Parallel Point Clouds: Hybrid Point Cloud Generation and 3D Model Enhancement via Virtual–Real Integration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
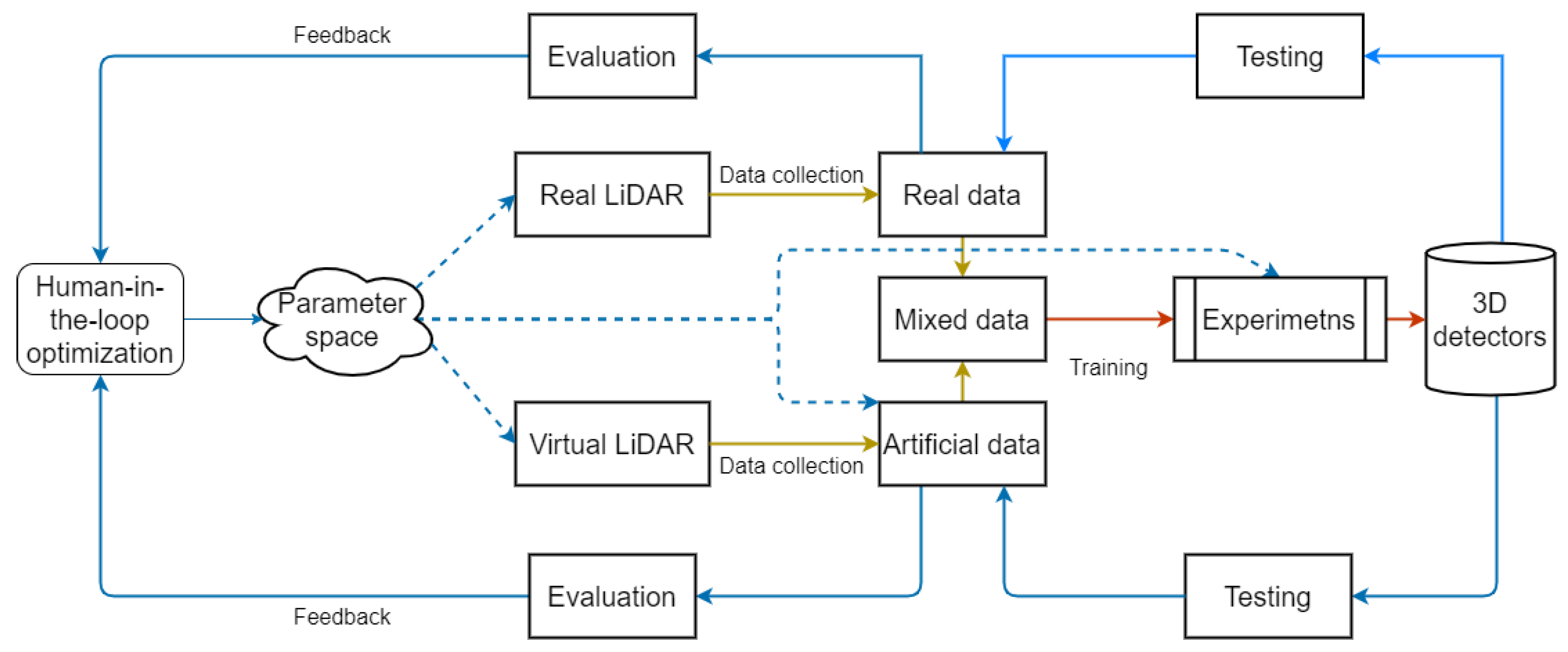
- We design a unified framework to integrate the point cloud generation and model enhancement, which changes the training of the model from an open-loop to a closed-loop mechanism. In this manner, both the performance of the models and the quality of point clouds are iteratively improved;
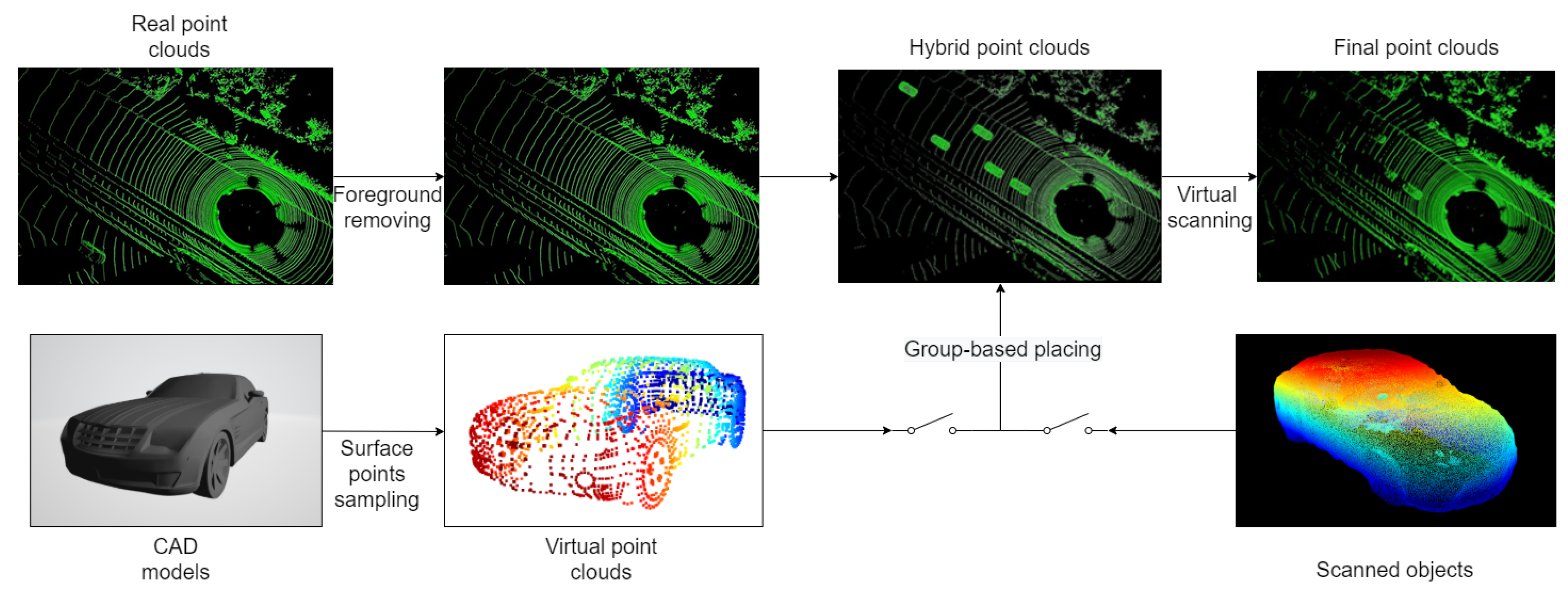
- The complexity of the collision computation between laser beams and meshes on objects can be totally avoided by our modeling of LiDAR sensors. In addition, a group-based placing method is put forward to solve the virtual object placing problem in real scenes;
- We build a hybrid point cloud dataset called ShapeKITTI with real point scenes and virtual objects and evaluate our method on 3D detection tasks. With almost zero annotation cost for newly added objects, we achieved 78.5% of the 3D performance of the model trained with the real KITTI dataset.
2. Related Works
2.1. ACP Methodology
2.2. Synthetic Datasets
2.3. Three-Dimensional Object Detection with Point Clouds
3. Method
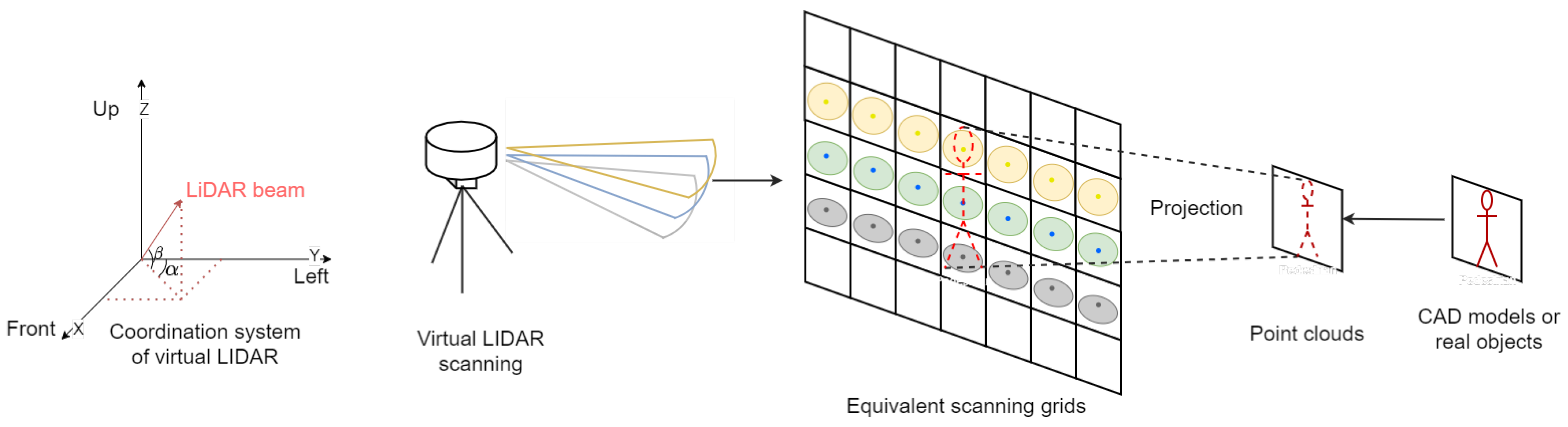
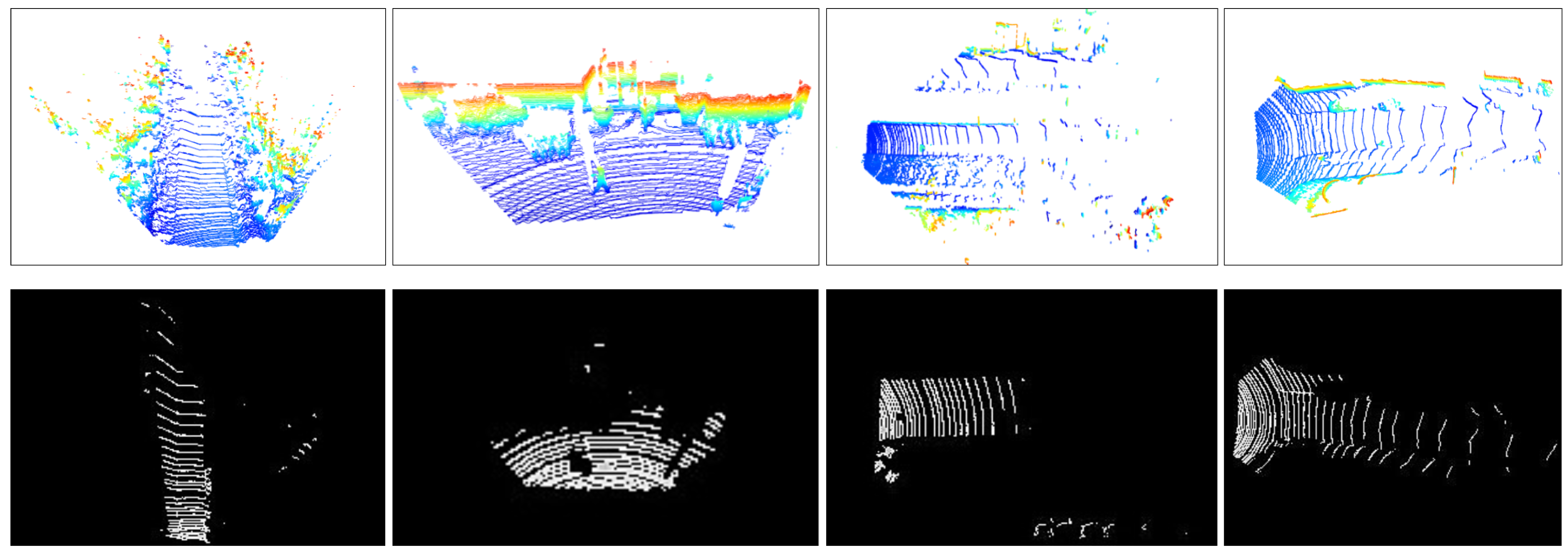
3.1. Point-Based LiDAR Simulation
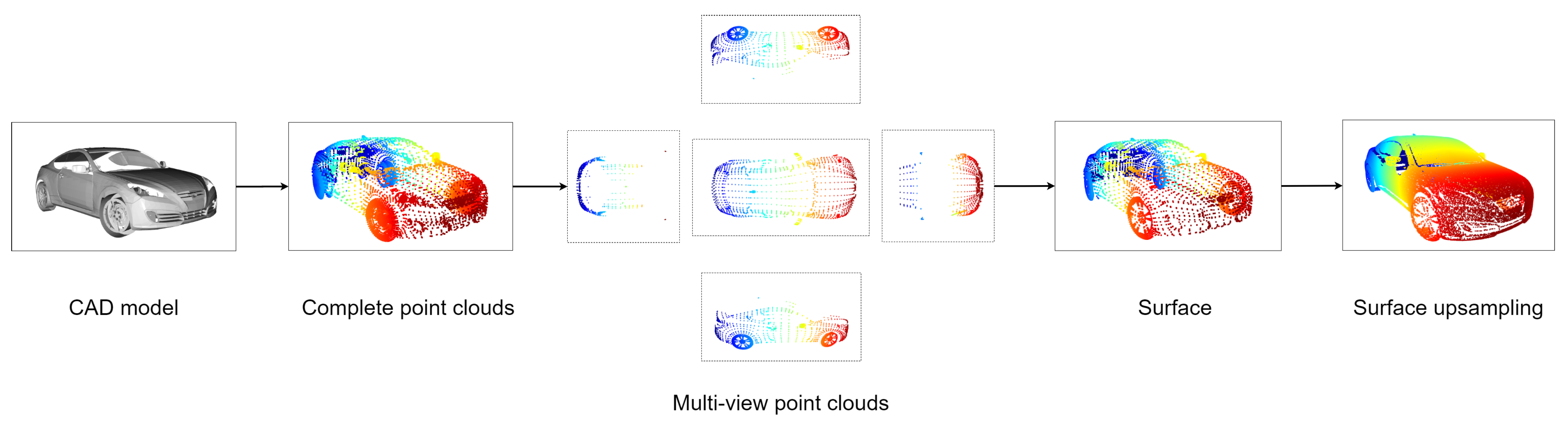
3.2. Hybrid Point Cloud Integration
3.3. Human-in-the-Loop Optimization
| Algorithm 1: Group-based placing algorithm. |
 |
4. Experiments
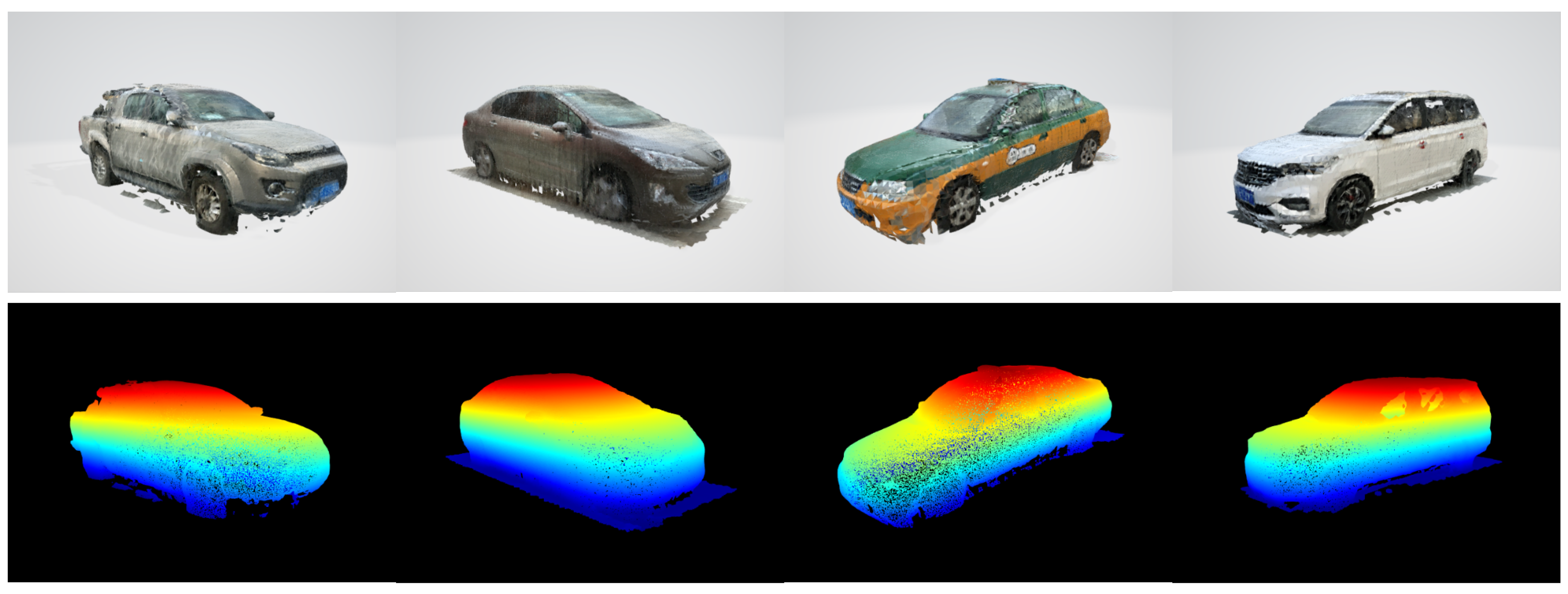
4.1. ShapeKITTI
4.2. MobilePointClouds
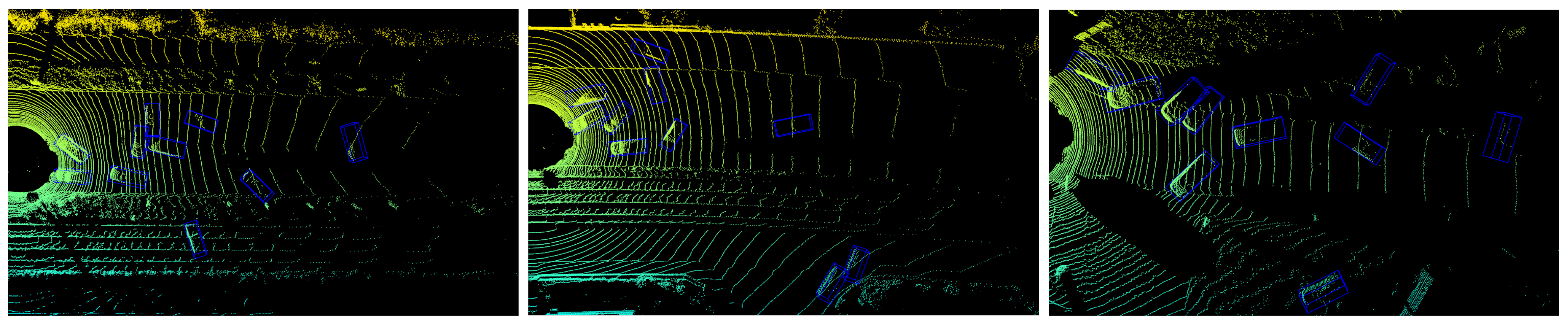
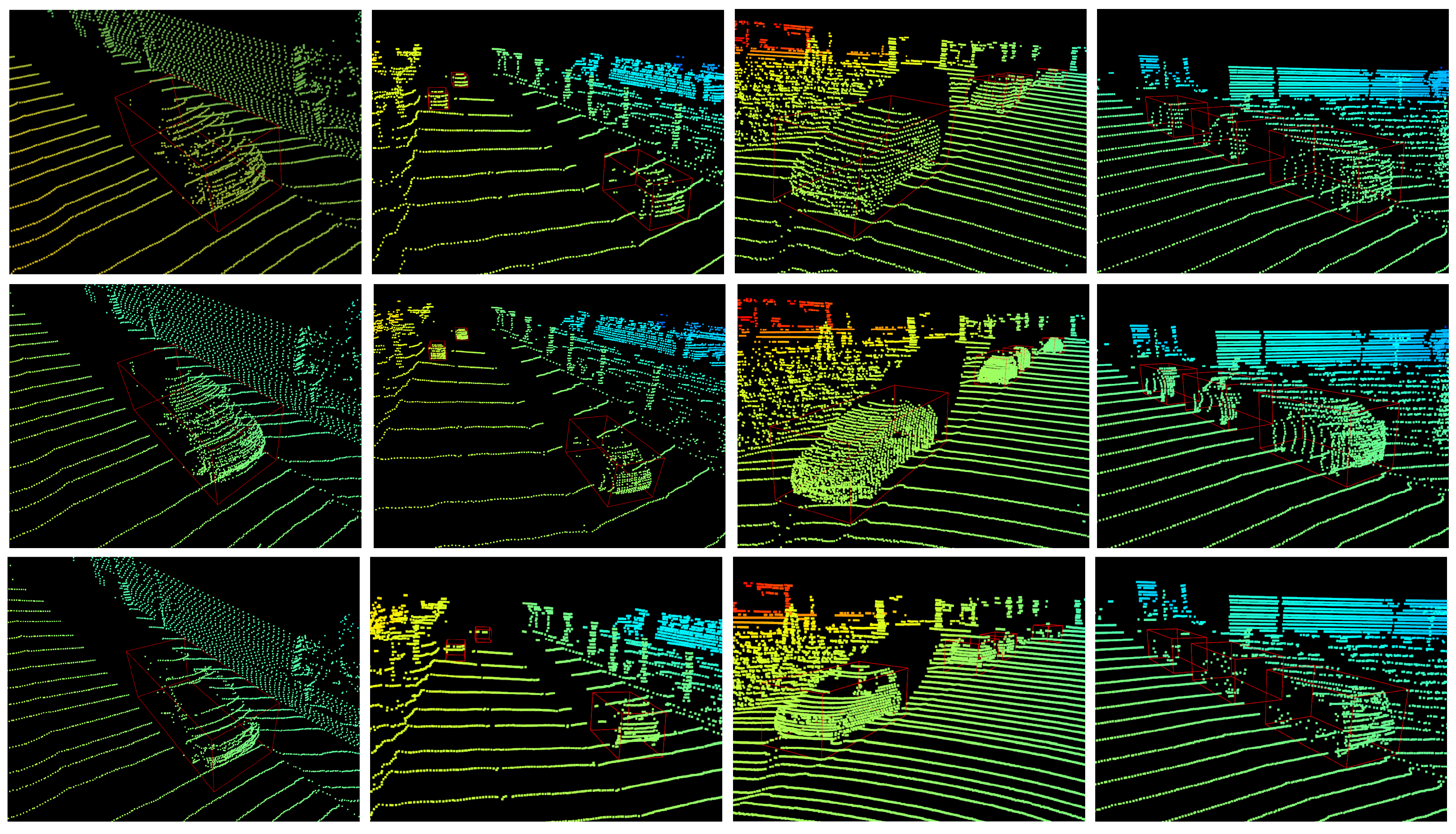
4.3. Three-Dimensional Object Detection
4.4. Human-in-the-Loop Optimization
5. Discussion
5.1. The Effectiveness of the Group-Based Placing Algorithm
5.2. The Receptive Field of the Virtual LiDAR
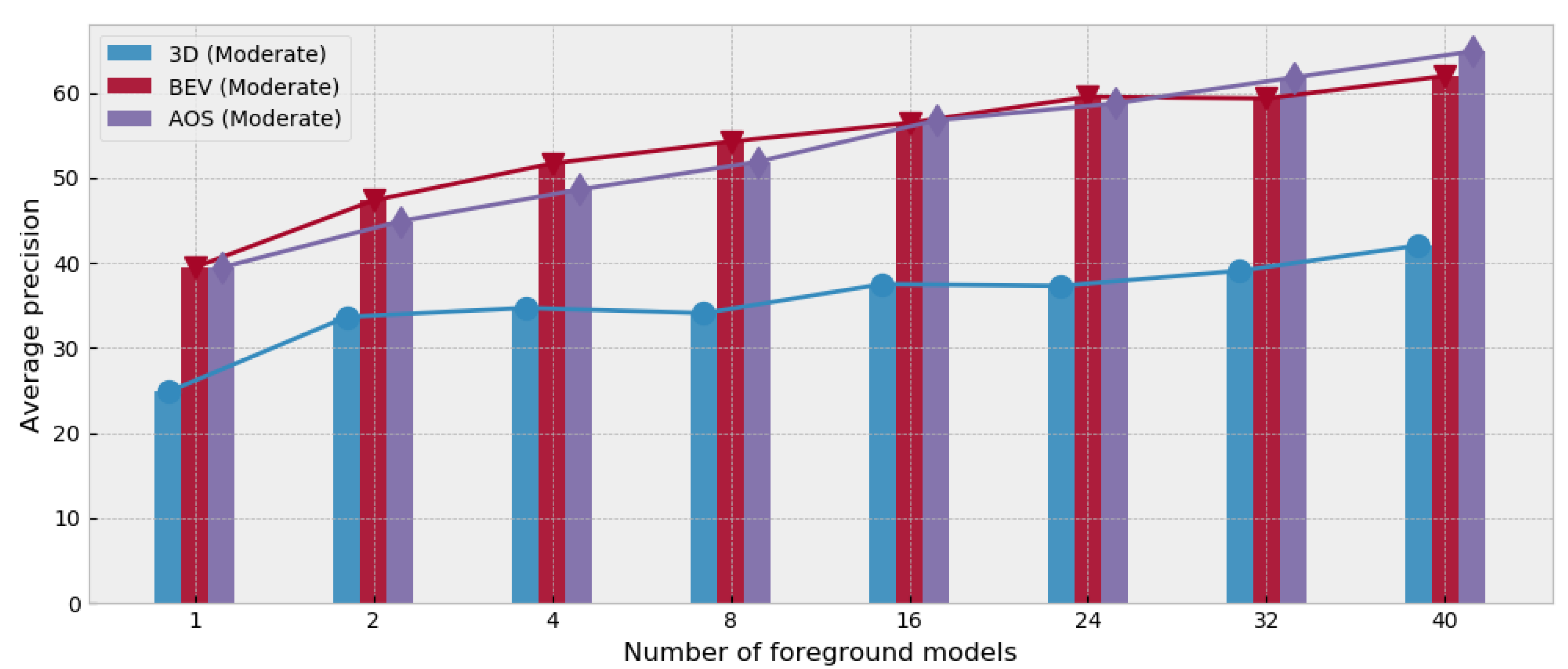
5.3. The Number of Foreground Models
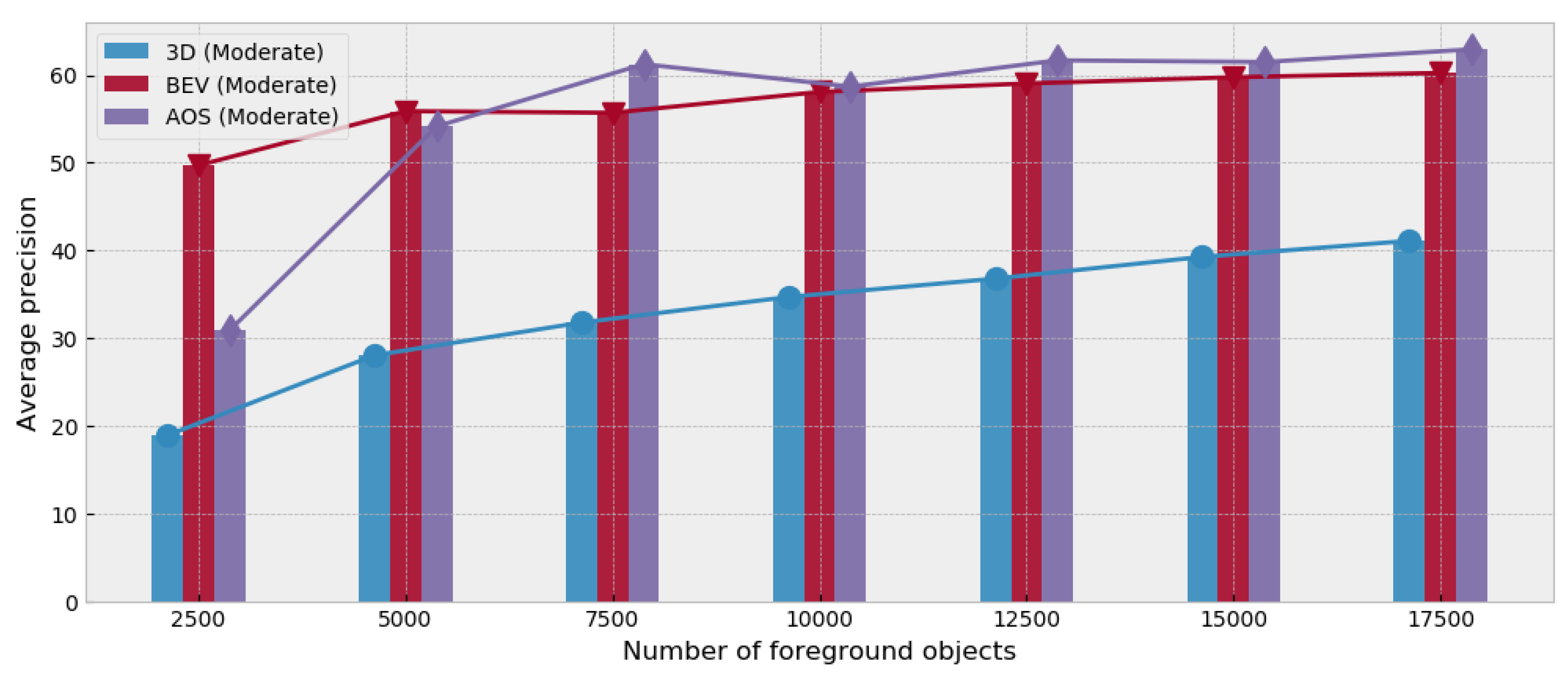
5.4. The Number of Objects in the Dataset
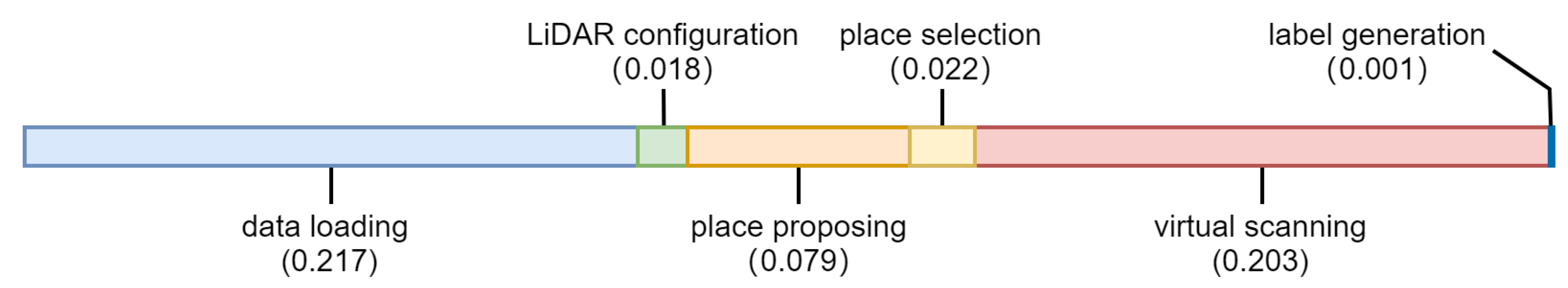
5.5. The Time Cost of Each Operation in the Pipeline
6. Conclusions and Future Works
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, ON, Canada, 7–12 December 2015; pp. 91–99. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Tian, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhang, W.; Wang, F.Y. Mask SSD: An Effective Single-Stage Approach to Object Instance Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 29, 2078–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Gou, C.; Wang, F.Y.; He, Z.; Chen, W. Learning from adversarial medical images for X-ray breast mass segmentation. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2019, 180, 105012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Wang, J.; Gou, C.; WANG, F. Hierarchical Fused Model with Deep Learning and Type-2 Fuzzy Learning for Breast Cancer Diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 28, 3204–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wu, W.; Zou, W.; Yan, J. End-to-end flow correlation tracking with spatial-temporal attention. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 548–557. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.R.; Su, H.; Mo, K.; Guibas, L.J. Pointnet: Deep learning on point sets for 3d classification and segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 652–660. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Ma, H.; Wan, J.; Li, B.; Xia, T. Multi-view 3d object detection network for autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1907–1915. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Xu, D.; Zhu, Y.; Martín-Martín, R.; Lu, C.; Li, F.F.; Savarese, S. Densefusion: 6d object pose estimation by iterative dense fusion. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 3343–3352. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Ros, G.; Codevilla, F.; Lopez, A.; Koltun, V. CARLA: An open urban driving simulator. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.03938. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Luo, G.; Tian, Y.; Wang, K.; He, H.; Wang, F.Y. A Virtual-Real Interaction Approach to Object Instance Segmentation in Traffic Scenes. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 22, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambasivan, N.; Kapania, S.; Highfill, H.; Akrong, D.; Paritosh, P.; Aroyo, L.M. “Everyone wants to do the model work, not the data work”: Data Cascades in High-Stakes AI. In Proceedings of the 2021 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Yokohama, Japan, 8–13 May 2021; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.Y. Parallel system methods for management and control of complex systems. Control Decis. 2004, 19, 485–489. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Gou, C.; Zheng, N.; Rehg, J.M.; Wang, F.Y. Parallel vision for perception and understanding of complex scenes: Methods, framework, and perspectives. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2017, 48, 299–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Wang, F.Y. Parallel imaging: A new theoretical framework for image generation. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 2017, 30, 577–587. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Lin, Y.; Zheng, N.; Wang, F.Y. Parallel learning: A perspective and a framework. IEEE CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2017, 4, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.Y.; Zheng, N.N.; Cao, D.; Martinez, C.M.; Li, L.; Liu, T. Parallel driving in CPSS: A unified approach for transport automation and vehicle intelligence. IEEE CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2017, 4, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.Y. Parallel control and management for intelligent transportation systems: Concepts, architectures, and applications. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2010, 11, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Li, H.; Wang, F.Y. Parallel control for continuous-time linear systems: A case study. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2020, 7, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Prendinger, H.; Gajananan, K.; Zaki, A.B.; Fares, A.; Molenaar, R.; Urbano, D.; van Lint, H.; Gomaa, W. Tokyo virtual living lab: Designing smart cities based on the 3d internet. IEEE Internet Comput. 2013, 17, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ros, G.; Sellart, L.; Materzynska, J.; Vazquez, D.; Lopez, A.M. The synthia dataset: A large collection of synthetic images for semantic segmentation of urban scenes. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 3234–3243. [Google Scholar]
- Gaidon, A.; Wang, Q.; Cabon, Y.; Vig, E. Virtual worlds as proxy for multi-object tracking analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 4340–4349. [Google Scholar]
- Geiger, A.; Lenz, P.; Urtasun, R. Are we ready for autonomous driving? the kitti vision benchmark suite. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 3354–3361. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, K.; Tian, Y.; Yan, L.; Deng, F.; Wang, F.Y. The ParallelEye dataset: A large collection of virtual images for traffic vision research. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 20, 2072–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, K.; Wang, F.Y. Training and testing object detectors with virtual images. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2018, 5, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yue, X.; Wu, B.; Seshia, S.A.; Keutzer, K.; Sangiovanni-Vincentelli, A.L. A lidar point cloud generator: From a virtual world to autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the 2018 ACM on International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval, Yokohama, Japan, 11–14 June 2018; pp. 458–464. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.; Zhou, D.; Yan, F.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, F.; Ma, Y.; Wang, L.; Yang, R. Augmented lidar simulator for autonomous driving. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 1931–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, C.R.; Liu, W.; Wu, C.; Su, H.; Guibas, L.J. Frustum pointnets for 3d object detection from rgb-d data. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 918–927. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.R.; Litany, O.; He, K.; Guibas, L.J. Deep hough voting for 3d object detection in point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27–28 October 2019; pp. 9277–9286. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Tuzel, O. Voxelnet: End-to-end learning for point cloud based 3d object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 4490–4499. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Mao, Y.; Li, B. Second: Sparsely embedded convolutional detection. Sensors 2018, 18, 3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lang, A.H.; Vora, S.; Caesar, H.; Zhou, L.; Yang, J.; Beijbom, O. Pointpillars: Fast encoders for object detection from point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 12697–12705. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, G.P.; Laddha, A.; Kee, E.; Vallespi-Gonzalez, C.; Wellington, C.K. Lasernet: An efficient probabilistic 3d object detector for autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 12677–12686. [Google Scholar]
- Bewley, A.; Sun, P.; Mensink, T.; Anguelov, D.; Sminchisescu, C. Range Conditioned Dilated Convolutions for Scale Invariant 3D Object Detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.09927. [Google Scholar]
- 3D Scanner APP. Available online: http://www.3dscannerapp.com/ (accessed on 1 December 2020).
- Cubuk, E.D.; Zoph, B.; Mane, D.; Vasudevan, V.; Le, Q.V. Autoaugment: Learning augmentation strategies from data. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 113–123. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, S.J.; Qiang, Y. A Survey on Transfer Learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2010, 22, 1345–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, F.; Qi, Z.; Duan, K.; Xi, D.; He, Q. A Comprehensive Survey on Transfer Learning. Proc. IEEE 2020, 109, 43–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Deng, W. Deep Visual Domain Adaptation: A Survey. Neurocomputing 2018, 312, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, G.; Cook, D.J. A survey of unsupervised deep domain adaptation. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. (TIST) 2020, 11, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Attribute | H-Resolution (Channels) | V-Resolution | H-FoV | V-FoV | Detection Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 0.4° (64) | 0.2° | [−45°, 45°] | [−24.8°, 2°] | 120 m |
| Method | 3D AP | BEV AP | AOS AP | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moderate | Easy | Hard | Moderate | Easy | Hard | Moderate | Easy | Hard | |
| PointPillars-K | 77.58 | 86.68 | 75.82 | 87.44 | 89.79 | 84.77 | 89.34 | 90.63 | 88.36 |
| PointPillars-SK | 60.94 | 75.54 | 58.26 | 75.93 | 86.49 | 73.95 | 74.23 | 86.90 | 72.38 |
| PointPillars-MPC | 46.28 | 56.32 | 45.81 | 71.86 | 85.49 | 71.53 | 71.08 | 85.51 | 70.62 |
| SECOND-K | 78.06 | 87.62 | 76.52 | 87.28 | 89.52 | 83.89 | 89.45 | 90.49 | 88.41 |
| SECOND-SK | 45.04 | 60.13 | 42.66 | 68.40 | 79.59 | 64.82 | 64.11 | 80.13 | 42.66 |
| SECOND-MPC | 38.83 | 53.62 | 36.87 | 54.33 | 70.35 | 55.01 | 58.52 | 74.22 | 55.90 |
| Version | Moderate | Easy | Hard | Feedback | Advice | AP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V0 | 10.32 | 10.64 | 10.53 | Works for a few types of car | Add more cars | - |
| V1 | 16.64 | 22.14 | 13.98 | Bad estimation for the size | Refine the size of the CAD models | 6.14 |
| V2 | 22.40 | 32.85 | 19.52 | Bad performance for sparse objects | Generate more sparse objects | 5.94 |
| V3 | 26.85 | 29.43 | 23.51 | Bad estimation for the height | Adjust the height of the objects | 4.45 |
| V4 | 29.74 | 38.99 | 27.10 | Bad performance for sparse objects | Generate more sparse objects | 2.89 |
| V5 | 31.04 | 39.22 | 30.30 | … | … | 2.30 |
| Method | 3D AP | BEV AP | AOS AP | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moderate | Easy | Hard | Moderate | Easy | Hard | Moderate | Easy | Hard | |
| FRP | 35.25 | 40.59 | 31.93 | 61.22 | 72.62 | 56.29 | 60.17 | 75.88 | 55.37 |
| GP | 42.03 | 52.91 | 38.72 | 61.96 | 76.94 | 58.48 | 64.86 | 83.74 | 60.35 |
| GTP | 45.24 | 54.36 | 44.13 | 70.91 | 82.54 | 68.66 | 72.93 | 83.88 | 70.36 |
| Value (m) | 3D AP | BEV AP | AOS AP | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moderate | Easy | Hard | Moderate | Easy | Hard | Moderate | Easy | Hard | |
| 0.5 | 18.24 | 22.44 | 16.11 | 45.23 | 60.34 | 39.70 | 39.68 | 49.81 | 35.51 |
| 1.0 | 40.63 | 43.41 | 37.66 | 57.01 | 68.05 | 55.02 | 62.85 | 75.67 | 58.52 |
| 1.5 | 42.03 | 52.91 | 38.72 | 61.96 | 76.94 | 58.48 | 64.86 | 83.74 | 60.35 |
| 2.0 | 39.10 | 46.50 | 37.05 | 57.77 | 70.25 | 56.58 | 62.31 | 71.64 | 57.07 |
| 2.5 | 38.28 | 41.04 | 34.68 | 54.05 | 63.11 | 52.73 | 60.63 | 69.11 | 55.56 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, Y.; Wang, X.; Shen, Y.; Guo, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, F.-Y. Parallel Point Clouds: Hybrid Point Cloud Generation and 3D Model Enhancement via Virtual–Real Integration. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2868. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13152868
Tian Y, Wang X, Shen Y, Guo Z, Wang Z, Wang F-Y. Parallel Point Clouds: Hybrid Point Cloud Generation and 3D Model Enhancement via Virtual–Real Integration. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(15):2868. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13152868
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Yonglin, Xiao Wang, Yu Shen, Zhongzheng Guo, Zilei Wang, and Fei-Yue Wang. 2021. "Parallel Point Clouds: Hybrid Point Cloud Generation and 3D Model Enhancement via Virtual–Real Integration" Remote Sensing 13, no. 15: 2868. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13152868
APA StyleTian, Y., Wang, X., Shen, Y., Guo, Z., Wang, Z., & Wang, F.-Y. (2021). Parallel Point Clouds: Hybrid Point Cloud Generation and 3D Model Enhancement via Virtual–Real Integration. Remote Sensing, 13(15), 2868. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13152868






