Spatio-Temporal Variability of Aerosol Components, Their Optical and Microphysical Properties over North China during Winter Haze in 2012, as Derived from POLDER/PARASOL Satellite Observations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Study Area
2.1. POLDER/PARASOL Satellite Observations
2.2. The Validation Ground—Based Data
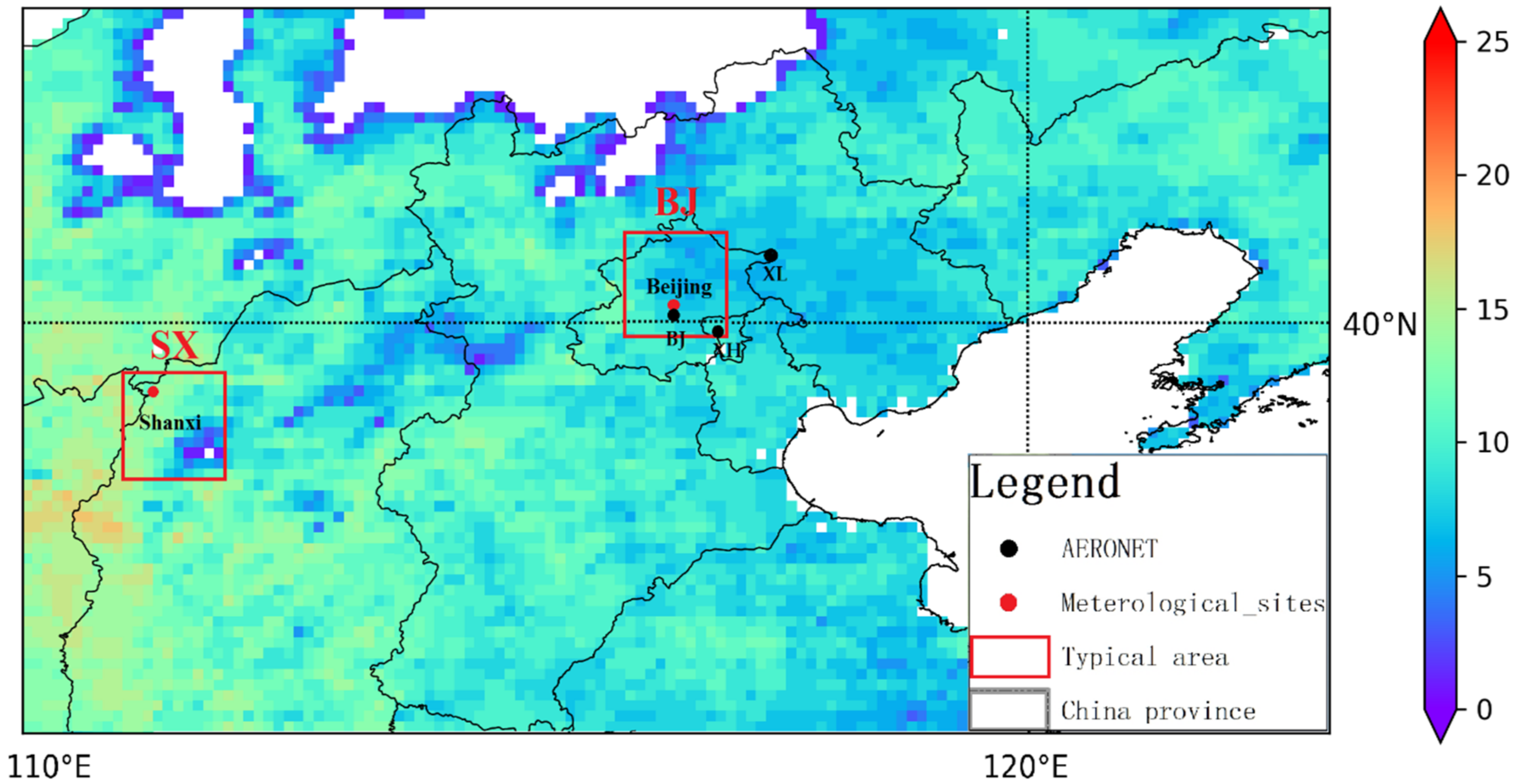
2.3. Study Area
3. Methods
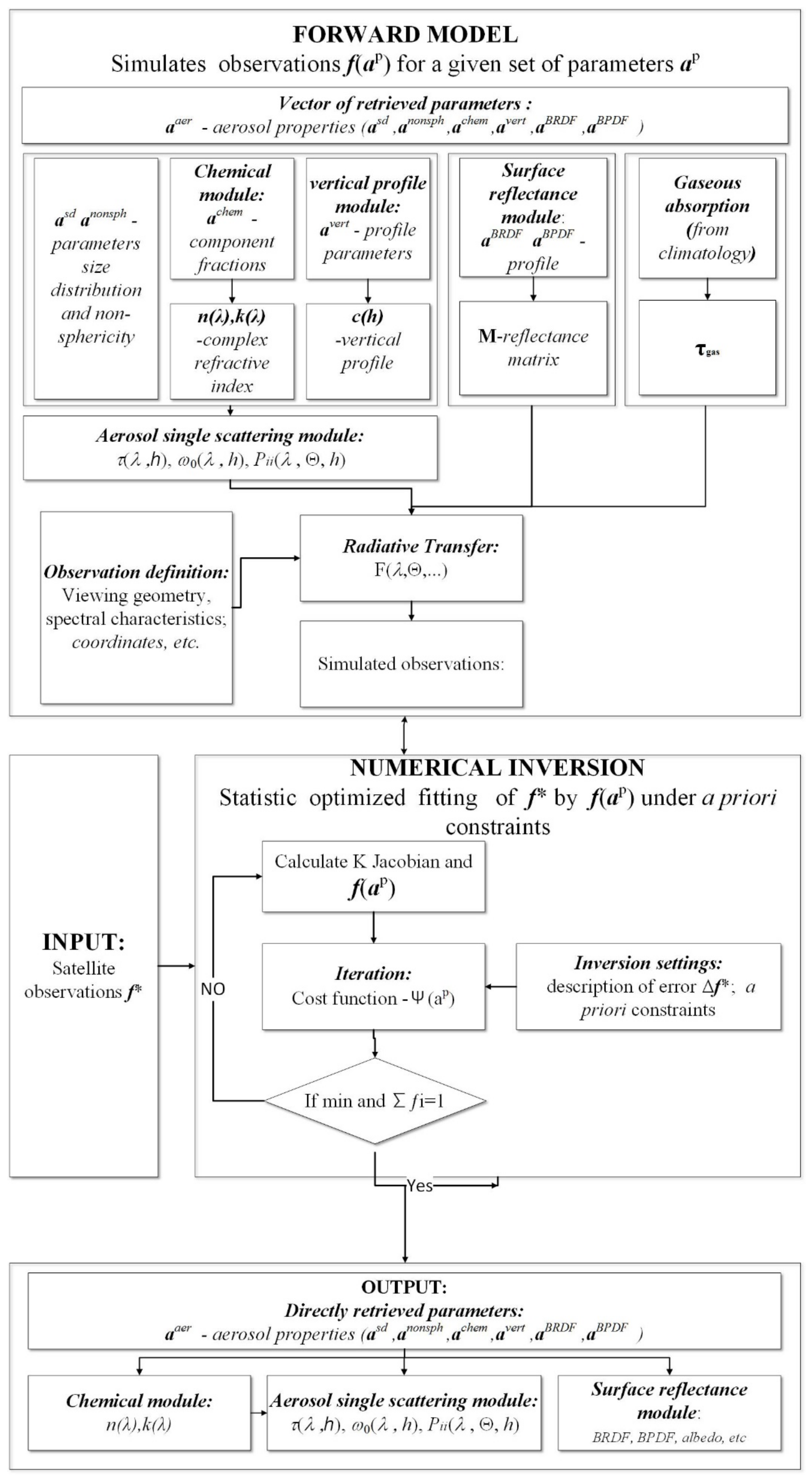
3.1. GRASP/Component Retrieval
3.2. Aerosol Mass to Volume Conversion
4. Results
4.1. GRASP/Component Retrieval
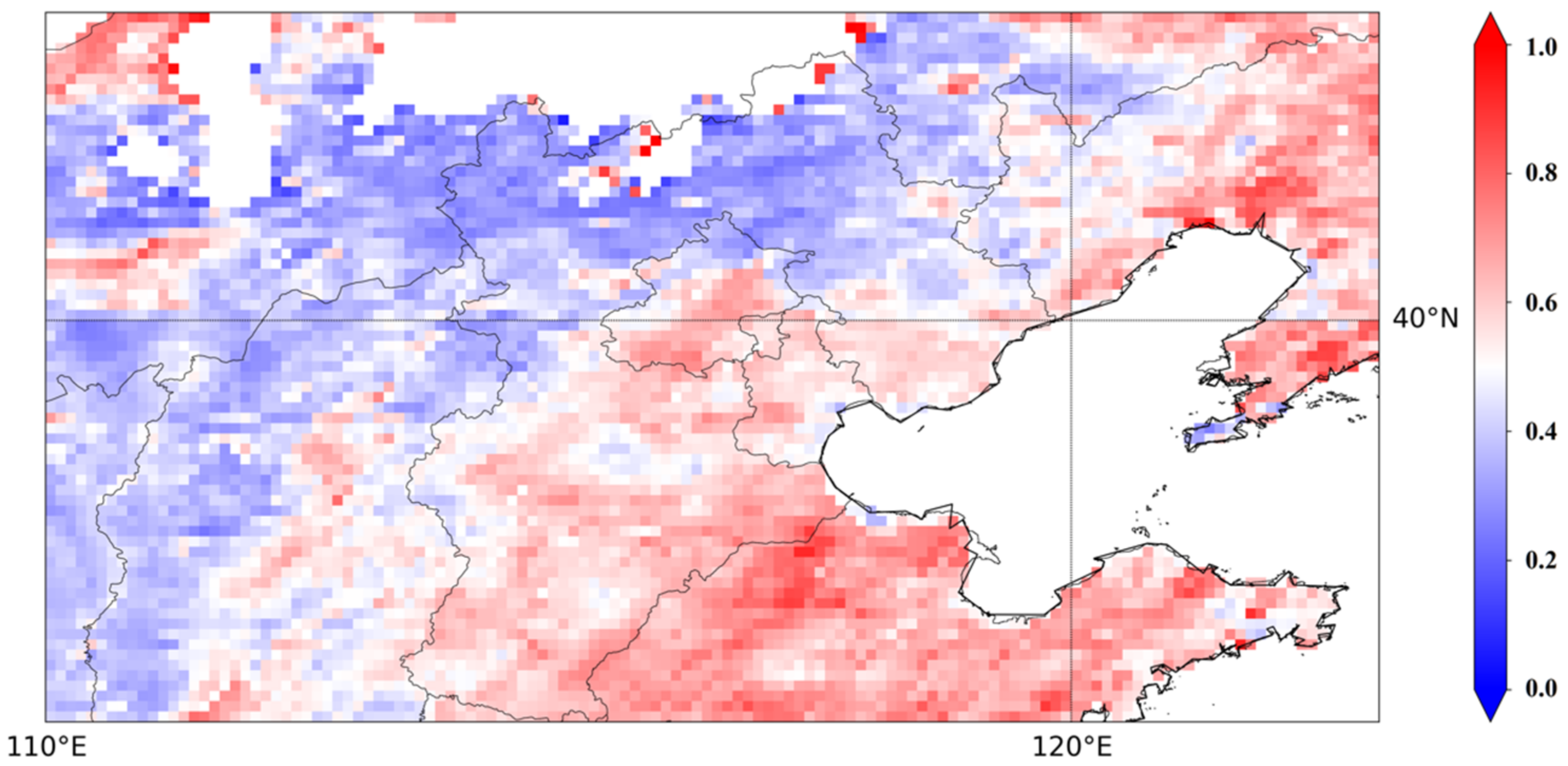
4.2. Spatial Distribution of Volume Size Distribution Properties
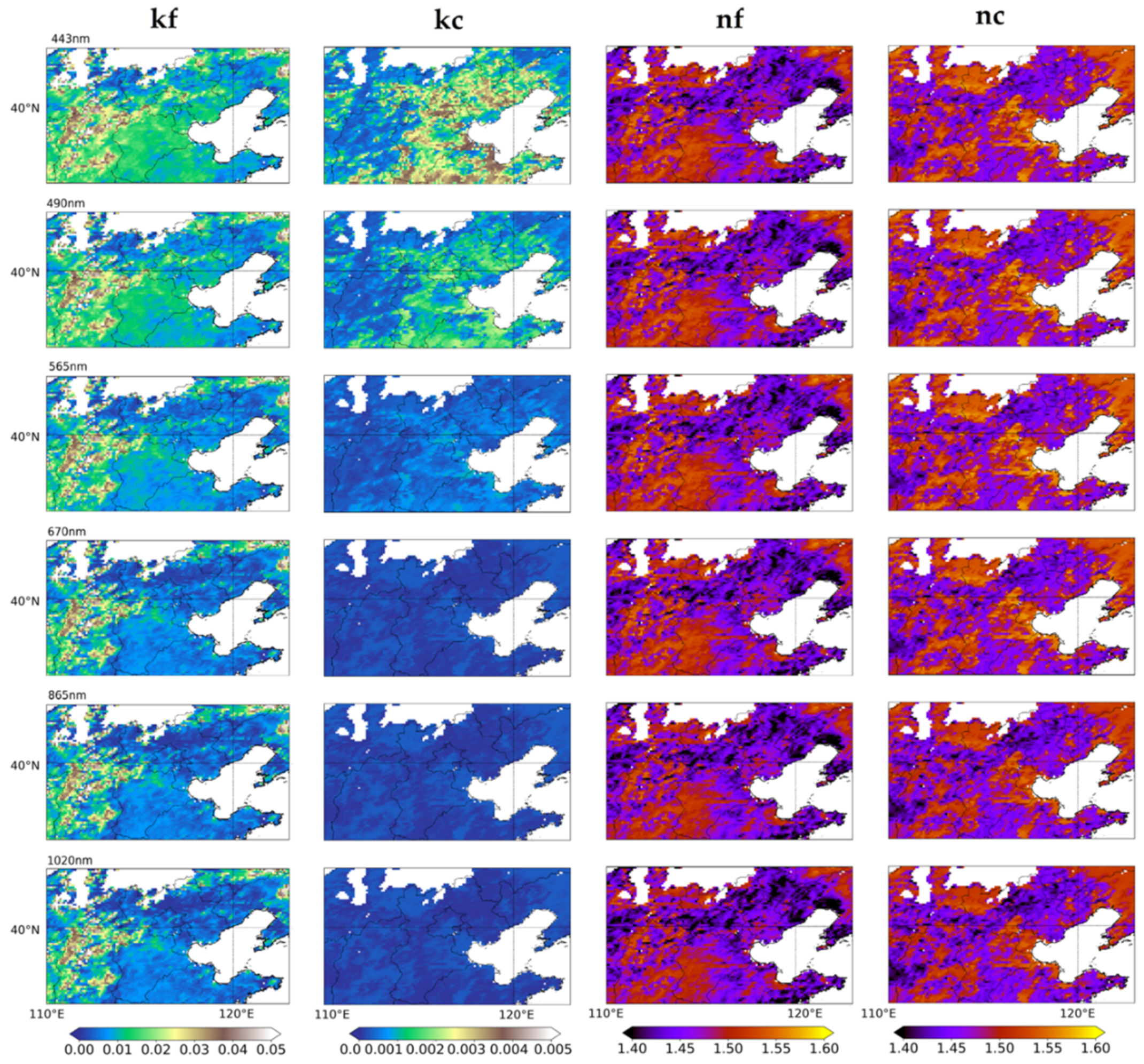
4.3. Spatial Distribution of Complex Refractive Index
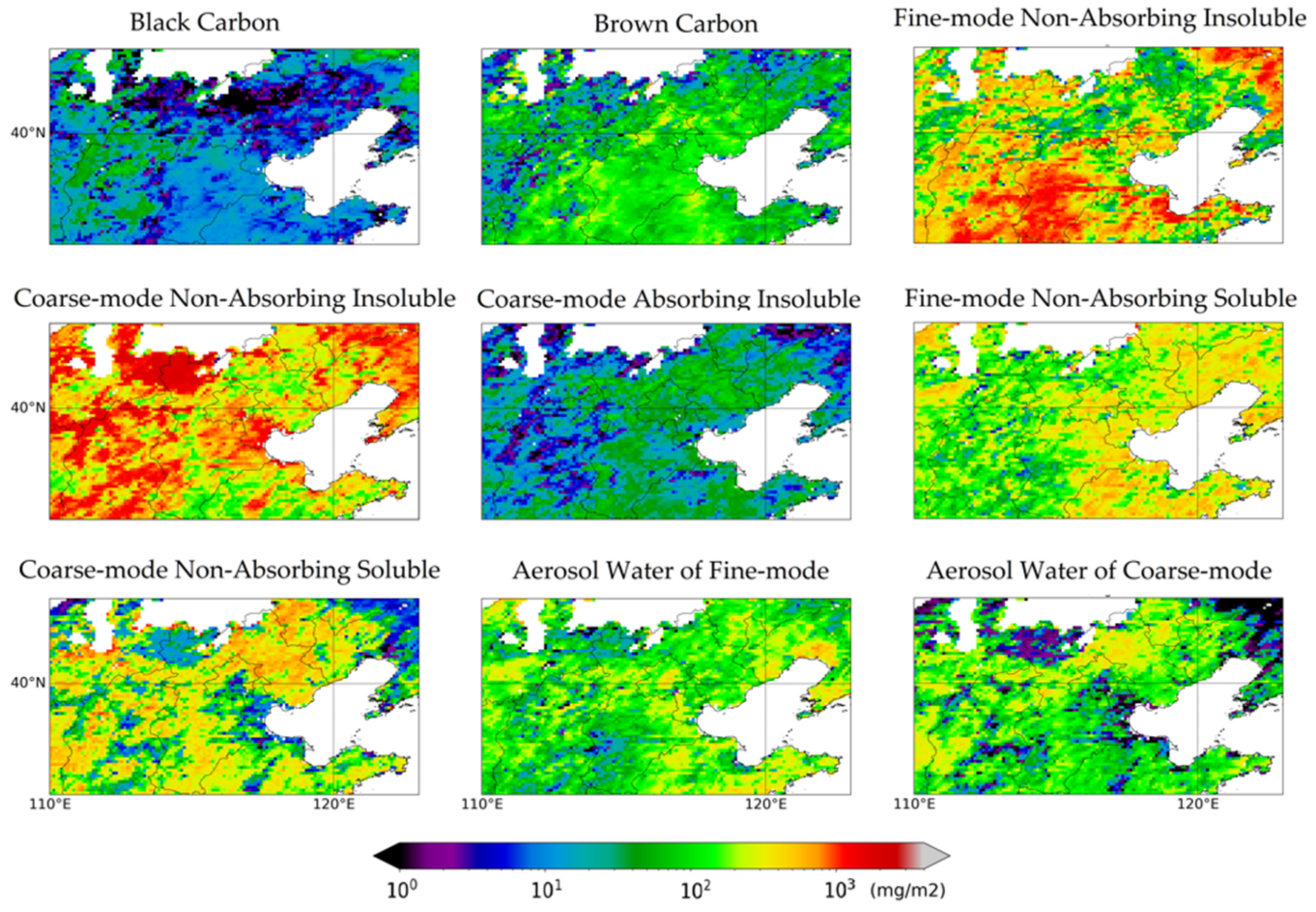
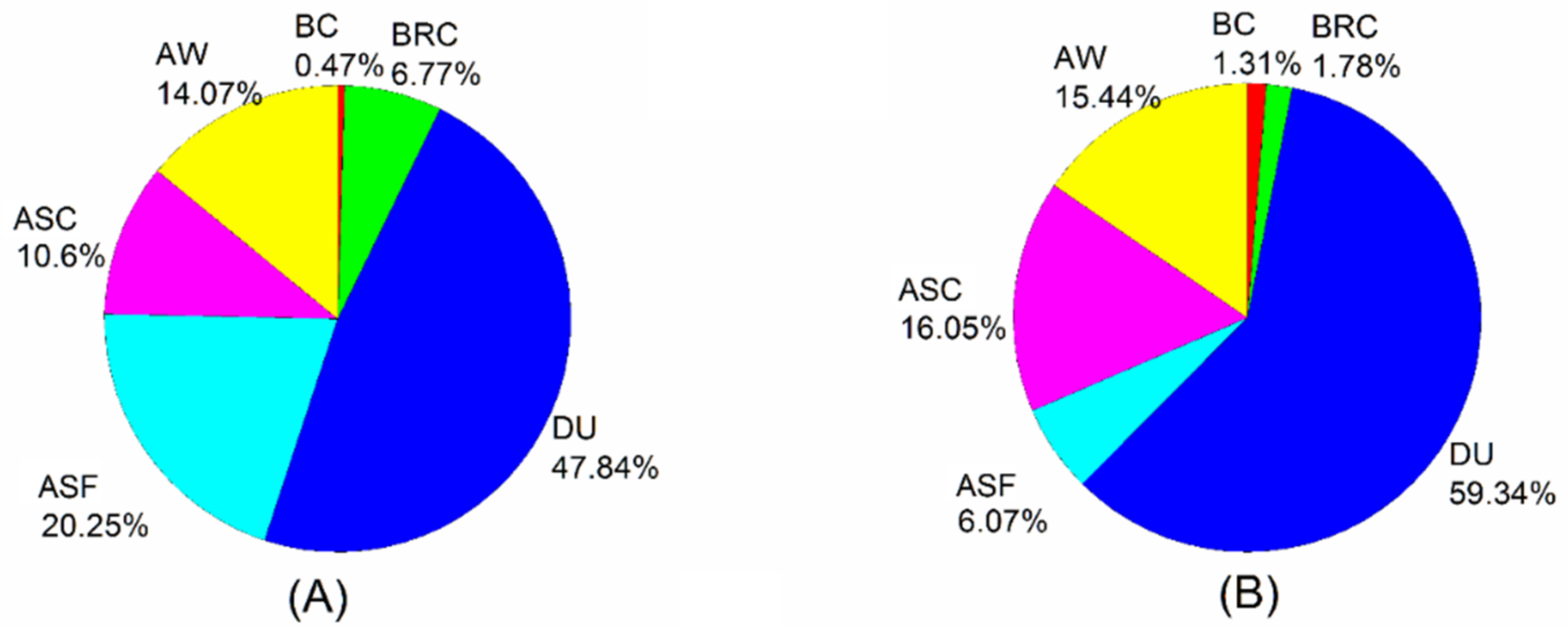
4.4. Spatial Distribution of Aerosol Components
5. Validation and Intercomparison
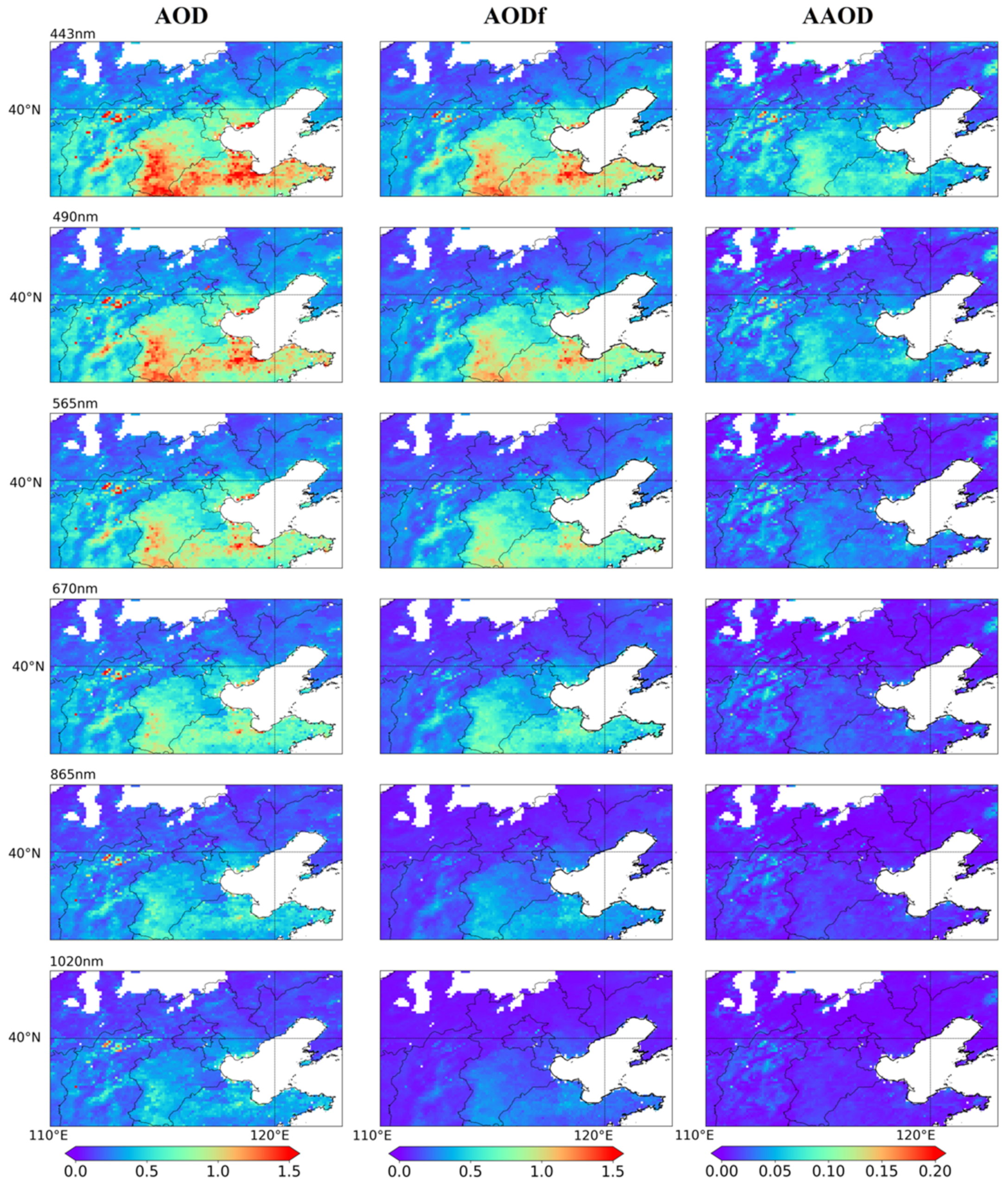
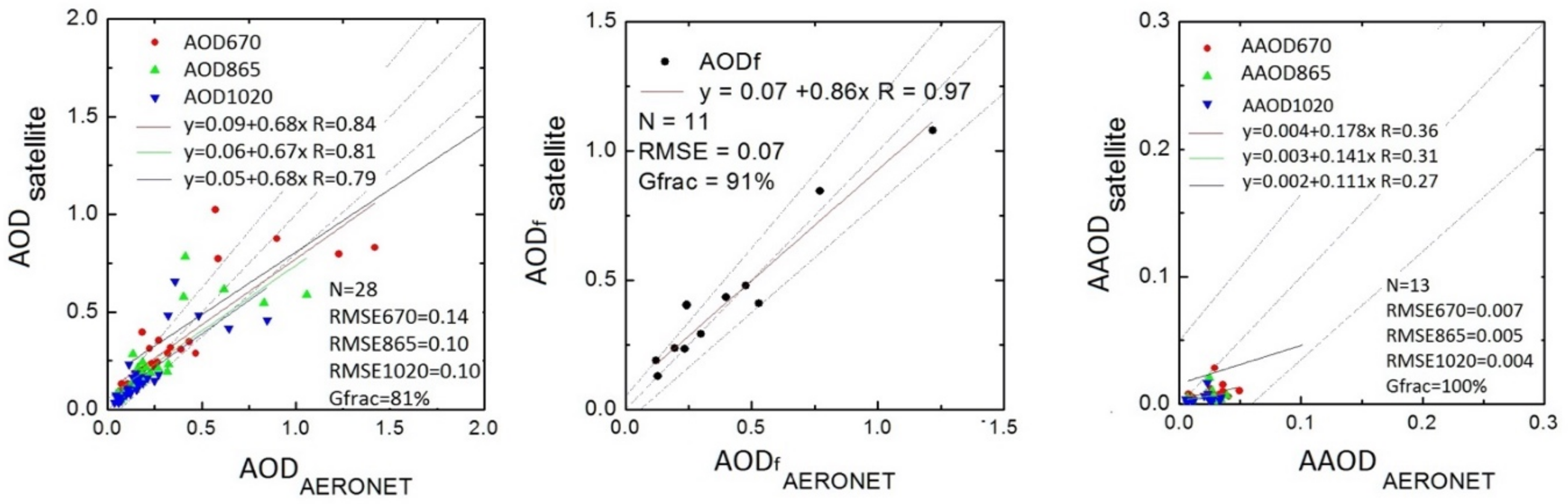
5.1. Validation of Aerosol Optical Properties
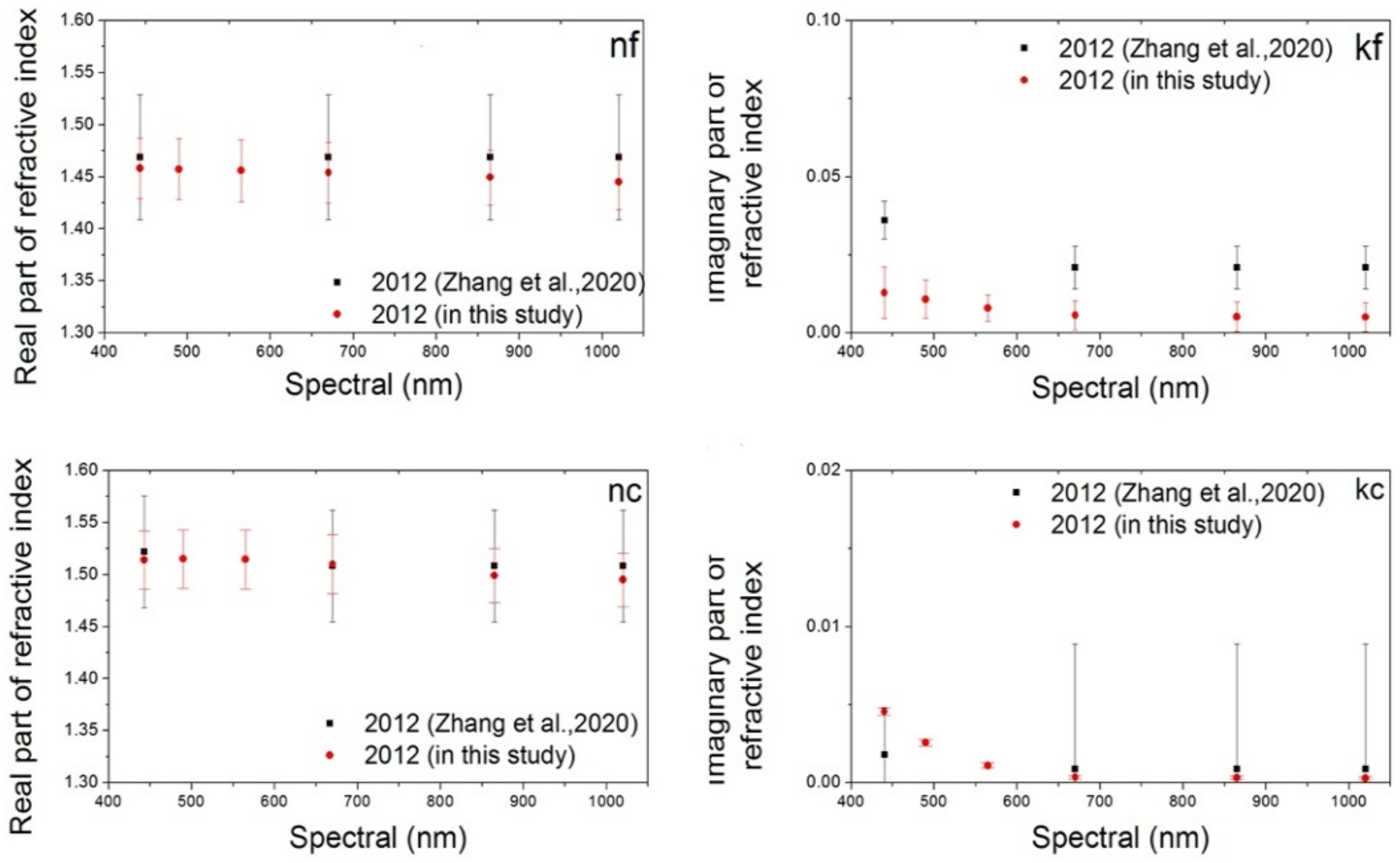
5.2. Complex Refractive Index
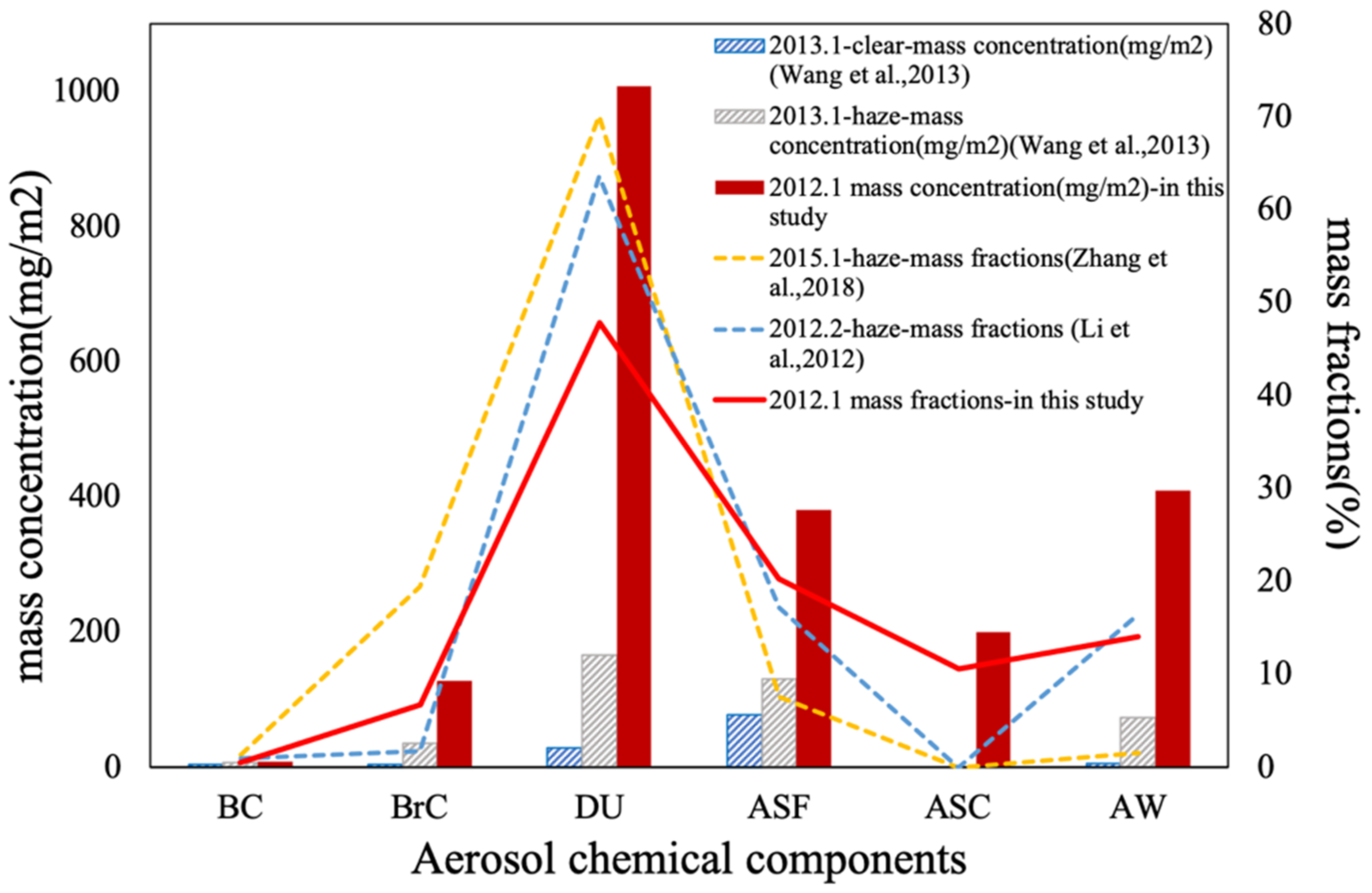
5.3. Intercomparison of Aerosol Component Distribution
6. Discussion
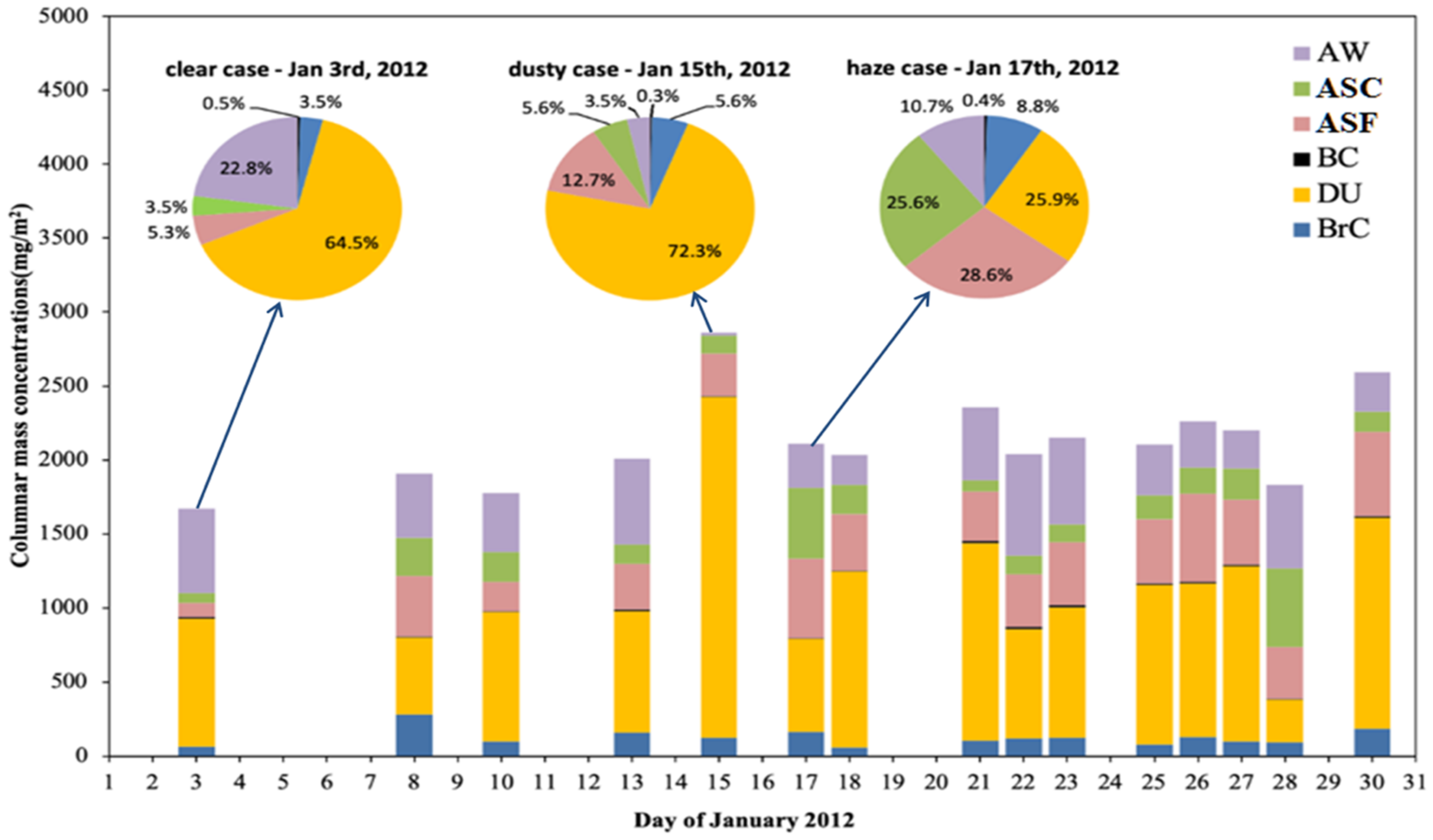
6.1. Aerosol Properties in Typical Regions
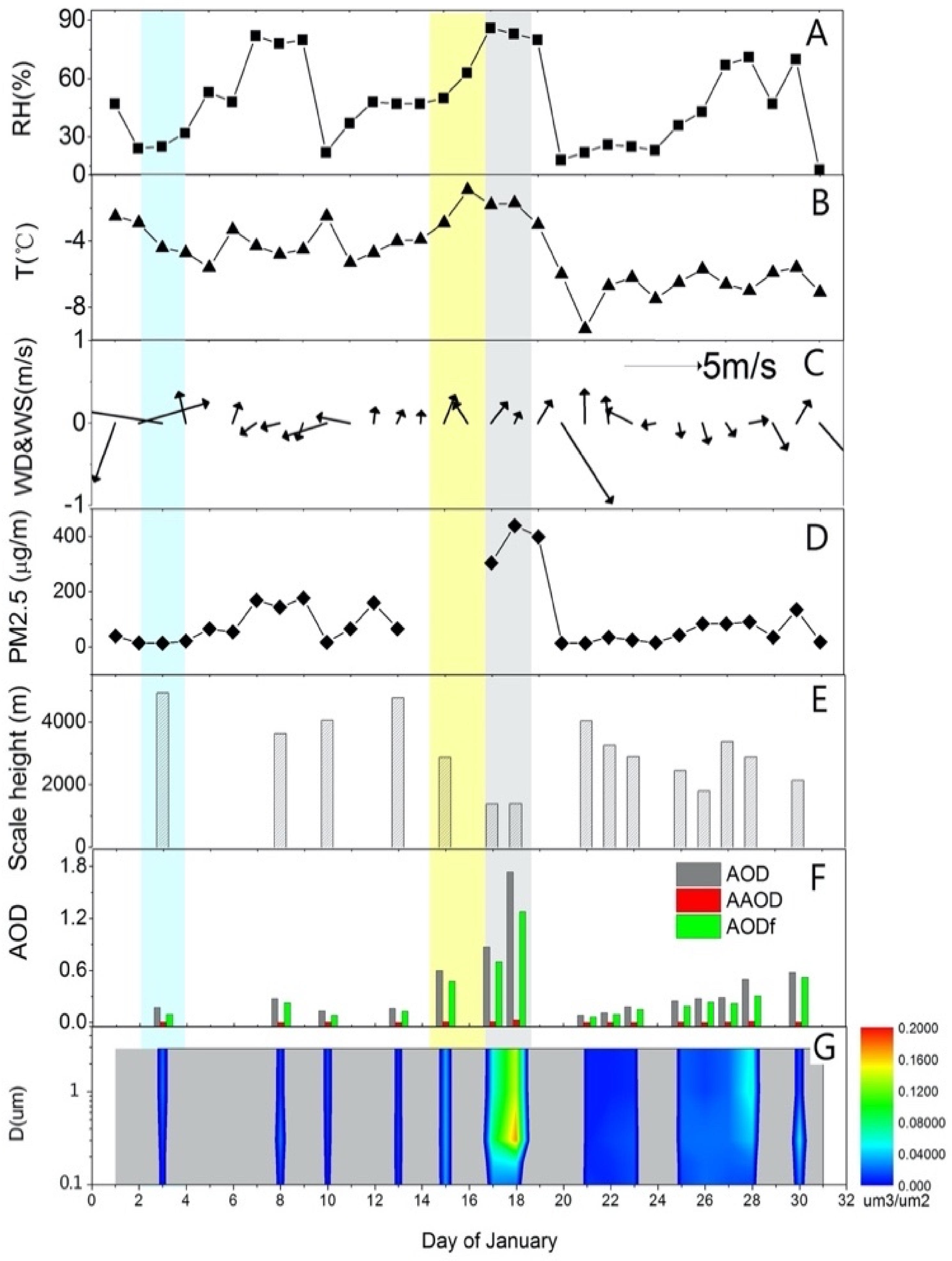
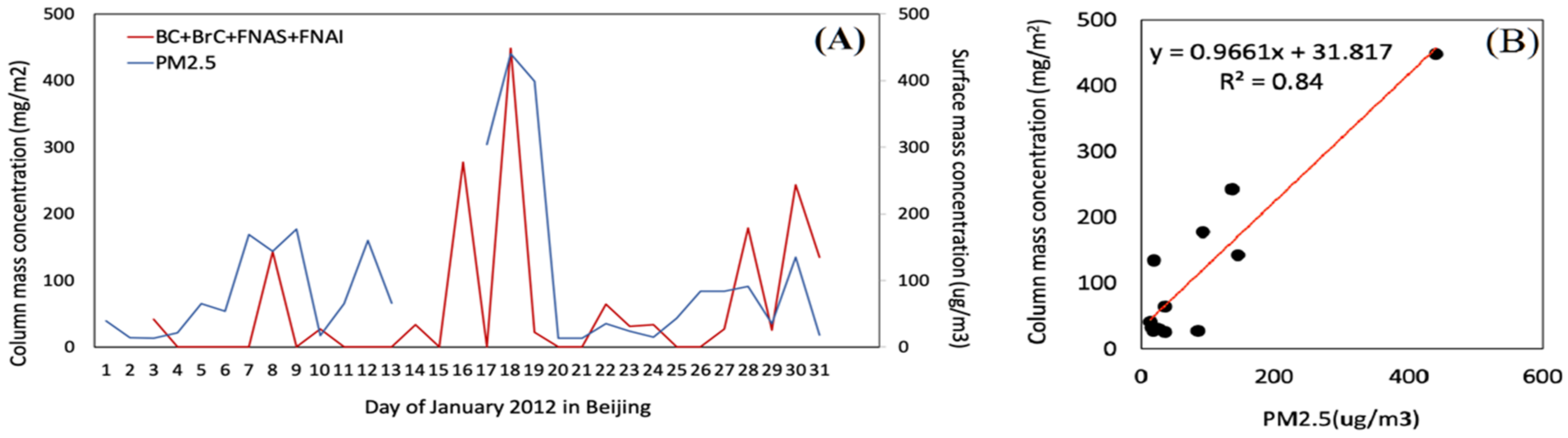
6.2. Temporal Variations of Aerosol Properties in Beijing Region
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Richter, A.; Burrows, J.P.; Nüß, H.; Granier, C.; Niemeier, U. Increase in tropospheric nitrogen dioxide over China observed from space. Nature 2005, 437, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.J.; Zhang, Y.; Bozzetti, C.; Ho, K.F.; Cao, J.J.; Han, Y.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Slowik, J.G.; Platt, S.M.; Canonaco, F.; et al. High secondary aerosol contribution to particulate pollution during haze events in China. Nature 2014, 514, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.J.; Shao, L.Y.; Buseck, P.R. Haze types in Beijing and the influence of agricultural biomass burning. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 8119–8130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhuang, G.; Sun, Y.; An, Z. The variation of characteristics and formation mechanisms of aerosols in dust, haze, and clear days in Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 6579–6591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yu, H.; Jiang, R. Components and optical properties of submicron aerosol during the lasting haze period in Nanjing. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2014, 59, 1955. [Google Scholar]
- Han, T.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, Y.; Zeng, L.; Hu, M.; Zhu, T. Role of secondary aerosols in haze formation in summer in the Megacity Beijing. J. Environ. Sci. Engl. 2015, 31, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, X.; Zheng, X.; Zhao, J.; Lv, M. Spatial Distribution, Sources Apportionment and Health Risk of Metals in Topsoil in Beijing, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.J.; Wu, F.; Chow, J.C.; Lee, S.C.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.W.; An, Z.S.; Fung, K.K.; Watson, J.G.; Zhu, C.S. Characterization and source apportionment of atmospheric organic and elemental carbon during fall and winter of 2003 in Xi’an, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 3127–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Lee, S.; Ho, K.F.; Zhang, X.; Zou, S.; Fung, K.; Chow, J.; Watson, J. Characteristics of carbonaceous aerosol in Pearl River Delta Region, China during 2001 winter period. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arola, A.; Schuster, G.; Myhre, G.; Kazadzis, S.; Dey, S.; Tripathi, S.N. Inferring absorbing organic carbon content from AERONET data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2010, 10, 215–225. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Gu, X.; Wang, L.; Li, D.; Xie, Y.; Li, K.; Dubovik, O.; Schuster, G.; Goloub, P.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Aerosol physical and chemical properties retrieved from ground-based remote sensing measurements during heavy haze days in Beijing winter. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 10171–10183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, L.; Zhang, F.; Li, D.; Xie, Y.; Xu, H. Comparison of aerosol properties over Beijing and Kanpur: Optical, physical properties and aerosol component composition retrieved from 12 years ground-based Sun-sky radiometer remote sensing data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 1520–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, G.L. Inferring black carbon content and specific absorption from Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) aerosol retrievals. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, G.L.; Bing, L.; Dubovik, O. Remote sensing of aerosol water uptake. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, G.L.; Dubovik, O.; Arola, A. Remote sensing of soot carbon—Part 1: Distinguishing different absorbing aerosol species. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 1565–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Sun, Y.; Lv, Y.; Xie, Y. Estimation of atmospheric columnar organic matter (OM) mass concentration from remote sensing measurements of aerosol spectral refractive. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 179, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; de Leeuw, G.; Zhang, C.; Xie, Y.; Li, K. Improved inversion of aerosol components in the atmospheric column from remote sensing data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 12795–12811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Dubovik, O.; Derimian, Y.; Schuster, G.L.; Lapyonok, T.; Litvinov, P.; Ducos, F.; Fuertes, D.; Chen, C.; Li, Z.; et al. Retrieval of aerosol components directly from satellite and ground-based measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 13409–13443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Li, Z.; Mishchenko, M.I.; Tanré, D.; Karol, Y.; Bojkov, B.; Cairns, B.; Diner, D.J.; Espinosa, W.R.; Goloub, P.; et al. Polarimetric remote sensing of atmospheric aerosols: Instruments, methodologies, results, and perspectives. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2019, 224, 474–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasekamp, O.P.; Litvinov, P.; Butz, A. Aerosol properties over the ocean from PARASOL multiangle photopolarimetric measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Herman, M.; Holdak, A.; Lapyonok, T.; Tanré, D.; Deuzé, J.L.; Ducos, F.; Sinyuk, A.; Lopatin, A. Statistically optimized inversion algorithm for enhanced retrieval of aerosol properties from spectral multi-angle polarimetric satellite observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2011, 4, 975–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, P.B.; Hamill, P.; Livingston, J.M.; Shinozuka, Y.; Strawa, A.W.; Redemann, J.; Omar, A.H.; Clarke, A.D.; Bergstrom, R.W.; Holben, B. Identifying Aerosol Type from Space: Absorption Angstrom Exponent as a Foundation for Multidimensional Supervised Clustering and Mahalanobis Classification. In AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Dubovik, O.; Henze, D.K.; Lapyonak, T.; Chin, M.; Ducos, F.; Litvinov, P.; Huang, X.; Li, L. Retrieval of desert dust and carbonaceous aerosol emissions over Africa from POLDER/PARASOL products generated by the GRASP algorithm. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 12551–12580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Dubovik, O.; Henze, D.K.; Chin, M.; Lapyonok, T.; Schuster, G.L.; Ducos, F.; Fuertes, D.; Litvinov, P.; Li, L.; et al. Constraining global aerosol emissions using POLDER/PARASOL satellite remote sensing observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 14585–14606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Lapyonok, T.; Litvinov, P.; Herman, M.; Federspiel, C. GRASP: A versatile algorithm for characterizing the atmosphere. Spienewsroom 2014, 25, 2-1201408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Che, H.; Derimian, Y.; Dubovik, O.; Luan, Q.; Li, Q.; Huang, X.; Zhao, H.; Gui, K.; Zheng, Y. Climatology of Fine and Coarse Mode Aerosol Optical Thickness Over East and South Asia Derived From POLDER/PARASOL Satellite. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2020JD032665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Che, H.; Derimian, Y.; Dubovik, O.; Zhang, X. Retrievals of fine mode light-absorbing carbonaceous aerosols from POLDER/PARASOL observations over East and South Asia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschamps, P.Y.; Breon, F.M.; Leroy, M.; Podaire, A.; Bricaud, A.; Buriez, J.C.; Seze, G. The POLDER mission: Instrument characteristics and scientific objectives. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1994, 32, 598–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deuzé, J.L.; Bréon, F.M.; Devaux, C.; Goloub, P.; Herman, M.; Lafrance, B.; Maignan, F.; Marchand, A.; Nadal, F.; Perry, G.; et al. Remote sensing of aerosols over land surfaces from POLDER-ADEOS-1 polarized measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 4913–4926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deuzé, J.L.; Goloub, P.; Herman, M.; Marchand, A.; Perry, G.; Susana, S.; Tanré, D. Estimate of the aerosol properties over the ocean with POLDER. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 15329–15346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanré, D.; Bréon, F.M.; Deuzé, J.L.; Dubovik, O.; Ducos, F.; François, P.; Goloub, P.; Herman, M.; Lifermann, A.; Waquet, F. Remote sensing of aerosols by using polarized, directional and spectral measurements within the A-Train: The PARASOL mission. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2011, 4, 1383–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Dubovik, O.; Fuertes, D.; Litvinov, P.; Lapyonok, T.; Lopatin, A.; Ducos, F.; Derimian, Y.; Herman, M.; Tanré, D.; et al. Validation of GRASP algorithm product from POLDER/PARASOL data and assessment of multi-angular polarimetry potential for aerosol monitoring. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2020, 12, 3573–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutgens, N.; Dubovik, O.; Hasekamp, O.; Torres, O.; Jethva, H.; Leonard, P.J.T.; Litvinov, P.; Redemann, J.; Shinozuka, Y.; de Leeuw, G.; et al. AEROCOM and AEROSAT AAOD and SSA study—Part 1: Evaluation and intercomparison of satellite measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 6895–6917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanré, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Nakajima, T. AERONET—A Federated Instrument Network and Data Archive for Aerosol Characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Song, C.H.; Kim, S.B.; Chun, Y.; Sohn, B.J.; Holben, B.N. Characteristics of aerosol types from AERONET sunphotometer measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 3110–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, D.M.; Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Sinyuk, A.; Smirnov, A.; Slutsker, I.; Dickerson, R.; Thompson, A.; Schafer, J. An analysis of AERONET aerosol absorption properties and classifications representative of aerosol source regions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Reid, J.S.; Dubovik, O.; Smirnov, A.; O’Neill, N.T.; Slutsker, I.; Kinne, S. Wavelength dependence of the optical depth of biomass burning, urban, and desert dust aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 31333–31349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.A.; Vokla, B.; Jckla, B.; Mp, B. How BLUE is the Sky? Estimating air qualities in Beijing during the Blue Sky Day period (2008–2012) by Bayesian Multi-task LSTM—ScienceDirect. Environ. Sci. Policy 2021, 116, 69–77. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Niu, T.; Wang, F.; Deng, M.; Wang, Y. Integration of multi-source measurements to monitor sand-dust storms over North China: A case study. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2013, 27, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.M.; Ma, Z.Q.; Lin, W.; Zhang, H.; Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Fuentes, J.D.; Xue, M. Impact of the Loess Plateau on the atmospheric boundary layer structure and air quality in the North China Plain: A case study. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 499, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; Fu, P.; Jiang, Q.; Yang, T.; Li, J.; Ge, X. The impact of relative humidity on aerosol composition and evolution processes during wintertime in Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xin, J.; Li, X.; Wang, Y. The variability of biomass burning and its influence on regional aerosol properties during the wheat harvest season in North China. Atmos. Res. 2015, 157, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.A.; Chen, H.B.; Wang, P.C.; Zong, X.M.; Qiu, J.H.; Gouloub, P. Aerosol properties and their spatial and temporal variations over North China in spring 2001. Tellus Ser. B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2005, 57, 28–39. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.J.; Zhao, P.S.; Xu, J.; Meng, W.; Pu, W.W.; Dong, F.; He, D.; Shi, Q.F. Analysis of a winter regional haze event and its formation mechanism in the North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 5685–5696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W. Exploring spatiotemporal patterns of PM2.5 in China based on ground-level observations for 190 cities. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, G.; Ren, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, C.; Han, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, C.; Meng, J. Identification of chemical compositions and sources of atmospheric aerosols in Xi’an, inland China during two types of haze events. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566–567, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavent-Oltra, J.A.; Román, R.; Granados-Muñoz, M.J.; Pérez-Ramírez, D.; Ortiz-Amezcua, P.; Denjean, C.; Lopatin, A.; Lyamani, H.; Torres, B.; Guerrero-Rascado, J.L.; et al. Comparative assessment of GRASP algorithm for a dust event over Granada (Spain) during ChArMEx-ADRIMED 2013 campaign. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 4439–4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, R.; Torres, B.; Fuertes, D.; Cachorro, V.E.; Dubovik, O.; Toledano, C.; Cazorla, A.; Barreto, A.; Bosch, J.L.; Lapyonok, T. Remote sensing of lunar aureole with a sky camera: Adding information in the nocturnal retrieval of aerosol properties with GRASP code. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 196, 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopatin, A.; Dubovik, O.; Fuertes, D.; Stenchikov, G.; Parajuli, S. Synergy processing of diverse ground-based remote sensing and in situ data using GRASP algorithm: Applications to radiometer, lidar and radiosonde observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 14, 2575–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, W.R.; Remer, L.A.; Dubovik, O.; Ziemba, L.; Beyersdorf, A.; Orozco, D.; Schuster, G.; Lapyonok, T.; Fuertes, D.; Martins, J.V. Retrievals of aerosol optical and microphysical properties from Imaging Polar Nephelometer scattering measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 811–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Sinyuk, A.; Lapyonok, T.; Holben, B.N.; Mishchenko, M.; Yang, P.; Eck, T.F.; Volten, H.; Muñoz, O.; Veihelmann, B.; et al. Application of spheroid models to account for aerosol particle nonsphericity in remote sensing of desert dust. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenoble, J.; Herman, M.; Deuzé, J.L.; Lafrance, B.; Santer, R.; Tanré, D. A successive order of scattering code for solving the vector equation of transfer in the earth’s atmosphere with aerosols. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2007, 107, 479–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O. Optimization of Numerical Inversion in Photopolarimetric Remote Sensing. In Photopolarimetry in Remote Sensing; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.; Ghim, Y.S. Estimation of columnar concentrations of absorbing and scattering fine mode aerosol components using AERONET data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 13628–13640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohren, C.F.; Huffman, D.R. Absorption and Scattering of Light by Small Particles; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Tian, Q.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Li, K.; Li, L. Estimate of aerosol absorbing components of black carbon, brown carbon, and dust from ground-based remote sensing data of sun-sky radiometers. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 6534–6543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.; Eck, T.F.; Smirnov, A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; King, M.D.; Tanré, D.; Slutsker, I. Variability of Absorption and Optical Properties of Key Aerosol Types Observed in Worldwide Locations. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 590–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, C.N. Size distribution of atmospheric particles. J. Aerosol. Sci. 1974, 5, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raabe, O.G. Particle size analysis utilizing grouped data and the log-normal distribution. J. Aerosol. Sci. 1971, 2, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitey, K.T. The physical characteristics of sulfur aerosols. Atmos. Environ. 1978, 12, 135–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitchison, J.; Brown, J.A.C. The lognormal distribution with special reference to its uses in economics. J. Polit. Econ. 1957, 25, 142–143. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, W.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Goloub, P.; Qie, L. Improving Remote Sensing of Aerosol Microphysical Properties by Near—Infrared Polarimetric Measurements Over Vegetated Land: Information Content Analysis. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 2215–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Niu, T.; Zhang, X.C.; Gong, S.L.; Zhang, Y.M.; Sun, J.Y. Atmospheric aerosol compositions in China: Spatial/temporal variability, chemical signature, regional haze distribution and comparisons with global aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 779–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.C.; Guo, W.; Gong, S.L. Carbonaceous aerosol composition over various regions of China during 2006. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, B.; Mei, X.; Li, Z.; Hou, W.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Li, K.; Wei, Y. An improved algorithm for retrieving high resolution fine-mode aerosol based on polarized satellite data: Application and validation for POLDER-3. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; Dubovik, O.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Li, K.; Chen, J.; Wang, H.; et al. Validation of POLDER GRASP aerosol optical retrieval over China using SONET observations. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2020, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streets, D.G.; Gupta, S.; Waldhoff, S.T.; Wang, M.Q.; Bond, T.C.; Bo, Y. Black carbon emissions in China. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 35, 4281–4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Crumeyrolle, S.; Zhao, W.; Xu, X.; Tong, Y. Real-time retrieval of aerosol chemical composition using effective density and the imaginary part of complex refractive index. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 245, 117959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Biedermann, L.; Bond, T.C. Color of brown carbon: A model for ultraviolet and visible light absorption by organic carbon aerosol. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koven, C.D.; Fung, I. Inferring dust composition from wavelength-dependent absorption in Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Beelen, A.J.; Roelofs, G.J.H.; Hasekamp, O.P.; Henzing, J.S.; Röckmann, T. Estimation of aerosol water and chemical composition from AERONET Sun–sky radiometer measurements at Cabauw, the Netherlands. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 5969–5987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.S.; Li, Z.Q.; Zhang, Y.X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.H.; Li, K.T.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Chen, X.F.; et al. Estimation of atmospheric aerosol composition from ground-based remote sensing measurements of Sun-sky radiometer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 498–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Abbreviations | Component | Densities |
|---|---|---|
| BC | black carbon | BC = 2.0 g/cm3 |
| BrC | brown carbon | BrC = 1.8 g/cm3 |
| CAI | coarse-mode absorbing insoluble | CAI = 4.77 g/cm3 |
| CNAI | coarse-mode non-absorbing insoluble | CNAI = 2.6 g/cm3 |
| FNAI | fine-mode non-absorbing insoluble | FNAI = 2.6 g/cm3 |
| FNAS | fine-mode non-absorbing soluble | FNAS = 1.76 g/cm3 |
| CNAS | coarse-mode non-absorbing insoluble | CNAS = 2.24 g/cm3 |
| AWF | aerosol water of fine-mode | FAWC = 1.0 g/cm3 |
| AWC | aerosol water of coarse-mode | CAWC = 1.0 g/cm3 |
| AOD | aerosol optical depth | |
| AODf | fine aerosol optical depth | |
| AAOD | absorbing aerosol optical depth | |
| CRI | complex refractive indices | |
| nf | real part of CRI for fine mode | |
| nc | real part of CRI for coarse mode | |
| kf | imaginary part of CRI for fine mode | |
| kc | imaginary part of CRI for coarse mode | |
| FMFv | fine-mode fraction by volume |
| BJ | SX | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | Mean | Min | SD | Max | Mean | Min | SD | |
| AOD (670 nm) | 1.09 | 0.96 | 0.41 | 1.56 | 0.94 | 0.91 | 0.46 | 0.77 |
| AODf (670 nm) | 0.94 | 0.82 | 0.32 | 1.41 | 0.50 | 0.45 | 0.21 | 0.43 |
| AAOD (670 nm) | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 |
| kf (670 nm) | 0.014 | 0.006 | 0.002 | 0.00 | 0.046 | 0.022 | 0.004 | 0.02 |
| kc (670 nm) | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.00 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.00 |
| nf (670 nm) | 1.52 | 1.45 | 1.40 | 0.03 | 1.56 | 1.50 | 1.40 | 0.02 |
| nc (670 nm) | 1.56 | 1.51 | 1.43 | 0.03 | 1.54 | 1.50 | 1.41 | 0.00 |
| FMFv | 0.79 | 0.78 | 0.60 | 0.08 | 0.64 | 0.62 | 0.38 | 0.20 |
| Scale height (m) | 4316 | 4157 | 3057 | 1168 | 4791 | 4464 | 2710 | 980 |
| BC (mg/m2) | 25 | 9 | 2 | 2 | 83 | 29 | 3 | 24 |
| BrC (mg/m2) | 271 | 127 | 34 | 53 | 113 | 33 | 3 | 18 |
| DU (mg/m2) | 3277 | 1008 | 175 | 233 | 3423 | 1608 | 399 | 299 |
| ASF (mg/m2) | 737 | 381 | 53 | 128 | 410 | 130 | 11 | 53 |
| ASC (mg/m2) | 664 | 200 | 30 | 129 | 761 | 167 | 6 | 126 |
| AW (mg/m2) | 966 | 410 | 65 | 83 | 858 | 230 | 7 | 64 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ou, Y.; Li, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Dubovik, O.; Derimian, Y.; Chen, C.; Fuertes, D.; Xie, Y.; Lopatin, A.; et al. Spatio-Temporal Variability of Aerosol Components, Their Optical and Microphysical Properties over North China during Winter Haze in 2012, as Derived from POLDER/PARASOL Satellite Observations. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2682. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13142682
Ou Y, Li L, Li Z, Zhang Y, Dubovik O, Derimian Y, Chen C, Fuertes D, Xie Y, Lopatin A, et al. Spatio-Temporal Variability of Aerosol Components, Their Optical and Microphysical Properties over North China during Winter Haze in 2012, as Derived from POLDER/PARASOL Satellite Observations. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(14):2682. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13142682
Chicago/Turabian StyleOu, Yang, Lei Li, Zhengqiang Li, Ying Zhang, Oleg Dubovik, Yevgeny Derimian, Cheng Chen, David Fuertes, Yisong Xie, Anton Lopatin, and et al. 2021. "Spatio-Temporal Variability of Aerosol Components, Their Optical and Microphysical Properties over North China during Winter Haze in 2012, as Derived from POLDER/PARASOL Satellite Observations" Remote Sensing 13, no. 14: 2682. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13142682
APA StyleOu, Y., Li, L., Li, Z., Zhang, Y., Dubovik, O., Derimian, Y., Chen, C., Fuertes, D., Xie, Y., Lopatin, A., Ducos, F., & Peng, Z. (2021). Spatio-Temporal Variability of Aerosol Components, Their Optical and Microphysical Properties over North China during Winter Haze in 2012, as Derived from POLDER/PARASOL Satellite Observations. Remote Sensing, 13(14), 2682. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13142682













