Assessment of Freeze–Thaw Hazards and Water Features along the China–Russia Crude Oil Pipeline in Permafrost Regions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and materials
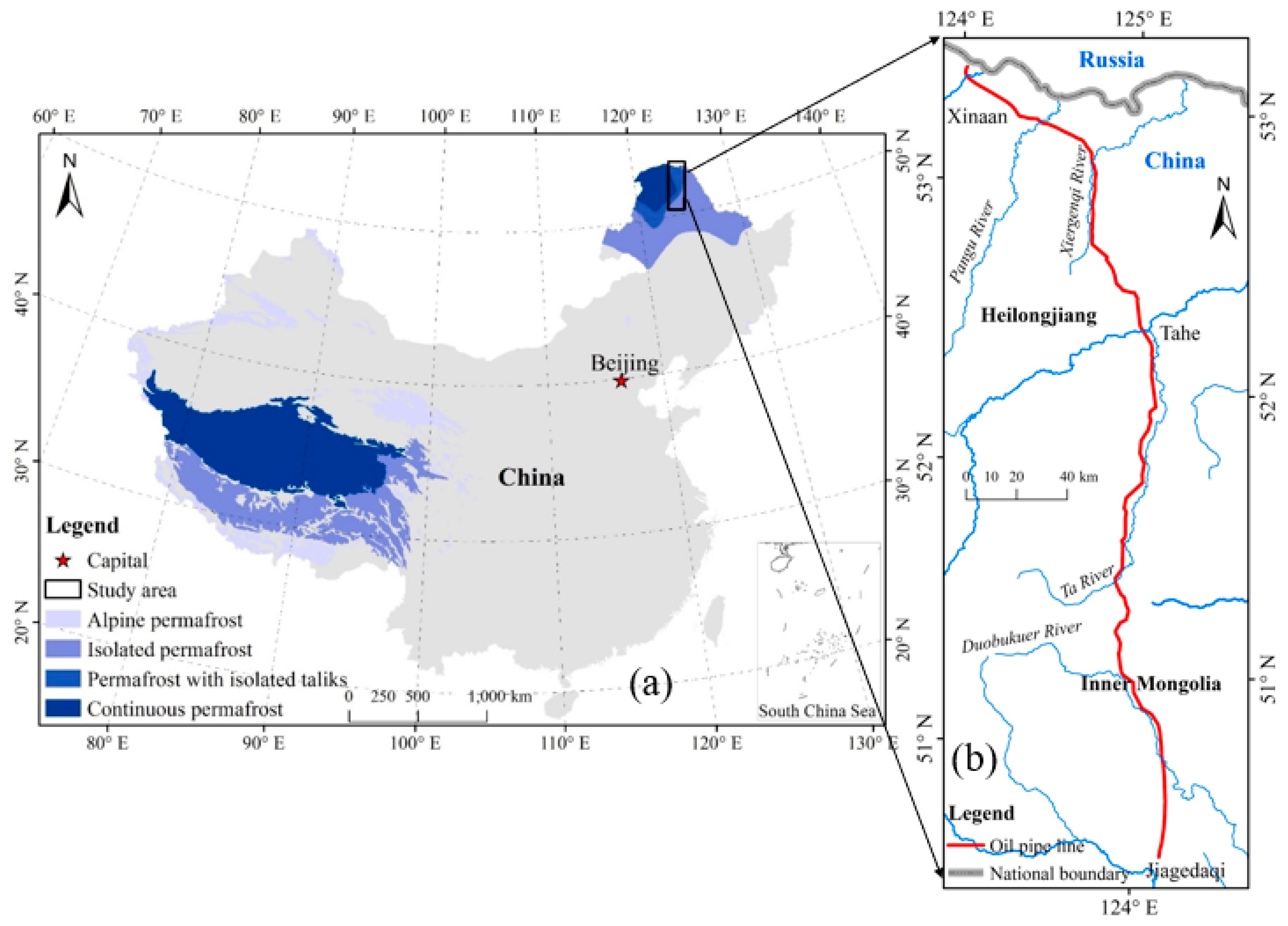
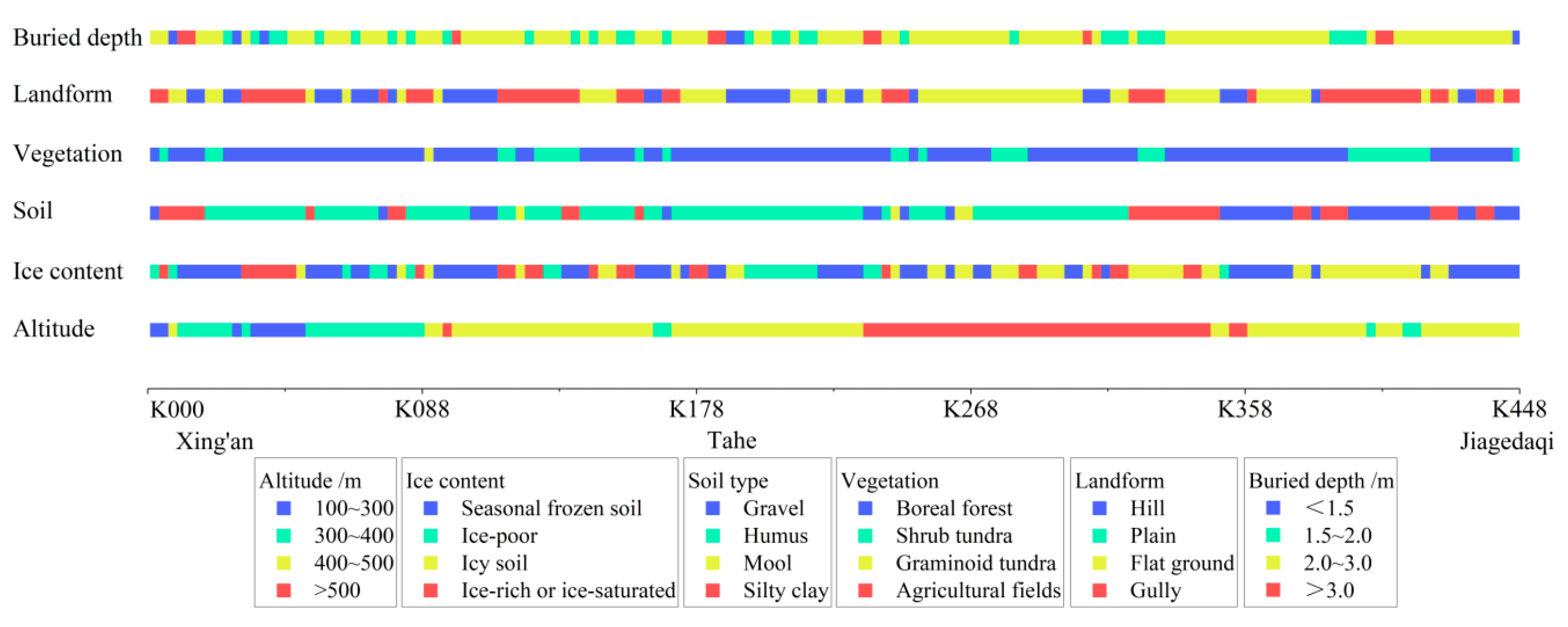
2.1. Test Case and Data
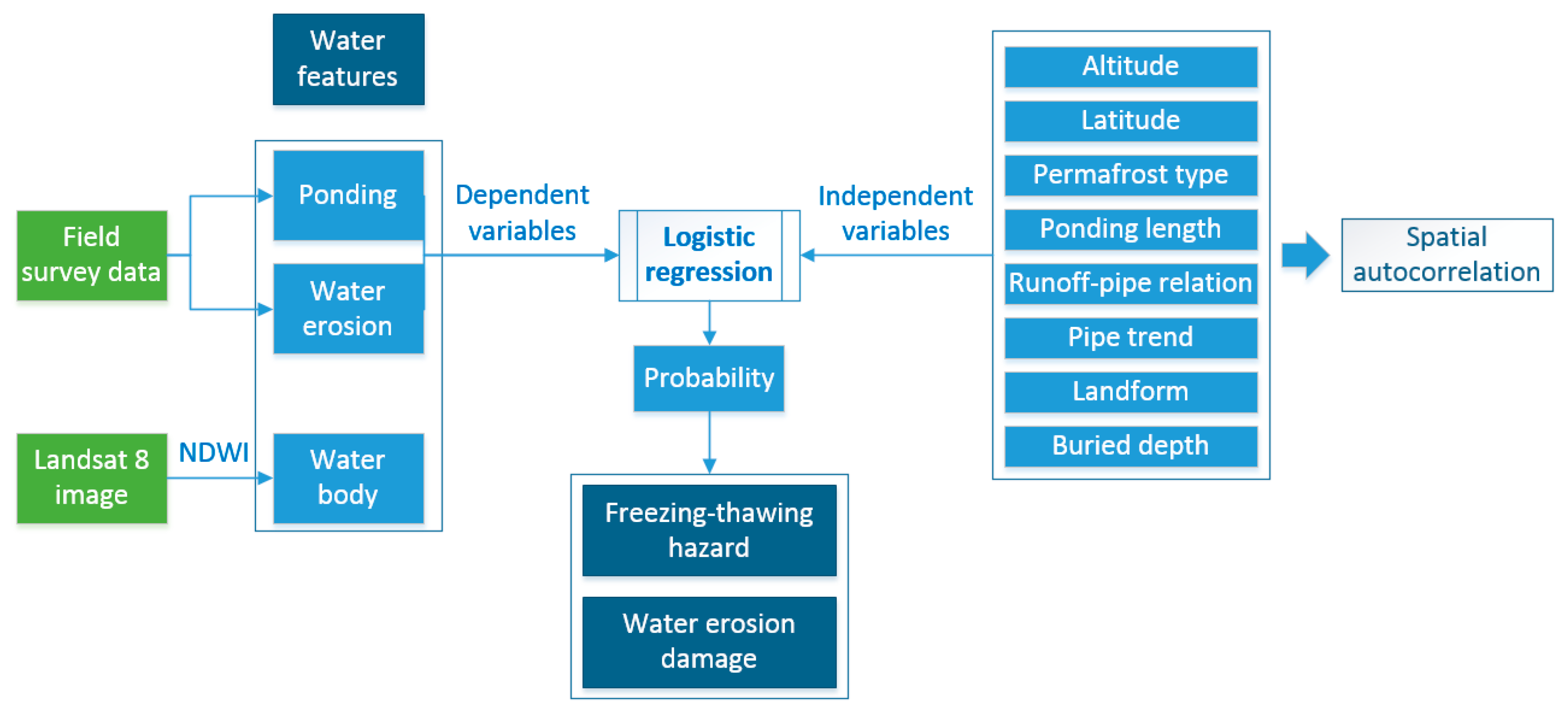
2.2. Methods
3. Results
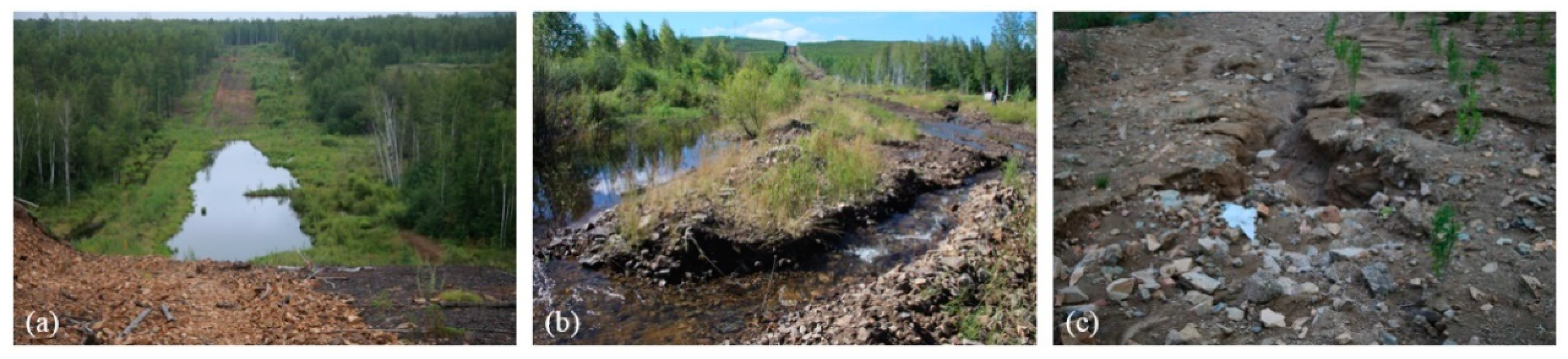
3.1. Distribution of Ponds and Water Erosion along the CRCOP
3.2. The Spatial Autocorrelation of Influential Factors
3.3. Probability of Frost Heave and Thawing Settlement along the CRCOP
3.4. Probability of Erosive Damage by Surface Flows
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jin, H.J.; Hao, J.Q.; Chang, X.L.; Zhang, J.M.; Qi, J.L.; Lü, L.Z.; Wang, S.L. Zonation and assessment of frozen-ground conditions for engineering geology along the China–Russia crude oil pipeline route from Mo’he to Daqing, Northeastern China. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2010, 64, 213–225. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Ding, L.; Liu, H.P. Study on permafrost thermal stability due to geohazards of China-Russia Crude Oil Pipeline. J. Eng. Res. 2020, 8, 89–106. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.P.; Jin, H.J.; Li, G.Y. Investigation of the freeze–thaw states of foundation soils in permafrost areas along the China–Russia Crude Oil Pipeline (CRCOP) route using ground-penetrating radar (GPR). Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2016, 126, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.Y.; Ma, W.; Wang, X.L.; Jin, H.J.; Wang, Y.P.; Zhao, Y.B.; Cai, Y.J.; Zhang, P. Frost hazards and mitigative measures following operation of Mohe-Daqing line of China-Russia crude oil pipeline. Rock Soil Mech. 2015, 36, 2963–2973. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Li, G.Y.; Ma, W.; Wu, Q.; Serban, M.; Vera, S.; Alexandr, F.; Jiang, N.; Wang, B. Pipeline–permafrost interaction monitoring system along the China–Russia crude oil pipeline. Eng. Geol. 2019, 254, 113–125. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Z.; Jin, H.J.; Zhang, J.M.; Yu, S.P.; Han, X.J.; Ji, Y.J.; He, R.X.; Chang, X.L. Prediction of permafrost changes in Northeastern China under a changing climate. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2011, 54, 924–935. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, H.J.; Yu, Q.H.; Lü, L.Z.; Guo, D.X.; He, R.X.; Yu, S.P.; Sun, G.Y.; Li, Y.W. Degradation of permafrost in the Xing’anling Mountains, Northeastern China. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2007, 18, 245–258. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.B.; Liu, W.B.; Lai, Y.M.; Chen, L.; Yi, X. Nonlinear analysis of coupled temperature-seepage problem of warm oil pipe in permafrost regions of Northeast China. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2014, 70, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Sheng, Y.; Jin, H.J.; Li, S.; Li, G.; Niu, Y. Thermal elasto-plastic computation model for a buried oil pipeline in frozen ground. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2010, 64, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.P.; Sheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jin, H.J.; Chen, W. Stresses and deformations in a buried oil pipeline subject to differential frost heave in permafrost regions. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2010, 64, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykes, J.F.; Lennon, W.C.; Unny, T.E. Two-dimensional heated pipeline in permafrost. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 1974, 100, 10956. [Google Scholar]
- Osterkamp, T.E. Establishing long-term permafrost observatories for active-layer and permafrost investigations in Alaska: 1977–2002. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2003, 14, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oswell, J.M. Pipelines in permafrost: Geotechnical issues and lessons. Can. Geotech. J. 2011, 48, 1412–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, M.M.; Wilkie, S.; Doblanko, R.; Konuk, I. Field observations of cyclical pipe-soil interactions in permafrost terrain, KP 5, Norman Wells Pipeline, Canada. In Proceedings of the 2000 3rd International Pipeline Conference, Calgary, AB, Canada, 1–5 October 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Slusarchuk, W.A.; Watson, G.H.; Speer, T.L. Instrumentation around a warm oil pipeline buried in permafrost. Can. Geotech. J. 1973, 10, 227–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.Y.; Sheng, Y.; Jin, H.J.; Ma, W.; Qi, J.L.; Wen, Z.; Zhang, B.; Mu, Y.H.; Bi, G.Q. Development of freezing–thawing processes of foundation soils surrounding the China–Russia Crude Oil Pipeline in the permafrost areas under a warming climate. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2010, 64, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.Y.; Wang, F.; Ma, W.; Fortier, R.; Mu, Y.H.; Zhou, Z.W.; Mao, Y.C.; Cai, Y.J. Field observations of cooling performance of thermosyphons on permafrost under the China-Russia Crude Oil Pipeline. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 141, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, M.M.; Harry, D.G. Norman Wells pipeline permafrost and terrain monitoring: Geothermal and geomorphic observations, 1984–1987. Can. Geotech. J. 1990, 27, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, M.T.; Mu, Y.H.; Li, G.Y.; Ma, W.; Wang, F. Relationship between ponding and topographic factors along the China-Russia Crude Oil Pipeline in permafrost regions. Sci. Cold Arid Reg. 2020, 11, 419–427. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, D.P.; Wulder, M.A.; Loveland, T.R.; Woodcock, C.E.; Allen, R.G.; Anderson, M.C.; Helder, D.; Irons, J.R.; Johnson, D.M.; Kennedy, R.; et al. Landsat-8: Science and Product Vision for Terrestrial Global Change Research. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 145, 154–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, S.K. The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, E.; Perkins, R.; Trainor, S. Thaw Settlement Hazard of Permafrost Related to Climate Warming in Alaska. Arctic 2014, 67, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Wu, Q.B. Thermal hazards zonation and permafrost change over the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Nat. Hazards 2012, 61, 403–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.Q.; Li, W.B.; Zhou, D.B.; Tian, L.; Ling, F.; Wang, H.; Gui, Y.; Sun, B. Analysis of Landsat-8 OLI imagery for land surface water mapping. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, G.Y.; Ma, W.; Mao, Y.C.; Mu, Y.H.; Serban, M.; Cai, Y.J. Permafrost warming along the Mo’he-Jiagedaqi section of the China-Russia crude oil pipeline. J. Mt. Sci. 2019, 16, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Bands | Wavelength (μm) | Spatial Resolution (m) | Radiometric Resolution (Bit) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1—Coastal aerosol | 0.43–0.45 | 30 | 12 |
| 2—Blue | 0.45–0.51 | 30 | 12 |
| 3—Green | 0.53–0.59 | 30 | 12 |
| 4—Red | 0.64–0.67 | 30 | 12 |
| 5—Near infrared | 0.85–0.88 | 30 | 12 |
| 6—Short wave infrared 1 | 1.57–1.65 | 30 | 12 |
| 7—Short wave infrared 2 | 2.11–2.29 | 30 | 12 |
| 8—Panchomatic | 0.50–0.68 | 15 | 12 |
| 9—Cirrus | 1.36–1.38 | 30 | 12 |
| Observed | Predicted | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Freeze–Thaw Hazards | Percentage Correct | ||||
| 0 | 1 | ||||
| Step 1 | Freeze–thaw hazards | 0 | 101 | 25 | 80.2 |
| 1 | 34 | 44 | 56.4 | ||
| Overall Percentage | 71.1 | ||||
| B | S.E. | Wald | df | Sig. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Altitude (m) | 0.008 | 0.002 | 18.475 | 1 | 0.000 |
| Permafrost type | 2.224 | 1.466 | 2.302 | 1 | 0.029 |
| Ponding length (m) | 0.001 | 0.001 | 3.831 | 1 | 0.050 |
| Relation of surface flow and pipe | −1.206 | 0.467 | 6.672 | 1 | 0.010 |
| Latitude (°) | 0.507 | 0.169 | 9.022 | 1 | 0.003 |
| Constant | −29.579 | 8.966 | 10.885 | 1 | 0.001 |
| Robust Standard Error | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Independent Variables | No Cluster | Cluster by Latitude | Cluster by Altitude | Cluster by PT | Cluster by PL | Cluster by RSFP |
| Latitude | 0.259 | 0.227 | 0.248 | 0.243 | 0.162 | 0.112 |
| Altitude | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| PT | 13.483 | 11.418 | 12.366 | 9.391 | 13.941 | 1.783 |
| PL | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| RSFP | 0.132 | 0.125 | 0.121 | 0.076 | 0.132 | 0.001 |
| Observed | Predicted | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Erosive Damage by Flow | Percentage Correct | ||||
| 0 | 1 | ||||
| Step 1 | Erosive damage by flow | 0 | 38 | 41 | 48.1 |
| 1 | 24 | 103 | 81.1 | ||
| Overall percentage | 68.4 | ||||
| B | S.E. | Wald | df | Sig. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Altitude (m) | −0.009 | 0.002 | 18.737 | 1 | 0.000 |
| Pipe orientation (°) | 0.006 | 0.005 | 1.372 | 1 | 0.041 |
| Influenced length (m) | −0.002 | 0.001 | 5.651 | 1 | 0.017 |
| Relation of surface flow and pipe | −1.359 | 0.455 | 8.917 | 1 | 0.003 |
| Landform | 0.127 | 0.114 | 1.238 | 1 | 0.066 |
| Buried depth of pipe | 0.326 | 0.315 | 1.071 | 1 | 0.001 |
| Constant | 2.592 | 1.379 | 3.533 | 1 | 0.060 |
| Independ-Ent Variables | Robust Standard Error | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No Cluster | Cluster by Altitude | Cluster by PT | Cluster by PL | Cluster by RSFP | Cluster by Landform | Cluster by BDP | |
| Altitude | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.001 |
| PT | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.003 |
| PL | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| RSFP | 1.745 | 1.649 | 1.849 | 1.777 | 0.056 | 0.766 | 1.832 |
| Landform | 0.132 | 0.114 | 0.097 | 0.129 | 0.069 | 0.066 | 0.147 |
| BDP | 0.414 | 0.379 | 0.369 | 0.327 | 0.244 | 0.549 | 0.386 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chai, M.; Li, G.; Ma, W.; Cao, Y.; Wu, G.; Mu, Y.; Chen, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Assessment of Freeze–Thaw Hazards and Water Features along the China–Russia Crude Oil Pipeline in Permafrost Regions. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3576. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12213576
Chai M, Li G, Ma W, Cao Y, Wu G, Mu Y, Chen D, Zhang J, Zhou Z, Zhou Y, et al. Assessment of Freeze–Thaw Hazards and Water Features along the China–Russia Crude Oil Pipeline in Permafrost Regions. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(21):3576. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12213576
Chicago/Turabian StyleChai, Mingtang, Guoyu Li, Wei Ma, Yapeng Cao, Gang Wu, Yanhu Mu, Dun Chen, Jun Zhang, Zhiwei Zhou, Yu Zhou, and et al. 2020. "Assessment of Freeze–Thaw Hazards and Water Features along the China–Russia Crude Oil Pipeline in Permafrost Regions" Remote Sensing 12, no. 21: 3576. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12213576
APA StyleChai, M., Li, G., Ma, W., Cao, Y., Wu, G., Mu, Y., Chen, D., Zhang, J., Zhou, Z., Zhou, Y., & Du, Q. (2020). Assessment of Freeze–Thaw Hazards and Water Features along the China–Russia Crude Oil Pipeline in Permafrost Regions. Remote Sensing, 12(21), 3576. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12213576






