Partitioned Relief-F Method for Dimensionality Reduction of Hyperspectral Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
2.1. Feature Extraction Methods
2.2. Feature Selection Methods
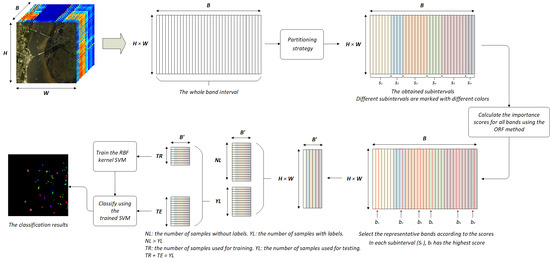
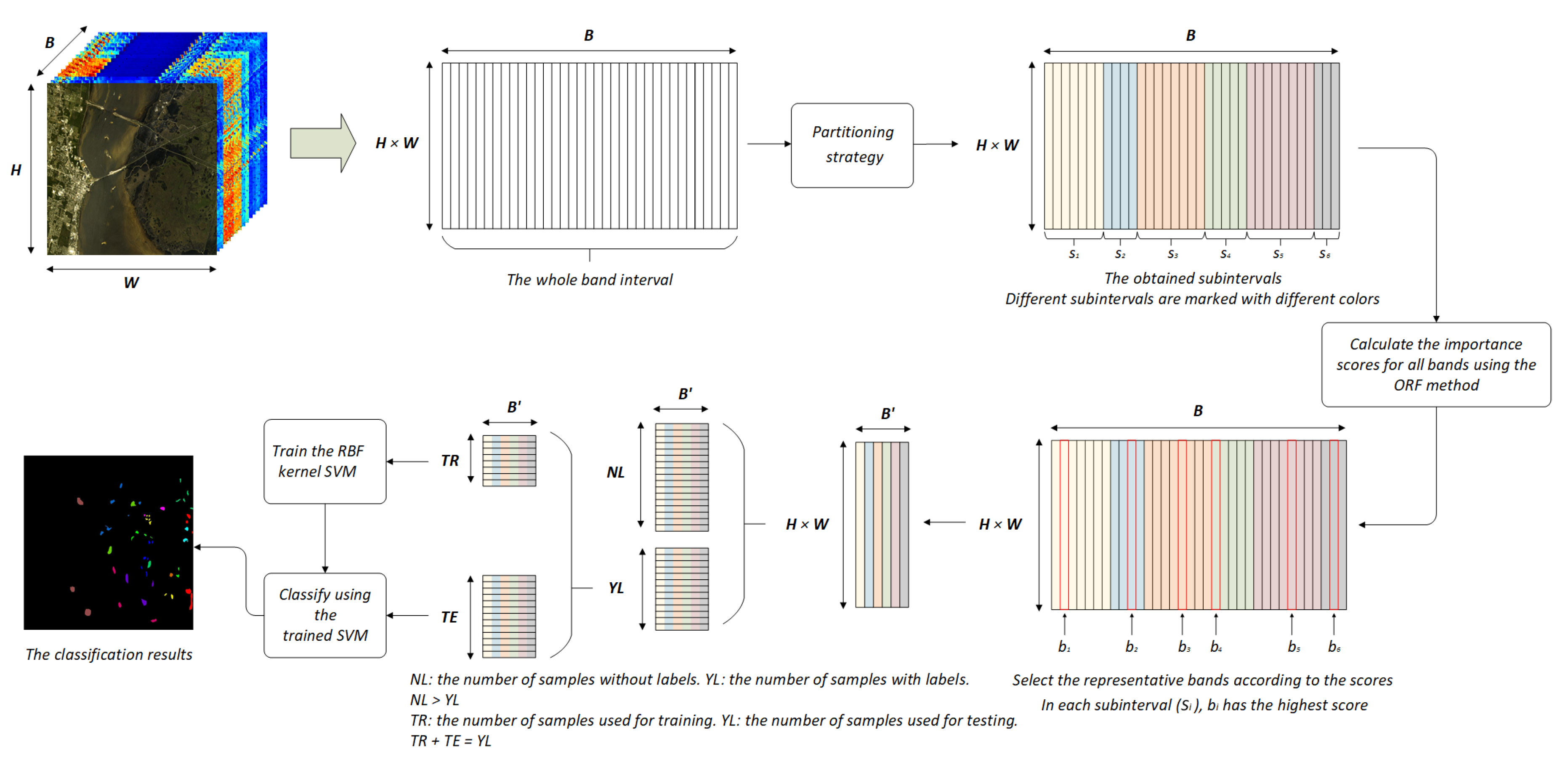
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Band Importance Score Calculation
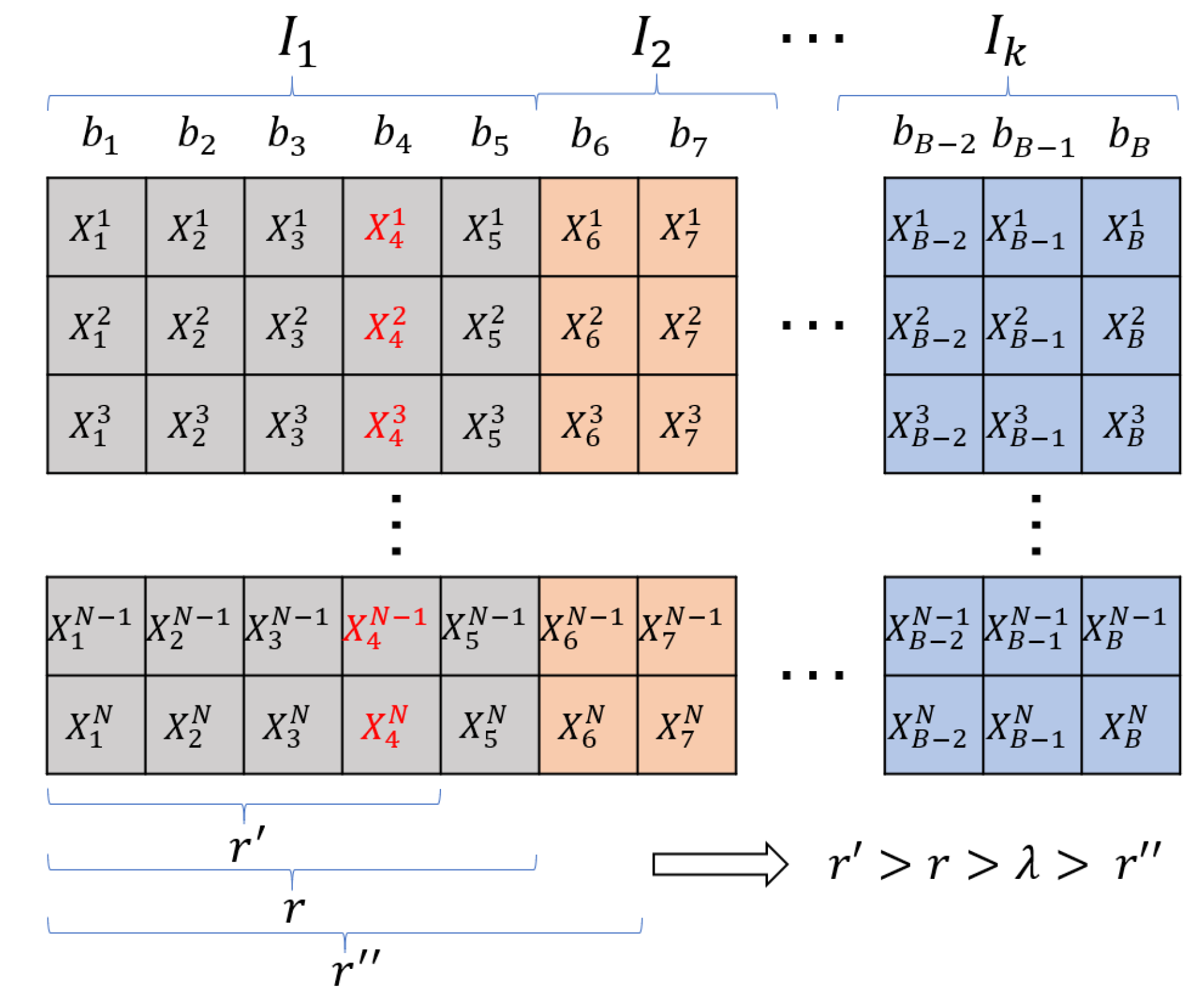
3.2. Correlation Test of Adjacent Bands
3.3. Partitioning Strategy
| Algorithm 1: Partitioning strategy of the Partitioned Relief-F method. |
 |
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
4.1. Data Sets
4.2. Verification of Two Assumptions
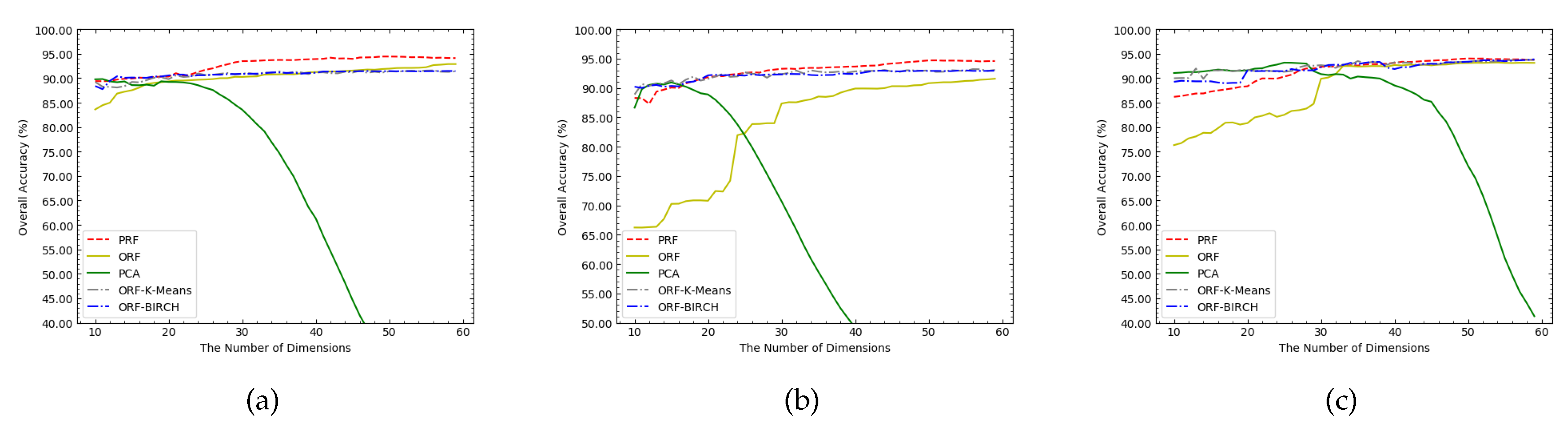
4.3. The Effectiveness and Advancement of the PRF Method
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chutia, D.; Bhattacharyya, D.K.; Sarma, K.K.; Kalita, R.; Sudhakar, S. Hyperspectral remote sensing classifications: A perspective survey. Trans. GIS 2015, 20, 463–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benediktsson, J.A.; Palmason, J.A.; Sveinsson, J.R. Classification of hyperspectral data from urban areas based on extended morphological profiles. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 480–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauvel, M.; Tarabalka, Y.; Benediktsson, J.A.; Chanussot, J.; Tilton, J.C. Advances in spectral-spatial classification of hyperspectral images. Proc. IEEE 2013, 101, 652–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellman, R.E. Rand Corporation. Dynamic Programming; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.I. Hyperspectral Data Exploitation: Theory and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Plaza, A.; Camps-Valls, G.; Scheunders, P.; Nasrabadi, N.; Chanussot, J. Hyperspectral remote sensing data analysis and future challenges. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2013, 1, 6–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Ma, J.; Chen, C.; Wang, Z.; Cai, Z.; Wang, L. SuperPCA: A superpixelwise PCA approach for unsupervised feature extraction of hyperspectral imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 4581–4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinkowska-Ochtyra, A.; Zagajewski, B.; Ochtyra, A.; Jarocińska, A.; Wojtuń, B.; Rogass, C.; Mielke, C.; Lavender, S. Subalpine and alpine vegetation classification based on hyperspectral APEX and simulated EnMAP images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 38, 1839–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chang, C.I. Independent component analysis-based dimensionality reduction with applications in hyperspectral image analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 1586–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Meng, Z.; Li, X. Locality adaptive discriminant analysis for spectral–spatial classification of hyperspectral images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 2077–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, A.J.; Darvas, F.; Bading, J.R.; Moats, R.A.; Conti, P.S.; Smith, D.J.; Cherry, S.R.; Leahy, R.M. Hyperspectral and multispectral bioluminescence optical tomography for small animal imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 2005, 50, 5421–5441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, L.M.; Koger, C.H.; Li, J. Dimensionality reduction of hyperspectral data using discrete wavelet transform feature extraction. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2331–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.L.; Zhang, R.Y.; Yu, J.; Hu, W.C.; Yin, Z.T. Detection of infected tephritidae citrus fruit based on hyperspectral imaging and two-band ratio algorithm. Adv. Mater. Res. Trans. Tech. Publ. 2011, 311, 1501–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wu, B.; Tao, D.; Jiao, L. Automatic band selection using spatial-structure information and classifier-based clustering. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 4352–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, Y.; Stow, D.A.; Coulter, L.L.; Jafolla, J.C.; Hendricks, L.W. Detecting Tamarisk species (Tamarix spp.) in riparian habitats of Southern California using high spatial resolution hyperspectral imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 109, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Yang, H.; Du, Q.; Sheng, Y. Semisupervised band clustering for dimensionality reduction of hyperspectral imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 8, 1135–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Du, Q.; Chen, G.; Du, P. Optimized hyperspectral band selection using particle swarm optimization. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 2659–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, H.; Lu, R.; Zhu, Q.; Mendoza, F. Nondestructive detection of chilling injury in cucumber fruit using hyperspectral imaging with feature selection and supervised classification. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2016, 111, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deronde, B.; Kempeneers, P.; Forster, R.M. Imaging spectroscopy as a tool to study sediment characteristics on a tidal sandbank in the Westerschelde. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 69, 580–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serpico, S.B.; Bruzzone, L. A new search algorithm for feature selection in hyperspectral remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 1360–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Guan, Q.; Luo, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J.; Liang, D.; Huang, L.; Zhang, D. New optimized spectral indices for identifying and monitoring winter wheat diseases. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 2516–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M.; Mather, P.M. Support vector machines for classification in remote sensing. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 1007–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, A.A. Kernel maximum autocorrelation factor and minimum noise fraction transformations. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2010, 20, 612–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauvel, M.; Chanussot, J.; Benediktsson, J.A. Kernel Principal Component Analysis for Feature Reduction in Hyperspectrale Images Analysis. In Proceedings of the 7th Nordic Signal Processing Symposium-NORSIG 2006, Rejkjavik, Iceland, 7–9 June 2006; pp. 238–241. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhang, L.; You, J. Hyperspectral Image Classification Based on Two-Stage Subspace Projection. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Su, H.; Shen, J. Hyperspectral Dimensionality Reduction Based on Multiscale Superpixelwise Kernel Principal Component Analysis. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binol, H. Ensemble Learning Based Multiple Kernel Principal Component Analysis for Dimensionality Reduction and Classification of Hyperspectral Imagery. Math. Probl. Eng. 2018, 2018, 9632569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Gao, L.; Zhang, B. An Optimized Method of Kernel Minimum noise Fraction for Dimensionality Reduction of Hyperspectral Imagery. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 48–51. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Chova, L.; Nielsen, A.A.; Camps-Valls, G. Explicit Signal to Noise Ratio in Reproducing Kernel Hilbert Spaces. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2011; pp. 3570–3573. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.; Zhou, H.; Qin, H.; Qian, K.; Cheng, K.; Qian, J. Hyperspectral Image Anomaly Detecting Based on Kernel Independent Component Analysis. In Proceedings of the Fourth Seminar on Novel Optoelectronic Detection Technology and Application, Nanjing, China, 24–26 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Z.; Wan, J.; Deng, L.; Liu, K. Oil Adulteration identification by hyperspectral imaging using QHM and ICA. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Tang, Y.Y.; Lu, Y.; Yang, L.; Luo, H. Spectral-spatial classification of hyperspectral image based on discriminant analysis. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 7, 2035–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Zhang, L. Rare signal component extraction based on kernel methods for anomaly detection in hyperspectral imagery. Neurocomputing 2013, 108, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Tan, K.; Xing, X. Wavelet SVM in reproducing kernel Hilbert space for hyperspectral remote sensing image classification. Opt. Commun. 2010, 283, 4978–4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenenbaum, J.B.; De Silva, V.; Langford, J.C. A global geometric framework for nonlinear dimensionality reduction. Science 2000, 290, 2319–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orts Gomez, F.J.; Ortega López, G.; Filatovas, E.; Kurasova, O.; Garzón, G.E.M. Hyperspectral Image Classification Using Isomap with SMACOF. Informatica 2019, 30, 349–365. [Google Scholar]
- Songyang, Z.; Kun, T.; Lixin, W. Hyperspectral image classification based on ISOMAP algorithm using neighborhood distance. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2014, 29, 695–700. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, L.; Roy, D.P. Improved time series land cover classification by missing-observation-adaptive nonlinear dimensionality reduction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 158, 478–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.E.; Chen, G. A New Nonlinear Dimensionality Reduction Method with Application to Hyperspectral Image Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Barcelona, Spain, 23–28 July 2007; pp. 270–273. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, F.; Li, W.; Du, Q.; Zhang, B. Dimensionality reduction of hyperspectral image with graph-based discriminant analysis considering spectral similarity. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Du, Q. Hyperspectral band selection: A review. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2019, 7, 118–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafri, H.Z.M.; Anuar, M.I.; Saripan, M.I. Modified vegetation indices for Ganoderma disease detection in oil palm from field spectroradiometer data. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2009, 3, 033556. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Z.; Jeong, M.K.; Kong, S.G. Band selection of hyperspectral images for automatic detection of poultry skin tumors. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2007, 4, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlein, A.K.; Rumpf, T.; Welke, P.; Dehne, H.W.; Plümer, L.; Steiner, U.; Oerke, E.C. Development of spectral indices for detecting and identifying plant diseases. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 128, 21–30. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Q. A new sequential algorithm for hyperspectral endmember extraction. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 9, 695–699. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Geng, X.; Ji, L.; Lu, Y. A new band selection method for hyperspectral image based on data quality. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 2697–2703. [Google Scholar]
- Ghamisi, P.; Couceiro, M.S.; Benediktsson, J.A. A novel feature selection approach based on FODPSO and SVM. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 53, 2935–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaiphasa, C.; Skidmore, A.K.; de Boer, W.F.; Vaiphasa, T. A hyperspectral band selector for plant species discrimination. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2007, 62, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MartÍnez-UsÓMartinez-Uso, A.; Pla, F.; Sotoca, J.M.; García-Sevilla, P. Clustering-based hyperspectral band selection using information measures. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 4158–4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbiriba, T.; Bermudez, J.C.M.; Richard, C.; Tourneret, J.Y. Band Selection in RKHS for Fast Nonlinear Unmixing of Hyperspectral Images. In Proceedings of the 2015 23rd European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Nice, France, 31 August–4 September 2015; pp. 1651–1655. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Qi, H. Sparse Representation Based Band Selection for Hyperspectral Images. In Proceedings of the 2011 18th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Brussels, Belgium, 11–14 September 2016; pp. 2693–2696. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Jiang, M.; Li, W.; Liu, Y. A symmetric sparse representation based band selection method for hyperspectral imagery classification. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Ramakrishnan, R.; Livny, M. BIRCH: An efficient data clustering method for very large databases. ACM Sigmod Rec. 1996, 25, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Data Set | Sensor | Spectral Range (nm) | Spectral Res. (nm) | Spatial Res. (m) | No. of Bands | No. of Classes | No. of Pixels |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salinas | AVIRIS | 400–2500 | 10 | 3.7 | 204 | 16 | 512 × 217 |
| PaviaU | ROSIS | 430–860 | 6 | 1.3 | 103 | 9 | 610 × 340 |
| KSC | AVIRIS | 400–2500 | 10 | 18 | 176 | 13 | 512 × 614 |
| Salinas | PaviaU | KSC | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Samples | Class | Samples | Class | Samples |
| Broccoli green weeds_1 | 2009 | Asphalt | 6631 | Scrub | 761 |
| Broccoli green weeds_2 | 3726 | Meadows | 18,649 | Willow swamp | 243 |
| Fallow | 1976 | Gravel | 2099 | Cabbage palm hammock | 256 |
| Fallow rough plow | 1394 | Trees | 3064 | Cabbage palm/oak hammock | 252 |
| Fallow smooth | 2678 | Painted metal sheets | 1346 | Slash pine | 161 |
| Stubble | 3959 | Bare Soil | 5029 | Oak/broadleaf hammock | 229 |
| Celery | 3579 | Bitumen | 1330 | Hardwood swamp | 106 |
| Grapes untrained | 11,271 | Self-Blocking Bricks | 3682 | Graminoid marsh | 431 |
| Soil vineyard develop | 6203 | Shadows | 947 | Spartina marsh | 520 |
| Corn senesced green weeds | 3278 | Cattail marsh | 404 | ||
| Lettuce romaine_4wk | 1068 | Salt marsh | 419 | ||
| Lettuce romaine_5wk | 1927 | Mud flats | 503 | ||
| Lettuce romaine_6wk | 916 | Water | 927 | ||
| Lettuce romaine_7wk | 1070 | ||||
| Vineyard untrained | 7268 | ||||
| Vineyard vertical trellis | 1807 | ||||
| Total Number | 54,129 | 42,777 | 5212 | ||
| Data Set | Band Indices | Importance Scores |
|---|---|---|
| Salinas | [31, 33, 30, 32, 28, 29, 34, 27, 26, 25, 24, 23, 35, 22, 21, 36, 44, 20, 43, 45, 19, 46, 41, 18, 47, 17, 14, 16, 13, 15] | [1.000, 0.988, 0.981, 0.952, 0.845, 0.837, 0.826, 0.807, 0.752, 0.750, 0.739, 0.673, 0.663, 0.638, 0.580, 0.554, 0.505, 0.499, 0.469, 0.463, 0.451, 0.447, 0.443, 0.417, 0.405, 0.391, 0.379, 0.367, 0.354, 0.343] |
| PaviaU | [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 14, 13, 17, 7, 15, 16, 18, 20, 19, 9, 12, 8, 10, 21, 11, 22, 88, 87, 25, 89, 24, 23, 82] | [1.000, 0.571, 0.468, 0.338, 0.311, 0.301, 0.276, 0.254, 0.252, 0.243, 0.235, 0.234, 0.233, 0.233, 0.230, 0.228, 0.219, 0.216, 0.216, 0.213, 0.213, 0.201, 0.186, 0.179, 0.177, 0.174, 0.173, 0.171, 0.170, 0.169] |
| KSC | [175, 16, 15, 18, 13, 14, 19, 17, 20, 10, 12, 9, 11, 8, 22, 24, 21, 7, 23, 25, 132, 26, 27, 30, 29, 6, 28, 5, 31, 70] | [1.000, 0.656, 0.655, 0.640, 0.616, 0.613, 0.595, 0.593, 0.588, 0.584, 0.563, 0.523, 0.508, 0.482, 0.435, 0.430, 0.424, 0.408, 0.396, 0.375, 0.369, 0.338, 0.304, 0.291, 0.269, 0.256, 0.254, 0.238, 0.199, 0.192] |
| Data Set | t | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salinas | 0.9956 | 0.9910 | −3.2989 | −1.6524 | ||
| PaviaU | 0.9987 | 0.9971 | −11.6331 | −1.6599 | ||
| KSC | 0.8203 | 0.5920 | 1.1991 | −1.6536 |
| Salinas | PaviaU | KSC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Bands | OA | No. of Bands | OA | No. of Bands | OA | |
| 0.02 | 11 | 0.8969 | 5 | 0.852 | 31 | 0.9192 |
| 0.01 | 15 | 0.8995 | 8 | 0.8947 | 35 | 0.926 |
| 0.001 | 32 | 0.935 | 31 | 0.932 | 42 | 0.9331 |
| 0.0001 | 51 | 0.9445 | 46 | 0.9471 | 57 | 0.9405 |
| 0.00001 | 78 | 0.9415 | 74 | 0.9466 | 82 | 0.9376 |
| Salinas | PaviaU | KSC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Bands | OA | No. of Bands | OA | No. of Bands | OA | |
| 0.02 | 11 | 0.8947 | 4 | 0.8411 | 29 | 0.9064 |
| 0.01 | 14 | 0.8944 | 7 | 0.883 | 33 | 0.9091 |
| 0.001 | 32 | 0.9393 | 29 | 0.9365 | 43 | 0.9314 |
| 0.0001 | 52 | 0.9439 | 44 | 0.9473 | 55 | 0.9366 |
| 0.00001 | 76 | 0.9435 | 70 | 0.9469 | 81 | 0.9294 |
| ORF | PCA | ORF-K-Means | ORF-BIRCH | PRF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salinas | 92.90 | 89.82 | 91.58 | 91.48 | 94.45 |
| PaviaU | 91.57 | 90.94 | 93.21 | 92.99 | 94.71 |
| KSC | 93.22 | 93.19 | 93.77 | 93.87 | 94.05 |
| ORF | PCA | ORF-K-Means | ORF-BIRCH | PRF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salinas | 7.34 | 0.57 | 19.06 | 9.64 | 7.99 |
| PaviaU | 1.67 | 0.33 | 6.49 | 2.22 | 1.87 |
| KSC | 2.37 | 0.05 | 3.28 | 2.53 | 2.41 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, J.; Wang, R.; Liu, G.; Feng, R.; Wang, Y.; Wu, W. Partitioned Relief-F Method for Dimensionality Reduction of Hyperspectral Images. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12071104
Ren J, Wang R, Liu G, Feng R, Wang Y, Wu W. Partitioned Relief-F Method for Dimensionality Reduction of Hyperspectral Images. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(7):1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12071104
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Jiansi, Ruoxiang Wang, Gang Liu, Ruyi Feng, Yuanni Wang, and Wei Wu. 2020. "Partitioned Relief-F Method for Dimensionality Reduction of Hyperspectral Images" Remote Sensing 12, no. 7: 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12071104
APA StyleRen, J., Wang, R., Liu, G., Feng, R., Wang, Y., & Wu, W. (2020). Partitioned Relief-F Method for Dimensionality Reduction of Hyperspectral Images. Remote Sensing, 12(7), 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12071104