Abstract
Rainfall erosivity (RE) is a significant indicator of erosion capacity. The application of Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) rainfall products to deal with RE estimation has not received much attention. It is not clear which temporal resolution of TRMM data is most suitable. This study quantified the RE in the Poyang Lake basin, China, based on TRMM 3B42 3-hourly, daily, and 3B43 monthly rainfall data, and investigated their suitability for estimating RE. The results showed that TRMM 3-hourly product had a significant systematic underestimation of monthly RE, especially during the period of April–June for the large values. The TRMM 3B42 daily product seems to have better performance with the relative bias of 3.0% in summer. At the annual scale, TRMM 3B42 daily and 3B43 monthly data had acceptable accuracy, with mean error of 1858 and −85 MJ∙mm/ha∙h and relative bias of 18.3% and −0.85%, respectively. A spatial performance analysis showed that all three TRMM products generally captured the overall spatial patterns of RE, while the TRMM 3B43 product was more suitable in depicting the spatial characteristics of annual RE. This study provides valuable information for the application of TRMM products in mapping RE and risk assessment of soil erosion.
1. Introduction
Rainfall erosivity (RE) is a significant indicator of erosion capacity [1,2,3]. RE combines the effects of rainfall amount, duration, and intensity [4,5] and measures the potential ability of rainfall to erode soils [6,7]. Thus, RE is widely used in many models for the quantitative assessment of soil erosion and soil loss [6,8], such as the world famous and widely used model, the Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE) [6] and its improved versions, RUSLE [9] and RUSLE2 [10], the Water Erosion Prediction Project model (WEPP) [11], the Soil Erosion Model for Mediterranean regions (SEMMED) [12], the European Soil Erosion Model (EUROSEM) [13], the Unit Stream Power-based Erosion Deposition model (USPED) [14], and so on. Accurate RE is critical in risk assessment of soil erosion and soil loss in the large-scale catchment, and it is also of great significance for agricultural management and sustainable land use planning [15,16,17].
The RE is conventionally calculated by a storm’s kinetic energy and the maximum intensity of rainfall during a short time period (at least 30 min) [6]. Since such detailed information is difficult to obtain at standard meteorological stations [18], the traditional rainfall observations from rain gauges (i.e., daily, monthly, or annual rainfall data) have often been used to estimate the RE [19,20,21,22,23,24,25]. On the other hand, the rapid development of remote sensing technology improved the temporal and spatial resolutions and the accuracy of satellite-based rainfall products [26,27,28], which also greatly improved their applicability [28]. Currently, several global and regional satellite-based rainfall products with good temporal and spatial resolutions have been considered as a possible alternative to the traditional rain gauge observations in present and foreseeable future [29], which are also accepted as promising strategies for RE estimation.
The TRMM (Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission) satellite was designed by America and Japan to measure the tropical and sub-tropical rainfall [30], which was the first satellite mission dedicated to increasing the understanding of distribution and variability of precipitation. TRMM carried multiple rain sensors, including one active sensor (precipitation radar, PR) and two passive sensors (the visible and infrared scanner, VIRS, and TRMM microwave imager, TMI) [31,32]. Multiple rainfall products are available from those individual sensors at varying spatial resolutions. Moreover, TRMM Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) combined the data from TRMM-PR, VIRS, TMI with passive microwave, infrared and visible measurements available from national and international satellites, and could provide rainfall data series with the temporal resolution of 3-hourly and spatial resolution of 0.25° × 0.25° at the coverage area of global 50° S to 50° N [28,29]. Numerous studies have validated that TRMM products have acceptable accuracy [28,29,33,34,35,36,37,38], and good performance has been achieved using TRMM rainfall data in many research fields, including hydrological modeling [33,39,40,41,42,43,44,45], rainfall characteristics [35,46,47], weather processes [48,49], latent heat flux [50,51,52], extreme precipitation [53,54], and drought/flood monitoring [55,56,57,58,59,60].
Recently, several studies also have attempted to use TRMM rainfall products, as complementary rainfall data, for RE estimation and evaluated its performance. For example, the authors in [61] presented a new method which merged the daily rain gauges observations with the TRMM 3B42 data to estimate the RE across China, and their results indicated that a combination of TRMM and gauge data provided the RE estimates with the best accuracy when compared with block kriging gauges and TRMM alone. The research in [62] examined the suitability of TRMM precipitation data for mapping RE in Africa and revealed that the spatial estimates of mean annual RE can be well characterized by monthly satellite-based precipitation. Authors in [63] also developed a new method for calculating RE using 3-hourly TRMM precipitation data. However, these previous attempts and preliminary studies mainly focused on the estimation of RE using one product of TRMM rainfall and lacked a comparative assessment of RE results based on TRMM data with different temporal resolutions. It is not clear which temporal resolutions of TRMM rainfall products, i.e., 3-hourly, daily or monthly, is most suitable for calculating RE. This situation has hampered the extensive application of TRMM rainfall products for mapping RE, and also affected soil loss prediction and risk assessment of soil erosion to a certain extent.
Therefore, this study extends the previous studies and quantifies the seasonal distribution and annual change of RE in Poyang Lake basin, China based on three TRMM rainfall products (TRMM 3B42 3-hourly, daily, and 3B43 monthly products) and rain gauges data, respectively. Subsequently, the suitability of those TRMM rainfall products for RE estimation is assessed and evaluated by several different evaluation indices of bias of RE. The outcomes of this study are expected to provide some useful references for the further application of TRMM products in calculating and mapping RE, and it is also valuable for the soil loss prediction, risk assessment of soil erosion, as well as land use management.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
In this study, the Poyang Lake basin was selected as the study area, which is located on the south bank of the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, China (28°22′–29°45′ N and 115°47′–116°45′ E) (Figure 1). The basin covers an area of 1.62 × 105 km2, and is one of the regions in South China with the most serious soil erosion problems [64]. The lake mainly receives the inflow of Ganjiang River, Fuhe River, Xiushui River, Xinjiang River, Raohe River, as well as runoff from the alluvial plains around the lake, and flows into the Yangtze River. In which, the Ganjiang River is the largest tributary of Poyang Lake water system and contributes about 55% of the total discharge into the lake [65]. The elevation of the basin vary from 30 m in the alluvial plains to more than 2200 m in the mountain area. The Poyang Lake basin is characterized by subtropical humid climate, with an average annual precipitation of 1626 mm and average temperature of 17.6 °C during 1960–2012. Generally, precipitation is mainly concentrated in the rainy season (during April–June), and the streamflow in rainy season accounts for more than 50% of total annual streamflow, but about only 13.7% during from October to the following January [66]. The spatial distribution of precipitation in the basin is also uneven, with the ratio of maximum to minimum ranging from 1.65 to 2.51. The highest annual rainfall was observed at Wuyuan station (3036 mm) in 1998 and the lowest was at Hukou station (776 mm) in 1978. The land use in the basin is mainly woodland, accounting for 46%, followed by shrubland and cropland, accounting for 25% and 24%, respectively (Figure 2). The area of grassland, town and open water is generally small [67].
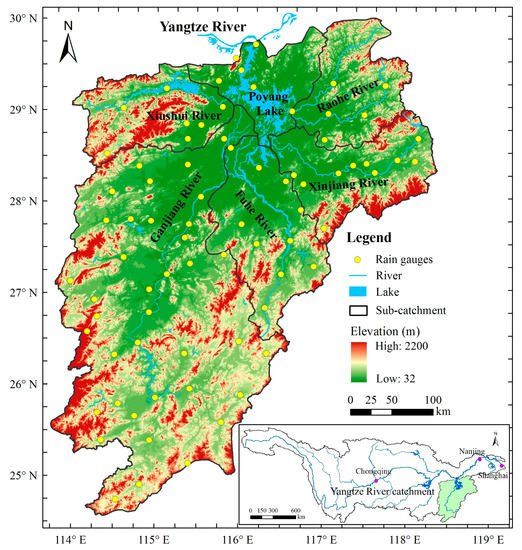
Figure 1.
The study area and the distribution of the rain gauges in the basin.
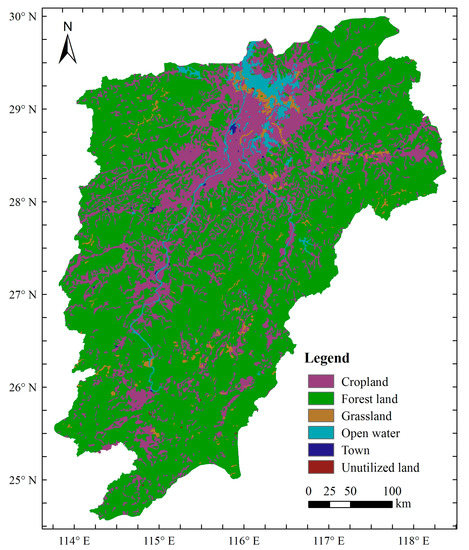
Figure 2.
The land use map of Poyang Lake basin.
2.2. Date
TRMM rainfall products used in this paper are the TRMM 3B42 3-hourly data, daily data and the 3B43 monthly data, respectively, which were derived from the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Goddard Earth Sciences (GES) Data and Information Services Center (DISC) (https://disc.gsfc.nasa.gov/datasets). The ranges of these data cover the time period from 1 January 1998 to 31 December 2012, and the spatial resolutions are all 0.25° × 0.25°. According to statistics, there are about 270 grids (0.25° × 0.25°) in the study area. And for the comparison and evaluation of RE results based on TRMM rainfall data with different temporal resolutions, the observed daily rainfall data of 76 traditional ground-based rainfall stations in the basin covering the same period were obtained from the National Meteorological Information Center, China (NMIC) (http://data.cma.cn). The monthly gauged rainfall was also aggregated from these daily values. The spatial distribution of these rainfall stations is shown in Figure 1.
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Estimation of RE
Due to the difficult collection of kinetic energy and intensity of rainfall with a time resolution of 30 min, several alternative methods using the routine meteorological records of rainfall have been proposed to calculate RE. In this study, three different quantitative models based on 3-hourly, daily, and monthly rainfall were used to estimate monthly and annual RE, respectively.
The model based on the TRMM 3B42 3-hourly rainfall product was a model developed by Zhu et al. [63], which improved the basic formula of RE and made it suitable for TRMM data. TRMM products can be directly used as data sources for RE calculation. This improvement has been applied in many areas in China, such as Daling River basin, Liaoning Province, and achieved good performance. The model equation is [63]:
where REk is a event-based rainfall erosivity; iavr is 3-hour average rainfall intensity from TRMM 3B42 3-hourly product; ΔV is the rainfall and I180 is the maximum 180-min rainfall intensity.
The monthly RE was obtained by summing up all erosion events in a month:
The annual RE was the sum of monthly RE values in a year.
The model based on daily rainfall (TRMM 3B42 daily product and the daily gauged rainfall) used in this study was improved and developed by Zhang et al. [68]. The model was validated and widely applied in many regions in China [69,70] and was also recommended to calculate the soil loss in the first general suvey of soil and water conservation in China [71]. The model equations are [68]:
where REi is the RE value of half-month; Pj is the erosive rainfall, according to the analysis results of observational data of China’s rainfall and surface runoff, a daily rainfall amount that exceeds 12 mm is the standard for China’s erosive rainfall (Pj is the actual daily rainfall when rainfall ≥12 mm, otherwise, Pj is 0) [72]; α and β are coefficients to reflect the rainfall characteristics; and are average daily and annual rainfall when daily rainfall ≥12 mm, respectively.
The monthly RE was obtained by summing up the REi in a month, and the annual RE was the sum of monthly RE values in a year.
The model based on monthly rainfall (TRMM 3B43 product and the monthly gauged rainfall) was the Modified Fourier Index (MFI) approach. Several studies have shown that RE and the rate of erosion are strongly correlated with the MFI [19,73]. Therefore, the MFI has often been applied in the estimation of annual RE and in the development of soil loss maps in regional-scale erosion models [74]. Additionally, the MFI-based model was also recommended to establish erosion risk areas by Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). Annual RE is estimated by the following equations [74]:
where ri is the monthly rainfall; P is the average annual rainfall. The coefficients 0.3598 and 1.9462 were obtained from the study of Zhang and Fu [69], which was suitable for Jiangxi Province (Poyang Lake basin), China.
In addition, the spatial distribution of RE from rain gauges data was interpolated by the inverse distance weighted (IDW) technique with a power of 2.
2.3.2. Evaluating Index
To quantitatively evaluate the suitability of TRMM 3B42 3-hourly, daily and 3B43 products for estimating RE, several evaluating indices, including the correlation coefficient (R), the mean error (ME), the root mean squared error (RMSE), and the relative bias (BIAS), were selected to assess the systematic bias of RE estimation compared with the results from the rain gauges data. The Equations for R, ME, RMSE, and BIAS were as follow:
where RETRMM i is the value of RE obtained by TRMM products; REgauge i is the value of RE obtained by rain gauges data; and and are the average values of their respective series; n is the total number of data.
In addition, the accuracy of annual RE based on TRMM rainfall products were further assessed by four statistical indicators: (1) the frequency bias index (FBI), which indicates whether the TRMM rainfall products underestimate (FBI < 1) or overestimate (FBI > 1) the RE values, (2) the false alarm ratio (FAR), which measures the fraction of RE that is actually false alarms, (3) the probability of detection (POD), which provides the proportion of RE that is correctly estimated, and (4) the equitable threat score (ETS), which provides the fraction of RE that is correctly detected, adjusted for the number of hits He that could be expected due purely to random chance [75,76,77]. Further information on these indicators and their implications can be found in the studies of Li et al. [34], Koo et al. [77] and Getirana et al. [78]. Their values were calculated using Equations (12)–(16), respectively:
where N is the total number of the rainfall series; a is the number of REs that are correctly estimated by the TRMM rainfall products; b is the number of false signal (RE is detected by the TRMM rainfall products but not presented in gauges data); and c represents the number of REs that are not detected by the TRMM rainfall products.
Moreover, in order to quantify the ability of each dataset in predicting light and heavy RE, the FBI, POD, FAR, and ETS were calculated at different RE thresholds of 2000, 4000, 6000, 8000, 10,000, 12,000 and 14,000 MJ∙mm/ha∙h, respectively.
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of the Intra-Annual Distribution of RE
The comparison of monthly RE from the TRMM 3B42 3-hourly and daily products and the gauges daily rainfall is summarized in Figure 3. The rain gauges RE showed a clear seasonal variation. Specifically, the RE values during the period of April–June was the highest in the whole year, especially in June, with the maximum value up to 5000 MJ∙mm/ha∙h and an average of 2324 MJ∙mm/ha∙h. This period was also the main rainy season of the Poyang Lake Basin, the heavy rainfall or rainstorm events usually occurred in this period, which may lead to a high risk of soil erosion. The lowest value of RE mainly presented during December–January, with the average of less than 200 MJ∙mm/ha∙h. Figure 3 also shows that TRMM 3-hourly product had a significant systematic underestimation of monthly RE, especially during the period of April–June.
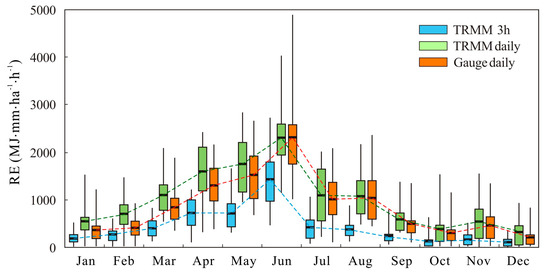
Figure 3.
Comparison of monthly rainfall erosivity (RE) from different rainfall data.
The changes of R, ME, RMSE, and BIAS of monthly RE from the TRMM 3B42 3-hourly and daily products are shown in Figure 4 and Table 1. The correlation coefficients had high variability in different months, the R values of TRMM 3B42 3-hourly data ranged from 0.72 to 0.93, while that of TRMM 3B42 daily data ranged from 0.76 to 0.95 (Figure 4d). The high values of R indicated that the RE estimates using TRMM rainfall products, regardless of 3-hourly or daily data, captured the change characteristics of RE. However, large errors were found in the TRMM 3-hourly data, with the ME ranging from −83 to −900 MJ∙mm/ha∙h, especially during the spring (−587 MJ∙mm/ha∙h) and summer months (−707 MJ∙mm/ha∙h). Positive errors were mainly found in the TRMM daily data, with the ME ranging between 233 and 308 MJ∙mm/ha∙h in spring and less than 109 MJ∙mm/ha∙h during second half of the year. This temporal pattern of errors could be presented more clearly through the changes in the RMSE (Figure 4b), which was larger for the TRMM 3-hourly data than for the TRMM daily data. In addition, the changes in the relative errors of the TRMM 3-hourly data were weak in different months, with a BIAS of approximately −49%. The TRMM daily data performed better in summer, with a BIAS of only 3.0%; however, these data performed worse in winter.
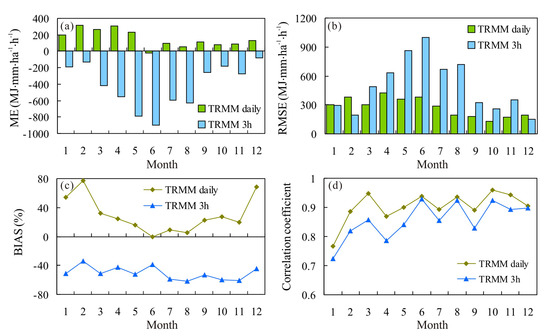
Figure 4.
Monthly changes in (a) the mean error (ME), (b) the root mean squared error (RMSE), (c) the relative bias (BIAS) and (d) the correlation coefficient (R).

Table 1.
Seasonal changes in bias between Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission products (TRMM) and rain gauges data.
Figure 5 shows the distribution of monthly RE values in different categories and their proportion to annual RE. The small RE category (0−500 MJ∙mm/ha∙h) had the largest frequency, occurring in 41% of all months, and this category contributed to approximately 11% of the total annual RE in the rain gauges data. The RE estimates from the TRMM 3-hourly data were much larger than that from the rain gauges data. Its frequency was over 71% for the small RE category, and the corresponding contribution rate was as high as 37% of the total annual RE. The statistics for the TRMM daily data were slightly smaller than those from rainfall gauge data, regardless of frequency and contribution rate. The second largest category was 500 < RE < 1000 MJ∙mm/ha∙h, with approximately 25% occurrence and 20.5% of the contribution to the total annual RE in the rain gauges data. Although the frequency estimated by the TRMM 3-hourly data was almost consistent with that of the gauge data, its contribution rate was large, accounting for as much as 41.1% of the total annual RE. For the TRMM daily data, the frequency and contribution were close to the results of the rain gauges data. It is found that both frequency and contribution estimated by the TRMM daily data generally became equivalent to that from the rain gauges data for middle and large RE categories (RE > 1000 MJ∙mm/ha∙h). However, both frequency and contribution rates from the TRMM 3-hourly data were grossly underestimated, especially in the categories of RE > 2000 MJ∙mm/ha∙h. Figure 5 indicates that the estimates of monthly RE using the TRMM 3B42 daily product were closer to the results of the rain gauges data. The TRMM 3-hourly data tended to overestimate the low values but underestimate the high values of monthly RE.
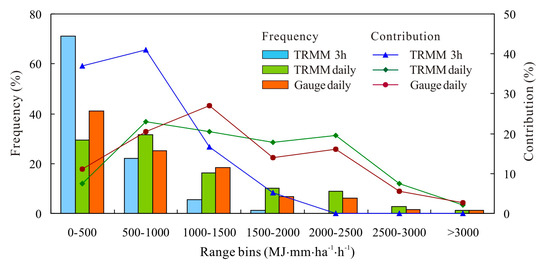
Figure 5.
Distribution of monthly RE values in different categories and their proportion to annual RE.
3.2. Evaluation of Interannual Variation in RE
Comparison of annual RE estimated by the 3-hourly, daily, and monthly rainfall data, respectively, is presented in Figure 6. The annual RE derived from the daily gauge data showed a obvious interannual variation, and the RE values ranged from 6893 MJ∙mm/ha∙h in 2007 to 14,637 MJ∙mm/ha∙h in 1998, with the average of 10,134 MJ∙mm/ha∙h during 1998–2012. The RE estimates derived from TRMM daily data showed a similar variability characteristic to the daily gauge data. However, the time series calculated by the TRMM 3-hourly data was obviously low, which ranged between 2557 and 7040 MJ∙mm/ha∙h. In addition, the two RE series based on the MFI approach (derived from the monthly gauge data and the TRMM 3B43 data, respectively) had roughly equivalent averages (9951 and 9866 MJ∙mm/ha∙h) and share similar interannual variation characteristics.
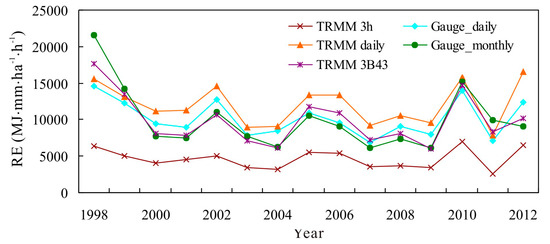
Figure 6.
Comparison of annual rainfall erosivity estimated by rainfall data with different temporal resolutions.
At the annual scale, the comparison of the ME, RMSE and BIAS of RE estimation from different TRMM rainfall products and rain gauges data are shown in Table 2, and the scatter plots of the RE estimates from TRMM rainfall products and the rain gauge data are shown in Figure 7. The TRMM 3-hourly data presented large errors for annual RE estimation, with an ME value of −5516 MJ∙mm/ha∙h, RMSE value of 5686 MJ∙mm/ha∙h and BIAS value of −54.4%. Moreover, the low slope value (0.49) of scatter fitting curve further revealed that the TRMM 3-hourly rainfall product significantly underestimated the annual RE. Comparatively, the TRMM daily and 3B43 products performed better for the annual RE estimation, with ME values of 1858 and −85 MJ∙mm/ha∙h, RMSE values of 2114 and 1336 MJ∙mm/ha∙h, and BIAS values of 18.3% and −0.85%, respectively (Table 2). Moreover, the R2 values of the scatter fitting curve between the TRMM RE and rain gauge RE were as high as 0.86 and 0.92 for the TRMM daily and 3B43 data, respectively. Figure 7b also reveals that the TRMM 3B43 product tended to overestimate the low values but underestimate the high values of annual RE.

Table 2.
Results of bias analysis for annual rainfall erosivity from the TRMM 3h, daily and 3B43 rainfall data.
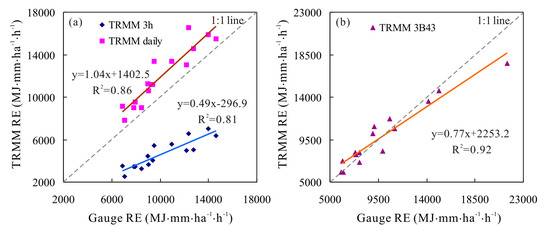
Figure 7.
Scatter plots of annual rainfall erosivity from (a) TRMM 3h and daily products and (b) TRMM 3B43.
Furthermore, the assessment of TRMM rainfall products for annual RE estimation was extended to utilize the indicators of FBI, FAR, POD and ETS, which were analyzed at different RE thresholds of 2000, 4000, 6000, 8000, 10,000, 12,000 and 14,000 MJ∙mm/ha∙h, respectively. As shown in Figure 8, TRMM 3-hourly product tended to underestimate the annual RE, with the decreasing FBI values, especially for heavy RE; however, there was a systematic overestimation of annual RE by the TRMM daily data. The POD of the TRMM daily data kept changing around 1.0, which indicated a good performance for RE detection; however, its FAR values increased from 0 to 0.46 as the RE threshold increased, which meant that the proportion of miscalculated values increased. The TRMM 3-hourly data performed poorly, with low POD and high FAR values, especially for heavy RE. Overall, the TRMM 3B43 product performed best in terms of estimating light and heavy RE among the three TRMM rainfall datasets with the highest ETS scores.
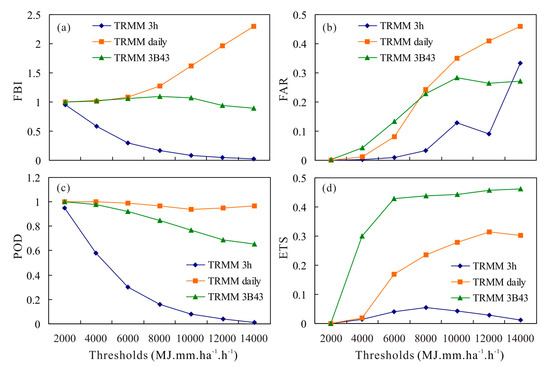
Figure 8.
Changes in the frequency bias index (a), the false alarm ratio (b), the probability of detection (c) and the equitable threat score (d) at different rainfall erosivity thresholds.
3.3. Performance of Spatial Pattern of RE
The spatial patterns of the average annual RE estimated from TRMM 3-hourly, daily and 3B43 rainfall data are shown in Figure 9. As a reference case for comparative purposes, the spatial distributions of RE from rain gauges data (both daily and monthly data), which were obtained by a interpolation method of inverse distance weighting (IDW) with a power of 2, are also shown in Figure 9. The distribution of annual gauge RE, both from daily and monthly gauge rainfall data, in different areas was quite different. The high RE was mainly distributed in the northeast (with annual RE over 12,000 MJ∙mm/ha∙h) and the low RE values in the southwest of the Poyang Lake basin (approximately 6000–7000 MJ∙mm/ha∙h) (Figure 9a,d). Additionally, the annual RE from TRMM 3-hourly, daily and 3B43 rainfall products had good spatial consistency with that from the rain gauges data, although the high RE values obtained from the TRMM 3-hourly data covered the wider area than that from rain gauges data. This spatial consistency was further validated by the high coefficient of determination (R2) (0.63 for TRMM 3-hourly data, 0.72 for TRMM daily data, and 0.71 for TRMM 3B43 data) between the satellite pixels and the rain gauges within the grids (Figure 10). However, the slope values of the regression lines were 0.49 and 1.24, respectively, for TRMM 3-hourly and TRMM daily estimates. These values indicated that TRMM 3-hourly rainfall product significantly underestimated the annual RE, while TRMM daily rainfall product overestimated it. Comparatively, the TRMM 3B43 data performed best in terms of depicting the spatial characteristics of annual RE.
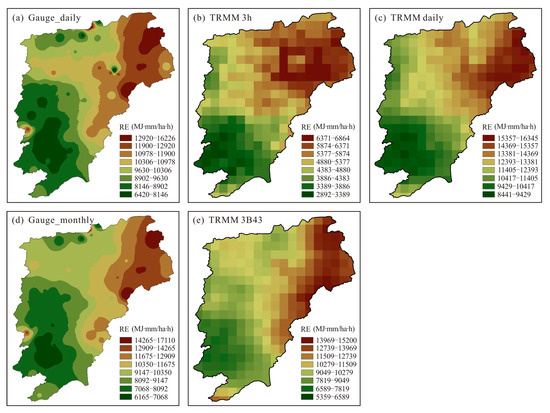
Figure 9.
Spatial patterns of average annual RE estimated by rainfall data with different temporal resolutions.
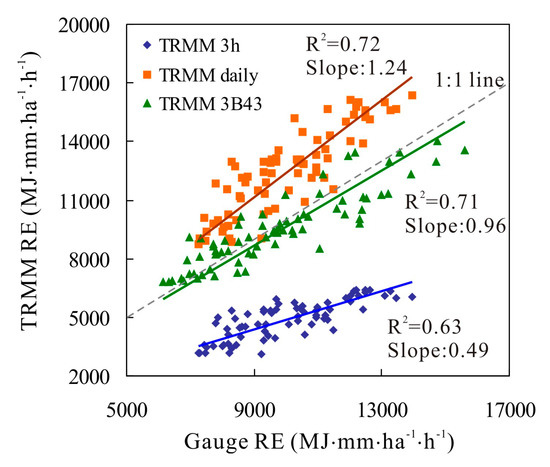
Figure 10.
Scatter plots of annual rainfall erosivity at rain gauges against their nearest satellite pixel.
Figure 11 shows the spatial distributions of four evaluating indices values (R, ME, RMSE, and BIAS) of annual RE estimation from TRMM rainfall products for every rain station. The statistical distributions of stations in different categories of evaluation indices were summarized in Table 3. The annual RE from the TRMM daily and 3B43 data correlated well with that from the rain gauges data, and their R values exceeded 0.8 at 45 (59.2%) and 46 (60.5%) of the 76 stations, respectively. The number of stations with R > 0.8 was only 20 (26.3%) for the TRMM 3-hourly data. However, all three TRMM rainfall products reflected similar spatial patterns of R, i.e., the most stations with large R located in the northeast of the Poyang Lake basin.
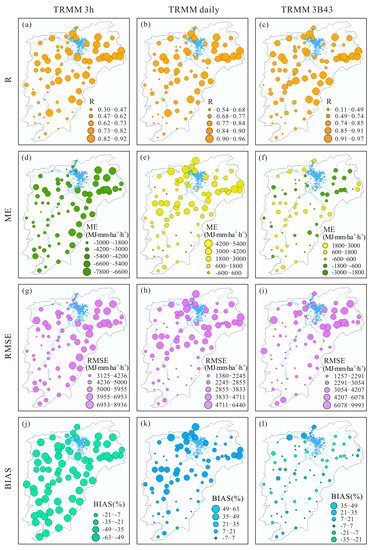
Figure 11.
Spatial distributions of R (a–c), ME (d–f), RMSE (g–i) and BIAS (j–l) of annual RE estimation from TRMM 3h (a,d,g,j), daily (b,e,h,k) and 3B43 (c,f,i,l) products.

Table 3.
Statistical distribution of bias of annual rainfall erosivity from TRMM 3h, daily and 3B43 rainfall data.
The ME values varied considerably in three TRMM data estimates. TRMM 3-hourly data showed negative MEs in all examined pixels in the basin, with the ME falling into the class of −3000–0 MJ∙mm/ha∙h at 6 (7.9%) stations and <−3000 MJ∙mm/ha∙h at 70 (92.1%) stations. However, the ME in the TRMM daily data showed positive errors at 71 (93.4%) of the 76 stations, 25 (32.9%) of which were larger than 3000 MJ∙mm/ha∙h. Moreover, the stations with a large ME (both negative in the TRMM 3-hourly and positive in the TRMM daily estimates) were primarily located in northern parts of the basin. TRMM 3B43 generally presented a small error, with MEs ranging between −3000 and 3000 MJ∙mm/ha∙h, and the stations with positive MEs (35 stations and accounting for 46.1%) were mainly located in middle and southern areas; furthermore, stations with negative MEs (41 stations and accounting for 53.9%) were distributed in the northern parts of the basin. The RMSE of TRMM 3-hourly data for more than 60% of stations (46 stations) was greater than 5000 MJ∙mm/ha∙h, and 39.5% of stations (30 stations) had RMSEs between 2000 and 5000 MJ∙mm/ha∙h. The number of stations with RMSE > 5000 MJ∙mm/ha∙h greatly decreased to 6 (7.9%) and 12 (15.8%) in the TRMM daily and 3B43 estimates, respectively; moreover, 7 (9.2%) stations and 14 (18.4%) stations had RMSE values smaller than 2000 MJ∙mm/ha∙h. As for the BIAS, its spatial distribution was almost the same as that of ME; that is, all examined pixels had negative BIAS values in the TRMM 3-hourly estimates, and more than 93% of stations (71 stations) showed positive BIAS values in the TRMM daily estimates. TRMM 3B43 generally presented a small BIAS, and positive values (33 stations and accounting for 43.4%) were mainly found in the middle and southern areas, while negative values (41 stations and accounting for 53.9%) were distributed in the north area of the basin.
4. Discussion
Previous results revealed that the largest monthly RE values were mainly concentrated in June, followed by that in May, and the smallest RE typically presented in December. The intra-annual distribution characteristics of RE corresponded to changes of precipitation in which more than 45% of the annual rainfall was concentrated during April–June. Both the TRMM 3B42 3-hourly and daily products depicted the intra-annual distribution characteristic correctly, i.e., greater than 70% of RE occurred during summer and spring, and only approximately 10% was concentrated in winter. However, the TRMM daily data performed better in summer, with a small BIAS (3.0%), and performed worse in winter, with a BIAS of 68.5%. This result was mainly associated with the seasonality of accuracy in TRMM rainfall products. Many researches have testified that the accuracy of TRMM rainfall products was influenced by season, rain type and climatological factors [79,80,81,82]. For example, the study of Han et al. [83] in urban areas revealed that TRMM precipitation had the higher accuracy during the warm seasons and there was a good correlation between the increasing temperature and the increasing accuracy of TRMM data. Wang et al. [45] noted that, compared with other satellite-based rainfall estimates, the TRMM performed best during the wet season. Ward et al. [84] also pointed out that TRMM 3B42 products may underestimated the rainfall in the dry season. For the TRMM 3-hourly data, this study revealed that it had the significant underestimation of monthly RE values, especially both the frequency and the contribution rates of high values of monthly RE were obviously underestimated. This result was principally associated with the underestimating of TRMM 3-hourly estimates for larger rainfall events, such as high-intensity storm events or heavy rainfall events [83]. On the other hand, the estimated RE from the TRMM 3-hourly data was compared with the results derived from the daily gauges data in this study. Differences in estimation methods of RE may inevitably resulted in systematic bias, as has been mentioned in many previous studies [85,86].
At the annual scale, this study found that TRMM 3B43 data performed best in terms of estimating annual RE, with the ME of −85 MJ∙mm/ha∙h, the RMSE of 1336 MJ∙mm/ha∙h, and the BIAS of −0.85%. This result was consistent with many previous studies on the accuracy of TRMM products. Dinku et al. [87] compared and evaluated the TRMM 3B43 data over Ethiopia with other satellite-based rainfall products and revealed that the TRMM 3B43 had the highest accuracy with the small BIAS (<10%) and RMSE (about 25%). Guo and Liu [88] pointed out that the accuracy of TRMM 3B43 was higher than that of TRMM 3B42 and 3B42RT in Poyang Lake basin. Fleming et al. [89] found that, in Australia, the TRMM 3B43 data was highly correlated (with R of higher than 0.80) with gridded rain gauges data during 1998–2007, especially the correlation was strongest in summer. Cao et al. [36] reported that the TRMM 3B43 product performed best in the Yangtze River Delta of China, with the BIAS values ranging between −10% and 10% and the R of 0.88 at an annual scale. The study by Semire et al. [90] in Malaysia also received similar results.
Spatially, this study revealed that all three TRMM rainfall products generally captured the overall spatial pattern of annual RE, which had good spatial consistency with results from rain gauges data. However, TRMM 3-hourly data significantly underestimated the RE, while the TRMM daily data overestimated the RE. The TRMM 3B43 data performed best in terms of depicting the spatial characteristics of annual RE. The spatial biases may be related to the weak ability of the TRMM 3-hourly and daily rainfall products to detect heavy or extreme precipitation, which occurred frequently in the northern regions of the Poyang Lake basin [91,92,93].
5. Conclusions
This work quantified the RE in the Poyang Lake basin based on three TRMM rainfall products and investigated their suitability for RE estimation compared with the results obtained from the traditional gauges rainfall. The results showed that TRMM 3B42 3-hourly product had a significant systematic underestimation of monthly RE, especially during the period of April–June for the large values. The TRMM 3B42 daily product seem to have better performance, especially in the summer, with a small BIAS (3.0%). At the annual scale, the TRMM 3-hourly data presented large errors in estimating the annual RE, with an ME of −5516 MJ∙mm/ha∙h, an RMSE of 5686 MJ∙mm/ha∙h and a BIAS of −54.4%. Comparatively, the TRMM 3B42 daily and 3B43 data had smaller errors, with the ME values of 1858 and −85 MJ∙mm/ha∙h, the RMSE values of 2114 and 1336 MJ∙mm/ha∙h, and the BIAS values of 18.3% and −0.85%, respectively. Moreover, the R2 values of the scatter fitting curve between the TRMM RE and rain gauge RE were as high as 0.86 and 0.92 for the TRMM daily and 3B43 data, respectively. A spatial performance analysis showed that the TRMM 3B42 3-hourly, daily and 3B43 rainfall products could correctly reflect the spatial patterns of the average annual RE, with spatial correlation coefficients of 0.63 for TRMM 3-hourly, 0.72 for TRMM daily, and 0.71 for TRMM 3B43 data. The slopes of the regression lines showed that TRMM 3-hourly product significantly underestimated the annual RE but overestimated the annual RE when using the TRMM daily data.
Finally, it is also important to recognize that this study is only an attempt at evaluating the suitability of TRMM products with different temporal resolution for RE estimation quantitatively. The outcomes of this study help in enhancing the understanding of the accuracy of use TRMM rainfall products to estimate RE. However, the study needs further deeper analyses and investigations; the above preliminary conclusions are derived only based on the given period and the characteristics of the region. Applying the conclusions drawn in this study to other regions should be considered with caution.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.L. and Z.L.; Data curation, Z.L. and Y.L.; Formal analysis, X.L. and Z.L.; Funding acquisition, X.L. and Y.L.; Investigation, X.L.; Methodology, X.L.; Project administration, X.L.; Resources, X.L.; Software, X.L.; Validation, Z.L.; Visualization, Y.L.; Writing—original draft, X.L.; Writing—review & editing, Z.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Project, grant number 2018YFE0206400, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 41871093.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Panagos, P.; Ballabio, C.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K.; Klik, A.; Rousseva, S.; Tadić, M.P.; Michaelides, S.; Hrabalíková, M.; Olsen, P.; et al. Rainfall erosivity in Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 511, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, C.R.; Viola, M.R.; Beskow, S.; Norton, L.D. Multivariate models for annual rainfall erosivity in Brazil. Geoderma 2013, 202, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nearing, M.A.; Yin, S.Q.; Borrelli, P.; Polyakov, V.O. Rainfall erosivity: An historical review. Catena 2017, 157, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Ballabio, C.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K. Spatio-temporal analysis of rainfall erosivity and erosivity density in Greece. Catena 2016, 137, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Nearing, M.A.; Borrelli, P.; Xue, X. Rainfall Erosivity: An Overview of Methodologies and Applications. Vadose Zone J. 2017, 16, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning; Agriculture Handbook No. 537; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1978.
- Hoyos, N.; Waylen, P.; Jaramillo, A. Seasonal and spatial patterns of erosivity in a tropical watershed of the Colombian Andes. J. Hydrol. 2005, 314, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, Q.; Ma, L.; Ding, S.; Xu, S.; Wu, C.; Liu, P. Spatiotemporal variations in rainfall erosivity during the period of 1960–2011 in Guangdong Province, southern China. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2017, 128, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; McCool, D.K.; Yoder, D.C. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); U.S. Departement of Agriculture, Agriculture Handbook, No. 703; Agricultural Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1997.
- Foster, G.R. User’s Reference Guide: Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE2); U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2004.
- Nearing, M.A.; Lane, L.J.; Lopes, V.L. Modeling Soil Erosion. In Soil Erosion: Research Methods; Lal, R., Ed.; St. Lucie Press: Delray Beach, FL, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- de Jong, S.M.; Paracchini, M.L.; Bertolo, F.; Folving, S.; Megier, J.; De Roo, A.P.J. Regional assessment of soil erosion using the distributed model SEMMED and remotely sensed data. Catena 1999, 37, 291–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.P.C.; Quinton, J.N.; Smith, R.E.; Govers, G.; Poesen, J.W.A.; Auerswald, K.; Chisci, G.; Torri, D.; Styczen, M.E. The European Soil Erosion Model (EUROSEM): A dynamic approach for predicting sediment transport from fields and small catchments. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1998, 23, 527–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitasova, H.; Mitasova, H. Distributed soil erosion simulation for effective erosion prevention. Water Resour. Res. 1998, 34, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamlaoui-Moulai, L.; Mesbah, M.; Souag-Gamane, D.; Medjerab, A. Detecting hydro-climatic change using spatiotemporal analysis of rainfall time series in Western Algeria. Nat. Hazards 2012, 65, 1293–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Guo, Q.K.; Zuo, C.Q.; Shan, Z.J.; Ma, L.; Sun, G. Spatial distribution and temporal trends of rainfall erosivity in mainland China for 1951–2010. Catena 2016, 147, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.J.; Duan, X.W.; Liu, B.; Hu, J.M.; He, J.N. The spatial distribution and temporal variation of rainfall erosivity in the Yunnan Plateau, Southwest China: 1960-2012. Catena 2016, 145, 291–300. [Google Scholar]
- Meusburger, K.; Steel, A.; Panagos, P.; Montanarella, L.; Alewell, C. Spatial and temporal variability of rainfall erosivity factor for Switzerland. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diodato, N.; Bellocchi, G. Estimating monthly (R)USLE climate input in a Mediterranean region using limited data. J. Hydrol. 2007, 345, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.H.; Wen, Y. Estimation of soil erosion using RUSLE in Caijiamiao watershed, China. Nat. Hazards 2014, 71, 2187–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luis, M.; Brunetti, M.; Gonzalez-Hidalgo, J.C.; Longares, L.A.; Martin-Vide, J. Changes in seasonal precipitation in the Iberian Peninsula during 1946-2005. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2010, 74, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiener, P.; Neuhaus, P.; Botschek, J. Long-term trends in rainfall erosivity-analysis of high resolution precipitation time series (1937-2007) from Western Germany. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 171, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vantas, K.; Sidiropoulos, E.; Loukas, A. Robustness Spatiotemporal Clustering and Trend Detection of Rainfall Erosivity Density in Greece. Water 2019, 11, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernando, D.; Romana, M.G. Estimating the rainfall erosivity factor from monthly precipitation data in the Madrid Region (Spain). J. Hydrol. Hydromech. 2015, 63, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meddi, M.; Toumi, S.; Assani, A.A. Spatial and temporal variability of the rainfall erosivity factor in Northern Algeria. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschalck, J.; Meng, J.; Rodell, M.; Houser, P. Analysis of multiple precipitation products and preliminary assessment of their impact on global land data assimilation system land surface states. J. Hydrometeorol. 2005, 6, 573–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.D.; Peters-Lidard, C.D. Systematic anomalies over inland water bodies in satellite-based precipitation estimates. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stisen, S.; Sandholt, I. Evaluation of remote-sensing-based rainfall products through predictive capability in hydrological runoff modelling. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Pandey, A.; Sharma, N.; Flugel, W.A. Evaluation of TRMM-Precipitation with Rain-Gauge Observation Using Hydrological Model J2000. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2017, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozante, J.R.; Moreira, D.S.; de Goncalves, L.G.G.; Vila, D.A. Combining TRMM and surface observations of precipitation: Technique and validation over South America. Weather Forecast. 2010, 25, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummerow, C.; Barnes, W.; Kozu, T.; Shiue, J.; Simpson, J. The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) sensor package. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1998, 15, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almazroui, M. Calibration of TRMM rainfall climatology over Saudi Arabia during 1998-2009. Atmos. Res. 2011, 99, 400–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.Y. Suitability of the TRMM satellite rainfalls in driving a distributed hydrological model for water balance computations in Xinjiang catchment, Poyang lake basin. J. Hydrol. 2012, 426, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.Y. Assessing the performance of satellite-based precipitation products and its dependence on topography over Poyang Lake basin. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2014, 115, 713–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michot, V.; Vila, D.; Arvor, D.; Corpetti, T.; Ronchail, J.; Funatsu, B.M.; Dubreuil, V. Performance of TRMM TMPA 3B42 V7 in Replicating Daily Rainfall and Regional Rainfall Regimes in the Amazon Basin (1998–2013). Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.Q.; Zhang, W.; Wang, W.J. Evaluation of TRMM 3B43 data over the Yangtze River Delta of China. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, M.; Asanjan, A.A.; Faridzad, M.; Gorooh, V.A.; Nguyen, P.; Hsu, K.; Sorooshian, S.; Braithwaite, D. Evaluation of PERSIANN-CDR Constructed Using GPCP V2.2 and V2.3 and A Comparison with TRMM 3B42 V7 and CPC Unified Gauge-Based Analysis in Global Scale. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Liu, J.T.; Wang, J.R.; Qiao, X.; Zhang, J. Evaluation of GPM IMERG V05B and TRMM 3B42V7 Precipitation Products over High Mountainous Tributaries in Lhasa with Dense Rain Gauges. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.M.; Du, J.; Cheng, L.L.; Xu, W. Applicability of TRMM satellite precipitation in driving hydrological model for identifying flood events: A case study in the Xiangjiang River Basin, China. Nat. Hazards 2017, 87, 1489–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Liu, T.; Meng, F.H.; Duan, Y.C.; Huang, Y.; Frankl, A.; De Maeyer, P. Proportional coefficient method applied to TRMM rainfall data: Case study of hydrological simulations of the Hotan River Basin (China). J. Water Clim. Chang. 2017, 8, 627–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Wu, W.Q.; He, D.M.; Li, Y.G.; Ji, X. Hydrological Simulation Using TRMM and CHIRPS Precipitation Estimates in the Lower Lancang-Mekong River Basin. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Li, Y.G.; Ji, X.; Luo, X.; Li, X. Evaluation and Hydrologic Validation of Three Satellite-Based Precipitation Products in the Upper Catchment of the Red River Basin, China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.X.; Tian, J.X.; Huang, Y.H.; Chen, X.; Chen, S.; Duan, Z. Hydrologic Evaluation of TRMM and GPM IMERG Satellite-Based Precipitation in a Humid Basin of China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belete, M.; Deng, J.S.; Wang, K.; Zhou, M.M.; Zhu, E.Y.; Shifaw, E.; Bayissa, Y. Evaluation of satellite rainfall products for modeling water yield over the source region of Blue Nile Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 134834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Liu, W.B.; Sun, F.B.; Yao, Z.H.; Wang, H.; Liu, W.Q. Evaluating satellite-based and reanalysis precipitation datasets with gauge-observed data and hydrological modeling in the Xihe River Basin, China. Atmos. Res. 2020, 234, 104746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.F.; Pan, X.; Xian, T.; Liu, G.S.; Zhong, L.; Liu, Q.; Li, R.; Wang, Y.; Ma, M. Precipitation characteristics over the steep slope of the Himalayas in rainy season observed by TRMM PR and VIRS. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 51, 1971–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guo, B.; Wang, K.C.; Wu, G.C.; Shi, C.M. Performance of TRMM Product in Quantifying Frequency and Intensity of Precipitation during Daytime and Nighttime across China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, C.A.M. Thunderstorm Efficiency Regimes in South America as Observed by STARNET and TRMM. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 11428–11451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyango, A.O.; Xu, H.M.; Lin, Z.H. Diurnal cycle of rainfall over Lake Victoria Basin during the long-rain season based on TRMM satellite estimate. Int. J. Climatol. 2020, 40, 4622–4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, H.C.; Zuluaga, M.D.; Houze, R.A. Latent heating characteristics of the MJO computed from TRMM Observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 1322–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Huang, K. Imprint of the ENSO on rainfall and latent heating variability over the Southern South China Sea from TRMM observations. J. Ocean Univ. China 2016, 15, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huaman, L.; Schumacher, C. Assessing the Vertical Latent Heating Structure of the East Pacific ITCZ Using the CloudSat CPR and TRMM PR. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 2563–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Zhang, W.C.; Wang, K. Evaluation of Heavy Precipitation Simulated by the WRF Model Using 4D-Var Data Assimilation with TRMM 3B42 and GPM IMERG over the Huaihe River Basin, China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Yang, W.T.; Luan, Y.B.; Du, J.; Lin, A.W.; Zhao, L. Evaluation of the TRMM 3B42 and GPM IMERG products for extreme precipitation analysis over China. Atmos. Res. 2019, 223, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.L.; He, B.; Nover, D.; Fan, J.L.; Yang, G.S.; Chen, W.; Meng, H.F.; Liu, C.M. Floods and associated socioeconomic damages in China over the last century. Nat. Hazards 2016, 82, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Zhang, Q.; Ye, X.C. Dry/Wet Conditions Monitoring Based on TRMM Rainfall Data and Its Reliability Validation over Poyang Lake Basin, China. Water 2013, 5, 1848–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano, F.; Wardlow, B.; Tadesse, T.; Lillo-Saavedra, M.; Lagos, O. Evaluating satellite-derived long-term historical precipitation datasets for drought monitoring in Chile. Atmos. Res. 2017, 186, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Chen, Q.Y.; Jiao, M.Y.; Wu, P.T.; Gao, X.R.; Ma, M.H.; Hong, Y. The Temporal-Spatial Characteristics of Drought in the Loess Plateau Using the Remote-Sensed TRMM Precipitation Data from 1998 to 2014. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.D.; Zhang, L.P.; Zhang, Y.J.; Guo, M.Y.; Liu, X. Evaluation of Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite precipitation products for drought monitoring over the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River Basin, China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atif, R.M.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Almazroui, M. Near-real-time spatiotemporal analysis of convection and extreme rainfall leading to a flash flood using MSG-SEVIRI and TRMM data: A case study of a flash flood in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia on the November 25, 2009. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2020, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrieling, A.; Sterk, G.; de Jong, S.M. Satellite-based estimation of rainfall erosivity for Africa. J. Hydrol. 2010, 395, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.F.; Ma, Z.Q.; Chappell, A.; Shi, Z.; Liang, Z.Z.; Yu, W. Improving Rainfall Erosivity Estimates Using Merged TRMM and Gauge Data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Chen, X.W.; Fan, Q.X.; Jin, H.P.; Li, J.R. A new procedure to estimate the rainfall erosivity factor based on Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) data. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2011, 54, 2437–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Jiang, G.H.; Zuo, C.Q.; Qiu, G.Y.; Huo, H.G. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of rainfall erosivity changes in Jiangxi province over more than 50 years. Trans CSAE 2009, 25, 61–68. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shankman, D.; Keim, B.D.; Song, J. Flood frequency in China’s Poyang Lake region: Trends and teleconnections. Int. J. Climatol. 2006, 26, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.C.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Li, X.H.; Xu, C.Y. Distinguishing the relative impacts of climate change and human activities on variation of streamflow in the Poyang Lake catchment, China. J. Hydrol. 2013, 494, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.C.; Zhang, Q.; Bai, L.; Hu, Q. A modeling study of catchment discharge to Poyang Lake under future climate in China. Quat. Int. 2011, 244, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.B.; Xie, Y.; Liu, B.Y. Rainfall erosivity estimation using daily rainfall amounts. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2002, 22, 705–711. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.B.; Fu, J.S. Rainfall erosivity estimation under different rainfall amount. Resour. Sci. 2003, 25, 35–41. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xin, Z.B.; Yu, X.X.; Li, Q.Y.; Lu, X.X. Spatiotemporal variation in rainfall erosivity on the Chinese Loess Plateau during the period 1956-2008. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2011, 11, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Y.; Huang, S.Z.; Xie, Y.Y.; Leng, G.Y.; Huang, Q.; Wang, L.; Xue, Q. Spatial-temporal changes of rainfall erosivity in the loess plateau, China: Changing patterns, causes and implications. Catena 2018, 166, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Liu, B.Y.; Zhang, W.B. Study on standard of erosive rainfall. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2000, 14, 6–11. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Loureiro, N.D.; Coutinho, M.D. A new procedure to estimate the RUSLE EI30 index, based on monthly rainfall data and applied to the Algarve region, Portugal. J. Hydrol. 2001, 250, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beskow, S.; Mello, C.R.; Norton, L.D.; Curi, N.; Viola, M.R.; Avanzi, J.C. Soil erosion prediction in the Grande River Basin, Brazil using distributed modeling. Catena 2009, 79, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilks, D.S. Statistical Methods in the Atmospheric Sciences, 2nd ed.; American Academic Press: Burlington, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Su, F.G.; Hong, Y.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Evaluation of TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) and its utility in hydrologic prediction in the La Plata Basin. J. Hydrometeorol. 2008, 9, 622–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, M.S.; Hong, S.Y.; Kim, J. An Evaluation of the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) Multi-Satellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) Data over South Korea. Asia Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2009, 45, 265–282. [Google Scholar]
- Getirana, A.C.V.; Espinoza, J.C.V.; Ronchail, J.; Rotunno, O.C. Assessment of different precipitation datasets and their impacts on the water balance of the Negro River basin. J. Hydrol. 2011, 404, 304–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artan, G.; Gadain, H.; Smith, J.L.; Asante, K.; Bandaragoda, C.J.; Verdin, J.P. Adequacy of satellite derived rainfall data for stream flow modeling. Nat. Hazards 2007, 43, 167–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinku, T.; Chidzambwa, S.; Ceccato, P.; Connor, S.J.; Ropelewski, C.F. Validation of high-resolution satellite rainfall products over complex terrain. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 2008, 29, 4097–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Halverson, J.B.; Zipser, E.J. Influence of environmental moisture on TRMM-derived tropical cyclone precipitation over land and ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, 17806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.U.; Chishtie, F.; Qazi, W.A.; Ghuffar, S.; Shahid, I.; Fatima, K. Evaluation of Three-Hourly TMPA Rainfall Products Using Telemetric Rain Gauge Observations at Lai Nullah Basin in Islamabad, Pakistan. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.S.; Burian, S.J.; Shepherd, J.M. Assessment of satellite-based rainfall estimates in urban areas in different geographic and climatic regions. Nat. Hazards 2011, 56, 733–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, E.; Buytaert, W.; Peaver, L.; Wheater, H. Evaluation of precipitation products over complex mountainous terrain: A water resources perspective. Adv. Water Resour. 2011, 34, 1222–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, S.H.; Tavangar, S. Development of stational models for estimation of rainfall erosivity factor in different timescales. Nat. Hazards 2015, 77, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Xie, Y.; Liu, B.; Nearing, M.A. Rainfall erosivity estimation based on rainfall data collected over a range of temporal resolutions. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 4113–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinku, T.; Ceccato, P.; Grover-Kopec, E.; Lemma, M.; Connor, S.J.; Ropelewski, C.F. Validation of satellite rainfall products over East Africa’s complex topography. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 1503–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.F.; Liu, Y.B. Evaluation of Satellite Precipitation Products with Rain Gauge Data at Different Scales: Implications for Hydrological Applications. Water 2016, 8, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, K.; Awange, J.L.; Kuhn, M.; Featherstone, W.E. Evaluating the TRMM 3B43 monthly precipitation product using gridded raingauge data over Australia. Aust. Meteorol. Oceanogr. J. 2011, 61, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semire, F.A.; Mohd-Mokhtar, R.; Ismail, W.; Mohamad, N.; Mandeep, J. Ground validation of space-borne satellite rainfall products in Malaysia. Adv. Space Res. 2012, 50, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xiao, M.; Singh, V.P.; Wang, Y. Spatiotemporal variations of temperature and precipitation extremes in the Poyang Lake basin, China. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2015, 124, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Hu, Q. Spatiotemporal Changes in Extreme Precipitation and Its Dependence on Topography over the Poyang Lake Basin, China. Adv. Meteorol. 2019, 2019, 1253932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.L.; Hanasaki, N.; Shiogama, H.; Chen, Y.N.; Zou, S.; Nover, D.; Zhou, B.T.; Wang, Y. Evaluation and Future Projection of Chinese Precipitation Extremes Using Large Ensemble High-Resolution Climate Simulations. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 2169–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).