Performance of TRMM Product in Quantifying Frequency and Intensity of Precipitation during Daytime and Nighttime across China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
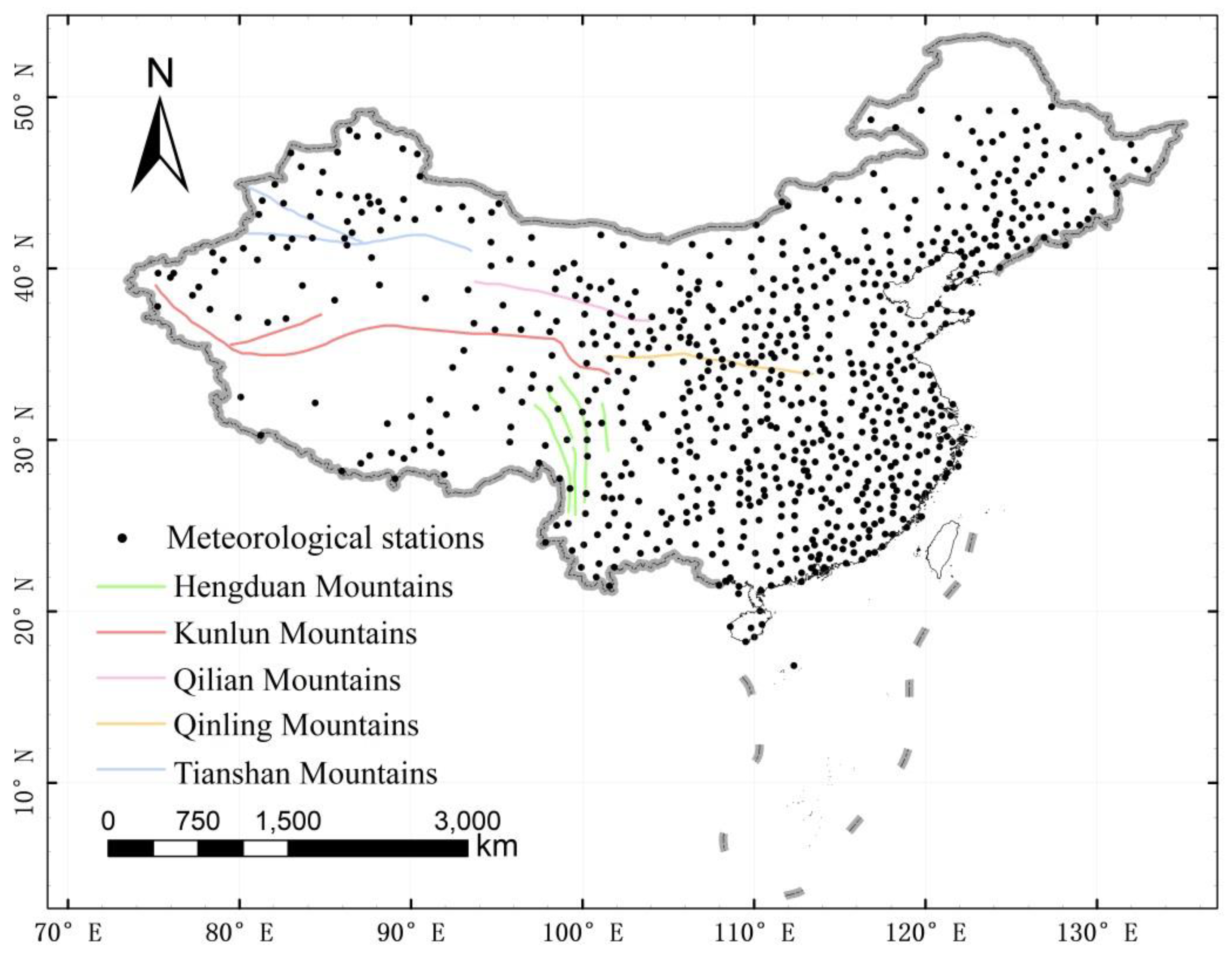
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Satellite-Based Precipitation Products
2.3. Gauge-Based Precipitation Observations
3. Methodology
3.1. Data Preprocessing
3.2. Precipitation Classification and Properties
3.3. Trend Calculation and Evaluation Indices
4. Results
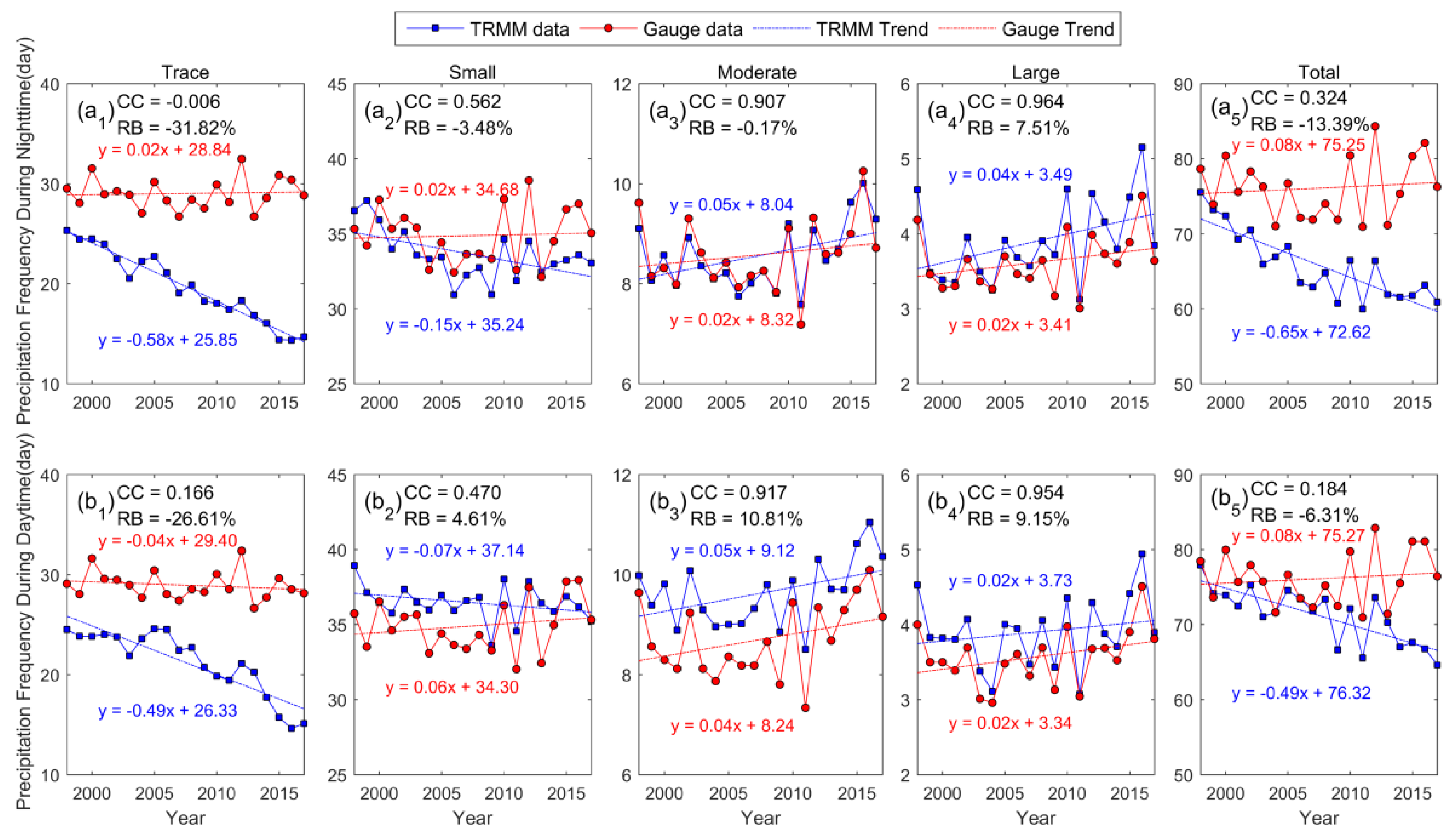
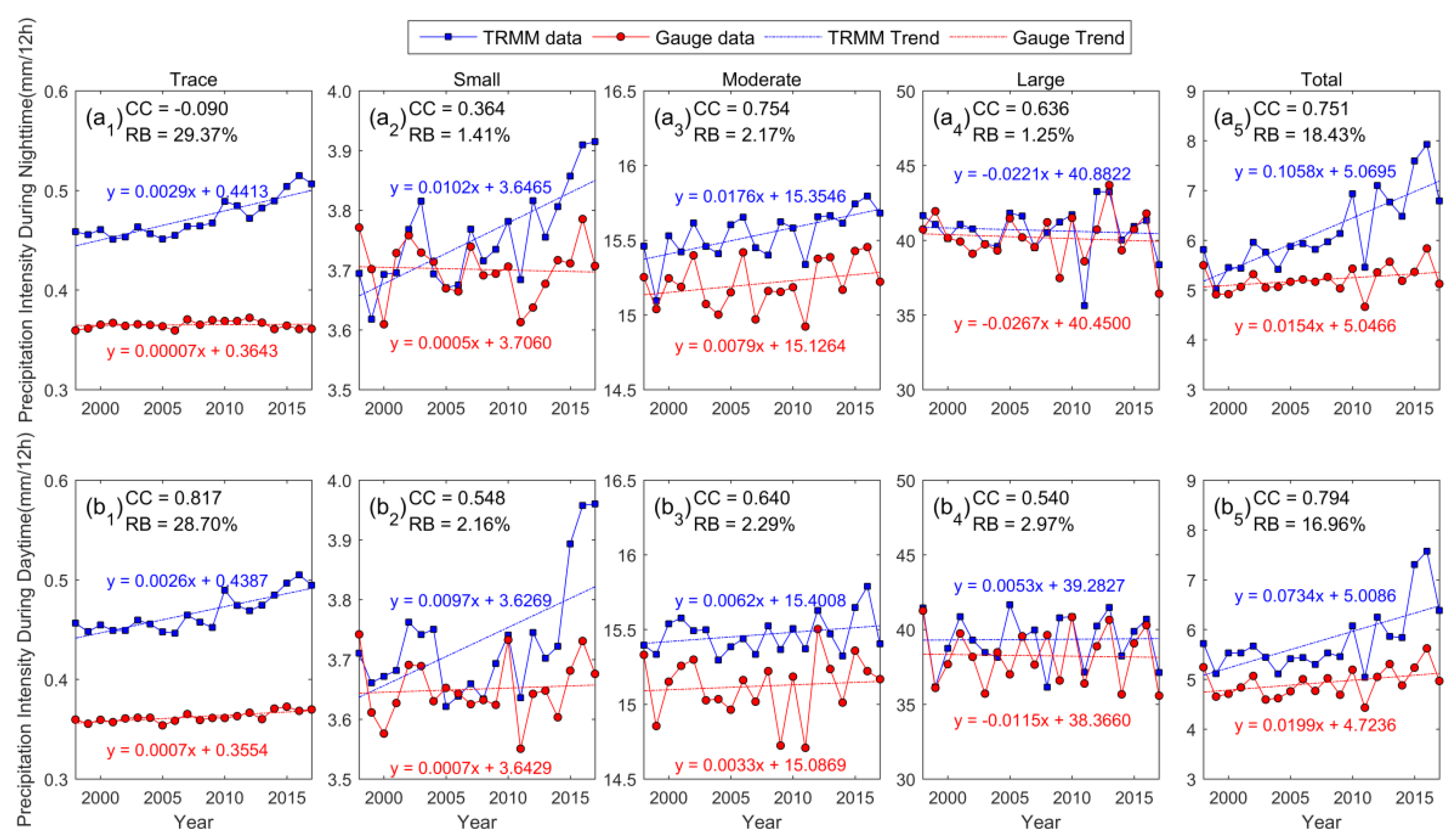
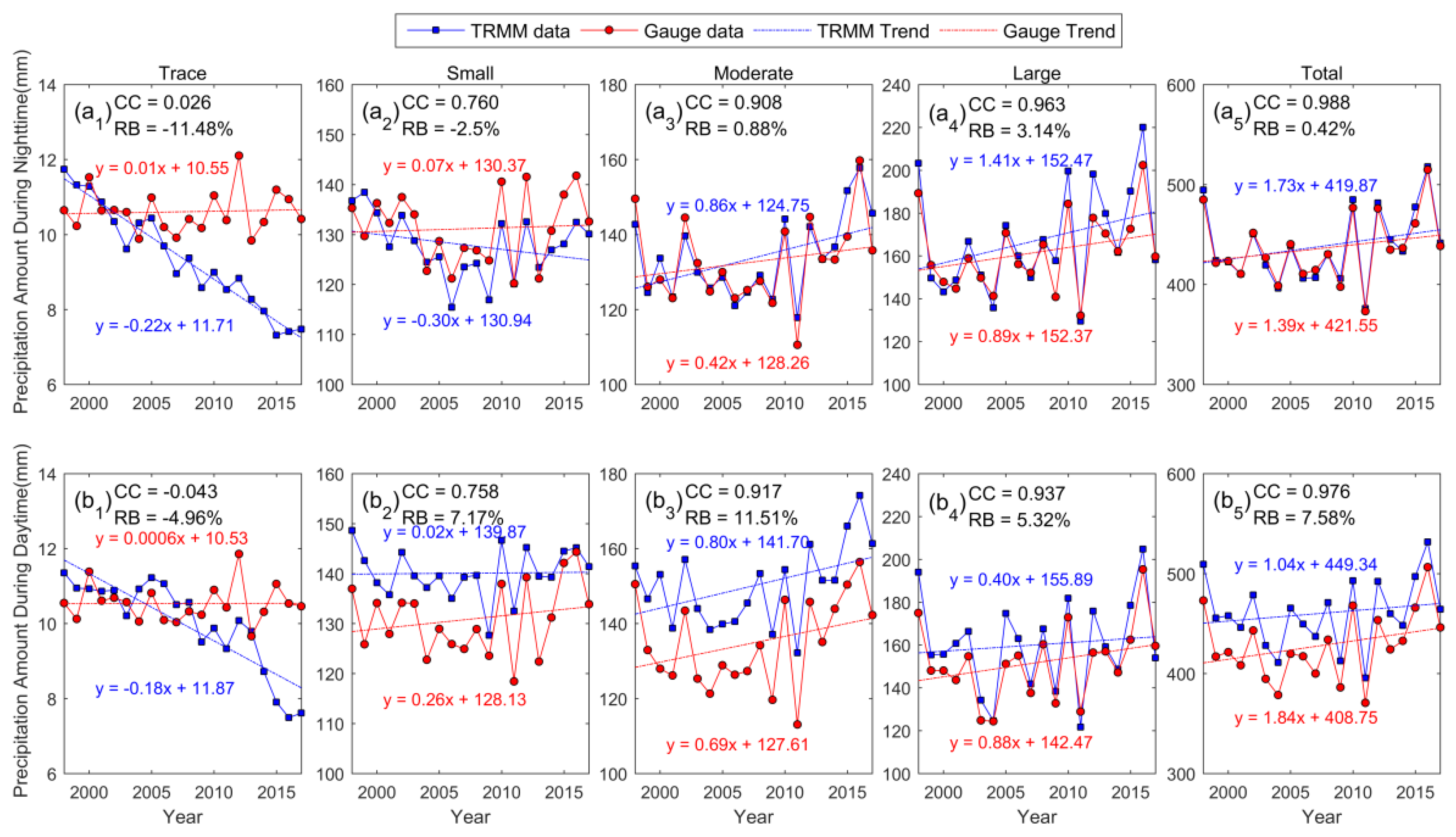
4.1. Interannual Variation in Subdaily Precipitation Properties
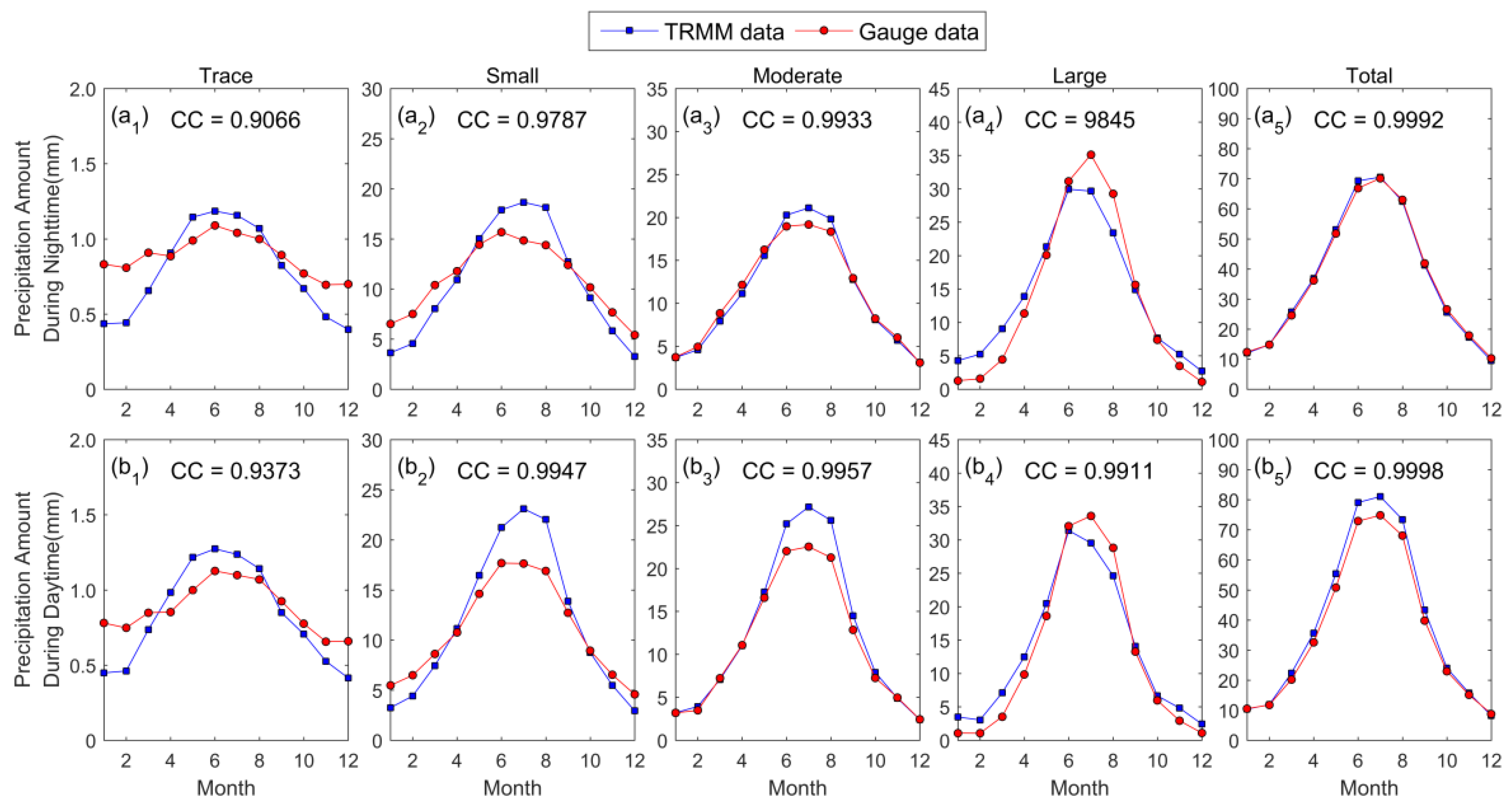
4.2. Properties of Seasonal Cycle of Subdaily Precipitation
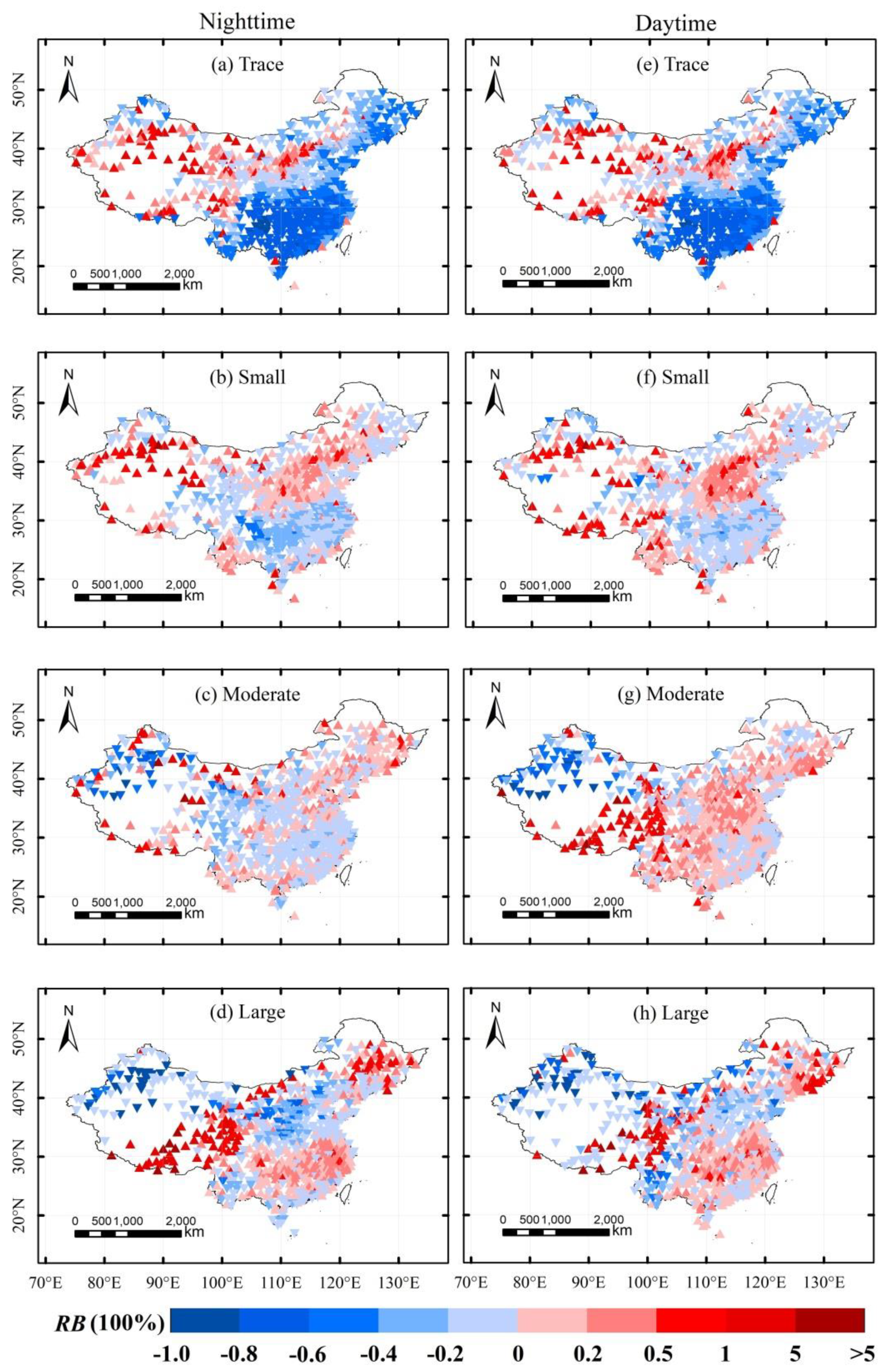
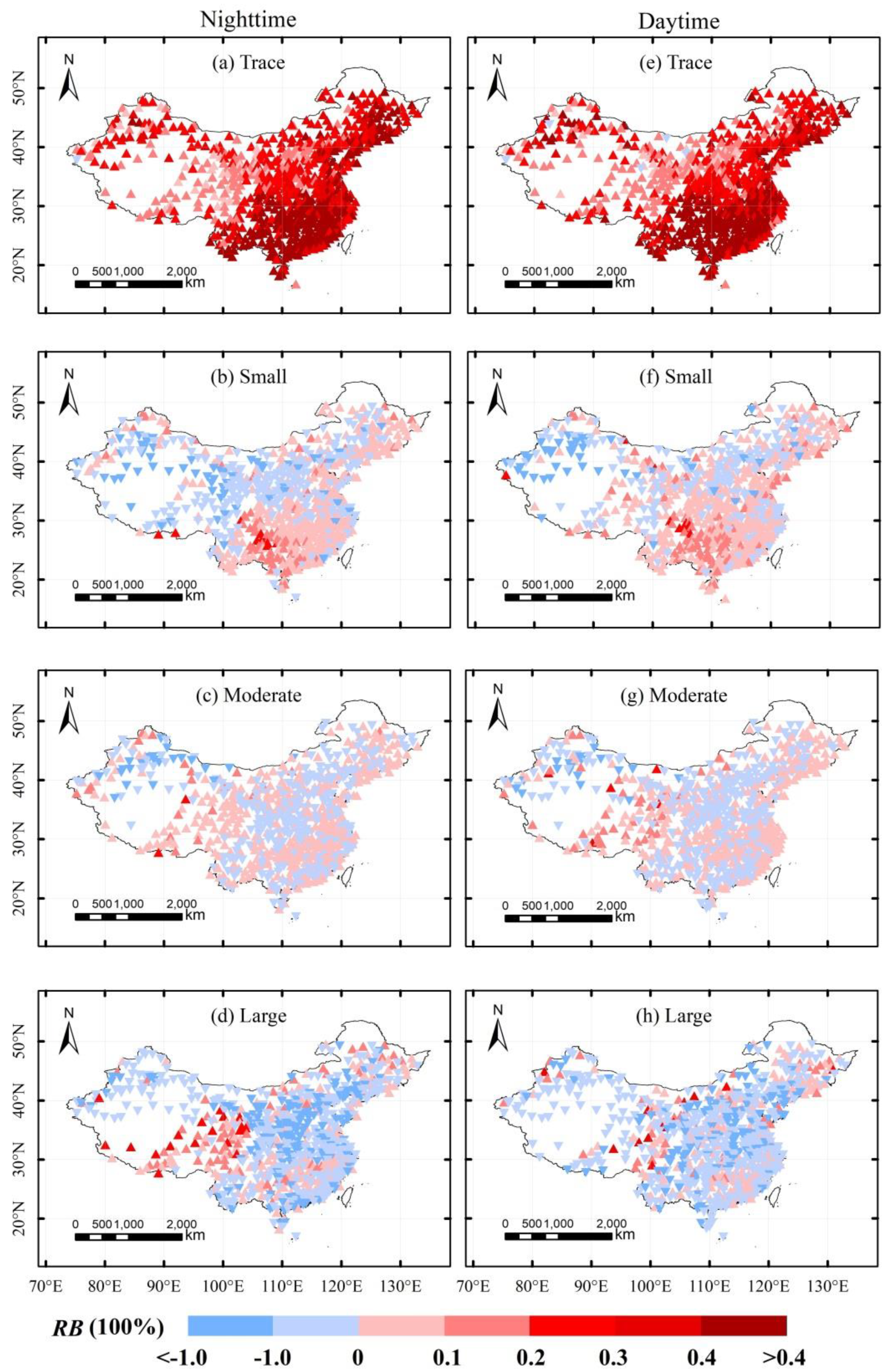
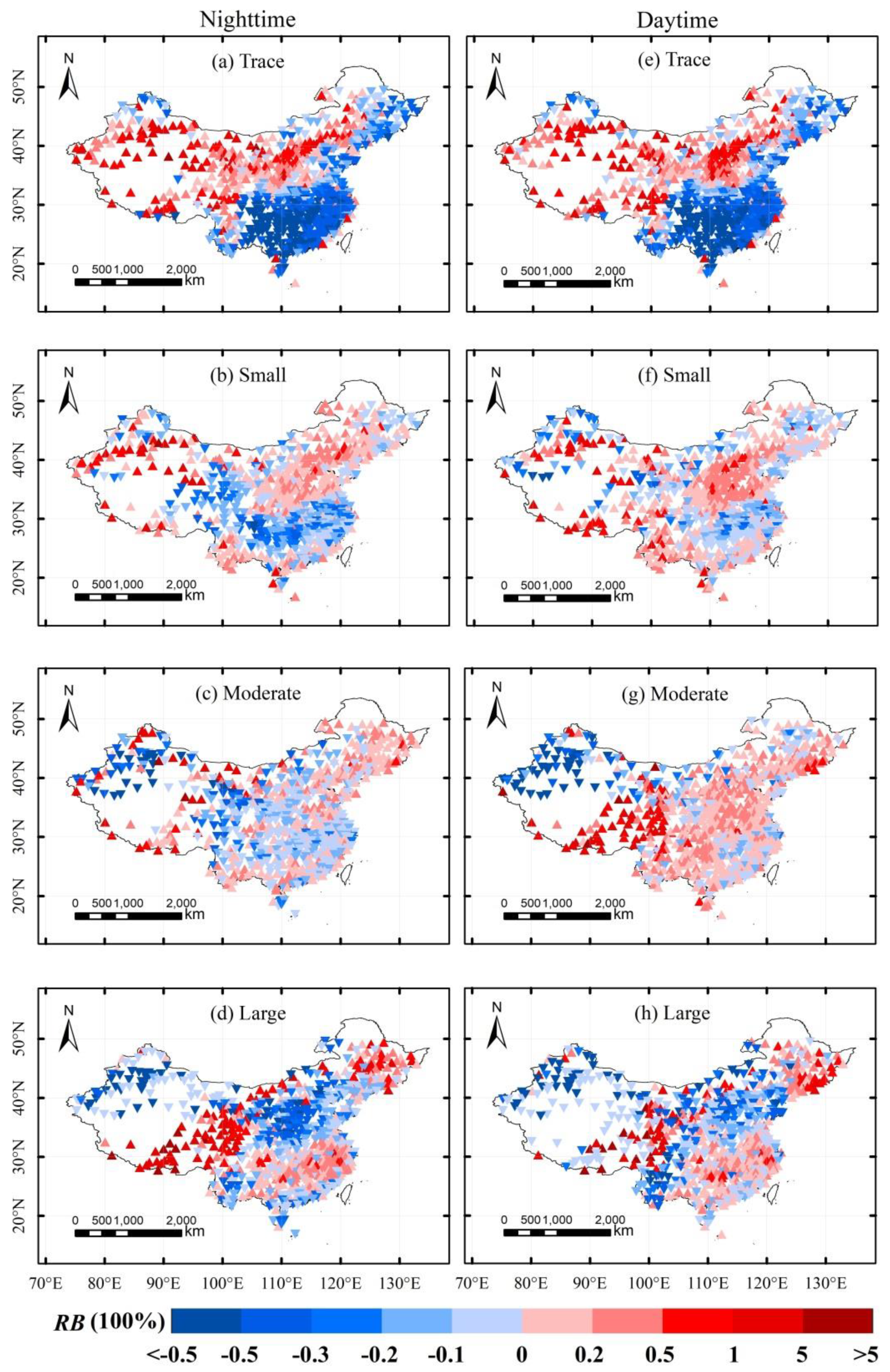
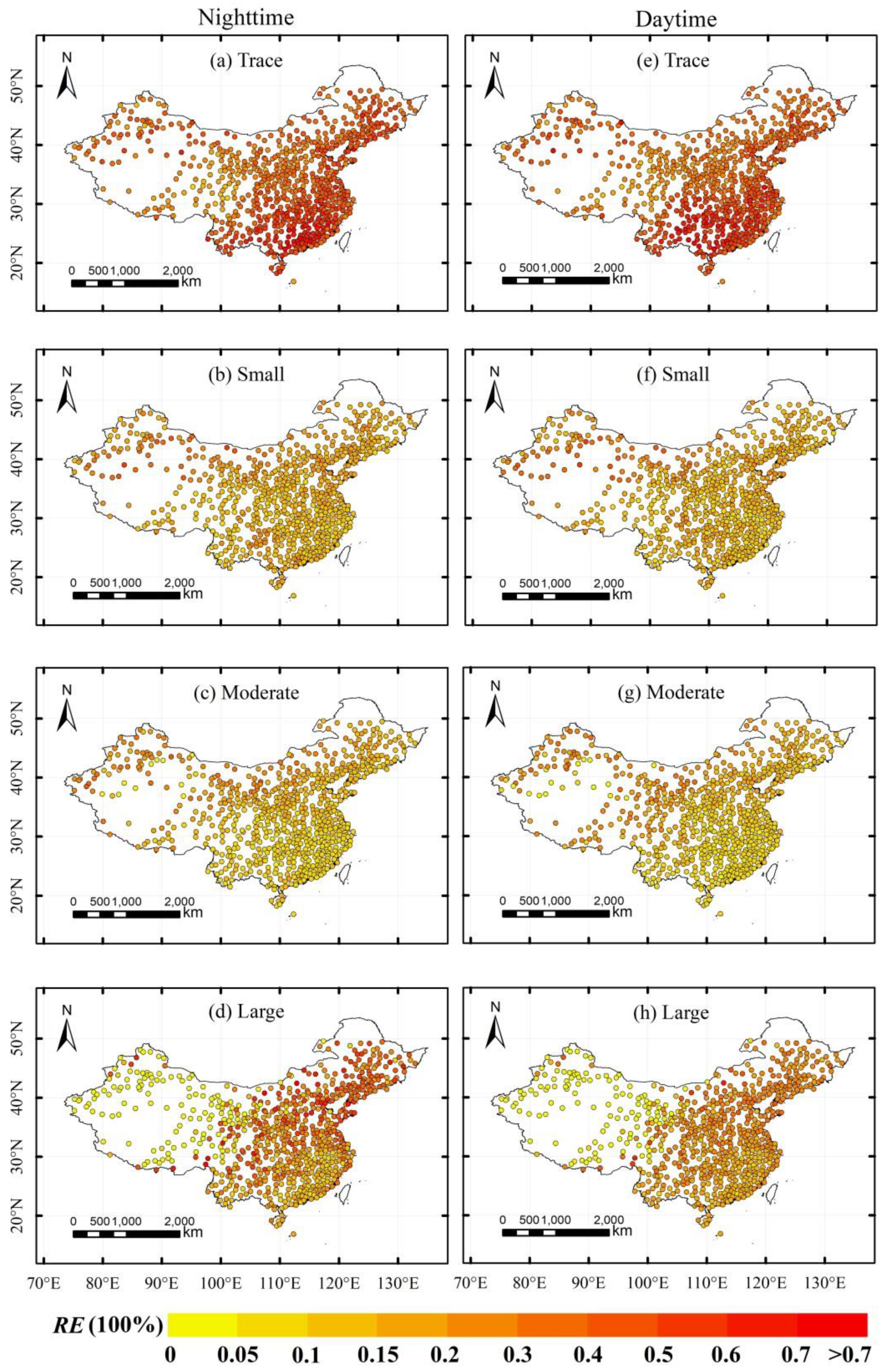
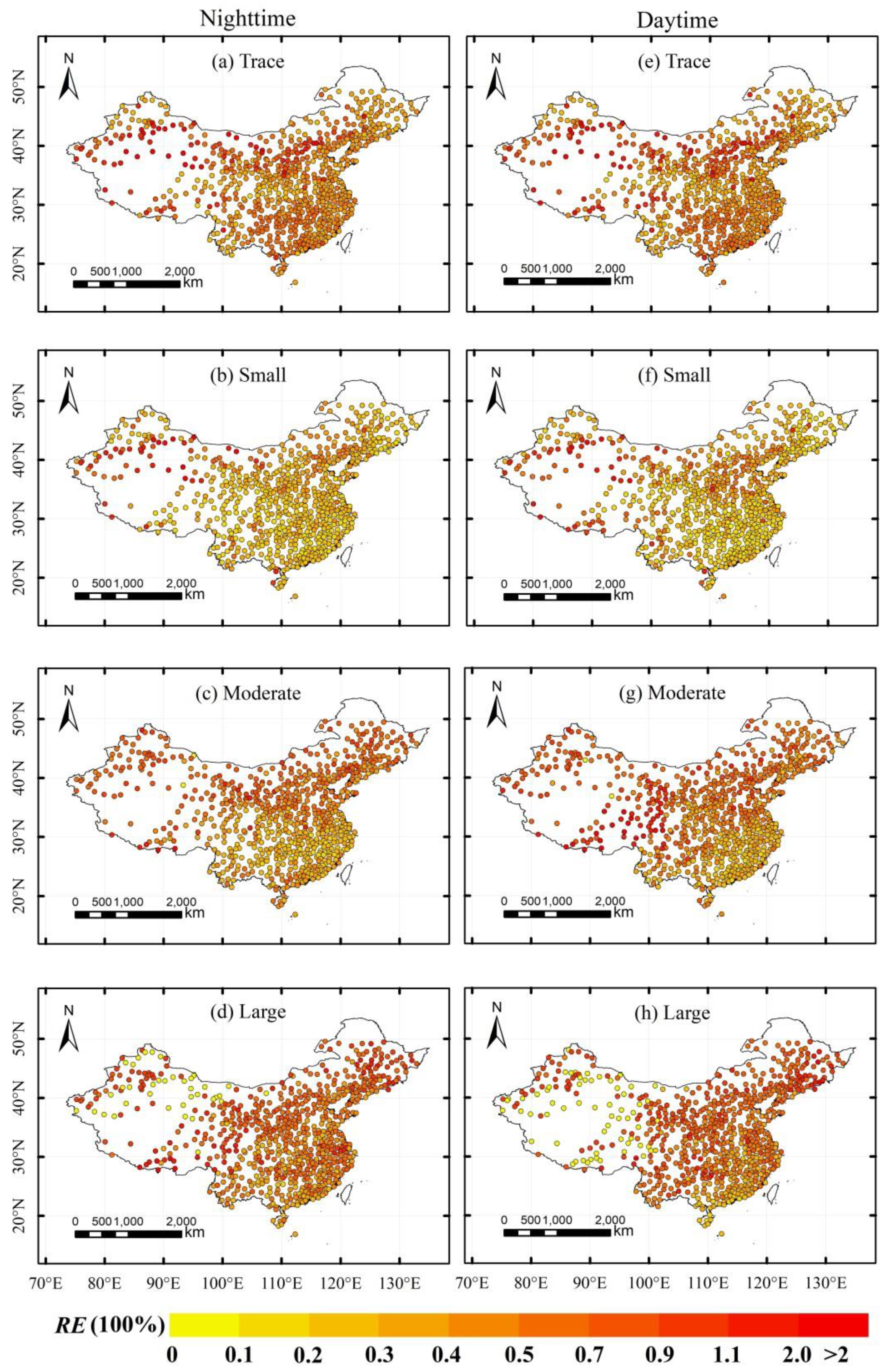
4.3. Properties of Spatial Distribution of Satellite Data and Stations in Subdaily Precipitation
5. Discussion
5.1. Uncertainties in Estimates of Trace Amounts of Rain
5.2. Negative Correlation between Frequency and Intensity
5.3. Poor Performance Areas
6. Conclusions
- 1)
- TRMM 3B42 products can successfully reproduce interannual trends of the frequency and amount of precipitation, with an averaged correlation coefficient of 0.84 over the past two decades, except for trace amounts of rain. The TRMM data and gauge data had the strongest correlation for moderate and large amounts of rain (CC > 0.9), a moderate correlation for small amounts of rain, and the weakest correlation for trace amounts of rain.
- 2)
- Satellite products can effectively represent the seasonal shape of the frequency and amount of precipitation during the nighttime and daytime (CC > 0.88). However, there are deficiencies in the estimated intensity of precipitation, especially for trace and small amounts of rain. The TRMM 3B42 tended to overestimate the precipitation frequency in rainy months (May–August) but underestimate it in rainless months (October–March). The precipitation intensity yielded results contrary to this. Therefore, the biases in the frequency and intensity of precipitation in different months offset one another, and there is improved performance in terms of the estimated amount of precipitation.
- 3)
- A spatial comparison showed that the TRMM 3B42 can effectively represent the distribution of the daily precipitation amount over most of the eastern regions of China, but did not perform well in the Tibetan Plateau and northwest China. Moreover, the satellite products tended to underestimate small precipitation amounts in south China and large precipitation amounts in north China, but overestimated small precipitation amounts in north China and large precipitation amounts in south China.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dai, A.; Lin, X.; Hsu, K.-L. The frequency, intensity, and diurnal cycle of precipitation in surface and satellite observations over low- and mid-latitudes. Clim. Dyn. 2007, 29, 727–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Zhu, W.; Lű, A.; Yan, T. A statistical spatial downscaling algorithm of TRMM precipitation based on NDVI and DEM in the Qaidam Basin of China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 3069–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baguis, P.; Roulin, E.; Willems, P.; Ntegeka, V. Climate change scenarios for precipitation and potential evapotranspiration over central Belgium. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2009, 99, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.L.; Ibrahim, A.L.; Yusop, Z.; Chua, V.P.; Chan, N.W. Climate change impacts under CMIP5 RCP scenarios on water resources of the Kelantan River Basin, Malaysia. Atmos. Res. 2017, 189, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Duan, Z. Assessment of GPM and TRMM Precipitation products over Singapore. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, R. Recent changes of precipitation in Gansu, Northwest China: An index-based analysis. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2016, 129, 397–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.; Anagnostou, E.N.; Nikolopoulos, E.I.; Borga, M. Error analysis of satellite precipitation products in mountainous basins. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 1778–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haile, A.T.; Yan, F.; Habib, E. Accuracy of the CMORPH satellite-rainfall product over Lake Tana Basin in Eastern Africa. Atmos. Res. 2015, 163, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.Z.; Wang, K.; Qi, D. Validating the integrated multisatellite retrievals for global precipitation measurement in terms of diurnal variability with hourly gauge observations collected at 50,000 stations in China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 10423–10442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Guo, B.; Ye, B.; Ye, Q.; Chen, H.; Ju, X.; Guo, J.; Wang, Z. Systematical evaluation of GPM IMERG and TRMM 3B42V7 precipitation products in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain, China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Ma, Y.; Long, D.; Zhong, L.; Hong, Y. Evaluation of GPM Day-1 IMERG and TMPA Version-7 legacy products over Mainland China at multiple spatiotemporal scales. J. Hydrol. 2016, 533, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einfalt, T.; Arnbjerg-Nielsen, K.; Golz, C.; Jensen, N.-E.; Quirmbach, M.; Vaes, G.; Vieux, B. Towards a roadmap for use of radar rainfall data in urban drainage. J. Hydrol. 2004, 299, 186–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneebeli, M.; Dawes, N.; Lehning, M.; Berne, A. High-resolution vertical profiles of x-band polarimetric radar observables during snowfall in the swiss alps. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2013, 52, 378–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-H.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.-Y. Suitability of the TRMM satellite rainfalls in driving a distributed hydrological model for water balance computations in Xinjiang catchment, Poyang lake basin. J. Hydrol. 2012, 426-427, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Tian, Q.; Yu, T.; Meng, Q.; Jancso, T.; Udvardy, P.; Huang, Y. A comprehensive drought monitoring method integrating MODIS and TRMM data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 23, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummerow, C.; Barnes, W.; Kozu, T.; Shiue, J.; Simpson, J. The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) sensor package. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1998, 15, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J.; Wolff, D.B.; Adler, R.F.; Gu, G.; Hong, Y.; Bowman, K.P.; Stocker, E.F. The TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA): Quasi-global, multiyear, combined-sensor precipitation estimates at fine scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JOYCE, R.J.; JANOWIAK, J.E.; ARKIN, P.A.; XIE, P. CMORPH:A Method that Produces Global Precipitation Estimates from Passive microwave and infrared fata at high spatial and temporal resolution. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HSU, K.-L.; GAO, X.; SOROOSHIAN, S.; GUPTA, H.V. Precipitation estimation from remotely sensed information using artificial neural networks. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1997, 36, 1176–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, A.Y.; Kakar, R.K.; Neeck, S.; Azarbarzin, A.A.; Kummerow, C.D.; Kojima, M.; Oki, R.; Nakamura, K.; Iguchi, T. The global precipitation measurement mission. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 701–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.L.; Ibrahim, A.L.; Duan, Z.; Cracknell, A.P.; Chaplot, V. Evaluation of six high-resolution satellite and ground-based precipitation products over Malaysia. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 1504–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Tan, K.; Chua, V.; Chan, N. Evaluation of TRMM product for monitoring drought in the Kelantan River Basin, Malaysia. Water 2017, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.L.; Santo, H. Comparison of GPM IMERG, TMPA 3B42 and PERSIANN-CDR satellite precipitation products over Malaysia. Atmos. Res. 2018, 202, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hsu, K.-L.; AghaKouchak, A.; Sorooshian, S. Object-Based assessment of satellite precipitation products. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varikoden, H.; Samah, A.A.; Babu, C.A. Spatial and temporal characteristics of rain intensity in the peninsular Malaysia using TRMM rain rate. J. Hydrol. 2010, 387, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pombo, S.; de Oliveira, R.P. Evaluation of extreme precipitation estimates from TRMM in Angola. J. Hydrol. 2015, 523, 663–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastos, P.T.; Kapsomenakis, J.; Philandras, K.M. Evaluation of the TRMM 3B43 gridded precipitation estimates over Greece. Atmos. Res. 2016, 169, 497–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Hong, Y.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Evaluation of TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) and Its Utility in Hydrologic Prediction in the La Plata Basin. J. Hydrometeorol. 2008, 9, 622–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michot, V.; Vila, D.; Arvor, D.; Corpetti, T.; Ronchail, J.; Funatsu, B.; Dubreuil, V. Performance of TRMM TMPA 3B42 V7 in replicating daily rainfall and regional rainfall regimes in the Amazon Basin (1998–2013). Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almazroui, M. Calibration of TRMM rainfall climatology over Saudi Arabia during 1998–2009. Atmos. Res. 2011, 99, 400–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekeli, A.E.; Fouli, H. Evaluation of TRMM satellite-based precipitation indexes for flood forecasting over Riyadh City, Saudi Arabia. J. Hydrol. 2016, 541, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.E.M. An analysis of the performance of hybrid infrared and microwave satellite precipitation algorithms over India and adjacent regions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 101, 63–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javanmard, S.; Yatagai, A.; Nodzu, M.I.; BodaghJamali, J.; Kawamoto, H. Comparing high-resolution gridded precipitation data with satellite rainfall estimates of TRMM_3B42 over Iran. Adv. Geosci. 2010, 25, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Hong, Y.; Cao, Q.; Gourley, J.J.; Kirstetter, P.-E.; Yong, B.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Hu, J.; et al. Similarity and difference of the two successive V6 and V7 TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis performance over China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 13060–13074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, S.; Cao, Q.; Hong, Y.; Wu, B.; Huang, M.; Qiao, L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, W.; et al. Evaluation of version-7 TRMM multi-satellite precipitation analysis product during the beijing extreme heavy rainfall event of 21 July 2012. Water 2013, 6, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Yatagai, A. Evaluation of TRMM 3B42 product using a new gauge-based analysis of daily precipitation over China. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 2749–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, E.; Henschke, A.; Adler, R.F. Evaluation of TMPA satellite-based research and real-time rainfall estimates during six tropical-related heavy rainfall events over Louisiana, USA. Atmos. Res. 2009, 94, 373–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Hong, Y.; Gourley, J.J.; Huffman, G.J.; Tian, Y.; Cao, Q.; Yong, B.; Kirstetter, P.-E.; Hu, J.; Hardy, J.; et al. Evaluation of the successive V6 and V7 TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis over the Continental United States. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 8174–8186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Hong, Y.; Chen, S.; Zou, C.B.; Gourley, J.J.; Yong, B. Performance assessment of the successive Version 6 and Version 7 TMPA products over the climate-transitional zone in the southern Great Plains, USA. J. Hydrol. 2014, 513, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feidas, H. Validation of satellite rainfall products over Greece. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2009, 99, 193–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, D.d.C.D.; Xavier, A.C.; Bianchi, T.; Oliveira, P.T.S.; Scanlon, B.R.; Lucas, M.C.; Wendland, E. Performance evaluation of rainfall estimates by TRMM multi-satellite precipitation analysis 3B42V6 and V7 over Brazil. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 9426–9436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Qiao, X.; Zhang, J. Evaluation of GPM IMERG V05B and TRMM 3B42V7 Precipitation products over high mountainous tributaries in lhasa with dense rain gauges. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Zhou, T.; Xiong, A.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J. Diurnal variations of summer precipitation over contiguous China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, T.; Li, J. Relation between rainfall duration and diurnal variation in the warm season precipitation over central eastern China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, M. Spatial and diurnal variation of precipitation systems over Asia observed by the TRMM Precipitation Radar. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KUMMEROW, C.; SIMPSON, J.; THIELE, O.; BARNES, W.; CHANG, A.T.C.; STOCKER, E.; ADLER, R.F.; HOU, A.; KAKAR, R.; WENTZ, F.; et al. The status of the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) after two years in orbit. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2000, 39, 1965–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, J.; Kummerow, C.; Tao, W.-K.; Adler, R.F. On the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM). Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 1996, 60, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z. Comparison of versions 6 and 7 3-hourly TRMM multi-satellite precipitation analysis (TMPA) research products. Atmos. Res. 2015, 163, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, S.; Mitra, A.K.; Momin, I.M.; Pai, D.S.; Rajagopal, E.N.; Basu, S. Comparison of TMPA-3B42 versions 6 and 7 precipitation products with gauge-based data over india for the southwest monsoon period. J. Hydrometeorol. 2015, 16, 346–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, B.; Chen, B.; Gourley, J.J.; Ren, L.; Hong, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, W.; Chen, S.; Gong, L. Intercomparison of the Version-6 and Version-7 TMPA precipitation products over high and low latitudes basins with independent gauge networks: Is the newer version better in both real-time and post-real-time analysis for water resources and hydrologic extremes? J. Hydrol. 2014, 508, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iguchi, T.; Kozu, T.; Kwiatkowski, J.; Meneghini, R.; Awaka, J.; Okamoto, K.i. Uncertainties in the rain profiling algorithm for the TRMM precipitation radar. J. Meteorol. Soc. Japan 2009, 87A, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinku, T.; Anagnostou, E.N. TRMM calibration of SSM/I algorithm for overland rainfall estimation. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2006, 45, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Gao, Y. Evaluation of precipitation trends from high-resolution satellite precipitation products over Mainland China. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 51, 3311–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, D.; Hong, Y. Multi-scale evaluation of high-resolution multi-sensor blended global precipitation products over the Yangtze River. J. Hydrol. 2013, 500, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, A. Precipitation characteristics in eighteen coupled climate models. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 4605–4630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.M.; Zhou, T.J.; Dai, A.G.; Han, Z.Y. Observed changes in the distributions of daily precipitation frequency and amount over China from 1960 to 2013. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 6960–6978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.-Q.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y.-C.; Huang, Y.; Kuang, X.-Y. Assessment of summer monsoon precipitation derived from five reanalysis datasets over East Asia. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 142, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, K. Contrasting Daytime and Nighttime Precipitation Variability between Observations and Eight Reanalysis Products from 1979 to 2014 in China. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 6443–6464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Bauer-Gottwein, P. How do GPM IMERG precipitation estimates perform as hydrological model forcing? Evaluation for 300 catchments across Mainland China. J. Hydrol. 2019, 572, 486–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Tian, F.; Yang, L.; Hu, H.; Lu, H.; Hou, A. Ground validation of GPM IMERG and TRMM 3B42V7 rainfall products over southern Tibetan Plateau based on a high-density rain gauge network. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 910–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Chen, Z.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Shi, R. Evaluation of satellite rainfall estimates over the Chinese Mainland. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 11649–11672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Gong, D.; Fan, J.; Leung, L.R.; Bennartz, R.; Chen, D.; Wang, W. Heavy pollution suppresses light rain in China: Observations and modeling. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Dan, L. Trends in the different grades of precipitation over South China during 1960–2010 and the possible link with anthropogenic aerosols. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 31, 480–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Dai, A.; RASMUSSEN, R.M.; PARSONS, D.B. The changing character of precipitation. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2003, 84, 1205–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OKI, T.; MUSIAKE, K. Seasonal change of the diurnal cycle of precipitation over Japan and Malaysia. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1994, 33, 1445–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Zhang, Y. How often does it really rain? Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 99, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, B.; Zhang, L.; Dong, X.; Fang, D.; Wu, Y. Evaluation of multisatellite precipitation products by use of ground-based data over China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 654–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinku, T.; Chidzambwa, S.; Ceccato, P.; Connor, S.J.; Ropelewski, C.F. Validation of high-resolution satellite rainfall products over complex terrain. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 4097–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggioni, V.; Meyers, P.C.; Robinson, M.D. A Review of merged high-resolution satellite precipitation product accuracy during the tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) era. J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17, 1101–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MCCOLLUM, J.R.; GRUBER, A.; BA, M.B. Discrepancy between Gauges and Satellite Estimates of Rainfall in Equatorial Africa. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2000, 39, 666–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahi, N.; Hsu, K.; Sorooshian, S. An artificial neural network model to reduce false alarms in satellite precipitation products using MODIS and CloudSat observations. J. Hydrometeorol. 2013, 14, 1872–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shige, S.; Kida, S.; Ashiwake, H.; Kubota, T.; Aonashi, K. Improvement of TMI rain retrievals in mountainous areas. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2013, 52, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.F.; Chen, Y.N.; Shi, X. Why does the temperature rise faster in the arid region of northwest China? J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Xue, H.; Zhao, C.; Lu, D. The roles of convective and stratiform precipitation in the observed precipitation trends in Northwest China during 1961–2000. Atmos. Res. 2016, 169, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Guo, B.; Wang, K.; Wu, G.; Shi, C. Performance of TRMM Product in Quantifying Frequency and Intensity of Precipitation during Daytime and Nighttime across China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12040740
Li Y, Guo B, Wang K, Wu G, Shi C. Performance of TRMM Product in Quantifying Frequency and Intensity of Precipitation during Daytime and Nighttime across China. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(4):740. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12040740
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yun, Bin Guo, Kaicun Wang, Guocan Wu, and Chunming Shi. 2020. "Performance of TRMM Product in Quantifying Frequency and Intensity of Precipitation during Daytime and Nighttime across China" Remote Sensing 12, no. 4: 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12040740
APA StyleLi, Y., Guo, B., Wang, K., Wu, G., & Shi, C. (2020). Performance of TRMM Product in Quantifying Frequency and Intensity of Precipitation during Daytime and Nighttime across China. Remote Sensing, 12(4), 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12040740






