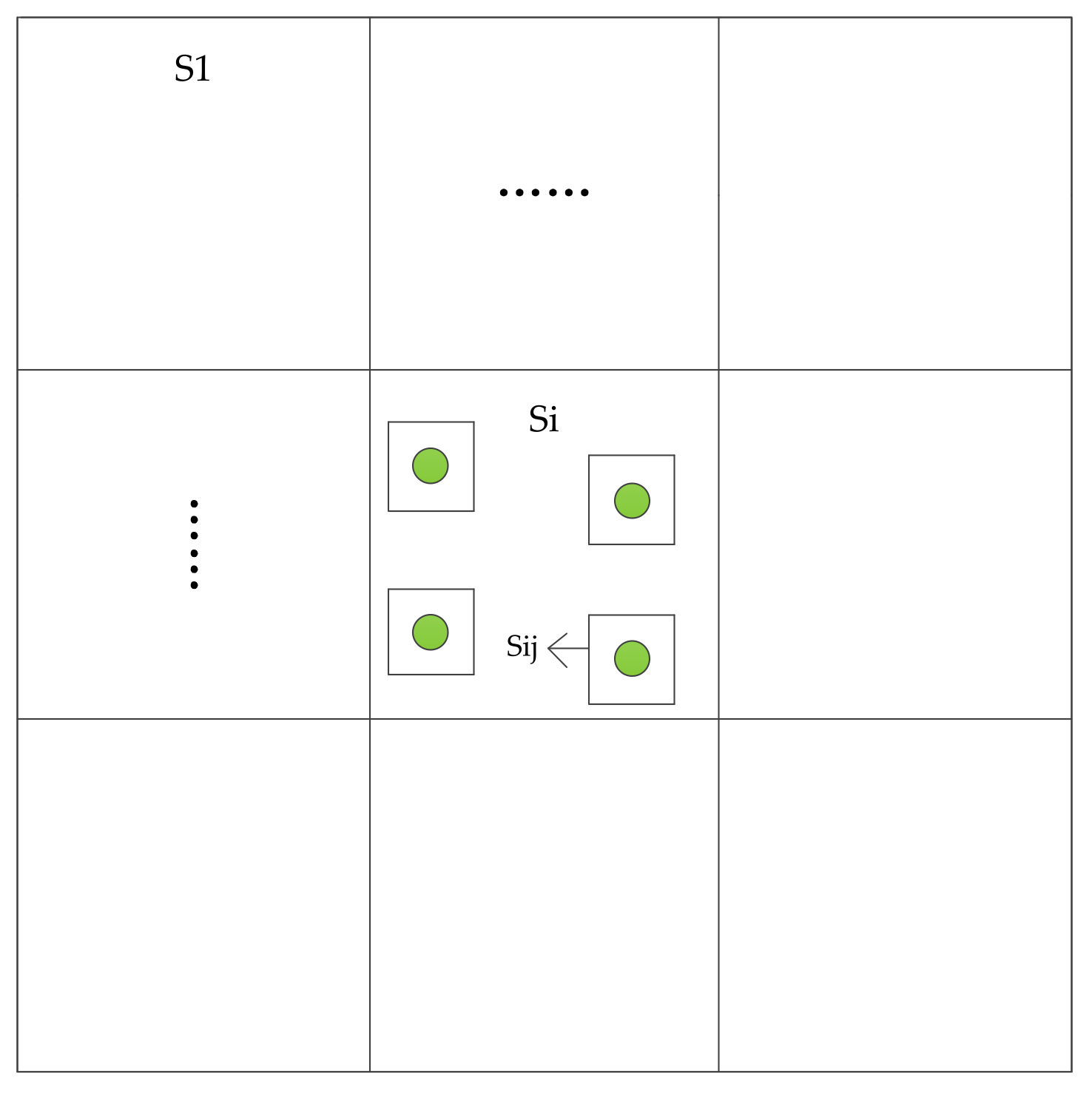
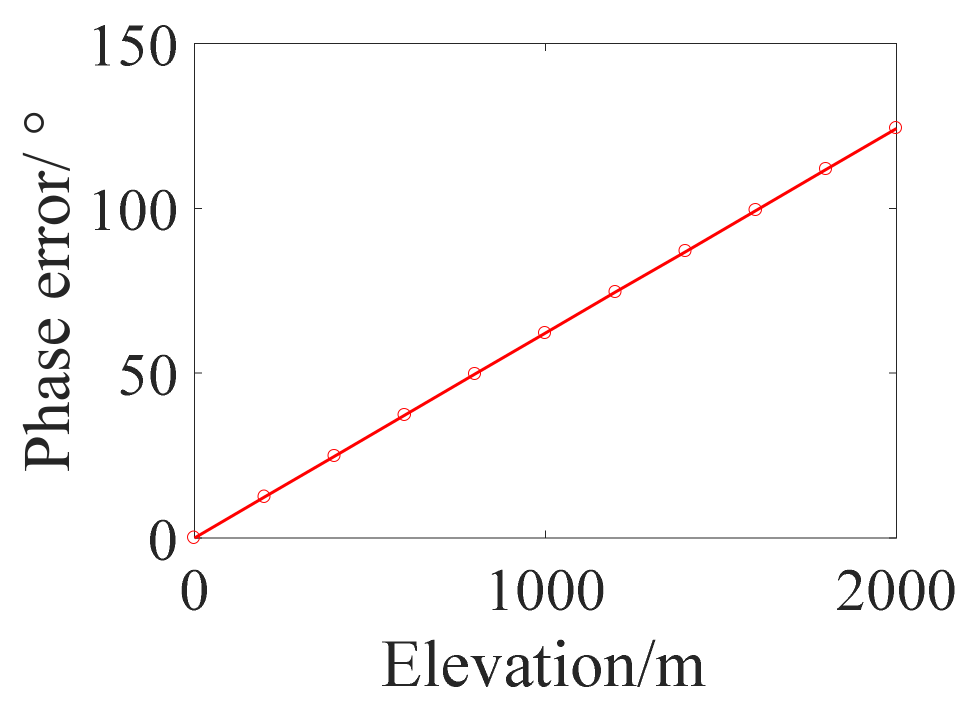
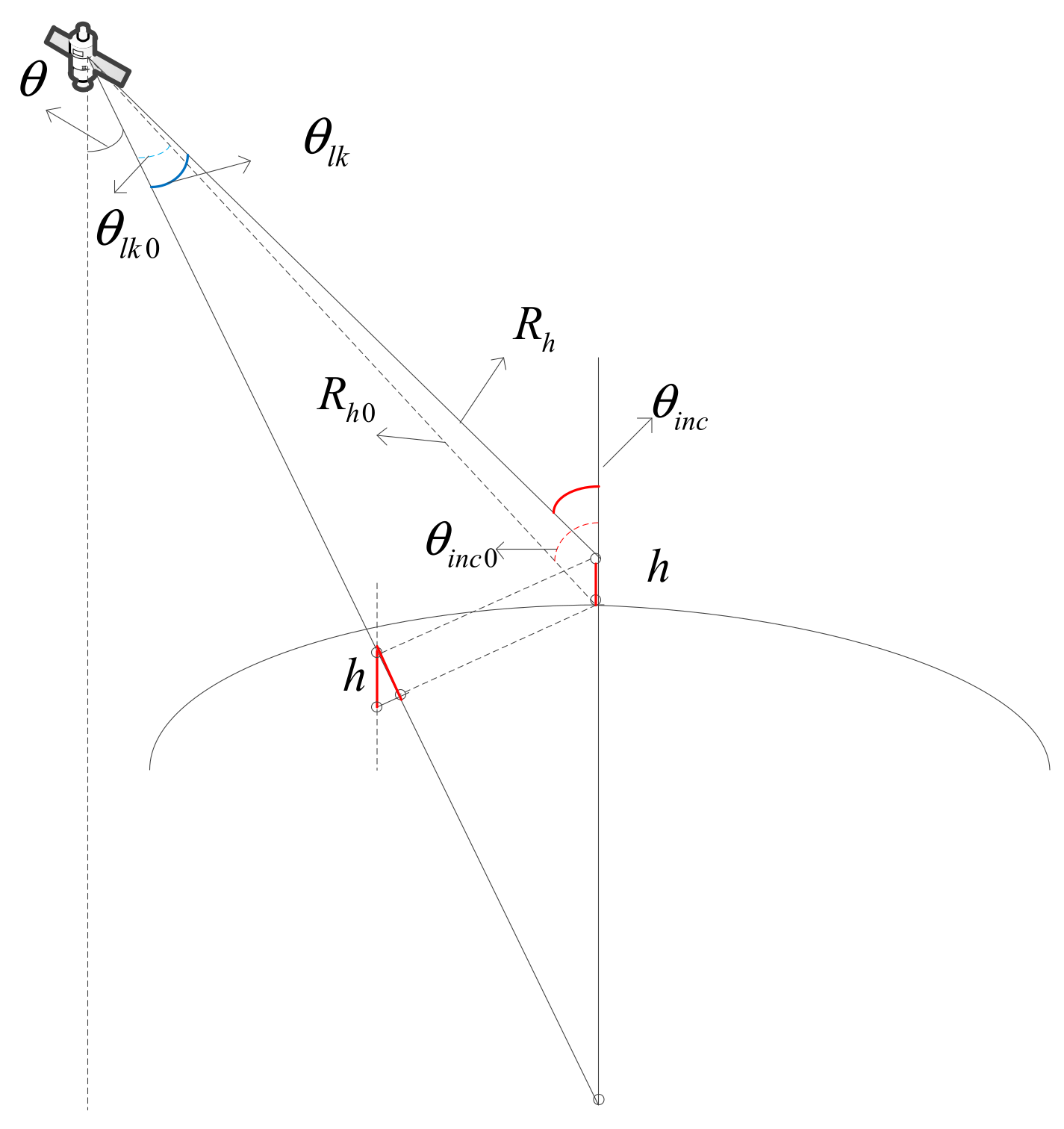
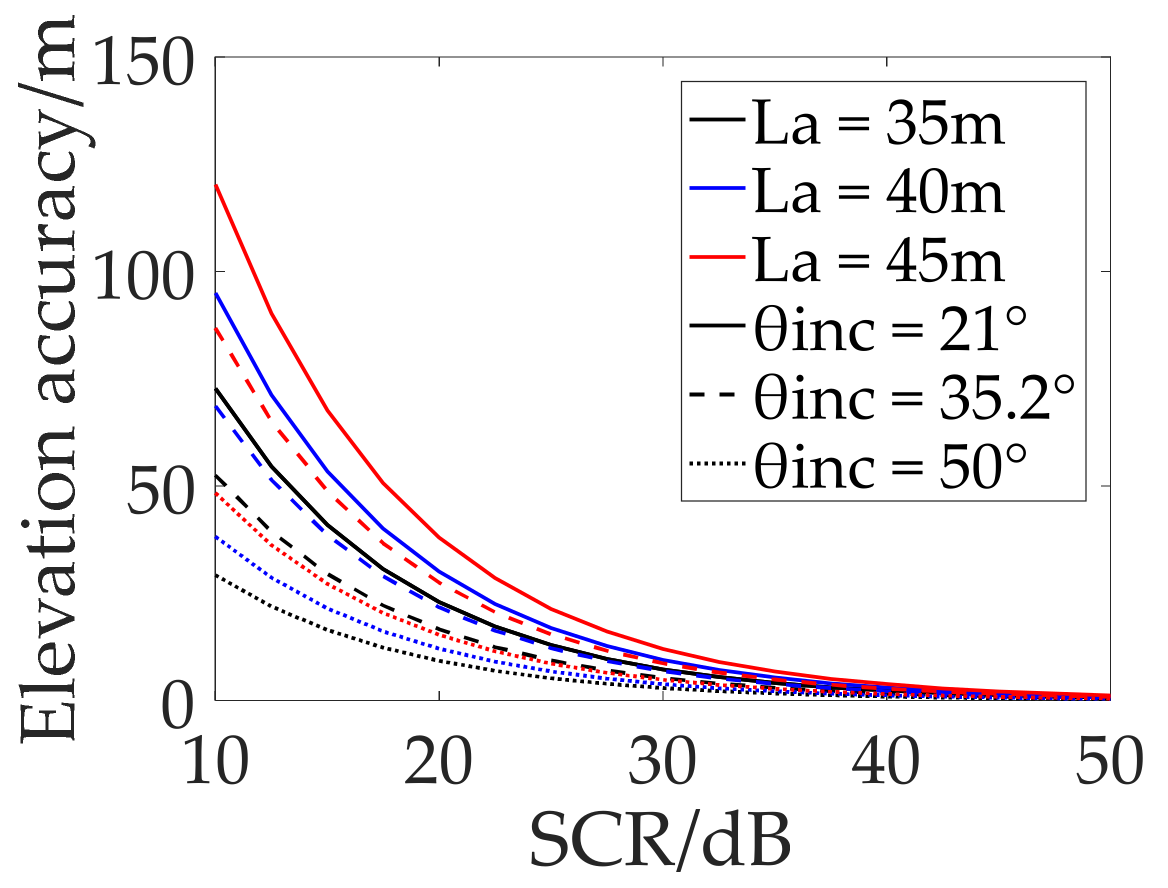
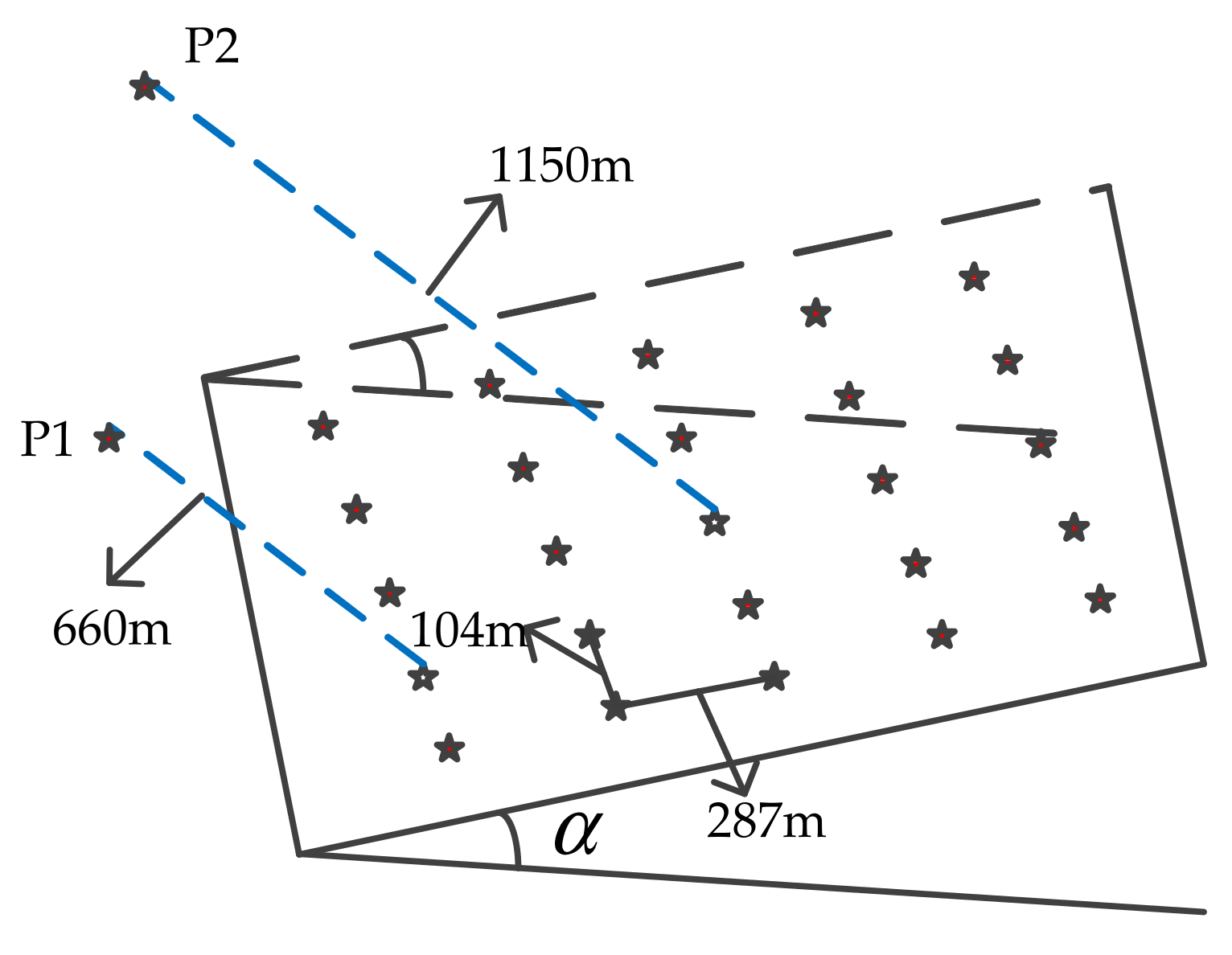
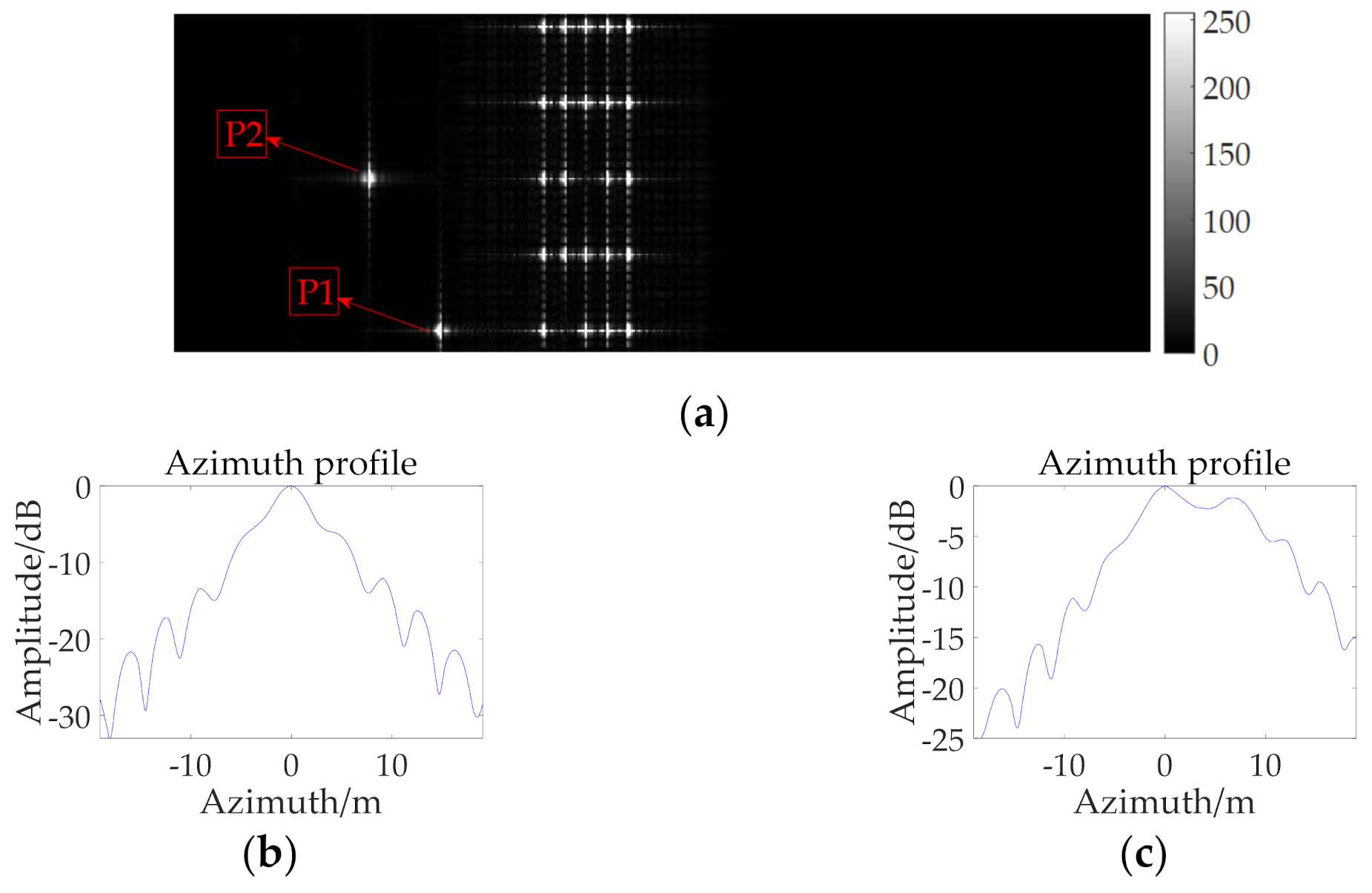

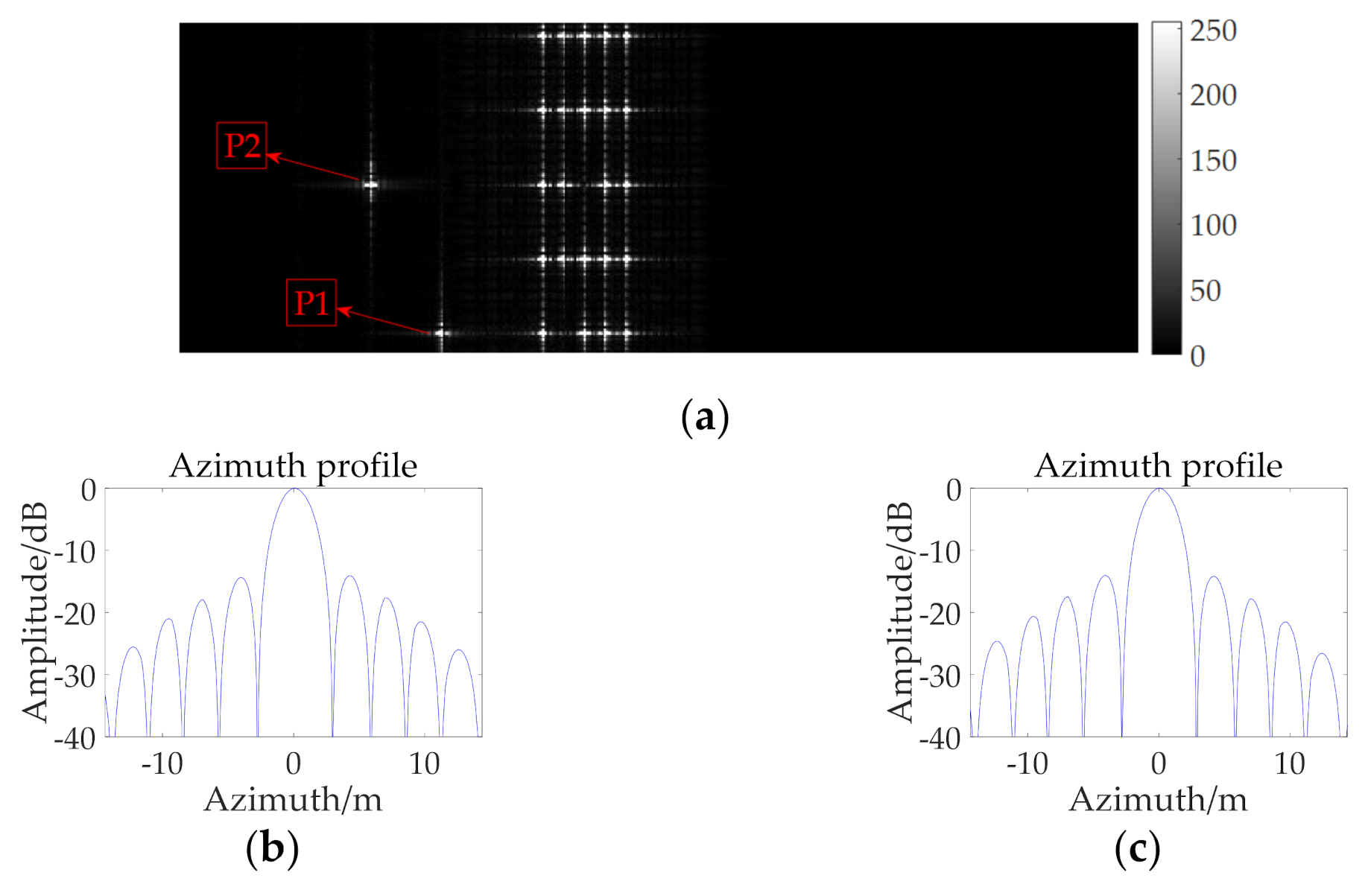
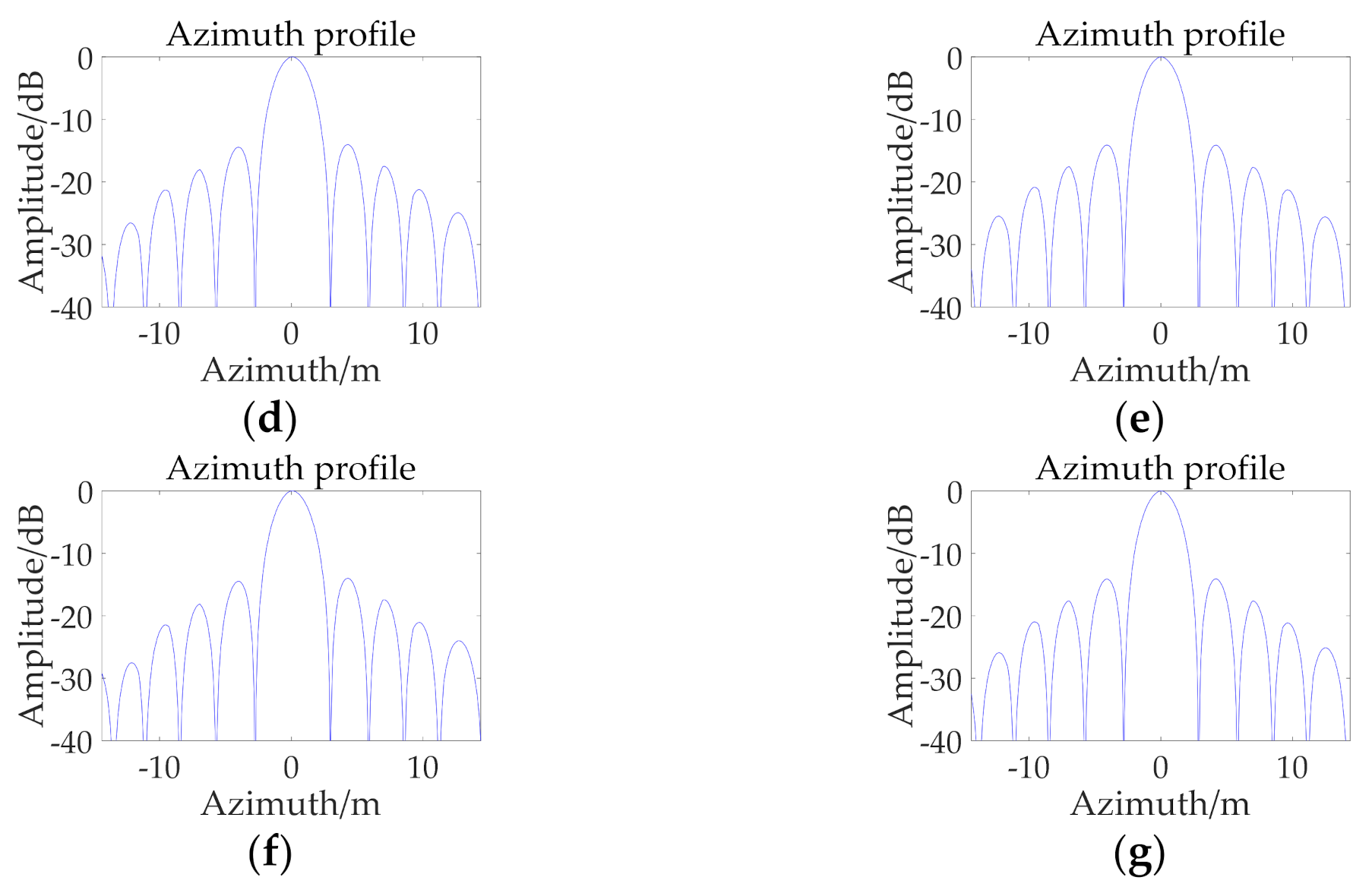
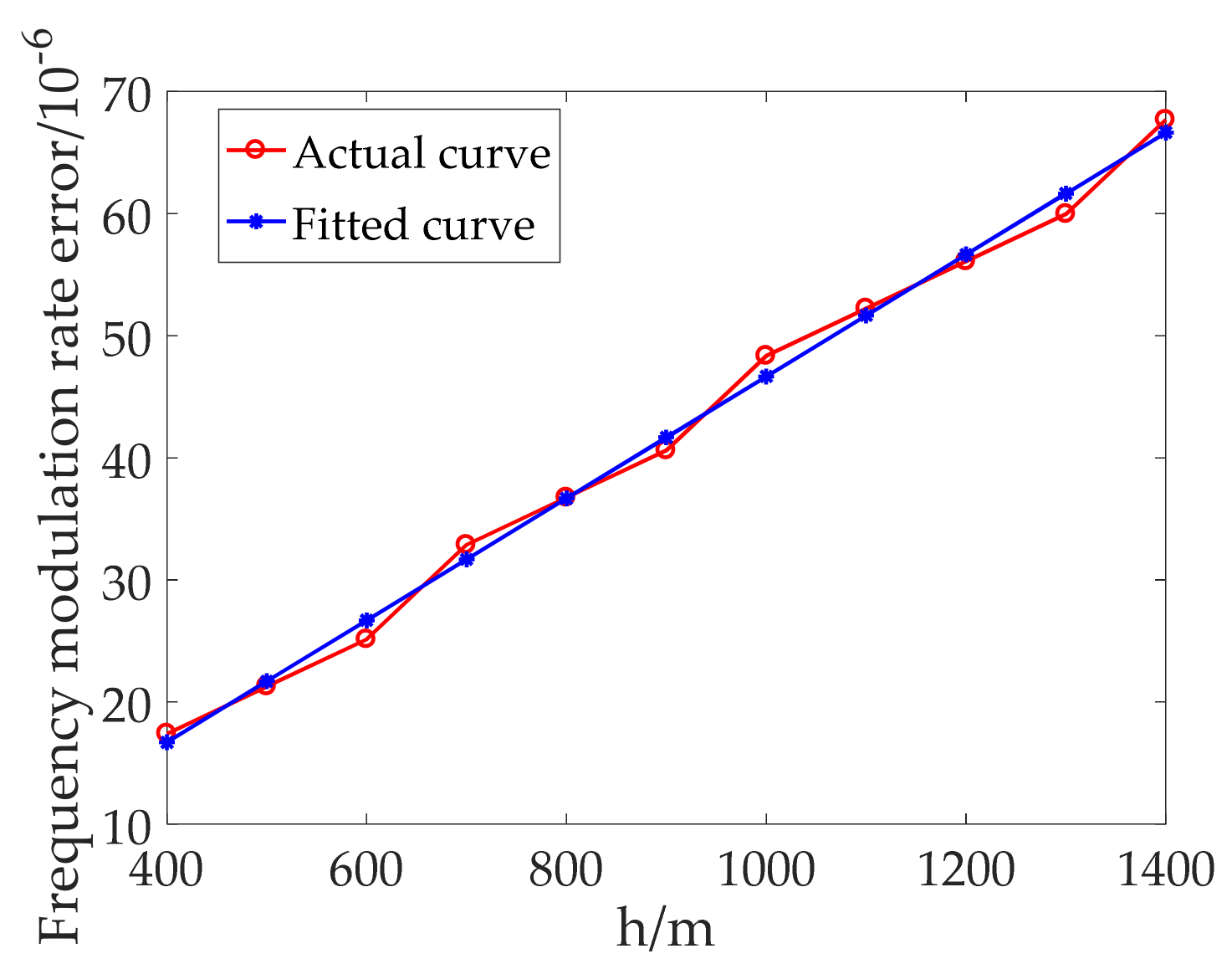


| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Semi-major axis | 42,164.17 km | Right ascension of ascending | 115° |
| Eccentricity | Perigee | 270° | |
| Orbital inclination | 60° | True anomaly | 90° |
| Carrier frequency | 1.25 GHz | Antenna size | 45 m |
| Squint angle | 0° | Incident angle | 35.2° |
| Pulse duration | Chirp bandwidth | 30 MHz |
| P1 | P1 | P2 |
|---|---|---|
| FM error (1 × 10−6) | 29.01 | 53.65 |
| True height (m) | 660 | 1150 |
| Inversion height (m) | 646.45 | 1139.95 |
| Estimation error (m) | 13.55 | 10.05 |
| Theoretical accuracy (m) | 27.48 | 27.48 |
| Point | IRW | PSLR (dB) | ISLR (dB) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| After first step | P1 | 1.2188 | −11.6457 | −8.4702 |
| P2 | 1.2417 | −9.9542 | −6.8024 | |
| After MD algorithm | P1 | 1.0313 | −13.1346 | −10.3346 |
| P2 | 1.0313 | −12.7472 | 10.3378 | |
| PGA iteration 3 times | P1 | 1.0313 | −13.3301 | −10.3011 |
| P2 | 1.0313 | −12.7632 | −10.3724 | |
| PGA iteration 5 times | P1 | 1.0313 | −13.4006 | −10.2912 |
| P2 | 1.0313 | −13.2143 | −10.3781 | |
| PGA iteration 10 times | P1 | 1.0313 | −13.4381 | −10.4419 |
| P2 | 1.0313 | −13.7262 | −10.5883 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, F.; Li, D.; Dong, Z.; Huang, Y.; He, Z. Elevation Spatial Variation Error Compensation in Complex Scene and Elevation Inversion by Autofocus Method in GEO SAR. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2916. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13152916
Chang F, Li D, Dong Z, Huang Y, He Z. Elevation Spatial Variation Error Compensation in Complex Scene and Elevation Inversion by Autofocus Method in GEO SAR. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(15):2916. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13152916
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Faguang, Dexin Li, Zhen Dong, Yang Huang, and Zhihua He. 2021. "Elevation Spatial Variation Error Compensation in Complex Scene and Elevation Inversion by Autofocus Method in GEO SAR" Remote Sensing 13, no. 15: 2916. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13152916
APA StyleChang, F., Li, D., Dong, Z., Huang, Y., & He, Z. (2021). Elevation Spatial Variation Error Compensation in Complex Scene and Elevation Inversion by Autofocus Method in GEO SAR. Remote Sensing, 13(15), 2916. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13152916






