Robust Loop Closure Detection Integrating Visual–Spatial–Semantic Information via Topological Graphs and CNN Features
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A robust loop closure detection approach that combines visual, spatial, and semantic information to improve the robustness for changes in viewpoint and dynamic scenes is proposed.
- A pre-trained semantic segmentation model is used to segment landmarks and a pre-trained AlexNet network is employed to extract CNN features that can be used without specific scene training. In addition, the semantic segmentation model and feature extraction network can be replaced by other models.
2. Materials and Methods
- (1)
- The extraction of the semantic landmarks.
- (2)
- The elimination of the dynamic landmarks and selection of the distinctive landmarks.
- (3)
- The calculation of the CNN features in landmark regions and dimensionality reduction processing on CNN features.
- (4)
- The construction of the semantic topological graphs and expression of random walk descriptors.
- (5)
- The calculation of geometric similarity with random walk descriptors.
- (6)
- The calculation overall similarity for loop closure detection.
- The extraction of the landmarks uses a pre-trained semantic segmentation network.
- It utilizes semantic information to eliminate dynamic landmarks and select of the distinctive landmarks.
- It adopts random walk descriptors to represent the topological graphs for graph matching.
- It adds geometric constraints on the basis of appearance similarity.
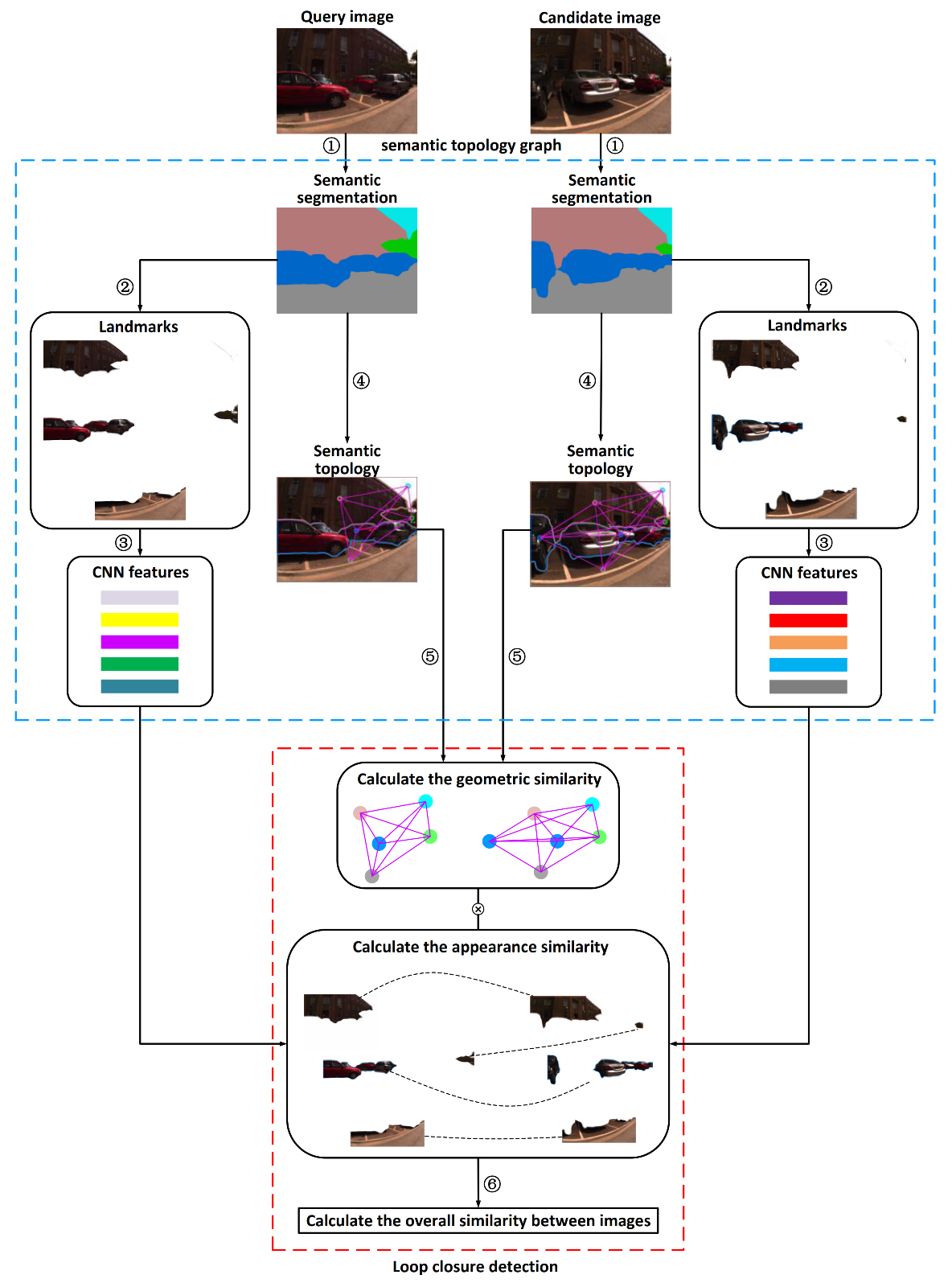
2.1. Semantic Topology Graph
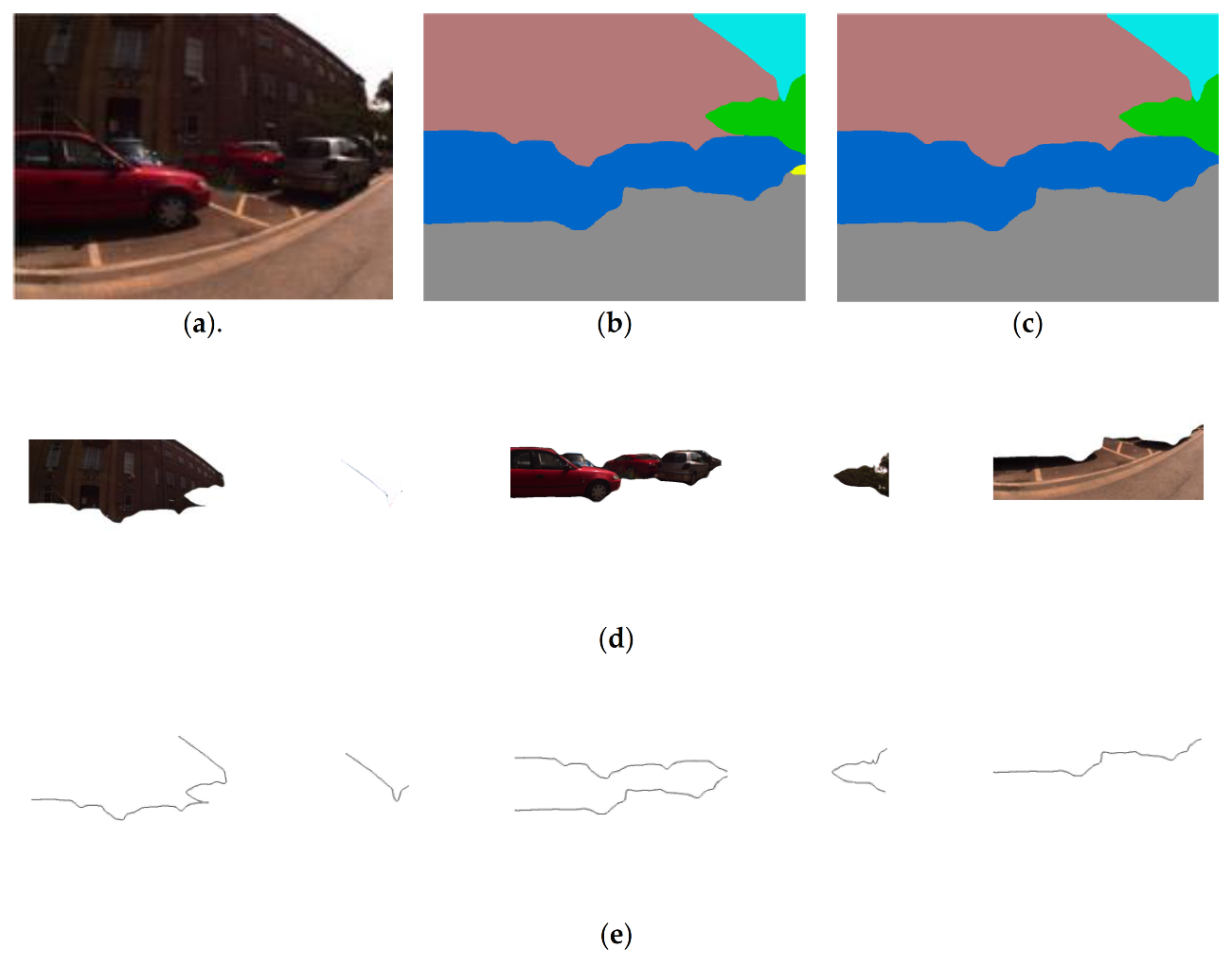
2.1.1. Landmark Extraction
2.1.2. Landmark Selection
2.1.3. CNN Features
2.1.4. Graph Representation
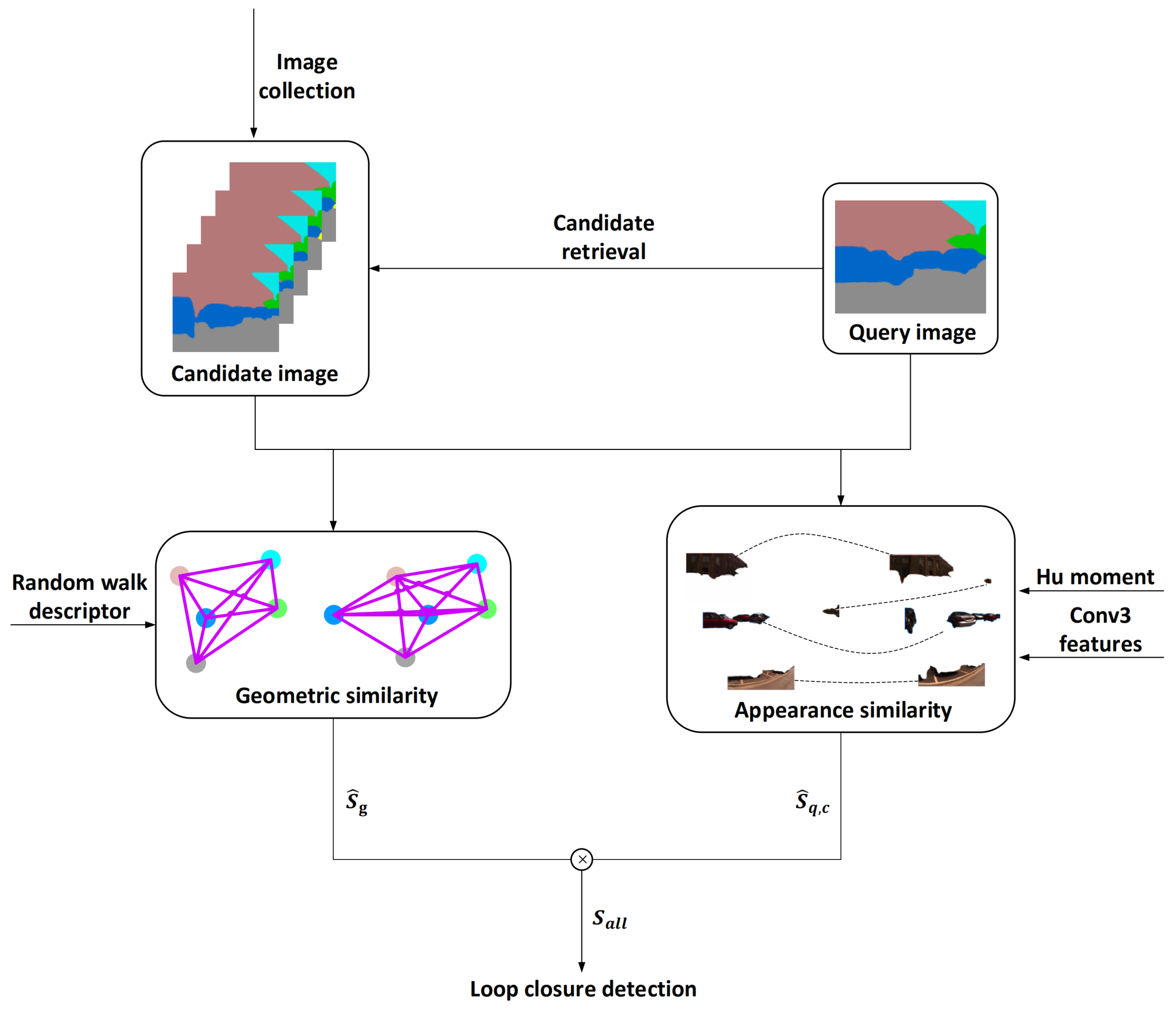
2.2. Loop Closure Detection
2.2.1. Obtain Candidate Images
2.2.2. Appearance Similarity
2.2.3. Geometric Similarity
2.2.4. Overall Similarity
3. Results
- (1)
- A state-of-the-art BoW-based method (named ‘DBoW2′) that did not need to recreate the vocabulary in different scenarios [11].
- (2)
- A CNN approach (named ‘Conv3′) that applied the global Conv3 feature to describe images [27].
- (3)
- A technique (named ‘CNNWL’) that combined global and local CNN features but ignored the spatial relationship of landmarks [30].
- (4)
- An approach (named ‘GOCCE’) that was based on local features and semi-semantic information [31]. It was closer to the proposed algorithm.
- (5)
- The proposed complete method (named ‘VSSTC’) that integrated visual, spatial, and semantic information through topological graphs and CNN features.
- (6)
- Two simplified versions of the random walk graph descriptor of our method. One version included only label information (named ‘VSSTC-Label’), and the other used only pixel number information (named ‘VSSTC-Pixel’).
- (7)
- A modified version of our method of landmark segmentation method (named ‘VSSTC-OP’) that used object proposal instead of semantic segmentation to extract landmark regions, while using the size of the bounding box instead of Hu moments.
- (8)
- Another reduced version of our method (named ‘VSSTC-LS’) that did not construct topological graphs and lacks spatial information. In order to compare the performance of the proposed method with that of the above methods, comparative experiments were carried out on the datasets and a mobile robot. Based on the experimental results, the proposed method was fully evaluated.
3.1. Dataset Experiments
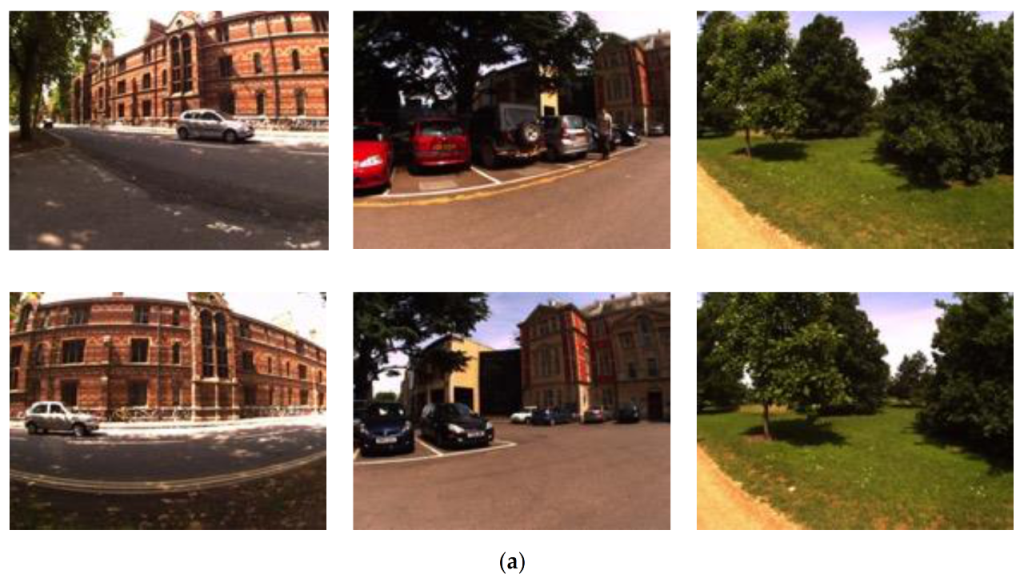
3.1.1. Datasets
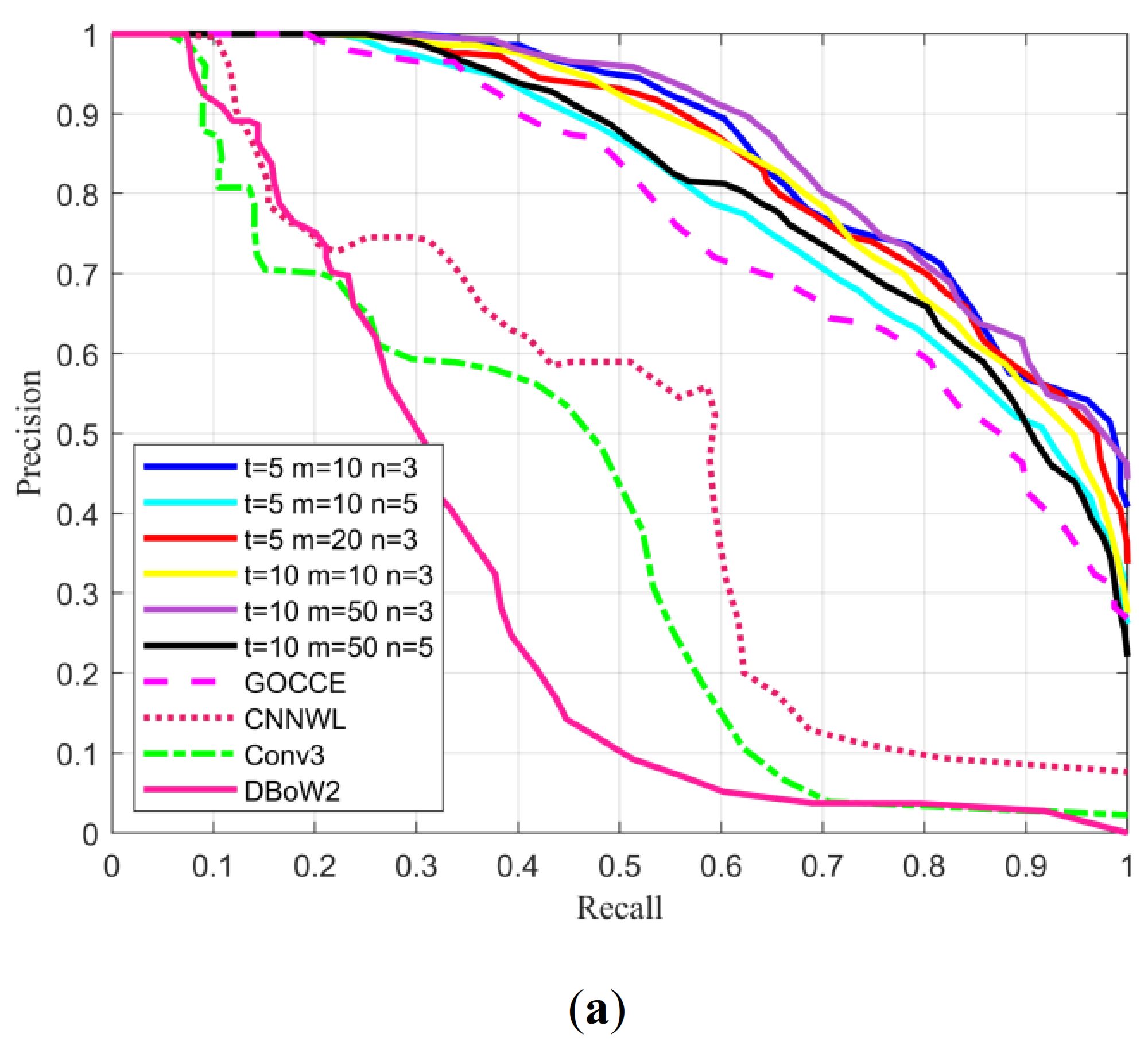
3.1.2. Experimental Results and Analysis
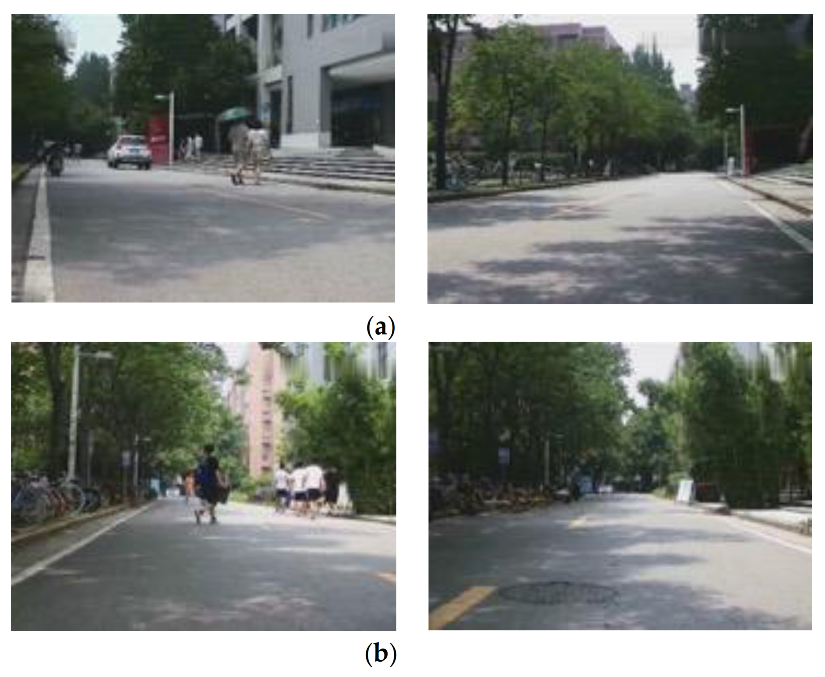
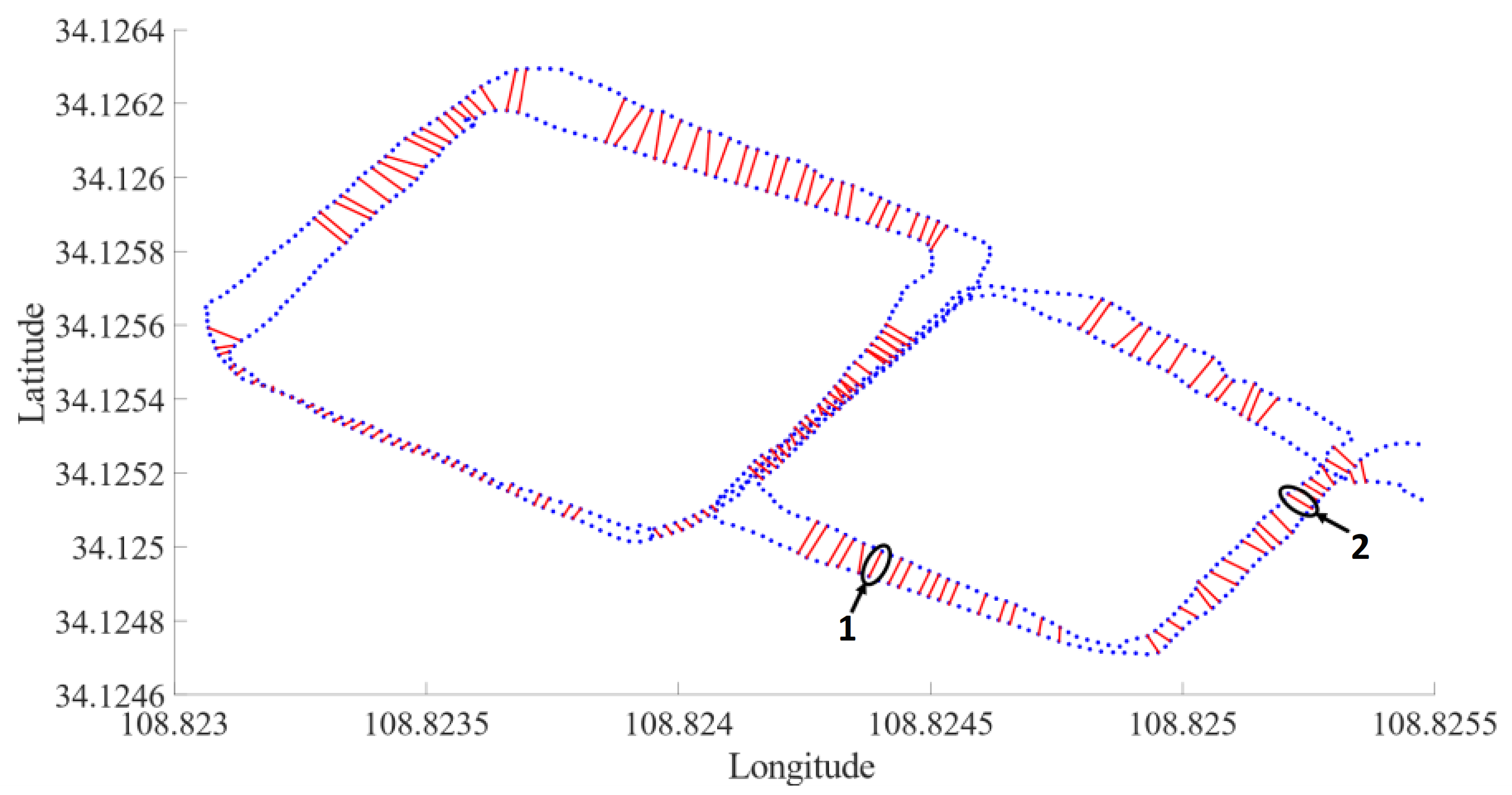
3.2. Mobile Robot Experiment
3.2.1. Experimental Platform
3.2.2. Experimental Results and Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, R.C.; Cheeseman, P. On the representation and estimation of spatial uncertainty. Int. J. Robot. Res. 1986, 5, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomeras, N.; Carreras, M.; Andrade-Cetto, J. Active SLAM for autonomous underwater exploration. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, K.-W.; Tsai, G.-J.; Li, Y.-H.; Li, Y.; El-Sheimy, N. Navigation Engine Design for Automated Driving Using INS/GNSS/3D LiDAR-SLAM and Integrity Assessment. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.L.; Newman, P. Detecting loop closure with scene sequences. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2007, 74, 261–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkesson, J.; Christensen, H. Graphical SLAM-a self-correcting map. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, New Orleans, LA, USA, 26 April–1 May 2004; pp. 383–390. [Google Scholar]
- Thrun, S.; Montemerlo, M. The Graph SLAM Algorithm with Applications to Large-Scale Mapping of Urban Structures. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2006, 25, 403–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisetti, G.; Kümmerle, R.; Stachniss, C.; Burgard, W. A tutorial on graph-based SLAM. IEEE Intell. Transp. Syst. Mag. 2010, 2, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triggs, B.; McLauchlan, P.F.; Hartley, R.I.; Fitzgibbon, A.W. Bundle adjustment—a modern synthesis. In Proceedings of the International workshop on vision algorithms, Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 21–22 September 1999; pp. 298–372. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, B.; Klein, G.; Reid, I. Automatic Relocalization and Loop Closing for Real-Time Monocular SLAM. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 33, 1699–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, M.; Newman, P. FAB-MAP: Probabilistic localization and mapping in the space of appearance. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2008, 27, 647–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gálvez-López, D.; Tardos, J.D. Bags of binary words for fast place recognition in image sequences. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2012, 28, 1188–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.G. Distinctive Image Features from Scale-Invariant Keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 60, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bay, H.; Ess, A.; Tuytelaars, T.; Gool, L.V. Speeded-Up Robust Features (SURF). Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2008, 110, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rublee, E.; Rabaud, V.; Konolige, K.; Bradski, G. ORB: An efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; pp. 2564–2571. [Google Scholar]
- Angeli, A.; Filliat, D.; Doncieux, S.; Meyer, J. Fast and Incremental Method for Loop-Closure Detection Using Bags of Visual Words. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2008, 24, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labbe, M.; Michaud, F. Online global loop closure detection for large-scale multi-session graph-based SLAM. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Chicago, IL, USA, 14–18 September 2014; pp. 2661–2666. [Google Scholar]
- Mur-Artal, R.; Tardós, J.D. Orb-slam2: An open-source slam system for monocular, stereo, and rgb-d cameras. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2017, 33, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sünderhauf, N.; Protzel, P. Brief-gist-closing the loop by simple means. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, San Francisco, CA, USA, 25–30 September 2011; pp. 1234–1241. [Google Scholar]
- Oliva, A.; Torralba, A. Modeling the Shape of the Scene: A Holistic Representation of the Spatial Envelope. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2001, 42, 145–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseer, T.; Spinello, L.; Burgard, W.; Stachniss, C. Robust visual robot localization across seasons using network flows. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Eighth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Québec City, QC, Canada, 27–31 July 2014; pp. 2564–2570. [Google Scholar]
- Milford, M.J.; Wyeth, G.F. SeqSLAM: Visual route-based navigation for sunny summer days and stormy winter nights. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Saint Paul, MN, USA, 14–18 May 2012; pp. 1643–1649. [Google Scholar]
- Abdollahyan, M.; Cascianelli, S.; Bellocchio, E.; Costante, G.; Ciarfuglia, T.A.; Bianconi, F.; Smeraldi, F.; Fravolini, M.L. Visual localization in the presence of appearance changes using the partial order kernel. In Proceedings of the European Signal Processing Conference, Rome, Italy, 3–7 September 2018; pp. 697–701. [Google Scholar]
- Pepperell, E.; Corke, P.I.; Milford, M.J. All-environment visual place recognition with SMART. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Hong Kong, China, 31 May–7 June 2014; pp. 1612–1618. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, P.; Browning, B. Visual place recognition using HMM sequence matching. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Chicago, IL, USA, 14–18 September 2014; pp. 4549–4555. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Y.; Jie, L.; Lin, Q.; Hui, Y.; Dong, J. An Evaluation of Deep Learning in Loop Closure Detection for Visual SLAM. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Internet of Things and IEEE Green Computing and Communications and IEEE Cyber, Physical and Social Computing and IEEE Smart Data, Exeter, UK, 21–23 June 2017; pp. 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, S. Convolutional neural network-based image representation for visual loop closure detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation, Lijiang, China, 8–10 August 2015; pp. 2238–2245. [Google Scholar]
- Sünderhauf, N.; Shirazi, S.; Dayoub, F.; Upcroft, B.; Milford, M. On the performance of ConvNet features for place recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015; pp. 4297–4304. [Google Scholar]
- Arroyo, R.; Alcantarilla, P.F.; Bergasa, L.M.; Romera, E. Fusion and Binarization of CNN Features for Robust Topological Localization across Seasons. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Daejeon, South Korea, 9–14 October 2016; pp. 4656–4663. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, T. Unsupervised learning to detect loops using deep neural networks for visual SLAM system. Auton. Robot. 2017, 41, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sünderhauf, N.; Shirazi, S.; Jacobson, A.; Dayoub, F.; Pepperell, E.; Upcroft, B.; Milford, M. Place recognition with convnet landmarks: Viewpoint-robust, condition-robust, training-free. Robot. Sci. Syst. 2015, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Cascianelli, S.; Costante, G.; Bellocchio, E.; Valigi, P.; Fravolini, M.L.; Ciarfuglia, T.A. Robust visual semi-semantic loop closure detection by a covisibility graph and CNN features. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2017, 92, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finman, R.; Paull, L.; Leonard, J.J. Toward object-based place recognition in dense rgb-d maps. In Proceedings of the ICRA Workshop Visual Place Recognition in Changing Environments, Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, J.; Jeon, J.; Lee, B. Place recognition for visual loop-closures using similarities of object graphs. Electron. Lett. 2014, 51, 44–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepperell, E.; Corke, P.; Milford, M. Routed roads: Probabilistic vision-based place recognition for changing conditions, split streets and varied viewpoints. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2016, 35, 1057–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumm, E.; Mei, C.; Lacroix, S.; Chli, M. Location graphs for visual place recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 5475–5480. [Google Scholar]
- Gawel, A.R.; Don, C.D.; Siegwart, R.; Nieto, J.; Cadena, C. X-View: Graph-Based Semantic Multi-View Localization. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 1687–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumm, E.; Mei, C.; Lacroix, S.; Nieto, J.; Siegwart, R. Robust Visual Place Recognition with Graph Kernels. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 4535–4544. [Google Scholar]
- Han, F.; Wang, H. Learning integrated holism-landmark representations for long-term loop closure detection. In Proceedings of the 32nd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; pp. 6501–6508. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Maffra, F.; Sa, I.; Chli, M. Only look once, mining distinctive landmarks from convnet for visual place recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; pp. 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Schönberger, J.L.; Pollefeys, M.; Geiger, A.; Sattler, T. Semantic visual localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 6896–6906. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, P.; Zhang, H. Long-Term Loop Closure Detection through Visual-Spatial Information Preserving Multi-Order Graph Matching. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Fourth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; pp. 10369–10376. [Google Scholar]
- Zitnick, C.L.; Dollár, P. Edge boxes: Locating object proposals from edges. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; pp. 391–405. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.-C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, Mass, USA, 7–13 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Zhao, H.; Puig, X.; Xiao, T.; Fidler, S.; Barriuso, A.; Torralba, A. Semantic understanding of scenes through the ade20k dataset. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2019, 127, 302–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Zhao, H.; Puig, X.; Fidler, S.; Barriuso, A.; Torralba, A. Scene parsing through ade20k dataset. Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 633–641. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in neural information processing systems, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 3–6 December 2012; pp. 1097–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z.; Karpathy, A.; Khosla, A.; Bernstein, M. Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2015, 115, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candes, E.J.; Tao, T. Near-optimal signal recovery from random projections: Universal encoding strategies? IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2006, 52, 5406–5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perozzi, B.; Al-Rfou, R.; Skiena, S. Deepwalk: Online learning of social representations. In Proceedings of the 20th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining, New York, USA, 24–27 August 2014; pp. 701–710. [Google Scholar]
- Cascianelli, S.; Costante, G.; Bellocchio, E.; Valigi, P.; Fravolini, M.L.; Ciarfuglia, T.A. A robust semi-semantic approach for visual localization in urban environment. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Smart Cities Conference, Trento, Italy, 12–15 September 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M.-K. Visual pattern recognition by moment invariants. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1962, 8, 179–187. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, J.; Goadrich, M. The relationship between Precision-Recall and ROC curves. In Proceedings of the 23rd international conference on Machine learning, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 25–29 June 2006; pp. 233–240. [Google Scholar]
- Abadi, M.; Agarwal, A.; Barham, P.; Brevdo, E.; Chen, Z.; Citro, C.; Corrado, G.S.; Davis, A.; Dean, J.; Devin, M. TensorFlow: Large-scale machine learning on heterogeneous systems. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1603.04467. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.; Shelhamer, E.; Donahue, J.; Karayev, S.; Long, J.; Girshick, R.; Guadarrama, S.; Darrell, T. Caffe: Convolutional architecture for fast feature embedding. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM international conference on Multimedia, Orlando, FL, USA, 3–7 November 2014; pp. 675–678. [Google Scholar]





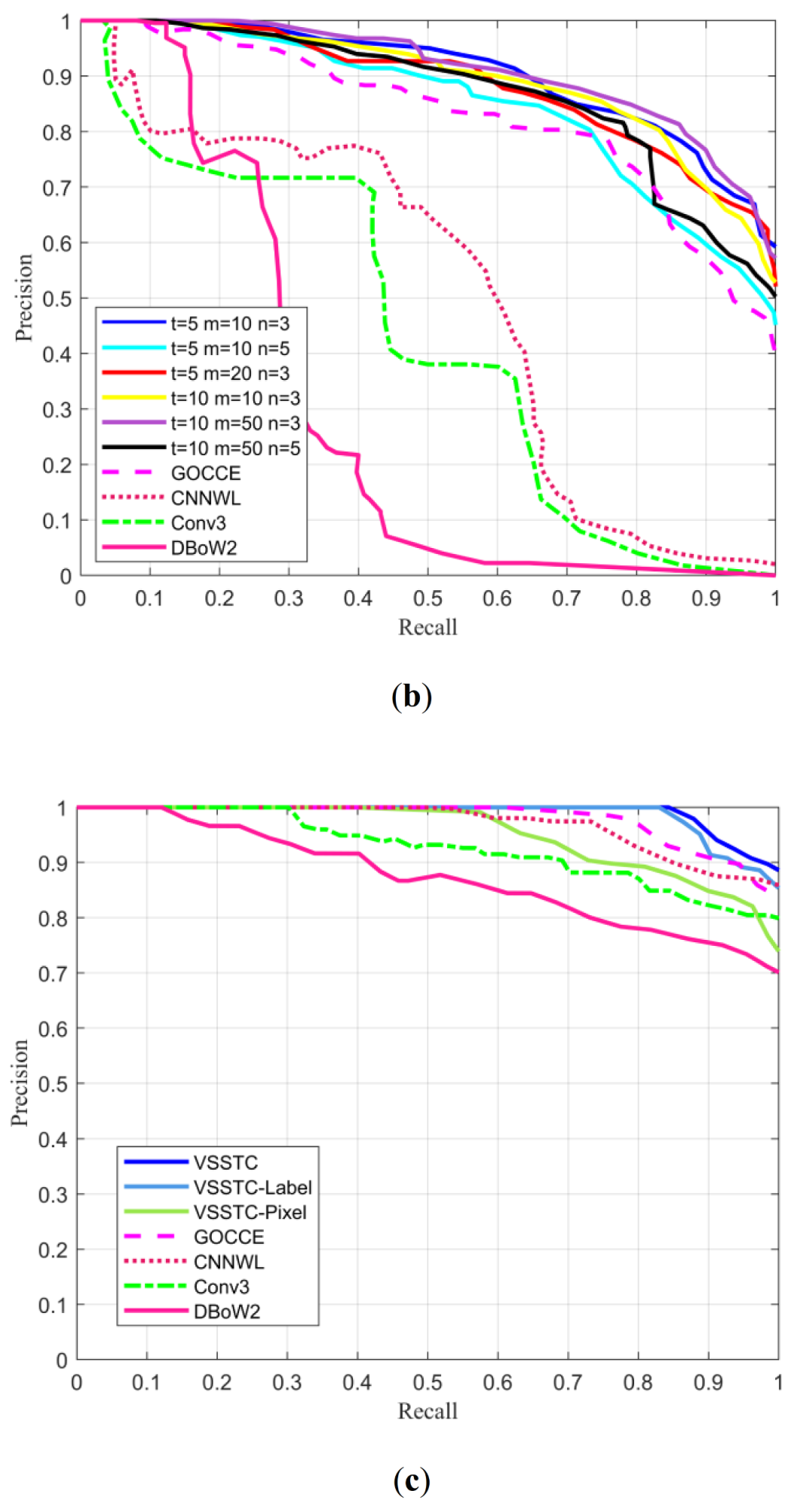
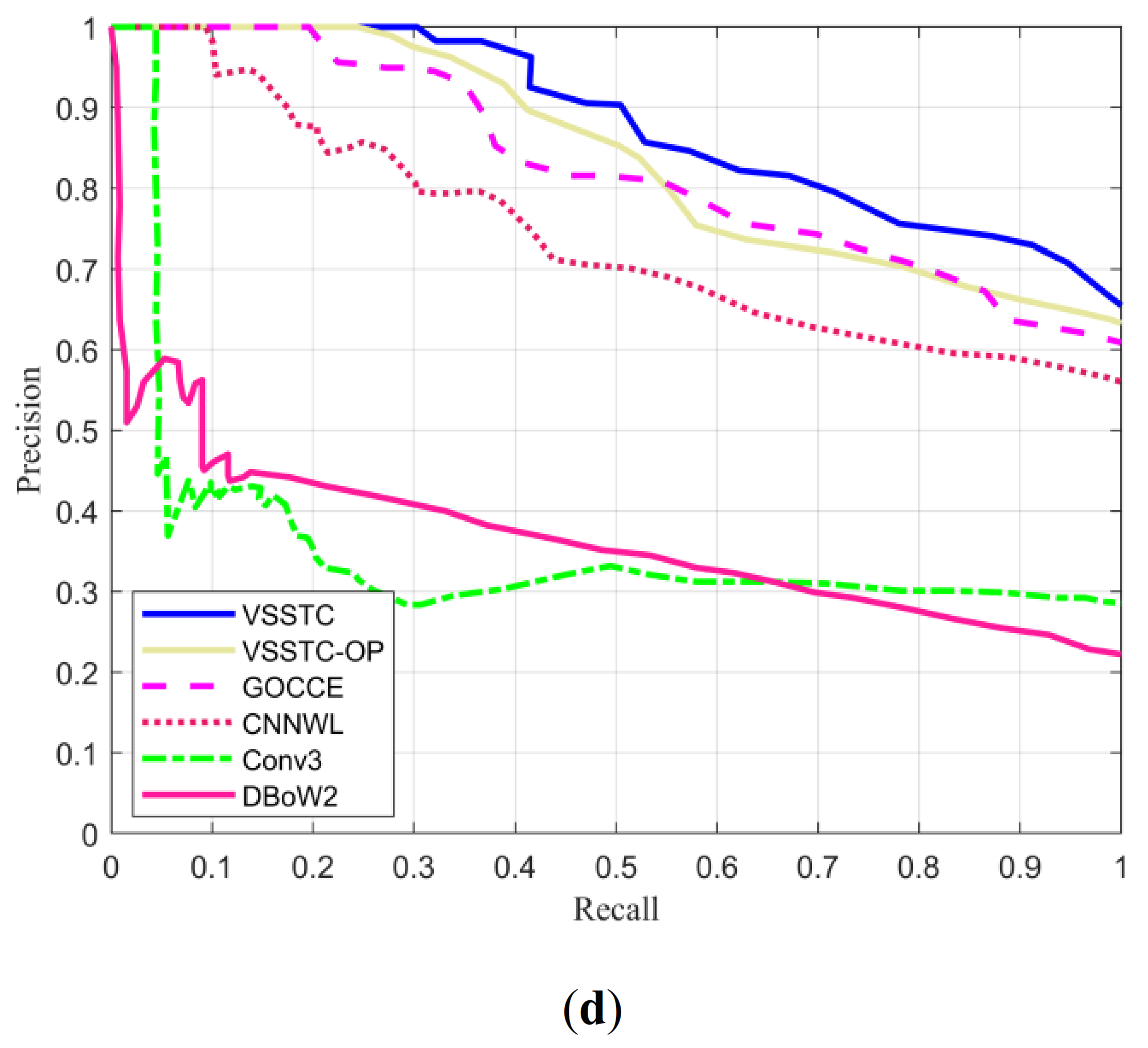


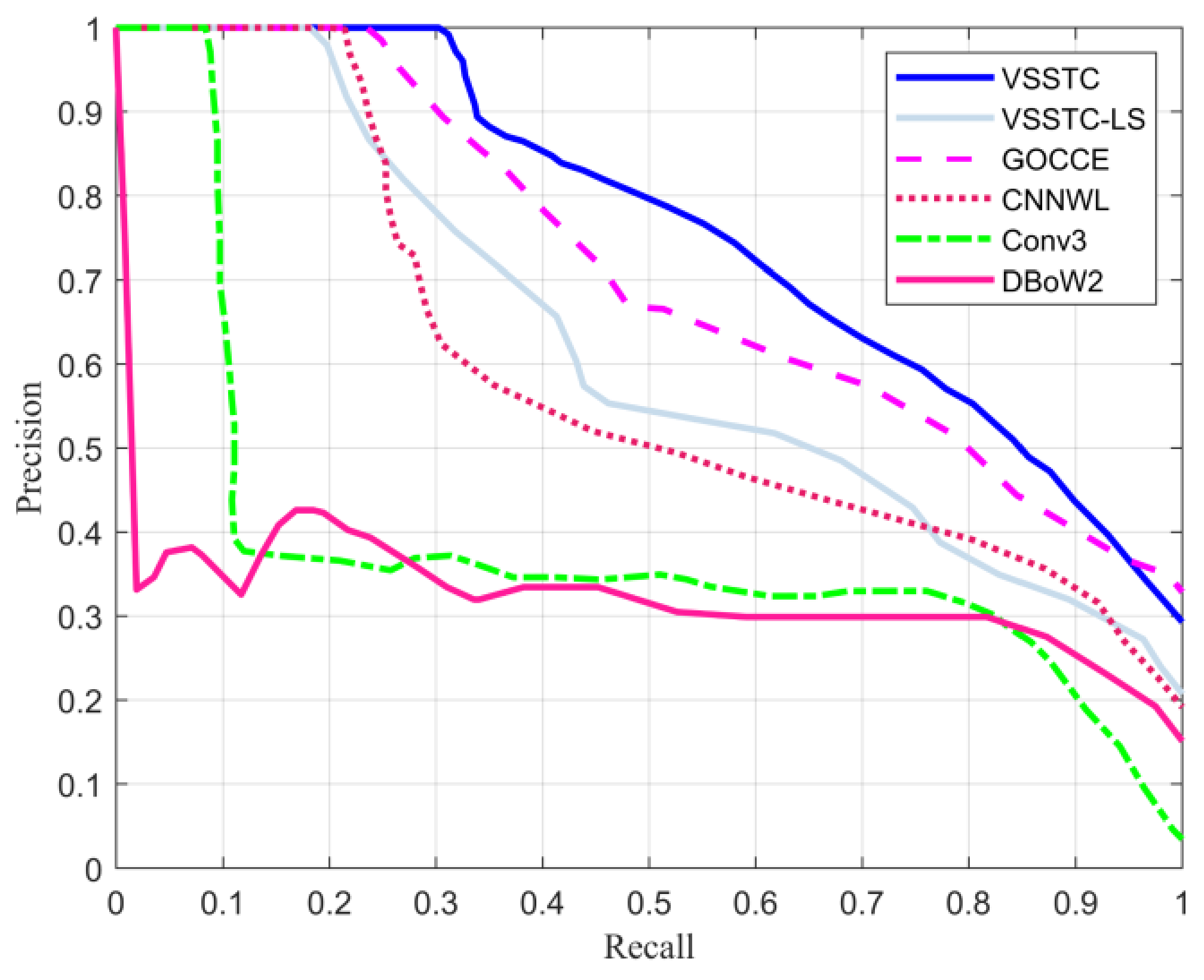

| Methods | City Centre | New College | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recall (%) | AUC | Recall (%) | AUC | |
| VSSTC (t = 5 m = 10 n = 3) | 29.81 | 0.8707 | 20.51 | 0.9042 |
| VSSTC (t = 5 m = 10 n = 5) | 22.44 | 0.8085 | 13.14 | 0.8492 |
| VSSTC (t = 5 m = 20 n = 3) | 24.68 | 0.8512 | 18.27 | 0.8848 |
| VSSTC (t = 10 m = 10 n = 3) | 21.47 | 0.8459 | 15.39 | 0.8923 |
| VSSTC (t =1 0 m = 50 n = 3) | 29.17 | 0.8636 | 22.76 | 0.9109 |
| VSSTC (t = 10 m = 50 n = 5) | 25.00 | 0.8186 | 14.42 | 0.8699 |
| GOCCE [31] | 19.23 | 0.7769 | 8.98 | 0.8284 |
| CNNWL [30] | 6.81 | 0.4882 | 5.09 | 0.5051 |
| Conv3 [27] | 5.72 | 0.3938 | 3.22 | 0.4258 |
| DBoW2 [11] | 7.36 | 0.3187 | 8.04 | 0.2975 |
| Methods | Gardens Point | Mapillary | Robot | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recall (%) | AUC | Recall (%) | AUC | Recall (%) | AUC | |
| VSSTC | 84.33 | 0.9906 | 30.32 | 0.8796 | 30.25 | 0.7628 |
| VSSTC-Label | 82.96 | 0.9871 | - 1 | - | - | - |
| VSSTC-Pixel | 39.52 | 0.9528 | - | - | - | - |
| VSSTC-OP | - | - | 24.36 | 0.8395 | - | - |
| VSSTC-LS | - | - | - | - | 18.14 | 0.6229 |
| GOCCE [31] | 60.99 | 0.9792 | 19.59 | 0.8260 | 23.49 | 0.7132 |
| CNNWL [30] | 49.57 | 0.9700 | 9.37 | 0.7397 | 20.09 | 0.5909 |
| Conv3 [27] | 30.15 | 0.9268 | 4.43 | 0.3544 | 8.35 | 0.3823 |
| DBoW2 [11] | 12.10 | 0.8730 | 0 | 0.3643 | 0 | 0.3249 |
| Product Name | Network Integrated Movement |
|---|---|
| Model | YM86 × 10M2N |
| Sensor | 1/2″ |
| Focal length | 10~860 mm |
| FOV | 42°~0.44° |
| Resolution | 1920 × 1080 |
| Aperture | F2.0~6.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Cheng, P.; Duan, X. Robust Loop Closure Detection Integrating Visual–Spatial–Semantic Information via Topological Graphs and CNN Features. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3890. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12233890
Wang Y, Qiu Y, Cheng P, Duan X. Robust Loop Closure Detection Integrating Visual–Spatial–Semantic Information via Topological Graphs and CNN Features. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(23):3890. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12233890
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yuwei, Yuanying Qiu, Peitao Cheng, and Xuechao Duan. 2020. "Robust Loop Closure Detection Integrating Visual–Spatial–Semantic Information via Topological Graphs and CNN Features" Remote Sensing 12, no. 23: 3890. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12233890
APA StyleWang, Y., Qiu, Y., Cheng, P., & Duan, X. (2020). Robust Loop Closure Detection Integrating Visual–Spatial–Semantic Information via Topological Graphs and CNN Features. Remote Sensing, 12(23), 3890. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12233890





