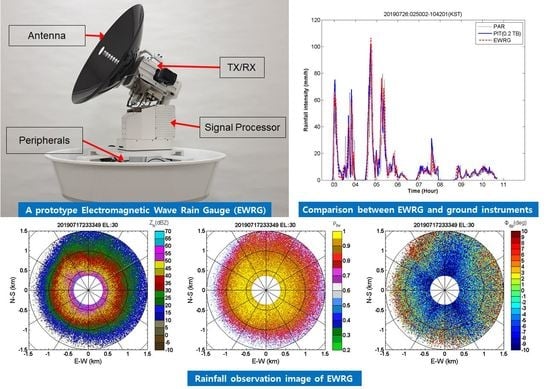
A Novel Electromagnetic Wave Rain Gauge and its Average Rainfall Estimation Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
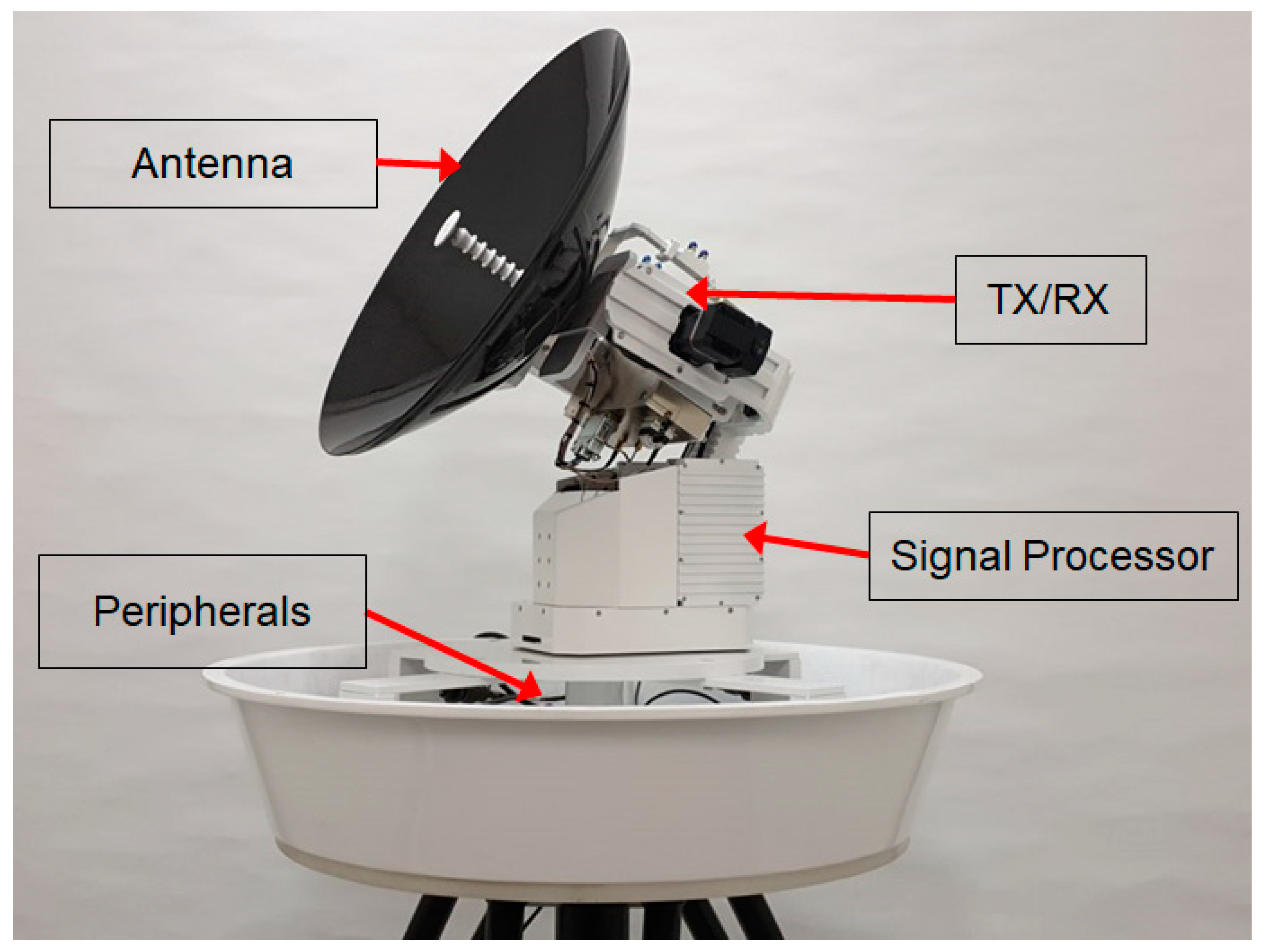
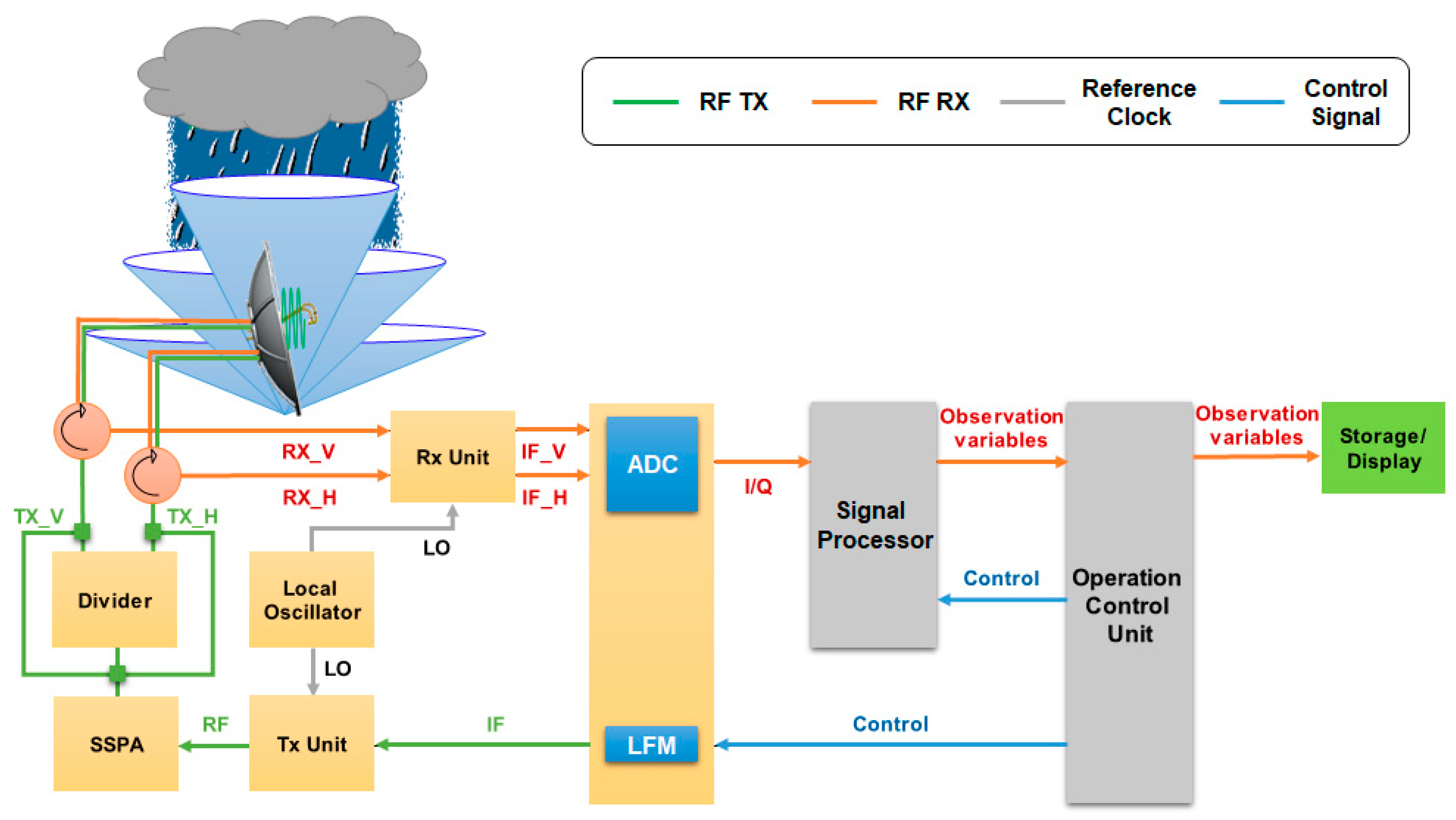
2. Description of the EWRG
2.1. EWRG Specifications
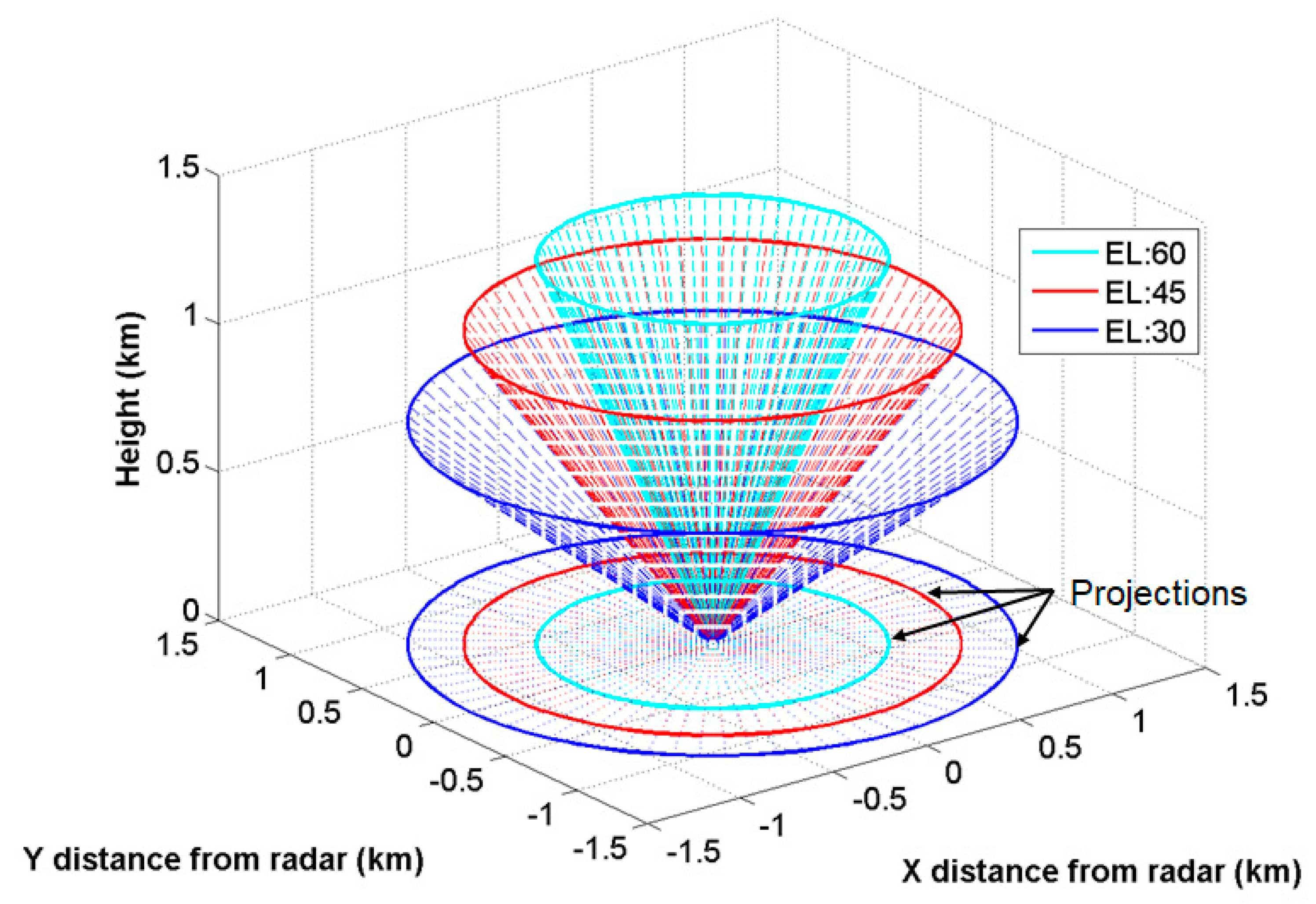
2.2. EWRG Scan Strategy
3. EWRG Average Rainfall Estimation Method
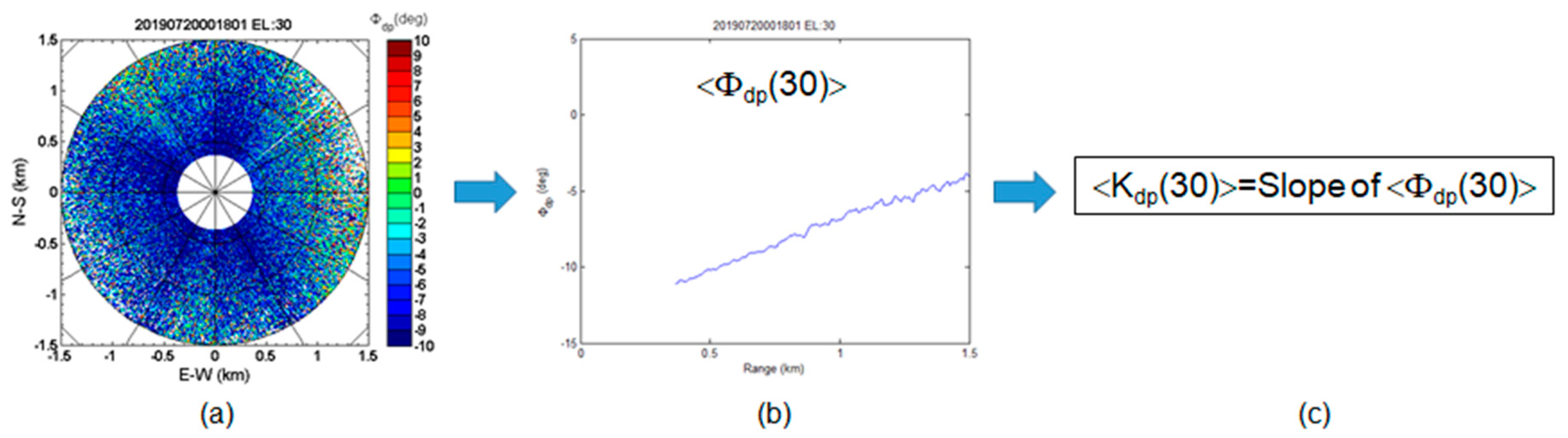
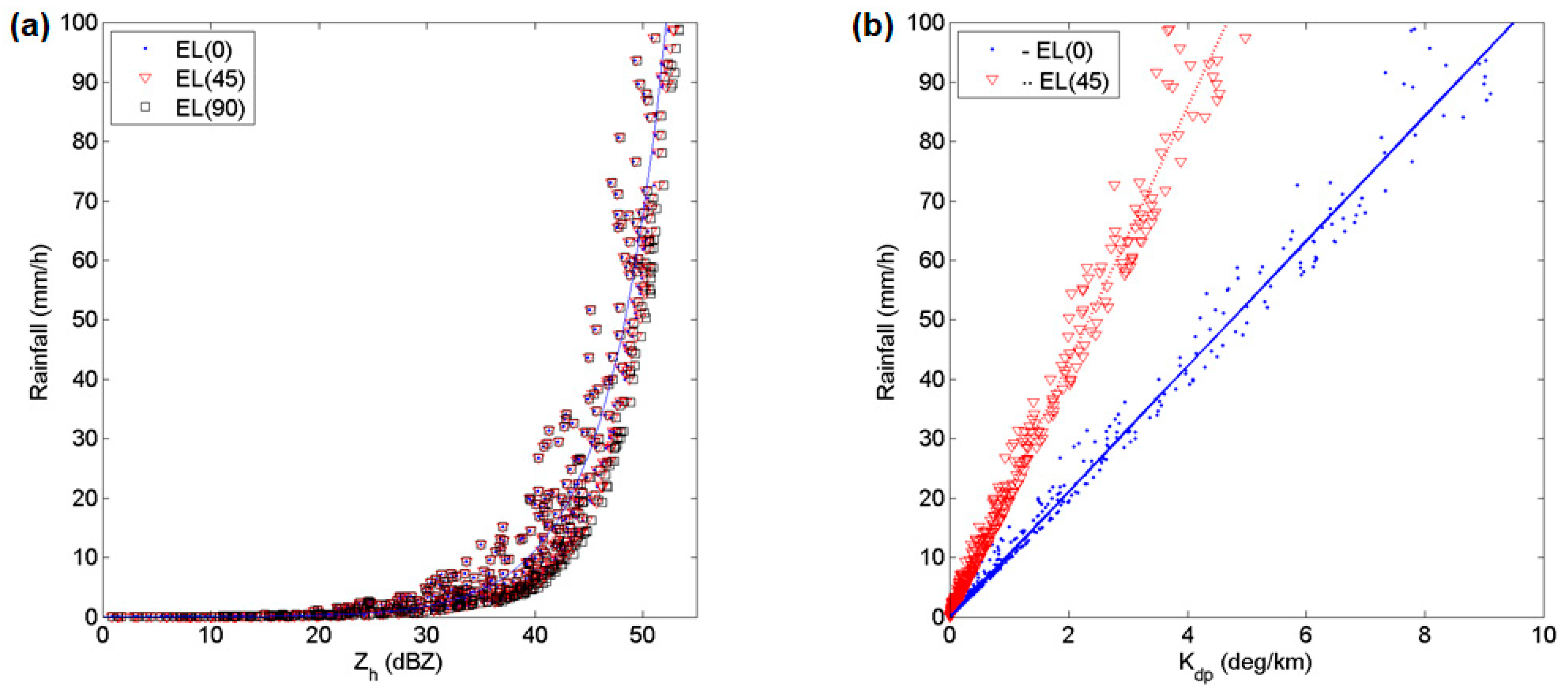
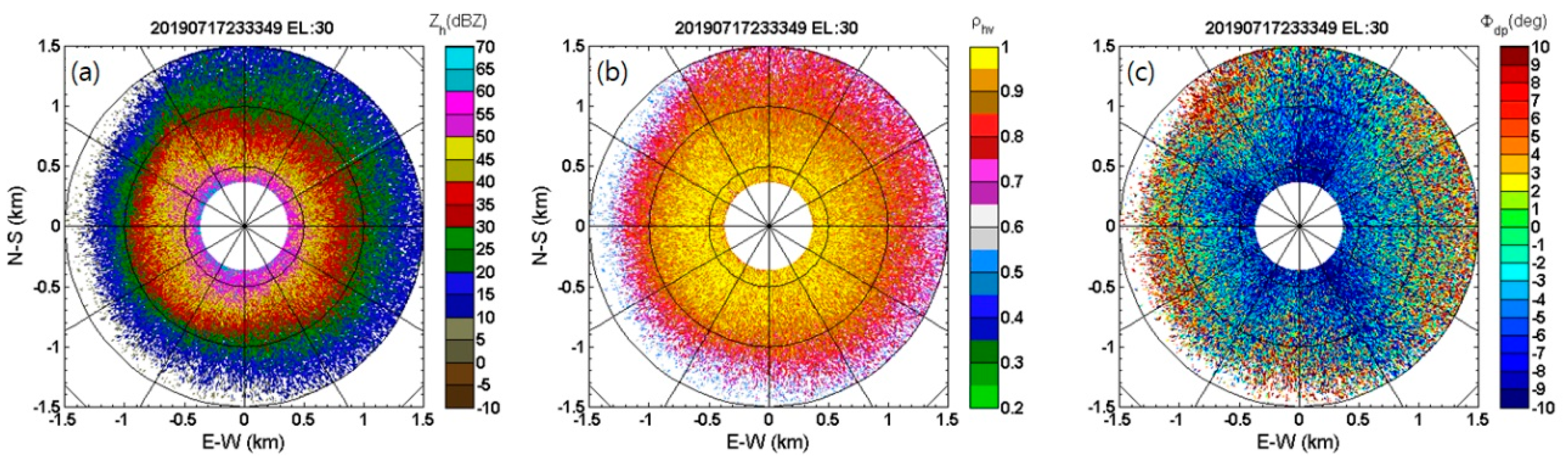
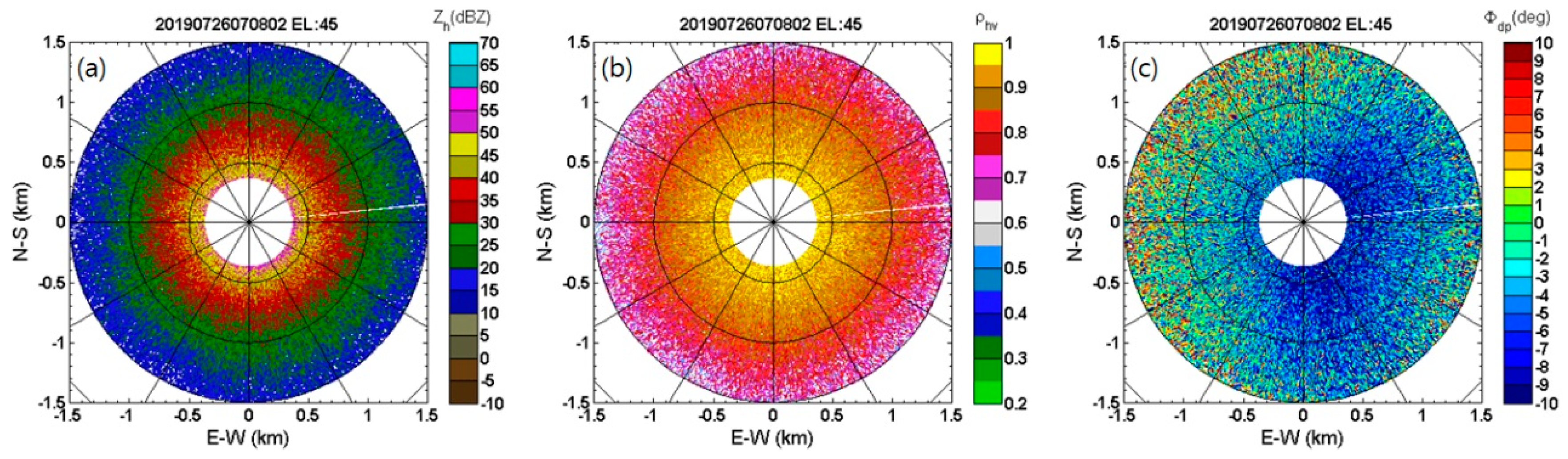
3.1. Reflectivity Calibration
3.2. EWRG Average Rainfall Estimation Procedure
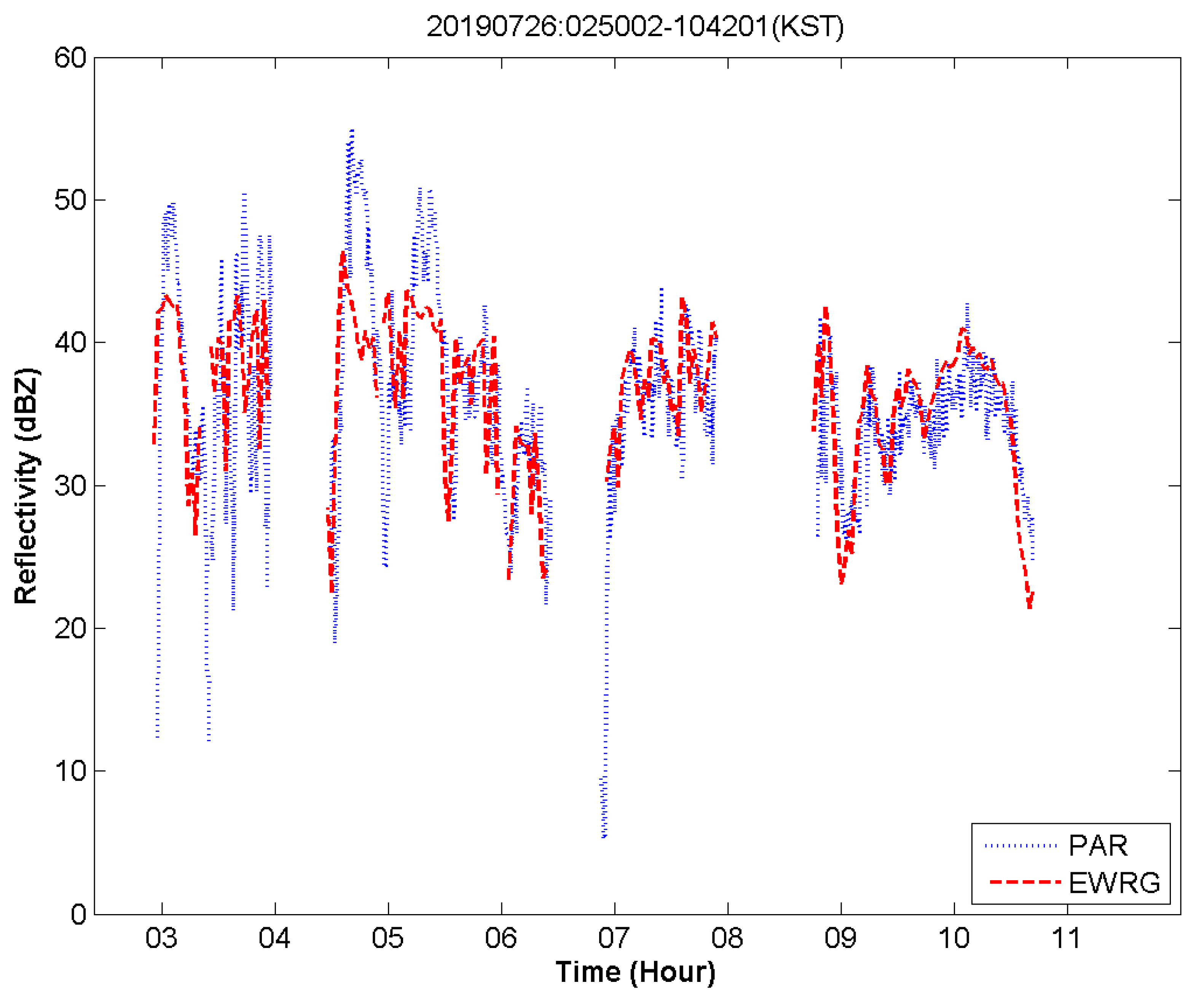
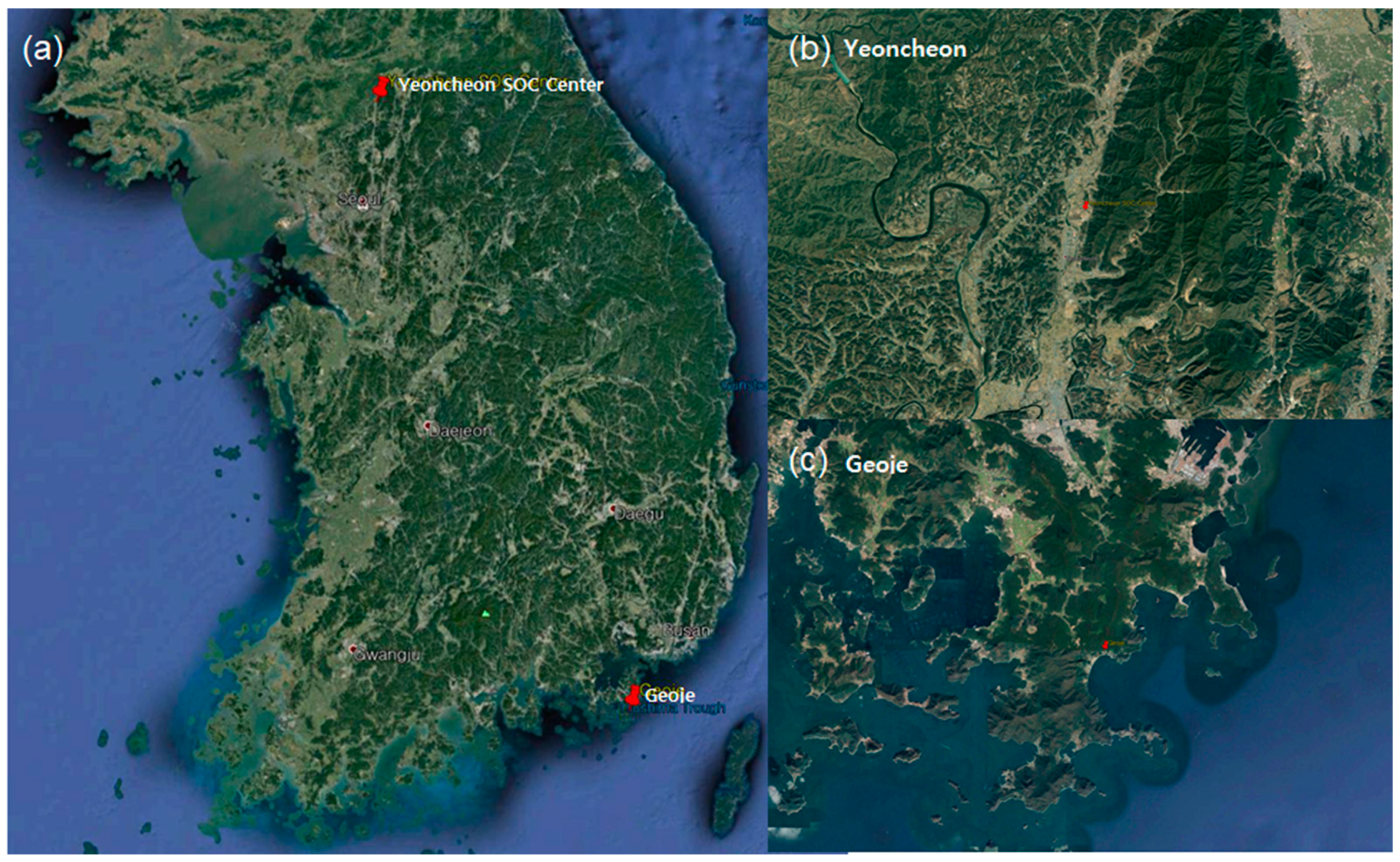
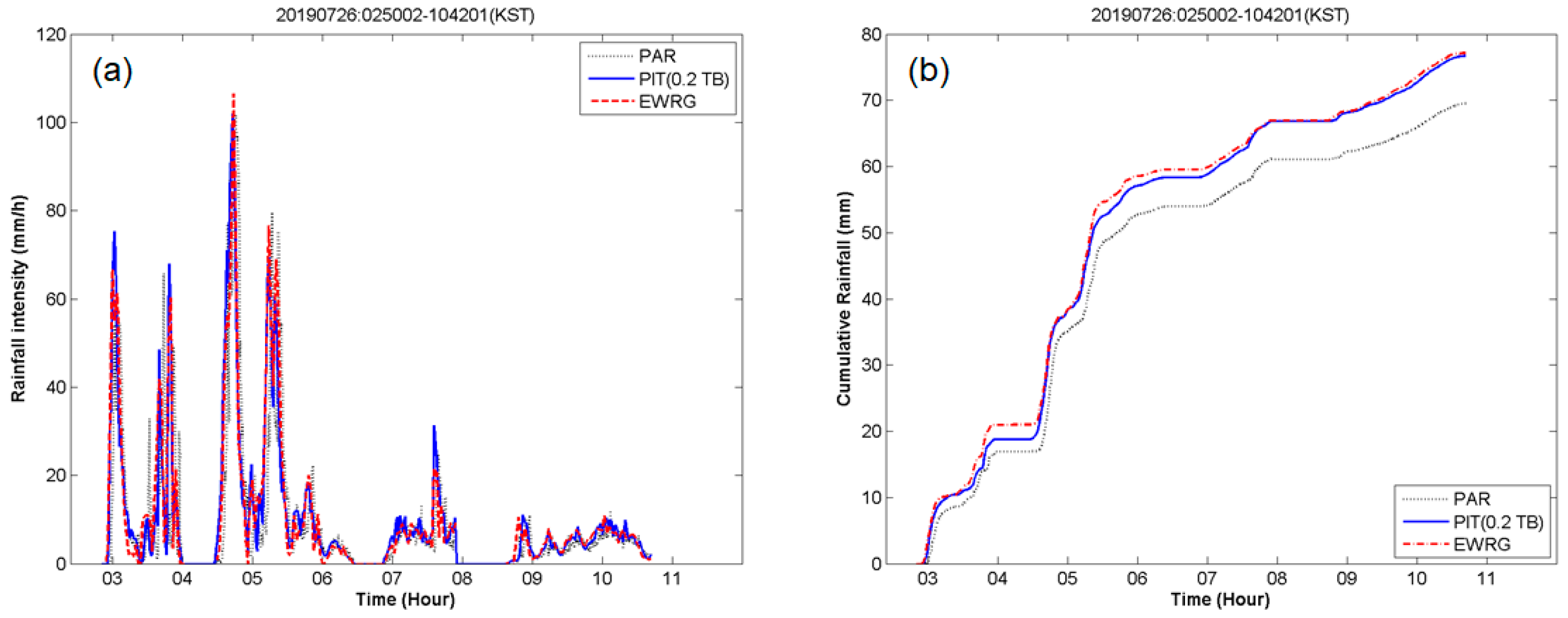
4. Evaluation of EWRG Average Rainfall Estimation and Discussion
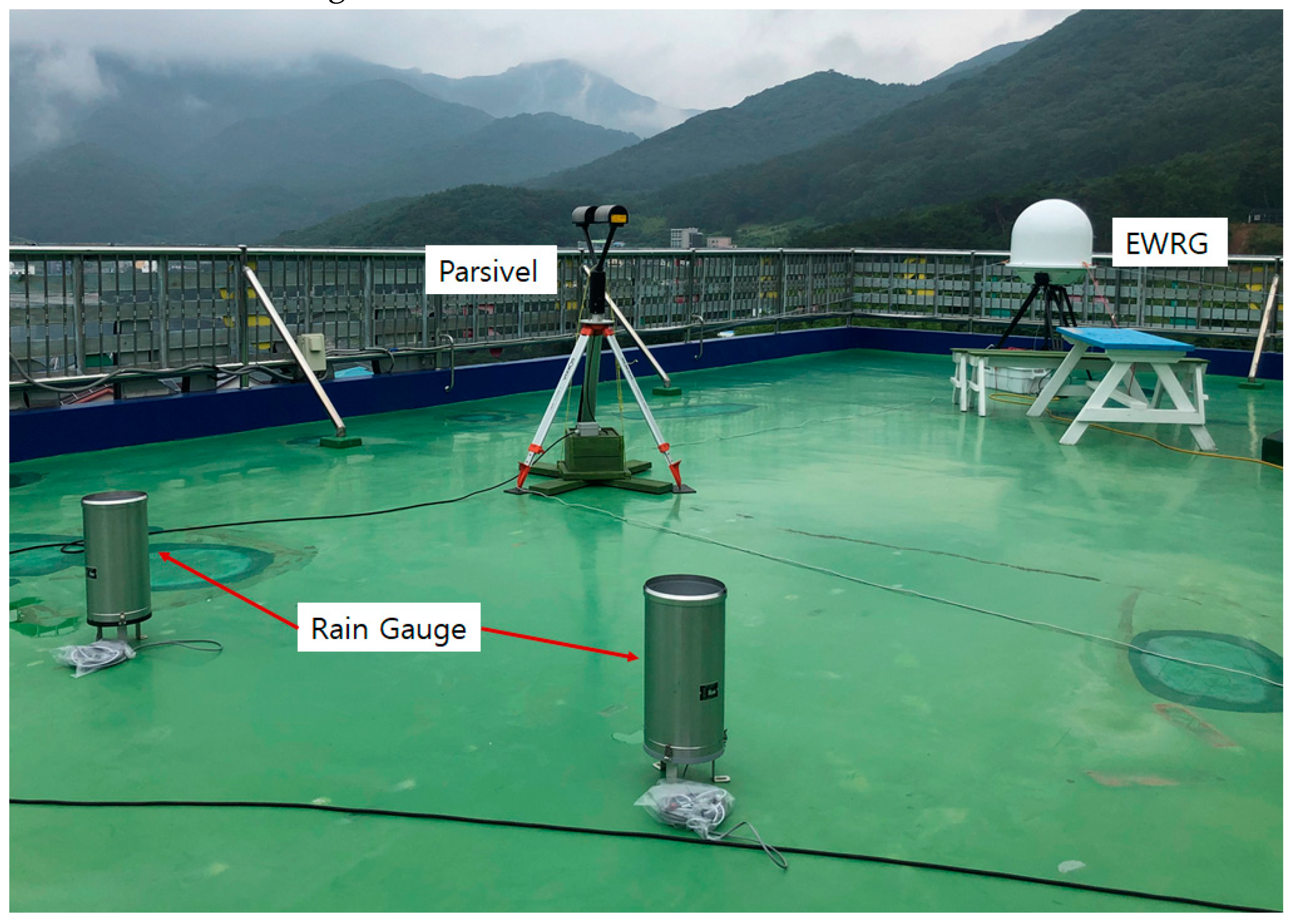
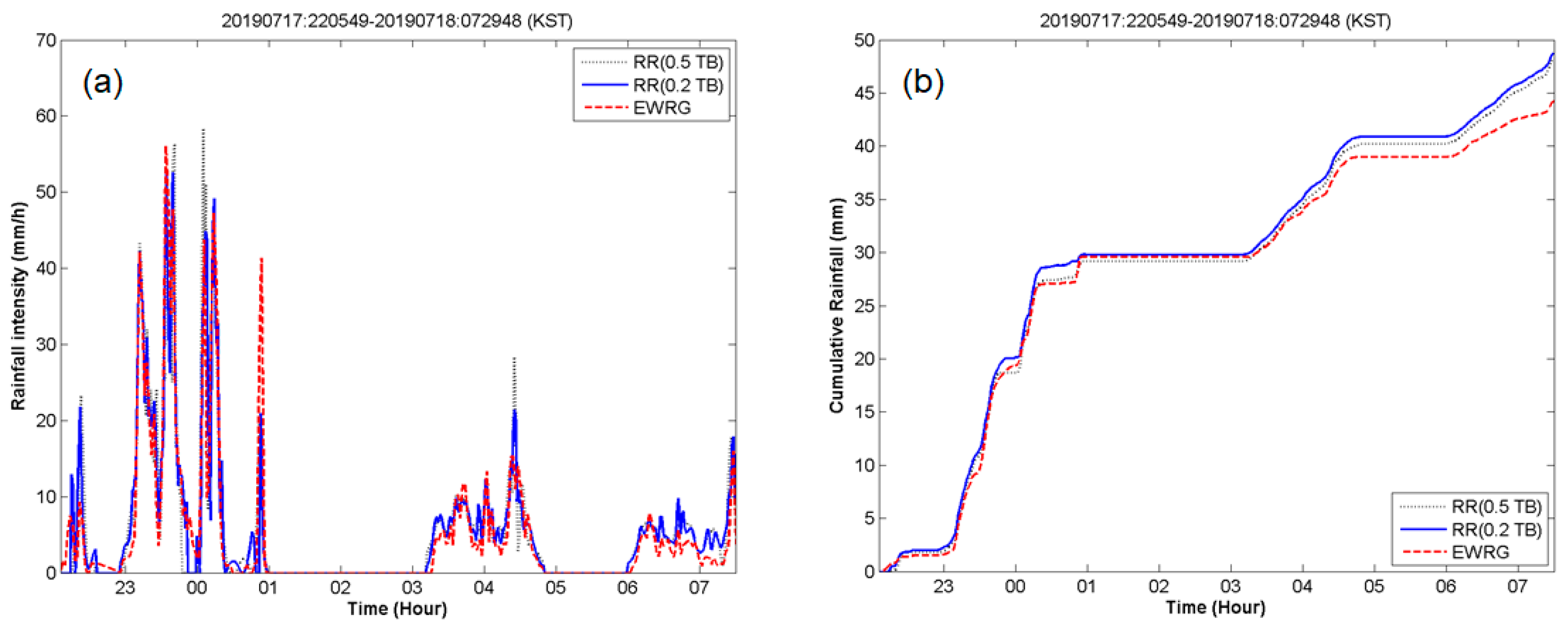
4.1. EWRG Field Test (Geoje)
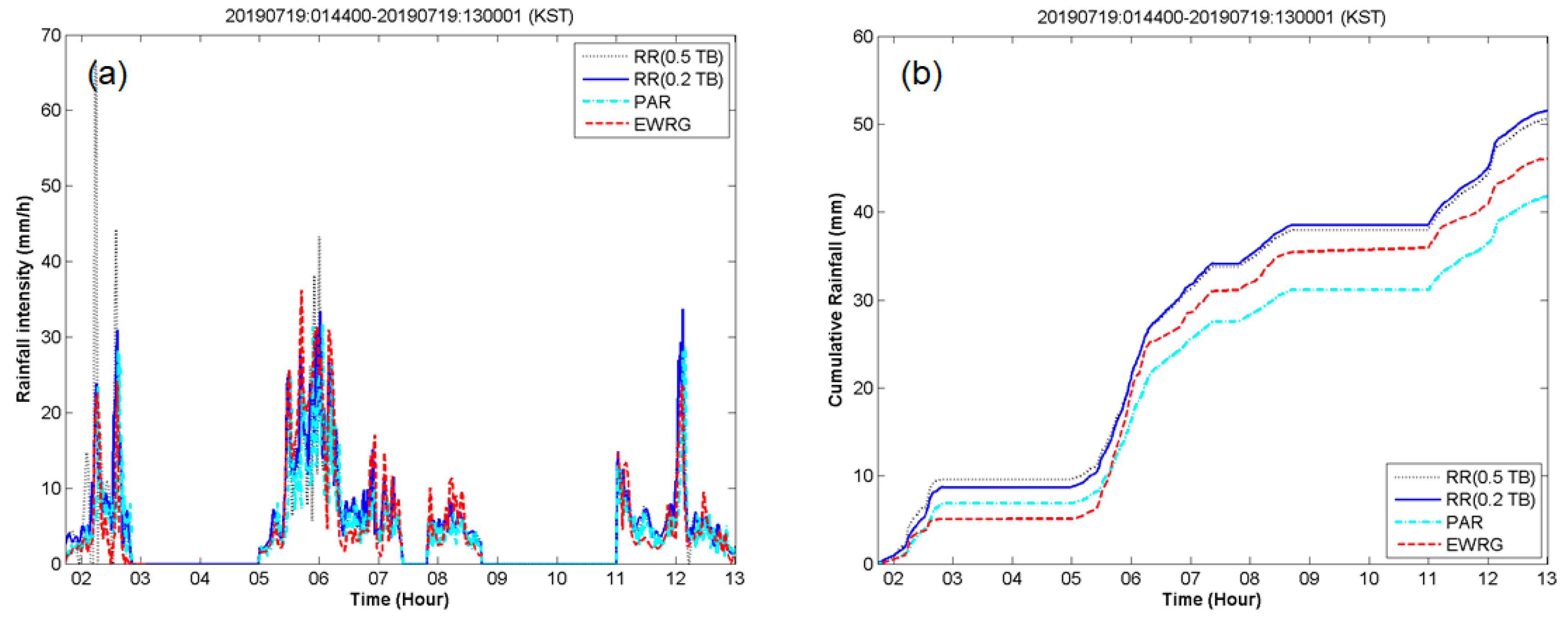
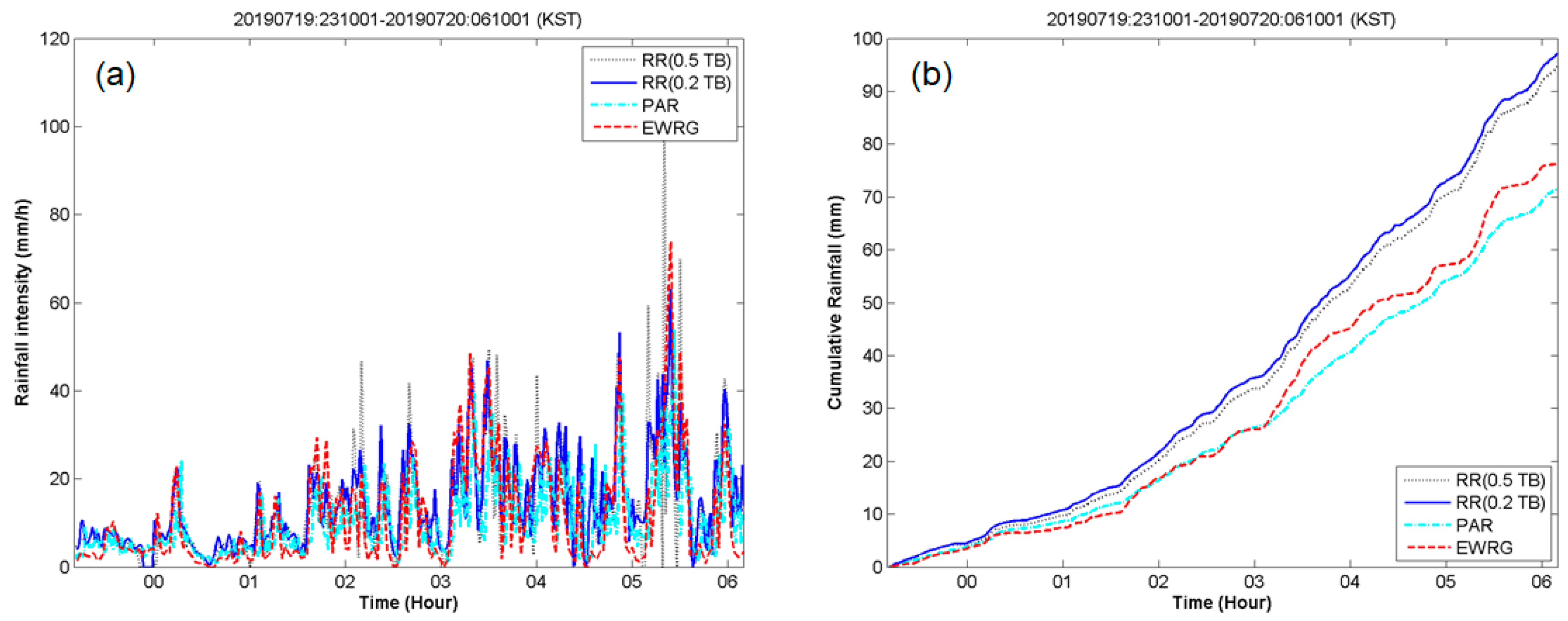
4.2. EWRG Field Test (Yeoncheon)
4.3. Comprehensive Analysis
5. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sandsborg, J. Local rainfall variations over small, flat, cultivated areas. Tellus 1969, 21, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, I.J. Tropical rainfall variations over a small area. J. Hydrol. 1969, 8, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, S.M. WSR-88D Radar rainfall estimation: Capabilities, limitations and potential improvements. Natl. Weather Dig. 1996, 20, 26–36. [Google Scholar]
- Desa, M.N.M.; Niemczynowicz, J. Dynamics of short rainfall storms in a small scale urban area in Coly Limper, Malaysia. Atmos. Res. 1997, 44, 293–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevruk, B. Adjustment of tipping-bucket precipitation gauge. Atmos. Res. 1996, 42, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringi, V.N.; Chandrasekar, V. Polarimetric Doppler Weather Wadar: Principles and Applications; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001; p. 636. [Google Scholar]
- Ryzhkov, A.V.; Schuur, T.J.; Burgess, B.W.; Heinselman, P.L.; Giangrande, S.; Zrnić, D.S. The joint polarization experiment polarimetric rainfall measurements and hydrometeor classification. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 2005, 86, 809–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chandrasekar, V.; Bechini, R. An improved dual-polarization radar rainfall algorithm (DROPS2.0): Application in NASA IFloodS field campaign. J. Hydrometeor. 2017, 18, 917–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chandrasekar, V. Quantitative precipitation estimation in the CASA X-band dual-polarization radar network. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2010, 27, 1665–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifelli, R.; Chandrasekar, V.; Lim, S.; Kennedy, P.C.; Wang, Y.; Rutledge, S.A. A new dual-polarization radar rainfall algorithm: Application in Colorado precipitation events. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2011, 28, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Cifelli, R.; Chandrasekar, V.; Matrosov, S.Y. Precipitation classification and quantification using X-band dual-polarization weather radar: Application in the hydrometeorology testbed. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2013, 30, 2108–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Lim, S.; Jang, B.; Lee, D. Quantitative rainfall estimation for S-band dual polarization radar using distributed specific differential phase. J. Korean Water Res. Assoc. 2015, 48, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jang, B.; Kim, W.; Lim, S.; Choi, J.; Kim, H. Analysis of rainfall cases and their observed signal from prototype of electromagnetic wave rain gauge. In Proceedings of the Institute of Electronics and Information Engineers Conference, Jeju, Korea, 27–29 June 2018; pp. 492–493. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, W.; Lee, C.; Lim, S.; Kim, D.; Jang, B. Development of electromagnetic wave rain gauge for the measurement of areal rainfall. In Proceedings of the KSCE 2019 Convention Conference & Civil Expo, Pyeongchang, Korea, 16–18 October 2019; pp. 93–94. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, G.; Fischer, B.; Andersson, T. Rain observations with a vertically looking Micro Rain Radar (MRR). Boreal Env. Res. 2002, 7, 353–362. [Google Scholar]
- Aydin, K.; Bringi, V.N.; Liu, L. Rain-rate estimation in the presence of hail using S-band specific differential phase and other radar parameters. J. Appl. Meteor. 1995, 34, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zrnić, D.S.; Ryzhkov, A. Advantages of rain measurements using specific differential phase. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1996, 13, 454–464. [Google Scholar]
- Kalina, E.A.; Friedrich, K.; Ellis, S.M.; Burgess, D.W. Comparison of disdrometer and X-band mobile radar observations in convective precipitation. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2014, 142, 2414–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frech, M.; Hagen, M.; Mammen, T. Monitoring the absolute calibration of a polarimetric weather radar. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2017, 34, 599–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringi, V.N.; Chandrasekar, V.; Hubbert, J.; Gorgucci, E.; Randeu, W.L.; Schoenhuber, M. Raindrop size distribution in different climatic regimes from disdrometer and dual-polarized radar analysis. J. Atmos. Sci. 2003, 60, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andsager, K.; Beard, K.V.; Laird, N.F. Laboratory measurements of axis ratios for large raindrops. J. Atmos. Sci. 1999, 56, 2673–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, K.V.; Chuang, C. A new model for the equilibrium shape of raindrops. J. Atmos. Sci. 1987, 44, 1509–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Item | Specification |
|---|---|
| Operating frequency | 24.15 GHz |
| Polarization | Simultaneous (H/V) |
| Transmit peak power | 4 W/channel (H/V) |
| Antenna shape | Parabolic reflector (Carbon) |
| Antenna diameter | 50 cm |
| Beamwidth | 1.6 degree |
| Gain | 40 dBi |
| Voltage standing wave ratio | <1.5:1 |
| Driving range (deg) | 0–360 (Azimuth), –2– +92 (Elevation) |
| Effective observation range | 1.5 km |
| Waveform | 5 MHz (LFM pulse) |
| Pulse width | 1 μs |
| Pulse repetition frequency | 10,000 Hz |
| Range resolution | 7.5 m |
| Event | Pit-Gauge (mm) | Tipping Gauge (0.2) (mm) | EWRG (mm) | Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | 48.9 | 44.2 | –9.6 |
| 2 | - | 51.9 | 46.1 | –11.2 |
| 3 | - | 96.4 | 76.2 | –21.0 |
| 4 | 76.7 | - | 77.2 | 0.7 |
| Event | NAME | CORR | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −13.48 | 99.20 | 0.93 |
| 2 | −15.04 | 95.72 | 1.30 |
| 3 | −19.94 | 95.01 | 3.37 |
| 4 | 7.17 | 99.35 | 0.88 |
| All | 14.30 | −96.90 | 1.83 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lim, S. A Novel Electromagnetic Wave Rain Gauge and its Average Rainfall Estimation Method. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3528. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12213528
Lim S. A Novel Electromagnetic Wave Rain Gauge and its Average Rainfall Estimation Method. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(21):3528. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12213528
Chicago/Turabian StyleLim, S. 2020. "A Novel Electromagnetic Wave Rain Gauge and its Average Rainfall Estimation Method" Remote Sensing 12, no. 21: 3528. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12213528
APA StyleLim, S. (2020). A Novel Electromagnetic Wave Rain Gauge and its Average Rainfall Estimation Method. Remote Sensing, 12(21), 3528. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12213528