Abstract
The International Space Station (ISS) offers a unique view from space that provides nighttime light (NTL) images of many parts of the globe. Compared with other NTL remote sensing data, ISS NTL multispectral images taken by astronauts with commercial digital single-lens reflex (DSLR) cameras have the characteristics of free access, high spatial resolution, abundant data and no light saturation, so it plays a unique advantage in the research of small-scale urban planning, optimization of lighting resource allocation and blue light pollution. In order to improve the radiation consistency of ISS NTL images, a relative radiation normalization method of ISS NTL images is proposed in this paper. Pseudo invariant features (PIF) were identified in the cloud-free Defense Meteorological Satellite Program/Operational Linescan System (DMSP/OLS) time series NTL remote sensing annual composite product, and then they were used to derive the relative radiation normalization model of ISS NTL images. The results show that the radiation brightness of ISS NTL images in different regions is normalized to the same gray level with that of DMSP/OLS NTL remote sensing images in the same year, which improves the radiation brightness comparability between different regions of ISS NTL images. This method is universally applicable to all ISS NTL images, which is beneficial to the NTL comparability of ISS NTL image in the regional horizontal and temporal vertical.
1. Introduction
Nighttime light (NTL) remote sensing is using airborne (or orbital) sensors to detect upward-directed light from the night side of the earth, whether natural or artificial in nature [1,2], such as aurorae, volcanic eruptions, marine bioluminescence, city lights, fishing boats, oil and gas well combustion, etc. In recent years, NTL remote sensing imagery has gradually come into people’s view because of its unique charm and its high correlation with human activities. Compared with ordinary remote sensing satellite images, NTL remote sensing images reflect more human activities from a different perspective, so they have been widely used in social and economic parameter estimation [3,4,5,6], urbanization monitoring and evaluation [7,8], major disasters (whether natural or human-caused) evaluation [9,10], light pollution research [11,12,13,14,15], fishery information extraction [16,17,18], epidemic disease research [15,19,20], extraction of street lights [21,22], and oil and gas field monitoring [23].
The development of NTL remote sensing has experienced an evolution from low spatial resolution to high spatial resolution and from panchromatic to multispectral information. The Defense Meteorological Satellite Program/Operational Linescan System (DMSP/OLS) of the United States is the first platform to provide long time-series global NTL remote sensing images with low spatial resolution [1,2,3,4,6,7]. As the successor of DMSP/OLS, Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite Day/Night Band (VIIRS/DNB) provides long time-series global NTL remote sensing images with higher spatial and temporal resolution [8]. Astronauts of the International Space Station (ISS) have taken many earth images with commercially available cameras since 2000, including NTL images of some areas [2]. The ISS is an important platform for earth observation, its images are widely distributed around the world [24]. Many nighttime (including dawn and dusk images) images have been catalogued with center points (Figure 1), and a large number of images have not been catalogued. These ISS NTL images have mid-high spatial resolution of 5–200 m per pixel and three bands of color information (red, green, and blue) [25,26,27].
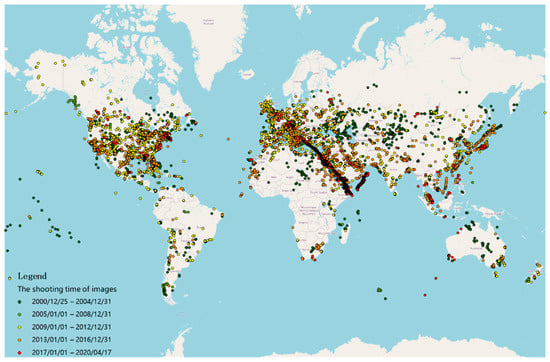
Figure 1.
The spatial and temporal distribution of International Space Station (ISS) nighttime (including dawn and dusk) images cataloged with center points (data as of 17 April 2020). The center points of the images are freely accessible via the Gateway of Astronaut Photography of the Earth (https://eol.jsc.nasa.gov).
The ISS NTL images are the first multispectral images recording visible light wavelengths emitted from the earth from a space perspective and constitute a unique and valuable dataset. They have unique application value in epidemiology research [28,29], ecological environment effect [30], light pollution analysis [26,27,28,29,30], economic analysis [31] and urban delineation [32,33,34]. However, due to the lack of accurate location and geographical reference, and the inconsistency of camera tilt angle, focal length and orbital height when photographing, these ISS NTL images not only have different imaging ranges and spatial resolutions, but also have no radiation consistency between images. For these reasons, many studies based on the ISS NTL RGB images mainly focus on the application analysis of single times and single areas. For example, by using the ISS NTL RGB image, Rybnikova and Portnov concluded that exposure to short-wavelength light had a greater impact on the hormone-dependent cancer incidence rate than exposure to green and red light [28]. Pauwels et al. found that light pollution would have a negative impact on bat activity using the ISS NTL imagery and ground streetlight location data, and that the variables based on the ISS NTL imagery better described this harmful impact than streetlight location [30]. Mazor et al. examined the relationship between the long term spatial patterns of sea turtle nests and the intensity of nighttime lights along Israel’s entire Mediterranean coastline, and found that sea turtles nests are negatively related to NTL intensity and are concentrated in darker sections along the coast by using high-resolution data derived from the SAC-C satellite and the ISS [35].
As mid-high spatial resolution multispectral NTL images without light saturation that can be obtained free of charge, the ISS NTL images not only have historical value, but are still being photographed. If the ISS NTL images of a region have time-series characteristics, they can be used for comparative analysis of different time phases in this region. In addition, NTL images taken by astronauts in different regions also have spatial comparability. In other words, these NTL images have the conditions for the comparative analysis in the temporal vertical and regional horizontal. Sánchez de Miguel et al. have made great contributions to proving that calibration of ISS NTL images is possible [25,26,27]. They applied standard procedures of image decoding, photometric calibration, and vignetting correction. However, the standard procedures are not only complicated, but also cannot be completed without nighttime radiation values obtained by airborne spectroradiometers and standard star fluxes, which greatly limits the application research of ISS NTL imagery. Therefore, from this point of view, this paper proposes a new heuristic method to improve the radiation consistency of ISS NTL images by using readily available global cloud-free time-series NTL remote sensing data [36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44]. We put these ISS NTL images on the same radiance level with other multisource NTL remote sensing data to realize the relative radiation normalization. The ISS NTL images available overlapped with DMSP/OLS and VIIRS/DNB time series respectively for a particular time span. The last year in which DMSP/OLS products were generally available to the public was 2013. Thus, for ISS NTL images before 2013, the DMSP/OLS time-series annual composite product can be used as reference images for relative radiation normalization, while for ISS NTL images after 2013, VIIRS/DNB time-series product can be considered for relative radiation normalization.
In this paper, taking ISS NTL images before 2013 as an example, the DMSP/OLS images were used as reference images, and the ISS NTL RGB images of Beijing of China, Dalian of China and Tel Aviv-Yafo of Israel in 2011 were selected for relative radiation normalization, so as to make the radiance of images in different regions comparable. The ISS RGB NTL image of Beijing of China in 2010 was added to compare the radiation of two epochs in the same region. This method corrects the ISS RGB NTL image to the same gray level as other multisource NTL remote sensing images, and improves the radiation brightness comparability and image availability of ISS images.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Areas and the NTL Images
China is a coastal country with rapid economic development [45,46]. As the capital of China, Beijing is one of the densely populated cities and its economic development is rapid. Dalian is an important port city in northern China. Israel is a country in the Levant region of Western Asia, located on the southeast coast of the Mediterranean Sea. Tel Aviv-Yafo is the second-largest city in Israel, with a developed coastal economy and the country’s densest population. It is also the economic hub of Israel. The NTL data of a region can directly reflect the characteristics of the light environment of the region. Therefore, it is necessary to study the relative radiation normalization of ISS NTL images for analyzing the nighttime radiance characteristics of cities, which is also the premise of using ISS NTL images for research purposes.
2.1.1. The ISS NTL Images
The ISS NTL images were taken by astronauts using commercial digital single-lens reflex cameras, and the ISS NTL images used in this paper particularly were taken by astronauts using Nikon D3S electronic still camera during Expedition 26. The ISS NTL raw images are in NEF format with 12 or 14-bit radiometric resolution that preserves linearity of the detector, that is, file values are proportional to the exposure received by each pixel [25,26,27]. As shown in Figure 2a, the noise of the ISS image in raw format is obvious. Due to the great difference of spatial resolution between DMSP/OLS and ISS, the ISS NTL raw image has higher bytes, more details and obvious noise. In fact, these details are not conducive to identifying pseudo-invariant feature (PIF) points. The high-frequency components of most images are relatively small, JPEG compression algorithms such as Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) can filter out the high-frequency components, which to some extent removes noise. Therefore, ISS RGB NTL images in JPEG format with 8 bits are used to relative radiation normalization in this paper.
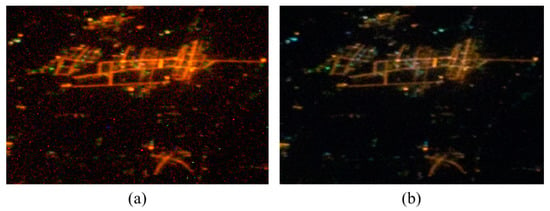
Figure 2.
Comparison of ISS raw image (a) and JPEG image (b) in the same region.
In order to meet the needs of promoting the development of international intelligent lighting, Beijing of China, Dalian of China and Tel Aviv-Yafo of Israel were selected as the study areas to carry out the relative radiation normalization in different regions at the same time for the regional horizontal comparison of nighttime lighting. At the same time, the temporal vertical comparison of nighttime lighting is realized by the relative radiation normalization of ISS RGB NTL images in the same region at different times. The detailed description of ISS RGB NTL images used in this paper is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Data description of ISS RGB Nighttime Light (NTL) images used in this paper.
The varying orbital height and camera tilt angle made the direction and distance of the ground light source received by the camera different; the different focal length made the photographing ranges and image spatial resolution different. They caused the radiance of different ISS NTL images to be incomparable, and that is a hindrance to using them for research purposes. The purpose of the relative radiation normalization in this paper is to normalize the incomparable ISS NTL images to the comparable DMSP/OLS NTL data, reducing the difference between the ISS NTL images generated by uncertain factors such as the camera tilt angle and orbital height, and make different ISS NTL images comparable relatively.
2.1.2. The DMSP/OLS Time-Series NTL Remote Sensing Data
The DMSP/OLS NTL annual composite product is the earliest and most widely studied time-series NTL remote sensing product [36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44]. Since DMSP/OLS NTL images were acquired by six sensors (F10, F12, F14, F15, F16, and F18) spanning 21 years without on-board calibration, many researchers had calibrated them to generate a consistent NTL time series [39,40]. At present, there are many mature methods for the relative radiation correction of DMSP/OLS time-series NTL remote sensing data of different sensors [39,40]. In this study, a consistent DMSP/OLS NTL time-series product generated by Zhang et al. using a robust ridge sampling regression (RSR) method [39] was selected to assist the relative radiation normalization of the ISS NTL images. The main considerations are: (1) the DMSP/OLS time-series annual product with 1000m spatial resolution has been corrected; (2) the time span of the data is 1992–2013, which has a large amount of overlap with the shooting time of ISS NTL images; (3) the pixel depth of the data is stretched to 16 bits (digital numbers 0–65535), such that the radiance brightness characteristics of the image are prominent compared with the original image.
Pseudo invariant features (PIFs) refer to some specific elements, whose reflection characteristics change little with time and light, such as concrete, asphalt, and rooftops [47,48,49]. Elvidge et al. proposed a PIF method that combines reference images to establish a long time series nighttime light model [23] in 2009. The invariant areas are directly related to the performance of the model. The selection of invariant areas has two conditions: (1) the social and economic development of the invariant area is stable, which ensures the NTL brightness changes very little; (2) the invariant area should cover all of the grayscale levels of NTL images to ensure model universality.
When the ISS RGB NTL image of 2010 in the Beijing study area is used as the target image, F182010 of the DMSP/OLS is used as the reference image. We selected the reference image and the DMSP/OLS NTL images of the year before (F162009) and after (F182011) the reference image as the data basis for pseudo-invariant feature points selection. Data selection methods for other years and other study areas are the same as above.
2.2. The Nighttime Light Image Processing
The processing flow of NTL images is shown in Figure 3, which includes three steps: image preprocessing, model establishment, and image post-processing.
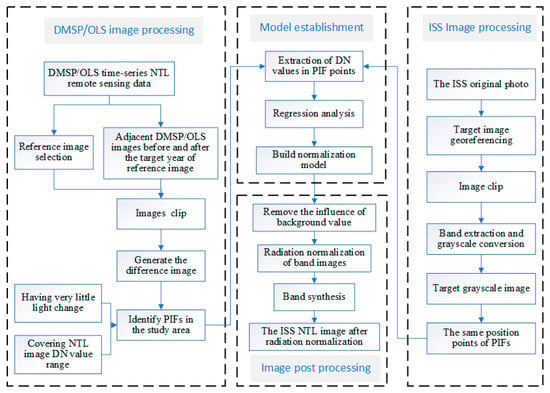
Figure 3.
The process flow of nighttime light images.
2.2.1. NTL Image Preprocessing
The preprocessing of NTL images is the preparation of identifying pseudo-invariant features, mainly including generating difference images and unifying grayscale levels. First, we clip the DMSP/OLS NTL remote sensing images in the study areas as the reference images. The adjacent images of DMSP/OLS before and after the target year are compared to get the difference image. The ISS NTL images with geographical coordinates are clipped as the target images of the study areas after georeferencing. The three single-band images of red, green and blue in study areas of the ISS are extracted respectively (Figure 4).
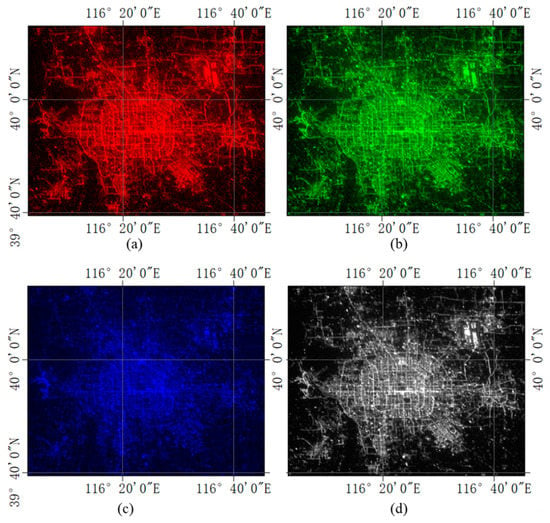
Figure 4.
The ISS NTL band images of the Beijing study area in 2010. (a) Red band image. (b) Green band image. (c) Blue band image. (d) grayscale image.
Second, the grayscale image can solve the band difference between the ISS NTL target image and the DMSP/OLS NTL remote sensing image. The spectrum range of DMSP/OLS NTL remote sensing image is 400–1100 nm, covering the visible spectrum range of the ISS NTL image. The multispectral ISS NTL image and the single band DMSP/OLS NTL remote sensing image are analyzed and compared on the grayscale level. The pixel digital number (DN) value of the NTL remote sensing image is the mean value of the radiant brightness of the NTL in the range of the ground pixel recorded by the sensor. To quantify the total radiation of the three bands, we transform the ISS NTL multispectral image of the study area into a grayscale image (Figure 4d). The formula is as follows [21,50,51]:
where is the DN value of the converted ISS NTL grayscale image. , , and correspond to the DN value of red, green and blue band of the ISS original image respectively.
In order to resolve the pixel scale difference between different NTL remote sensing images, we calculate the mean DN value of all ISS pixels contained in each DMSP/OLS pixel. The calculation formula is:
where represents the mean DN value of all ISS pixels in the DMSP/OLS pixel, represents the DN value of the ith ISS pixel in the DMSP/OLS pixel, and represents the number of ISS pixels in the DMSP/OLS pixel.
2.2.2. Building the Radiation Normalization Model: Pseudo Invariant Feature and Regression Method
As there is no time continuity in the ISS NTL images, these images are inconsistent in DN values and cannot be applied to perform comparative analyses directly. Therefore, it is necessary to build a model to improve image comparability with other time series NTL remote sensing images. The pseudo-invariant feature method is a common method to study the relative radiation normalization of multisource and multitemporal remote sensing data. Many scholars have studied the relative radiation normalization method based on PIF, such as automatic scatter control regression (ASCR) [52], multivariate change detection transformation method [53,54], and iterative weighted least square regression method [55]. In this paper, the change detection method is used to identify the PIFs, then the difference images are obtained, and finally, the pseudo-invariant feature areas are identified artificially.
Image change detection is the basic method to identify PIFs. To identify the PIFs, the change of image should be detected at the pixel level. The image difference method is the simplest and most widely used pixel-level image change detection method. The basic principle of the image difference method is to subtract the grayscale value of multitemporal corresponding pixels. That is to say, the corresponding pixels of two registered images are subtracted to generate a difference image.
We selected the pixels whose DN values do not change significantly in the 3-year time-series when using the difference images to identify the PIFs. In order to exclude the area without nighttime lights where the pixel value is always 0, it is necessary to combine the DN value of the light brightness of the reference image for secondary screening. For example, because the epoch of observation of the ISS target image in Beijing is 2010, F182010 image of DMSP/OLS was selected as the reference image, and then the difference was calculated between the F182010 image and the F162009 and F182011 images, respectively (Figure 5). Finally, a new composite image is obtained by band synthesis (Figure 6). In this example of the band synthesis process, F182010 image is the red channel, F182010 and F162009 difference image is the green channel, and F182010 and F182011 difference image is the blue channel. According to the DN value range of DMSP/OLS NTL images, the dark red areas in the composite image and the black areas at the edge of the city in the difference images represent the areas where the DN value varies little over time. In addition, the large area of the same color in the center of the city should be excluded, and the selected PIFs should cover the DN range of the DMSP/OLS images. Dalian and Tel Aviv-Yafo are coastal cities, so PIFs selection does not consider the sea surface areas.
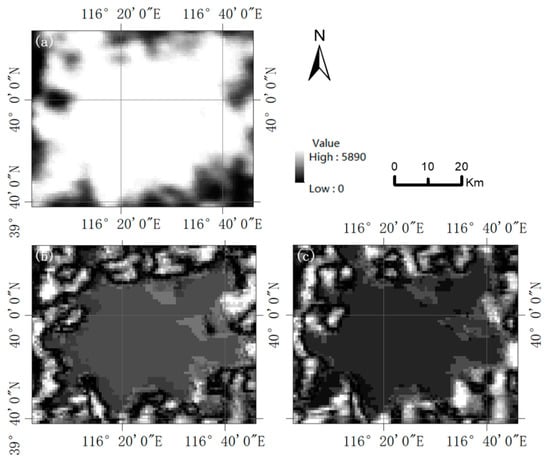
Figure 5.
Difference images used to identify pseudo-invariant feature points of Beijing in 2010. (a) Defense Meteorological Satellite Program/Operational Linescan System (DMSP/OLS) reference F182010 image. (b) Difference image of F182010 and F162009. (c) Difference image of F182010 and F182011.
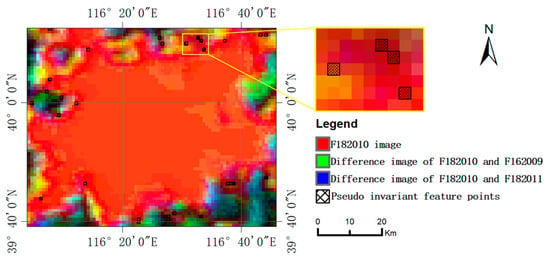
Figure 6.
Identifying pseudo-invariant feature points. In this band synthesis image, F182010 image is the red channel, F182010 and F162009 difference image is the green channel, and F182010 and F182011 difference image is the blue channel. The selected pseudo-invariant feature points are like the shadow pixels in the top enlarged region.
Pseudo invariant feature points were identified by using difference images, and then we use these data points to build the regression model between the ISS NTL target image and DMSP/OLS reference image. Many researchers have studied the consistent calibration of NTL remote sensing data by using the pseudo-invariant feature method, and the results show that they all have good linear relationships or quadratic polynomial relationships [56]. Based on the scatter plot distribution of these data points, the linear regression function and the quadratic polynomial regression function are used to fit the target image and the reference image. In order to ensure that the brightness of the dark target area does not change when the pixel DN value is 0 and the normalized image pixel value does not show a negative value, the linear equation and quadratic equation with intercept 0 are used for regression in this paper:
where y represents the DN value of the reference image, represents the DN value of the target grayscale image, , , and are coefficients of the regression model.
The radiation normalization model obtained by this method is applied to the red, green, and blue bands of the ISS NTL image in the study area. In this way, the radiation grayscale level of the image is normalized horizontally on the basis of maintaining the internal differences of the original red, green and blue bands, and then the three bands are synthesized to obtain the normalized ISS NTL multispectral image.
2.2.3. Image Post Processing
Due to the difference of spatial resolution, land and sea location and research scope in different research areas, the total nighttime light (TNL) or nighttime light mean (NTM) of normalized ISS NTL images cannot be directly used for regional comparison in subsequent research and application. To make the nighttime lights of different research areas have radiation comparability, we need to carry out image post-processing. The areas that do not participate in the comparison and have low radiance are defined as the image background that affects the inter-regional comparison of ISS NTL images, and then the influence of background values is removed.
In this paper, the method of removing the influence of background value is the natural breaks (Jenks) method. Its basic principle is to identify the classification interval based on the natural grouping inherent in the data, and to minimize the difference within the class and maximize the difference between each class. The DN values of NTL images in each study area are divided into five categories by the natural breaks (Jenks) method, and the one with the lowest value is used as the background value to remove.
In this paper, the classification results of the DN value of ISS NTL grayscale images were used to select the background threshold. Based on this method, the background thresholds of ISS026-E-10155, ISS026-E-24048, ISS026-E-24057, and ISS026-E-28917 images are 27, 20, 9.95, and 23 respectively (Figure 7). The background values of red, green and blue band images and DMSP/OLS NTL images are also removed according to the natural breaks (Jenks) method. The radiation normalization results after removing the background value will not be affected by the size of the study area, but they will also reduce the influence of land and ocean conditions in different study areas (Figure 8).
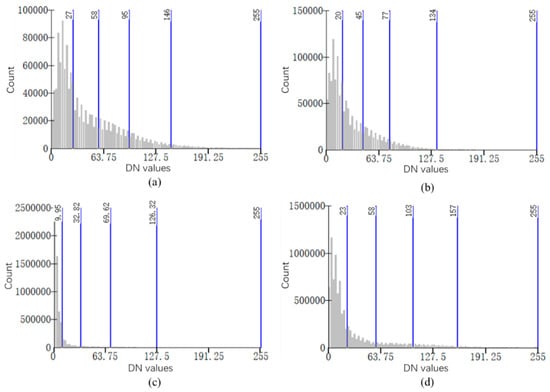
Figure 7.
The ISS NTL grayscale images in each study area are divided into five categories by using the natural breaks (Jenks) method, and the classification threshold is obtained. (a) Beijing in 2010. (b) Beijing in 2011. (c) Dalian in 2011. (d) Tel Aviv-Yafo in 2011.
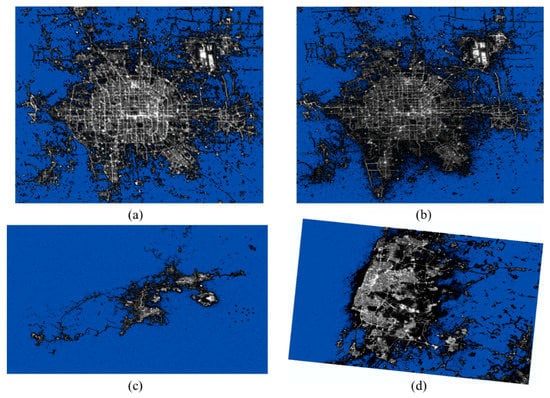
Figure 8.
Removing the background values of NTL images in each study area based on the natural breaks (Jenks) method. The blue areas represent the background areas. (a) The ISS grayscale image of Beijing in 2010 after removing the background value. (b) The ISS grayscale image of Beijing in 2011 after removing the background value. (c) The ISS grayscale image of Dalian in 2011 after removing the background value. (d) The ISS grayscale image of Tel Aviv-Yafo in 2011 after removing the background value. (This image is rotated to keep each image aligned with north up and east at right.).
2.2.4. Test and Verification Methods
In this paper, the correlation coefficient () and root mean square error () of four linear regression models are calculated, and then the , and regression coefficient (a and b) of the regression model are tested. and of each regression model in each study area were calculated respectively, which are defined as:
where is the DN value of ISS target grayscale image after radiation normalization, is the DN value of reference DMSP/OLS image, is the mean DN value of reference DMSP/OLS image, and is the number of pseudo-invariant feature points.
The feasibility and correctness of the normalization method are verified by the combination of qualitative analysis and quantitative test. In addition to the visual effect comparison, the DN value of the normalized ISS grayscale image is compared with that of the DMSP/OLS NTL remote sensing panchromatic image quantitatively. The spatial resolution of the ISS image is quite different from that of the DMSP/OLS image, so the average nighttime light index () in the study area is used instead of the total nighttime light index () to test the normalization result. In order to improve the comparability of radiance between different study areas, the background value is removed when the mean DN value of the study area is calculated.
where is the pixel radiation value of each grid unit in the region; is the number of pixels in the region; is the total nighttime light index in the region; is the average nighttime light index in a region.
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Linear Regression Results
30 pseudo-invariant feature points of each study area were selected to build the regression model between the pixel DN value of ISS NTL target image and DMSP/OLS NTL reference image (Figure 9). Figure 9a,b show the scatter distribution of PIF points on the target image and reference image of Beijing in 2010 and 2011. Figure 9c shows the scatter distribution of PIF points on the target image and reference image of Dalian in 2011. Figure 9d shows the scatter distribution of PIF points on the target image and reference image of Tel Aviv-Yafo in 2011. Table 2 shows the correlation coefficient (R2) and root mean square error (RMSE) of each regression model. The significance of the four regression models is less than 0.05, indicating that all the four models have passed the F-statistic test, and the models have statistical significance. The correlation coefficients are all greater than 0.7, it indicates that the regression models are reasonable.
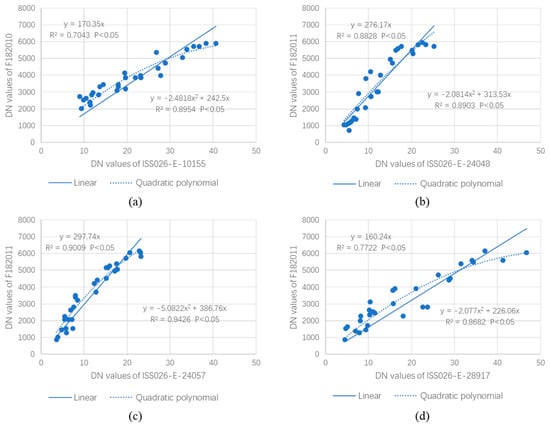
Figure 9.
The regression model between the pixel DN values of ISS RGB NTL target image and DMSP/OLS NTL reference image. (a) The ISS grayscale image and reference image of Beijing in 2010. (b) The ISS grayscale image and reference image of Beijing in 2011. (c) The ISS grayscale image and reference image of Dalian in 2011. (d) The ISS grayscale image and reference image of Tel Aviv-Yafo in 2011.

Table 2.
Regression model coefficients of the target image and reference image.
From the fitting coefficients of linear regression models, the correlation coefficient of Dalian NTL images in 2011 is the highest, followed by Beijing NTL images in 2011 and Tel Aviv-Yafo in 2011, and finally Beijing NTL images in 2010. From the fitting coefficients of univariate quadratic polynomial regression models, the correlation coefficient of Dalian NTL images in 2011 is the highest, followed by Beijing NTL images in 2010 and in 2011, and finally Tel Aviv-Yafo NTL images in 2011.
It can be seen from Table 2 that the quadratic polynomial fitting results between the four target images and their corresponding reference images are better than the linear fitting results. However, the quadratic polynomial is subject to over-fitting, which will increase the uncertainty of the fitting results. This is because the DMSP/OLS NTL image pixels are subject to saturation, whereas the ISS NTL image pixels are rarely saturated. Further explanation is provided in Section 3.2.
There are obvious linear and quadratic polynomial relationships between the target image and the reference image. Beijing and Tel Aviv-Yafo have a similar range of DN values at pseudo-invariant feature points on ISS RGB NTL images in 2011 and the regression model coefficients of NTL image of Beijing and Tel Aviv-Yafo in the same year are also similar, which may be due to the similar degree of economic development and population density between the two cities. Dalian and Tel Aviv-Yafo are both coastal cities, but their urban built-up area proportion and development mode are different, so the regression coefficient of their regression model is obviously different. The nighttime lights of Beijing and Tel Aviv-Yafo are significantly brighter than those of Dalian in the evening peak, which may be the reason for the difference of proportion and population density of urban built-up areas. In addition to the reason for different years, the local time of the two ISS NTL images in Beijing is also different. ISS026-E-10155 was photographed at 10 p.m. Beijing time, whereas ISS026-E-24048 was filmed at 3 a.m. Beijing time during the Spring Festival in China. The reason for the difference of image regression between 2010 and 2011 in the Beijing area is the camera shooting difference of ISS RGB NTL images and the change of nighttime light with time.
Generally speaking, the fit of the regression model of Chinese cities with large urban areas is better than that of Tel Aviv-Yafo with its small urban area. A city with a large area has the advantage of a large fault tolerance rate, which can offset some errors.
3.2. Visual Effect of Radiation Normalization Results
In order to evaluate the radiation normalization effect of ISS NTL images, we evaluate them from two aspects: visual qualitative analysis and DN values quantitative analysis. Although the correlation coefficient of the quadratic polynomial model in the above experimental results is higher, because the DN value range (0–255) of the ISS image is not fully covered, the over-fitting phenomenon of the quadratic polynomial is obvious. That is to say, at higher DN values, the normalized DN values may decrease or even appear negative, which does not conform to the actual situation, so we choose the linear regression model as the relative radiation normalization model. The linear model, which is the best relative radiation normalization model obtained from the above experimental results, is used to normalize the ISS NTL images of red, green, and blue bands in each study area, and then these three stretched band images are synthesized into a new normalized image. From the qualitative comparison of the visual effect of Figure 10, the relative radiation normalized ISS NTL image has a clearer color, higher contrast and better visual effect.
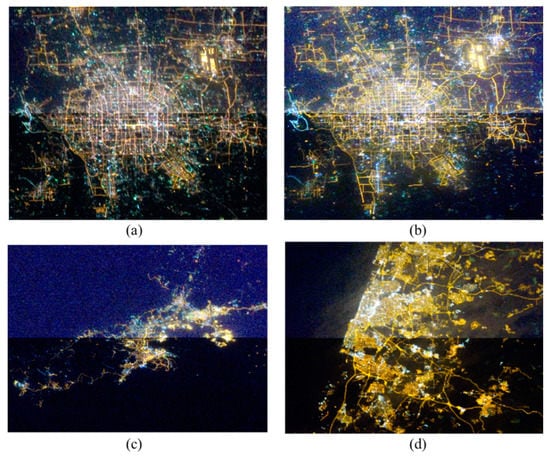

Figure 10.
Relative radiation normalization results. In each panel, the upper half represents the image before normalization, while the lower half represents the result after normalization. (a) The ISS nighttime light image of Beijing in 2010. (b) The ISS nighttime light image of Beijing in 2011. (c) The ISS nighttime light image of Dalian in 2011. (d) The ISS nighttime light image of Tel Aviv-Yafo in 2011.
Although the time gap is very short, it still can be observed that the brightness of some roads changed in these two ISS NTL images of the Beijing study area. We observed that the nighttime lights in the Beijing area and Dalian area are mainly white, and the nighttime lights in Tel Aviv-Yafo are mainly yellow, which may be due to the different types of lighting lamps in these three cities.
3.3. Quantitative Analysis of Radiation Normalization Results
The ISS NTL grayscale image of the study area is normalized according to the relative radiation normalization model obtained in this paper, and then compared with the DMSP/OLS NTL remote sensing panchromatic image of the same area in the same year. Figure 11 shows the comparison of the pixel DN value at the same location between the normalized ISS NTL grayscale image and the same year DMSP/OLS NTL remote sensing image. The results show that the trend of DN values of the ISS NTL image and DMSP/OLS NTL remote sensing image in the same position are basically the same. The peak position of DN value of two images is the same, and the valley position is the same. The pixel DN value of radiation normalized ISS NTL grayscale image fits well with DMSP/OLS at the low value and shows the difference of DN value of different pixels at the high value. The high-resolution ISS NTL image without the phenomenon of pixel saturation can also reflect the details of NTL brightness that DMSP/OLS NTL remote sensing image cannot express.
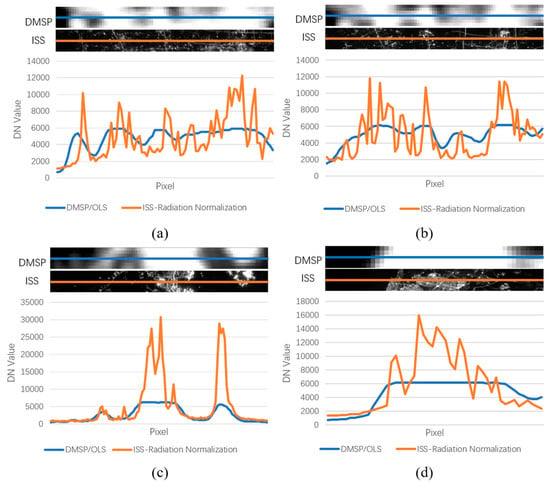
Figure 11.
Comparison of Digital Number (DN) value of the ISS NTL grayscale image and DMSP/OLS NTL remote sensing panchromatic image at the same location after relative radiation normalization. (a) North of Beijing in 2010. (b) North of Beijing in 2011. (c) Midland of Dalian in 2011. (d) North of Tel Aviv-Yafo in 2011.
Since the background value will reduce the average DN values of nighttime lights in the study areas, we remove the background influence, and then calculate the average nighttime light index (ANTL). The average DN values of radiation normalized ISS NTL grayscale image and three single-band images still maintain the relative size of the original image in different study areas (Table 3). The DN values of ISS NTL images are normalized to the same level as DMSP/OLS NTL images. Therefore, this relative radiation normalization method keeps the difference between different spectral of the original ISS NTL images, and reduces the radiation difference between the original ISS NTL images and the DMSP/OLS time series NTL remote sensing images in the same year.

Table 3.
The Average Nighttime Light Index (ANLI) of the ISS NTL images before and after linear radiation normalization in each study area.
According to the relative radiation normalization results in Table 3, the mean DN value of each normalized ISS image is significantly higher than that of DMSP/OLS. This is due to the phenomenon of pixel saturation in DMSP/OLS, and the brightness details of high brightness areas in the city centers cannot be displayed in DMSP. The blue curves in Figure 11 illustrate the saturation of the DMSP/OLS images. It also can be seen that the radiation brightness trend of ISS NTL grayscale images after relative radiation normalization is relatively consistent with that of the DMSP/OLS NTL images. The nighttime radiance of Beijing is the strongest, followed by Tel Aviv-Yafo, and Dalian is the weakest in the same year, which is related to the relative prosperities of different cities. However, the blue light radiation brightness of Dalian is much higher than that of Tel Aviv-Yafo, which shows that in the case of similar red and green wavelengths. The main reason may be because of the different lighting facilities in the two cities. Not only that, the nighttime light radiation brightness of Beijing in 2011 is higher than that in 2010, especially in the red band and green band. This may be due to the fact that the ISS NTL image of Beijing in 2011 was taken during the Spring Festival, and the use of decorative lights made its red band and green band much higher than that in 2010.
3.4. Comparison of Nighttime Lighting in Typical Public Space Lighting Areas between Different Cities
The upward-directed radiance has spatial heterogeneity among different objects. The purpose of relative radiation normalization of the ISS NTL image is to be able to directly compare the radiance values of light sources in different parts of the world through the relative means of the normalization procedure.
In this paper, we choose four kinds of public space lighting areas among different cities in 2011: roads, residential areas, landscape areas and commercial areas to compare the nighttime lighting [57]. According to Google maps, a section of the main road at the edge of each city that is less affected by other lighting radiation was selected (Figure 12). We selected a section of S214 road in Beijing, G202 road in Dalian, and Ayalon Darom road in Tel Aviv-Yafo. The typical residential areas in the city center were Hepingli Community in Beijing, Chunliu Street Community in Dalian, Jabot insky Street Community in Tel Aviv-Yafo. The Olympic Forest Park in Beijing, Xinghai Square in Dalian and Hayarkon Park in Tel Aviv-Yafo were selected as landscape areas. The Financial Street in Beijing, Xinghai Exhibition Center in Dalian, and Midtown Commerce in Tel Aviv-Yafo were selected as commercial areas.
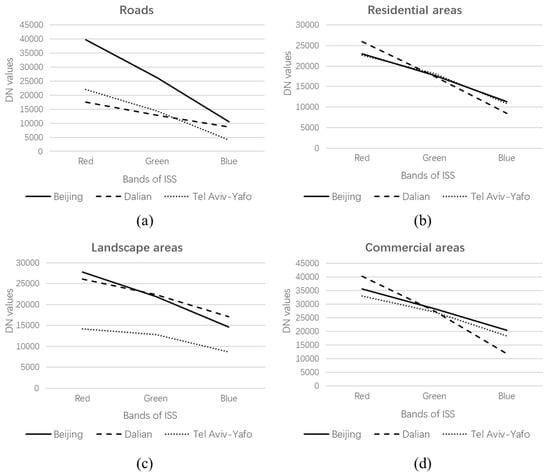
Figure 12.
Comparison of nighttime light radiation brightness after relative radiation normalization of different light sources in different study areas. (a) Roads. (b) Residential areas. (c) Landscape areas. (d) Commercial areas.
The nighttime light radiation brightness of road, residential area, landscape, and commercial area after relative radiation normalization in different research areas were analyzed based on the multispectral ISS NTL images. We can see that the nighttime light spectrum curve of the typical objects of the three study areas after radiation normalization is close. The nighttime light radiation brightness of the typical objects in Beijing is higher than that of the other two study areas after radiation normalization, which is the same as shown in Table 3. The nighttime light radiation of residential areas and commercial areas in three study areas is similar in the visible light band in 2011. The nighttime road radiation in Beijing is significantly higher than that in the other two study areas. It may be the roads in Beijing lit more brightly than in the other cities, or it may also be related to the lamp spacing and traffic flow. The nighttime landscape radiation in Tel Aviv-Yafo is significantly lower than that in the other two study areas, which may be due to landscape lighting differences in different countries. The relative radiation normalization makes the ground objects in different study areas have radiation comparability.
4. Discussion
Compared with the DMSP/OLS NTL remote sensing data, as a multispectral NTL image with mid-high spatial resolution, ISS NTL imagery plays a unique role in the research of small-scale urban planning, allocation of lighting resources and blue light pollution. ISS NTL imagery can also clearly show the distribution of the urban road traffic network and effectively highlight the location of important urban transport hubs.
As an important part of urban life, night lighting is closely related to human activities. The rapid development of NTL remote sensing technology provides an important new idea and way for the planning of smart cities. High spatial resolution NTL remote sensing products can be used to objectively and efficiently analyze urban lighting conditions and urban–rural development differences, and reflect its unique social and economic value in the process of developing people-oriented intelligent lighting systems and intelligent urban–rural resource allocation systems. It is a trend to study light pollution and urban intelligent lighting by using medium and high spatial resolution multispectral NTL images from platforms such as the International Space Station.
The relative radiation normalization of ISS NTL images makes the radiance of different cities comparable, which is conducive to the use and comparative analysis of cross-regional images, and improves the utility of ISS NTL images. At the same time, relative radiation normalization plays a positive role in the radiance contrast between discontinuous time-series ISS NTL images in the same region. The radiation-normalized ISS NTL images still have the characteristics of multispectral and high spatial resolution, which is conducive to the analysis of urban lighting attributes and impact on people’s lives.
In this paper, the relative radiation normalization results of ISS NTL images based on the readily available global DMSP/OLS time series NTL remote sensing annual composite product still have some problems and uncertainties:
- The DMSP/OLS images are calibrated images, and ISS RGB NTL imagery attempts to reproduce the sensitivity of the human eye with logarithmic response, which has the loss of linearity, and both data have tilt angle problem. Thus, they bring uncertainty to the relative radiation normalization of ISS NTL images.
- The spatial resolution difference between ISS and DMSP/OLS NTL images is large, which also affects the accuracy of relative radiation normalization.
- The DMSP/OLS images have pixel saturation, whereas ISS images have almost none, and this method uses artificial recognition of pseudo-invariant feature points, and the selection of data points has certain subjectivity.
- There must be some residual flux stemming from the fact that the gray conversion formula doesn’t perfectly match the DMSP-OLS sensitivity curve, which will introduce uncertainty to the relative radiation normalization.
- VIIRS/DNB time series NTL data is the successor of DMSP/OLS, and its spatial and temporal resolution are better than that of DMSP/OLS. Thus, it can be considered for the relative radiation correction of ISS NTL images after 2013.
- The ISS NTL photos are essentially instantaneous images, whereas the cloud-free composite images may be composed of individual frames taken over longer timescales of days to years, which will reduce the accuracy of relative radiation normalization.
The method proposed in this paper is universal to the relative radiation normalization of all ISS RGB NTL images. However, due to the above problems, the relative radiation normalization model obtained by this method has limitations, which affects the relative radiation normalization accuracy of ISS NTL images. In the future research, the relative radiation normalization of the ISS NTL images will be realized by combining the multispectral image with higher temporal and spatial resolution and the ground optical measurement data, so as to improve the radiation correction accuracy.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, a radiation normalization method of the ISS RGB NTL image is proposed. The DMSP/OLS time series NTL annual composite product was used to study the relative radiation normalization of the ISS NTL image. The relative radiation normalization model is established by identifying the pseudo-invariant feature points. The results show that there is a good linear and quadratic polynomial relationship between the ISS NTL image and DMSP/OLS NTL image. The correlation coefficients of pseudo-invariant feature points are more than 0.86, which shows that it is feasible to relative radiation normalize the ISS NTL image by the pseudo-invariant feature and regression method. The radiation normalization results are evaluated from the visual appearance and the DN value of study areas, and the ideal results are obtained, which provides a solution for improving the utility and comparability of the ISS NTL image. The radiation brightness of the relative radiation normalized ISS NTL image has the same trend as that of the DMSP/OLS NTL image. The ISS NTL image not only retains the multispectral and high-resolution characteristics of the study area, but also shows clear radiant brightness details in the light saturation position of the DMSP/OLS image. The ISS NTL multispectral photos without time continuity and geographical coordinates are placed on the same radiation level. It can effectively improve the radiation consistency of the ISS NTL image and realize the radiation brightness comparability between ISS NTL images in different regions and at different times.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.J. (Weili Jiao) and S.W.; methodology, T.L. and S.W.; validation, S.W., W.J. (Weili Jiao), H.L. and L.B.; data curation, S.W.; writing—original draft preparation, S.W.; writing—review and editing, W.J. (Weili Jiao), T.L., H.L., W.J. (Wei Jiang), B.A.P. and M.L.; supervision, W.J. (Weili Jiao), T.L. and H.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Programs of China (grant number 2017YFE0125900), the program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 61731022), and National Science Foundation for Young Scientists of China (grant number 61701495).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank editors and the anonymous reviewers for their valuable and constructive comments to improve our manuscript. The ISS nighttime light images were downloaded from the website: https://eol.jsc.nasa.gov. The DMSP/OLS nighttime light images used in this paper were downloaded from doi:10.1109/TGRS.2016.2572724.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Li, D.; Li, X. An Overview on Data Mining of Nighttime Light Remote Sensing. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2015, 44, 591–601. [Google Scholar]
- Levin, N.; Kyba, C.C.; Zhang, Q.; De Miguel, A.S.; Román, M.O.; Li, X.; Portnov, B.A.; Molthan, A.L.; Jechow, A.; Miller, S.D.; et al. Remote sensing of night lights: A review and an outlook for the future. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.E.; Kihn, E.A.; Kroehl, H.W.; Davis, E.R.; Davis, C.W. Relation between satellite observed visible-near infrared emissions, population, economic activity and electric power consumption. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1997, 18, 1373–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, D.J. Multi-scale analysis of the relationship between economic statistics and DMSP-OLS night light images. GIScience Remote Sens. 2013, 50, 483–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, H.; Chen, X.; Li, C. Potential of NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light Imagery for Modeling the Regional Economy of China. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 3057–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Miguel, A.S.; Zamorano, J.; Gómez, C.J.; Pascual, S. European street lighting power consumption estimation using DMSP/OLS images. In Proceedings of the ALAN Conference, Berlin, Germany, 28–30 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Small, C.; Pozzi, F.; Elvidge, C. Spatial analysis of global urban extent from DMSP-OLS night lights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 96, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.; Zhizhin, M.; Hsu, F.C.; Ghosh, T. VIIRS night-time lights. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 5860–5879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirmer, A.; Gallemore, C.; Liu, T.; Magle, S.; Dinello, E.; Ahmed, H.; Gilday, T. Mapping behaviorally relevant light pollution levels to improve urban habitat planning. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Shao, X.; Uprety, S. Detecting Light Outages After Severe Storms Using the S-NPP/VIIRS Day/Night Band Radiances. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 1582–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, D. Can night-time light images play a role in evaluating the Syrian Crisis? Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 6648–6661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; He, G.; Long, T.; Wang, C.; Ni, Y.; Ma, R. Assessing Light Pollution in China Based on Nighttime Light Imagery. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; He, G.; Leng, W.; Long, T.; Wang, G.; Liu, H.; Peng, Y.; Yin, R.; Guo, H. Characterizing Light Pollution Trends across Protected Areas in China Using Nighttime Light Remote Sensing Data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; He, G.; Long, T.; Guo, H.; Yin, R.; Leng, W.; Liu, H.; Wang, G. Potentiality of Using Luojia 1-01 Nighttime Light Imagery to Investigate Artificial Light Pollution. Sensors 2018, 18, 2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kloog, I.; Haim, A.; Stevens, R.G.; Barchana, M.; Portnov, B.A. Light at Night Co-distributes with Incident Breast but not Lung Cancer in the Female Population of Israel. Chronobiol. Int. 2008, 25, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waluda, C.M.; Yamashiro, C.; Elvidge, C.D.; Hobson, V.R.; Rodhouse, P.G. Quantifying light-fishing for Dosidicus gigas in the Eastern Pacific using satellite remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 91, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waluda, C.M.; Griffiths, H.J.; Rodhouse, P.G. Remotely sensed spatial dynamics of the Illex argentinus fishery, Southwest Atlantic. Fish. Res. 2008, 91, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyofuji, H.; Saitoh, S. Use of nighttime visible images to detect Japanese common squid Todarodes pacificus fishing areas and potential migration routes in the Sea of Japan. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2004, 276, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, S.E.; Wagner, S.; Burch, J.B.; Bayakly, R.; Vena, J.E. A case-referent study: Light at night and breast cancer risk in Georgia. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2013, 12, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, N.; Tatem, A.J.; Ferrari, M.J.; Grais, R.F.; Djibo, A.; Grenfell, B.T. Explaining Seasonal Fluctuations of Measles in Niger Using Nighttime Lights Imagery. Science 2011, 334, 1424–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Chen, Z.; Yu, B.; Li, Q.; Wang, C.; Li, B.; Wu, B.; Li, Y.; Wu, J. Automated Extraction of Street Lights from JL1-3B Nighttime Light Data and Assessment of Their Solar Energy Potential. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Weng, Q.; Huang, L.; Wang, K.; Deng, J.; Jiang, R.; Ye, Z.; Gan, M. A new source of multi-spectral high spatial resolution night-time light imagery—JL1-3B. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 215, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Ziskin, D.; Baugh, K.E.; Tuttle, B.T.; Ghosh, T.; Pack, D.W.; Erwin, E.H.; Zhizhin, M. A Fifteen Year Record of Global Natural Gas Flaring Derived from Satellite Data. Energies 2009, 2, 595–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Miguel, A.S.; Castaño, J.G.; Zamorano, J.; Pascual, S.; Angeles, M.; Cayuela, L.; Martinez, G.M.; Challupner, P.; Kyba, C.C.M. Atlas of astronaut photos of Earth at night. Astron. Geophys. 2014, 55, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Miguel, A.S. Variación Espacial, Temporal y Espectral de la Contaminación Lumínica y sus Fuentes: Metodología y Resultados. Ph.D. Thesis, Familia Sánchez de Miguel, Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Madrid, Spain, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- de Miguel, A.S.; Zamorano, J.; Pascual, S.; López Cayuela, M.; Ocaña, F.; Challupner, P.; Gómez Castaño, J.; Fernández-Renau, A.; Gómez, J.A.; de Miguel, E. ISS Nocturnal Images as a Scientific Tool Against Light Pollution: Flux Calibration and Colors. In Highlights of Spanish A Strophysics VII; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 916–919. [Google Scholar]
- De Miguel, A.S.; Kyba, C.C.M.; Aubé, M.; Zamorano, J.; Cardiel, N.; Tapia, C.; Bennie, J.; Gaston, K.J. Colour remote sensing of the impact of artificial light at night (I): The potential of the International Space Station and other DSLR-based platforms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 224, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybnikova, N.A.; Portnov, B.A. Population-level study links short-wavelength nighttime illumination with breast cancer incidence in a major metropolitan area. Chronobiol. Int. 2018, 35, 1198–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Saenz, A.; De Miguel, A.S.; Espinosa, A.; Valentin, A.; Aragonés, N.; Llorca, J.; Amiano, P.; Sánchez, V.M.; Guevara, M.; Capelo, R.; et al. Evaluating the Association between Artificial Light-at-Night Exposure and Breast and Prostate Cancer Risk in Spain (MCC-Spain Study). Environ. Health Perspect. 2018, 126, 047011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauwels, J.; Le Viol, I.; Azam, C.; Valet, N.; Julien, J.-F.; Bas, Y.; LeMarchand, C.; De Miguel, A.S.; Kerbiriou, C. Accounting for artificial light impact on bat activity for a biodiversity-friendly urban planning. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 183, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, N.; Duke, Y. High spatial resolution night-time light images for demographic and socio-economic studies. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 119, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotarba, A.Z.; Aleksandrowicz, S. Impervious surface detection with nighttime photography from the International Space Station. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 176, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuffer, M.; Pfeffer, K.; Sliuzas, R.; Taubenböck, H.; Baud, I.; Van Maarseveen, M.F.A.M. Capturing the Urban Divide in Nighttime Light Images from the International Space Station. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 2578–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicht, M.; Kuffer, M. The continuous built-up area extracted from ISS night-time lights to compare the amount of urban green areas across European cities. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 52, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazor, T.; Levin, N.; Possingham, H.P.; Levy, Y.; Rocchini, D.; Richardson, A.J.; Kark, S. Can satellite-based night lights be used for conservation? The case of nesting sea turtles in the Mediterranean. Biol. Conserv. 2013, 159, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, L.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Liu, L. An improved method of night-time light saturation reduction based on EVI. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 4114–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; He, S.; Peng, J.; Li, W.; Zhong, X. Intercalibration of DMSP-OLS night-time light data by the invariant region method. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 7356–7368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, F.; Li, H. Automatic intercalibration of night-time light imagery using robust regression. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 4, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Pandey, B.; Seto, K.C. A Robust Method to Generate a Consistent Time Series from DMSP/OLS Nighttime Light Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 5821–5831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, F.-C.; Baugh, K.E.; Ghosh, T.; Zhizhin, M.; Elvidge, C.D. DMSP-OLS Radiance Calibrated Nighttime Lights Time Series with Intercalibration. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 1855–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Cao, C.Y.; Zhang, B.; Qiu, S.; Elvidge, C.D.; Von, H.M. Radiometric calibration of DMSP-OLS Sensor using VIIRS Day/Night Band. In Proceedings of the SPIE 9264, Earth Observing Missions and Sensors: Development, Implementation, and Characterization III 2014, Beijing, China, 19 November 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chand, T.R.K.; Badarinath, K.; Elvidge, C.D.; Tuttle, B.T. Spatial characterization of electrical power consumption patterns over India using temporal DMSP-OLS night-time satellite data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 647–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyytimäki, J.; Tapio, P.; Assmuth, T. Unawareness in environmental protection: The case of light pollution from traffic. Land Use Policy 2012, 29, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, S.; Câmara, G.; Monteiro, A.M.V.; Quintanilha, J.A.; Elvidge, C.D. Estimating population and energy consumption in Brazilian Amazonia using DMSP night-time satellite data. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2005, 29, 179–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Liu, S.; Cai, J.; Lu, X.; Nielsen, C.P. Spatial pattern and its evolution of Chinese provincial population: Methods and empirical study. J. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 1507–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Yang, Y.; Jin, F. China’s economic development stage and its spatio-temporal evolution: A prefectural-level analysis. J. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 23, 297–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schott, J.R.; Salvaggio, C.; Volchok, W.J. Radiometric scene normalization using pseudoinvariant features. Remote Sens. Environ. 1988, 26, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caselles, V.; García, M.J.L. An alternative simple approach to estimate atmospheric correction in multitemporal studies. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1989, 10, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, F.; Strebel, D.; Nickeson, J.; Goetz, S.J. Radiometric rectification: Toward a common radiometric response among multidate, multisensor images. Remote Sens. Environ. 1991, 35, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Peng, F. A method of selective image graying. Comput. Eng. 2006, 32, 198–200. [Google Scholar]
- Grundland, M.; Dodgson, N.A. Decolorize: Fast, contrast enhancing, color to grayscale conversion. Pattern Recognit. 2007, 40, 2891–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Yuan, D.; Weerackoon, R.D.; Lunetta, R.S. Relative Radiometric Normalization of Landsat Multispectral Scanner (Mss) Data Using an Automatic Scattergram-Controlled Regression. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1995, 61, 1255–1260. [Google Scholar]
- Canty, M.J.; Nielsen, A.A.; Schmidt, M. Automatic radiometric normalization of multitemporal satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 91, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canty, M.J.; Nielsen, A.A. Automatic radiometric normalization of multitemporal satellite imagery with the iteratively re-weighted MAD transformation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 1025–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, L.; Lin, H.; Liao, M. Automatic relative radiometric normalization using iteratively weighted least square regression. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Bian, J.H.; Li, A.N.; Feng, W.L.; Lei, G.B.; Zhang, Z.J.; Zuo, J.Q. Consistent intercalibration of nighttime light data between DMSP/OLS and NPP/VIIRS in the China–Pakistan Economic Corridor. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 24, 149–160. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Liu, H.; Song, W.; Yu, B.; Xiu, C. Normalization of time series DMSP-OLS nighttime light images for urban growth analysis with Pseudo Invariant Features. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 128, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).