Cloud-to-Ground Lightning Response to Aerosol over Air-Polluted Urban Areas in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data Collections
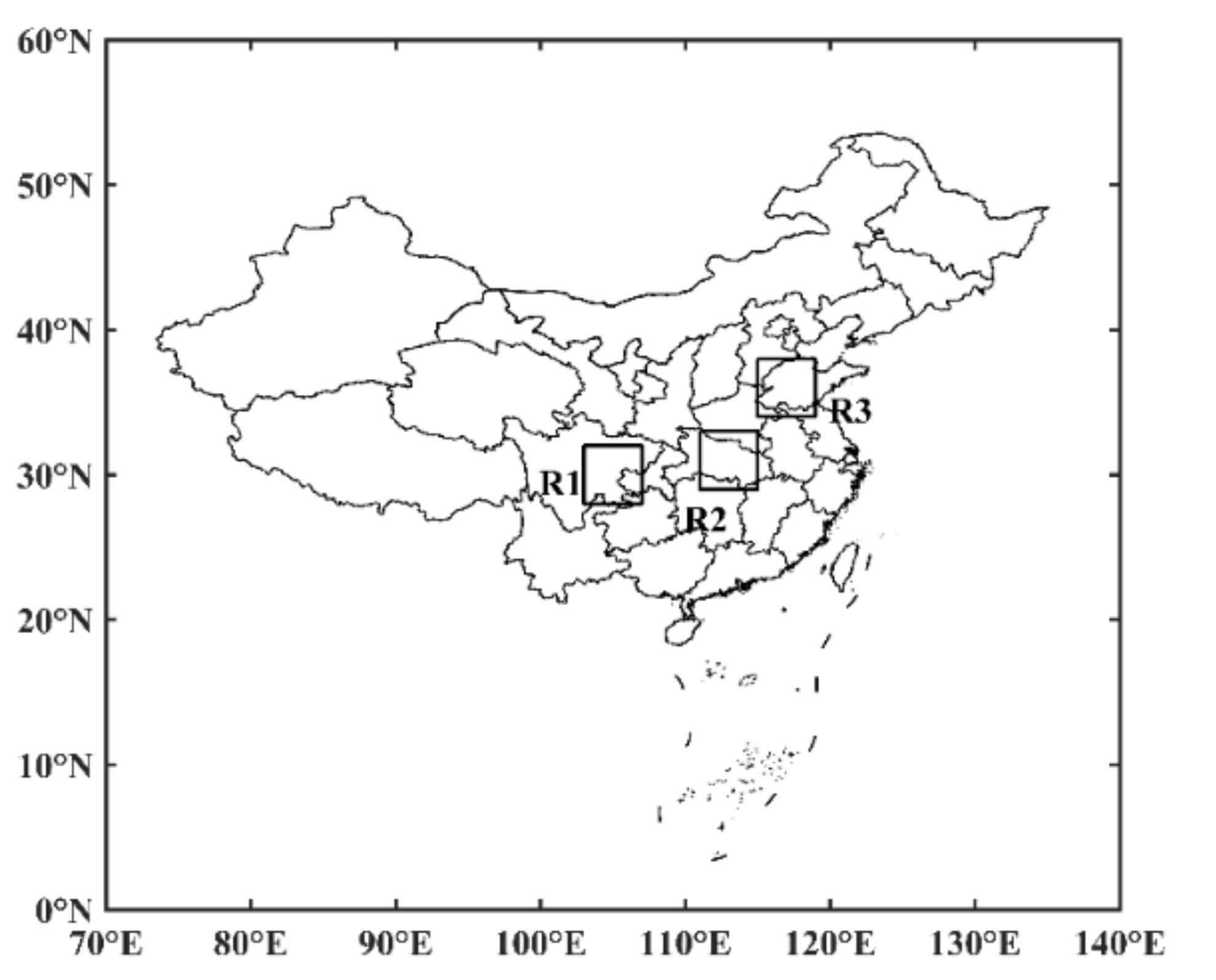
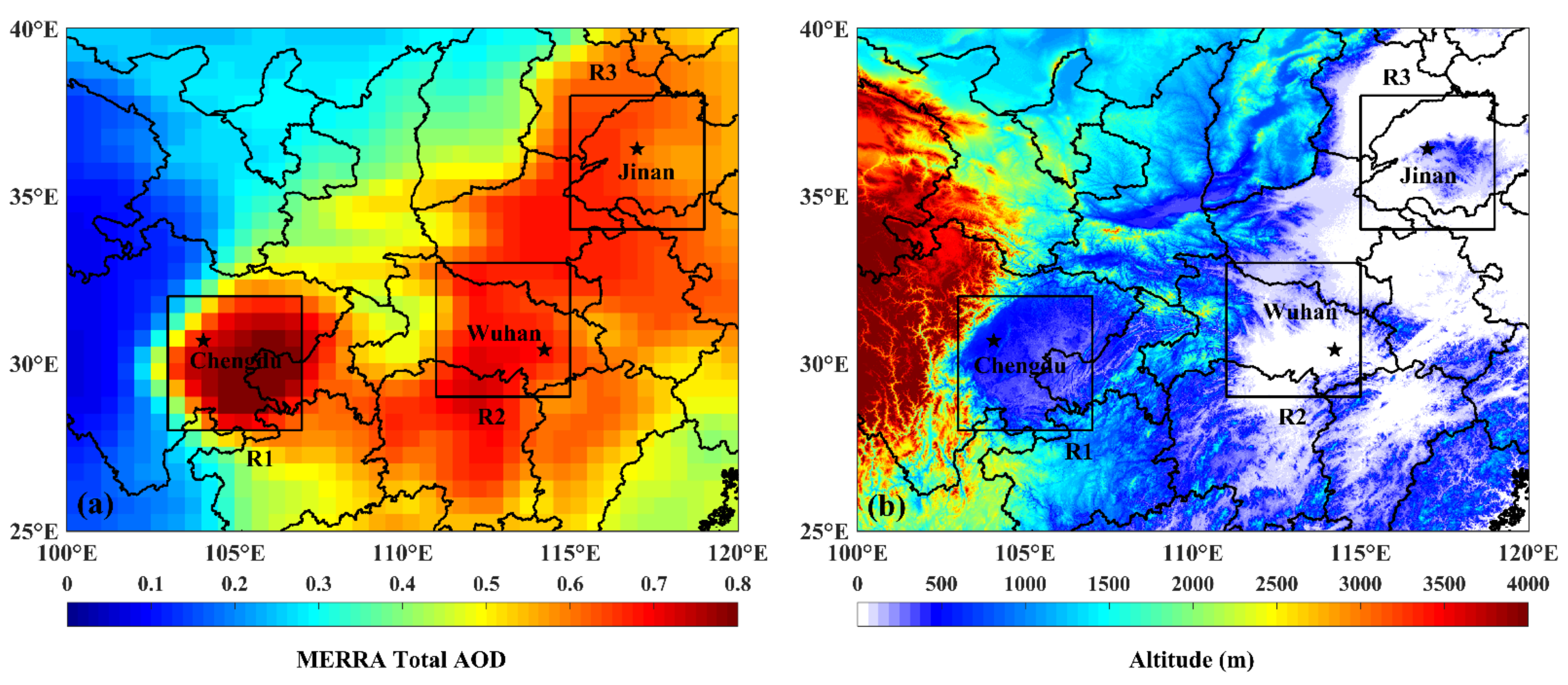
2.2. Regions of Interest
2.3. Methods
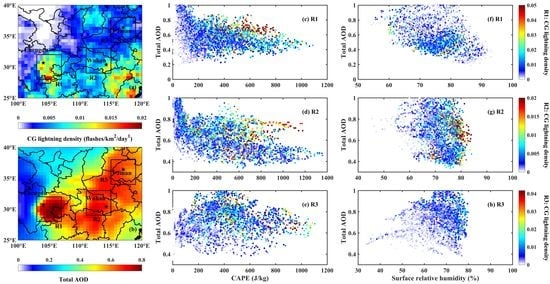
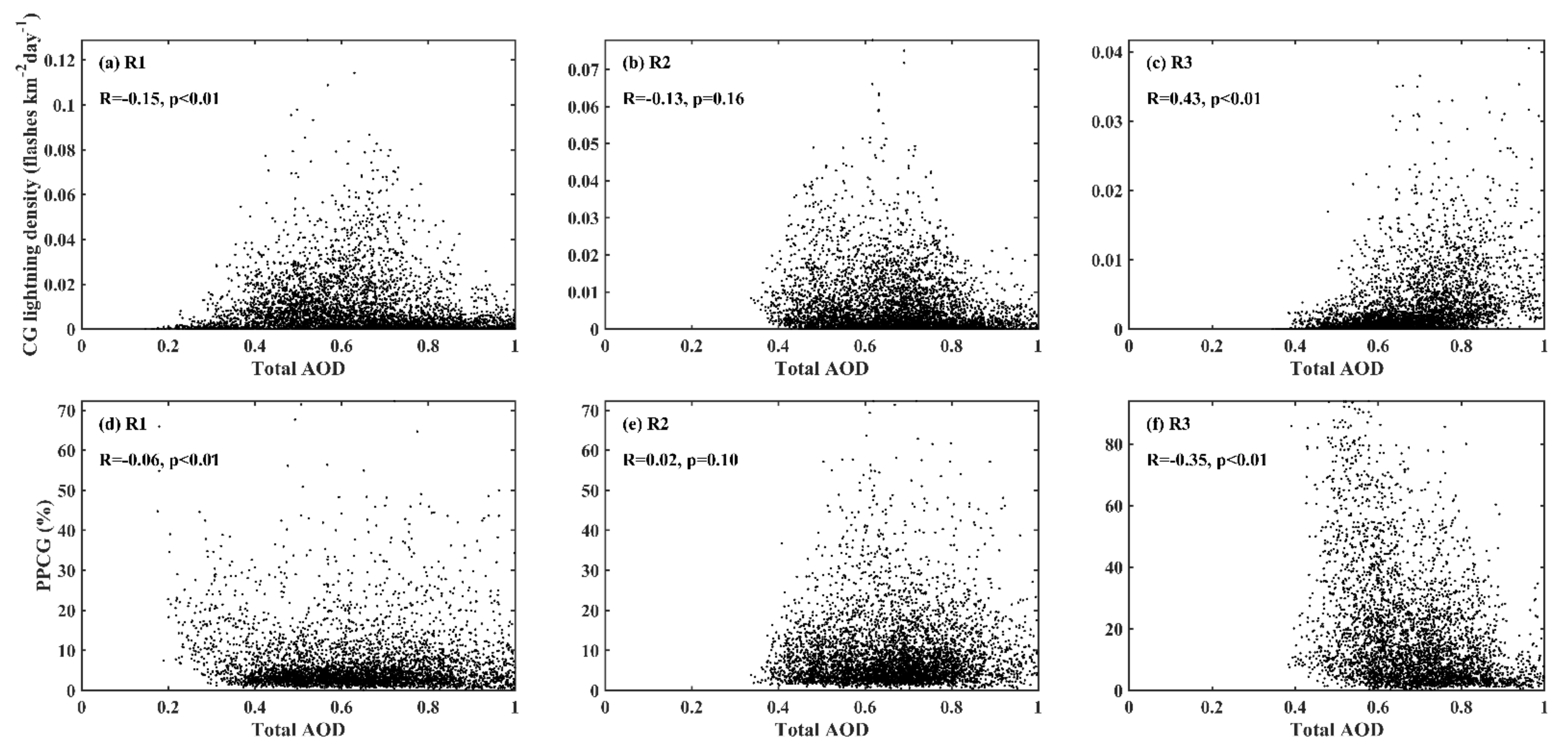
3. Results
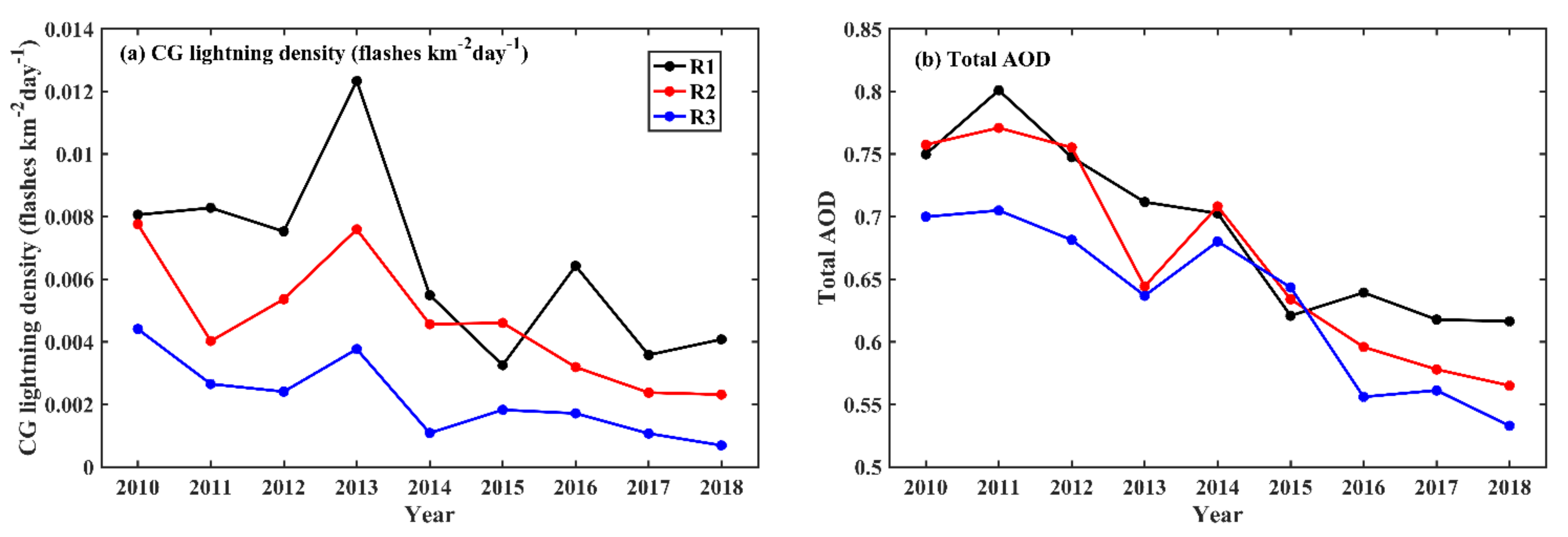
3.1. Temporal Variations of Total AOD and CG Lightning
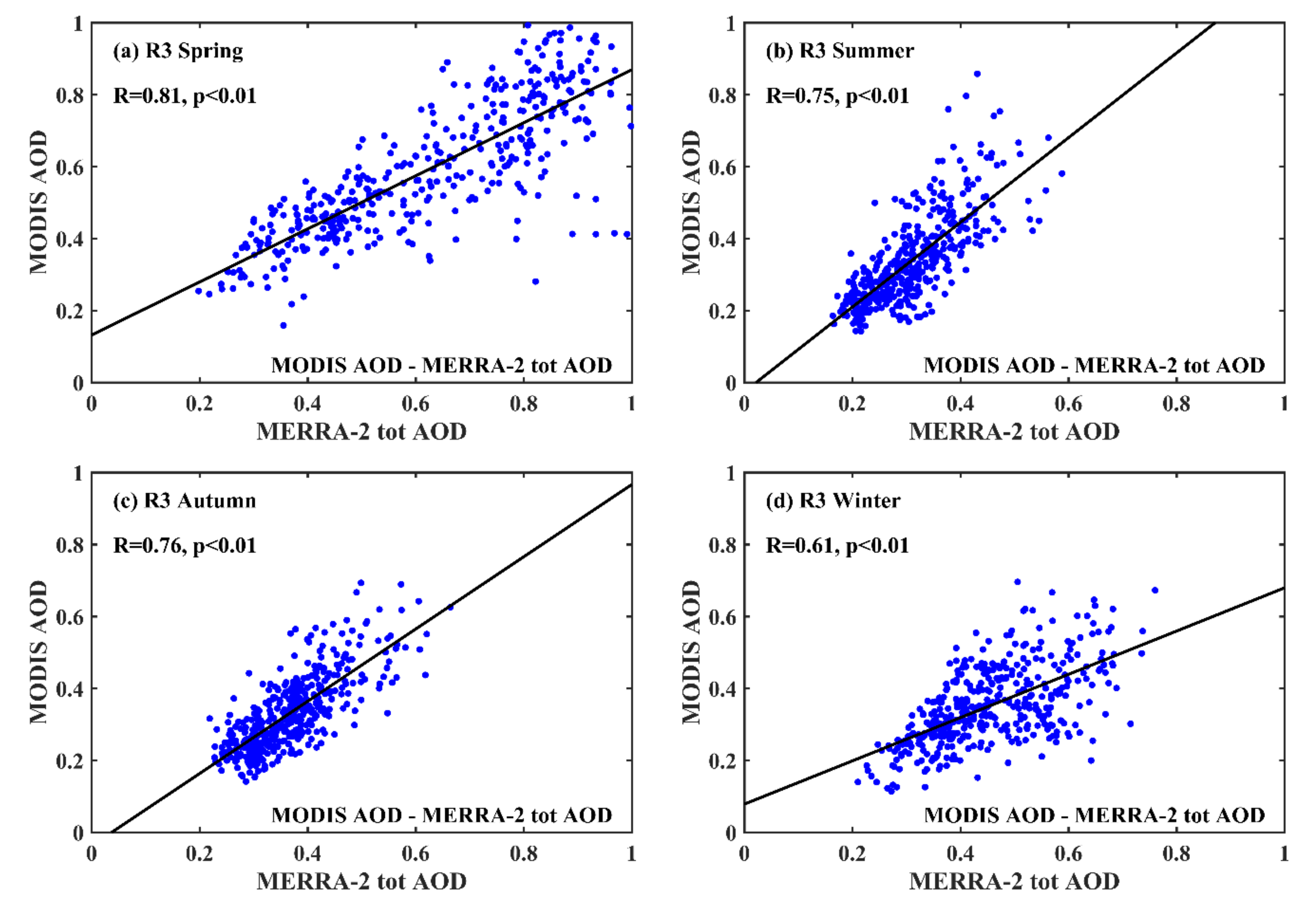
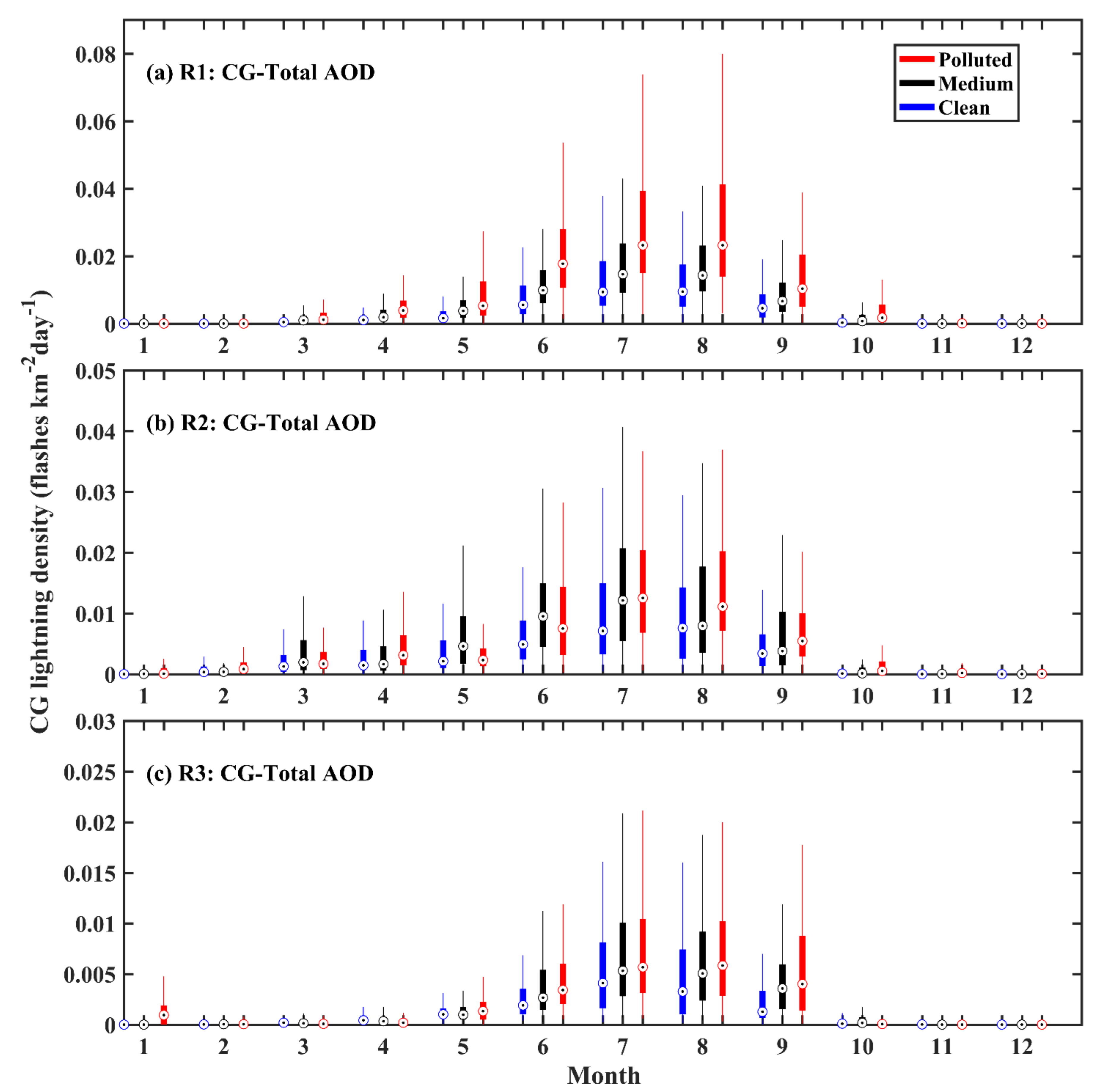
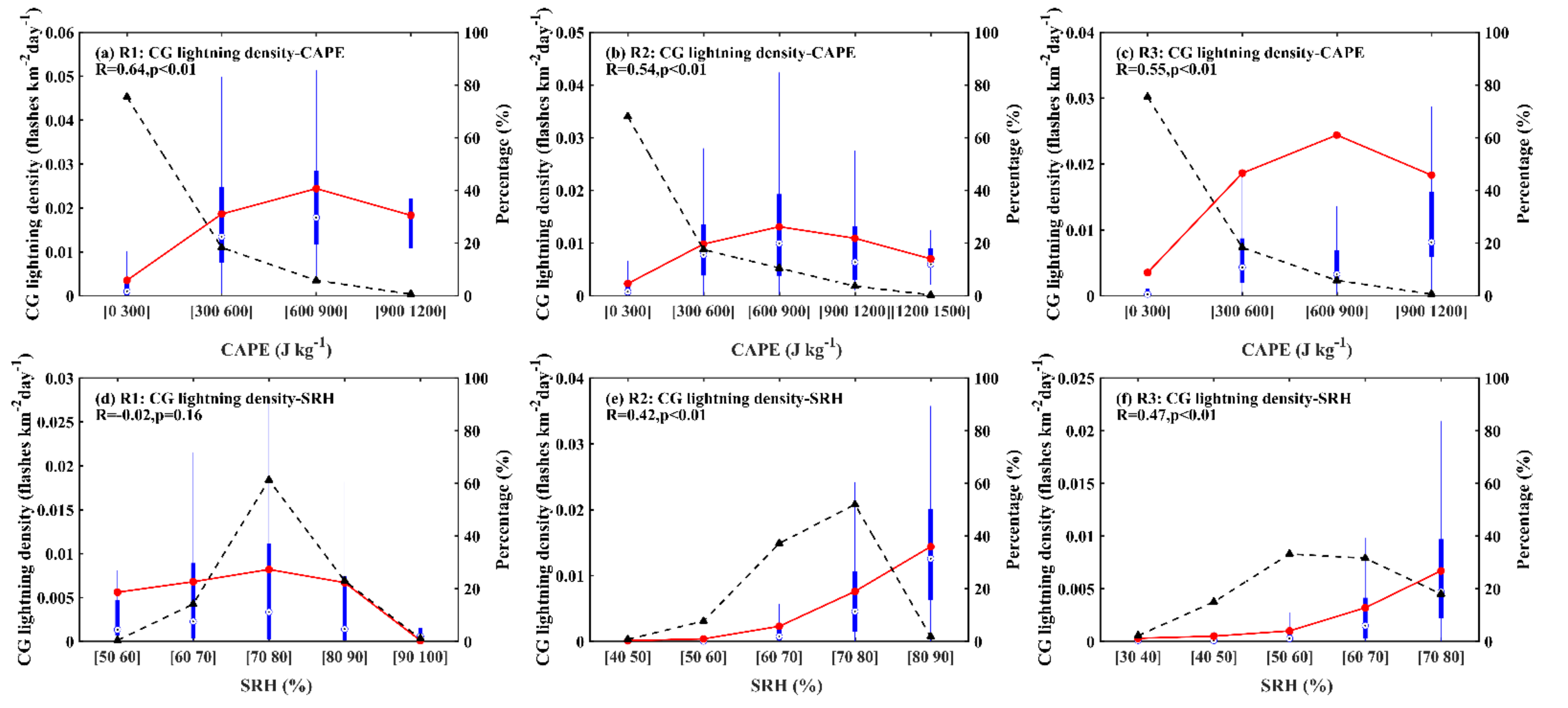
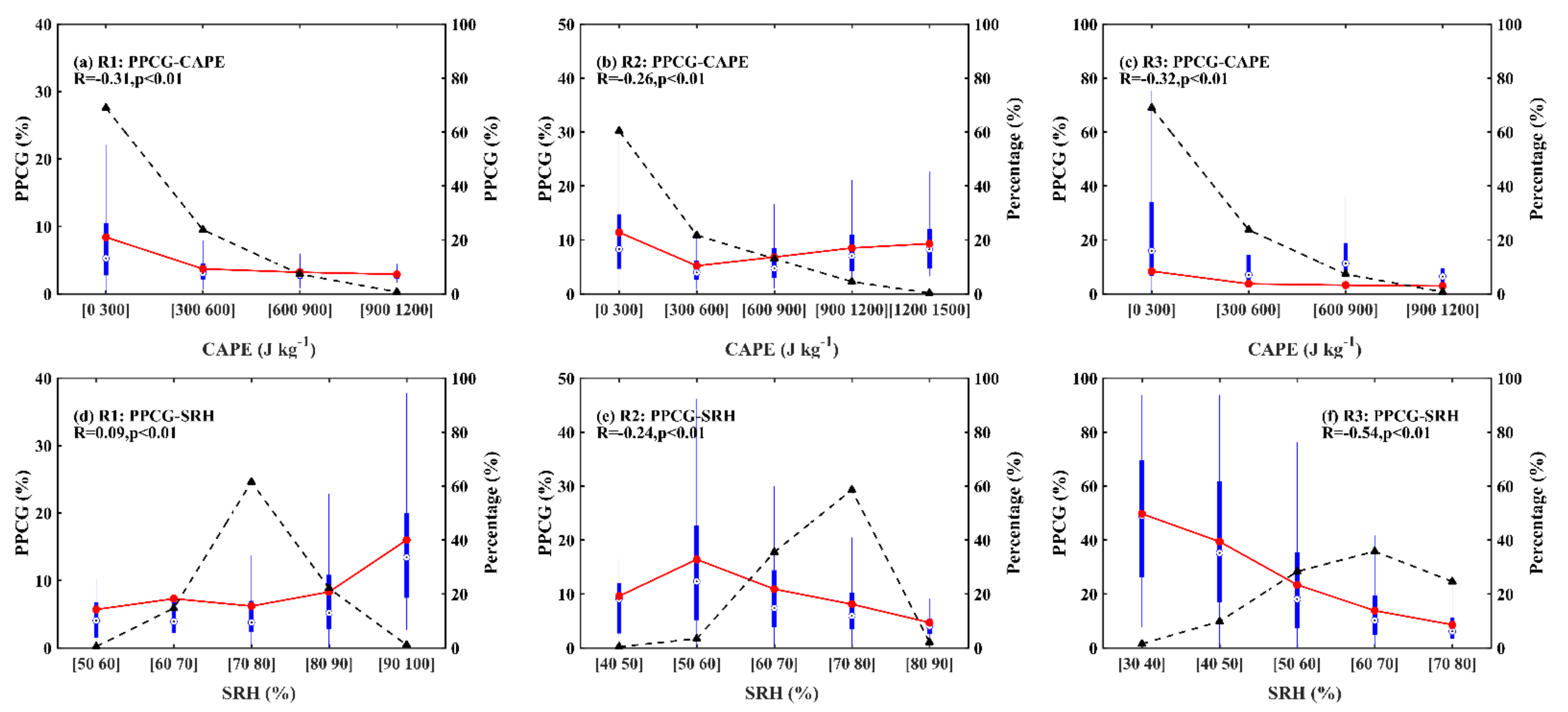
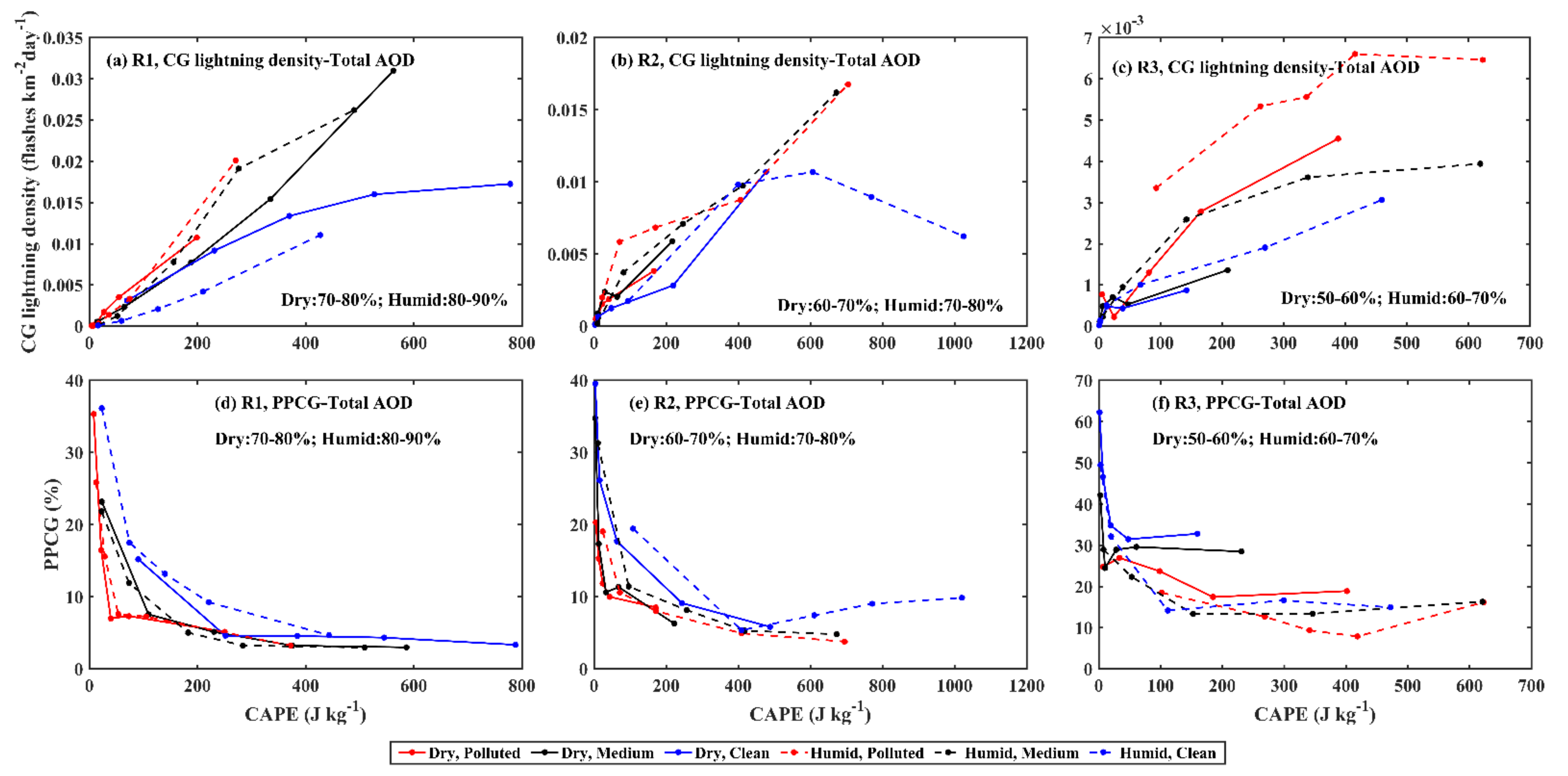
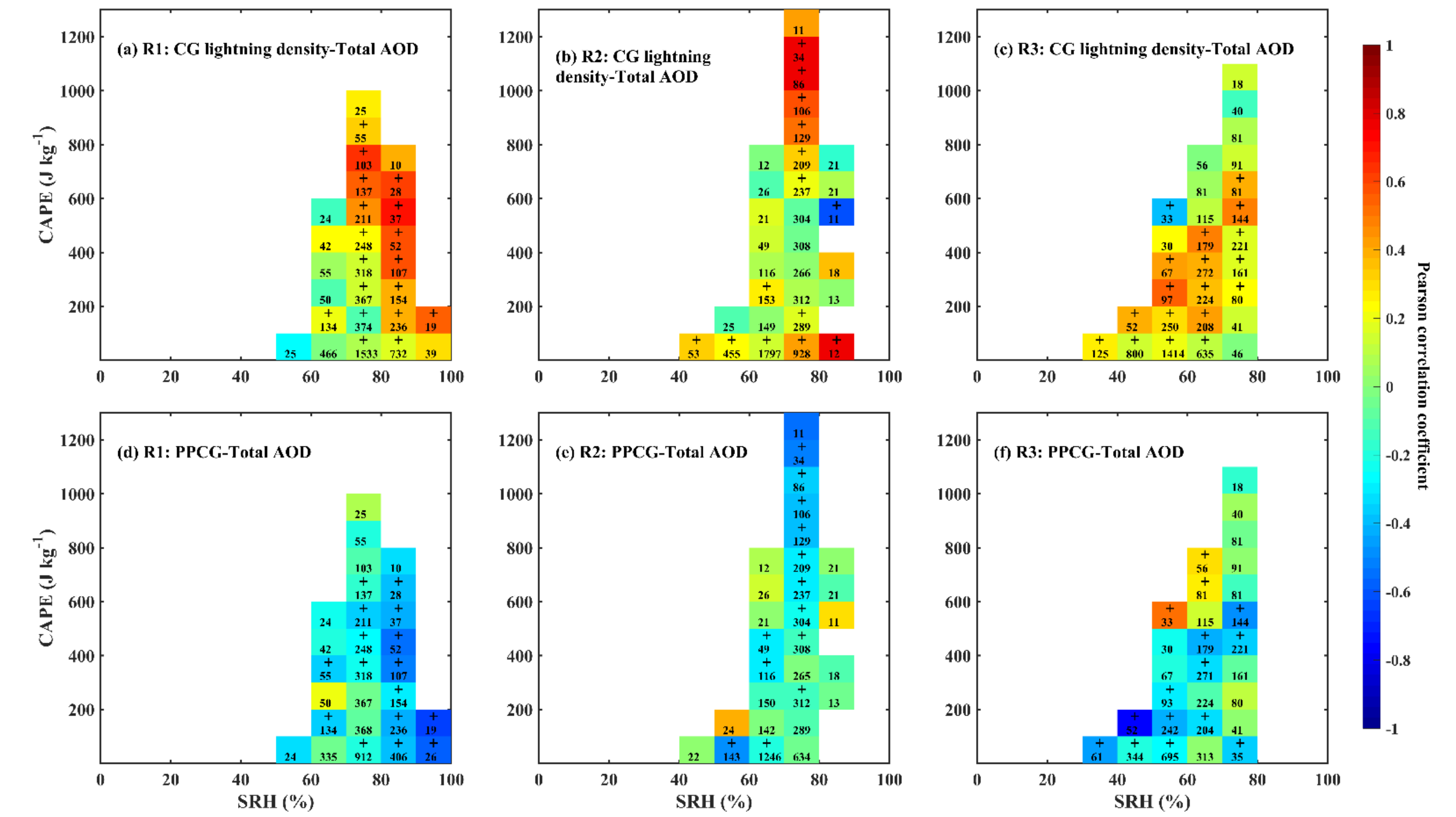
3.2. Response of CG Lightning to Total AOD and Thermodynamic Factors
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A


| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 49 | 125 | 150 | 181 | 192 | 192 | 192 | 192 | 192 | 188 | 148 | 67 |
| R2 | 129 | 165 | 184 | 192 | 192 | 192 | 192 | 192 | 192 | 188 | 132 | 114 |
| R3 | 50 | 144 | 189 | 192 | 192 | 192 | 181 | 186 | 192 | 183 | 120 | 60 |
| CG Lightning Density-CAPE | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Sum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 4517 | 1095 | 346 | 33 | - | 5991 |
| R2 | 4272 | 1102 | 662 | 228 | 17 | 6281 |
| R3 | 3977 | 1271 | 397 | 59 | - | 5704 |
| CG Lightning Density-SRH | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Sum |
| R1 | 26 | 850 | 3673 | 1376 | 66 | 5991 |
| R2 | 53 | 486 | 2366 | 3264 | 112 | 6281 |
| R3 | 125 | 857 | 1891 | 1803 | 1028 | 5704 |
| PPCG-CAPE | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Sum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 3267 | 1095 | 346 | 33 | - | 4741 |
| R2 | 3065 | 1101 | 662 | 228 | 17 | 5073 |
| R3 | 2408 | 1270 | 397 | 59 | - | 4134 |
| PPCG-SRH | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Sum |
| R1 | 25 | 697 | 2917 | 1049 | 53 | 4741 |
| R2 | 22 | 174 | 1800 | 2972 | 105 | 5073 |
| R3 | 51 | 407 | 1170 | 1479 | 1017 | 4134 |
References
- Krause, A.; Kloster, S.; Wilkenskjeld, S.; Paeth, H. The sensitivity of global wildfires to simulated past, present, and future lightning frequency. J. Geophys. Res. 2014, 119, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdollahi, M.; Dewan, A.M.; Hassan, Q.K. Applicability of remote sensing-based vegetation water content in modeling lightning-caused forest fire occurrences. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holle, R.L.; Dewan, A.; Said, R.; Brooks, W.A.; Hossain, M.F.; Rafiuddin, M. Fatalities related to lightning occurrence and agriculture in Bangladesh. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2019, 41, 101264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Meng, Q.; Ma, M.; Zhang, Y. Lightning Casualties and Damages in China from 1997 to 2009. Nat. Hazards 2011, 57, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westcott, N.E. Summertime Cloud-to-Ground lightning activity around major midwestern urban areas. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 1995, 34, 1633–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaratz, O.; Koren, I.; Yair, Y.; Price, C. Lightning response to smoke from Amazonian fires. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L07801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, T.; Remer, L.A.; Pickering, K.E.; Yu, H. Observational evidence of aerosol enhancement of lightning activity and convective invigoration. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L04701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, J.A.; Virts, K.S.; Holzworth, R.H.; Mitchell, T.P. Lightning enhancement over major oceanic shipping lanes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 9102–9111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyons, W.A.; Nelson, T.E.; Williams, E.R.; Cramer, J.A.; Turner, T.R. Enhanced positive cloud-to-ground lightning in thunderstorms ingesting smoke from fires. Science 1998, 282, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, N.D.; Orville, R.E.; Huffines, G.R. Effect of pollution from Central American fires on cloud-to-ground lightning in May 1998. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 2249–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, T.J.; Rutledge, S.A. Cloud-to-ground lightning downwind of the 2002 Hayman forest fire in Colorado. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L03804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naccarato, K.P.; Pinto, O., Jr.; Pinto, I.R.C.A. Evidence of thermal and aerosol effects on the cloud-to-ground lightning density and polarity over large urban areas of Southeastern Brazil. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steiger, S.M.; Orville, R.E. Cloud-to-ground lightning enhancement over Southern Louisiana. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, S.K.; Liou, Y.A.; Ha, K.J. Aerosol effects on the enhancement of cloud-to-ground lightning over major urban areas of South Korea. Atmos. Res. 2009, 92, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, S.K.; Liou, Y.A. Enhancement of cloud-to-ground lightning activity over Taipei, Taiwan in relation to urbanization. Atmos. Res. 2014, 147, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, D.M.; Pawar, S.D. Effect of urbanization on lightning over four metropolitan cities of India. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Rosenfeld, D.; Ryzhkov, A.; Zrnic, D.; Williams, E.; Zhang, P.; Snyder, J.C.; Zhang, R.; Weitz, R. Polarimetric Radar Convective Cell Tracking Reveals Large Sensitivity of Cloud Precipitation and Electrification Properties to CCN. J. Geophys. Res. 2019, 124, 12194–12205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Rosenfeld, D.; Fan, J. Aerosols and their impact on radiation, clouds, precipitation, and severe weather events. In Oxford Research Encyclopedia Environmental Science; Oxford University Press: Cary, NC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenfeld, D.; Itamar, M.L. Satellite-based insights into precipitation formation processes in continental and maritime convective clouds. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 2457–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenfeld, D.; Lohmann, U.; Raga, G.B.; O’Dowd, C.D.; Kulmala, M.; Fuzzi, S.; Reissell, A.; Andreae, M.O. Flood or drought: How do aerosols affect precipitation? Science 2008, 321, 1309–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, J.; Leung, L.R.; Rosenfeld, D.; Chen, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yan, H. Microphysical effects determine macrophysical response for aerosol impacts on deep convective clouds. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 201316830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khain, A.; Rosenfeld, D.; Pokrovsky, A. Aerosol impact on the dynamics and microphysics of deep convective clouds. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 131, 2639–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, W.K.; Chen, J.P.; Li, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, C. Impact of aerosols on convective clouds and precipitation. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, T. Riming electrification as a charge generation mechanism in thunderstorms. J. Atmos. Sci. 1978, 35, 1536–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaratne, E.R.; Saunders, C.P.R.; Hallett, J. Laboratory studies of the charging of soft hail during ice crystal interactions. Q. J. R. Meteor. Soc. 1983, 109, 609–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.R. The Electrification of Thunderstorms. Sci. Am. 1988, 259, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanré, D.; Holben, B.N.; Mattoo, S.; Remer, L.A.; Eck, T.F.; Vaughan, J.; Chatenet, B. Aerosol radiative impact on spectral solar flux at the surface, derived from principal-plane sky measurements. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koren, I.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Remer, L.A.; Martins, J.V. Measurement of the effect of Amazon smoke on inhibition of cloud formation. Science 2004, 303, 1342–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koren, I.; Martins, J.V.; Remer, L.A.; Afargan, H. Smoke invigoration versus inhibition of clouds over the Amazon. Science 2008, 321, 946–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siingh, D.; Buchunde, P.S.; Singh, R.P.; Nath, A.; Kumar, S.; Ghodpage, R.N. Lightning and convective rain study in different parts of India. Atmos. Res. 2014, 137, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, D.M.; Ghude, S.D.; Mahakur, M.; Waghmare, R.T.; Tiwari, S.; Srivastava, M.K.; Meena, G.S.; Chate, D.M. Relationship between aerosol and lightning over Indo-Gangetic Plain (IGP), India. Clim. Dynam. 2018, 50, 3865–3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, D.; Williams, E.; Andreae, M.O.; Freud, E.; Pöschl, U.; Rennó, N.O. The scientific basis for a satellite mission to retrieve CCN concentrations and their impacts on convective clouds. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 2039–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keith, D.S.; Matthew, D.P. Climatology and ingredients of significant severe convection in high-shear, low-CAPE environments. Weather Forecast. 2014, 29, 854–877. [Google Scholar]
- Murugavel, P.; Pawar, S.D.; Gopalakrishnan, V. Trends of convective available potential energy over the Indian region and its effect on rainfall. Int. J. Climatol. 2012, 32, 1362–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewan, A.; Ongee, E.T.; Rafiuddin, M.; Rahman, M.M.; Mahmood, R. Lightning activity associated with precipitation and CAPE over Bangladesh. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 1649–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.J.; Qie, X.S.; Zhou, Y.J.; Yuan, T.; Zhang, Y.L. Regional response of lightning activities to relative humidity of the surface. Chin. J. Geophys. 2006, 49, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Zhang, R.; Li, G.; Tao, W. Effects of aerosols and relative humidity on cumulus clouds. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, D14204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Tan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Lin, X.; Wang, M.; Luan, J. Effects of relative humidity on electrification and lightning discharges in thunderstorms. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2018, 29, 695–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhou, L.; Cribb, M.; Zhang, F. Distinct weekly cycles of thunderstorms and a potential connection with aerosol type in China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 8760–8768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Z.; Guo, J.; Zhao, C.; Cribb, M. The climate impact of aerosols on the lightning flash rate: Is it detectable from long-term measurements? Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 12797–12816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, P.; Li, Z.; Xiao, H.; Wu, F.; Zheng, Y.; Cribb, M.C.; Jin, X.; Zhou, Y. Distinct aerosol effects on cloud-to-ground lightning in the plateau and basin regions of Sichuan, Southwest China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yao, Z.; Li, Z.; Fan, T. Heavy air pollution suppresses summer thunderstorms in central China. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2013, 95, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, Z. Increases in thunderstorm activity and relationships with air pollution in southeast China. J. Geophys. Res. 2014, 119, 1835–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.B.; Peng, L.; Shi, Z.; Chen, H.R. Lightning flash density in relation to aerosol over Nanjing (China). Atmos. Res. 2016, 174, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wan, Q.; Meng, W.; Liao, F.; Tan, H.; Zhang, R. Long-term impacts of aerosols on precipitation and lightning over the Pearl River Delta megacity area in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 12421–12436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Tao, M.; Wang, Z.; Tao, J.; Yu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, M.; Gu, J.; Su, L. Satellite record of the transition of air quality over China. Big Earth Data 2018, 2, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, K.L.; Murphy, M.J.; Bardo, E.A.; Hiscox, W.L.; Pyle, R.B.; Prfer, A.E. A combined TOA/MDF technology upgrade of the, U.S. national lightning detection network. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 9035–9044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Sun, J.; Li, W. An analysis of cloud-to-ground lightning in China during 2010–2013. Weather Forecast. 2015, 30, 1537–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, R.; Zhang, D.L.; Wang, B. A 6-yr cloud-to-ground lightning climatology and its relationship to rainfall over central and eastern China. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2015, 54, 2443–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, K.L.; Murphy, M.J. An overview of lightning locating systems: History, techniques, and data uses, with an in-depth look at the U.S. NLDN. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2009, 51, 499–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.-S.; Purser, R.J.; Parrish, D.F. Three-dimensional variational analysis with spatially inhomogeneous covariances. Mon. Weather Rev. 2002, 130, 2905–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kleist, D.T.; Parrish, D.F.; Derber, J.C.; Treadon, R.; Wu, W.-S.; Lord, S. Introduction of the GSI into the NCEP Global Data Assimilation System. Weather Forecast. 2009, 24, 1691–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chin, M. Coauthors, Tropospheric aerosol optical thick ness from the GOCART model and comparisons with satellite and sun photometer measurements. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 461–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colarco, P.R.; da Silva, A.; Chin, M.; Diehl, T. Online simulations of global aerosol distributions in the NASA GEOS-4 model and comparisons to satellite and ground-based aerosol optical depth. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D14207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buchard, V.; Randles, C.A.; Silva, A.M.D.; Darmenov, A.; Colarco, P.R.; Govindaraju, R.; Ferrare, R.; Hair, J.; Beyersdorf, A.J.; Ziemba, L.D.; et al. The MERRA-2 aerosol reanalysis, 1980 onward. Part II: Evaluation and case studies. J. Climate. 2017, 30, 6851–6872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, E.; Xu, X.; Che, H.; Tang, Z.; Gui, K.; An, L.; Lu, C.; Shi, G. Variation in MERRA-2 aerosol optical depth and absorption aerosol optical depth over China from 1980 to 2017. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2019, 186, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, K., VII. Mathematical contributions to the theory of evolution—III. Regression, heredity, and panmixia. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1896, 187, 253–318. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Chen, Q.; Che, H.; Zhang, R.; Gui, K.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, T. Spatial distribution and temporal variation of aerosol optical depth in the Sichuan basin, China, the recent ten years. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 147, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Pan, Y.; Mo, Z. Joint Effects of Several Factors on Cloud-to-Ground Lightning and Rainfall in Nanning (China). Atmos. Res. 2018, 212, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Wang, H.; Tan, Y.; Li, L.; Li, C. Influence of Aerosols on Lightning Activities in Central Eastern Parts of China. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2020, 21, e957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khain, A.P.; BenMoshe, N.; Pokrovsky, A. Factors Determining the Impact of Aerosols on Surface Precipitation from Clouds: An Attempt at Classification. J. Atmos. Sci. 2008, 65, 1721–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, D.; Rudich, Y.; Lahav, R. Desert dust suppressing precipitation: A possible desertification feedback loop. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 5975–5980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khain, A.; Pokrovsky, A.; Pinsky, M.; Seifert, A.; Phillips, V. Simulation of effects of atmospheric aerosols on deep turbulent convective clouds using a spectral microphysics mixed-phase cumulus cloud model. Part I: Model description and possible applications. J. Atmos. Sci. 2004, 61, 2963–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, C.; Tie, X.; Lin, Y. A possible positive feedback of reduction of precipitation and increase in aerosols over eastern central China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L11814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khain, A.P. Notes on state-of-the-art investigations of aerosol effects on precipitation: A critical review. Environ. Res. Lett. 2009, 4, 015004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.S. Dependence of aerosol–precipitation interactions on humidity in a multiple-cloud system. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 2179–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, J.; Yuan, T.; Comstock, J.M.; Ghan, S.; Khain, A.; Leung, L.R.; Li, Z.Q.; Martins, M.J.; Ovchinnikov, M. Dominant role by vertical wind shear in regulating aerosol effects on deep convective clouds. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, D22206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiger, S.M.; Orville, R.E.; Huffines, G. Cloud-to-ground lightning characteristics over Houston, Texas: 1989–2000. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, 4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Yin, Y.; Xiao, H. The effects of aerosol on development of thunderstorm electrification: A numerical study. Atmos. Res. 2015, 153, 376–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Tao, S.; Liang, Z.; Zhu, B. Numerical study on relationship between lightning types and distribution of space charge and electric potential. J. Geophys. Res. 2014, 119, 1003–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, T.C.; Rust, W.D. Electric field soundings through thunderstorms. J. Geophys. Res. 1991, 96, 22297–22306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siingh, D.; Singh, A.K.; Patel, R.P.; Singh, R.; Singh, R.P.; Veenadhari, B.; Mukherjee, M. Thunderstorms, lightning, sprites and magnetospheric whistler-mode radio waves. Surv. Geophys. 2008, 29, 499–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Avila, E.E.; Pereyra, R.G.; Varela, G.G.A.; Caranti, G.M. The effect of the cloud-droplet spectrum on electrical-charge transfer during individual ice-ice collisions. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1999, 125, 1669–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Shi, Z.; Wang, X.; Tan, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, L.; Lin, X. Cloud-to-Ground Lightning Response to Aerosol over Air-Polluted Urban Areas in China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13132600
Wang H, Shi Z, Wang X, Tan Y, Wang H, Li L, Lin X. Cloud-to-Ground Lightning Response to Aerosol over Air-Polluted Urban Areas in China. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(13):2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13132600
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Haichao, Zheng Shi, Xuejuan Wang, Yongbo Tan, Honglei Wang, Luying Li, and Xiaotong Lin. 2021. "Cloud-to-Ground Lightning Response to Aerosol over Air-Polluted Urban Areas in China" Remote Sensing 13, no. 13: 2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13132600
APA StyleWang, H., Shi, Z., Wang, X., Tan, Y., Wang, H., Li, L., & Lin, X. (2021). Cloud-to-Ground Lightning Response to Aerosol over Air-Polluted Urban Areas in China. Remote Sensing, 13(13), 2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13132600