A New Approach for Estimating Soil Salinity Using A Low-Cost Soil Sensor In Situ: A Case Study in Saline Regions of China’s East Coast
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
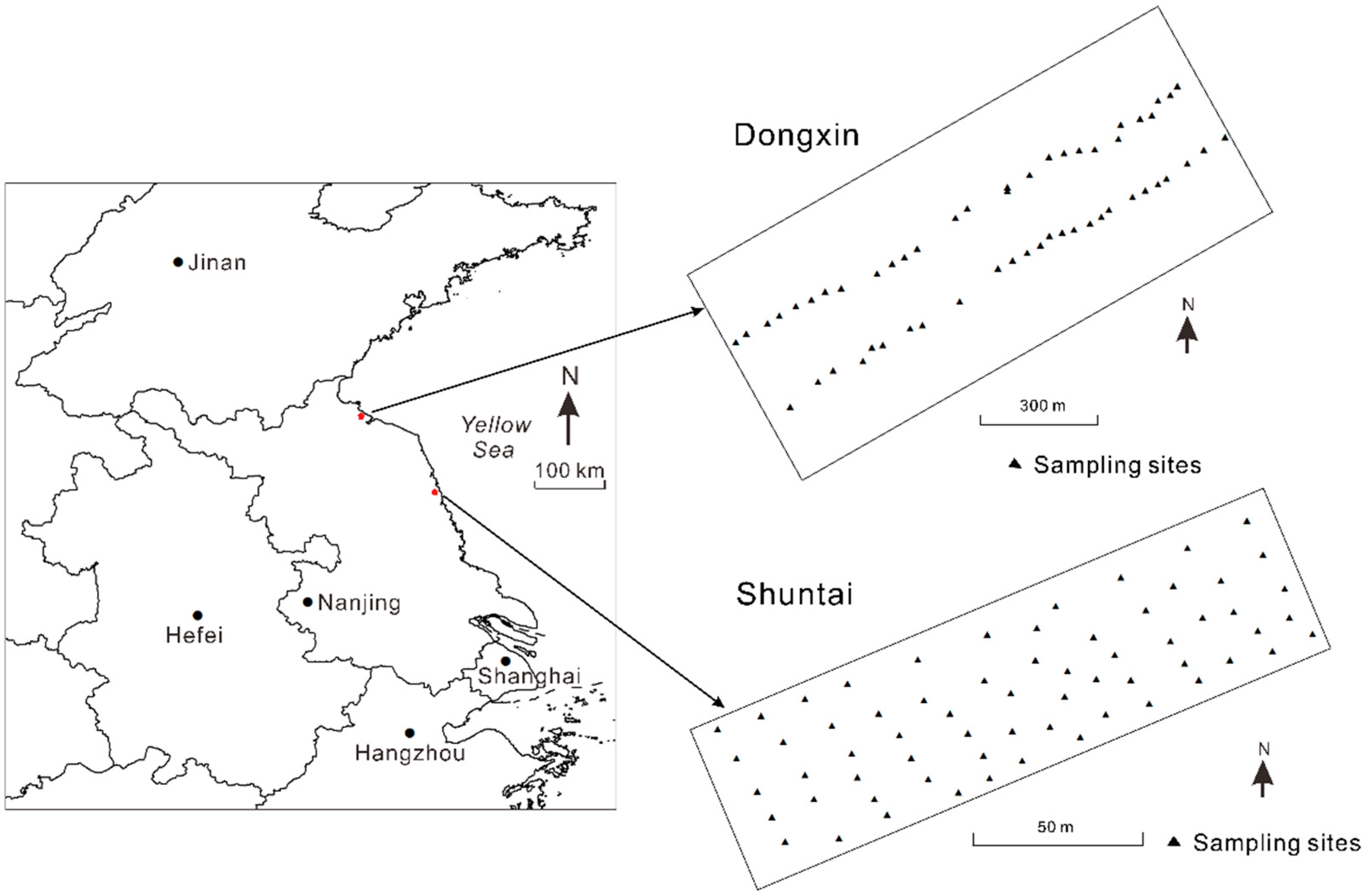
2.1. Study Areas and Data Acquisition
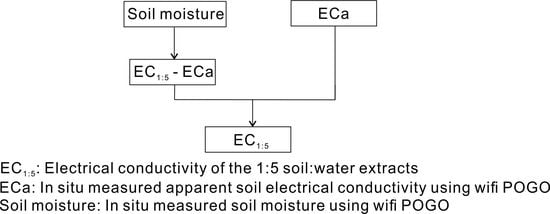
2.2. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
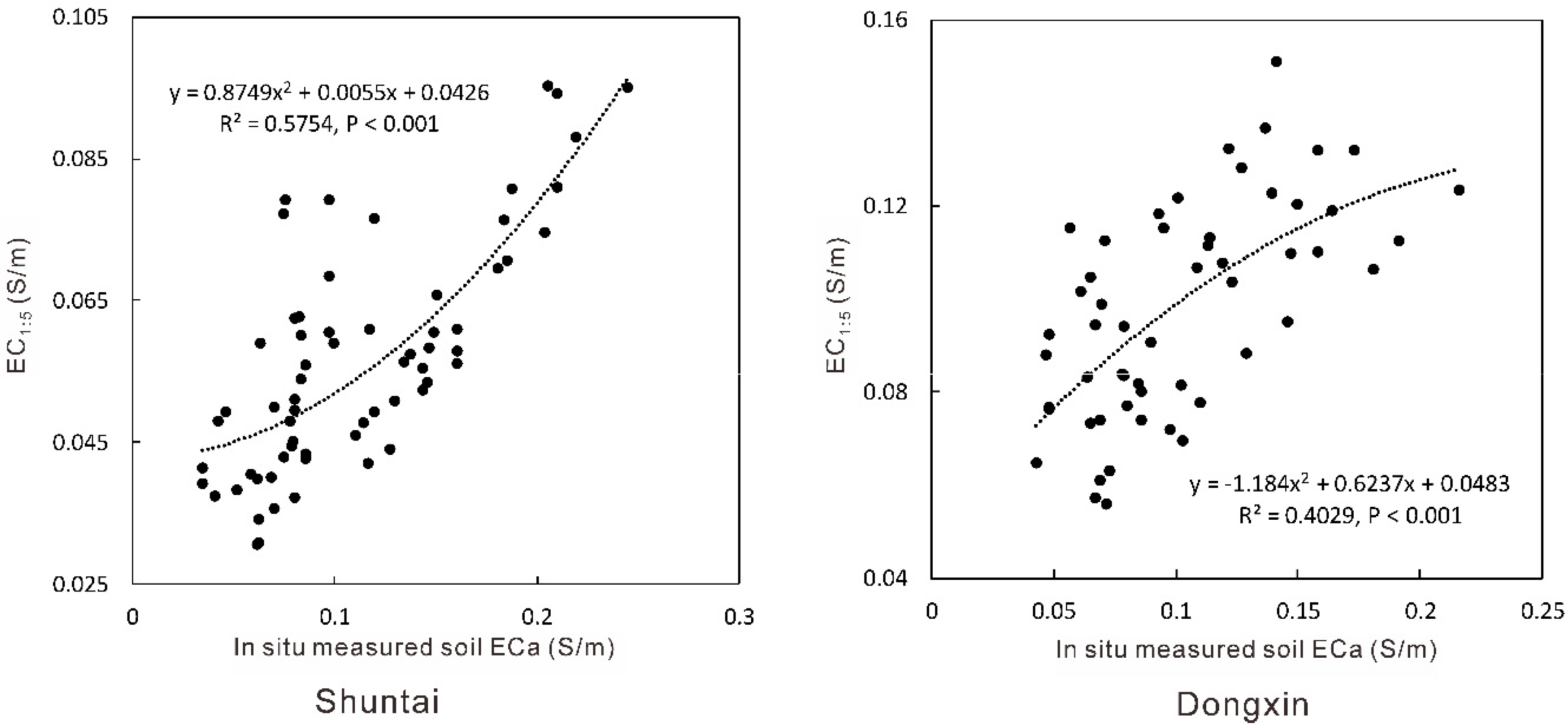
3.1. Relationships between ECa and EC1:5
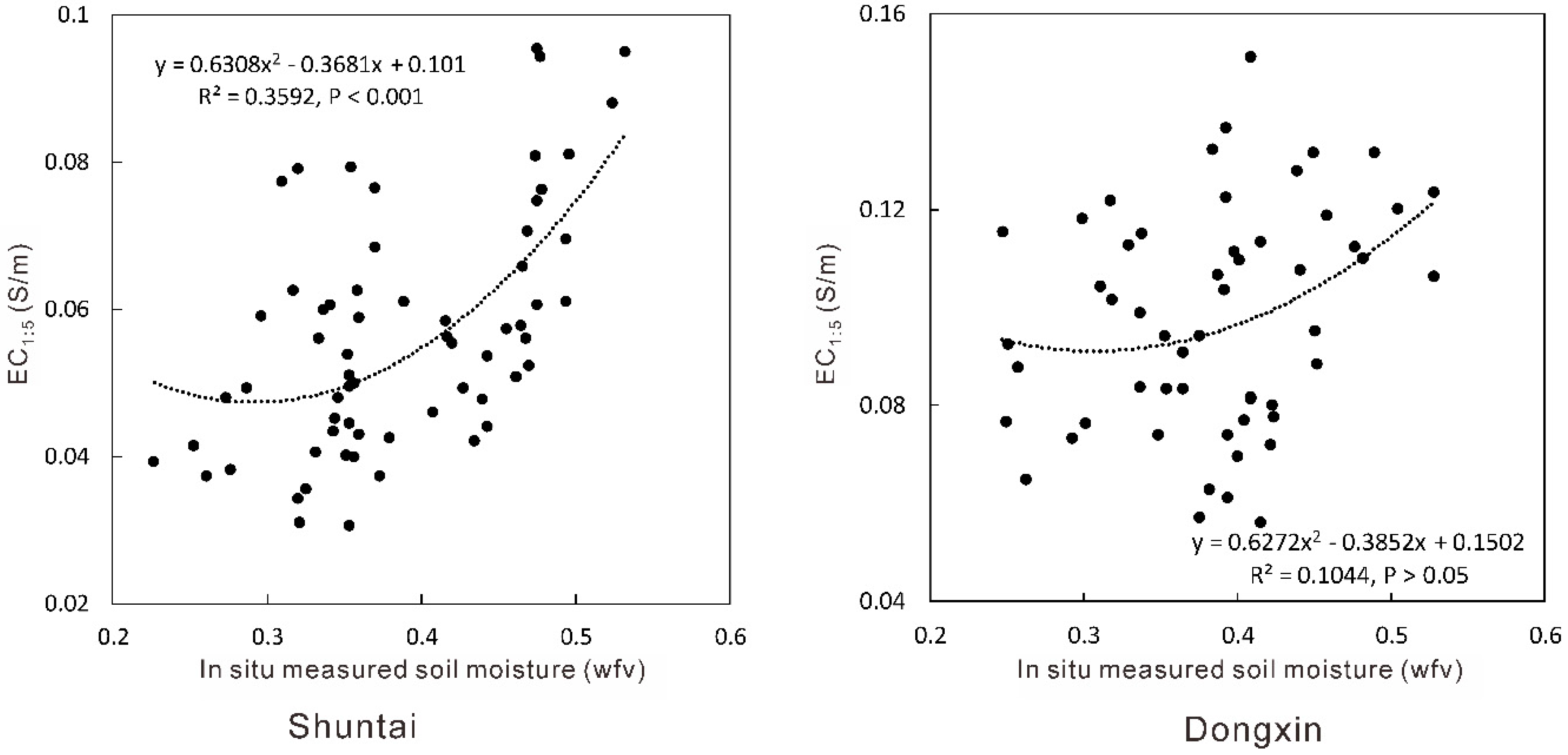
3.2. Relationships between Soil Moisture and EC1:5
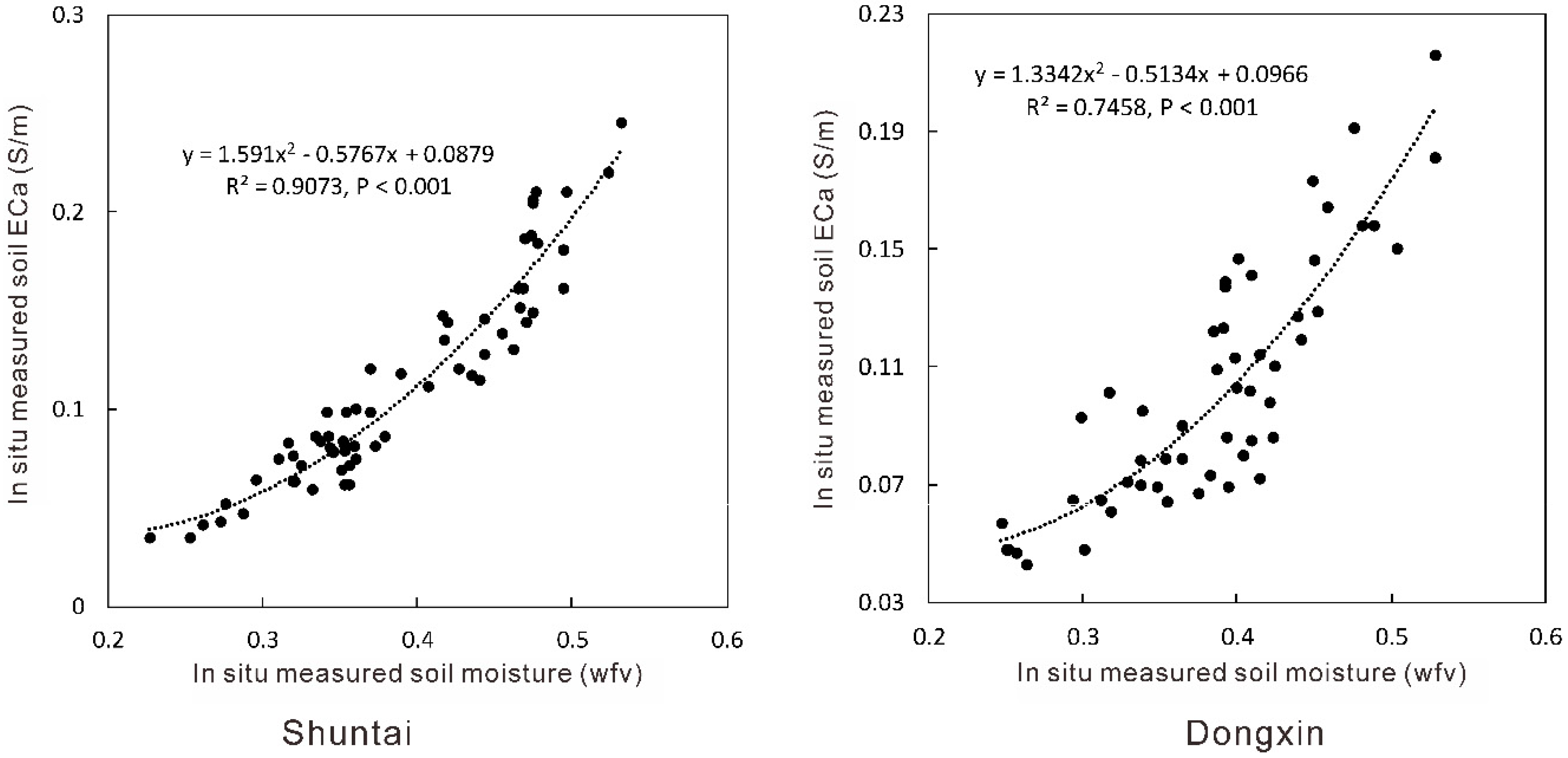
3.3. Relationships between Soil Moisture and ECa
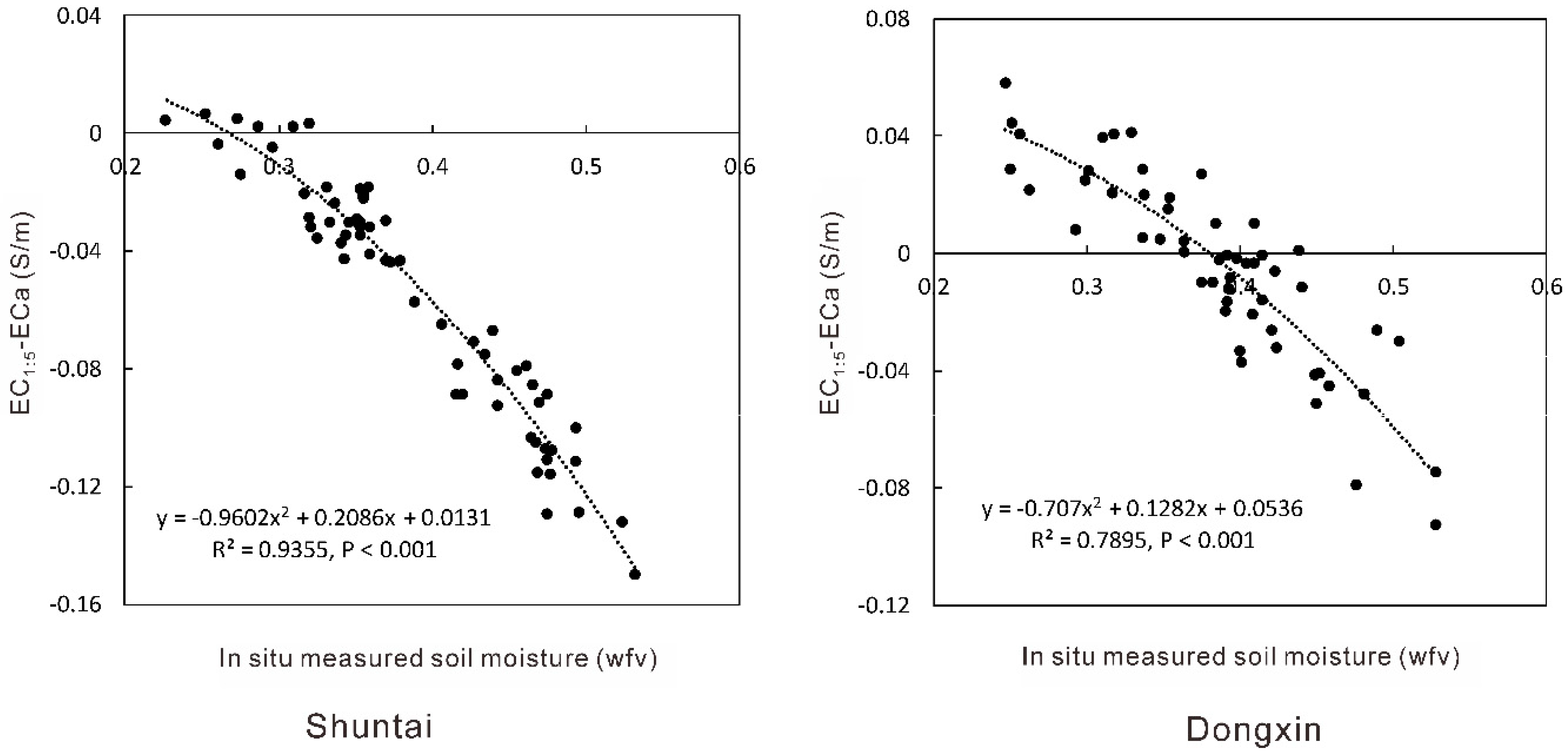
3.4. Relationships between Soil Moisture and EC1:5-ECa
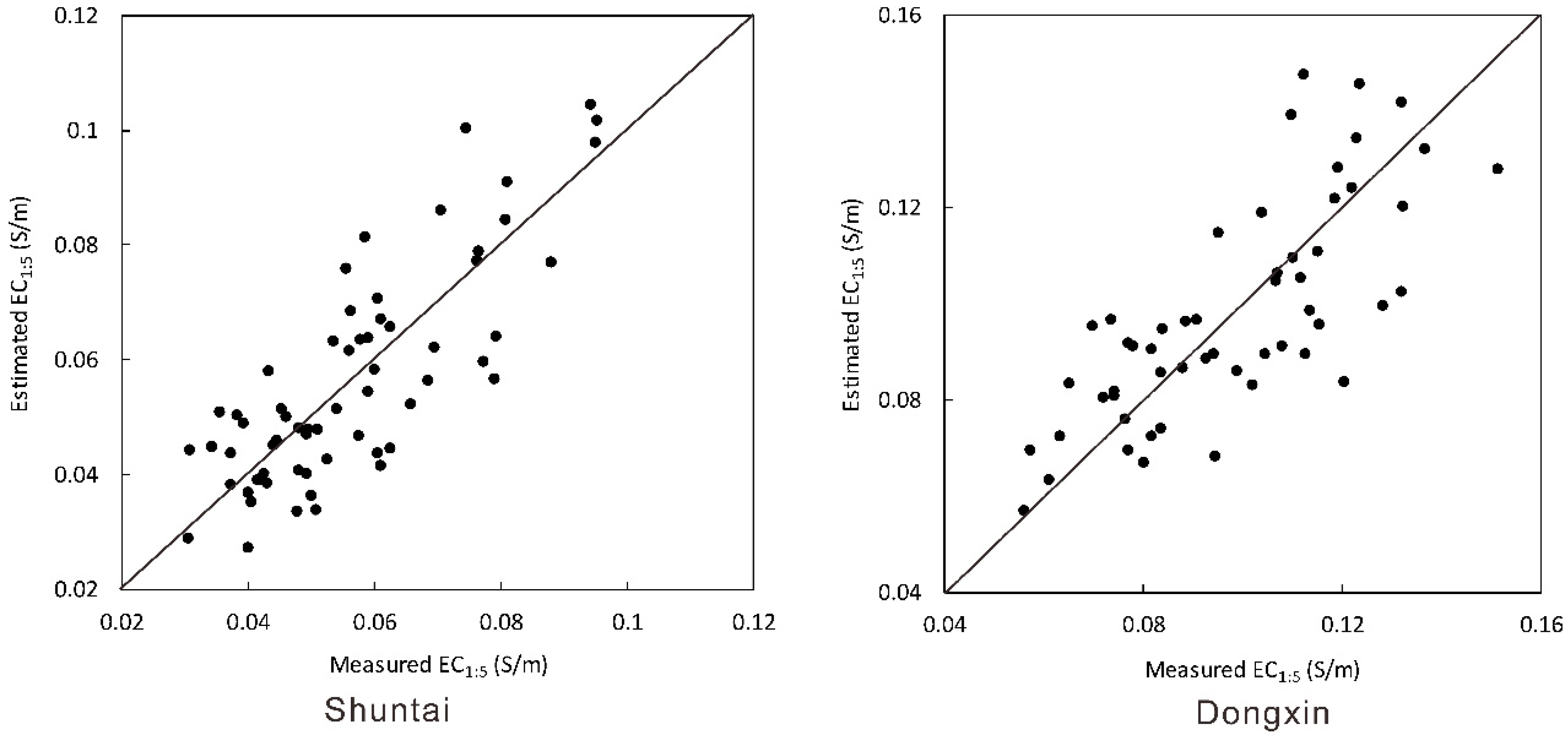
3.5. Deriving EC1:5 from In Situ Measured Soil ECa and Moisture
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghassemi, F.; Jakeman, A.J.; Nix, H.A. Salinisation of Land and Water Resources: Human Causes, Extent, Management and Case Studies; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Metternicht, G.I.; Zinck, J.A. Remote sensing of soil salinity: Potentials and constraints. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 85, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Huang, X.J.; Zhong, T.Y.; Chen, Z.G. Review on sustainable utilization of salt-affected land. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2011, 66, 673–684. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Vaid, N.; Pandey, P.; Srivastava, V.K.; Tuteja, N. Pea lectin receptor-like kinase functions in salinity adaptation without yield penalty, by alleviating osmotic and ionic stresses and upregulating stress responsive genes. Plant Mol. Biol. 2015, 88, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omisun, T.; Sahoo, S.; Saha, B.; Panda, S.K. Relative salinity tolerance of rice cultivars native to north east India: A physiological, biochemical and molecular perspective. Protoplasma 2018, 255, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munns, R.; Tester, M. Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 651–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, B.; Md, N.A.; Gantait, S. Response of rice under salinity stress: A review update. Rice Res. Open Access 2016, 4, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargas, G.; Chatzigiakoumis, I.; Kollias, A.; Spiliotis, D.; Kerkides, P. An investigation of the relationship between the electrical conductivity of the soil saturated paste extract ece with the respective values of the mass soil/water ratios 1:1 and 1:5 (EC1:1 and EC1:5). Proceedings 2018, 2, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, P.; Kumar, R. Soil salinity: A serious environmental issue and plant growth promoting bacteria as one of the tools for its alleviation. Saudi J Biol. Sci. 2015, 22, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Department of Agriculture. Diagnoses and Improvement of Saline and Alkali Soils; Agriculture Handbook No 60; USSL: Riverside, CA, USA, 1954.
- Rhoades, J.D.; Manteghi, N.A.; Shouse, P.J.; Alves, W.J. Estimating soil salinity from saturated soil-paste electrical conductivity. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1989, 53, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longenecker, D.E.; Lyerly, P.J. Making soil pastes for salinity analysis: A reproducible capillary procedure. Soil Sci. 1964, 97, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Desutter, T.; Hopkins, D.; Jia, X.; Wysocki, D.A. Predicting ECe of the saturated paste extract from value of EC1:5. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2013, 93, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorsandi, F.; Yazdi, F.A. Gypsum and texture effects on the estimation of saturated paste electrical conductivity by two extraction methods. Commun. Soil Sci. Plan Anal. 2007, 38, 1105–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amakor, X.N.; Cardon, G.E.; Symanzik, J.; Jacobson, A.R. A new electromagnetic induction calibration model for estimating low range salinity in calcareous soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2013, 77, 985–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, M.; Savage, M.; Moolman, J.; du Plessis, H. Evaluation of calibration methods for interpreting soil salinity from electromagnetic induction measurements. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1997, 61, 1627–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdes, R.; Miralles, J.; Franco, J.A.; Sanchez-Blanco, M.J.; Banon, S. Using soil bulk electrical conductivity to manage saline irrigation in the production of potted poinsettia. Sci. Hortic. 2014, 170, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shi, Z.; Wu, C.; Li, F.; He, F. EM38-based in-situ determination of electrical conductivity of coastal saline soil in profile. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2013, 6, 1231–1235. [Google Scholar]
- Gebbers, R.; Luck, E.; Dabas, M.; Domsch, H. Comparison of instruments for geoelectrical soil mapping at the field scale. Near Surf. Geophys. 2009, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldeiry, A.A.; Garcia, L.A. Evaluating the performance of ordinary kriging in mapping soil salinity. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2012, 138, 1046–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doolittle, J.A.; Brevik, E.C. The use of electromagnetic induction techniques in soils studies. Geoderma 2014, 223, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.G.; Baker, G. An electromagnetic induction technique for reconnaissance surveys of soil salinity hazards. Soil Res. 1982, 20, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.Y. Experimental survey for the effects of soil water content and soil salinity on soil electrical conductivity. J. China Agric. Univ. 2000, 5, 39–41, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Farahani, H.J.; Buchleiter, G.W.; Brodahl, M.K. Characterization of apparent soil electrical conductivity variability in irrigated sandy and non-saline fields in Colorado. Am. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2005, 48, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heil, K.; Schmidhalter, U. The application of EM38: Determination of soil parameters, selection of soil sampling points and use in agriculture and archaeology. Sensors 2017, 17, 2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slavich, P.G.; Petterson, G.H. Estimating average rootzone salinity from electromagnetic induction (EM-38) measurements. Aust. J. Soil Res. 1990, 28, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafilis, J.; Laslett, G.M.; McBratney, A.B. Calibrating an electromagnetic induction instrument to measure salinity in soil under irrigated cotton. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.J.; Yang, J.S.; Liu, G.M. Calibration of soil electromagnetic conductivity in inverted salinity profiles with an integration method. Pedosphere 2007, 17, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesch, S.M. Statistical models for the prediction of field-scale and spatial salinity patterns from soil conductivity survey data. In Agricultural Salinity Assessment and Management; Wallender, W.W., Tanji, K.K., Eds.; ASCE: Reston, VA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, K.; Jiang, Y.; Tang, J.; Dai, Q. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer rate and transplanting density on yield and grain quality of rice on saline-alkaline land. Chin. Soils Fert. 2018, 2, 67–74, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Zuo, P.; Wang, J.; Gao, Z.; Wu, Q. Changes of vegetation carbon storage in yancheng coastalwetlands for six periods. Wetl. Sci. 2014, 12, 709–713, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Q.D.; Du, H.Y. Effects of different nitrogen application levels on agronomic traits and nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) of paddy rice. Agric. Sci. Jiangsu 2013, 41, 46–48. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J. Characteristics of drought and its strategy of mitigation in Lianyungang, Jiangsu. Chin. Flood Drought Manag. 2013, 5, 28–30. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yao, R.J.; Yang, J.S.; Wu, D.H.; Xie, W.P.; Cui, S.Y.; Wang, X.P.; Yu, S.P.; Zhang, X. Determining soil salinity and plant biomass response for a farmed coastal cropland using the electromagnetic induction method. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2015, 119, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvier, M.; Durrieu, S.; Fournier, R.A.; Renaud, J.P. Generalizing predictive models of forest inventory attributes using an area-based approach with airborne LiDAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghany, A.H.; Omara, A.M.; El Nagar, M.A. Testing Electromagnetic Induction Device (EM 38) Under Egyptian Conditions; Vlotman, W.F., Ed.; EM38 Workshop: New Delhi, India, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Hanson, B.R.; Kaita, K. Response of electromagnetic conductivity meter to soil salinity and soil-water content. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 1997, 123, 141–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corwin, D.L.; Lesch, S.M. Apparent soil electrical conductivity measurements in agriculture. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2005, 46, 11–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, L.; Dhankhar, R.; Chhikara, S. Soil characteristics affected by long term application of sewage wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2010, 4, 513–518. [Google Scholar]
| Study Area | Soil Texture | Sample Number | Moisture (wfv) | ECa (S/m) | EC1:5 (S/m) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shuntai | salty | 64 | Min | 0.227 | 0.035 | 0.031 |
| sandy | Max | 0.532 | 0.245 | 0.095 | ||
| loam | Mean | 0.388 | 0.112 | 0.056 | ||
| Dongxin | salty | 54 | Min | 0.247 | 0.043 | 0.056 |
| clay | Max | 0.528 | 0.216 | 0.151 | ||
| soil | Mean | 0.384 | 0.102 | 0.098 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Sun, Q.; Shang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wu, F.; Zhou, G.; Dai, Q. A New Approach for Estimating Soil Salinity Using A Low-Cost Soil Sensor In Situ: A Case Study in Saline Regions of China’s East Coast. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12020239
Wang J, Sun Q, Shang J, Zhang J, Wu F, Zhou G, Dai Q. A New Approach for Estimating Soil Salinity Using A Low-Cost Soil Sensor In Situ: A Case Study in Saline Regions of China’s East Coast. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(2):239. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12020239
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jianjun, Quan Sun, Jiali Shang, Jiahua Zhang, Fei Wu, Guisheng Zhou, and Qigen Dai. 2020. "A New Approach for Estimating Soil Salinity Using A Low-Cost Soil Sensor In Situ: A Case Study in Saline Regions of China’s East Coast" Remote Sensing 12, no. 2: 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12020239
APA StyleWang, J., Sun, Q., Shang, J., Zhang, J., Wu, F., Zhou, G., & Dai, Q. (2020). A New Approach for Estimating Soil Salinity Using A Low-Cost Soil Sensor In Situ: A Case Study in Saline Regions of China’s East Coast. Remote Sensing, 12(2), 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12020239