Multi-Scale Spatiotemporal Change Characteristics Analysis of High-Frequency Disturbance Forest Ecosystem Based on Improved Spatiotemporal Cube Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
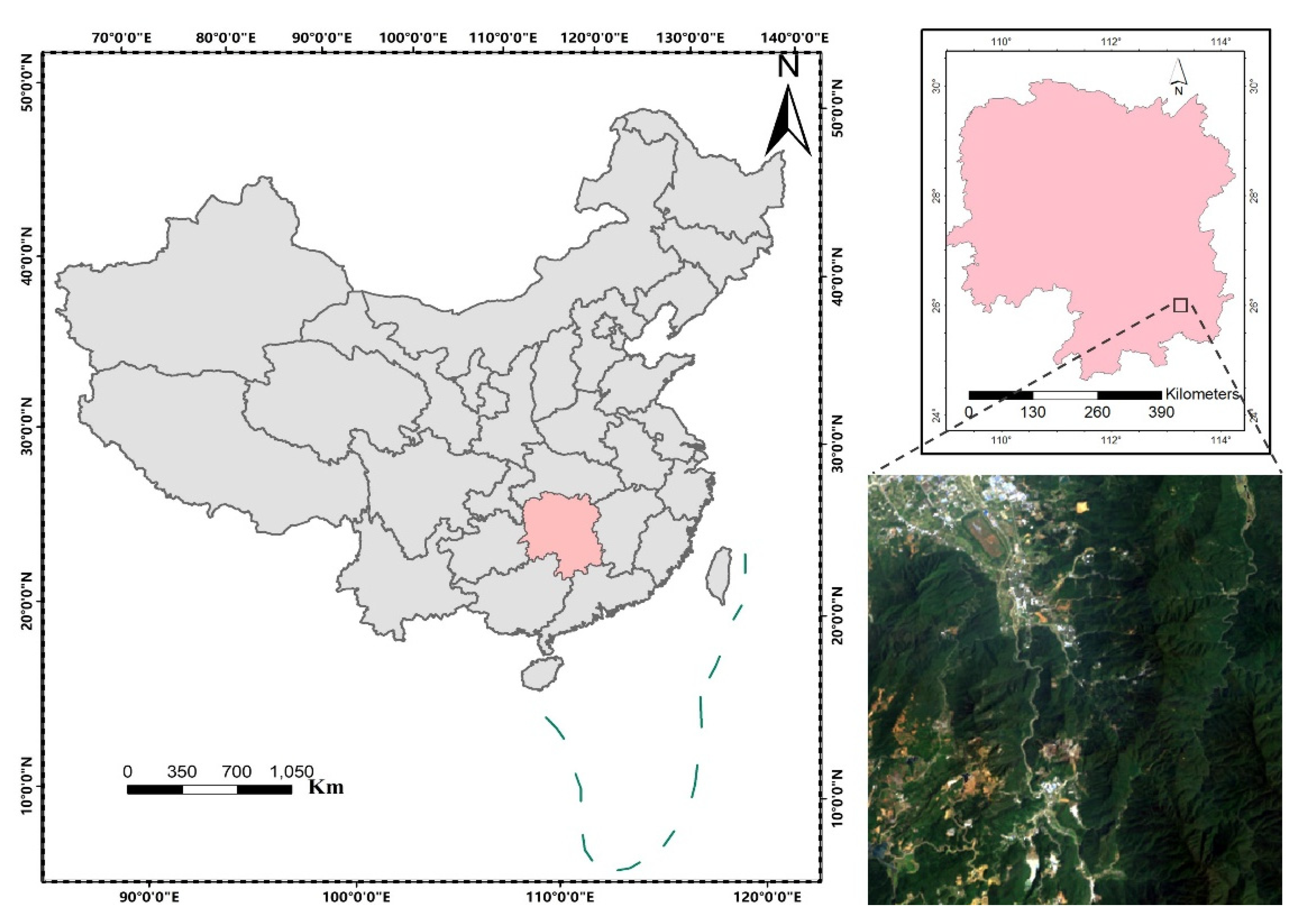
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Preparation
2.2.1. Landsat Time Series and Annual Composite Data
2.2.2. Meteorological Data
2.3. Methodology
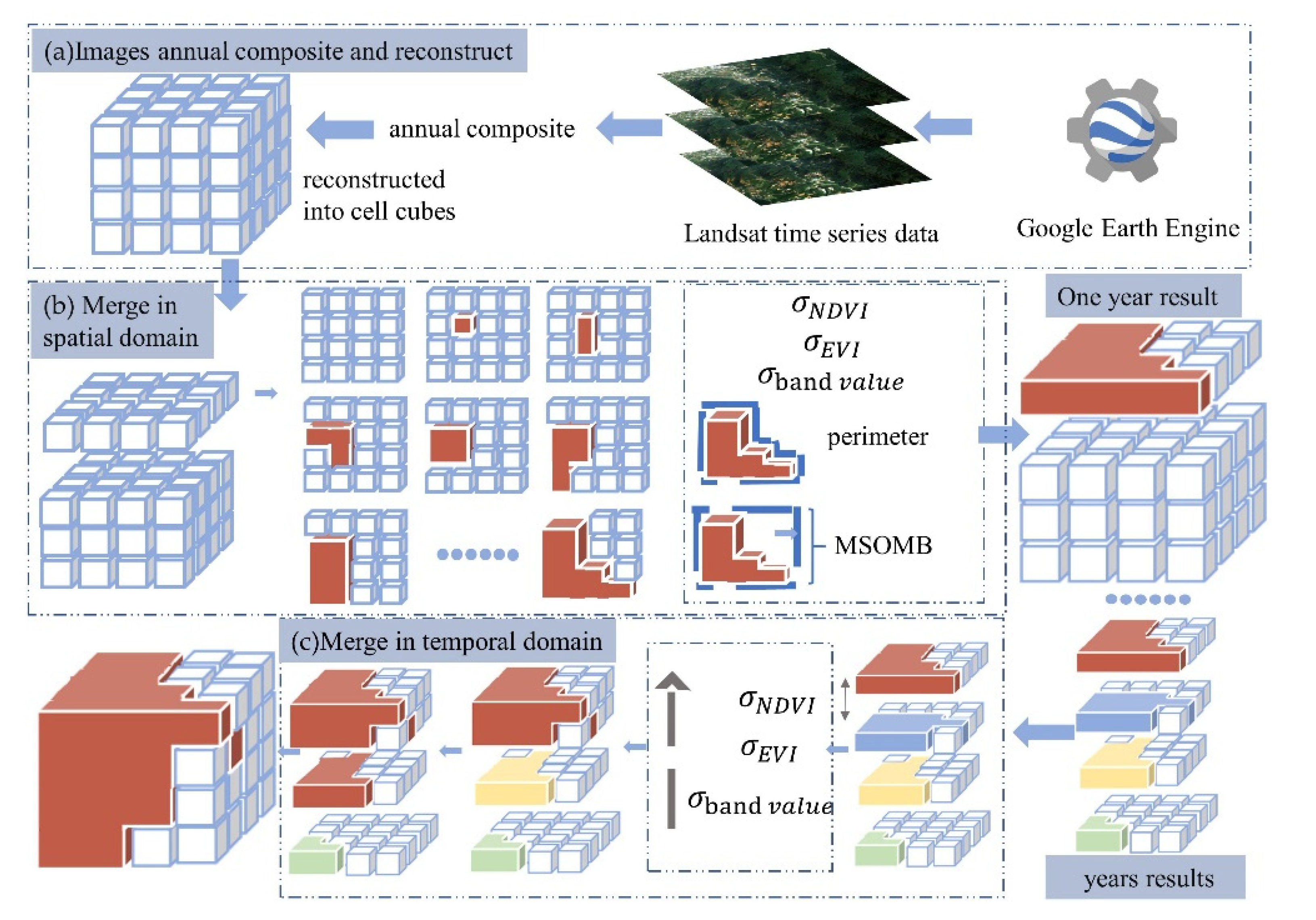
2.3.1. Overview of ST-Cube Model
- (1)
- Expression and representative significance of ST-cube
- (2)
- Spatiotemporal neighborhoods
- (3)
- Spatiotemporal heterogeneity criterion
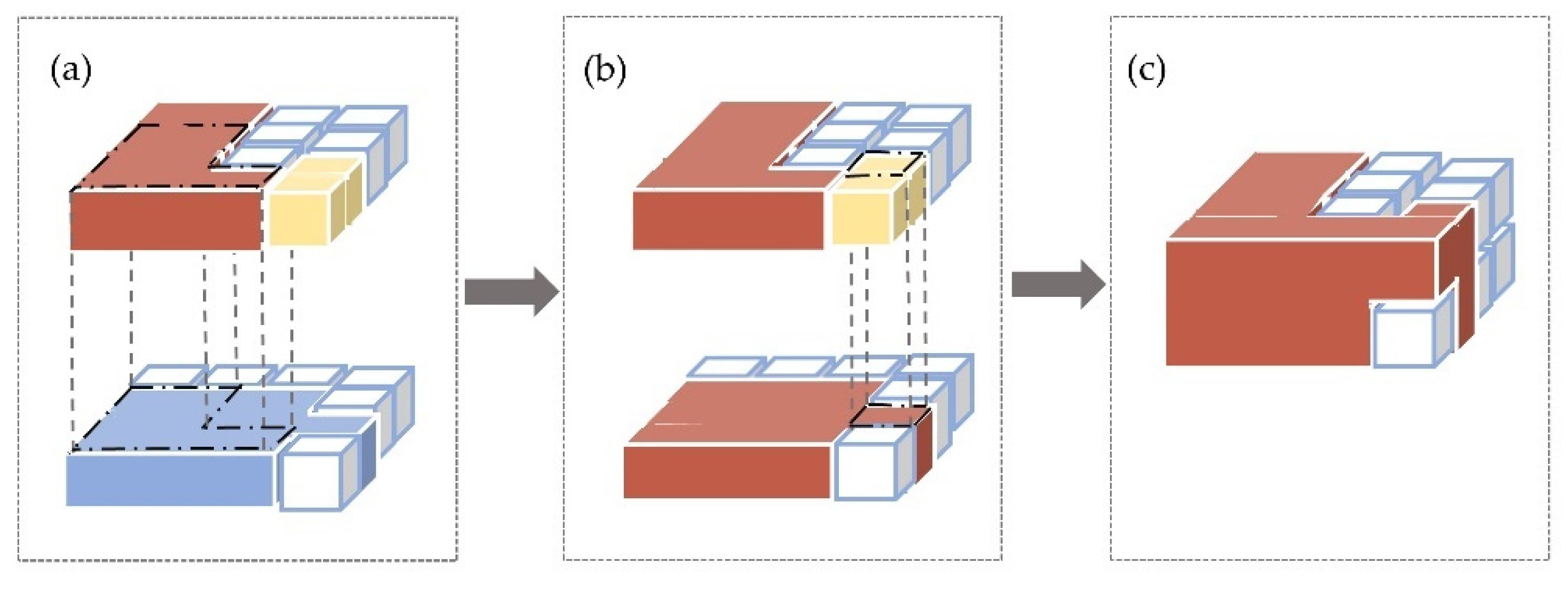
2.3.2. IST-Cube Model
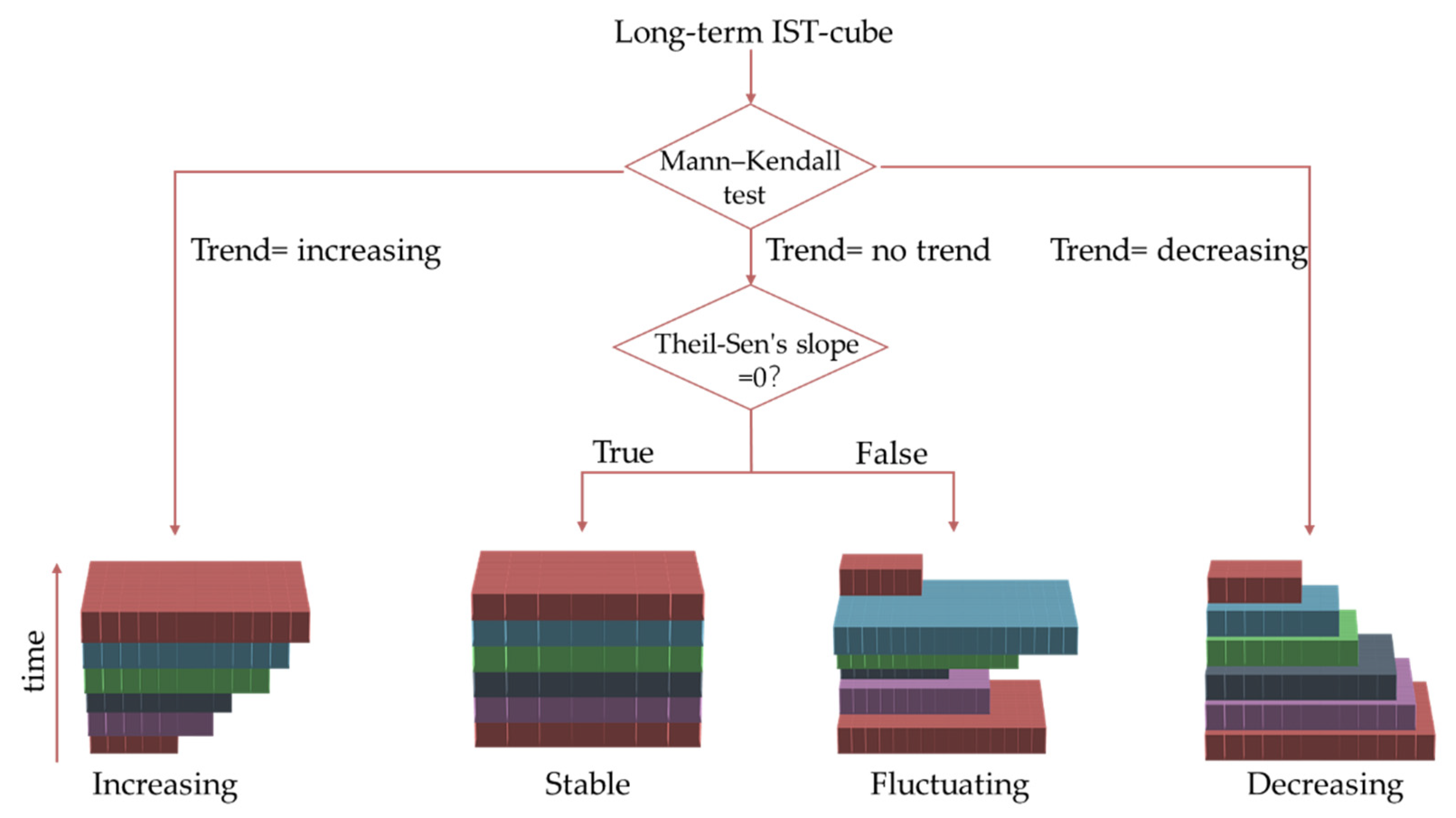
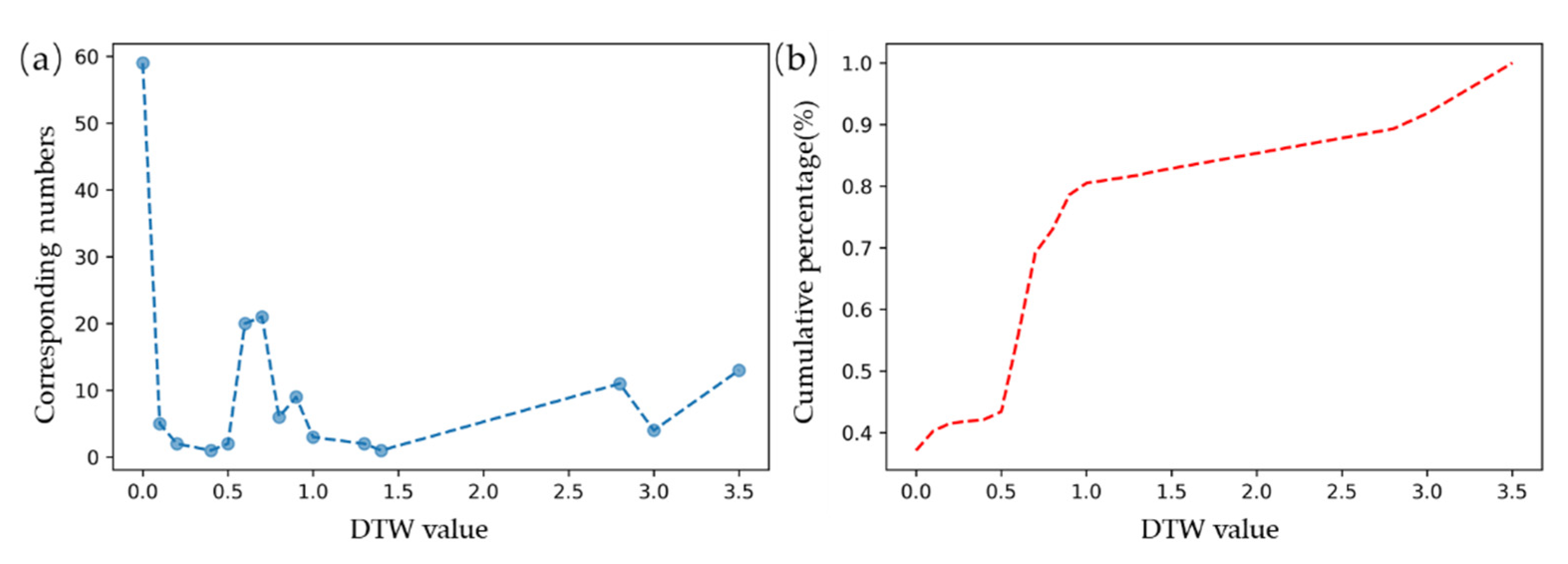
2.3.3. Characteristic Analysis of the IST-Cube
3. Results
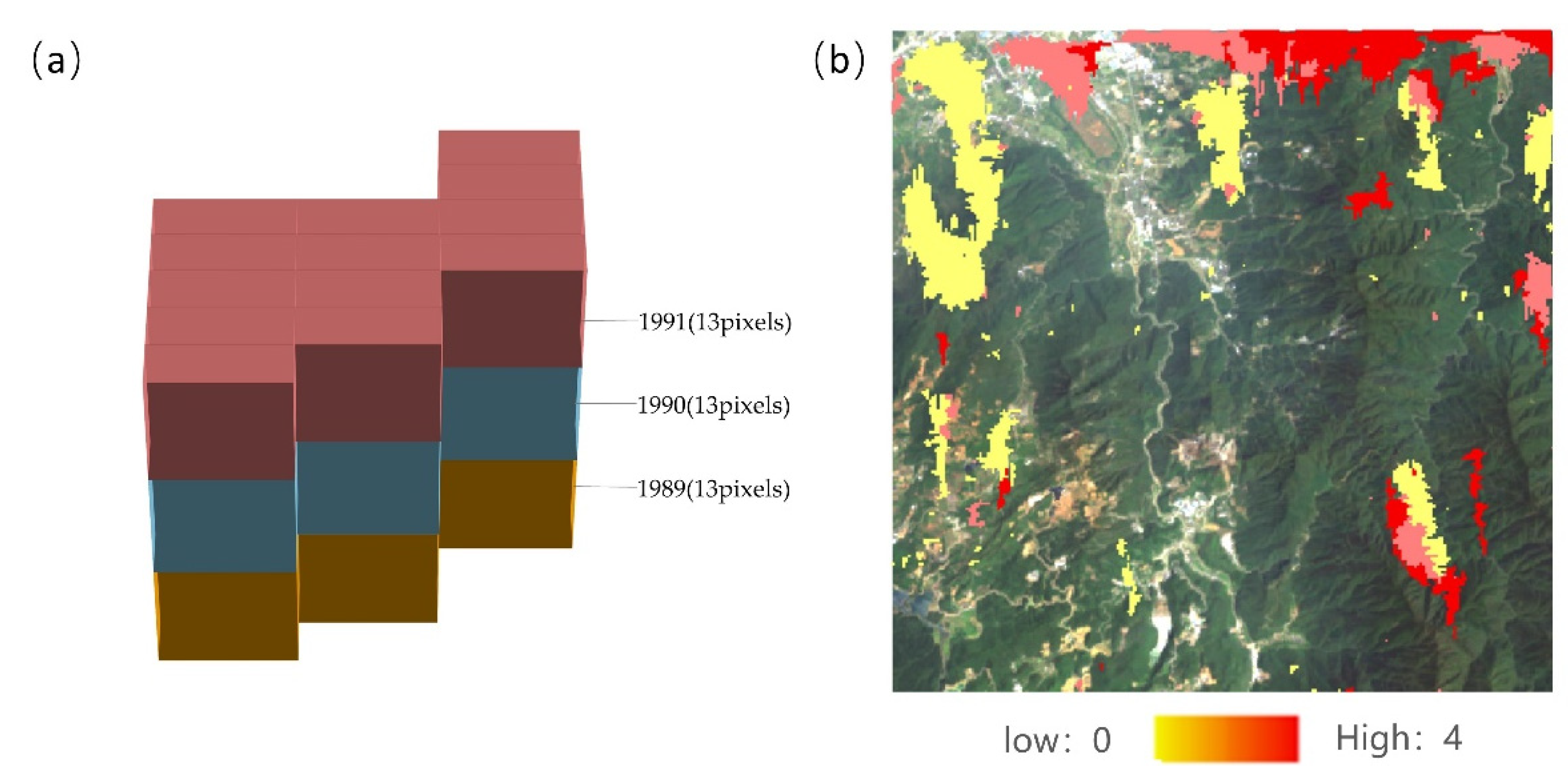
3.1. Long-Term Large Scope IST-Cube
3.2. Long-Term Small Scope IST-Cube
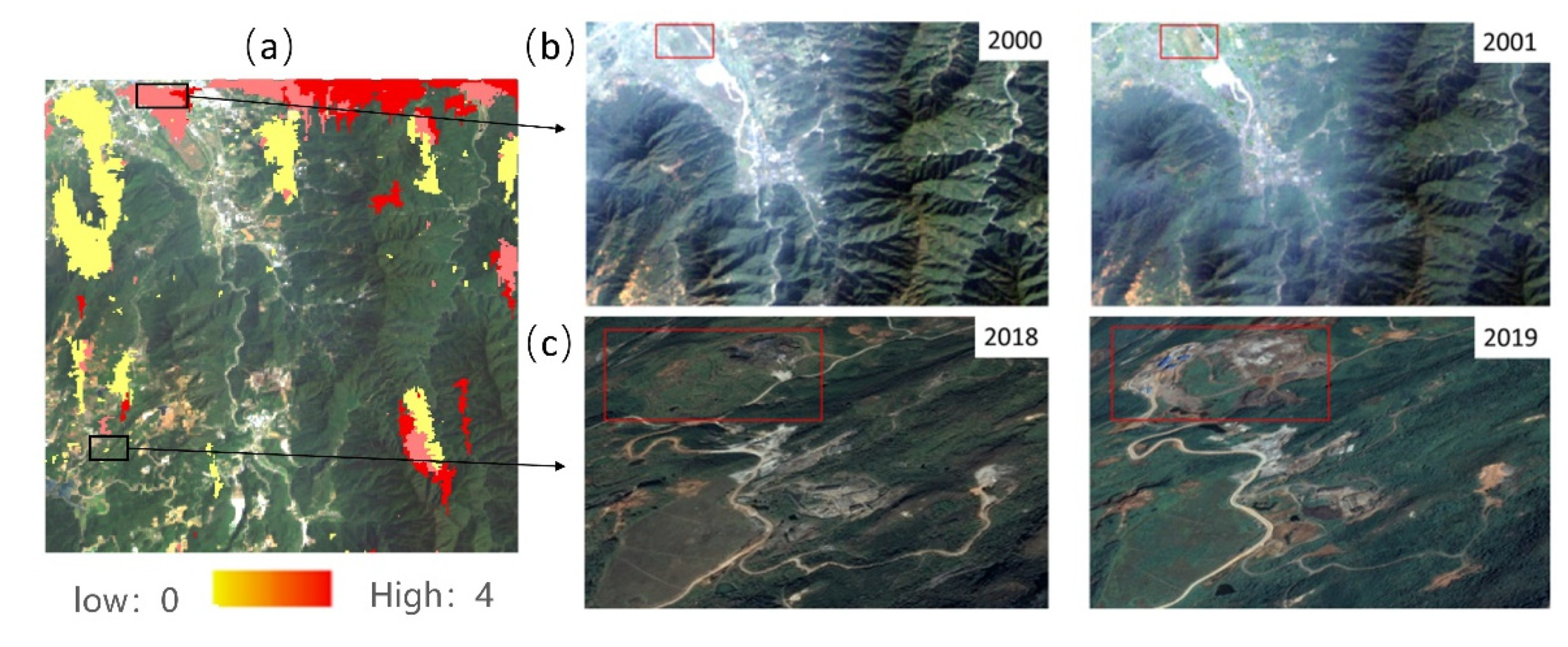
3.3. Short-Term Large Scope IST-Cube
3.4. Short-Term Small Scope IST-Cube
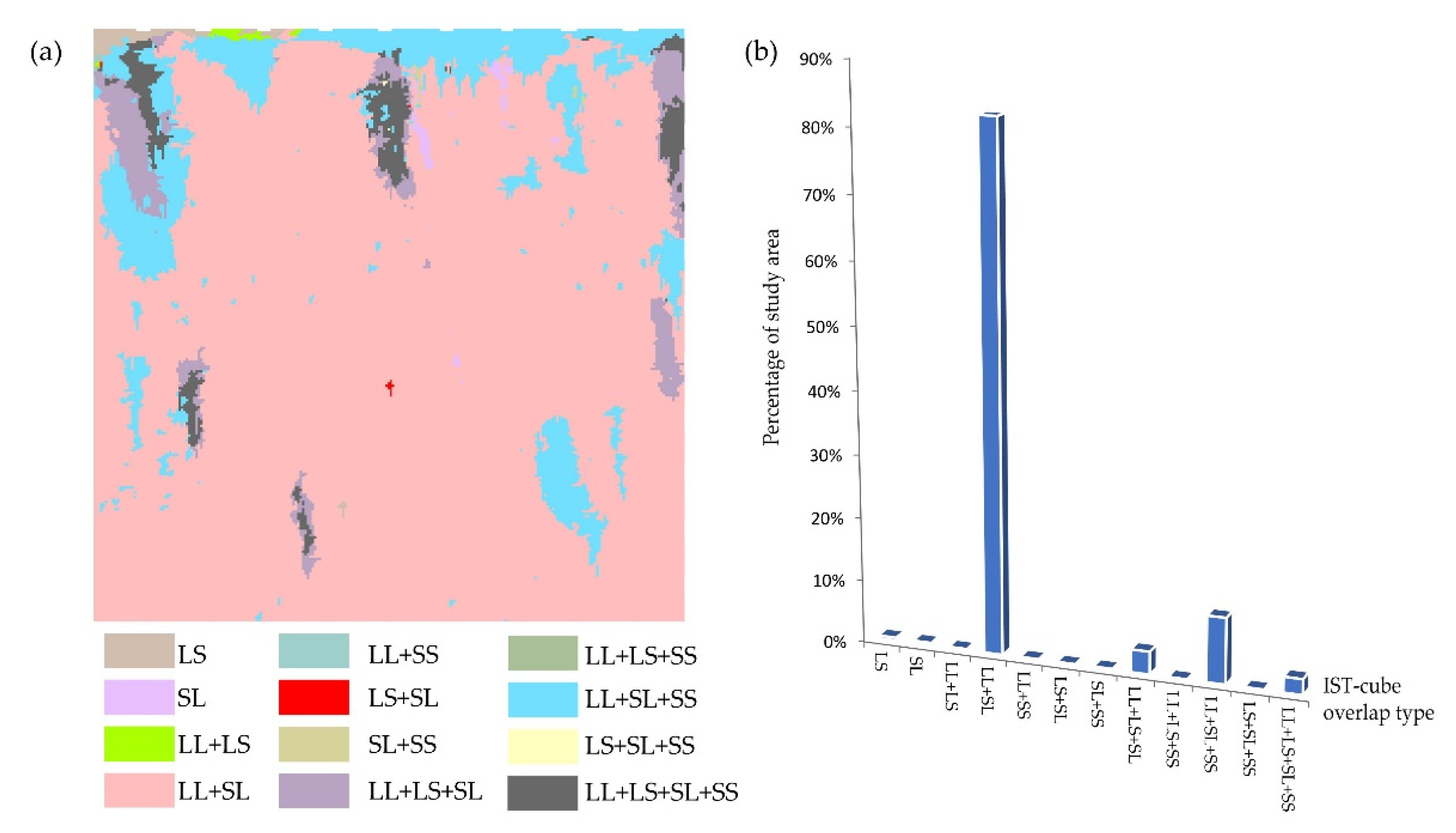
3.5. Overlap of Different IST-Cube Types
4. Discussion
4.1. Validation with Literature
4.2. Advantages of IST-Cube and Other Potential Uses
4.3. Limitations and Future Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fujii, S.; Mori, A.S.; Koide, D.; Makoto, K.; Matsuoka, S.; Osono, T.; Isbell, F. Disentangling relationships between plant diversity and decomposition processes under forest restoration. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 54, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, P.G.; Slay, C.M.; Harris, N.L.; Tyukavina, A.; Hansen, M.C. Classifying drivers of global forest loss. Science 2018, 361, 1108–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturrock, R.; Frankel, S.; Brown, A.; Hennon, P.; Kliejunas, J.; Lewis, K.; Worrall, J.; Woods, A. Climate change and forest diseases. Plant Pathol. 2011, 60, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, J.E.; Evans, T.; Venter, O.; Williams, B.; Tulloch, A.; Stewart, C.; Thompson, I.; Ray, J.C.; Murray, K.; Salazar, A. The exceptional value of intact forest ecosystems. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overpeck, J.T.; Rind, D.; Goldberg, R. Climate-induced changes in forest disturbance and vegetation. Nature 1990, 343, 51–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynard, D.; Paré, D.; Thiffault, E.; Lafleur, B.; Hogg, K.; Kishchuk, B. How do natural disturbances and human activities affect soils and tree nutrition and growth in the Canadian boreal forest? Environ. Rev. 2014, 22, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Forest soils and carbon sequestration. For. Ecol. Manag. 2005, 220, 242–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Karger, D.N.; Wilson, A.M. Spatial detection of alpine treeline ecotones in the Western United States. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawchuk, M.A.; Meigs, G.W.; Cartwright, J.M.; Coop, J.D.; Davis, R.; Holz, A.; Kolden, C.; Meddens, A.J. Disturbance refugia within mosaics of forest fire, drought, and insect outbreaks. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2020, 18, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshleman, K.N.; McNeil, B.E.; Townsend, P.A. Validation of a remote sensing based index of forest disturbance using streamwater nitrogen data. Ecol. Indic. 2009, 9, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, N.G.; Coops, N.C.; Beck, P.S.; Chambers, J.Q.; Gangodagamage, C.; Hicke, J.A.; Huang, C.-y.; Kennedy, R.; Krofcheck, D.J.; Litvak, M. Global satellite monitoring of climate-induced vegetation disturbances. Trends Plant Sci. 2015, 20, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wulder, M.A.; Kurz, W.A.; Gillis, M. National level forest monitoring and modeling in Canada. Prog. Plan. 2004, 61, 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermosilla, T.; Wulder, M.A.; White, J.C.; Coops, N.C. Prevalence of multiple forest disturbances and impact on vegetation regrowth from interannual Landsat time series (1985–2015). Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 233, 111403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banskota, A.; Kayastha, N.; Falkowski, M.J.; Wulder, M.A.; Froese, R.E.; White, J.C. Forest monitoring using Landsat time series data: A review. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 40, 362–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, K.; Ota, T.; Mizoue, N. Detecting forest changes using dense Landsat 8 and Sentinel-1 time series data in tropical seasonal forests. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kayet, N.; Pathak, K.; Chakrabarty, A.; Singh, C.P.; Sahoo, S. Forest health assessment for geo-environmental planning and management in hilltop mining areas using Hyperion and Landsat data. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 106, 105471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-L.; Zhao, H.-M.; Li, P.-X.; Yin, Z.-Y. Remote sensing image-based analysis of the relationship between urban heat island and land use/cover changes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 104, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.D.; Chen, D. Segmentation for object-based image analysis (obia): A review of algorithms and challenges from remote sensing perspective. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 150, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhao, H.; Yin, P.; Jia, D.; Li, G. Remote sensing classification method of vegetation dynamics based on time series Landsat image: A case of opencast mining area in China. EURASIP J. Image Video Process. 2018, 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero Espejo, J.; Messinger, M.; Román-Dañobeytia, F.; Ascorra, C.; Fernandez, L.E.; Silman, M. Deforestation and forest degradation due to gold mining in the Peruvian Amazon: A 34-year perspective. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Souza-Filho, P.W.M.; Nascimento, W.R.; Santos, D.C.; Weber, E.J.; Silva, R.O.; Siqueira, J.O. A GEOBIA approach for multitemporal land-cover and land-use change analysis in a tropical watershed in the southeastern Amazon. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hermosilla, T.; Wulder, M.A.; White, J.C.; Coops, N.C.; Hobart, G.W. Regional detection, characterization, and attribution of annual forest change from 1984 to 2012 using Landsat-derived time-series metrics. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 170, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, J.; Zipper, C.E.; Shen, Y.; Miao, H.; Donovan, P.F. Identification of the disturbance and trajectory types in mining areas using multitemporal remote sensing images. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 916–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Liu, X.; Ding, C.; Xu, B.; Zhou, G.; Zhu, L. Analysis of ecological resilience to evaluate the inherent maintenance capacity of a forest ecosystem using a dense Landsat time series. Ecol. Inform. 2020, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, W.B.; Yang, Z.; Healey, S.P.; Kennedy, R.E.; Gorelick, N. A LandTrendr multispectral ensemble for forest disturbance detection. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 205, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, W.B.; Healey, S.P.; Yang, Z.; Stehman, S.V.; Brewer, C.K.; Brooks, E.B.; Gorelick, N.; Huang, C.; Hughes, M.J.; Kennedy, R.E. How similar are forest disturbance maps derived from different Landsat time series algorithms? Forests 2017, 8, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelmann, J.E.; Tolk, B.; Zhu, Z. Monitoring forest changes in the southwestern United States using multitemporal Landsat data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1739–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, R.E.; Yang, Z.; Cohen, W.B. Detecting trends in forest disturbance and recovery using yearly Landsat time series: 1. LandTrendr—Temporal segmentation algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2897–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Cho, N.; Son, S. Spatiotemporal characteristics of elderly population’s traffic accidents in Seoul using space-time cube and space-time kernel density estimation. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mo, C.; Tan, D.; Mai, T.; Bei, C.; Qin, J.; Pang, W.; Zhang, Z. An analysis of spatiotemporal pattern for COIVD-19 in China based on space-time cube. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 1587–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xi, W.; Du, S.; Wang, Y.-C.; Zhang, X. A spatiotemporal cube model for analyzing satellite image time series: Application to land-cover mapping and change detection. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trumbore, S.; Brando, P.; Hartmann, H. Forest health and global change. Science 2015, 349, 814–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Upadhyay, T.; Sankhayan, P.L.; Solberg, B. A review of carbon sequestration dynamics in the Himalayan region as a function of land-use change and forest/soil degradation with special reference to Nepal. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 105, 449–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Venevsky, S.; Wu, C.; Wang, M. NDVI-based vegetation dynamics and its response to climate changes at Amur-Heilongjiang River Basin from 1982 to 2015. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2051–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamchin, M.; Lee, W.-K.; Jeon, S.W.; Wang, S.W.; Lim, C.H.; Song, C.; Sung, M. Long-term trend and correlation between vegetation greenness and climate variables in Asia based on satellite data. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.J.; Holben, B.N.; Goff, T.E. Intensive forest clearing in Rondonia, Brazil, as detected by satellite remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 1984, 15, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Fu, Y.; Woodcock, C.E.; Olofsson, P.; Vogelmann, J.E.; Holden, C.; Wang, M.; Dai, S.; Yu, Y. Including land cover change in analysis of greenness trends using all available Landsat 5, 7, and 8 images: A case study from Guangzhou, China (2000–2014). Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Peng, W.; Lan, Y.; Luo, S.; Shao, J.; Chen, D.; Wang, G. Assessing climate impact on forest cover in areas undergoing substantial land cover change using Landsat imagery. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 732–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurung, R.B.; Breidt, F.J.; Dutin, A.; Ogle, S.M. Predicting Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI) curves for ecosystem modeling applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2186–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tan, R. Trace Element Geochemistry of Devonian Strata in the Shizhuyuan Ore District, Hunan Province. Acta Geol. Sin. 2017, 1, 175–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frazier, R.J.; Coops, N.C.; Wulder, M.A.; Hermosilla, T.; White, J.C. Analyzing spatial and temporal variability in short-term rates of post-fire vegetation return from Landsat time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 205, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, N.; Hassan, M.A.; Zhao, L. Assessing the defoliation of pine forests in a long time-series and spatiotemporal prediction of the defoliation using Landsat data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, Z.; Phinn, S.R.; Game, E.T.; Pannell, D.J.; Hobbs, R.J.; Briggs, P.R.; McDonald-Madden, E. Using Landsat observations (1988–2017) and Google Earth Engine to detect vegetation cover changes in rangelands-A first step towards identifying degraded lands for conservation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 232, 111317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-scale geospatial analysis for everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, E.M.; Gorelick, S.M. Drying drives decline in muskrat population in the Peace-Athabasca Delta, Canada. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 124026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, L.J.; Burnett, R.; Tietz, J.; Veloz, S. Recent drought and tree mortality effects on the avian community in southern Sierra Nevada: A glimpse of the future? Ecol. Appl. 2019, 29, e01848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; McBratney, A.B.; Malone, B.P.; Field, D.J. Mapping the transition from pre-European settlement to contemporary soil conditions in the Lower Hunter Valley, Australia. Geoderma 2018, 329, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K.; Braithwaite, D.; Ashouri, H. The NOAA CDR Program, 2014: NOAA Climate Data Record (CDR) of Precipitation Estimation from Remotely Sensed Information using Artificial Neural Networks (PERSIANN-CDR), version 1, revision 1. NOAA Natl. Cent. Environ. Inf. Accessed 2015, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashouri, H.; Hsu, K.L.; Sorooshian, S.; Braithwaite, D.K.; Knapp, K.R.; Cecil, L.D.; Nelson, B.R.; Prat, O.P. PERSIANNCDR: Daily precipitation climate data record from multisatellite observations for hydrological and climate studies. Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 2015, 96, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hunan Meteorological Bureau. Classification standard of flood and waterlogging weather in Hunan Province. Available online: http://hn.cma.gov.cn/xxgk/gkml/tzgg/202012/t20201202_2449482.html (accessed on 7 January 2021).
- Palmer, W.C. Meteorological Drought; US Department of Commerce, Weather Bureau: Washington, DC, USA, 1965; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, H.; Wang, S.Q.; Wang, J.B.; Lu, H.Q.; Guo, A.H.; Zhu, Z.C.; Myneni, R.B.; Shugart, H.H. Assessing spatiotemporal variation of drought in China and its impact on agriculture during 1982–2011 by using PDSI indices and agriculture drought survey data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 2283–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abatzoglou, J.T.; Dobrowski, S.Z.; Parks, S.A.; Hegewisch, K.C. TerraClimate, a high-resolution global dataset of monthly climate and climatic water balance from 1958–2015. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Tarpley, D.; Sullivan, J.T. Diverse responses of vegetation phenology to a warming climate. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Chen, Y.; Shen, M.; Chen, J.; Zhou, J.; Wang, C.; Yang, W. A simple method to improve the quality of NDVI time-series data by integrating spatiotemporal information with the Savitzky-Golay filter. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 217, 244–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinojo-Hinojo, C.; Goulden, M.L. Plant Traits Help Explain the Tight Relationship between Vegetation Indices and Gross Primary Production. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, D.A.; Rahman, A.F.; Cordova, V.D.; El-Masri, B.Z.; Baldocchi, D.D.; Flanagan, L.B.; Goldstein, A.H.; Hollinger, D.Y.; Misson, L.; Monson, R.K.; et al. On the use of MODIS EVI to assess gross primary productivity of North American ecosystems. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hashimoto, H.; Wang, W.; Milesi, C.; White, M.A.; Ganguly, S.; Gamo, M.; Hirata, R.; Myneni, R.B.; Nemani, R.R. Exploring Simple Algorithms for Estimating Gross Primary Production in Forested Areas from Satellite Data. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 303–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Son, N.; Chen, C.; Chen, C.; Minh, V.; Trung, N. A comparative analysis of multitemporal MODIS EVI and NDVI data for large-scale rice yield estimation. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 197, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liang, Q.; Liang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xie, S. Remote-sensing disturbance detection index to identify spatio-temporal varying flood impact on crop production. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 269–270, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Miura, T.; Rodriguez, E.P.; Gao, X.; Ferreira, L.G. Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Z.; Aljaddani, A.H.; Cohen, W.B.; Qiu, S.; Zhou, C. Continuous monitoring of land disturbance based on Landsat time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.; Bischof, L. Seeded region growing. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1994, 16, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ming, D.; Zhou, W.; Xu, L.; Wang, M.; Ma, Y. Coupling relationship among scale parameter, segmentation accuracy, and classification accuracy in geobia. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2018, 84, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baatz, M. Multi resolution segmentation: An optimum approach for high quality multi scale image segmentation. In Beutrage zum AGIT-Symposium; Salzburg: Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 12–23. [Google Scholar]
- Drăguţ, L.; Csillik, O.; Eisank, C.; Tiede, D. Automated parameterisation for multi-scale image segmentation on multiple layers. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 88, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hussain, M.M.; Mahmud, I. pyMannKendall: A python package for non parametric Mann Kendall family of trend tests. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellman, R.; Kalaba, R. On adaptive control processes. IRE Trans. Autom. Control 1959, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitjean, F.; Inglada, J.; Gançarski, P. Satellite image time series analysis under time warping. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 3081–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Huang, C.; Liu, G.; Meng, X.; Liu, Q. Mapping rice cropping systems in Vietnam using an NDVI-based time-series similarity measurement based on DTW distance. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wannes Meert, K.H. Toon Van Craenendonck. (Version v2.0.0). Available online: https://github.com/wannesm/dtaidistance (accessed on 8 January 2021).
- Mueen, A.; Keogh, E. Extracting optimal performance from dynamic time warping. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 2129–2130. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Zhan, Q.; Yang, C.; Wang, J. Characterizing the spatio-temporal pattern of land surface temperature through time series clustering: Based on the latent pattern and morphology. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chazdon, R.L. Tropical forest recovery: Legacies of human impact and natural disturbances. Perspect. Plant Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2003, 6, 51–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Canadell, J.G.; Kirschbaum, M.U.; Kurz, W.A.; Sanz, M.-J.; Schlamadinger, B.; Yamagata, Y. Factoring out natural and indirect human effects on terrestrial carbon sources and sinks. Environ. Sci. Policy 2007, 10, 370–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetter, M.; Wirth, C.; Böttcher, H.; Churkina, G.; Schulze, E.D.; Wutzler, T.; Weber, G. Partitioning direct and indirect human-induced effects on carbon sequestration of managed coniferous forests using model simulations and forest inventories. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2005, 11, 810–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, K.; Behera, B. Forest cover change and flood hazards in India. Land Use Policy 2017, 67, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Tan, H.; Zhou, J.; Li, S.; Yang, T.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Tang, X.; Sun, Z.; Wen, S.W. An epidemiologic study of posttraumatic stress disorder in flood victims in Hunan China. Can. J. Psychiat. 2006, 51, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Tan, H.; Zhou, J.; Yang, T.; Benjamin, A.; Wen, S.W.; Li, S.; Liu, A.; Li, X.; Fen, S. Flood hazard in Hunan province of China: An economic loss analysis. Nat. Hazard. 2008, 47, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Fang, J.; Xu, W.; Shi, P. Analysis of dry/wet conditions using the standardized precipitation index and its potential usefulness for drought/flood monitoring in Hunan Province, China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2013, 27, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Yin, H.; Xu, S.; Zhao, Y. Risk factors for posttraumatic stress reactions among Chinese students following exposure to a snowstorm disaster. BMC Public Health 2011, 11, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, L.; Fan, Y. Yearbook of Meterorological Disasters in China; China Meteorological Press: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, S.A.; Nakagoshi, N. Forest fragmentation and its correlation to human land use change in the state of Selangor, peninsular Malaysia. For. Ecol. Manag. 2007, 241, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viedma, O.; Moreno, J.M.; Rieiro, I. Interactions between land use/land cover change, forest fires and landscape structure in Sierra de Gredos (Central Spain). Environ. Conserv. 2006, 33, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Li, J.; Sheng, C.; Xu, J.; Wu, L. A review of wetland remote sensing. Sensors 2017, 17, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, C.; Ren, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Man, W.; Yu, H.; Gao, Y.; Liu, M. Monitoring and Assessment of Wetland Loss and Fragmentation in the Cross-Boundary Protected Area: A Case Study of Wusuli River Basin. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keppel, G.; Van Niel, K.P.; Wardell-Johnson, G.W.; Yates, C.J.; Byrne, M.; Mucina, L.; Schut, A.G.T.; Hopper, S.D.; Franklin, S.E. Refugia: Identifying and understanding safe havens for biodiversity under climate change. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2012, 21, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lausch, A.; Bastian, O.; Klotz, S.; Leitão, P.J.; Jung, A.; Rocchini, D.; Schaepman, M.E.; Skidmore, A.K.; Tischendorf, L.; Knapp, S. Understanding and assessing vegetation health by in situ species and remote-sensing approaches. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2018, 9, 1799–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Rogan, J.; Zhu, Z.; Eastman, J.R. A near-real-time approach for monitoring forest disturbance using Landsat time series: Stochastic continuous change detection. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 252, 112167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masek, J.G.; Goward, S.N.; Kennedy, R.E.; Cohen, W.B.; Moisen, G.G.; Schleeweis, K.; Huang, C. United States forest disturbance trends observed using Landsat time series. Ecosystems 2013, 16, 1087–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


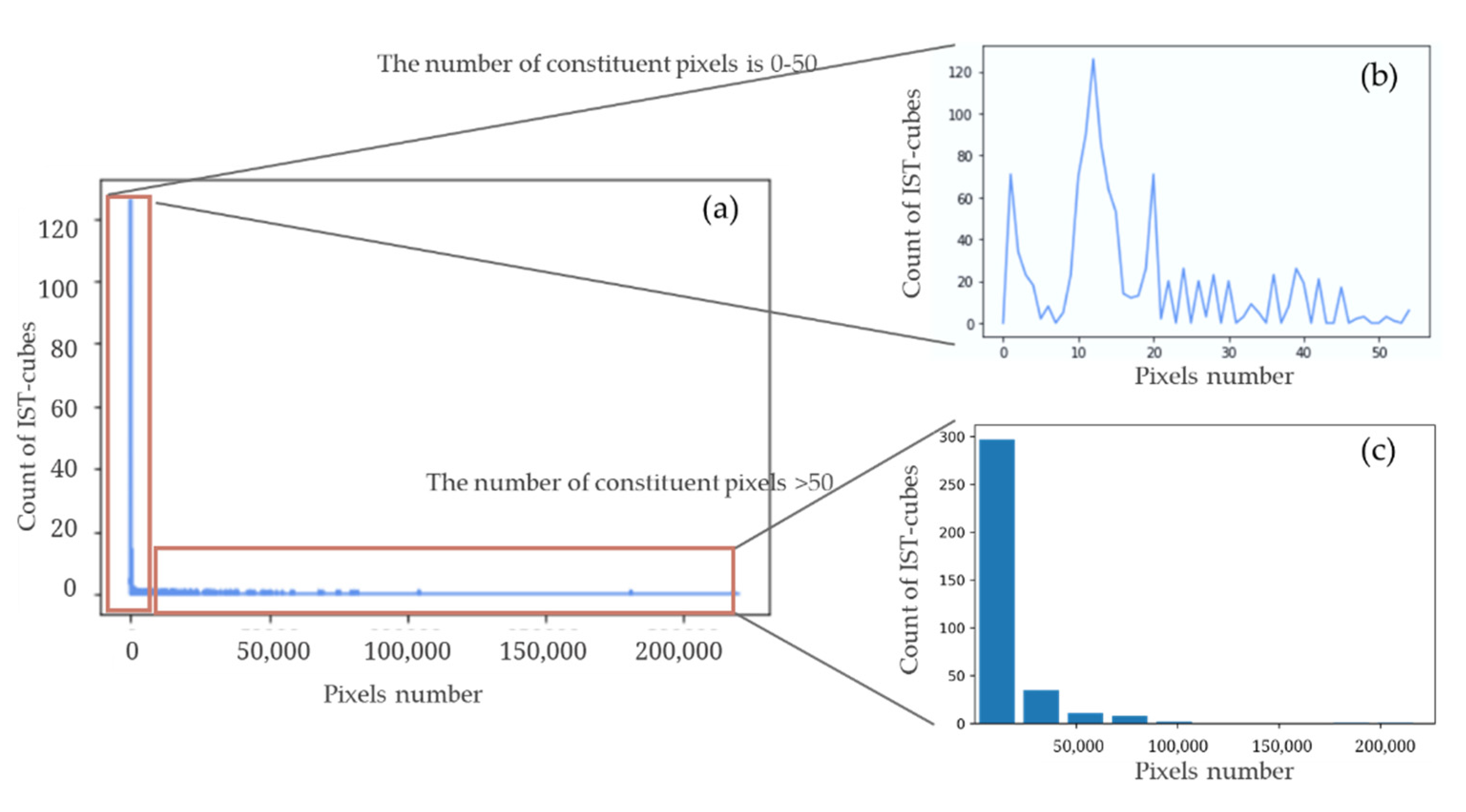


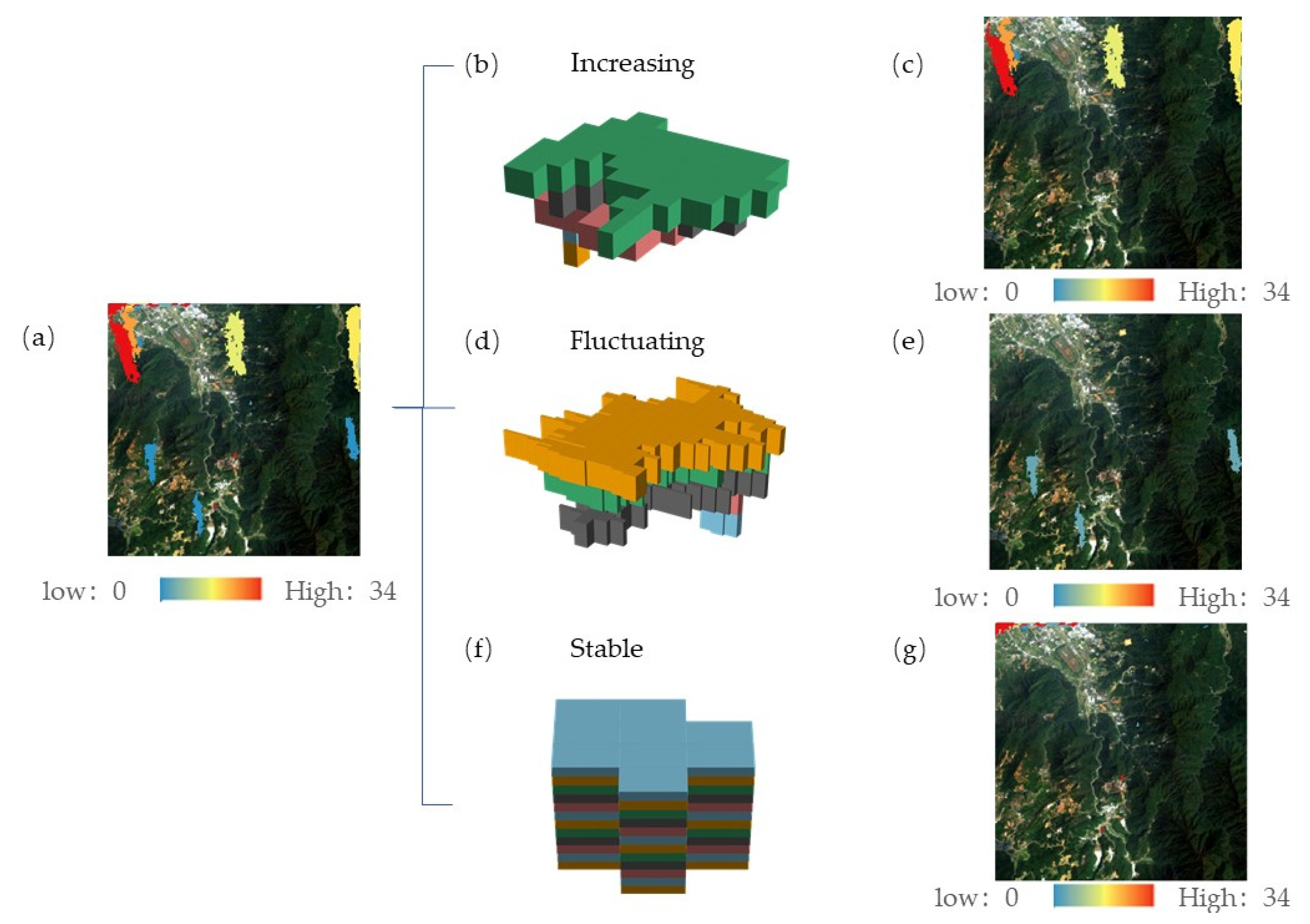
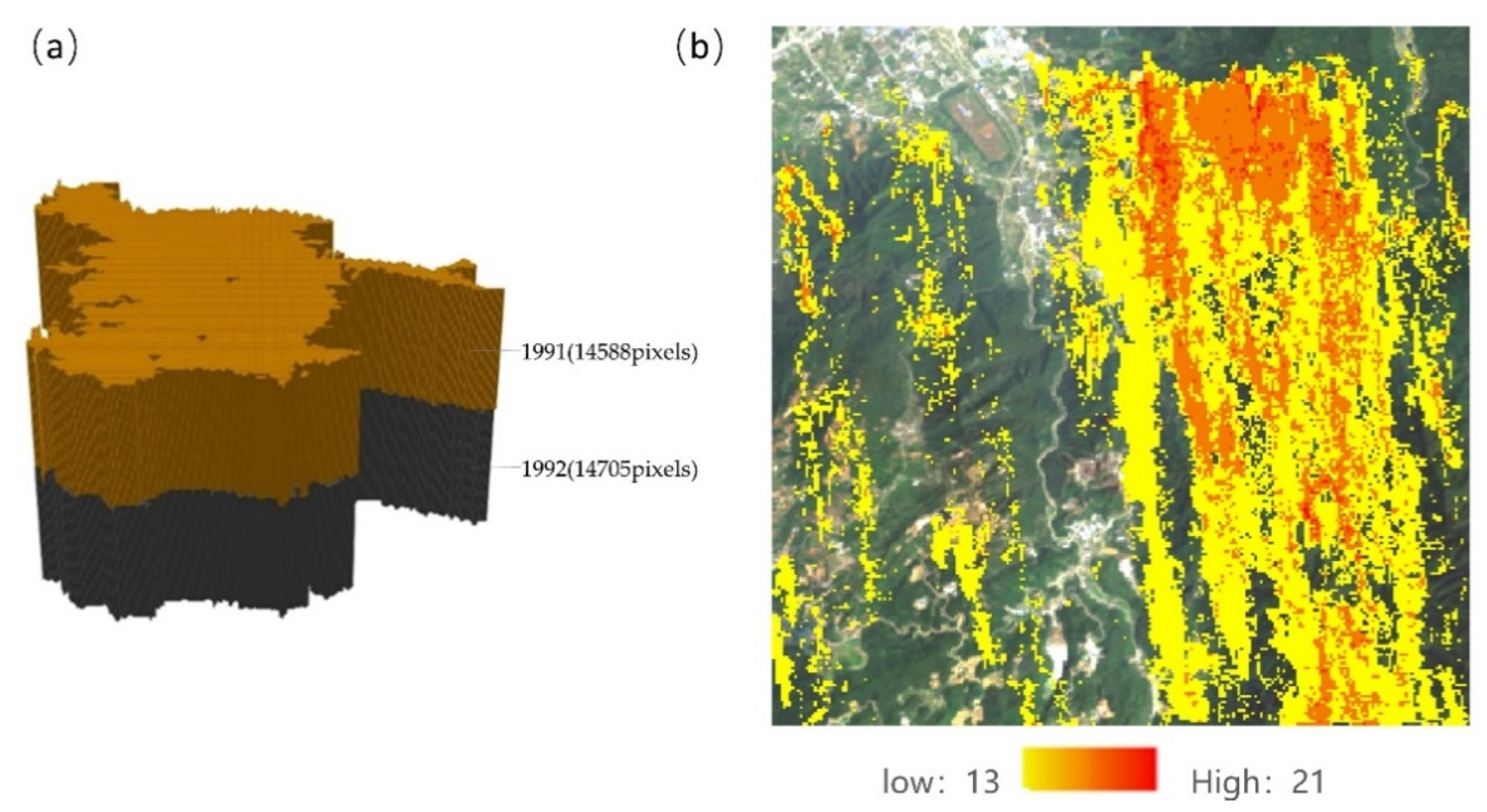

| Duration ≥ 5 Years | Average Number of Pixels per Year ≥ 300 Pixels | IST-Cube Type | Abbreviations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | Yes | long-term-large scope | LL |
| Yes | No | long-term-small scope | LS |
| No | Yes | short-term-large scope | SL |
| No | No | short-term-small scope | SS |
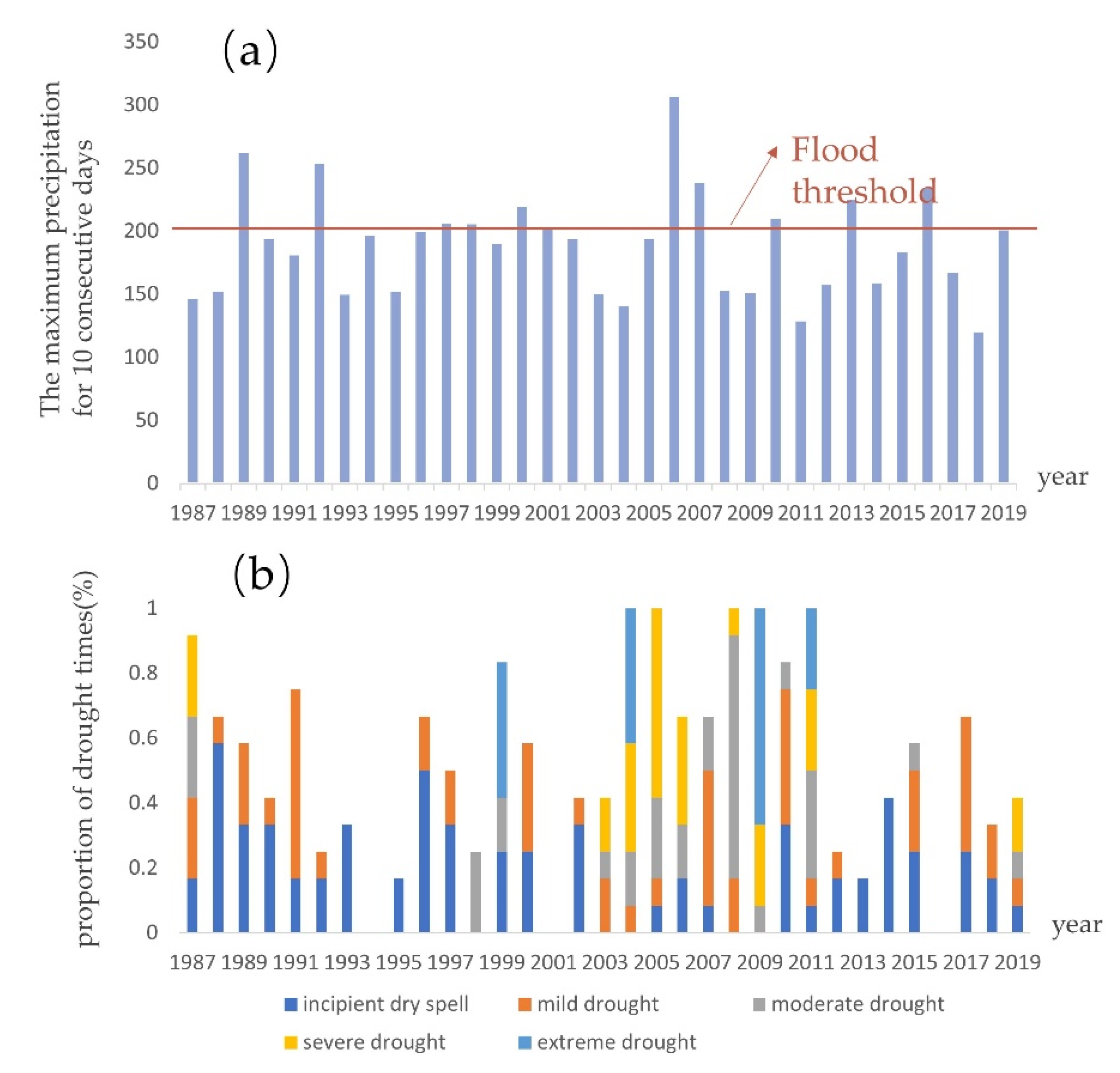
| Year | Flood | Drought Class | Is Detected |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1987 | none | Severe | no |
| 1988 | none | Moderate | yes |
| 1989 | moderate | Moderate | no |
| 1990 | none | Mild | yes |
| 1991 | none | Severe | no |
| 1992 | moderate | Mild | yes |
| 1993 | none | Mild | no |
| 1994 | none | None | no |
| 1995 | none | None | no |
| 1996 | mild | Moderate | yes |
| 1997 | mild | Moderate | no |
| 1998 | mild | Mild | yes |
| 1999 | none | Severe | no |
| 2000 | mild | Moderate | no |
| 2001 | mild | None | no |
| 2002 | none | Mild | no |
| 2003 | none | Mild | no |
| 2004 | none | Severe | no |
| 2005 | none | Severe | no |
| 2006 | severe | Moderate | yes |
| 2007 | mild | Moderate | no |
| 2008 | none | Severe | yes |
| 2009 | none | Severe | no |
| 2010 | mild | Severe | yes |
| 2011 | none | Severe | no |
| 2012 | none | Mild | yes |
| 2013 | mild | None | no |
| 2014 | none | Mild | yes |
| 2015 | none | Moderate | no |
| 2016 | mild | None | yes |
| 2017 | none | Moderate | no |
| 2018 | none | Mild | no |
| 2019 | mild | Mild | no |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, M.; Zou, X.; Zhang, Q.; Peng, T. Multi-Scale Spatiotemporal Change Characteristics Analysis of High-Frequency Disturbance Forest Ecosystem Based on Improved Spatiotemporal Cube Model. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2537. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13132537
Zhang Y, Liu X, Liu M, Zou X, Zhang Q, Peng T. Multi-Scale Spatiotemporal Change Characteristics Analysis of High-Frequency Disturbance Forest Ecosystem Based on Improved Spatiotemporal Cube Model. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(13):2537. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13132537
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yangcen, Xiangnan Liu, Meiling Liu, Xinyu Zou, Qian Zhang, and Tao Peng. 2021. "Multi-Scale Spatiotemporal Change Characteristics Analysis of High-Frequency Disturbance Forest Ecosystem Based on Improved Spatiotemporal Cube Model" Remote Sensing 13, no. 13: 2537. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13132537
APA StyleZhang, Y., Liu, X., Liu, M., Zou, X., Zhang, Q., & Peng, T. (2021). Multi-Scale Spatiotemporal Change Characteristics Analysis of High-Frequency Disturbance Forest Ecosystem Based on Improved Spatiotemporal Cube Model. Remote Sensing, 13(13), 2537. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13132537






