An Effective and Efficient Enhanced Fixed Rank Smoothing Method for the Spatiotemporal Fusion of Multiple-Satellite Aerosol Optical Depth Products
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Basic Principles of the FRS Model
2.2. The FRS-EE Method for AOD Product Fusion
3. Datasets and FRS-EE Model Building
3.1. Dataset Collection
3.1.1. Satellite AOD Products
3.1.2. Ground AERONET Data
3.2. Spatiotemporal Trend Removal
3.3. Selection of Spatial Basis
3.4. Separation of Measurement Noise and Fine-Scale Spatial Variation
3.5. Determination of FRS-EE Parameters Using EM Iteration
3.6. Missing Data Interpolation and Inaccurate Data Removal
4. Results
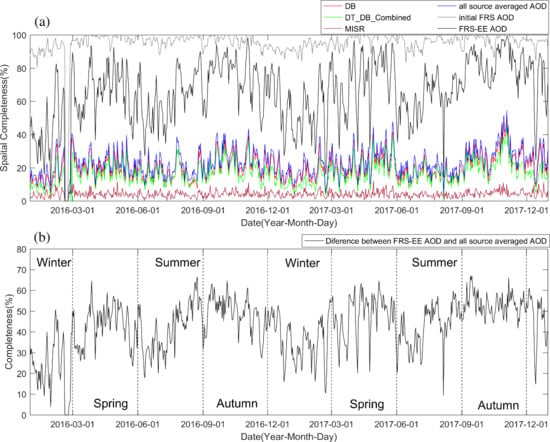
4.1. Spatial Completeness Analysis of Fused AODs
4.2. Temporal Completeness Analysis of Fused AODs
4.3. Accuracy Validation and Time Efficiency Analysis of FRS-EE
4.4. Overall Effectiveness Analysis of Fused AOD
5. Discussion
6. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Dominici, F.; Greenstone, M.; Sunstein, C.R. Particulate Matter Matters. Science 2014, 344, 257–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, B.; Li, S.; Lin, Y.; Wang, B.; Cao, S.; Zhao, X.; Peng, F.; Qin, N.; Guo, Q.; Feng, H.; et al. Efforts in reducing air pollution exposure risk in China: State versus individuals. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.X.; Zou, B.; Fang, X.; Lin, Y. Time series modeling of PM2.5 concentrations with residual variance constraint in eastern mainland China during 2013–2017. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 135755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Mao, F.Y.; Zou, B.; Guo, J.P.; Wu, L.X.; Pan, Z.X.; Zang, L. Two-stage Model for Estimating the Spatiotemporal Distribution of Hourly PM1.0 Concentrations over Central and East China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 675, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, B.; Pu, Q.; Bilal, M.; Weng, Q.; Zhai, L.; Nichol, J.E. High-Resolution Satellite Mapping of Fine Particulates Based on Geographically Weighted Regression. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.; Li, S.; Zou, B.; Sang, H.; Fang, X.; Xu, S. An improved geographically weighted regression model for PM2.5 concentration estimation in large areas. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 181, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokhanovsky, A.A.; Breon, F.-M.; Cacciari, A.; Carboni, E.; Diner, D.; Di Nicolantonio, W.; Grainger, R.G.; Grey, W.M.F.; Höller, R.; Lee, K.-H.; et al. Aerosol remote sensing over land: A comparison of satellite retrievals using different algorithms and instruments. Atmos. Res. 2007, 85, 372–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mélin, F.; Zibordi, G.; Djavidnia, S. Development and validation of a technique for merging satellite derived aerosol optical depth from SeaWiFS and MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 108, 436–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Guang, J.; Xue, Y.; de Leeuw, G.; Che, Y.H.; Guo, X.J.; He, W.; Wang, T.K. A consistent aerosol optical depth (AOD) dataset over mainland China by integration of several AOD products. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 114, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Gu, X.; Yu, T.; Cheng, T.; Chen, H.; Xie, D. Trend analysis of the aerosol optical depth over China using fusion of MODIS and MISR aerosol products via adaptive weighted estimate algorithm. In Proceedings of the SPIE 8866, Earth Observing Systems XVIII, 88661X, San Diego, CA, USA, 23 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.; Xu, H.; Guang, J.; Mei, L.; Guo, J.; Li, C.; Mikusauskas, R.; He, X. Observation of an agricultural biomass burning in central and east China using merged aerosol optical depth data from multiple satellite missions. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 5971–5983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Pinker, R.T.; Holben, B.N. A global view of aerosols from merged transport models, satellite, and ground observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110, D10S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Nichol, J.E.; Wang, L. New customized methods for improvement of the MODIS C6 Dark Target and Deep Blue merged aerosol product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 197, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Qiu, Z.; Campbell, J.R.; Spak, S.N.; Shen, X.; Nazeer, M. A new MODIS C6 dark target and Deep Blue merged aerosol product on a 3 km spatial grid. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.; Michalak, A.M.; Kahn, R.A.; Paradise, S.R.; Braverman, A.J.; Miller, C.E. A geostatistical data fusion technique for merging remote sensing and ground-based observations of aerosol optical thickness. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D20207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Brown, D.G.; Hammerling, D. Geostatistical inverse modeling for super-resolution mapping of continuous spatial processes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 139, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.; Cressie, N.; Braverman, A. Spatial Statistical Data Fusion for Remote Sensing Applications. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2012, 107, 1004–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cressie, N.; Shi, T.; Kang, E.L. Fixed Rank Filtering for Spatio-Temporal Data. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 2010, 19, 724–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Hu, M. Filling the missing data gaps of daily MODIS AOD using spatiotemporal interpolation. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Bo, Y.; Zhu, Y. Spatiotemporal fusion of multiple satellite aerosol optical depth (AOD) products using Bayesian maximum entropy method. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 4034–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christakos, G. Modern Spatiotemporal Geostatistics, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2008; pp. 260–261. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, E.L.; Cressie, N.; Shi, T. Using temporal variability to improve spatial mapping with application to satellite data. Can. J. Stat. 2010, 38, 271–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cressie, N.; Johannesson, G. Fixed Rank Kriging for Very Large Spatial Data Sets. J. R. Statist. Soc. B. 2008, 70, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzfuss, M.; Cressie, N. Spatio-temporal smoothing and EM estimation for massive remote-sensing data sets. J. Time Ser. Anal. 2011, 32, 430–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, A.M.; Hsu, N.C.; Bettenhausen, C.; Jeong, M.J. Validation and uncertainty estimates for MODIS Collection 6 “Deep Blue” aerosol data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 7864–7872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, A.M.; Munchak, L.A.; Hsu, N.C.; Levy, R.C.; Bettenhausen, C.; Jeong, M.J. MODIS Collection 6 aerosol products: Comparison between Aqua’s e-Deep Blue, Dark Target, and “merged” data sets, and usage recommendations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 13965–13989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, N.C.; Jeong, M.-J.; Bettenhausen, C.; Sayer, A.M.; Hansell, R.; Seftor, C.S.; Huang, J.; Tsay, S.-C. Enhanced Deep Blue aerosol retrieval algorithm: The second generation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 9296–9315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S.; Munchak, L.A.; Remer, L.A. The Collection 6 MODIS aerosol products over land and ocean. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2989–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garay, M.J.; Kalashnikova, O.V.; Bull, M.A. Development and assessment of a higher-spatial-resolution (4.4 km) MISR aerosol optical depth product using AERONET-DRAGON data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 5095–5106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diner, D.J.; John, V.M.; Ralph, A.K.; Bernard, P.; Nadine, G.; David, L.N.; Brent, N.H. Using angular and spectral shape similarity constraints to improve MISR aerosol and surface retrievals over land. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 94, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Reid, J.S.; Dubovik, O.; Smirnov, A.; O’Neill, N.T.; Slutsker, I.; Kinne, S. Wavelength dependence of the optical depth of biomass burning, urban, and desert dust aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 31333–31349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, D.M.; Sinyuk, A.; Sorokin, M.G.; Schafer, J.S.; Smirnov, A.; Slutsker, I.; Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Lewis, J.R.; Campbell, J.R.; et al. Advancements in the Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) Version 3 database—Automated near-real-time quality control algorithm with improved cloud screening for Sun photometer aerosol optical depth (AOD) measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 169–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ångström, A.; Annaler, G. On the atmospheric transmission of Sun radiation and on dust in the air. Geogr. Ann. 1929, 2, 156–166. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver, M.A.; Webster, R. A tutorial guide to geostatistics: Computing and modelling variograms and kriging. Catena 2014, 113, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichoku, C.; Chu, D.A.; Mattoo, S.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Remer, L.A.; Tanré, D.; Slutsker, I.; Holben, B.N. A spatio-temporal approach for global validation and analysis of MODIS aerosol products. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Tao, J.; Che, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y. Comparison and evaluation of the MODIS Collection 6 aerosol data in China. J. Geophys. Res. 2015, 120, 6992–7005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Date | DB | DT_DB_Combined | MISR | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nugget | Sill | Nugget | Sill | Nugget | Sill | |
| 3 November 2017 | 0.002 | 0.010 | 0.003 | 0.010 | 0.001 | 0.002 |
| 5 November 2017 | 0.002 | 0.009 | 0.002 | 0.008 | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| 30 October 2017 | 0.002 | 0.007 | 0.002 | 0.012 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| 4 November 2017 | 0.003 | 0.010 | 0.002 | 0.008 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| 25 May 2017 | 0.002 | 0.005 | 0.003 | 0.006 | 0.001 | 0.002 |
| 26 May 2017 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.006 | 0.002 | 0.001 |
| 29 October 2017 | 0.002 | 0.009 | 0.002 | 0.012 | 0.001 | 0.002 |
| 27 October 2017 | 0.003 | 0.011 | 0.003 | 0.013 | 0.001 | 0.003 |
| 16 May 2017 | 0.001 | 0.005 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.003 |
| 1 November 2017 | 0.002 | 0.010 | 0.003 | 0.010 | 0.001 | 0.002 |
| Averaged | 0.0022 | 0.008 | 0.0024 | 0.0089 | 0.0013 | 0.0019 |
| Season | MAM | JJA | SON | DJF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DB | 21.49 | 15.96 | 25.19 | 16.66 |
| DT_DB_Combined | 18.12 | 14.74 | 21.16 | 11.62 |
| MISR | 4.34 | 3.54 | 4.68 | 4.06 |
| All source averaged AOD | 24.25 | 19.65 | 28.11 | 19.20 |
| FRS-EE fused AOD | 69.91 | 61.59 | 79.17 | 52.60 |
| Improvement | 45.66 | 41.94 | 51.05 | 33.40 |
| Province | DB | DT_DB_Combined | MISR | All Source Averaged | FRS-EE Fused | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qinghai | 7.71 | 4.49 | 3.01 | 10.55 | 81.58 | 71.02 |
| Yunnan | 14.76 | 13.04 | 2.45 | 17.92 | 79.36 | 61.43 |
| Gansu | 25.23 | 20.87 | 5.30 | 28.65 | 86.27 | 57.63 |
| Sichuan | 7.84 | 6.04 | 2.00 | 10.73 | 67.14 | 56.41 |
| Guizhou | 7.78 | 8.05 | 1.00 | 9.53 | 65.65 | 56.12 |
| Ningxia | 28.73 | 25.00 | 5.65 | 32.56 | 86.70 | 54.14 |
| Taiwan | 5.19 | 9.24 | 1.68 | 11.19 | 63.74 | 52.55 |
| Tibet | 6.87 | 3.01 | 2.70 | 9.28 | 61.36 | 52.08 |
| Fujian | 11.72 | 10.70 | 2.47 | 14.81 | 58.64 | 43.83 |
| Hainan | 6.49 | 10.10 | 1.71 | 11.58 | 53.84 | 42.26 |
| Neimenggu | 30.90 | 24.54 | 6.64 | 33.95 | 75.96 | 42.01 |
| Xinjiang | 28.29 | 24.18 | 5.20 | 30.47 | 71.69 | 41.22 |
| Hongkong | 0.67 | 0.94 | 1.55 | 2.62 | 41.98 | 39.36 |
| Chongqing | 9.94 | 10.76 | 1.42 | 12.95 | 50.43 | 37.48 |
| Shaanxi | 23.95 | 23.56 | 4.05 | 28.26 | 64.85 | 36.59 |
| Guangdong | 10.62 | 10.72 | 2.28 | 13.48 | 49.30 | 35.82 |
| Guangxi | 9.99 | 10.53 | 1.57 | 12.48 | 48.06 | 35.58 |
| Heilongjiang | 16.87 | 14.46 | 3.19 | 19.90 | 52.39 | 32.49 |
| Shanxi | 28.29 | 27.08 | 5.98 | 33.79 | 64.91 | 31.11 |
| Jilin | 20.27 | 17.28 | 4.21 | 23.93 | 53.64 | 29.70 |
| Beijing | 33.81 | 31.49 | 7.74 | 40.89 | 68.96 | 28.07 |
| Tianjin | 33.81 | 28.65 | 7.40 | 38.37 | 64.38 | 26.00 |
| Hebei | 33.94 | 29.99 | 6.58 | 38.32 | 64.25 | 25.93 |
| Zhejiang | 13.86 | 12.55 | 2.43 | 17.87 | 43.70 | 25.83 |
| Liaoning | 31.31 | 28.41 | 6.65 | 36.11 | 61.69 | 25.59 |
| Hunan | 13.08 | 11.74 | 2.37 | 15.54 | 40.53 | 25.00 |
| Jiangxi | 15.41 | 13.44 | 2.95 | 18.32 | 42.85 | 24.53 |
| Hubei | 18.97 | 15.95 | 3.34 | 22.17 | 43.29 | 21.12 |
| Shandong | 32.04 | 28.21 | 5.65 | 36.75 | 55.39 | 18.64 |
| Henan | 26.89 | 22.03 | 4.94 | 30.46 | 48.59 | 18.12 |
| Jiangsu | 21.86 | 15.82 | 4.08 | 26.00 | 42.97 | 16.97 |
| Anhui | 23.74 | 17.78 | 4.60 | 26.63 | 43.46 | 16.83 |
| Shanghai | 7.16 | 7.34 | 1.90 | 11.17 | 27.90 | 16.73 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, B.; Liu, N.; Wang, W.; Feng, H.; Liu, X.; Lin, Y. An Effective and Efficient Enhanced Fixed Rank Smoothing Method for the Spatiotemporal Fusion of Multiple-Satellite Aerosol Optical Depth Products. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1102. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12071102
Zou B, Liu N, Wang W, Feng H, Liu X, Lin Y. An Effective and Efficient Enhanced Fixed Rank Smoothing Method for the Spatiotemporal Fusion of Multiple-Satellite Aerosol Optical Depth Products. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(7):1102. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12071102
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Bin, Ning Liu, Wei Wang, Huihui Feng, Xiangping Liu, and Yan Lin. 2020. "An Effective and Efficient Enhanced Fixed Rank Smoothing Method for the Spatiotemporal Fusion of Multiple-Satellite Aerosol Optical Depth Products" Remote Sensing 12, no. 7: 1102. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12071102
APA StyleZou, B., Liu, N., Wang, W., Feng, H., Liu, X., & Lin, Y. (2020). An Effective and Efficient Enhanced Fixed Rank Smoothing Method for the Spatiotemporal Fusion of Multiple-Satellite Aerosol Optical Depth Products. Remote Sensing, 12(7), 1102. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12071102