Abstract
The volume of data generated by earth observation satellites has increased tremendously over the last few decades and will increase further in the coming decade thanks in particular to the launch of nanosatellites constellations. These data should open new avenues for Earth surface monitoring due to highly improved spectral, spatial and temporal resolution. Many applications depend, however, on the accuracy of the image geometric model. The geometry of optical images, whether acquired from pushbroom or frame systems, is now commonly represented using a Rational Function Model (RFM). While the formalism has become standard, the procedures used to generate these models and their accuracies are diverse. As a result, the RFM models delivered with commercial data are commonly not accurate enough for 3-D extraction, subpixel registration or ground deformation measurements. In this study, we present a methodology for RFM optimization and demonstrate its potential for 3D reconstruction using tri-stereo and multi-date Cubesat images provided by SkySat and PlanetScope, respectively. We use SkySat data over the Morenci Mine, Arizona, which is the largest copper mine in the United States. The re-projection error after the RFM refinement is 0.42 pix without using ground control points (GCPs). Comparison of our Digital Elevation Model (DEM with ~3 m GSD) with a reference DEM obtained from an airborne LiDAR survey (with ~1 m GSD) over stable areas yields a standard deviation of the elevation differences of ~3.9 m. The comparison of the two DEMs allows detecting and measuring the topographic changes due to the mine activity (excavation and stockpiles). We assess the potential of PlanetScope data, using multi-date DOVE-C images from the Shisper glacier, located in the Karakoram (Pakistan), which is known for its recent surge. We extracted DEMs in 2017 and 2019 before and after the surge. The re-projection error after the RFM refinement is 0.38 pix without using GCPs. The accuracy of our DEMs (with ~9 m GSD) is evaluated through comparison with the SRTM DEM (GSD ~30 m) and with a DEM (GSD ~2 m) calculated from Geoeye-1 (GE-1) and World-View-2 (WV-2) stereo images. The standard deviation of the elevation differences in stable areas between the PlanetScope DEM and SRTM is ~12 m, and ~7 m with the GE-1&WV-2 DEM. The mass transfer due to the surge is clearly revealed from a comparison of the 2017 and 2019 DEMs. The study demonstrates that, with the proposed scheme for RFM optimization, times series of DEM extracted from SkySat and PlanetScope images can be used to measure topographic changes due to mining activities or ice flow, and could also be used to monitor geomorphic processes such as landslides, or coastal erosion for example.
1. Introduction
The impact of environmental changes and human activities has increased the need for monitoring the Earth surface. The recognition of this need has stimulated an exponential increase in Earth Observation (EO) satellites, in particular Cubesat nano-satellites for optical remote sensing. Due to their low cost, a great number of Cubesats has been launched over the last six years by a variety of private companies, universities and non-conventional actors in the space industry, enabling unprecedented high spatial and temporal resolution optical images []. Planet Labs has been a leading actor in this area. Since 2014, Planet Labs has launched over than 280 Cubesats which image the entire Earth surface every day []. Further deployments are planned by Planet Labs and other operators in the upcoming years [,]. For instance, SatRevolution is planning to launch 1024 6U Cubesats by 2026, which will offer the possibility of a Real-Time Earth Observation constellation []. The capability to acquire multi-temporal data with improved spatial, spectral, radiometric and temporal resolution should enhance our ability to monitor geomorphic processes (e.g. landslides, coastal erosion, Aeolian processes), ground deformation due to earthquakes or landslides, mountain glaciers and ice caps disaster damages, and human activities (e.g., urbanization, infrastructure development, mining operations). These applications require a good knowledge of the geometry of the images to allow for the calculation of accurate Digital Elevation Models (DEM) and for precise georeferencing of the images, ideally with a sub-pixel precision. Recall that a good-quality DEM is generally required for a precise georeferencing, as even nominally nadir-looking images are affected to some degree by stereoscopic effects due to the telescope aperture and its finite elevation above the ground. Good quality DEMs and precise ortho-rectification are therefore paramount to most monitoring applications with optical remote sensing. Nano-satellites offer in principle the potential to generate multi temporal DEMs for any region in the world at any time, but the calculation of DEMs from Cubesat data has been a challenge [,]. The traditional approach consists of using images close enough in time so that the topography can be assumed unchanged and with view angles large enough for measurable stereoscopic effects. DEMs can then be extracted based on a Rigorous Sensor Modeling (RSM) of the image geometry, taking into account both the internal (optical distortions, CCD misalignments) and external (telescope position and orientation) parameters. The implementation of such an approach is specific to the particular sensor used in the data acquisition and requires the knowledge of technical characteristics that are rarely provided by the operators. As a standardized substitute to the rigorous sensor model, the geometry of optical images is now commonly represented using a Rational Function Model (RFM) [,]. The methods used to generated RFMs are, however, varied and often yield rather imprecise geometric models. The development of methods for RFM optimization and automatic DEM extraction from conventional satellites (i.e., stereo or tri-stereo push-broom high resolution satellite imagery) has therefore been an area of active research for the last few years (e.g., [,,,,]). This issue is relevant to Cubesat images in particular as the RFM standard has been widely adopted in the nanosatellite industry.
In this study, we present a method for RFM optimization and demonstrate its potential for 3D reconstruction using tri-stereo and multi-date Cubesat images. We test and assess the performance of our method to extract digital elevation models and quantify topographic changes using SkySat data from the Morenci Mine, Arizona, which is the largest copper mine in the United States, and multi-date PlanetScope DOVE-C images from a surging glacier located in the Karakoram, Pakistan. Hereafter, we present our methodology for RFM optimization first, and then for DEM extraction. We next describe the results obtained on our two test examples and discuss the performance of the method. The proposed method is implemented in an open-source module of the Coregistration of Optical Sensed Images and Correlation software (COSI-Corr) [,]. An overview of the SkySat and PlanetScope push-frame imaging systems is provided in Appendix A.
2. RFM Optimization
2.1. Method
The image orientation model, which relates the image and ground coordinates, can be based on the rigorous Sensor Model (RSM) of the imaging system or can be approximated by a generic sensor model known as a rational functional model (RFM). The flowchart in Figure 1 shows schematically how these models might be determined and optimized.
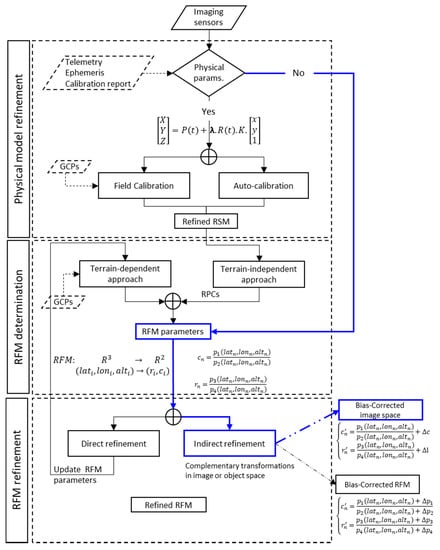
Figure 1.
Workflow for image geometry refinement including physical model (Rigorous Sensor Model) and rational function model (RFM) approaches. The blue color pathway shows the processing path described in this study and is added as an additional module in the COSI-Corr package.
The rigorous sensor model (RSM) accounts for the interior orientation (defined by the focal length, principal point location, pixel size, and the lens distortion) and the external orientation (defined by the position and attitude of the satellite during the image acquisition) []. This formalism is based on the extended collinearity equations for the external orientation model,
where is the ground coordinate of the pixel in the image geometry after correction for the distortions represented by the internal orientation model. and denote the unknown scaling factor and the calibration matrix, respectively. indicates the satellite position, and is the satellite attitude rotation matrix. These parameters represent the exterior orientation and they are functions of time, .
The internal and external orientation parameters can be determined from a field calibration or from field-independent block adjustment. In the first case, the parameters are solved by using ground control points (GCPs) measured in the field or extracted from existing maps [,,]. In the second case, often called the “auto-calibration” method, the parameters are solved from a block adjustment using a large set of overlapping images [,,]. The RSM is, for example, implemented in the Coregistration of Optical Sensed Images and Correlation software (COSI-Corr) [,].
The main difficulty with the RSM is that the model cannot be standardized as it must be tailored to the technical characteristics of each imaging system. In addition, the information needed for its implementation is not always provided by the operators []. This issue has become more acute with the increasing number of Earth Observation satellites.
By contrast, the rational function model (RFM) is sensor agnostic and allows for a standardization of the metadata. The RFM relates image pixel coordinates to object coordinates in the form of rational functions expressed as the ratios of polynomials, usually of the third order [,,],
where is the normalized values of the image point coordinates , and is the normalized latitude, longitude and altitude of the corresponding ground point, respectively. The normalization of the coordinates is performed according to the process described in []. refers to the coefficients of the polynomials . There are two ways to determine the RFM (Figure 1). In the terrain-independent approach, the physical model is used to generate virtual GCPs, which are then used to compute the parameters of the RFM []. In the terrain-dependent approach, the RFM is based on GCPs measured in the field or extracted from an existing reference map [,].
In practice, the RFM models provided by the operators are most often not sufficiently accurate for 3-D extractions or precise georeferencing so that they generally need to be refined [,,,]. There can indeed be significant bias introduced either by the inaccuracy of the method used or by the reference data used as an input in the determination of the RFM. The RFM may be either determined anew (“direct refinement”) or refined by determining a corrective term (“indirect refinement”). We adopt the latter approach and express the corrective terms in the image space (Figure 1),
where , are the adjustment parameters for image , and are the image coordinates of point on image .
We can then use a least-squares adjustment routine to minimize the re-projection errors of a selection of tie points,
where () are the image-space coordinates of tie point on image , are the nominal image coordinates computed with the RFM function model given in Equation (2), and are the bias compensation functions (cf. Equations (4) and (5)).
The normal equations then write,
where is the Jacobian matrix, is the discrepancy vector and is the parameter vector .
The method described here is implemented as an open source module of the COSI-Corr software package. This module allows: (1) to correct the RFM bias of a single image using GCPs; (2) to correct the RFM bias of a large block of overlapping images, and (3) to incorporate the bias compensation into the original supplied RFMs, similar to the method proposed in []. This package can be employed to process any type of image delivered with RFMs.
2.2. Application to Push-Frame Images
In this study, we apply the RFM refinement procedure described above to push-frame images from two CubeSat platforms, PlanetScope and SkySat. See Appendix A for technical details on these platforms. With both systems, the images are acquired by several arrays of CCDs as the satellite is moving along its track. The frame rate and the location of the sensors in the focal plane of the telescope were designed to insure some degree of overlap between the different sub-scenes, whether acquired by different sensors at a given time or at successive times by the same sensor. Each sub-scene is provided with its own RFM and is considered as a separate image in our procedure. We use Level L1B products, which contain the images and associated RFMs, which were determined by the provider using a terrain-dependent approach. Prior to RFM refinement, we pre-select image pairs for each type of satellite using a specific procedure.
2.2.1. SkySat
The images are acquired by 3 staggered sensors (Figure 2). The overlap of consecutive scenes from the same sensor and within different sensors is very small, as well as the baseline. Thus rays between tie points are almost collinear, which can lead to high uncertainty and singularities during the refinement of the RFM. To avoid this issue, the tie points are constrained using a reference DEM []. Since the SkySat imagery is acquired in a tri-stereo mode, we perform the refinement in two steps: (1) we subdivide the triplet image scenes into three groups according to the imaging sensor. Next, we perform the RFM refinement for each group separately. (2) We estimate a 3D transformation using the images from the central sensor as a reference (sensor 2 in Figure 2).
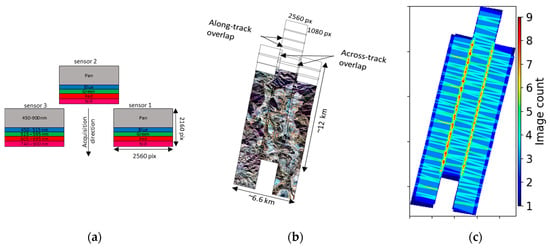
Figure 2.
(a) A scheme of a single set of SkySat raw sensor footprint, three raw frames corresponding to the three 2D-CMOS image sensors; (b) Morenci Mine area as seen by SkySat, the black bounding boxes show the individual scenes of each detector. (c) Number of images overlap of SkySat tri-stereo configuration.
2.2.2. PlanetScope (Doves)
The PlanetScope CubSats acquire data in a push-frame nadir-pointing mode (Figure 3). As with SkySat, the overlap of consecutive images from the same DOVE is very small, ~8%, as well as the baseline. Thus, rays between tie points are almost collinear. Therefore, to perform the RFMs refinement, we select image pairs with maximum overlap, hence the maximum convergence angle. Then, we extract tie points between the selected image pairs and estimate the bias RFM correction.
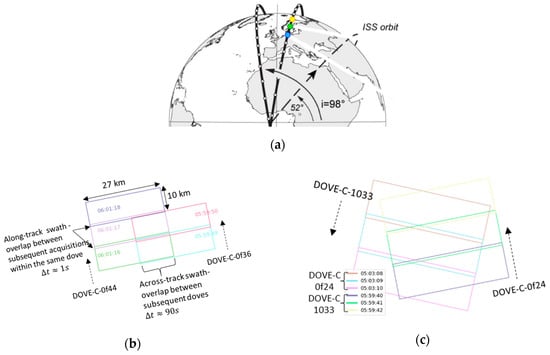
Figure 3.
(a) A schematic representation of Doves positions on ascending and descending orbits, modified from []. (b) Projection view of Doves footprints (Dove-C- of44 and Dove-C–of36) featuring along-track overlap between subsequent acquisitions of the same dove, and across-track overlap between successive doves in the same orbit. (c) Projection view of Doves footprints featuring overlap between ascending (Dove-C–0f24) and descending (Dove-C-1033) acquisitions. Rectangles denote individual dove footprint and each color represent the time acquisition. Dash arrows depict the direction of the dove acquisition as seen on ground.
In both cases, the refinement of RFMs can be additionally constrained with GCPs extracted from an external ortho-image and a DEM.
The angle between incidence view vectors from overlapping scenes , also called the “convergence angle” [,], is determined by computing the angle of intersection of two ray vectors and ,
The ray vector is computed as follows: for a pixel p with coordinates , we define two ground points and , where and , is a scale factor. Then, the vector is defined with respect to these two points.
The base-to-height (B/H) ratio is estimated, ignoring the Earth curvature, from
3. DEM Extraction
In practice, a 3D reconstruction from a set of images can be performed in either the image space or the object space. The image space approach is mostly used with stereo pairs or triplets of images. The object space approach is commonly used with multiple overlapping images, such as images acquired with drone and close range photogrammetry.
In this study, we adopt the object space approach, as it is well adapted to process images from push frame systems like those delivered by SkySat and PlanetScope. We also use the image-space method to a subset of data, using tri-stereo SkySat images, for comparison.
The main steps for 3D extraction in image space are (Figure 4):
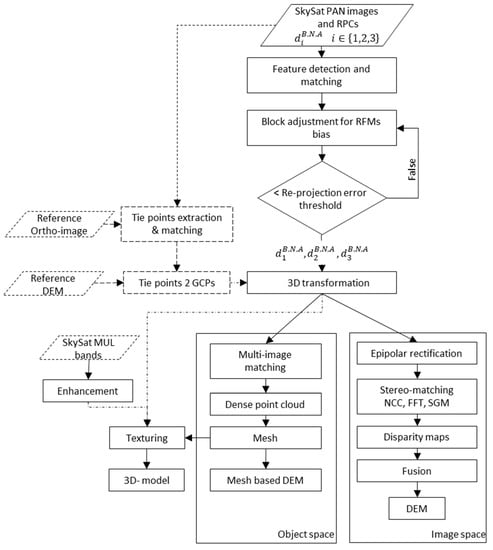
Figure 4.
Schematic workflow for SkySat image geometry refinement and 3D extraction.
- (1)
- Epipolar rectification: it consists in resampling stereo pairs based on the adjusted RFM, so that the two images have a common orientation and the matching features between the images appear along a common axis [].
- (2)
- Stereo-matching: it consists in computing the correspondences between pixels of the image pairs. These correspondences are computed using a correlation technique (e.g., NCC, FFT) or using a Semi-global matching scheme []. Results are displayed as disparity maps.
- (3)
- Disparity maps fusion: intermediate results generated from each possible stereo are merged to produce a final DSM map. The fusion is performed using local approaches (e.g., mean, median) or global optimization (e.g., total variation, gradient decent) [].
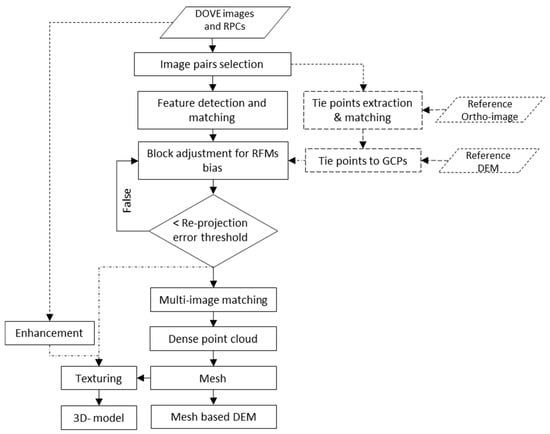
Figure 5.
Schematic workflow for PlanetScope image geometry refinement and 3D extraction.
- (1)
- Multi-image matching: an object-based matching algorithm, e.g. OSGM [], is applied directly in the object space, hence the epipolar rectification is no longer necessary; the transformation between object space and image space relies on the refined RFMs.
- (2)
- Spatial forward intersection: this leads directly to dense 3D point cloud.
- (3)
- Meshing: it consists in deriving 3D surfaces by interpolating the dense point cloud.
- (4)
- Mesh-based DEM: gridded terrain model (i.e., 2.5D raster map) is derived from the 3D mesh.
In addition, for rendering, a 3D-textured model is generated using (see Supplementary Materials):
- -
- The 3D mesh model, which has rich geometric information;
- -
- The image collection (RGB spectral bands), which provides high photorealistic details about the texture of the objects;
- -
- The free-bias RFMs.
SkySat and PlanetScope images have a high-dynamic range. This makes it difficult to visualize and compress the full range for display, which can result in loss of details. Therefore, before generating the texture map, a contrast enhancement is performed. We apply Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization (CLAHE) in order to amplify the image contrast while preserving details []. The operator is also implemented in the COSI-Corr RFM package. Each image is divided into small tiles; then the histogram is equalized by tile. The radiometric noise gets amplified during this process. Therefore, contrast limiting is applied to limit the contrast below a specific limit threshold (). Then, if any histogram bin is above the specified contrast limit (), those pixels are clipped and distributed uniformly to other bins before applying histogram equalization. Ultimately, to remove artifacts in tile borders, bilinear interpolation is applied. The 3D-textured models are used to generate the flyover animations provided in Supplementary Materials.
4. Results and Discussion
The performance of the methodology described above and its usefulness to measure temporal changes of the topography is illustrated using two different case examples. The first one is the Morenci Mine in Arizona USA, where we use SkySat tri-stereo data to document topographic changes due to the mining operations. The second one is the Shisper Glacier in Pakistan, where we use multi-date PlanetScope data to document the change of the glacier topography due to a surge.
4.1. Morenci Mine (USA)-SkySat
The Morenci mine is known for its high copper production. For example, in 2016, 848 million pounds were produced []. The test site is shown in Figure 6. The ellipsoidal terrain heights of the region of interest ranges from 1048 m to 2417 m and spans over an area of ~122 km2, consisting of mountainous and vegetated areas, rugged terrain and buildings. A triplet of stereo SkySat images was acquired on 28 January 2019 (Table 1). We used both the basic-panchromatic and basic-multispectral L1Bs to generate a DEM and compared it with a high-quality of LiDAR DEM available from the 3D Elevation Program (3DEP). This program is managed by the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) National Geospatial Program to respond to the growing need for high-quality topographic data []. The LiDAR DEM is available as raster data in the UTM 12 North map projection and WGS84 datum at 1 m GSD with ellipsoidal heights. The LIDAR data were acquired 4 years before SkySat acquisitions, a period during which changes have occurred due to mining activity and vegetation growth or clear-cut. The LiDAR DEM was downloaded via Global Mapper software.
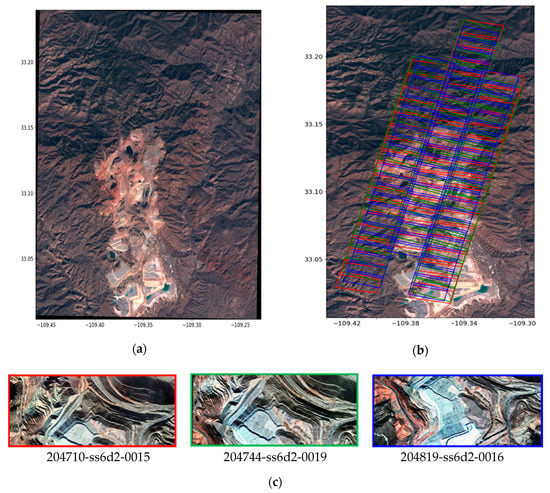
Figure 6.
The test site Morenci Mine, AZ, USA. (a) Subset of Sentinel-2 true color ortho-image (TCI) over the study area captured on 1 February 2020; (b) Outlines of SkySat triplets on a Sentinel-2 ortho-image. Red, Green and Blue bounding boxes delineate the individual scenes of along track forward, nadir and backward views, respectively; (c) Tri-stereo RGB SkySat scenes for visual interpretation, from left to right, backward, nadir and forward.

Table 1.
Acquisition parameters for the SkySat tri-stereo over Morenci Mine study area.
We refined the RFMs of image triplets of each sensor separately as described in the method section. Each of the 174 scenes is separated into three subsets corresponding to the three tri-stereo sensors. Then we estimated a 3D transformation using the overlap between the different detectors, in order to adjust the sensor-1 and -3 group to the sensor-2 group. To that effect, about 149,419 tie points were extracted and matched using the SIFT+ feature detector included in the open-source software MicMac [,]. This particular algorithm allows the identification of points efficiently in large images, irrespective of their position and is robust to affine transformations (changes in scale, rotation, size and position) and contrast variations []. After correcting the RFMs using a first-order polynomial obtained from our least-squares procedure, the overall re-projection error, estimated from the standard deviations of the distribution of residuals, is 0.42 pix. Given the nominal GSD of 71 cm, it corresponds to a geo-location error of ~37 cm on the ground.
We generated DEMs in the image and object spaces. The panchromatic scenes, and our refined RFMs, were imported to Metashape software [,] to perform the DEM reconstruction in object space. First, a multi-view stereo matching on the aligned scenes was applied using a variant of Semi-Global Matching algorithm in object space (OSGM) []. A total of 4,785,824 points were generated over an area of 123 km2. Second, a 3D mesh model was created from the dense point cloud. Then, a mesh-based DSM was extracted. The GSD of the mesh-based DSM was set to 3 m. Figure 7 shows the complete ~123 km2 DSM. Elevations vary within 1.2 km and to 2.2 km. The flyover animation generated with the textured model is shown in the supplement.
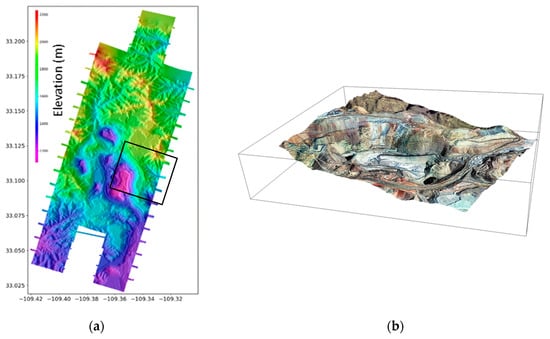
Figure 7.
(a) DEM of Morenci Mine are computed in the object space from tri-stereo SkySat on 1 January 2019; (b) a zoom view of 3D-textured model (a flyover animation of the 3D model is available in the Supplementary Materials).
It is worth mentioning that, if only two sets of images (backward and nadir or forward and nadir) are used, the DEMs have blind areas (Figure 8). Therefore, the tri-stereo yields both a better accuracy and a more complete coverage.
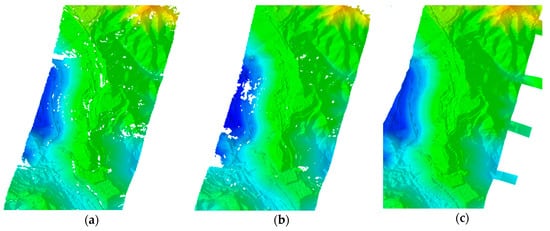
Figure 8.
Subset of SkySat shaded DEMs over Morenci Mine using (a) backward and nadir images, (b) nadir and forwards images, (c) backward, nadir and forwards images.
We were also able to apply the classical DEM extraction work-flow in the image space [,]. The epipolar rectification was performed between pairs of images that overlap by more than 50%. This criterion excludes pairs of consecutive scenes, or of scenes from different sensors. A total of 156 pairs were selected. Then, the SGM algorithm is used for the dense matching. Ultimately, the resulting 156 DSMs were merged using a mean approach to build a final DSM of 1.5 m GSD. The image base DSM reconstruction was performed using the OrthoEngine module of PCI Geomatics software. To allow a visual assessment of our results, a subset of the extracted DSM is depicted in Figure 9. The stepped benches related to the open-pit mine (which are typically 2.25 km wide and 4–5 m in height) are clearly visible in the DEM obtained from the DEM obtained with traditional photogrammetry in the image space. They are also visible in the DEM obtained in the object space but are less well resolved.
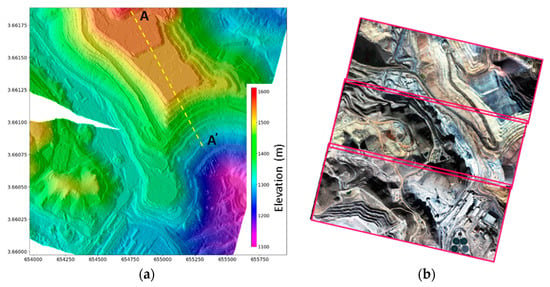
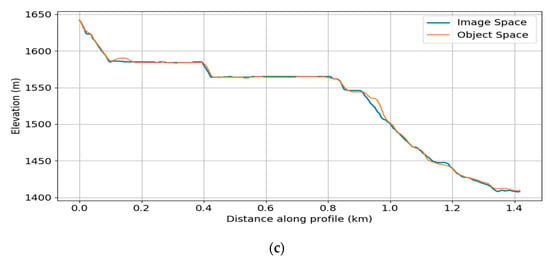
Figure 9.
(a) Shaded DEM of the Morenci Mine are computed using SGM in the image space from tri-stereo SkySat images acquired on 1 January 2019; (b) Example of sub-scenes covering the area. (c) Profile along the transect (AA’) extracted from image space DEM and object space DEM.
We now compare the LiDAR DEM with DEM extracted from the SkySat triplet in the object space. We down-sample the LiDAR DEM to the 3 m GSD of the SkySat DEM which was generated in the object space. Figure 10 shows the complete map of elevation differences between SkySat and LiDAR DEMs. It shows large differences up to 200 m in amplitude. Visual inspection of the images shows that the large differences are clearly due to mining operations, constructions or vegetation clearing. We selected an area not affected by any obvious temporal changes (outlined box in Figure 10). Panel (b) in Figure 10 shows the histograms of the differences within that ~10.56 km2 area. The mean difference is only ~0.22 m, the standard deviation is ~3.9 m and 95% of the differences are less than 10 m. The normalized median absolute deviation (NMAD), a quantity commonly used to compare DEMs [], is 5.3 m.
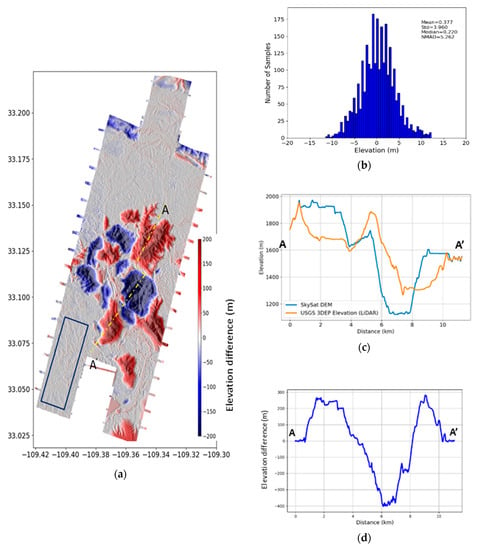
Figure 10.
(a) Elevation changes over the Morenci Mine area computed from the difference of 2016 3DEP LiDAR and January 2019 SkySat DEM; (b) Histogram of the elevation difference over stable terrain (panel (a) blue box); (c) Elevation profiles from SkySat and LiDAR DEMs; (d) Elevation difference profile. Profiles are extracted along transect AA’ indicated in panel (a).
Clearly, the large topographic changes revealed by the DEM comparison (for example along profile AA’ in Figure 10) are real and can be used to quantify the mining operation (excavation or stock piling) or clearing activities.
4.2. Shisper Glacier (Pakistan), PlanetScope DOVE
The study area is located in the north flank of the Hunza Valley in the Central Karakoram. The Shisper glacier covers ~53.7 km2 at an elevation ranging between ~2500 and 4500 m a.s.l. It has gained the attention of the scientific community and disaster response agencies due to a recent surge []. In 2018, the glacier surged beyond the confluence with the outlet stream of the Mochwar glacier. The blockage resulted in the creation of a lake, which then drained causing a GLOF (Glacial Lake Outbreak Flood) and has recently begun reforming []. The melt water from the two glaciers feeds hydropower plants in the Hunza valley and is a major source of fresh water for agriculture. Glacier-related hazards threaten both the town of Hassanabad and the Karakoram Highway, the only paved road crossing the Karakorum (Figure 11) [,,]. Here, we show the potential of CubSat data to monitor such glaciers, which are not easily accessible to field observation, and assess their potential impact on power generation, water resources and infrastructure.
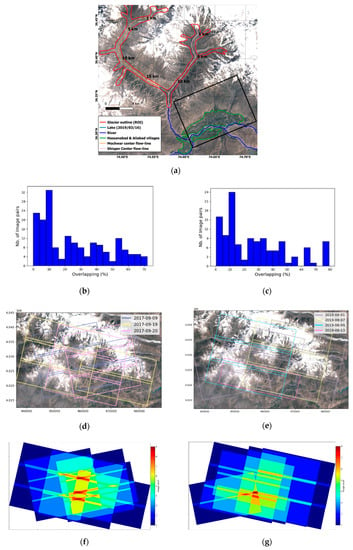
Figure 11.
The test site Shisper Glacier, Karakoram, Pakistan. (a) Subset of Sentinel 2 true color ortho-image (TCI) over the study area captured on 16 March 2019. Randolf Glacier Inventory [] outline of both glaciers are shown in red. Location of the ice-dammed lake is shown in light blue. Rivers are denoted in dark blue and Hassanabad village is outlined in green. (b,c) Histogram distribution corresponding to the percentage of overlapping images within image pairs in the dataset of 2017 (d) and 2019 (e). (d) Outlines of PlanetScope scenes over the study area between 9 September and 20 September 2017. (e) Outlines of PlanetScope scenes over the study area between 1 August and 13 August 2019. (f,g) Number of image overlap during 2017 (f) and 2019 (g).
We used multi-date L1B DOVE-C PlanetScope data to extract two DEMs in 2017 and 2019 in order to compute the elevation difference caused by the glacier surge. The data set consists of 16 DOVE-C images acquired in three days in September 2017 before the surge, and 14 DOVE-C images acquired in 4 days in August 2019 after the surge (Figure 11d–e for a plot of the extent of different overpasses of PlanetScope images). Table A2 and Table A3 in Appendix B lists the acquisition parameters of the 2017 and 2019 scenes, respectively. Cloud-free images and pairs with more than 20% of overlap were selected to perform the RFM refinement Figure 11b–c contains a plot of the overlapping histogram between different image pairs). Additionally, a DEM computed from WorldView-2 (WV-2) and GeoEye-1 (GE-1) collections acquired on 5 July 2019 and on 9 September 2019 respectively is used for comparison with our 2019 PlanetScope DEM (Appendix B).
The DOVE-C PlanetScope data were used to generate DEMs in the object space with no ground control points. SIFT was used to extract and match tie points between the different image pairs. Then, the refinement was performed using the COSI-Corr-RFM package following the procedure described above. The re-projection error after the RFMs refinement is ~0.38 pix and ~0.35 pix with 2017 and 2019 PlanetScope data, respectively. Given the nominal GSD of these data, it corresponds to ~1 m on the ground. In a second step, we generated the two DEMs using the image space approach described in Section 3. We used Metashape software [,] with the NIR bands and our optimized RFMs. We chose the NIR band because it contains the fewest fraction of saturated pixels, especially in snow-covered and glaciated areas. The results are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
PlanetScope DEM results.
Two mesh-based DEMs and 3-D textured models were created with a GSD of 9 m, covering an area of ~400 km2. Figure 12 shows the complete textured 3D-model and the extracted DEMs over the Shisper Glacier site before and after the surge. The terrain height values are scaled within 2 km (purple) to 6 km (red). The movement of the glacier downstream the valley due to the recent surge is clearly visible from comparing the 3D textured models or the DEMs.
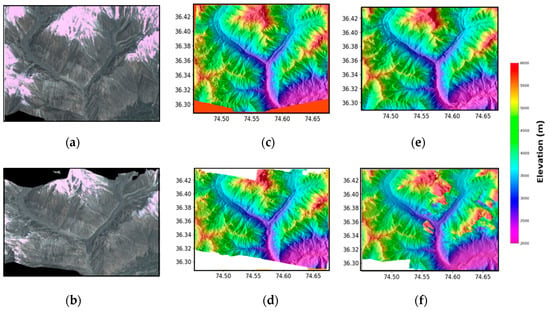
Figure 12.
DEMs and textured 3D models over the Shisper area. (a,b) Textured 3D models from 2017 (a) and 2019 (b). (c,d) DEMs extracted from PlanetScope data in 2017 (c) and 2019 (d). (e) SRTM DEM. (f) DEM generated by combining WV-2 and GE-1 stereo images acquired on 5 July 2019 and on 9 September 2019, respectively.
The accuracy of the DEMs is evaluated through comparison with the SRTM DEM [] (Figure 12e) and with a DEM generated from WV-2 and GE-1 stereo images acquired in 2019 [] (Figure 12f). Due to the temporal difference between the various DEMs, and the rapid glacier movement, we first selected some presumably stable areas. Note that the slope motion could have altered the topography, but in the absence of clear evidence for such a motion in that area we assume that the topography has not changed between 2000 (the year of the data acquisition used to generate SRTM []) and 2019. An area of ~5 km2 free of clear temporal changes was selected as a reference (Black box in Figure 11). The Normalized Median Absolute Deviation (NMAD) of the elevation differences in the stable area between PlanetScope DEM and SRTM is ~12 m, and ~7 m when calculated with the WV-2 and GE-1 DEM, respectively. The statistics of the elevation differences summarized in the histograms in Figure 13 show a better accuracy of the 2019-DEM than the 2017-DEM. This difference is probably due to smaller time difference between the DEMs and their closer spatial resolution. WV-2 and GE-1 data were acquired ~20 days apart from PlanetScope data and the extracted DEM has a GSD of 2 m; however the last update of the SRTM DEM dates back to 2014 and has a spatial resolution of 30 m.
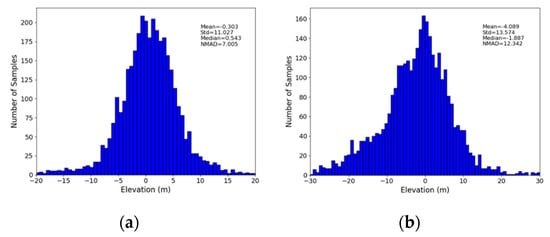
Figure 13.
Histogram distribution and statistics of elevation differences between (a) 2019 Planetscope DEM and Ge-1 and WV-2 DEM (b) 2017 DEM PlanetScope and SRTM.
We used the DEMs calculated from the PlanetScope data to assess the change of the glacier topography due to the 2018 surge. The mass transfer due to the surge is clearly revealed from the comparison of the 2017 and 2019 DEMs (Figure 14). The comparison shows a clear thinning of the glacier at elevations above ~2900 m, where the ice surface dropped by ~50 ± 10 m on average, and ice gains were at lower elevations. The glacier front advanced by 3.2 km downstream, reaching a thickness of ~170 ± 10 m just 1 km upstream of the terminus, downstream of the confluence with the Mochwar valley.
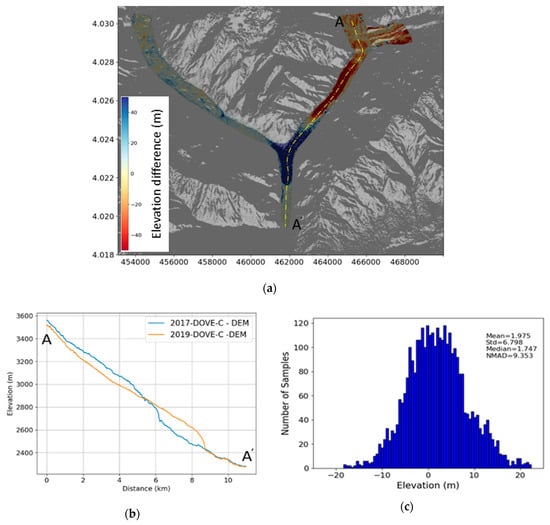
Figure 14.
(a) Elevation changes over Shisper glacier computed from the difference of 2019 and 2017 DOVE-C DEMs, overlaid with a hill-shaded DOVE-C 2017 DEM; (b) Elevation profiles from 2017 and 2019 Dove-C DEMs. Profiles are extracted along the transect AA’ indicated in panel (a); (c) histogram of the elevation difference over stable terrain.
A recent study [] presents elevation differences over the Shisper glacier using ASTER and SRTM DEMs. In this study, 12-ASTER DEMs were generated from September 2017 to September 2018. Most of the ASTER DEMs failed to provide a complete elevation information over the Shisper glacier due to steep slope (>40°) and cloud cover. In order to compute the elevation differences, the multiple generated ASTER DEMs were stacked and compared to the SRTM elevation model. Results showed that 60 ± 21 m of ice was increased compared to SRTM and the thickness at the terminus was 127 ± 21 m. These results seem reasonably consistent with our measurements. It should be noted that the PlanetScope daily coverage data offers a higher probability to obtain cloud-free images within a short time period than ASTER imagery. Therefore, it overcomes the cloud cover issue. In addition, our image preselection method designed to maximize the convergence angle alleviates the steep slope issue.
To reach better vertical accuracy with PlanetScope images, the RFM refinement process described here could additionally make use of GCPs as outlined in []. In any case, our study shows that, with our image preselection method for estimating orientation bias, our technique provides a tool to measure topographic changes in areas not easily accessible for ground data collection, or due to past event (an ice surge, or a landslide for example) for which no ground data might exist.
5. Conclusions
This study presents a methodology for RFM optimization and demonstrates its potential for precise image registration and 3D reconstruction using tri-stereo and multi-date CubeSat images. Our method relies on a first order polynomial bias compensation in the image-space, and, as implemented in the open source COSI-Corr RFM module, can be applied to any image with a geometry model provided in the RFM standard. So it can also be applied to push-broom images delivered in the RFM format. Note however that, when applicable, a Rigorous Sensor Model should yield even better geometric accuracy than any RFM refinement method, including ours. Using data from SkySat, we demonstrated that, if each acquisition is decomposed in sub-images corresponding each to a single detector array, we could achieve a sub-pixel relative orientation. Without using GCPs, we obtain reprojection errors of 0.4 pix (at the 68% confidence level) with SkySat tri-stereo images and is 0.6 pix with PlanetScope Classic Dove images. The refinement of the RFMs allows for effective 3-D extraction, when combined with our sub-images pairing strategy. Our DEM of the Morenci Mine area is comparable to a DEM obtained from a LiDAR airborne survey in terms of spatial resolution and elevation. The comparison of the two DEMs, which were acquired 4 years apart, demonstrate that the DEMs calculated from Cubesat images should be accurate enough to detect and measure topographic changes due to mining operations, constructions or vegetation changes. We show that even better measurements can be achieved with DEM calculated in the image space compared with using standard photogrammetric techniques. This approach is however more demanding than the object-space approach. The application to the Shispher glacier shows the potential of Cubesat repeated imagery to monitor ice surges and the evolution of mountain glaciers due to climate change.
This study demonstrates the huge potential of Cubesat optical imaging systems for environmental monitoring. With the existing constellations, it is already possible to use such data to detect and measure changes of the topography of various origin, due for example to mining, landslides, ice flow or coastal erosion. SkySat and PlanetScope platforms appear to be quite complementary in that regard. Thanks to its daily global coverage, PlanetScope can be used to produce DEMs over any area of interest with 10 to 15 m accuracy. If a better post event topography is needed, SkySat can be tasked to cover the area of interest with an optimal accuracy.
Avenues for further improvement that are left for future research include the determination of the optimum number and distribution of GCPs to improve the orientation of push-frame images, and the application of a rigorous sensor model refinement methods on level L1A images.
6. Patents
A provisional patent application CIT File No.: CIT-8522-P was filed on 9 November 2020.
Supplementary Materials
Flyover animation of textured 3D model using SkySat and PlanetScope are available online at https://zenodo.org/record/4009926 []. Full resolution DEMs and figures using PlanetScope data are available at https://zenodo.org/record/4039798 [].
Author Contributions
S.A. and J.-P.A. conceived the project and wrote the article. S.A. performed all the calculations and generated the figures. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research and the APC was partially funded by NASA Grant #80NSSC20K0492.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Ignacio Zuleta, Antonio Martos, Arin Jumpasut, Shomik Chakravarty, Trevor McDonald and Aparna Singh for helpful discussions. The authors also thank Planet Labs for access to their imagery. DigitalGlobe data were provided by the Commercial Archive Data for NASA investigators (cad4nasa.gsfc.nasa.gov) under the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency’s NextView license agreement.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A. Overview of the SkySat and PlanetScope Push-Frame Imaging System
Appendix A.1. SkySat
The SkySat constellation consists of 14 individual nano-satellites with a size of 60 × 60 × 95 cm and a weight of approximately ~110 kg. These satellites operate in the same sun synchronous orbit at an altitude of ~500 km, offering a sub-daily revisit capability. They are equipped with a Cassegrain telescope with a focal length of 3.6 m, and a focal plane consisting of three 5.5 megapixel CMOS imaging detectors. Each detector consists of five distinct bands arranged vertically along-track with a size of 2560 × 2160 pixels and a pixel size of 6.35 µm: the upper half of each detector is used for panchromatic band (450–900 nm), and the lower half is used for four multi-spectral bands (blue: 150–515 nm; green: 515–595 nm; red: 506–695 nm; near infra-red: 740–900 nm) [,]. A schematic of the focal plane layout (arrangement) is shown in Figure 2.
The SkySat system can provide images and videos with a spatial resolution of less than one meter. For the video product, only the panchromatic band of the central detector (Figure 2a) records videos with 30 to 120 frames per second. For the imagery product, larger areas can be covered using a push-frame imaging mode, where the three detectors acquire a continuous strip of single frame images named as “scene”, resulting in overlap along-track between consecutive scenes of the same detector and across-track overlap between different detectors Figure 2b).
The swath width of SkySat image data is ~6.6 km on the ground, which corresponds to ~74,834 pixels in the across-track direction (Figure 2b). The ground sampling distance (GSD) at the nadir of the SkySat-1 and Skysat-2 is 0.86 m for panchromatic bands and 1.1 m for multispectral-bands. As for the new generation of SkySat satellites (i.e., SkySat-3 to SkySat-14), they have a resolution of 0.65 m and 0.81 m in the Panchromatic and the Multi-spectral bands, respectively.
SkySat system is agile enough to acquire data in stereo mode similar to the present Very High Resolution (VHR) mission of Ikonos, Spot or WorldView. The pointing angle can be triggered in a range of ±40° (i.e., a convergence angle of 20°–40°). A significant advantage of SkySat is the aptitude to acquire up to three images for an area, taken from the same orbit at along-track forward-, nadir-and backward-view of the sensor. Such image triplets acquisition mode is denoted as tri-stereo mode [], which is similar to the Pléiades mission [,,].
Planet has three SkySat imagery products that can be used for 3D extraction, referred to as L1A All Frames, L1A Fast Track and Basic L1B []. L1A All Frames includes all frames collected as panchromatic Level 1A with a ground sampling at nadir ~0.9, within this level we have all frames acquired by each detectors at a high overlapping sequence. This level is delivered with the physical camera model and interpleaded RPCs derived from the physical parameters of each satellite (i.e., solved using the terrain-independent approach, Figure 1). L1A Fast Track, includes all the panchromatic scenes that match the footprints of the composite L1Bs (2560 × 1080 pixels, Figure 2b) with a GSD of 0.9 m at nadir, delivered with RPCs derived from the satellite telemetry. As with the Basic L1B level, the panchromatic and multi-spectral scenes are co-registered and fused using a super-resolution algorithm with a single panchromatic scene, called ”Panchromatic anchor frame”. The “Panchromatic anchor frame” scenes are chosen in a manner to have roughly an overlap in the along-track direction, as well as an across-track overlap between detector 2 and detectors 1 and 3 (cf. Figure 2b for an overview). During the fusion, a super-resolution process is used to increase the resolution from 0.9 m to ~0.72 m. Downstream of the super-resolution step, a pan-sharpening process combines the panchromatic and the multispectral bands to create high-resolution 4-band images [,]. The composite L1B images are delivered with RPCs derived from external high resolution DEMs and GCPs extracted from ortho-images (i.e., using the terrain-dependent approach, Figure 1).
SkySat is an on-demand collection data (i.e., require tasking). Users can specify the collection angles through a web service application “Tasking Dashboard“ [].
Appendix A.2. PlanetScope
PlanetScope constellation consists of around 150 individual nano-satellites named “Doves”, which continuously image the entire Earth surface in two near-polar orbits of ~8° and ~98° inclinations respectively, without requiring tasking or acquisition planning (Figure 3). Each Dove is a CubeSat of a 3U form factor (i.e., 10 cm × 10 cm × 30 cm) providing an image with a ground sampling distance of ~3.7 m at an altitude of ~475 km [,].
PlanetScope has three generations of imaging sensors referred to as Dove-classic (Dove-C), Dove-R and SuperDove (data not available yet). Each has a different sensor plane configuration and optic, but none has a panchromatic band. Basic characteristics of the PlanetScope satellite constellation and sensor specifications are shown in Figure 3.
The imaging payload of the Dove-C consists of a telescope coupled to a CCD frame camera (6600 × 4400 pixels) equipped with a Bayer-Mask filter. The upper half of the CCD array has an RGB Bayer pattern filter separating the light wavelength into three spectral bands (Bleu, Green and Red), and the lower half allows only the NIR wavelengths. The RGB half of each frame is then combined with the NIR half of the adjacent frame in order to generate the resulting 4-band image.
The Dove-R imaging sensor consists of the same type of telescope and frame size, but with a different CCD configuration. The sensor focal-plane consists of four distinct bands stripes arranged vertically along-track with each band stripe having a size of 6600 × 1100 pixels. The Bayer pattern filter in the Dove-C was replaced with a butcher-block filter providing 4-band images (Blue, Green, Red and NIR). The final composite image is produced by stacking up four frames ahead and four frames behind the anchor frame.

Table A1.
PlanetScope constellation overview.
Table A1.
PlanetScope constellation overview.
| Dove-C | Dove-R | |
|---|---|---|
| Scene footprint (km) | ~24 × 8 | ~24 × 16 |
| Pixel size (um) | 5.5 | 5.5 |
| Frame size (pixels) | 6600 × 1100 | 6600 × 1100 |
| Spectral Bands (λ nm) | Blue: 455–515 Green: 500–590 Red: 590–670 NIR: 780–860 | Blue: 464–517 Green: 547–585 Red: 650–682 NIR: 846–888 |
PlanetScope imagery is captured continuously in a push-frame mode. Each Dove acquires images in a continuous strip of a single frame image known as “scene” with approximately 1 sec interval, resulting in ~8% along-track overlap between consecutive scenes (Figure 3).
The Dove constellations are designed to operate in nadir pointing mode. In addition, the distance between consecutive Doves in both orbits is designed in a way so that the longitudinal progression between them over the rotating Earth leads to a void-less scan of the surface and guarantees the daily coverage. To ensure the void-less surface imaging, there is a variation in the view angle from the strict nadir pointing to ± 5 degrees off nadir [,]. This variation in viewing angle results in an across-track overlap ~40% between subsequent Doves with a time lag of ~1.5 min (Figure 3b).
PlanetScope constellation also involves another overlap depending on the latitude between acquisitions from ascending and descending orbits with a time lag of ~1 h (Figure 3c).
Planet has three PlanetScope imagery products, referred to as an Ortho Tile product, an Ortho Scene product and a Basic Scene product []. Ortho Tiles are multiple ortho-rectified scenes in a single strip that have been merged and resampled according to a defined grid size. Ortho Scenes represent georeferenced single-frame images, corrected for systematic distortions due to the sensor and earth rotation and curvature. The Basic Scene product is a Scaled Top of Atmosphere Radiance (at sensor) and a sensor-corrected product, providing imagery as seen from the spacecraft without correction for any geometric distortions. The product is delivered with RPCs derived from external high resolution DEMs and GCPs extracted from a reference Ortho-images (i.e., using the terrain-dependent approach, Figure 1).
Planet offers free monthly limited PlanetScope images to the scientific research community through the Education and Research Program [].
Appendix B

Table A2.
Acquisition parameters for the PlanetScope imagery over Shisper glacier study area.
Table A2.
Acquisition parameters for the PlanetScope imagery over Shisper glacier study area.
| Acq. Date | ID | Acq. Time | GSD | Incidence Angle | View Angle | Azimuth Angle | Orbit Direction |
| 09 September 2017 | 0f36 | 05:59:49 | 3.6063 | 0.191 | 0.177 | 348 | Descending |
| 0f36 | 05:59:50 | 3.6063 | 0.187 | 0.173 | 348 | Descending | |
| 0f44 | 06:01:16 | 3.6072 | 2.69 | 2.47 | 348 | Descending | |
| 0f44 | 06:01:17 | 3.6073 | 2.69 | 2.47 | 348 | Descending | |
| 0f44 | 06:01:18 | 3.6074 | 2.69 | 2.47 | 348 | Descending | |
| 19 September 2017 | 1004 | 05:02:24 | 3.9588 | 3.01 | 2.75 | 12.1 | Ascending |
| 1004 | 05:02:25 | 3.9588 | 3.03 | 2.77 | 12.0 | Ascending | |
| 0e26 | 05:08:47 | 3.9093 | 4.28 | 3.91 | 12.4 | Ascending | |
| 0e26 | 05:08:48 | 3.9093 | 4.26 | 3.89 | 12.3 | Ascending | |
| 0e26 | 05:08:49 | 3.9092 | 4.27 | 3.89 | 12.3 | Ascending | |
| 20 September 2017 | 1033 | 05:03:08 | 3.9354 | 2.25 | 2.06 | 12.3 | Ascending |
| 1033 | 05:03:09 | 3.9353 | 2.19 | 2.00 | 12.5 | Ascending | |
| 1033 | 05:03:10 | 3.9352 | 2.13 | 1.94 | 12.1 | Ascending | |
| 0f24 | 05:59:40 | 3.6529 | 5.38 | 4.94 | 348 | Descending | |
| 0f24 | 05:59:41 | 3.653 | 5.36 | 4.91 | 348 | Descending | |
| 0f24 | 05:59:42 | 3.653 | 5.38 | 4.94 | 348 | Descending | |
| Acq. Date | ID | Acq. Time | GSD | Incidence Angle | View Angle | Azimuth Angle | Orbit Direction |
| 01 August 2019 | 0f49 | 04:17:26 | 3.5188 | 2.17 | 2.00 | 348.3 | Descending |
| 0f49 | 04:17:27 | 3.5189 | 1.96 | 1.79 | 348.3 | Descending | |
| 1021 | 05:22:29 | 3.9434 | 4.36 | 3.97 | 11.9 | Ascending | |
| 1021 | 05:22:30 | 3.9433 | 4.38 | 3.99 | 11.9 | Ascending | |
| 1021 | 05:22:31 | 3.9434 | 4.39 | 4.00 | 11.9 | Ascending | |
| 101f | 05:26:36 | 3.9349 | 5.03 | 4.55 | 12.5 | Ascending | |
| 101f | 05:26:37 | 3.9348 | 5.45 | 4.97 | 12.5 | Ascending | |
| 07 August 2019 | 1006 | 05:24:20 | 3.9209 | 1.06 | 0.9641 | 12.1 | Ascending |
| 1006 | 05:24:21 | 3.9208 | 1.09 | 0.9641 | 12.1 | Ascending | |
| 1006 | 05:24:22 | 3.9207 | 1.07 | 0.968 | 12.1 | Ascending | |
| 09 August 2019 | 100c | 05:24:18 | 3.9245 | 1.11 | 1.01 | 12.1 | Ascending |
| 100c | 05:24:19 | 3.9244 | 1.01 | 0.909 | 12.1 | Ascending | |
| 100c | 05:24:21 | 3.9243 | 1.10 | 1.00 | 12.1 | Ascending | |
| 13 August 2019 | 100c | 05:26:09 | 3.9284 | 4.33 | 3.95 | 12.4 | Ascending |
Appendix B.1. WV-2 and GE-1 DEM Generation
Reference DEM computed in 2019 was generated using WV-2 and GE-1 stereo-pairs products Table A3. These products were obtained from the Commercial Archive Data for NASA investigators (cad4nasa.gsfc.nasa.gov) under the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency’s NextView license agreement []. We generated the DEM using PCI Geomatics software without using any ground control points (GCPs).

Table A3.
Details for GE-1 and WV-2 satellites images used for DEM generation over Shisper glacier study area.
Table A3.
Details for GE-1 and WV-2 satellites images used for DEM generation over Shisper glacier study area.
| Data | ID | Acq. Date | Sun Elevation |
|---|---|---|---|
| WV-2 Stereo pair | 05JUL19WV020500019JUL05054713 P1BS_R4C1 03171048010_02_P002 | 05 July 2019 | +68.21 |
| 05JUL19WV020500019JUL05054822 P1BS_R4C103171048010_02_P002 | 05 July 2019 | +68.4 | |
| GE-1 Stereo pair | 19SEP29053925-P1BS- 503911006010_01_P001 | 29 September 2019 | +48.0 |
| 19SEP29053928-P1BS-503911006010_01_P002 | 29 September 2019 | +49.9 | |
| 19SEP29054028-P1BS-503911006020_01_P001 | 29 September 2019 | +48.0 | |
| 19SEP29054031-P1BS-503911006020_01_P002 | 29 September 2019 | +47.9 |
References
- Nagel, G.W.; de Novo, E.M.L.M.; Kampel, M. Nanosatellites applied to optical Earth observation: A review. Rev. Ambient. Água 2020, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planet Labs Education and Research Program. Available online: https://www.planet.com/markets/education-and-research/ (accessed on 4 June 2020).
- Villela, T.; Costa, C.A.; Brandão, A.M.; Bueno, F.T.; Leonardi, R. Towards the Thousandth CubeSat: A Statistical Overview. Int. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planet Labs Planet Tasking On-Demend High-Resolution Intellignece. Available online: https://learn.planet.com/rs/997-CHH-265/images/PlanetTaskingOne-pager_Letter_Print.pdf (accessed on 6 August 2020).
- D’Angelo, P.; Kuschk, G.; Reinartz, P. Evaluation of Skybox Video and Still Image products. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2014, XL–1, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghuffar, S. DEM generation from multi satellite PlanetScope imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, C.V.; Hu, Y. A Comprehensive Study of the Rational Function Model for Photogrammetric Processing. Photogramm. Eng. Remote. Sens. 2001, 67, 1347–1357. [Google Scholar]
- Poli, D.; Toutin, T. Review of developments in geometric modelling for high resolution satellite pushbroom sensors. Photogramm. Rec. 2012, 27, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Franchis, C.; Meinhardt-Llopis, E.; Michel, J.; Morel, J.-M.; Facciolo, G. Automatic sensor orientation refinement of Pléiades stereo images. In Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Quebec City, QC, Canada, 13–18 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Qin, R. Multi-View Large-Scale Bundle Adjustment Method for High-Resolution Satellite Images. In Proceedings of the ASPRS 2019 Annual Conference, Denver, CO, USA, 28–30 January 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rupnik, E.; Deseilligny, M.P.; Delorme, A.; Klinger, Y. Refined satellite image orientation in the free open-source photogrammetric tools Apero/Micmac. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2016, 3, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perko, R.; Raggam, H.; Schardt, M.; Roth, P.M. Very high resolution mapping with the Pleiades satellite constellation. Am. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 6, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jacobsen, K.; Topan, H. DEM generation with short base length pleiades triplet. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2015, 40, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leprince, S.; Barbot, S.; Ayoub, F.; Avouac, J. Automatic and Precise Orthorectification, Coregistration, and Subpixel Correlation of Satellite Images, Application to Ground Deformation Measurements. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2007, 45, 1529–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leprince, S.; Muse, P.; Avouac, J. In-Flight CCD Distortion Calibration for Pushbroom Satellites Based on Subpixel Correlation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 2675–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaku, J.; Tadono, T. PRISM On-Orbit Geometric Calibration and DSM Performance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 4060–4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubik, P.; Lebègue, L.; Fourest, S.; Delvit, J.-M.; de Lussy, F.; Greslou, D.; Blanchet, G. First in-flight results of Pleiades 1A innovative methods for optical calibration. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Space Optics 2012, Ajaccio, France, 9–12 October 2012; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2017; Volume 10564. [Google Scholar]
- Habib, A.F.; Morgan, M.; Lee, Y. Bundle Adjustment with Self–Calibration Using Straight Lines. Photogramm. Rec. 2002, 17, 635–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xu, K.; Huang, W. Auto-calibration of GF-1 WFV images using flat terrain. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 134, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Tao, V.; Croitoru, A. Understanding the Rational Function Model: Methods and Applications. In Proceedings of the XXth International Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing Congress, Istanbul, Turkey, 12–23 July 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Grodecki, J.; Dial, G. Block adjustment of high-resolution satellite images described by Rational polynomials. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2003, 69, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Zhang, Y. A generic method for RPC refinement using ground control information. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2009, 75, 1083–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, C.; Hanley, H. Bias Compensation in Rational Functions for IKONOS Satellite Imagery. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2003, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Angelo, P.; Máttyus, G.; Reinartz, P. Skybox image and video product evaluation. Int. J. Image Data Fusion 2016, 7, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kääb, A.; Altena, B.; Mascaro, J. River-ice and water velocities using the Planet optical cubesat constellation. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 4233–4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perko, R.; Raggam, H.; Roth, P.M. Mapping with Pléiades—End-to-End Workflow. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusiello, A.; Trucco, E.; Verri, A. A compact algorithm for rectification of stereo pairs. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2000, 12, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschmuller, H. Stereo Processing by Semiglobal Matching and Mutual Information. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2008, 30, 328–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bethmann, F.; Luhmann, T. Semi-Global Matching in Object Space. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2015, XL-3/W2, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Jung, C.; Ke, P.; Song, H.; Hwang, J. Automatic Contrast-Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization With Dual Gamma Correction. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 11782–11792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mining Technology Morenci Copper Mine, Arizona 2020.
- Carswell, W.J., Jr. The 3D Elevation Program: Summary for Arizona; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2014.
- Pierrot Deseilligny, M.; Clery, I. Apero, an Open Source Bundle Adjusment Software for Automatic Calibration and Orientation of Set of Images. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2011, 3816, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupnik, E.; Daakir, M.; Pierrot Deseilligny, M. MicMac—A free, open-source solution for photogrammetry. Open Geospatial Data Softw. Stand. 2017, 2, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scovanner, P.; Ali, S.; Shah, M. A 3-Dimensional Sift Descriptor and Its Application to Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the 15th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Augsburg, Germany, 23–28 September 2007; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 357–360. [Google Scholar]
- Agisoft Metashape Professional; Version 1.6.0.; Agisoft LLC: St. Petersburg, Russia, 2019.
- Aati, S.; Rupnik, E.; Nejim, S. Comparative study of photogrammetry software in industrial field. Rev. Française Photogrammétrie Télédétection 2020, 1, 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Bhambri, R.; Watson, C.S.; Hewitt, K.; Haritashya, U.K.; Kargel, J.S.; Pratap Shahi, A.; Chand, P.; Kumar, A.; Verma, A.; Govil, H. The hazardous 2017–2019 surge and river damming by Shispare Glacier, Karakoram. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, I.; Majeed, U.; Jan, A.; Glasser, N. The January 2018 to September 2019 surge of Shisper Glacier, Pakistan, detected from remote sensing observations. Geomorphology 2019, 351, 106957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Ali, K.; Syed, M.; Nizami, I.; Jan, I.; Hussain; Begum, F. Risk assessment of Shishper Glacier, Hassanabad Hunza, North Pakistan. J. Himal. Earth Sci. 2019, 52, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- RGI Consortium. Randolph Glacier Inventory—A Dataset of Global Glacier Outlines: Version 6.0; GLIMS Technical Report; Global Land Ice Measurements from Space: Boulder, CO, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Santillan, J.; Makinano-Santillan, M. Vertical Accuracy Assessment Of 30-M Resolution Alos, Aster, And Srtm Global Dems Over Northeastern Mindanao, Philippines. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2016, XLI-B4, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, M.Á.; del Mar Saldaña, M.; Aguilar, F.J. Generation and Quality Assessment of Stereo-Extracted DSM From GeoEye-1 and WorldView-2 Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 1259–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGS Shuttle Radar Topography Mission. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/centers/eros/science/usgs-eros-archive-digital-elevation-shuttle-radar-topography-mission-srtm-void?qt-science_center_objects=0#qt-science_center_objects (accessed on 4 May 2020).
- AATI, S. Textured 3D Model over Morenci Mine and Shisper Glacier Using SkySat and PlanetScope Satellite Imagery 2020. Available online: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4009926 (accessed on 6 August 2020).
- AATI, S. Topography Extraction and Topographic Change Measurements Using PlanetScope Data: Shisper Glacier (Pakistan) 2020. Available online: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4039798 (accessed on 6 August 2020).
- Murthy, K.; Shearn, M.; Smiley, B.D.; Chau, A.H.; Levine, J.; Robinson, M.D. SkySat-1: Very high-resolution imagery from a small satellite. In Proceedings of the Sensors, Systems, and Next-Generation Satellites XVIII, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 22–25 September 2014; Meynart, R., Neeck, S.P., Shimoda, H., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2014; Volume 9241, pp. 367–378. [Google Scholar]
- Raggam, H. Surface mapping using image triplets. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2006, 72, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, D.; Remondino, F.; Angiuli, E.; Agugiaro, G. Evaluation Of Pleiades-1a Triplet On Trento Testfield. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2013, XL-1/W1, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, D.; Remondino, F.; Angiuli, E.; Agugiaro, G. Radiometric and geometric evaluation of GeoEye-1, WorldView-2 and Pléiades-1A stereo images for 3D information extraction. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 100, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planet Team Planet Satellite Imagery Prodcuts 2020. Available online: https://storage.googleapis.com/planet-ditl/day-in-the-life/index.html (accessed on 6 August 2020).
- Neigh, C.S.R.; Masek, J.G.; Nickeson, J.E. High-Resolution Satellite Data Open for Government Research. Eos. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2013, 94, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).