Improved Method to Suppress Azimuth Ambiguity for Current Velocity Measurement in Coastal Waters Based on ATI-SAR Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
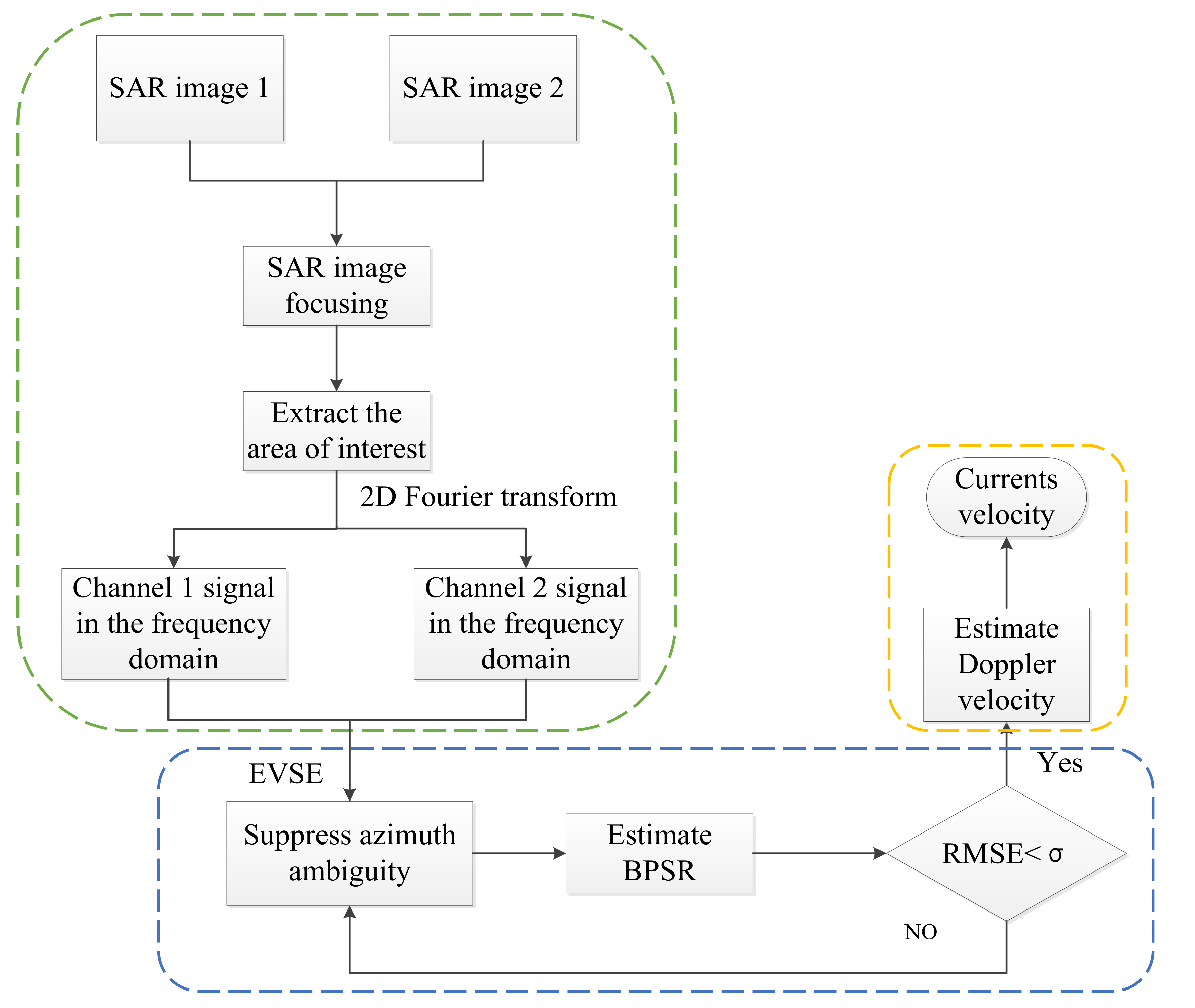
2.1. Overview of EVSE Analysis
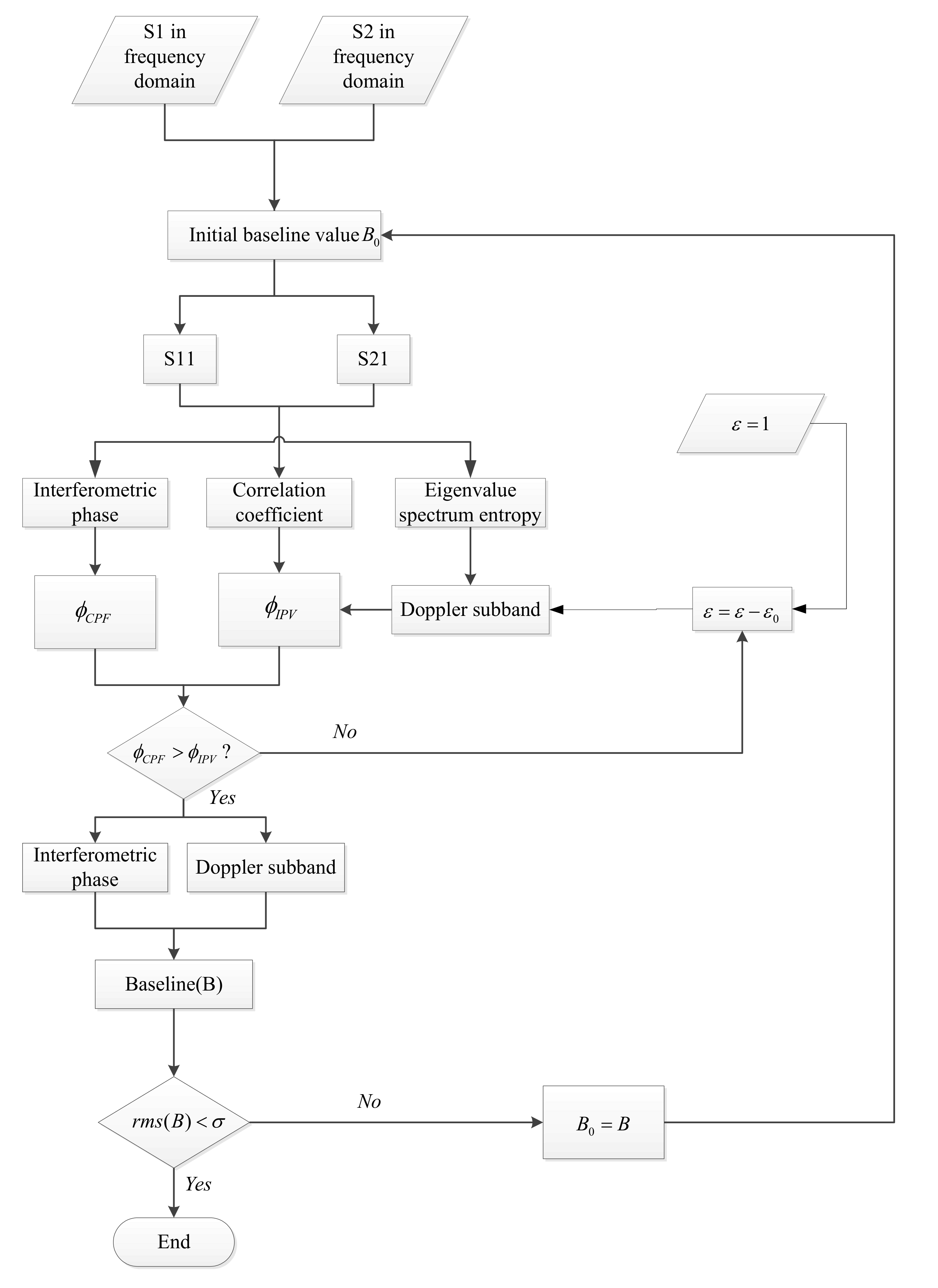
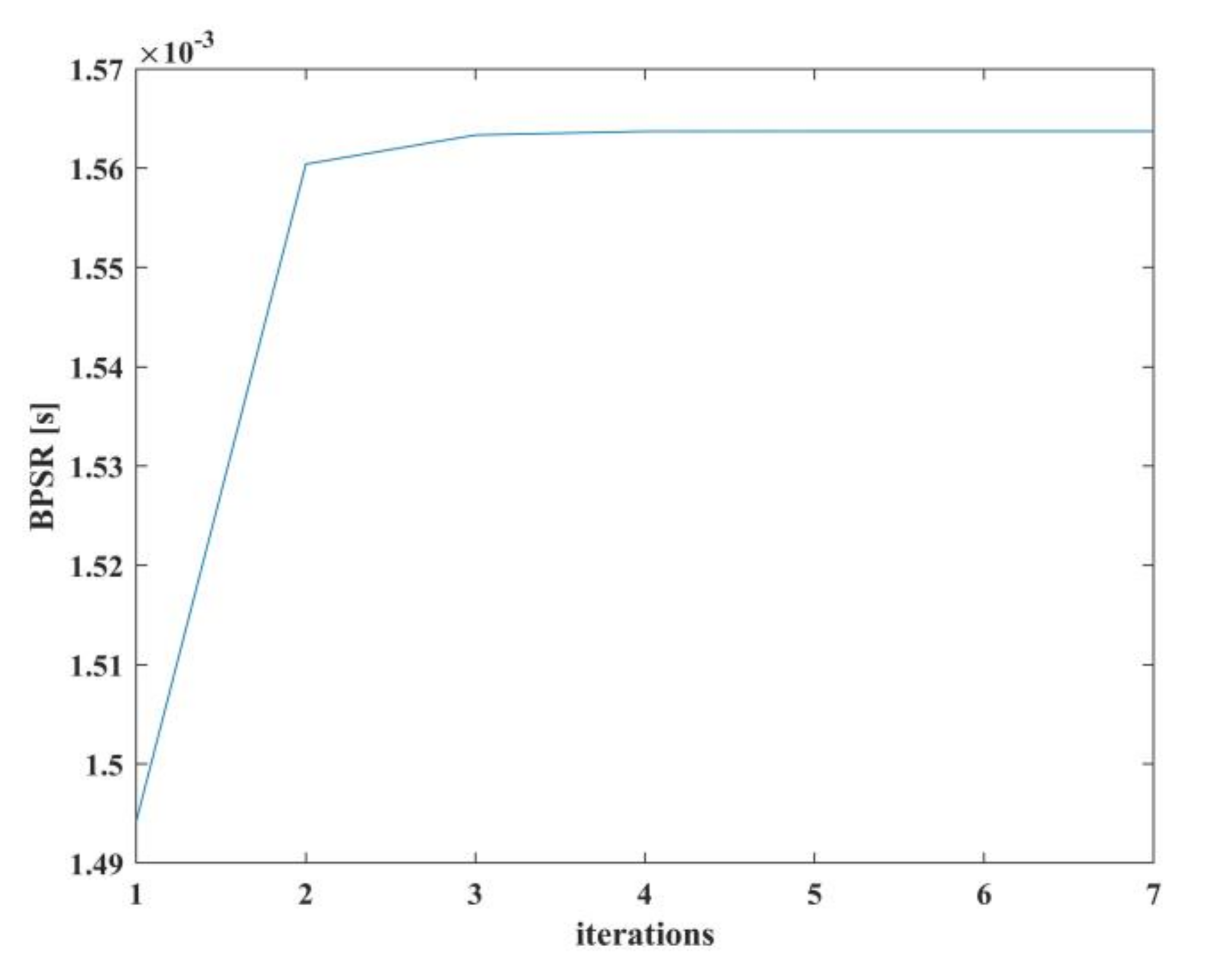
2.2. Alternate Iteration Algorithm for Azimuth Ambiguity Suppression and BPSR Estimation
2.3. Correction of IPV and CPF Based on EVSE Analysis
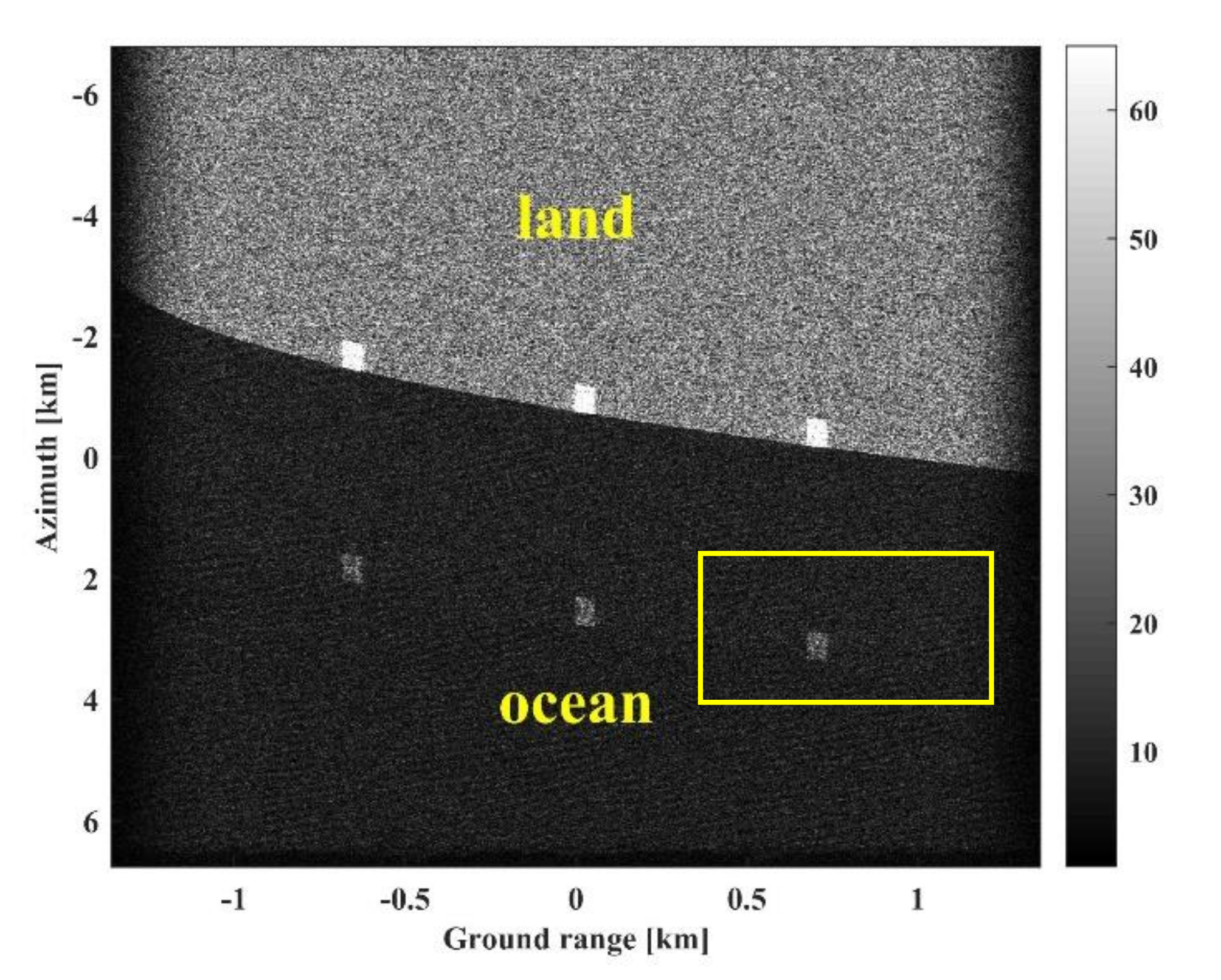
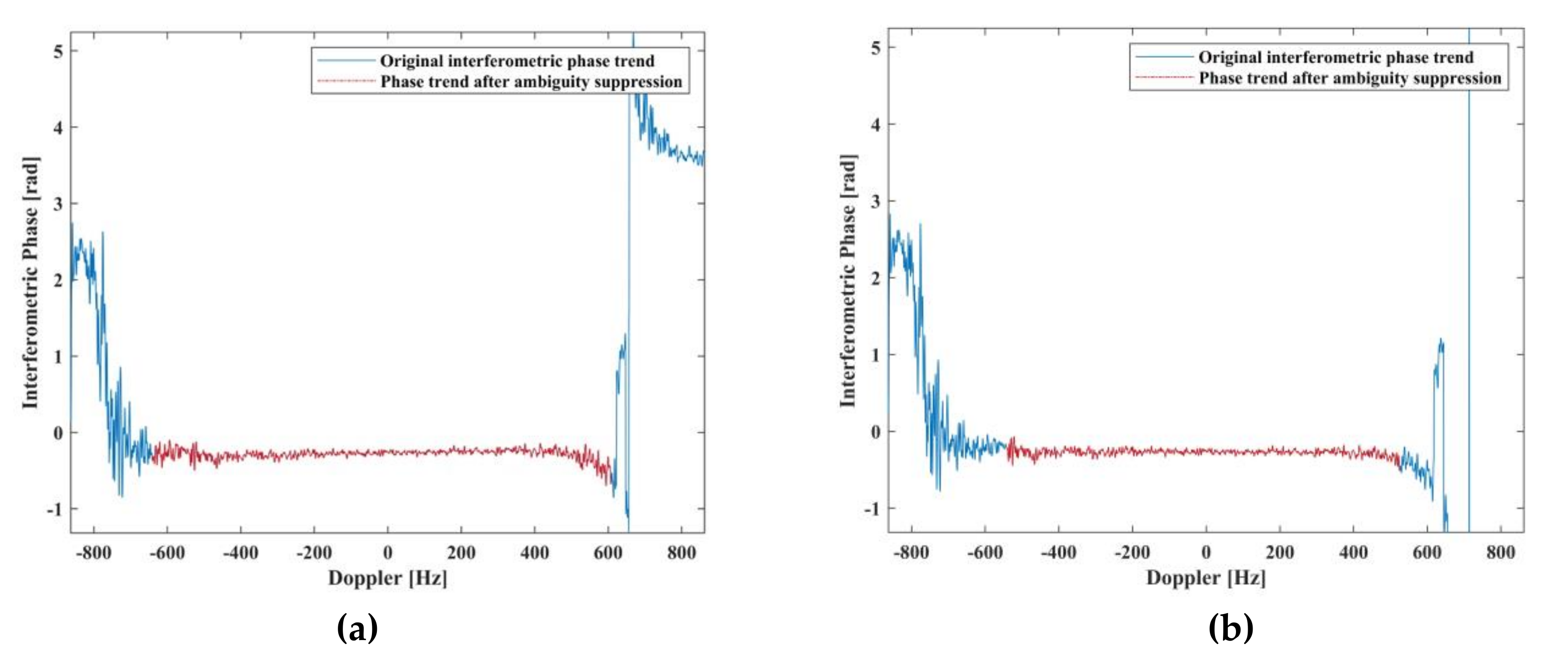
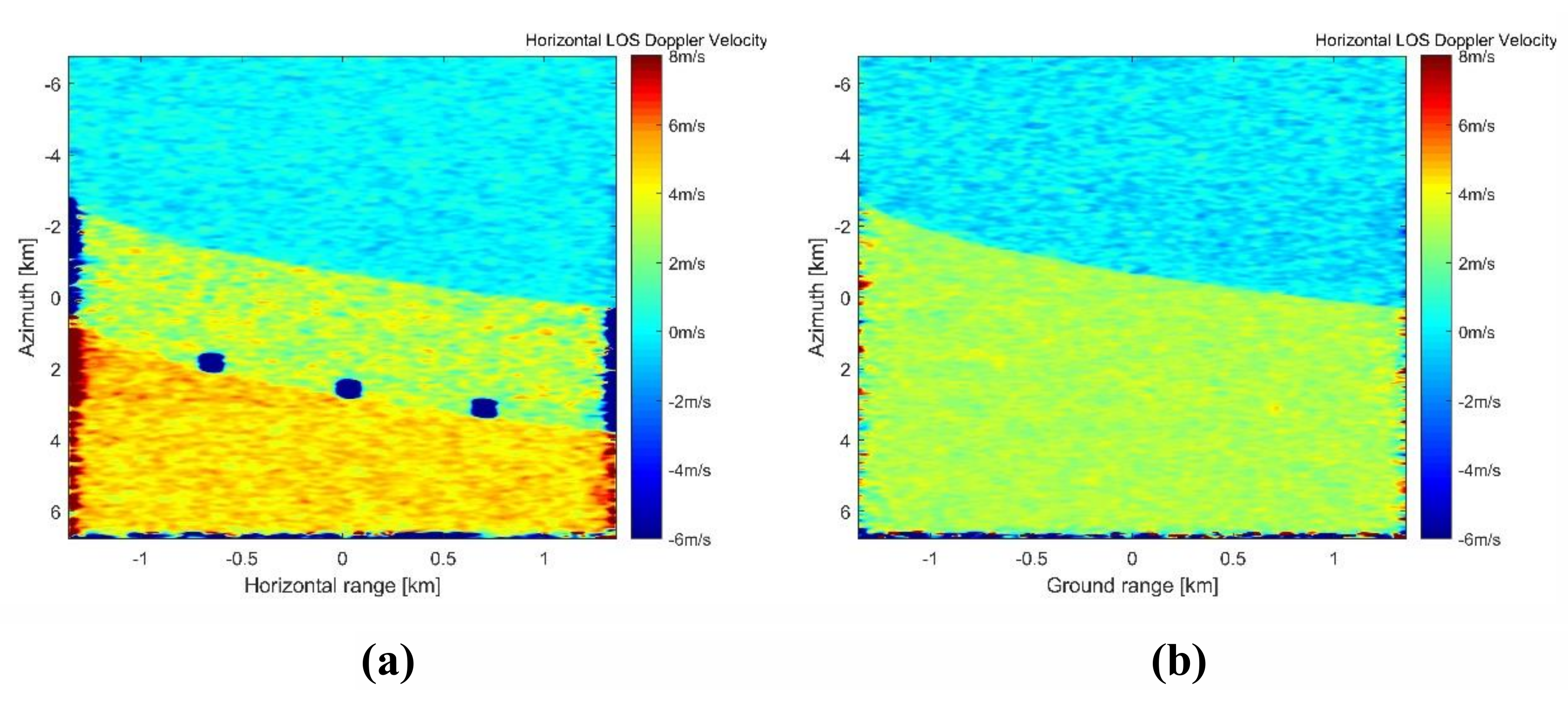
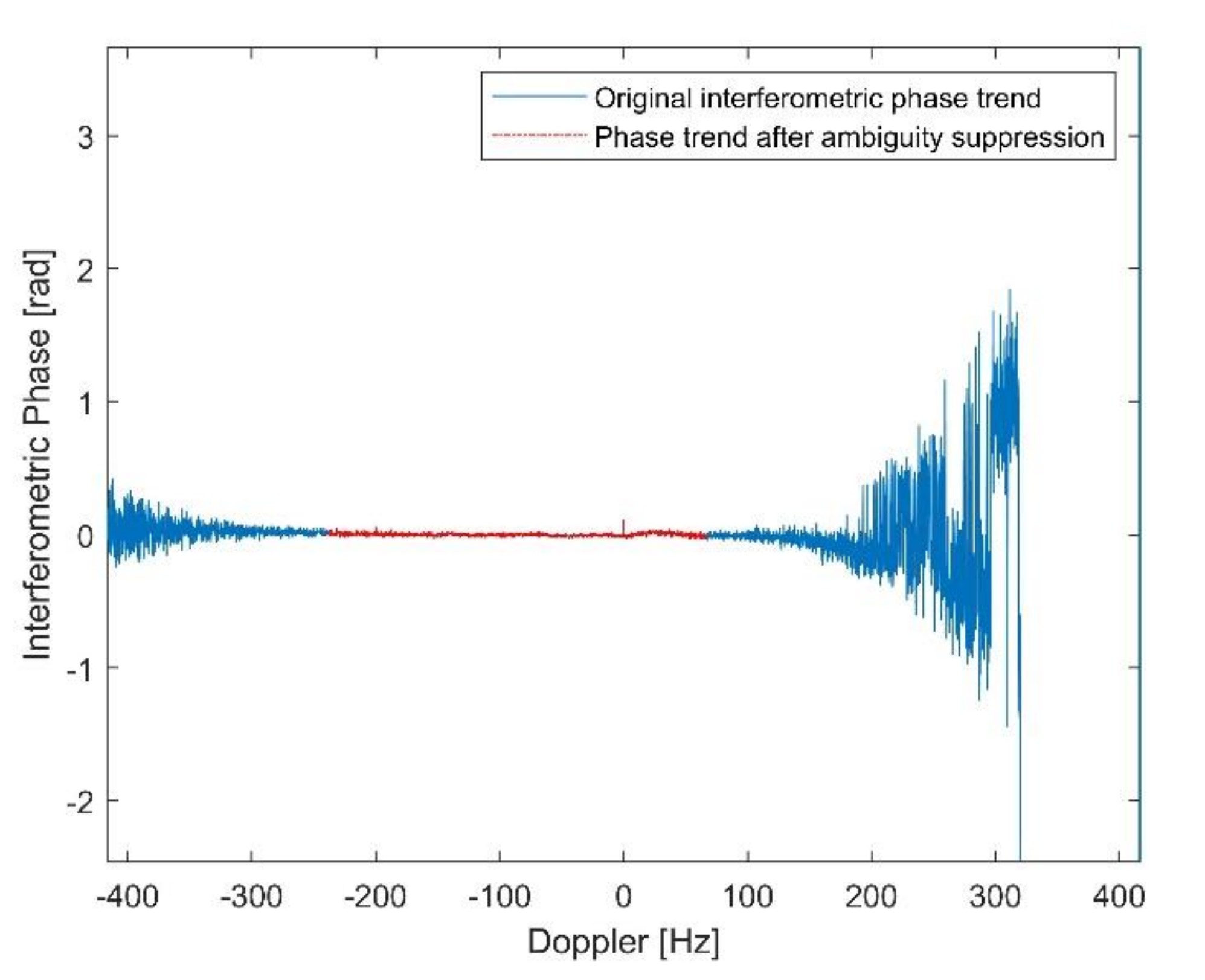
3. Results
3.1. Application to Simulated Data
3.1.1. Simulated Data
3.1.2. Results after Processing of the Simulated Data
3.2. Application to Measured Data
3.2.1. Measured Data
3.2.2. Results after Processing of Measured Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosen, P.A.; Hensley, S.; Joughin, I.R.; Li, F.K.; Madsen, S.N.; Rodriguez, E.; Goldstein, R.M. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry. Proc. IEEE 2000, 88, 333–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toporkov, J.; Perkovic, D.; Farquharson, G.; Sletten, M.; Frasier, S. Sea surface velocity vector retrieval using dual-beam interferometry: First demonstration. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 2494–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prats-Iraola, P.; Scheiber, R.; Reigber, A.; Andres, C.; Horn, R. Estimation of the surface velocity field of the Aletsch glacier using Multibaseline airborne SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 47, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purkis, S.; Klemas, V. Remote sensing and global environmental change. Remote Sens. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2011, 29, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemer, L.; Marom, M.; Markman, D. Estimates of currents in the nearshore ocean region using interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1993, 98, 7001–7010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeiser, R.; Runge, H.; Suchandt, S.; Sprenger, J.; Weilbeer, H.; Sohrmann, A.; Stammer, D. Current measurements in rivers by Spaceborne along-track InSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 4019–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeiser, R.; Suchandt, S.; Runge, H.; Steinbrecher, U.; Grunler, S. First analysis of TerraSAR-X along-track InSAR-derived current fields. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 48, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollstadt, S.; Lopez-Dekker, P.; De Zan, F.; Younis, M. Design principles and considerations for Spaceborne ATI SAR-based observations of ocean surface velocity vectors. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 4500–4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Moon, W.M. Measurements of ocean surface waves and currents using L- and C-band along-track interferometric SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 2821–2832. [Google Scholar]
- Romeiser, R. Current measurements by airborne along-track InSAR: Measuring technique and experimental results. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2005, 30, 552–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Rheem, C.-K. Time-domain simulation of along-track Interferometric SAR for moving ocean surfaces. Sensors 2015, 15, 13644–13659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, A.C.H.; Gommenginger, C.; Marquez, J.; Doody, S.; Navarro, V.; Buck, C. Wind-wave-induced velocity in ATI SAR ocean surface currents: First experimental evidence from an airborne campaign. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2016, 121, 1640–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.C.H.; Gommenginger, C.P.; Quilfen, Y. Simultaneous ocean surface current and wind vectors retrieval with squinted SAR interferometry: Geophysical inversion and performance assessment. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 216, 798–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, R.M.; Zebker, H.A. Interferometric radar measurement of ocean surface currents. Nat. Cell Biol. 1987, 328, 707–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersten, P.R.; Toporkov, J.V.; Ainsworth, T.L.; Sletten, M.A.; Jansen, R.W. Estimating surface water speeds with a single-phase center SAR versus an along-track Interferometric SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 3638–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Li, X.; Ren, Y.; Chen, X. Exploratory research on the retrieval of internal wave parameters and sea surface current velocity based on TerraSAR-X satellite data. Haiyang Xuebao 2020, 42, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeiser, R.; Thompson, D. Numerical study on the along-track interferometric radar imaging mechanism of oceanic surface currents. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardini, F.; Griffiths, H.D.; Gini, F. Ocean surface velocity estimation in multichanne1 ATI-SAR systems. Electron. Lett. 1998, 34, 2429–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besson, O.; Gini, F.; Griffiths, H.; Lombardini, F. Estimating ocean surface velocity and coherence time using multichannel ATI-SAR systems. IEEE Proc. Radar Sonar Navig. 2000, 147, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wang, T.; Li, Y.; Shen, F.; Bao, Z. Effects of doppler aliasing on baseline estimation in multichannel SAR-GMTI and solutions to address these effects. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 6471–6487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondi, F.; Addabbo, P.; Clemente, C.; Orlando, D. Measurements of surface river doppler velocities with along-track InSAR using a single antenna. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 987–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.R.; Jensen, J.R. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry applied to ship-generated internal waves in the 1989 Loch Linnhe experiment. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1993, 98, 10259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graber, H.C.; Thompson, D.R.; Carande, R.E. Ocean surface features and currents measured with synthetic aperture radar interferometry and HF radar. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1996, 101, 25813–25832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farquharson, G.; Junek, W.N.; Ramanathan, A.; Frasier, S.J.; Tessier, R.; McLaughlin, D.J.; Sletten, M.A.; Toporkov, J.V. A pod-based dual-beam SAR. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2004, 1, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeiser, R.; Breit, H.; Eineder, M.; Runge, H.; Flament, P.; De Jong, K.; Vogelzang, J. Current measurements by SAR along-track interferometry from a Space Shuttle. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 2315–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchandt, S.; Runge, H. Ocean surface observations using the TanDEM-X satellite formation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 5096–5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeiser, R.; Runge, H.; Suchandt, S.; Kahle, R.; Rossi, C.; Bell, P.S. Quality assessment of surface current fields from TerraSAR-X and TanDEM-X along-track interferometry and doppler centroid analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 52, 2759–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeiser, R.; Runge, H. Theoretical evaluation of several possible along-track InSAR modes of TerraSAR-X for ocean current measurements. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 45, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Wu, Y.; Ye, Z.; Li, C. Azimuth ambiguity suppression in SAR images based on compressive sensing recovery algorithm. J. Radars 2016, 5, 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Klemas, V. Remote sensing of coastal and ocean currents: An overview. J. Coast. Res. 2012, 28, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; He, Y.; Li, Y.; Duan, H.; Song, X. A new azimuth ambiguity suppression algorithm for surface current measurement in coastal waters and rivers with along-track InSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 57, 3148–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarnieri, A. Adaptive removal of azimuth ambiguities in SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapron, B.; Collard, F.; Ardhuin, F. Direct measurements of ocean surface velocity from space: Interpretation and validation. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2005, 110, 07008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryavtsev, V.N.; Chapron, B.; Myasoedov, A.G.; Collard, F.; Johannessen, J.A.; Myasoedov, A.G.; Johannessen, J.A. On dual co-polarized SAR measurements of the ocean surface. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 10, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Lee, H.; Cao, N.; Lan, Y. Optimal baseline design for Multibaseline InSAR phase unwrapping. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 5738–5750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; He, Y. SAR raw data simulation for ocean scenes using inverse omega-K algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 6151–6169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouche, A.A.; Collard, F.; Chapron, B.; Dagestad, K.-F.; Guitton, G.; Johannessen, J.A.; Kerbaol, V.; Hansen, M.W. On the use of doppler shift for sea surface wind retrieval from SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 2901–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elyouncha, A.; Eriksson, L.E.; Romeiser, R.; Carvajal, G.K.; Ulander, L.M.H. Wind-wave effect on ATI-SAR measurements of ocean surface currents in the Baltic Sea. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 3982–3985. [Google Scholar]
- Long, Y.; Zhao, F.; Zheng, M.; Jin, G.; Zhang, H. An azimuth ambiguity suppression method based on local azimuth ambiguity-to-signal ratio estimation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
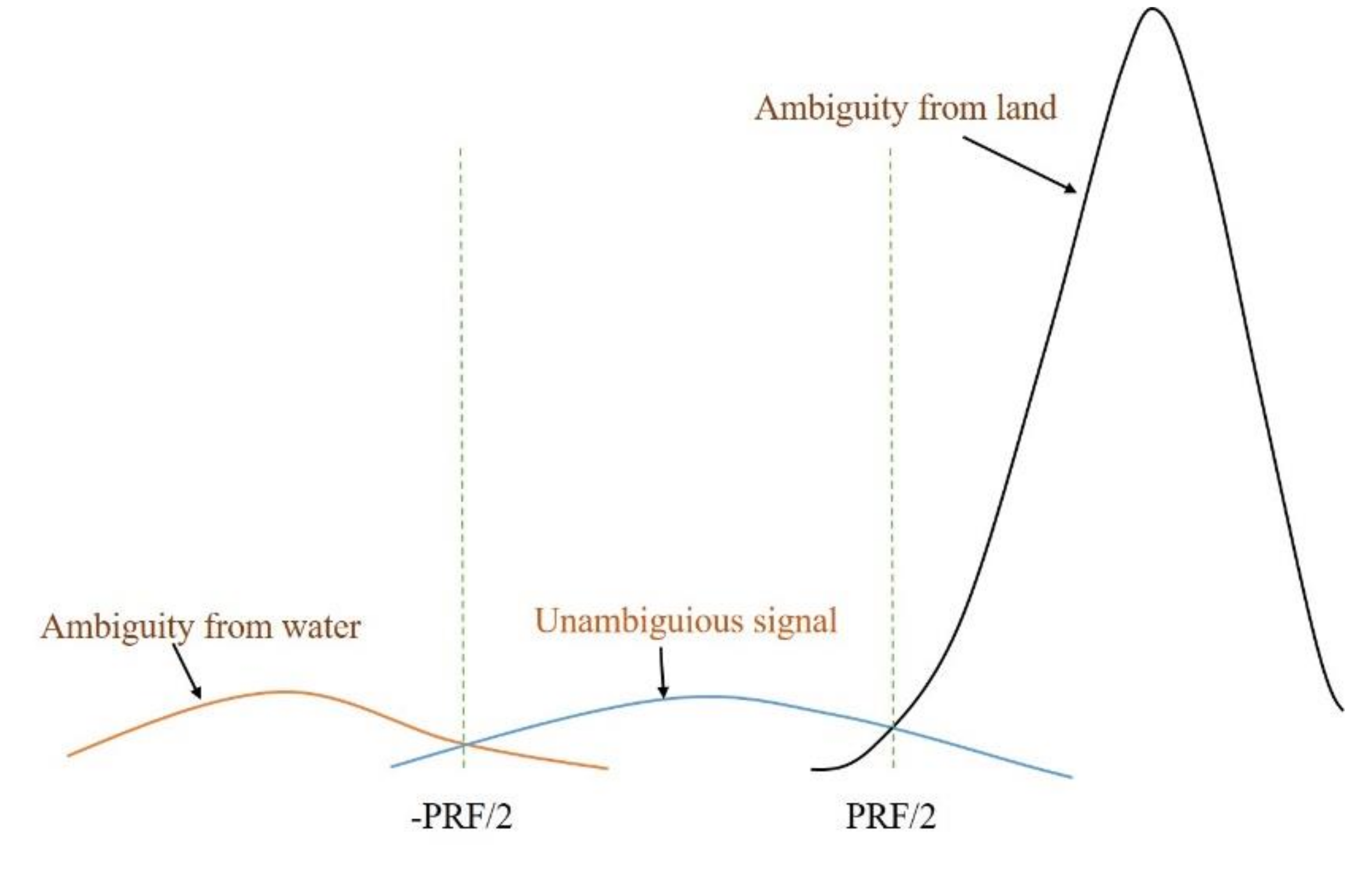
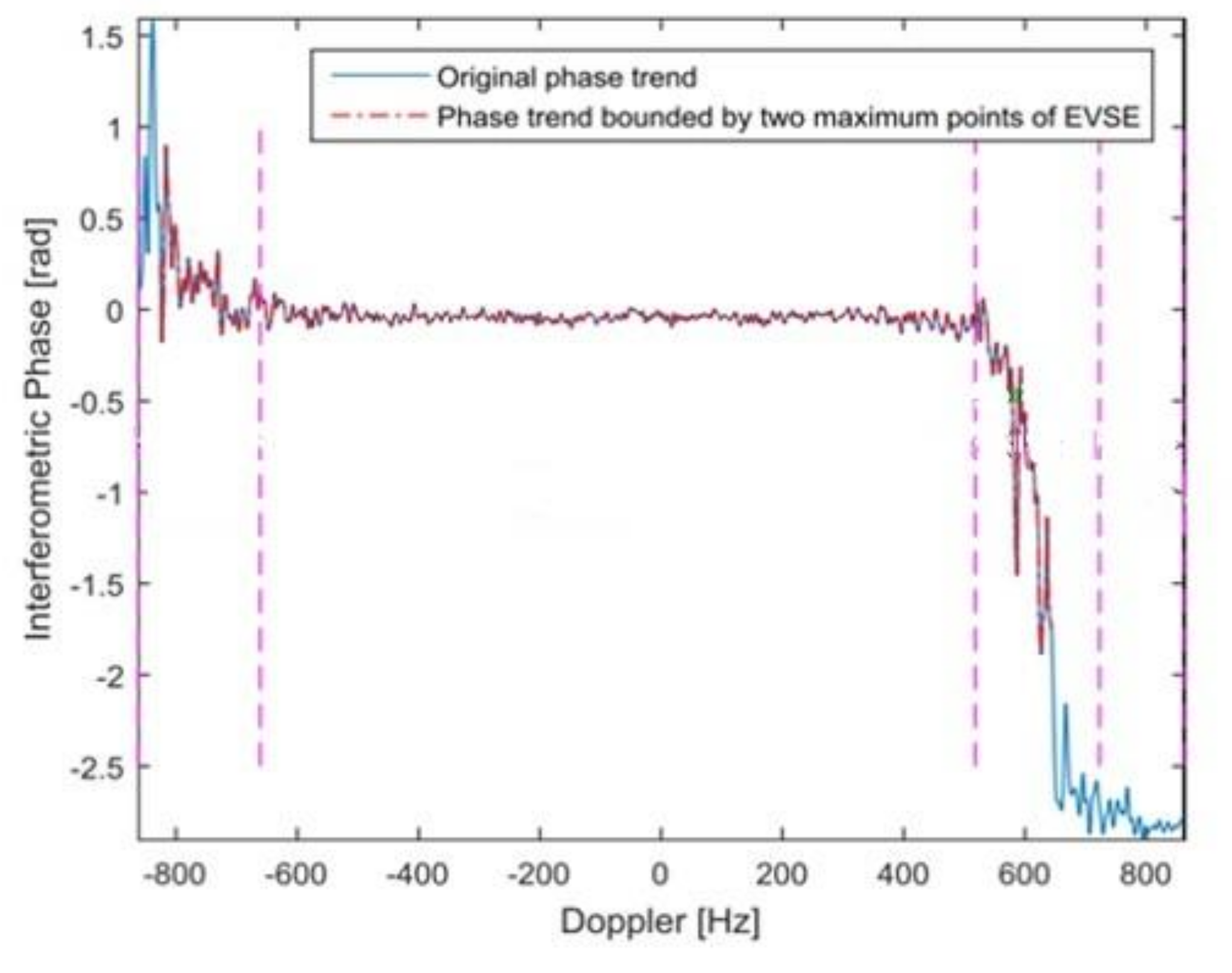


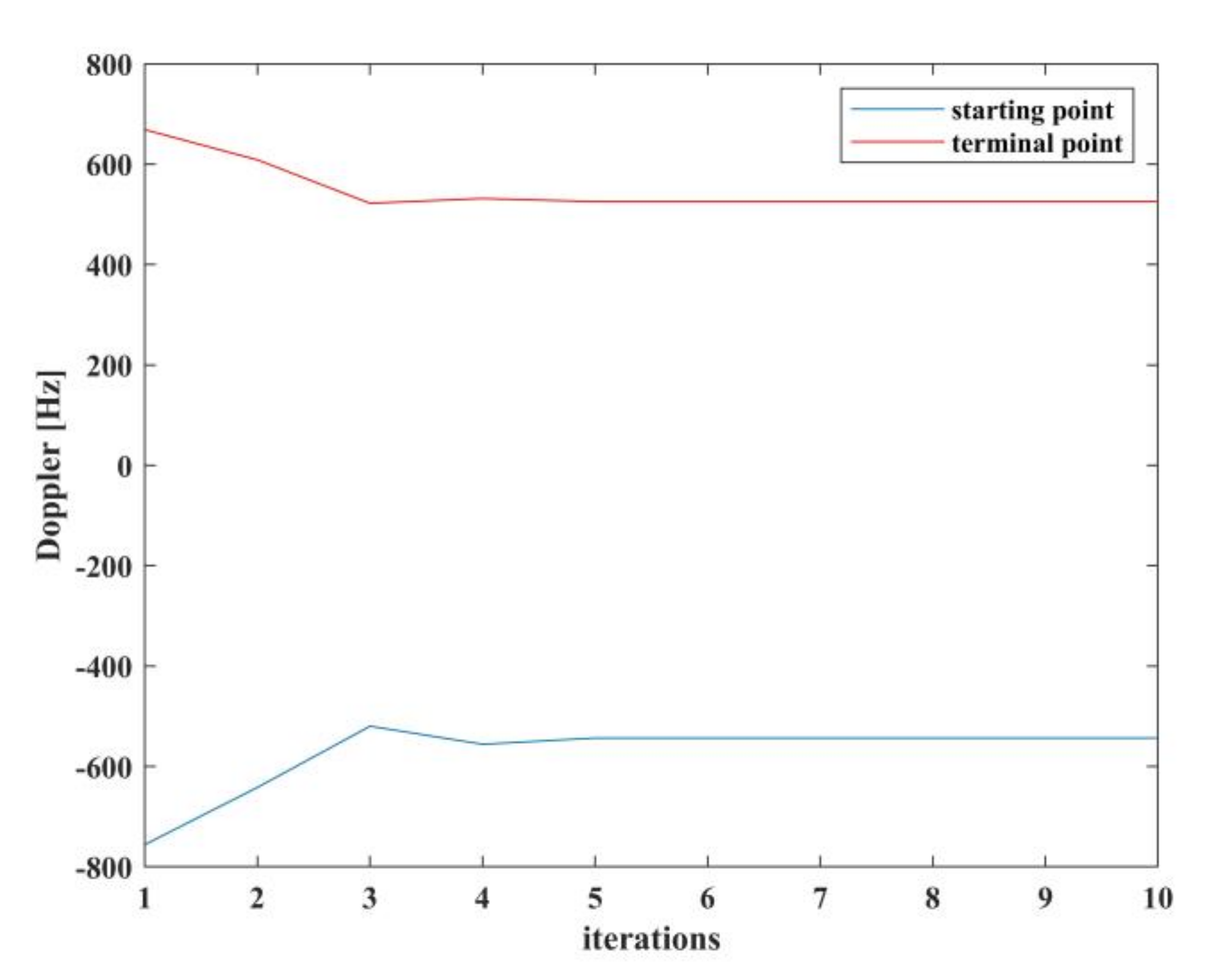
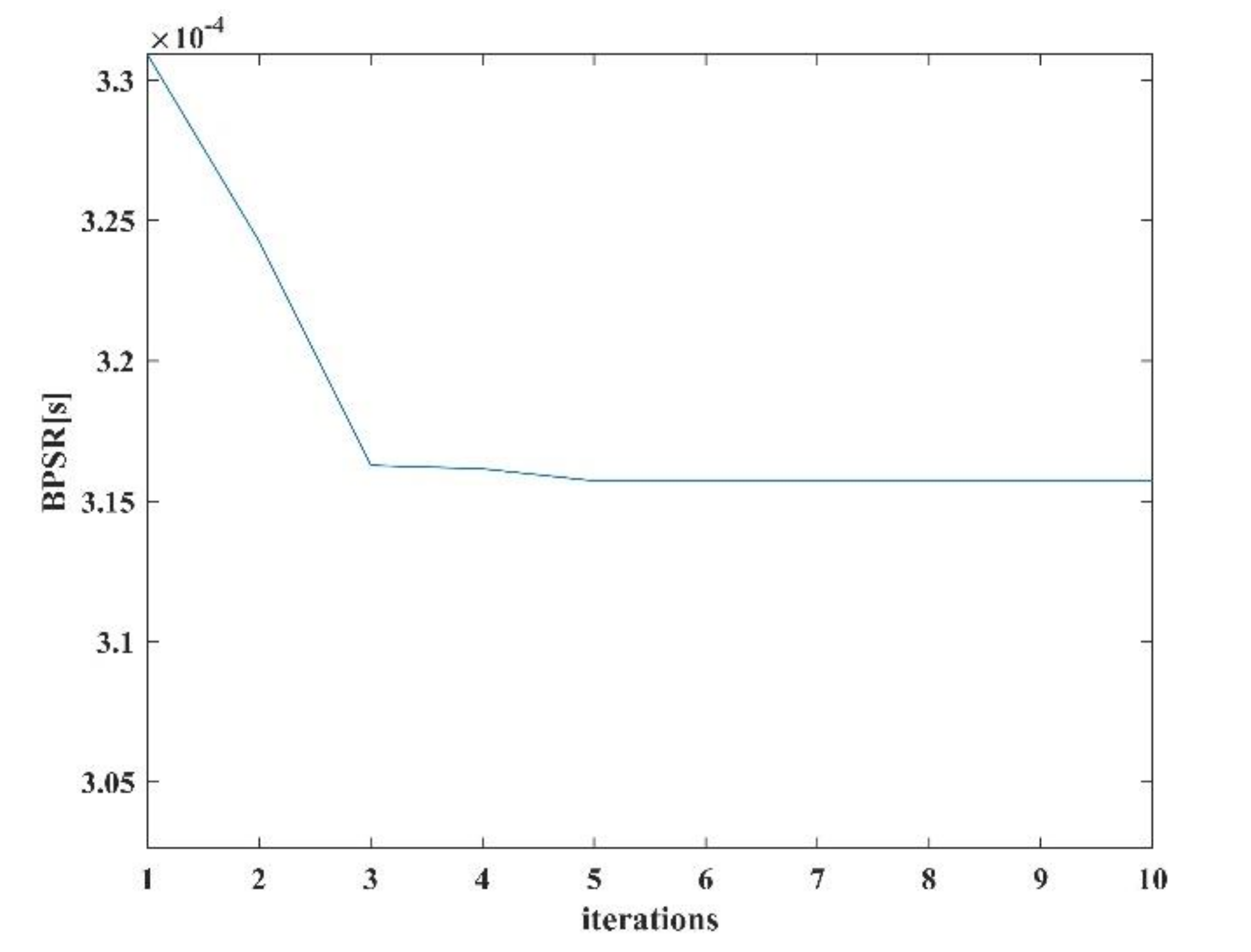
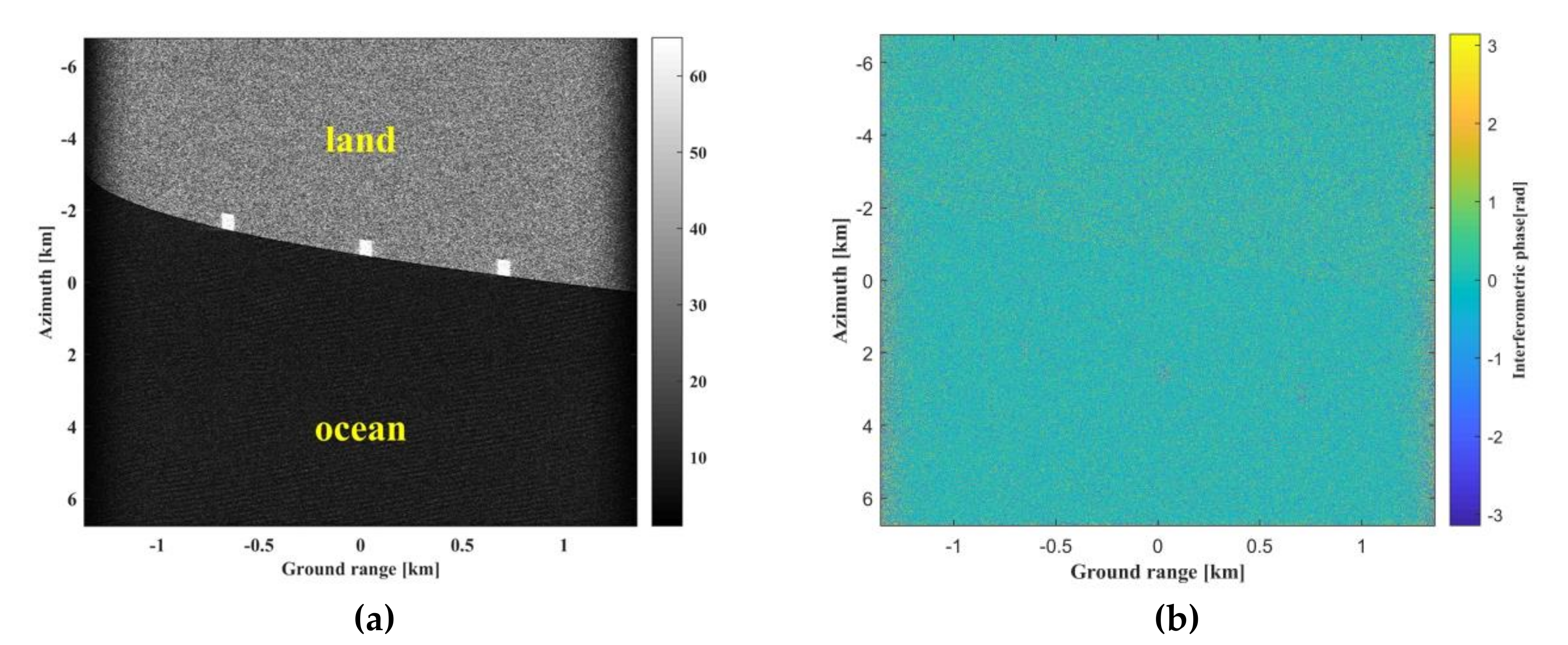



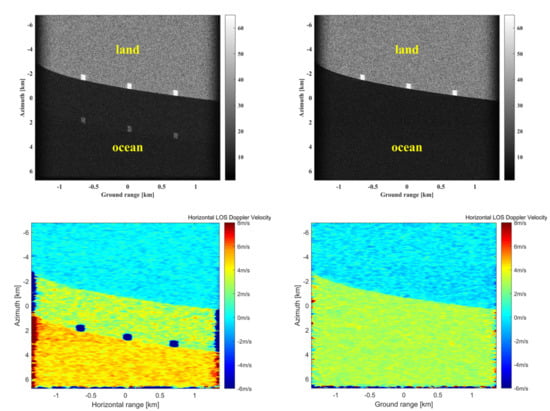
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| PRF (pulse repetition frequency) | 1725 Hz |
| Polarization | VV |
| Radar carrier frequency | 9.6 GHz |
| Effective baseline | 2.4 m |
| Radar platform velocity | 7600 m/s |
| SNR (signal-to-noise ratio) | 6.5 dB |
| Mean water-to-land intensity ratio | −12 dB |
| AASR (azimuth-ambiguity-to-signal ratio) | −20 dB |
| Method | True Horizontal LOS (Line-of-Sight) Current Velocity | Estimated Mean LOS Current Velocity | Mean Bias | STD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liu’s method [31] | 3.0 m/s | 2.543 m/s | 0.457 m/s | 0.457 m/s |
| Algorithm proposed in this paper | 3.0 m/s | 3.025 m/s | −0.025 m/s | 0.025 m/s |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Wavelength | 0.03 m |
| PRF | 830 Hz |
| Radar carrier frequency | 10 GHz |
| Effective baseline | 0.2 m |
| Radar platform velocity | 110 m/s |
| SNR | 18 dB |
| AASR | −20 dB |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yi, N.; He, Y.; Liu, B. Improved Method to Suppress Azimuth Ambiguity for Current Velocity Measurement in Coastal Waters Based on ATI-SAR Systems. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3288. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12203288
Yi N, He Y, Liu B. Improved Method to Suppress Azimuth Ambiguity for Current Velocity Measurement in Coastal Waters Based on ATI-SAR Systems. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(20):3288. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12203288
Chicago/Turabian StyleYi, Na, Yijun He, and Baochang Liu. 2020. "Improved Method to Suppress Azimuth Ambiguity for Current Velocity Measurement in Coastal Waters Based on ATI-SAR Systems" Remote Sensing 12, no. 20: 3288. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12203288
APA StyleYi, N., He, Y., & Liu, B. (2020). Improved Method to Suppress Azimuth Ambiguity for Current Velocity Measurement in Coastal Waters Based on ATI-SAR Systems. Remote Sensing, 12(20), 3288. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12203288