Abstract
The air quality in China has experienced dramatic changes during the last few decades. To improve understanding of distribution, variations, and main influence factors of air pollution in central China, long-term multiple satellite observations from moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) and ozone monitoring instrument (OMI) are used to characterize particle pollution and their primary gaseous precursors, sulfur dioxide (SO2), and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) in Hubei province during 2005–2017. Unlike other regions in eastern China, particle and gaseous pollutants exhibit distinct spatial and temporal patterns in central China due to differences in emission sources and control measures. OMI SO2 of the whole Hubei region reached the highest value of ~0.2 Dobson unit (DU) in 2007 and then declined by more than 90% to near background levels. By contrast, OMI NO2 grew from ~3.2 to 5.9 × 1015 molecules cm−2 during 2005–2011 and deceased to ~3.9 × 1015 molecules cm−2 in 2017. Unlike the steadily declining SO2, variations of OMI NO2 flattened out in 2016 and increased ~0.5 × 1015 molecules cm−2 during 2017. As result, MODIS AOD at 550 nm increased from 0.55 to the peak value of 0.7 during 2005–2011 and then decreased continuously to 0.38 by 2017. MODIS AOD and OMI SO2 has a high correlation (R > 0.8), indicating that annual variations of SO2 can explain most changes of AOD. The air pollution in central China has notable seasonal variations, which is heaviest in winter and light in summer. While air quality in eastern Hubei is dominated by gaseous pollution such as O3 and NOx, particle pollutants are mainly concentrated in central Hubei. The high consistency with ground measurements demonstrates that satellite observation can well capture variations of air pollution in regional scales. The increasing ozone (O3) and NO2 since 2016 suggests that more control measures should be made to reduce O3-related emissions. To improve the air quality in regional scale, it is necessary to monitor the dynamic emission sources with satellite observations at a finer resolution.
1. Introduction
Air pollution is a dynamic and complicated mixture of particulate matter and gaseous pollutants that emitted from anthropogenic activities and natural processes into the atmosphere. During the last decades, rapid industrialization and urbanization in China has caused serious air quality problems [1]. Massive anthropogenic emissions in populated regions of China lead to widespread air pollution [2,3,4,5], which is characterized by high concentration and diverse sources [6,7,8]. With a lifetime of several days to one-week, fine particle (PM2.5, fine particulate matter with aerodynamic diameter less than 2.5 μm) is the most-watched atmospheric pollutant in air quality monitoring. Moreover, as the main gaseous precursors of PM2.5, sulfur dioxide (SO2), and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) is usually measured to monitor emission levels for combustion of fossil fuels and vehicle exhaust. Ozone (O3) pollution from photochemical reaction between NOx and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) is apt to occur under intense sunshine and high temperature conditions. Numerous epidemic studies have shown robust correlation between exposure level to atmospheric pollutants and increase in morbidity and mortality of respiratory and cardiovascular diseases [9].
Owing to adverse effects of air pollution on human health and daily life, the Chinese government has implemented continuous emission control measures. The anthropogenic emission sources and their amount in China have undergone dramatic changes during last decades due to both the rapid transition of economic structures and environmental policies [10]. There is also a large spatial difference in anthropogenic emissions sources [11], exerting considerable challenges for making timely and effective improvement measures. While ground measurements can accurately measure mass concentration of atmospheric pollutants, the national ground network for air quality monitoring in China since 2013 is only concentrated in major cities with very limited spatial coverage. Since late 1990s, advanced satellite sensors including moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) and ozone monitoring instrument (OMI) provide an unprecedented opportunity to observe atmospheric particles and trace gases from regional to global scales [12,13].
The heavy air pollution in China has drawn the attention of numerous observational studies from various perspectives. Besides ground-based measurements and chemistry model simulations, satellite studies have greatly renewed knowledge concerning spatial distribution of air pollution hotspots and variations of their major emissions in northern China [14,15,16], the Yangtze River Delta (YRD) [17], and Pearl River Delta (PRD) [18]. However, previous studies mostly focused on economically developed regions with extensive urban agglomeration. As an emerging economic center located between polluted northern China and clean southern China, air quality in central China has been rarely concerned under the background of rapid development. Although recent air pollution such as PM2.5 in central China (~40–60 µg/m3) is obviously lower than that in northern China (~60–80 µg/m3) [19,20], the magnitude of the atmospheric pollutants in central China is at a high level compared with health standard (e.g., PM2.5: 35 µg/m3), which can further be seriously aggravated by [21]. By now, spatial patterns of major atmospheric pollutants in central China and how they change over space and time remain unclear due to few comprehensive observational studies.
In this study, we first provide comprehensive insight into spatial patterns and long-term trend of primary atmospheric pollutants including aerosols, SO2, and NO2 in central China during 2005–2017 by utilizing multiple satellite products. Section 2 introduces satellite products and ground measurements used in this work. A comprehensive analysis regarding spatial and temporal variations of aerosol optical depth (AOD), SO2, and NO2 in central China is given in Section 3. Further, its implication of on emission control is discussed in Section 4. At last, a brief summary is shown in Section 5. The main purpose of this work is to reveal spatial changes of pollution hotspot and temporal trends of the primary air pollutants in central China, giving a reference for future air quality improvements.
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Ground Measurments
We selected Hubei province as our study area (Figure 1), which is the main part of central China. Surrounded by mountains with evaluation at ~600–1000 m, Hubei is relatively isolated from other regions. The mountains around Hubei provide a barrier for the transport of heavy pollution from northern China. In the other hand, the basin-like terrain in Hubei is not conductive for dispersion of atmospheric pollutants. Unlike the concentrated urban agglomeration in northern China, YRD, and PRD, only the megacity of Wuhan has a population of more than 10 million in Hubei, and other cities have much smaller scales.
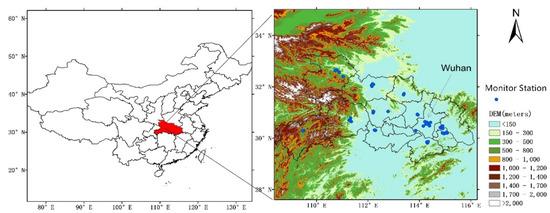
Figure 1.
Terrain of central China and the ambient monitoring stations. DEM: Digital elevation model.
The Environmental Protection Agency of China established a national air quality monitoring network in 2013, which releases hourly concentration of six main atmospheric pollutants (PM2.5, PM10, SO2, NO2, O3, and CO) in major cities with the same ambient air quality standard. Spatial distribution of air quality monitoring sites in Hubei is shown in Figure 1. There are 57 national air quality monitoring sites in Hubei, with nine sites in the megacity of Wuhan. In addition, the statistical emission inventory data of SO2 and NOx from the statistical yearbook of China is used for comparison and reference.
The meteorological background of central China is shown in Figure 2, utilizing the National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP) Final (FNL) and Operational Global Analysis data in the 1° × 1° grid. Seasonal characteristics regard the height of the planetary boundary layer (PBL) with 925 hPa winds, temperature, and relative humidity (RH). The PBL height of central China is around ~1000 m at similar levels as in northern China except a little lower (~800 m) in autumn. While northerly winds prevail in winter and spring within the PBL, southerly and easterly air flows are predominant in summer and autumn, respectively. In particular, wind speed over central China is obviously higher (~1–3 m/s) than adjacent areas. Central is located in the transition zone, with temperature and RH higher than in northern China and lower than in southern China. There is a high contrast in temperature near surface between the cold winter and hot summer, indicating distinct atmospheric stability.
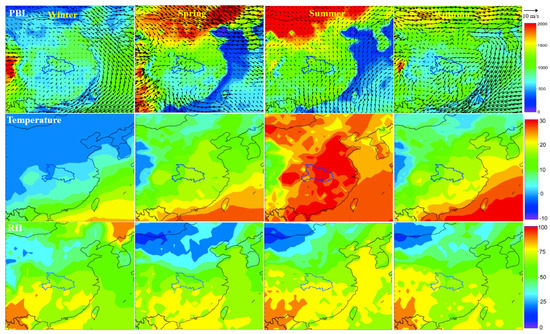
Figure 2.
Seasonal characteristics of the meteorological conditions including height (m) of the planetary boundary layer (PBL) with 925 hPa winds (top), temperature (°C) (middle), and relative humidity (%) (RH) (bottom) at 14:00 local time of 2017 in eastern China.
2.2. MODIS Aerosol Dataset
The MODIS sensor onboard Terra and Aqua satellite since 2000 and 2002, respectively, can provide near daily global observations of aerosol and cloud properties with a wide swath of ~2330 km and broad spectrum between 0.4–14 µm at high spatial resolution of 250–1000 m. MODIS aerosol retrieval over land was firstly implemented at 10 km by the dart target (DT) algorithm utilizing spectral relationship between surface reflectance in visible and short infrared bands over dense vegetation [12]. Owing to the widely application of MODIS aerosol products in air quality research, DT aerosol products are at a much higher resolution of 3 km and are added in the Collection (C) 6 MODIS aerosol algorithm [22]. However, MODIS DT AOD is usually not available over urban areas and heavy pollution conditions [23]. To retrieve aerosols over bright surface such as deserts and urban regions, MODIS Deep Blue (DB) algorithm was developed to utilize pre-calculated surface reflectance database, and externed to all the cloud-free and snow/ice-free areas since C6 [24].
Both MODIS DT and DB AOD at 550 nm exhibits well accuracy compared with ground observations [23,25]. Ground validations show that retrieval error of MODIS AOD is generally better than 0.05 + 20% relative to Aerosol Robotic Network observations. The current version of MODIS DT and DB aerosol products is C6.1, which only conducts some slight improvements without changes in algorithm principle. Compared with C6 products, the C6.1 DB aerosol products have refined instrument calibration and aerosol models [26]. Quality assurance flags of MODIS DB AOD depend on number of retrieved pixels and their standard deviation. Usually, MODIS AOD of best estimate quality is suggested in application, but it is found that such selection can filter out many high-AOD (>1.0) cases in eastern China with only slight improvement in accuracy [23]. Considering the limitation of MODIS DT and MODIS DB products of best estimate, we selected C6.1 MODIS DB AOD of all quality at 10 km to investigate aerosol trends in central China.
2.3. OMI Products of Trace Gases
OMI onboard Aura since 2004 is a hyperspectral instrument that measures backscattered sunlight in ultraviolet-visible range (270 nm to 500 nm) with a spectral resolution of about 0.5 nm. As a sun-synchronous satellite instrument, OMI crosses the equator around local time of 13:30. With a 2600 km swath, OMI has a daily global coverage with a pixel size of 13 × 24 km at nadir. By deriving abundance of various trace gases with their respective absorption characteristics, OMI products include vertical column density (VCD) of trace gases such as NO2 and SO2. Considering the much shorter lifetime of gaseous pollutants of SO2 and NO2 (~one hour to half day) than aerosols’, the continuous data record of OMI products has been widely used to infer anthropogenic pollution sources and verify emission inventory [27]. While NO2 is the production from combustion of fossil fuels such as vehicle emissions in urban regions, SO2 mainly originates from coal-burning sources.
The OMI NO2 and SO2 data was obtained from the NASA Goddard Earth Sciences (GES) Data and Information Services Center (DISC). OMI tropospheric NO2 VCD was retrieved by the common differential optical absorption spectroscopy (DOAS) algorithm with uncertainties of <20% in polluted regions [28]. There are three key steps in NO2 retrieval: spectral fitting of OMI backscattered radiances to laboratory absorption spectra, separating stratospheric contribution, and converting satellite observed slant column densities to VCDs. By contrast, the principal component analysis (PCA) technique was used in the current planetary boundary layer (PBL) SO2 retrieval with priori profiles and a PBL height of 3 km (700 hPa) assumed [29]. The OMP PBL SO2 derived using the PCA method registered a small bias (<0.1 DU) over background regions [30]. Unlike the common unit of OMI NO2 products (1015 molecules cm−2), Dobson units (1 DU = 2.69 × 1016 molecule cm−2) are usually used for OMI SO2 for convenience of retrieval calculation and error estimation. The pixel size of OMI has a large variation from 13 × 24 km at nadir to 26 × 120 km at the edge. Different from satellite AOD derived from aerosol scattering, OMI retrieval of trace gases by their absorption is not very sensitive to cloud contamination. To ensure representativity of OMI products, NO2 retrievals with a cloud fraction >30% and for SO2 with O3 < 1500 DU in the data cell are filtered out. We selected a standard Level 3 OMI grid products at 0.25 × 0.25° resolution.
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. The Characteristics of SO2 and NO2 Variation during 2005–2017
As the main water-soluble components, sulfate, and nitrate together accounted for a significant fraction (~20–50%) in mass concentration of PM2.5 particles in China [4,11]. Other major particle components such as organic aerosol was generated via complicated chemistry reactions and mineral dust that originated from long-range transport and diverse local sources [4]. By contrast, emission sources of sulfate and nitrate’s gaseous precursors, SO2 and NOx, are mostly from coal-burning power plants and industry activities, which are the main control targets of the government due to the practicability for unified management. Since the short lifetime of SO2 and NO2, satellite VCD products of SO2 and NO2 are usually used to map anthropogenic emission sources as well as their emission levels [13,17].
Figure 3 displays variations of OMI SO2 in Hubei during 2005–2017. There was a notable overall increase in the amount of SO2 in 2005–2007, with the largest SO2 hotspot in the megacity of Wuhan. SO2 in Wuhan increased from ~0.4 to >0.5 DU and from ~0.25 to ~0.35–0.4 DU in other several hotspots. Then, SO2 concentration in Wuhan exhibited a large decrease by ~0.1–0.2 DU in 2008 and reached a lower level since 2009, which can be connected with implementation of the 2006 desulfurization policy in China [31]. By contrast, new SO2 hotspots emerged in 2009 in the southeastern part of Wuhan and in the southwestern part of Hubei, and reached peak values (~0.4) in 2011. In 2012, SO2 amount displayed a continuous decline and arrives at a very low level (<0.1) in the entire Hubei region by 2016 without large emission sources. Despite low concentration, it should be noted that SO2 in urban region of Wuhan got higher (~0.2) as a hotspot in 2017.
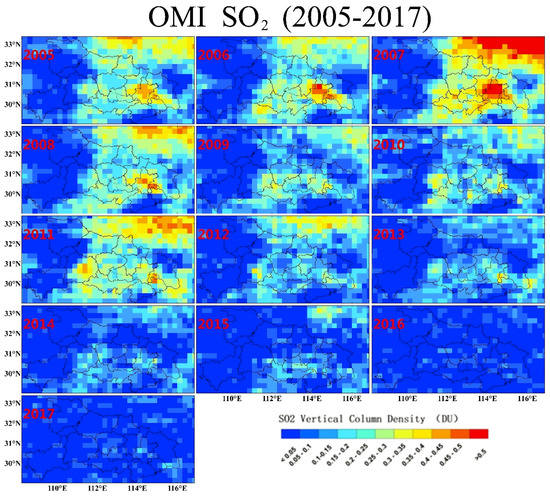
Figure 3.
Spatial and temporal distribution of annual ozone monitoring instrument (OMI), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and vertical column density (VCD) over Hubei province during 2005–2017.
To have a long-term view of the changes in the overall SO2 level in central China, spatial means of OMI SO2 compared with statistical SO2 emission amount during 2005–2017 (Figure 4). There is a generally consistent trend between OMI SO2 concentration and emission amount. Different from the peak value of SO2 concentration in 2007, statistical SO2 emissions in Figure 3 show the largest SO2 amount of ~760,000 tons in 2006. In 2007, the much higher OMI SO2 VCD in both Hubei and its adjacent part to the north demonstrates that the bottom-up statistical emission can miss some substantial emission sources (Figure 2), especially in the early stage of SO2 control. Considering the desulfurization policy in China from 2006 [31], the emission peak in 2006 can be partly caused by statistics of mainly large SO2 sources. On the other hand, OMI retrievals show a more rapid decline of SO2 amount (~50%) than statistical amount (~10%) since 2008. The increase of SO2 (~50%) in 2010–2011 can be connected with the recovery from the economic downturn in 2009 [32]. Considering that SO2 mainly originates from coal-burning combustion of fossil fuels, the low-level SO2 (~210,000 tons) after 2014 indicates effective effects of SO2 control policy. The striking deviation of the annual OMI SO2 shows large temporal variations of the SO2 level and the variances increase obviously with the mean concentration. Although there is no coal-burning heating during winter in central China as there is in northern China, the formation of sulfate from SO2 and their lifetime can have considerable seasonal differences due to variations of meteorological conditions such as illumination, temperature, and relative humidity (Figure 2).
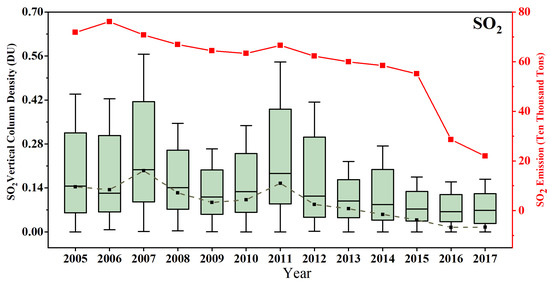
Figure 4.
Box plots of annual OMI SO2 VCD and statistical SO2 emissions (red) over Hubei province during 2005–2017. In each box, the black line in the center is the median and the lower and upper limits are the first and the third quartiles, respectively. The lines extending vertically from the box indicate the maximum and minimum values. The black squares indicate the annual means of OMI SO2.
Compared with SO2, OMI NO2 VCD during 2005–2017 exhibited distinct spatial and temporal variations (Figure 5). There is only one prominent NO2 hotspot in Hubei located in the urban region of the megacity, Wuhan. Despite no obvious emission sources shown in the OMI results except Wuhan, NO2 in the central and eastern parts of Hubei was higher than background mountain areas. There was a steady overall increase in NO2 concentration in central China during 2005–2011. OMI NO2 in Wuhan increased from ~10 during 2005 to >14 × 1015 molecules cm−2 in 2011. The NO2 in the whole region also reached a maximum in 2011 with an increase of ~4 × 1015 molecules cm−2, almost >100% compared with that in 2005. It is worth noting that NO2 in Wuhan also declined slightly (by ~2 × 1015 molecules cm−2) as SO2 in the economic downturn period in 2009. Then, NO2 in the whole east-central Hubei began to decrease, except for a recovery of ~2 × 1015 molecules cm−2 in Wuhan during 2013. By 2016, OMI NO2 was at a close level with that in 2005. However, there was a slight increase for NO2 in Wuhan during 2017.
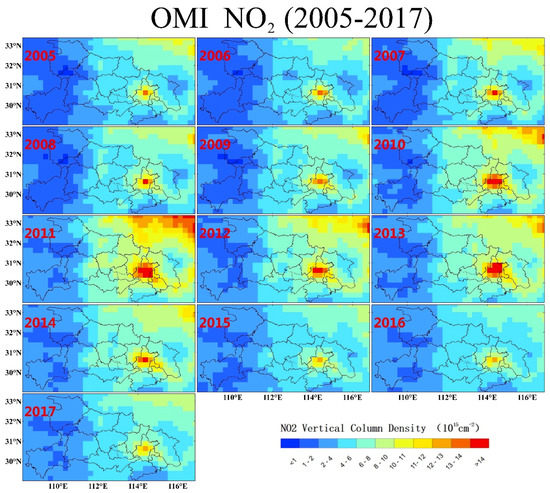
Figure 5.
Spatial and temporal distribution of annual OMI nitrogen dioxide (NO2) VCD over Hubei province during 2005–2017.
Different from the spatial shift of SO2 hotspot, NO2 in the megacity of Wuhan was highest in Hubei during that time, where the number of vehicles exceeded three million by 2017 with rapid increases. Figure 6 gives comparison of variations of OMI NO2 VCD and statistical NOx emissions. It can be seen that the overall NO2 in central China increased by almost ~90% to 100% from ~3.2 to 5.9 × 1015 molecules cm−2 in 2005–2011. Although the overall level of NO2 amount since 2011 had a general downward trend as SO2, there were two notable increases in NO2 during 2013 and 2017, respectively, which were not reflected in statistical NOx emissions. The large anthropogenic sources such as power and steel plants not only emitted SO2, but also lots of NOx. By 2011, NOx emissions of ~690,000 tons were a little higher than SO2. Different from SO2 emissions mainly concentrated in coal-burning sources, NOx also originated from dispersed vehicle emissions. Since 2011, the Chinese EPA began to control NOx emissions from large sources such as coal-burning plants, but the number of vehicles kept rapidly increasing. OMI NO2 in 2017 (~3.9 × 1015 molecules cm−2) indicated that NOx emissions tended to increase under the current background. It should be noted that NOx emission of ~380,000 tons in 2017 was nearly twice of SO2 (~210,000 tons), demonstrating the more important role of NOx emission in the future control. Similar as SO2, the yearly OMI NO2 exhibited a large deviation from the mean.
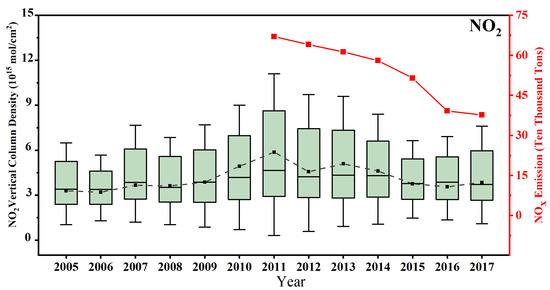
Figure 6.
The same as Figure 3 but for NO2.
To further examine spatial patterns of NO2 pollution, seasonal distribution of OMI tropospheric NO2 VCD is shown in Figure 7. The NO2 concentration was highest in winter and then in Autumn, with the lowest NO2 in summer. Since chemical reactions of NOx highly depend on ambient temperature [10], the hot and cold weather in summer and winter were the main drivers of this great seasonal contrast in NO2 levels. Moreover, the more stagnant weather in winter favored accumulation of NOx emissions (Figure 2). It can be seen that NO2 hotspots (~12–13 × 1015 molecules cm−2) existed over several smaller cities of Hubei during winter and exceeded ~14 × 1015 molecules cm−2 in the entire Wuhan region. There is a notable connection for high NO2 between Hubei and adjacent areas, indicating potential transport from northern China [14,21]. By contrast, the NO2 hotspots in central China were independent in other seasons. Compared with very low SO2 concentration that was close to the background level in region scale by 2017, the considerable NOx emission with a slight increase can have a much larger contribution to PM2.5.
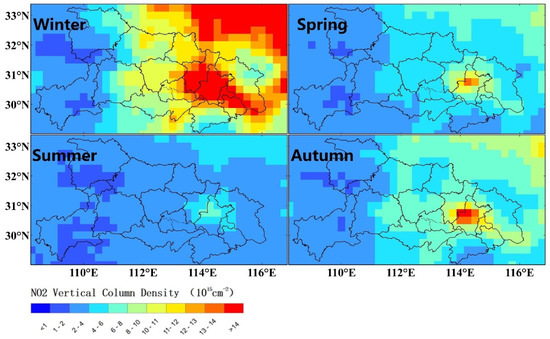
Figure 7.
Seasonal OMI tropospheric NO2 and VCD during 2013–2017.
3.2. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Particle Pollution in 2005–2017
The spatial variations of annual MODIS AOD at 550 nm over Hubei during 2005–2017 are displayed in Figure 8. There were dramatic changes in aerosol loading over Hubei at both temporal and spatial scales. The aerosol particles were concentrated over the non-mountain areas with large spatial differences. Unlike gaseous precursors of SO2 and NO2 concentrated around Wuhan, particle pollution was mainly in the central part of Hubei and communicated with polluted regions in other provinces to the north and south. The high-AOD area (>0.8) grew and extended to the eastern part of Hubei in 2005, and in 2011 nearly covered the entire non-mountain area, including Wuhan. Then, the high-AOD area retreated to the central part of Hubei, which implies large changes in emission sources as well as control policies. It is worth noting that the high AOD in central part of Hubei have rapidly decreased since 2014. By 2017, the aerosol loading in non-mountain areas became homogeneous with an AOD around ~0.6.
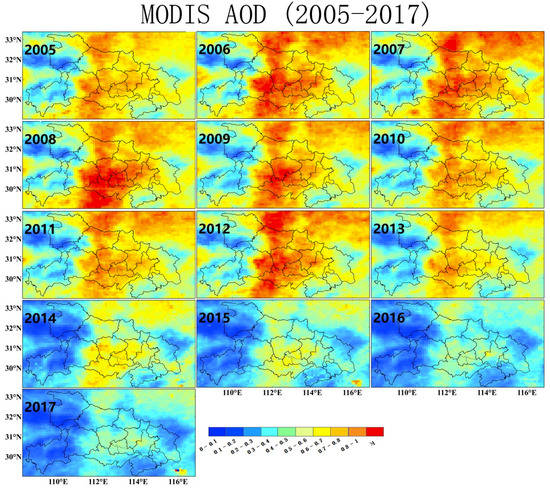
Figure 8.
Spatial and temporal distribution of annual moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) aerosol optical depth (AOD) at 550 nm over Hubei province during 2005–2017.
Moreover, there were drastic temporal changes in aerosol loading over all the non-mountain areas of Hubei (Figure 8). Compared with the persistent heavy aerosol loading (>0.8) in central Hubei during 2005–2011, there was an annual AOD increase from ~0.6–0.7 to ~1.0. In contrast, AOD in the eastern part (i.e., Wuhan) exhibited large yearly variations (>0.3), which indicates the obvious influence of regional transport. In addition, consistent or even larger increases in the magnitude of aerosol loading in adjacent areas of other provinces contributed to part of the heavy particle pollution in central Hubei. The overall decrease of AOD in Hubei began in 2011 wherein AOD declined from >1.0 to ~0.5–0.7. In 2017, there was more than a ~30–50% decrease in AOD over most non-mountain areas.
Considering that there was no aerosol retrieval when land surface was covered by clouds, sampling frequency of available satellite AOD within one year is significant for whether its annual mean value can well represent the true variations. As shown in the available frequency of MODIS AOD (Figure 9), the annual sampling frequency of MODIS DB AOD of all quality is ~120–150 days/per year, which is statistically adequate to capture the AOD gradient [33], even with some yearly difference. Moreover, long-term observations show that there are no significant changes for clouds during the last decade, except in 2013 [20]. Thus, the long-term trend of aerosol loading derived from MODIS AOD is generally representative of central China.
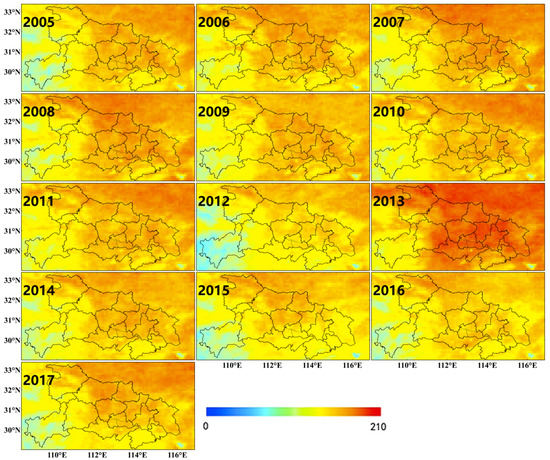
Figure 9.
Annual retrieval frequency of MODIS AOD over Hubei province during 2005–2017.
As shown in numerous studies, annual or seasonal mean maps of satellite AOD is usually used to denote particle pollution [19,33]. Different from the consistent distribution between gaseous precursors (NO2 and SO2) and AOD in northern China [15], the hotspots of gaseous pollutants and particles in central China are concentrated in completely different spatial locations of central China. Although sulfate and nitrate only account for at most about half of PM2.5 in major cities of China [11], anthropogenic emissions of SO2 and NOx have a much larger amount than organic Carbon (OC) and black Carbon (BC) [31]. In particular, as the major control targets of the government, the overall reduction of SO2 and NOx emission throughout China is approximately ~5–10 times of that for OC and BC [4]. Thus, despite the spatial inconsistency, the substantial variability of SO2 and NOx in central China can cause a considerable contribution to overall variations of overall aerosol loading.
Spatial mean of aerosol loading is usually used to evaluate variations of regional emission levels [34]. The annual average of MODIS AOD values within Hubei province during 2005–2017 are shown in Figure 10. Consistent with spatial variations, there was a slow increasing trend (0.55–0.61) in AOD during 2005–2008 with an obvious decrease (0.56) in 2009. This indicates significant changes in anthropogenic emissions or regional meteorological conditions. The increase of AOD from 2010 (0.61) was much larger and annual AOD of the entire Hubei region reached a peak value of ~0.7 in 2011. Unlike northern China’s growing AOD in 2013 [30], aerosol loading in Hubei continuously decreased from ~0.7 in 2011 to the lowest value of ~0.38 in 201. This was largely due to spatial difference in emission trends. Although the annual mean of MODIS AODs was at similar levels around 0.5 in most years, their daily values had very large fluctuations from ~0.1 to ~1.3, which was consistent with the frequent heavy pollution events and their cleanups in eastern China [20,21]. The particle pollution in central China is obviously lower than in northern China [19]. However, it should be noted that regional AOD exceeds 0.8 for about more than one quarter of the days during 2005–2014. After the clean air actions taken by the Chinese government in 2013, there has been a rapid decline in particle pollution in eastern China [35]. While there has been a continuous decrease in SO2 and particle pollutants in central China, the notable increase in NOx indicates a transition from air pollution, i.e., a larger fraction of OC and enhanced O3 pollution.
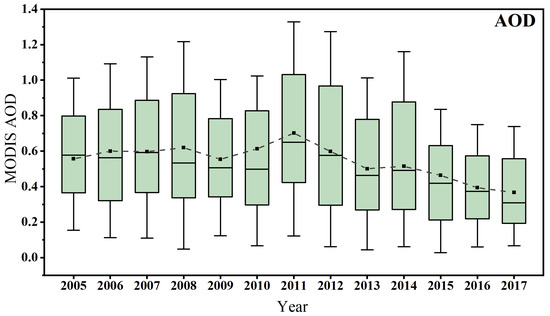
Figure 10.
Box plots of annual MODIS AOD at 550 nm over Hubei province during 2005–2017.
Seasonal mean of MODIS AOD at 550 nm showed variations of particle pollution in different meteorological conditions (Figure 11). Similar to gaseous pollution, MODIS AOD had the highest AOD in winter and autumn. MODIS AOD in central Hubei exceeded ~0.8–1.0 and influenced the northern part by adjacent transport under the prevailing northerly winds in winter [2,21]. By contrast, MODIS AOD reached moderate levels (~0.6) in the spring and summer. Different from the regional particle hotspot in winter, high AOD values were only concentrated in certain parts of central Hubei during the other seasons. Moreover, these AOD hotspots exhibited notable spatial variations in different seasons, which implies a significant intra-transport due to higher wind speeds in central China (Figure 2). The mountains around Hubei have an obvious blocking effect on outside transport of particle pollutants, even in the polluted winter. On the other hand, the limited spatial coverage of aerosol hotspots (except in winter) can partly explain the lack of gaseous pollution hotspots in central Hubei from OMI products with a coarse resolution.
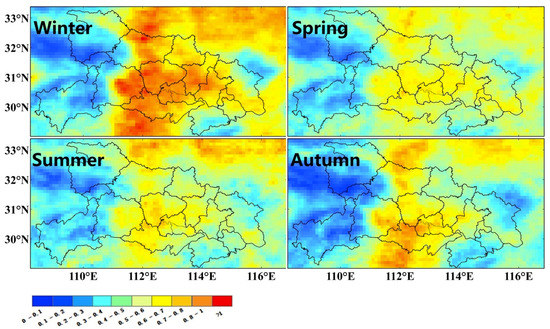
Figure 11.
Seasonal MODIS Dobson unit (DU) AOD at 550 nm during 2013–2017.
3.3. The Implication of Changing Air Pollution in Central China
Spatial variations of gaseous precursors, SO2 and NOx, can provide a visible view on their major emission sources and the effects of control measures [13]. Moreover, comparison of MODIS AOD and OMI trace gases that exhibit a significant correlation in main global pollution hotspots [36]. Although other components such as OC and mineral dust account for a considerable fraction (~30–60%) in PM2.5 of China [11], sulfate and nitrate had a much larger variability in the last decade due to specific and strict control of their emissions [4]. Variations of regional AOD in Hubei showed consistent trends with SO2 and NO2 (Figure 12). In particular, there was almost a linear relationship between regional mean value of MODIS AOD and OMI SO2 with a high correlation coefficient (R), 0.84. Despite a much lower R (0.366) between AOD and NO2, it can be seen that variations of AOD and NO2 had a close relation. Conversely, the connection between MODIS AOD and OMI SO2 and NO2 was weaker in seasonal scales. The yearly variations of seasonal meteorological conditions as well as their influence on the amount of atmospheric pollutants and satellite sampling frequency had considerable magnitude compared with the actual trends of air pollution [20,21]. The MODIS AOD in Hubei had slow changes from 2005 to 2008, with a decrease in SO2 and increase in NO2. While the reduction of SO2 emission in Hubei was ~60,000 tons and growth of NOx emission approximately 150,000 tons—inferred from comparison with OMI NO2—it is clear that the effect of desulfurization was exceeded by the increase of NOx and other emissions.
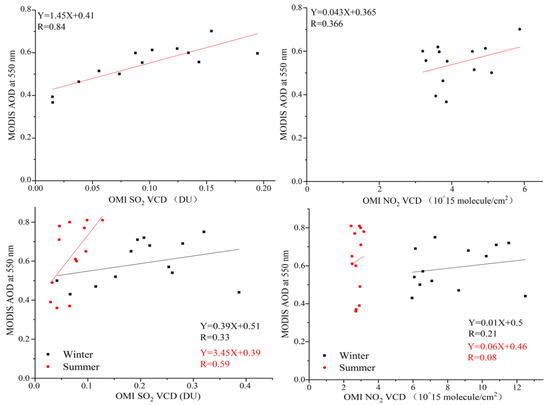
Figure 12.
Correlation of annual (top) MODIS AOD at 550 nm, with SO2 and VCD (left), and NO2 and VCD (right) over Hubei, in winter and summer (bottom), respectively.
The high correlation coefficient (R > 0.8) between AOD and SO2 shows that variation of SO2 can explain most changes of particle pollution in central China. Despite the slight increase of NO2 in 2009 (Figure 5), MODIS AOD in Hubei exhibited consistent decline in 2009 and then rose in 2010–2011 as SO2 (Figure 4 and Figure 6). There was a persistent and rapid decline in MODIS AOD with the decrease of both SO2 and NOx from 2012. Although OMI NO2 became slightly higher (~0.5 × 1015 molecules cm−2) and SO2 did not change, MODIS AOD fell by ~0.03 during 2017 as SO2 and NOx emissions. It has to be stated that other anthropogenic emission sources as well as natural dust also make important contributions to aerosol loading [3]. Different from the notable gaseous hotspot in Wuhan, high-AOD (>0.8) that converge in central Hubei mainly originated from emissions of primary aerosols and small local sources.
To have an examination on reliability and representativity of satellite observations, annual variation of the main atmospheric pollutants during 2013–2017 was analyzed based on ground measurements in Hubei (Figure 13). It can be seen that there was a rapid decline of PM2.5 concentration from ~100 µg/m3 in 2013 to ~52 µg/m3 during 2017, which was consistent with variations of MODIS AOD. An annual average of SO2 concentration from the ground network exhibited nearly the same trends with PM2.5 and declined from ~53 µg/m3 to ~13 µg/m3. Moreover, NO2 concentration decreased rapidly in 2013−2015 by ~22 µg/m3, but flattened out during 2016, exhibiting an obvious rise in NO2 concentration by ~5 µg/m3 in 2017 with similar trends as OMI NO2. The high consistency with ground measurements demonstrated that satellite observations well captured temporal variations of the overall anthropogenic emission in central China.
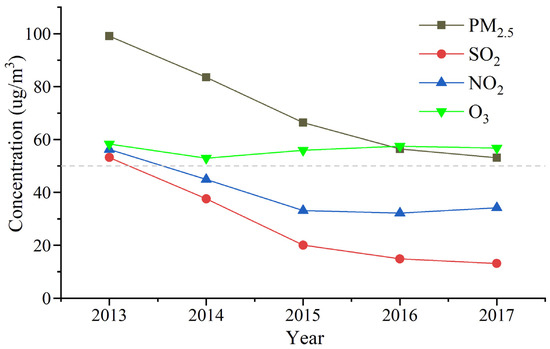
Figure 13.
Annual variations of ground-level PM2.5, SO2, NO2, and O3 observed by ambient monitoring stations located in Hubei during 2013–2017.
Despite the large overall decrease of PM2.5, SO2, and NOx during 2013–2015, O3 pollution became more serious in early 2014. The precursors of O3 included NOx and VOCs, but there was also a notable rise in O3, as NO2 decreased in 2014–2016. Considering the nonlinear relationship between O3 and its precursors, the decrease of NO2 in high NOx/VOC ratio conditions promoted O3 formation [37]. In addition, it was found that the large reduction of aerosol loading enhanced O3 production rate to stronger photolysis [38]. By now, NOx emission has become the main gaseous pollutant in central China and increases with continuous growth in the number of motor vehicles. Therefore, it is significant to strengthen the control measures for NOx emissions as well as VOCs in the eastern and central regions of Hubei in the future.
4. Discussion
The spatial and temporal variations of satellite AOD, SO2, and NO2 reveal dramatic changes of anthropogenic pollutants in central China and their emission levels. OMI NO2 (~15 × 1015 molecules cm−2) and SO2 (~0.5 DU) in the hotspot of Wuhan in central China is much lower than the high concentrations of NO2 (~20 × 1015 molecules cm−2) and SO2 (~1.0 DU) in northern China [15,16]. Unlike the concentrated air pollution in northern China, pollution hotspots in central China have smaller scales and larger spatial variations. Temporal changes (~30–50%) in the amount of main atmospheric pollutants in central China is similar to northern China, demonstrating that the control measure of the government is the main driver for changes of air quality in China. In particular, the large spatial difference of MODIS AOD has reached a close level after 2016 in all the non-mountain areas (Figure 8). For instance, in 2017, MODIS AOD ranged between 0.5–0.6 in both central and eastern Hubei.
Ground measurements from the air quality monitoring network showed similar spatial patterns of atmospheric pollutants (Figure 14). While PM2.5 hotspots are concentrated in central China as high values of MODIS AOD, NO2 is mainly distributed in Wuhan. Despite the low concentration <~35 µg/m3 in central Hubei, small SO2 and NO2 hotspots indicate the existence of emission sources in these small cities, which cannot be detected in OMI trace gases due largely to the small scale and limited amount. On the other hand, new problems of air pollution begin to emerge in central China due to different reduction amounts of the anthropogenic emissions. There have been great improvements in particle pollution and its gaseous precursors. Recently, rapid increases in motor vehicles has led to more NO2 in urban regions of central China, especially in Wuhan. Spatial distribution of O3 pollution covers both central and eastern Hubei, implying that O3 pollution is a regional air quality problem. The photochemical pollution has become the primary air pollution in most cities, which is characterized by high O3 centration (>160 µg/m3) in the daytime of summer. Besides NOx, VOCs are another type of complicated precursor for O3, as they consist of numerous volatile gases. By now, only few VOCs can be measured by satellite observations with much lower accuracy than SO2 and NO2 [27], exerting large challenges for constraining their spatial and temporal distributions.
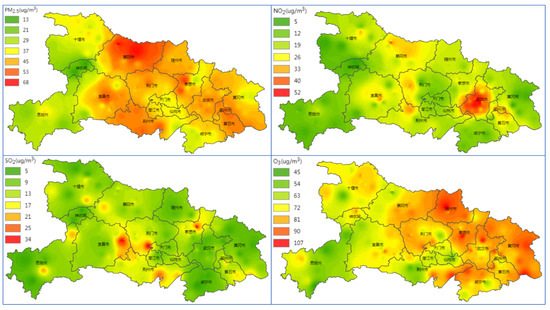
Figure 14.
Annual mean of interpolated PM2.5, SO2, NO2, and O3 values from ambient monitoring stations with the Kriging method in Hubei during 2017.
The high consistency with ground measurements indicates that satellite observations can provide reliable information regarding the overall trends of SO2, NO2, and particles in regional scales. The distinct seasonal patterns of satellite AOD, SO2, and NO2 give further insight into the main factors of air pollution in central China. Unlike the close connection between the annual mean of AOD and SO2 and NO2 (Figure 12), their lower correlation in seasonal scales indicates that other factors such as outside transport can also have important influence on air quality in central China during certain periods.
Our results demonstrate that different control measures should be taken in view of the large spatial discrepancy of gaseous and particle pollutants in central China. It should be stated that spatial resolution of MODIS AOD and OMI gaseous products we used is 10 × 10 km and 0.25 × 0.25°, respectively, which can be too coarse to reveal point sources such as steel plants and small cities in central Hubei. Other than SO2 and NOx emissions, trace gases such as ammonia (NH3) and formaldehyde (HCHO) also have important contribution to air pollution in central China. Although satellite products of HCHO and NH3 are available, their accuracy is much lower compared with NO2 and SO2 [27,35]. Despite much smaller variations in emissions than sulfate and nitrate [4], the long-term changes of other major components in PM2.5 including OC and mineral dust have to be considered in central China. They cannot by be quantified by current satellite observations and have no corresponding ground measurements.
As an enhanced version of OMI, the TROPOspheric monitoring instrument (TROPOMI) onboard Sentinel-5 satellite since 2017 has a higher spatial resolution of 7 × 3.5 km, which can capture much finer emission sources [39]. Additionally, satellite observations can provide an observational constraint in emission sources for chemistry transport models [40]. To improve air quality on the regional scale, it is necessary to monitor spatial and temporal variations of emission sources and make detailed control measures timely.
5. Conclusions
During the last few decades, air pollution in China has drawn wide attention due to high-level anthropogenic emissions and drastic changes. However, most studies focus on economically developed and densely populated regions such as northern China, the YRD, and PRD. As an emerging pollution hotspot with diverse emission sources, air pollution in central China has been of less concern. To have a long-term insight into the spatial pattern, variations, and influence factors of atmospheric pollutants in central China, we utilized ground measurements and long-term multiple satellite observations including MODIS AOD, OMI SO2, and NO2 during 2005–2017.
Satellite observation showed large spatial and temporal variations in AOD, SO2, and NO2 over central China. The air quality exhibited notable seasonal differences, which was heaviest in winter and lightest in summer. There was a large overall decrease in atmospheric pollutants in central China due to continuous control measures. Different from the common collocation of gaseous and particle pollution, eastern Hubei was mainly influenced by gaseous pollutants including NOx and O3, whereas particle pollution was predominant in central Hubei. Despite slight recovery in 2011, OMI SO2 in Hubei declined by more than 90%, which was close to the background level. By contrast, with a later emission control, OMI NO2 reached its peak value in 2011 and fell back to the level of 2005 with a ~50% reduction in 2017. Thus, before 2011, MODIS AOD slowly changed due to the offset of decreased SO2 and increased NO2 and then sharply declined as the combined reduction of both SO2 and NO2. It should be noted that there was a slight rise in OMI NO2 during 2017, which was consistent with an increase in vehicle usage.
High consistency with ground measurements shows that satellites can reliably reflect the overall trends of atmospheric pollutants in regional scales. Annual concentration of PM2.5, SO2, and NO2 in ground network declines ~45 (45%), ~40 (75%), and ~17 (29%) µg/m3 during 2013–2017, respectively. There is a high correlation (R > 0.8) between satellite SO2 and AOD, demonstrating that reduction of SO2 emissions has a large contribution to decrease of PM2.5. Despite the large overall decrease of PM2.5 and its gaseous precursors, increased O3 has become the main air pollution problem in eastern Hubei with growth of NOx emissions. For air quality improvement in central Hubei, primary emission of particle pollutants should be controlled. To improve air quality on a regional scale, it is necessary to monitor the distinct spatial and temporal variations of atmospheric pollutants in central China via satellite observation at finer resolution in the future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.L. and X.M.; methodology, R.L.; software, L.C.; validation, L.W. and Z.W.; formal analysis, Y.J.; investigation, R.L.; resources, L.C.; data curation, L.W.; writing—original draft preparation, R.L.; writing—review and editing, L.C.; visualization, R.L.; supervision, X.M.; project administration, L.C.; funding acquisition, R.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key R and D Program of China (Grant NO. 2017YFB0503901 and 2016YFA0600203) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.41601472).
Acknowledgments
We appreciate MODIS and OMI team for the aerosol, and SO2 and NO2 products used.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Xu, P.; Chen, Y.; Ye, X. Haze, air pollution, and health in China. Lancet 2013, 382, 2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Chen, L.; Su, L.; Tao, J. Satellite observation of regional haze pollution over the North China Plain. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D12203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pani, S.K.; Ou-Yang, C.F.; Wang, S.H.; Ogren, J.A.; Sheridan, P.J.; Sheu, G.R.; Lin, N.H. Relationship between long-range transported atmospheric black carbon and carbon monoxide at a high-altitude background station in East Asia. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 210, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Tong, D.; Li, M.; Liu, F.; Hong, C.; Geng, G.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Peng, L.; Qi, J.; et al. Trends in China’s anthropogenic emissions since 2010 as the consequence of clean air actions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 14095–14111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Niu, T.; Zhang, X.; Gong, S.L.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.L. Atmospheric aerosol compositions in China: Spatial/temporal variability, chemical signature, regional haze distribution and comparisons with global aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 779–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, L.K.; Kondo, Y.; Miyazaki, M.; Kuwata, M.; Koike, N.; Takegawa, H.; Tanimoto, H.; Matsueda, S.; Yoon, C.; Kim, Y.J. Anthropogenic aerosols observed in Asian continental outflow at Jeju Island, Korea, in spring 2005. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaya, Y.; Pan, X.; Miyakawa, T.; Komazaki, Y.; Taketani, F.; Uno, I.; Kondo, Y. Long-term observations of black carbon mass concentrations at Fukue Island, western Japan, during 2009–2015: Constraining wet removal rates and emission strengths from East Asia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 10689–10705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, M.T.; Chou, C.C.K.; Lin, N.H.; Takami, A.; Hsiao, T.C.; Lin, T.H.; Fu, J.S.; Pani, S.K.; Lu, Y.R.; Yang, T.Y. A Simulation Study on PM2.5 Sources and Meteorological Characteristics at the Northern Tip of Taiwan in the Early Stage of the Asian Haze Period, Aerosol. Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 3166–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, C.A., III; Burnett, R.T.; Thun, M.J.; Calle, E.E.; Krewski, D.; Ito, K.; Thurston, G.D. Lung cancer, cardiopulmonary mortality, and long-term exposure to fine particulate air pollution. JAMA 2002, 287, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Mei, X.; Wei, L.; Han, X.; Zhang, M.; Jing, Y. Study on the contribution of transport to PM2.5 in typical regions of China using the regional air quality model RAMS-CMAQ. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 214, 116856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Zhang, L.; Cao, J.; Zhang, R. A review of current knowledge concerning C chemical composition, aerosol optical properties and their relationships across China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 9485–9518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanré, D.; Remer, L.A.; Vermote, E.F.; Chu, A.; Holben, B.N. Operational remote sensing of tropospheric aerosol over land from EOS moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 17051–17067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krotkov, N.A.; McLinden, C.A.; Li, C.; Lamsal, L.N.; Celarier, E.A.; Marchenko, S.V.; Swartz, W.H.; Bucsela, E.J.; Joiner, J.; Duncan, B.N.; et al. Aura OMI observations of regional SO2 and NO2 pollution changes from 2005 to 2015. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 4605–4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Chen, L.; Xiong, X.; Zhang, M.; Ma, P.; Tao, J.; Wang, Z. Formation process of the widespread extreme haze pollution over northern China in January 2013: Implications for regional air quality and climate. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 98, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Wang, H.; Cai, K.; Chen, L.; Zhou, Z.; Li, S. Long-term (2006–2015) variations and relations of multiple atmospheric pollutants based on multi-remote sensing data over the North China Plain. Environ. Pollution 2019, 255, 113323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Lee, C.S.; Zhang, R.; Chen, L. Spatial and temporal evaluation of long term trend (2005–2014) of OMI retrieved NO2 and SO2 concentrations in Henan Province, China. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 154, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H.; Lin, J.; Zhang, R.; Liu, M.; Weng, H.; Ni, R.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, Q. High-resolution (0.05° × 0.05°) NOx emissions in the Yangtze River Delta inferred from OMI. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 12835–12856. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Shao, M.; Chen, L.; Tao, M.; Zhong, L.; Chen, D.; Fan, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Space view of the decadal variation for typical air pollutants in the Pearl River Delta (PRD) region in China. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2016, 10, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Liu, R.; Liu, Y.; Bi, J. Effects of air pollution control policies on PM2.5 pollution improvement in China from 2005 to 2017: A satellite-based perspective. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 6861–6877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Tao, J.; Wang, X. Did the widespread haze pollution over China increase during the last decade? A satellite view from space. Environ. Res. Let. 2016, 11, 054019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Chen, L.; Li, R.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Tang, G.; Tao, J. Spatial oscillation of the particle pollution in eastern China during winter: Implications for regional air quality and climate. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 144, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remer, L.A.; Mattoo, S.; Levy, R.C.; Munchak, L.A. MODIS 3 km aerosol product: Algorithm and global perspective. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 1829–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Tao, J.; Che, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y. Comparison and evaluation of the MODIS Collection 6 aerosol data in China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 6992–7005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, N.C.; Jeong, M.J.; Bettenhausen, C.; Hansell, A.M.; Seftor, C.S.; Huang, J.; Tsay, S.C. Enhanced Deep Blue aerosol retrieval algorithm: The second generation. J. Geohys. Res. 2013, 118, 9296–9315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S.; Munchak, L.A.; Remer, L.A.; Sayer, A.M.; Patadia, F.; Hsu, N.C. The Collection 6 MODIS aerosol products over land and ocean. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2989–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, A.M.; Hsu, N.C.; Lee, J.; Kim, W.V.; Dutcher, S.T. Validation, Stability, and Consistency of MODIS Collection 6.1 and VIIRS Version 1 Deep Blue Aerosol Data Over Land. J. Geophys. Res. 2019, 124, 4658–4688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levelt, P.F.; Joiner, J.; Tamminen, J.; Veefkind, J.P.; Bhartia, P.K.; Carn, S. The Ozone Monitoring Instrument: Overview of 14 years in space. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 5699–5745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boersma, K.F.; Eskes, H.J.; Dirksen, R.J.; Veefkind, J.P.; Stammes, P.; Huijnen, V.; Kleipool, Q.L.; Sneep, M.; Claas, J.; Leitão, J.; et al. An improved tropospheric NO2 column retrieval algorithm for the Ozone Monitoring Instrument. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2011, 4, 1905–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krotkov, N.S.; Carn, A.; Krueger, P.; Yang, K. Band residual difference algorithm for retrieval of SO2 from the aura ozone monitoring instrument (OMI). IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Joiner, J.; Krotkov, N.A.; Bhartia, P.K. A fast and sensitive new satellite SO2 retrieval algorithm based on principal component analysis: Application to the ozone monitoring instrument. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 6314–6318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Streets, D.G. Sulfur dioxide and primary carbonaceous aerosol emissions in China and India, 1996–2010. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 9839–9864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.T.; McElroy, M.B. Detection from space of a reduction in anthropogenic emissions of nitrogen oxides during the Chinese economic downturn. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 8171–8188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Li, R.; Wang, L.; Lan, F.; Wang, Z.; Tao, J.; Che, H.; Wang, L.; Chen, L. A critical view of long-term AVHRR aerosol data record in China: Retrieval frequency and heavy pollution. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 223, 117246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogacheva, L.E.; Rodriguez, P.; Kolmonen, T.H.; Virtanen, G.; de Leeuw, G.; Georgoulias, A.K.; Alexandri, G.; Kourtidis, K.; van der, R.J. Spatial and seasonal variations of aerosols over China from two decades of multi-satellite observations – Part 2: AOD time series for 1995–2017 combined from ATSR ADV and MODIS C6.1 and AOD tendency estimations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 16631–16652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Wang, L.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Tao, J. Reversal of Aerosol Properties in Eastern China with Rapid Decline of Anthropogenic Emissions. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veefkind, J.; Boersma, K.; Wang, J.; Kurosu, T.; Krotkov, N.; Chance, K.; Levelt, P. Global satellite analysis of the relation between aerosols and short-lived trace gases. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 1255–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Li, M.; Liao, Z.; Sun, Y.; Song, T.; Gao, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Ji, D.; et al. Quantifying the impact of synoptic circulation patterns on ozone variability in northern China from April to October 2013–2017. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 14477–14492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, X.; Shao, M.; Hu, M.; Zeng, L.; Wu, Y.; Tan, T. The impact of aerosols on photolysis frequencies and ozone production in Beijing during the 4-year period 2012–2015. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 9413–9429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, D.; Zhao, X.; McLinden, C.A.; Boersma, F.; Bourassa, A.; Dammers, E.; Degenstein, D.; Eskes, H.; Fehr, L.; Fioletov, V.; et al. High-Resolution Mapping of Nitrogen Dioxide With TROPOMI: First Results and Validation Over the Canadian Oil Sands. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, J.; Henze, D.K.; Qu, W.; Kopacz, M. Constraints on aerosol sources using GEOS-Chem adjoint and MODIS radiances, and evaluation with multisensor (OMI, MISR) data. J. Geophys. Res. 2013, 118, 6396–6413. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).