Time Reversal Linearly Constrained Minimum Power Algorithm for Direction of Arrival Estimation in Diffuse Multipath Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
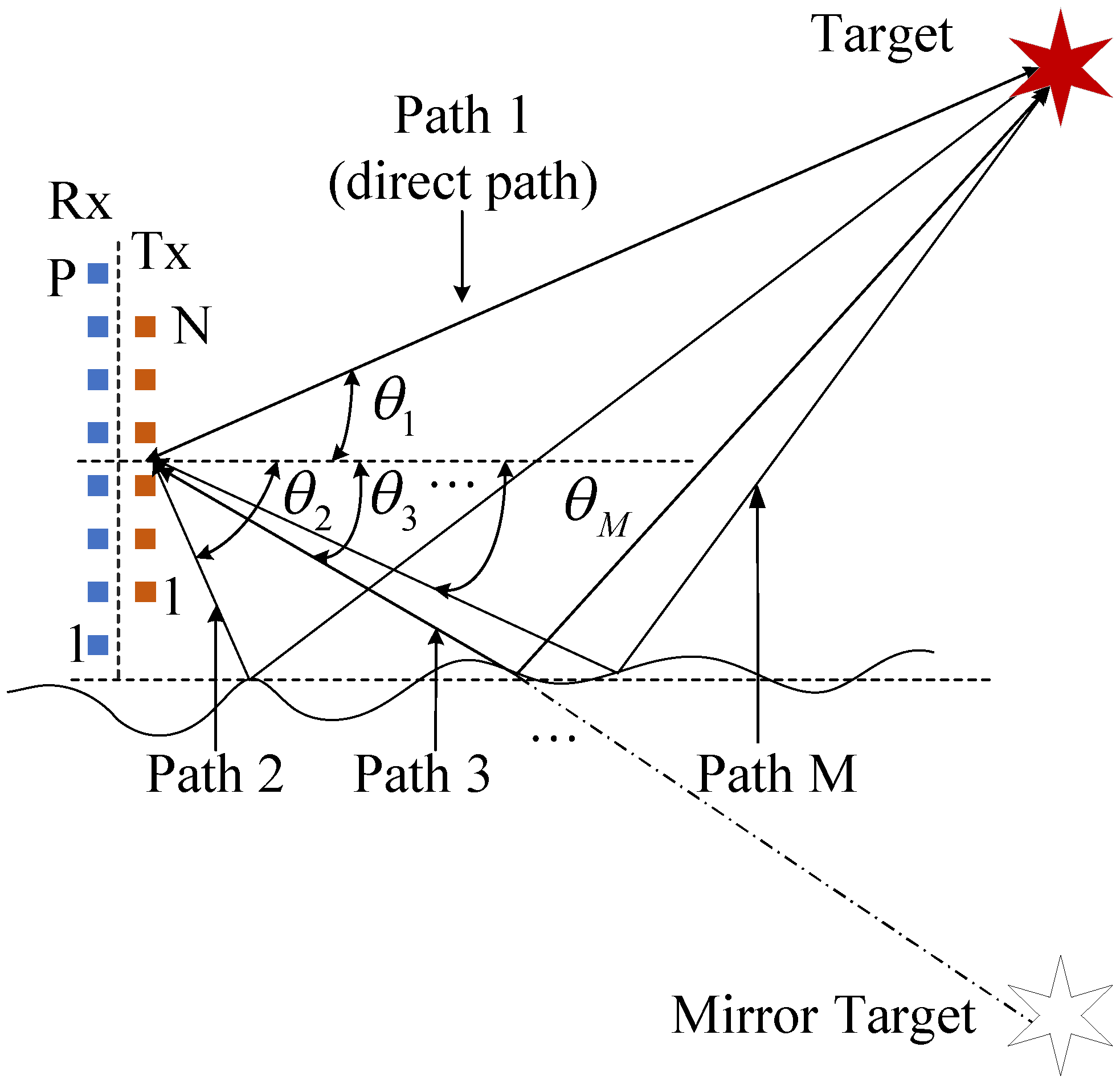
2. Multipath System Model
2.1. MIMO Radar
2.2. TR MIMO Radar
3. TR LCMP Algorithm
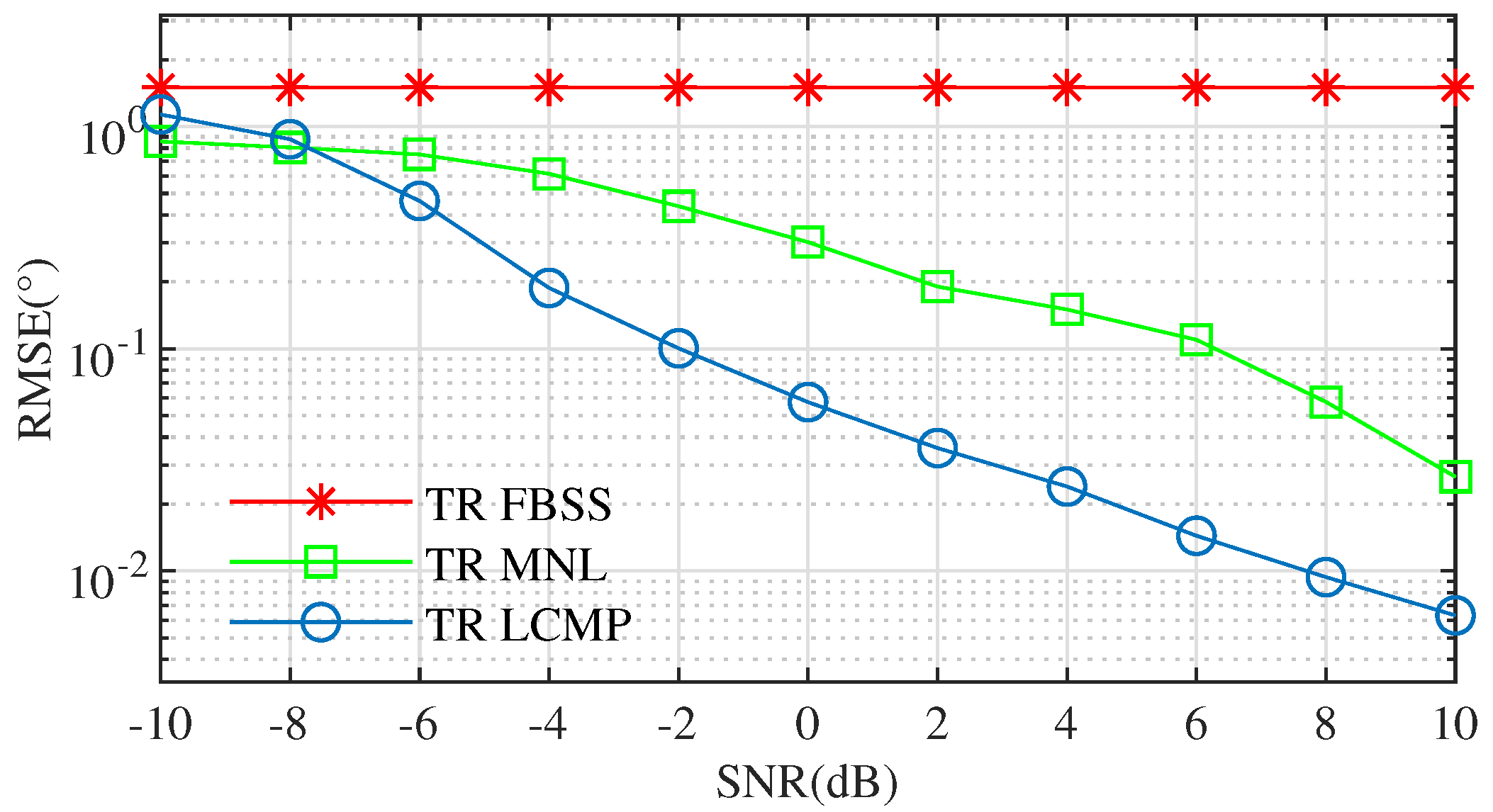
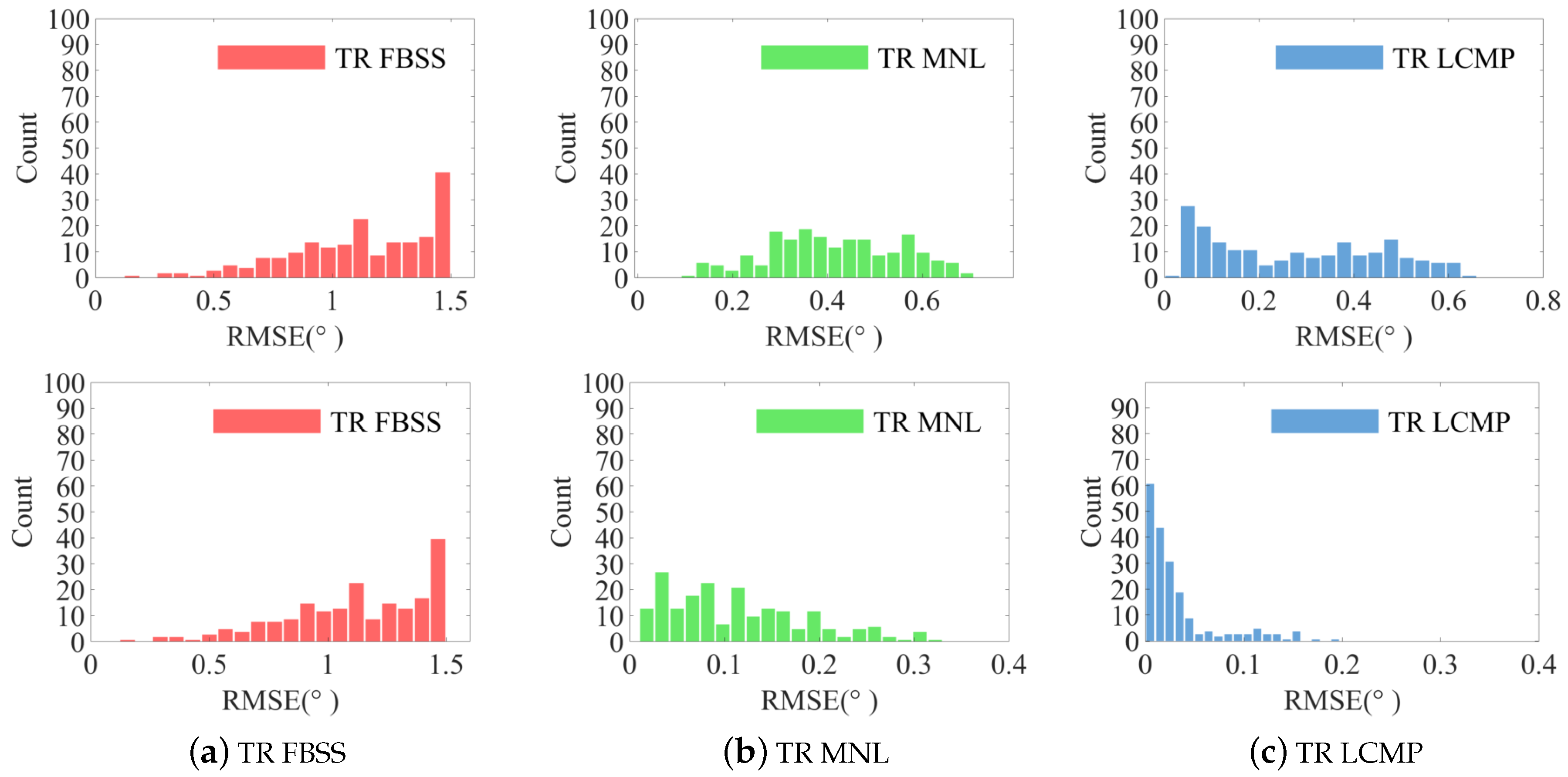
4. Simulation Results
4.1. RMSE vs. SNRs
4.2. RMSE Histograms
4.3. RMSE of Different DOAs
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burkholder, R.J.; Pino, M.R.; Obelleiro, F. Low angle scattering from 2-D targets on a time-evolving sea surface. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 1185–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Chen, J. Low-angle reflectivity modeling of land clutter. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2006, 3, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Xia, X.; Zhang, L.; Jiu, B. Projection Techniques for Altitude Estimation Over Complex Multipath Condition-Based VHF Radar. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 2362–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Yang, E.; Ahn, S.; Chun, J. Adaptive beamforming for low-angle target tracking under multipath interference. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2014, 50, 2564–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, M. Time reversal of ultrasonic fields. I. Basic principles. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 1992, 39, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Thomas, J.; Fink, M. Time reversal of ultrasonic fields. Il. Experimental results. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 1992, 39, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, M. Time-Reversal Acoustics. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2008, 118, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, M.; Prada, C. Acoustic time-reversal mirrors. Inverse Probl. 2001, 17, R1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerbrat, E.; Prada, C.; Cassereau, D.; Fink, M. Ultrasonic nondestructive testing of scattering media using the decomposition of the time-reversal operator. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2002, 49, 1103–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakroun, N.; Fink, M.A.; Wu, F. Time reversal processing in ultrasonic nondestructive testing. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 1995, 42, 1087–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henty, B.E.; Stancil, D.D. Multipath-Enabled Super-Resolution for rf and Microwave Communication using Phase-Conjugate Arrays. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 93, 243904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerosey, G.; Rosny, J.D.; Tourin, A.; Derode, A.; Fink, M. Time reversal of wideband microwaves. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 34–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rosny, J.; Lerosey, G.; Fink, M. Theory of Electromagnetic Time-Reversal Mirrors. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2010, 58, 3139–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.D.; Mohan, A.S.; Abedin, M.J. Beamspace Time-Reversal Microwave Imaging for Breast Cancer Detection. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2013, 12, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Udpa, L.; Udpa, S.; Rothwell, E.J.; Deng, Y. A Time Reversal-Based Microwave Imaging System for Detection of Breast Tumors. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2019, 67, 2062–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Yang, M.; Chen, B.; Jin, Y. Estimation of direction of arrival by time reversal for low-angle targets. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2018, 54, 2675–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abduljabbar, A.M.; Yavuz, M.E.; Costen, F.; Himeno, R.; Yokota, H. Continuous Wavelet Transform-Based Frequency Dispersion Compensation Method for Electromagnetic Time-Reversal Imaging. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2017, 65, 1321–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuz, M.E.; Teixeira, F.L. Ultrawideband Microwave Sensing and Imaging Using Time-Reversal Techniques: A Review. Remote Sens. 2009, 1, 466–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.H.; Han, F.; Liu, K.J.R. Time-Reversal Wideband Communications. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2013, 20, 1219–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Monfared, S.; Determe, J.F.; Louveaux, J.; Doncker, P.D.; Horlin, F. Performance Analysis of Frequency Domain Precoding Time-Reversal MISO OFDM Systems. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2020, 24, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishler, E.; Haimovich, A.; Blum, R.; Chizhik, D.; Cimini, L.; Valenzuela, R. MIMO radar: An idea whose time has come. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE Radar Conference (IEEE Cat. No.04CH37509), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 29 April 2004; pp. 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Hu, G.; Zong, B.; Chen, M. DOA Estimation Using Multipath Echo Power for MIMO Radar in Low-Grazing Angle. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 6087–6094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Manikas, A. MIMO Radar with Array Manifold Extenders. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2019, 56, 1942–1954. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, J.; Nie, Z. Polarisation smoothing generalised MUSIC algorithm with PSA monostatic MIMO radar for low angle estimation. Electron. Lett. 2018, 54, 527–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Hu, G.; Lei, T. DOA estimation algorithms for low-angle targets with MIMO radar. Electron. Lett. 2016, 52, 652–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroozan, F.; Asif, A.; Jin, Y. Cramer-Rao bounds for time reversal mimo radars with multipath. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2016, 52, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Nie, Z.; Peng, S. Adaptive Time Reversal MUSIC Algorithm with Monostatic MIMO Radar for Low Angle Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Boston, MA, USA, 22–26 April 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.B.; Hu, G.P.; Shi, J.P.; Zhou, H. DOA estimation method for multi-path targets based on TR MIMO radar. J. Eng. 2019, 2019, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, J. Low angle estimation in diffuse multipath environment by time-reversal minimum-norm-like technique. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2017, 11, 1483–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroozan, F.; Asif, A. Time reversal MIMO radar for angle-Doppler estimation. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Statistical Signal Processing Workshop (SSP), Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 5–8 August 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 860–863. [Google Scholar]
- Sajjadieh, M.H.; Asif, A. Compressive sensing time reversal mimo radar: Joint direction and doppler frequency estimation. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2015, 22, 1283–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Moura, J.M.; O’Donoughue, N.; Harley, J. Single antenna time reversal detection of moving target. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Dallas, TX, USA, 14–19 March 2010; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 3558–3561. [Google Scholar]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiong, C.; Fan, C.; Huang, X. Time Reversal Linearly Constrained Minimum Power Algorithm for Direction of Arrival Estimation in Diffuse Multipath Environments. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3344. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12203344
Xiong C, Fan C, Huang X. Time Reversal Linearly Constrained Minimum Power Algorithm for Direction of Arrival Estimation in Diffuse Multipath Environments. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(20):3344. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12203344
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiong, Chao, Chongyi Fan, and Xiaotao Huang. 2020. "Time Reversal Linearly Constrained Minimum Power Algorithm for Direction of Arrival Estimation in Diffuse Multipath Environments" Remote Sensing 12, no. 20: 3344. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12203344
APA StyleXiong, C., Fan, C., & Huang, X. (2020). Time Reversal Linearly Constrained Minimum Power Algorithm for Direction of Arrival Estimation in Diffuse Multipath Environments. Remote Sensing, 12(20), 3344. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12203344




