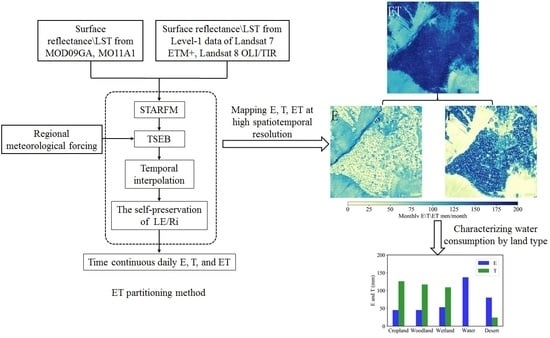
Evapotranspiration Partitioning at Field Scales Using TSEB and Multi-Satellite Data Fusion in The Middle Reaches of Heihe River Basin, Northwest China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
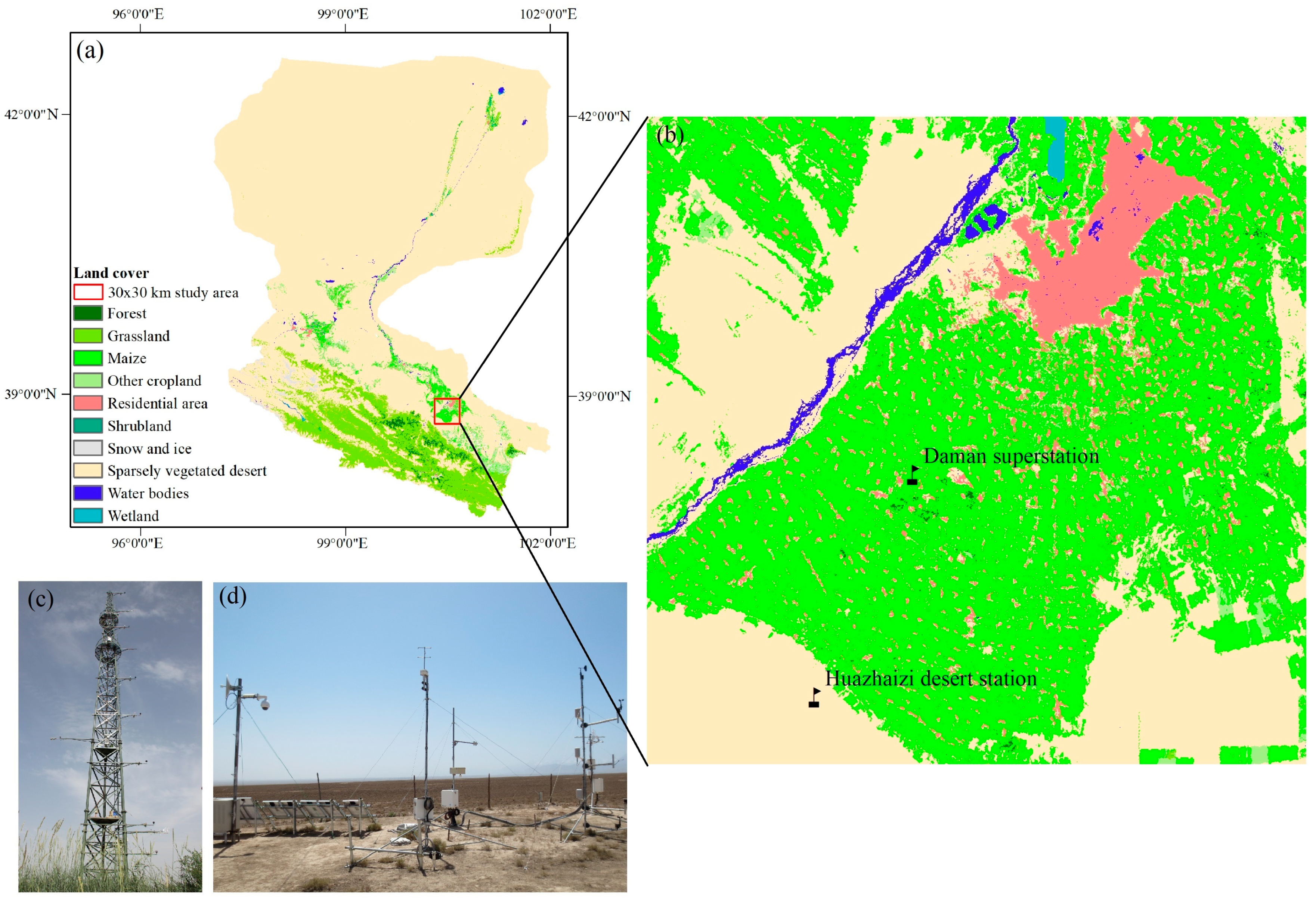
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Field Measurements
2.3. Model Inputs
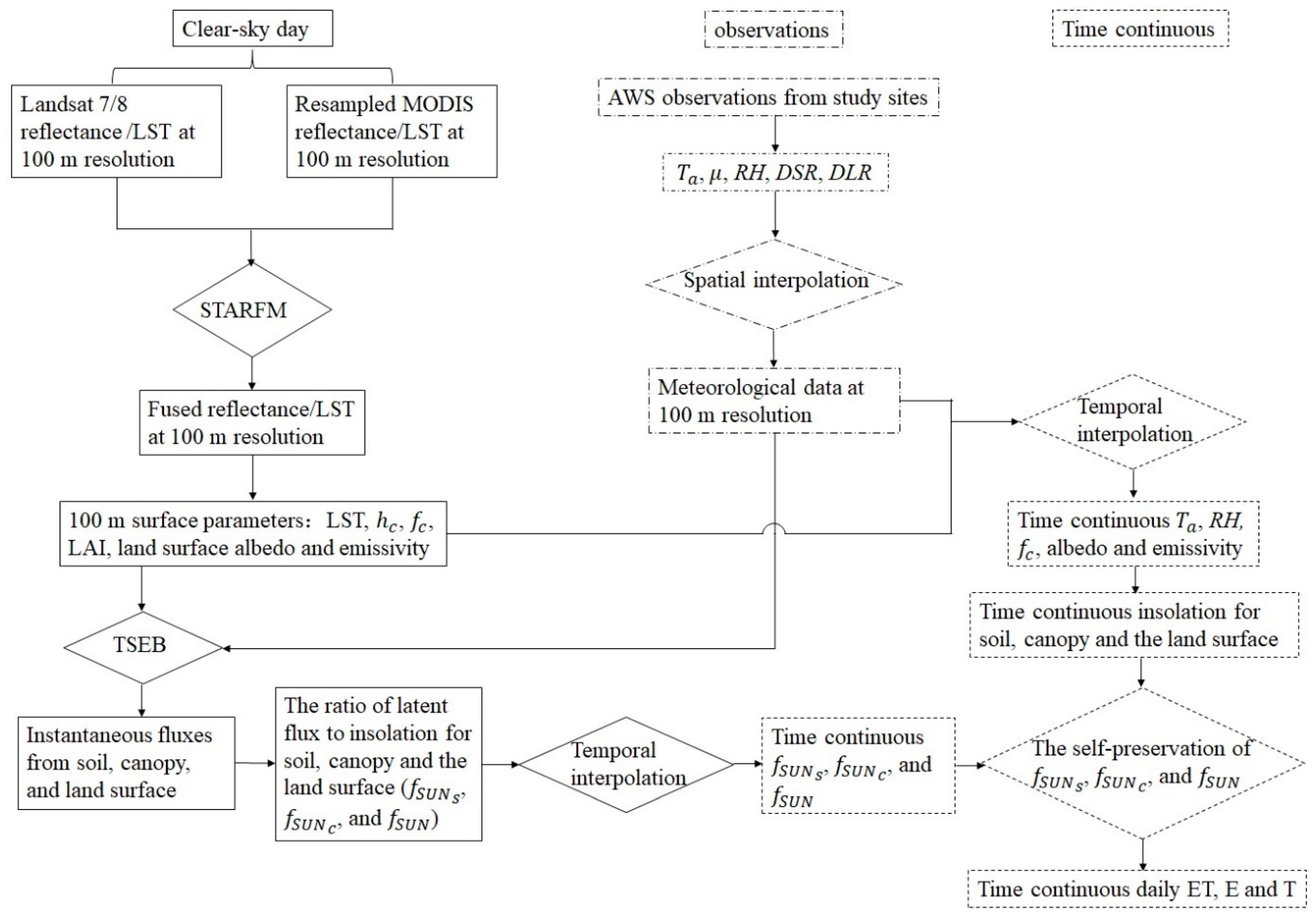
2.4. ET Partitioning Method
2.5. TSEB Model
2.6. STARFM
2.7. Landsat-Only Interpolation
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Land Surface Fluxes at The Study Sites
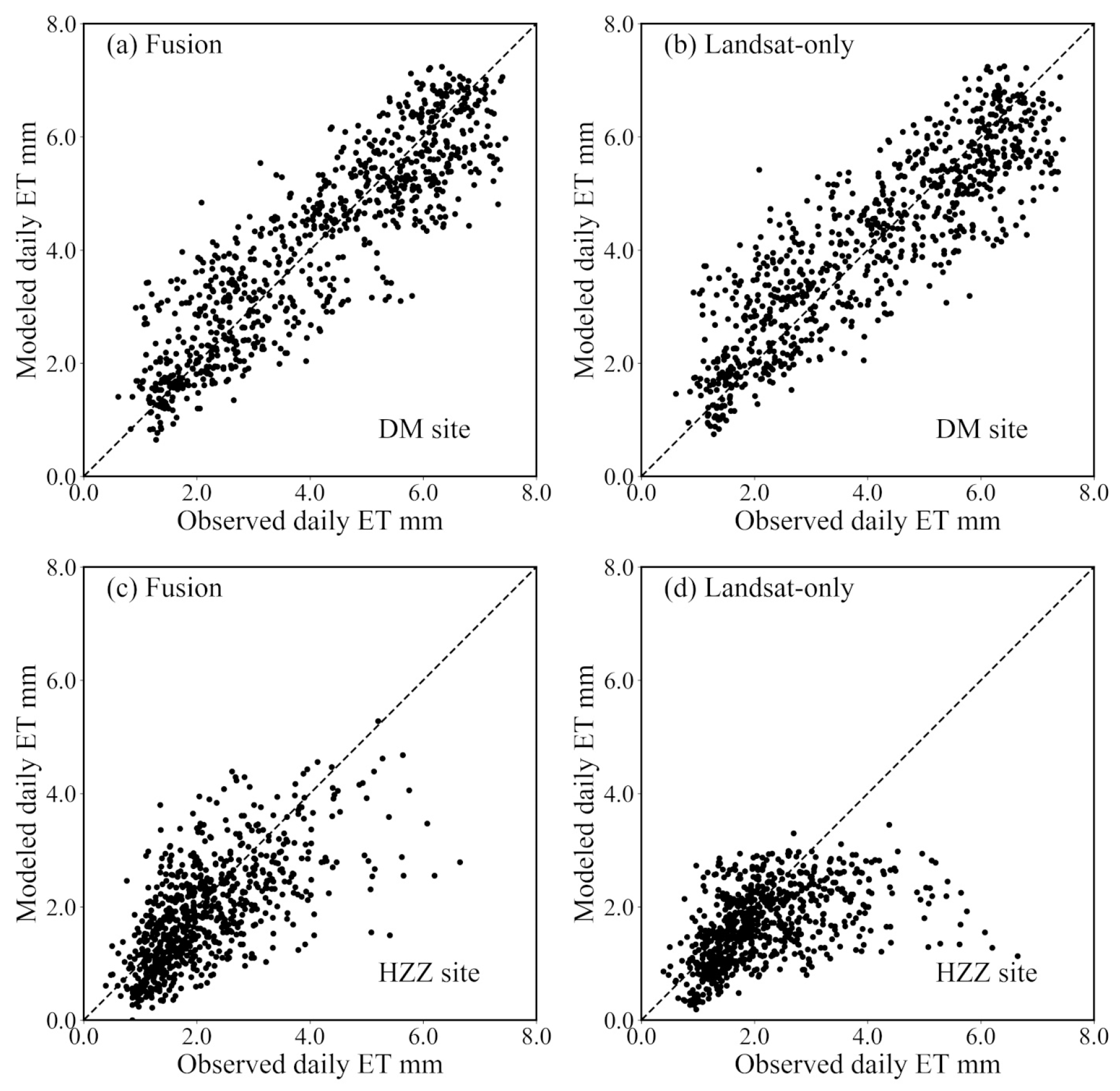
3.2. Evaluation of Daily ET at The Study Sites
3.3. Evaluation of ET Partitioning Over The Cropland
4. Discussion
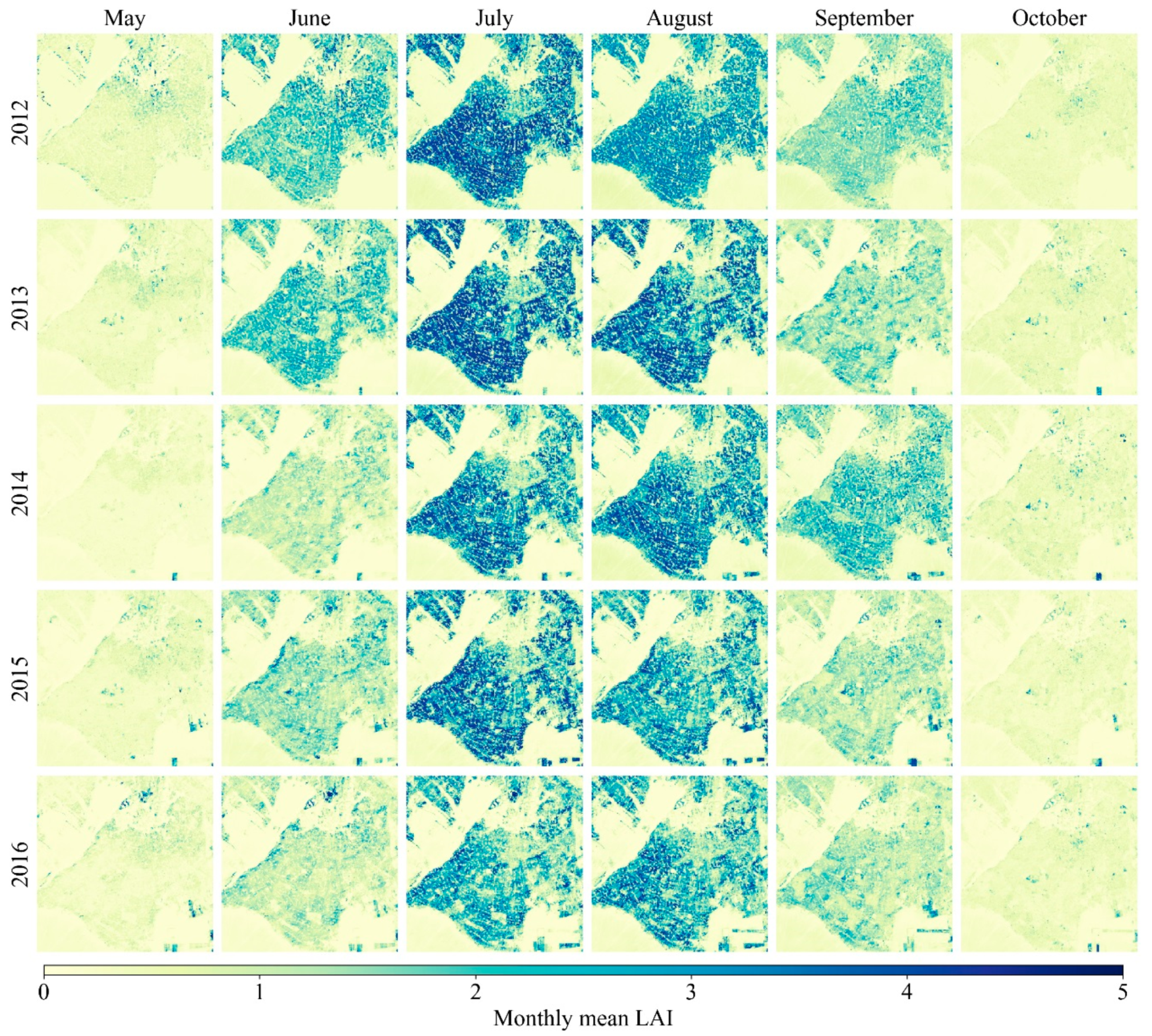
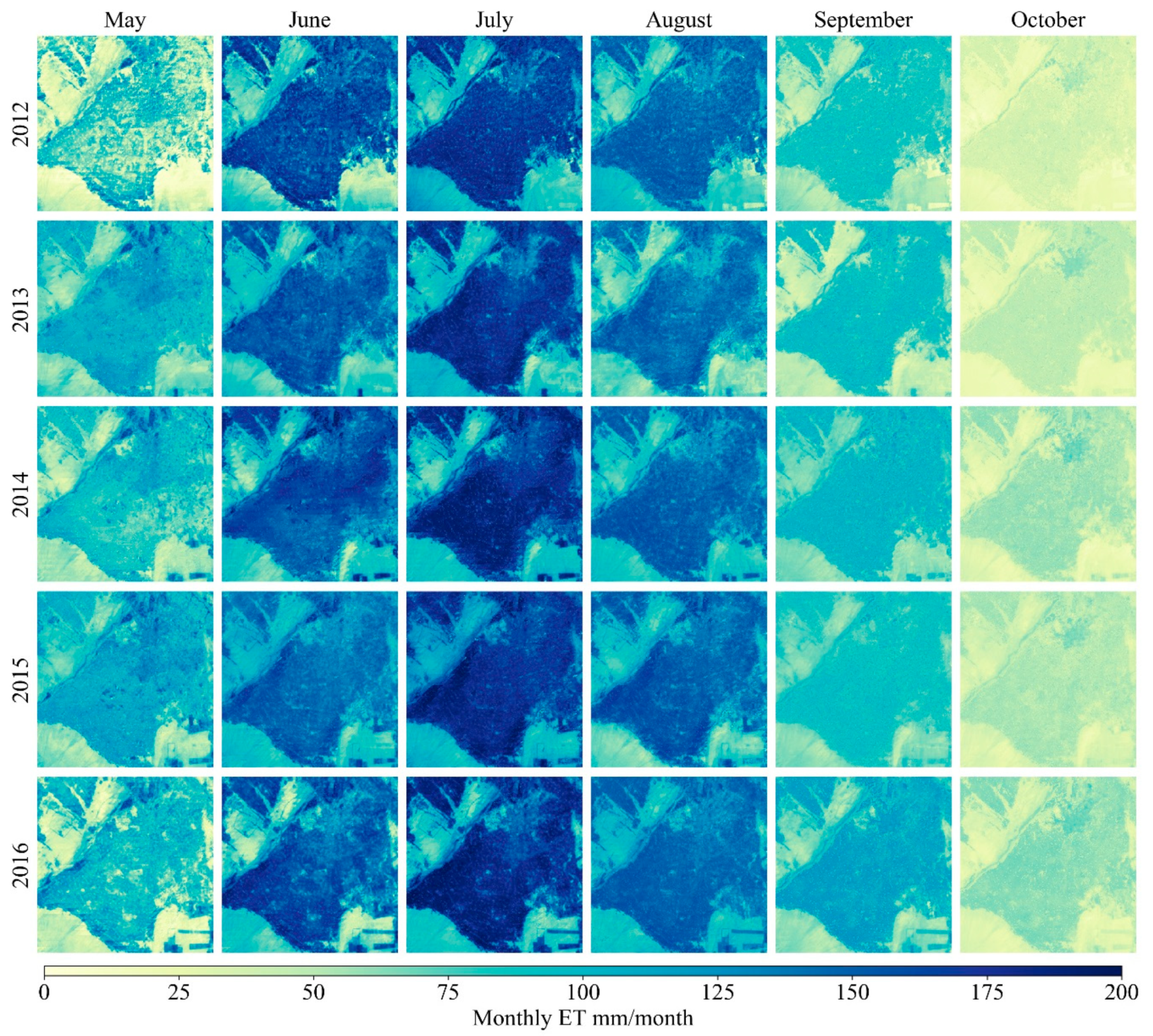
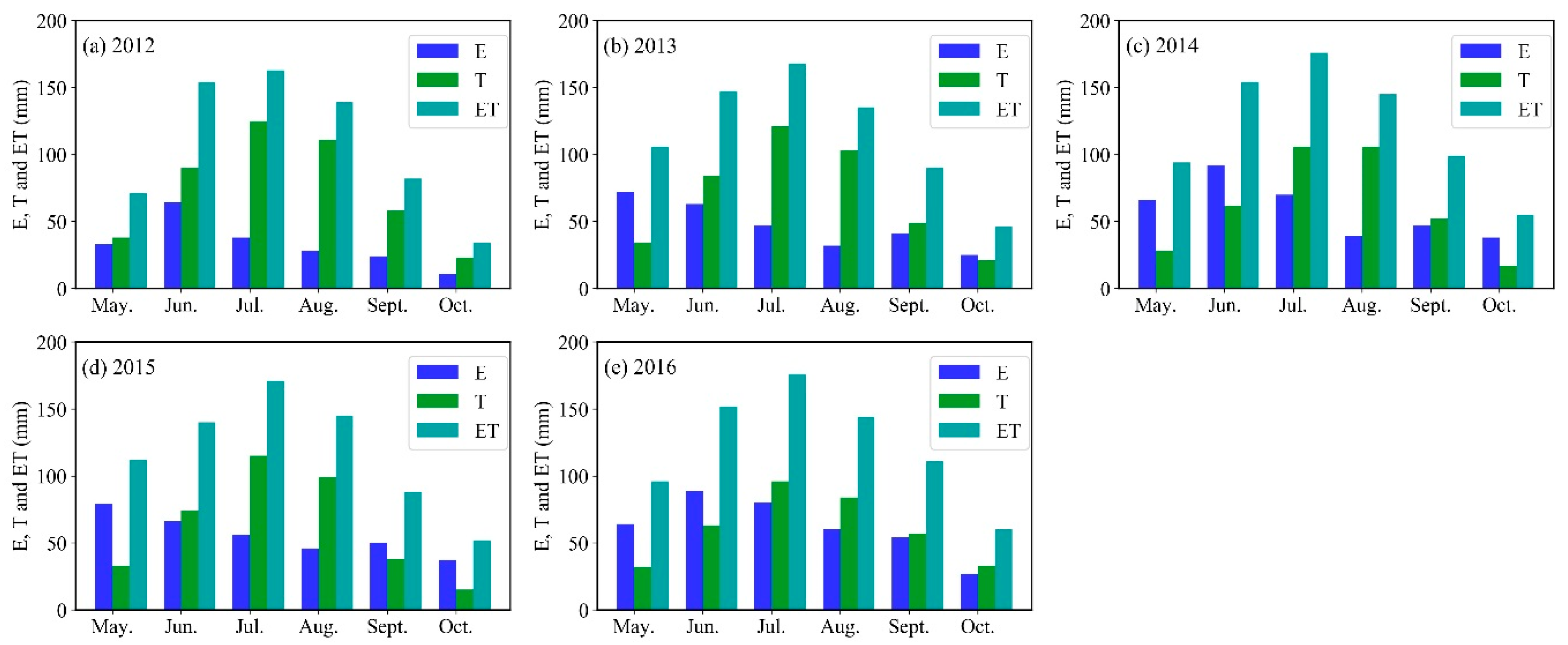
4.1. Spatiotemporal Patterns of E, T, and ET
4.2. Water Consumption by Land Type
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kirda, C.; Kanber, R. Water, no longer a plentiful resource, should be used sparingly in irrigated agriculture. In Crop Yield Response to Deficit Irrigation; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández, J.E.; Slawinski, C.; Moreno, F.; Walczak, R.T.; Vanclooster, M. Simulating the fate of water in a soil–crop system of a semi-arid Mediterranean area with the wave 2.1 and the euro-access-ii models. Agric. Water Manag. 2002, 56, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.S.; Liu, S.M.; Kustas, W.P.; Nieto, H.; Sun, L.; Xu, Z.W.; Skaggs, T.H.; Yang, Y.; Ma, M.G.; Xu, T.R.; et al. Monitoring and validating spatially and temporally continuous daily evaporation and transpiration at river basin scale. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 219, 72–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kool, D.; Agam, N.; Lazarovitch, N.; Heitman, J.L.; Sauer, T.J.; Ben-Gal, A. A review of approaches for evapotranspiration partitioning. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 184, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustas, W.P.; Alfieri, J.G.; Nieto, H.; Wilson, T.G.; Gao, F.; Anderson, M.C. Utility of the two-source energy balance (TSEB) model in vine and interrow flux partitioning over the growing season. Irrig. Sci. 2019, 37, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, M.S. Thermal infrared measurement as an indicator of plant ecosystem health. In Thermal Remote Sensing in Land Surface Processes; CRC press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; pp. 257–282. [Google Scholar]
- Semmens, K.A.; Anderson, M.C.; Kustas, W.P.; Gao, F.; Alfieri, J.G.; McKee, L.; Prueger, J.H.; Hain, C.R.; Cammalleri, C.; Yang, Y.; et al. Monitoring daily evapotranspiration over two California vineyards using landsat 8 in a multi-sensor data fusion approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courault, D.; Seguin, B.; Olioso, A. Review on estimation of evapotranspiration from remote sensing data: From empirical to numerical modeling approaches. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2005, 19, 223–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalma, J.D.; Mcvicar, T.R.; Mccabe, M.F. Estimating land surface evaporation: A review of methods using remotely sensed surface temperature data. Surv. Geophys. 2008, 29, 421–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.C.; Dickinson, R.E. A review of global terrestrial evapotranspiration: Observation, modeling, climatology, and climatic variability. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, C.; Sun, R.; Xu, Z.W.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.Y.; Hao, L.Y.; Jiang, G.Q. A study of shelterbelt transpiration and cropland evapotranspiration in an irrigated area in the middle reaches of the Heihe river in northwestern china. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.F.; Yang, B.; Sun, X.M.; Lee, X.H. Evapotranspiration partitioning through in-situ Oxygen isotope measurements in an oasis cropland. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 230–231, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, T.M.; Kustas, W.P. Partitioning evapotranspiration using an eddy covariance-based technique: Improved assessment of soil moisture and land–atmosphere exchange dynamics. Vadose Zone J. 2012, 11, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, T.M.; Schmidt, D.F.; Skaggs, T.H. Correlation-based flux partitioning of water vapor and carbon dioxide fluxes: Method simplification and estimation of canopy water use efficiency. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 279, 107732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talsma, C.J.; Good, S.P.; Carlos, J.; Brecht, M.; Fisher, J.B.; Miralles, D.G.; McCabe, M.; Purdy, A.J. Partitioning of evapotranspiration in remote sensing-based models. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 260–261, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, J.M.; Kustas, W.P.; Humes, K.S. Source approach for estimating soil and vegetation energy fluxes in observations of directional radiometric surface temperature. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1995, 77, 263–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustas, W.P.; Norman, J.M. Evaluation of soil and vegetation heat flux predictions using a simple two-source model with radiometric temperatures for partial canopy cover. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1999, 94, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.B.; Tu, K.P.; Baldocchi, D.D. Global estimates of the land–atmosphere water flux based on monthly AVHRR and ISLSCP-II data, validated at 16 FLUXNETsites. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 901–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miralles, D.G.; Gash, J.H.; Holmes, T.R.H.; Jeu, R.A.M.D.; Dolman, A.J. Global canopy interception from satellite observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D16122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.Z.; Zhao, M.S.; Running, S.W. Improvements to a MODIS global terrestrial evapotranspiration algorithm. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1781–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellvert, J.; Jofre-Cekalovic, C.; Pelecha, A.; Mata, M.; Nieto, H. Feasibility of using the two-source energy balance model (TSEB) with Sentinel-2 and Sentinel-3 images to analyze the spatio-temporal variability of vine water status in a vineyard. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Anderson, M.C.; Gao, F.; Hain, C.; Alfieri, J.G.; Sharifi, A.; McCarty, G.W.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Kustas, W.P.; et al. Investigating water use over the Choptank river watershed using a multisatellite data fusion approach. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 5298–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.R.; Bateni, S.; Margulis, S.; Song, L.S.; Liu, S.M.; Xu, Z.W. Partitioning evapotranspiration into soil evaporation and canopy transpiration via a two-source variational data assimilation system. J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17, 2353–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.J.; Liang, S.L.; Yu, J.; Chen, J.Q.; Liu, S.M.; Lin, Y.; Fisher, J.B.; McVicar, T.R.; Cheng, J.; Jia, K.; et al. A simple temperature domain two-source model for estimating agricultural field surface energy fluxes from Landsat images. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 5211–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammalleri, C.; Anderson, M.C.; Gao, F.; Hain, C.R.; Kustas, W.P. A data fusion approach for mapping daily evapotranspiration at field scale. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 4672–4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.C.; Kustas, W.P.; Norman, J.M.; Hain, C.R.; Mecikalski, J.R.; Schultz, L.; Gonzalez-Dugo, M.P.; Cammalleri, C.; d’Urso, G.; Pimstein, A.; et al. Mapping daily evapotranspiration at field to continental scales using geostationary and polar orbiting satellite imagery. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustas, W.P.; Norman, J.M.; Anderson, M.C.; French, A.N. Estimating subpixel surface temperatures and energy fluxes from the vegetation index–radiometric temperature relationship. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 85, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.L.; Cai, J.B.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, B.Z.; Huang, L.X. Responses of field evapotranspiration to the changes of cropping pattern and groundwater depth in large irrigation district of Yellow river basin. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 188, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammalleri, C.; Anderson, M.C.; Gao, F.; Hain, C.R.; Kustas, W.P. Mapping daily evapotranspiration at field scales over rainfed and irrigated agricultural areas using remote sensing data fusion. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 186, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knipper, K.R.; Kustas, W.P.; Anderson, M.C.; Alfieri, J.G.; Prueger, J.H.; Hain, C.R.; Gao, F.; Yang, Y.; Mckee, L.G.; Nieto, H.; et al. Evapotranspiration estimates derived using thermal-based satellite remote sensing and data fusion for irrigation management in California vineyards. Irrig. Sci. 2019, 37, 431–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Anderson, M.C.; Gao, F.; Hain, C.; Noormets, A.; Sun, G.; Wynne, R.; Thomas, V.; Sun, L. Investigating impacts of drought and disturbance on evapotranspiration over a forested landscape in North Carolina, USA using high spatiotemporal resolution remotely sensed data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 238, 111018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Anderson, M.C.; Gao, F.; Hain, C.R.; Semmens, K.A.; Kustas, W.P.; Noormets, A.; Wynne, R.H.; Thomas, V.A.; Sun, G. Daily Landsat-scale evapotranspiration estimation over a forested landscape in North CarolinaUSA, using multi-satellite data fusion. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci 2017, 21, 1017–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Anderson, M.C.; Gao, F.; Wardlow, B.; Hain, C.R.; Otkin, J.A.; Alfieri, J.; Yang, Y.; Sun, L.; Dulaney, W. Field-scale mapping of evaporative stress indicators of crop yield: An application over mead, NE, USA. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 210, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzinski, R.; Nieto, H. Evaluating the feasibility of using Sentinel-2 and Sentinel-3 satellites for high-resolution evapotranspiration estimations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 221, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, C.L.; Hou, J.L.; Gu, J.; Zhu, G.F.; Li, X. Mapping daily evapotranspiration based on spatiotemporal fusion of ASTER and MODIS images over irrigated agricultural areas in the Heihe River Basin, Northwest China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 244, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.F.; Liu, S.M.; Song, L.S.; Xu, Z.W.; Liu, Y.L.; Xu, T.R.; Zhu, Z.L. Estimation of daily evapotranspiration and irrigation water efficiency at a landsat-like scale for an arid irrigation area using multi-source remote sensing data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 216, 715–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Masek, J.; Schwaller, M.; Hall, F. On the blending of the Landsat and MODIS surface reflectance: Predicting daily Landsat surface reflectance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2207–2218. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.D.; Li, X.; Zhao, W.Z.; Xu, Z.M.; Feng, Q.; Xiao, S.C.; Xiao, H.L. Integrated study of the water-ecosystem-economy in the Heihe River Basin. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2014, 1, 413–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cheng, G.D.; Ge, Y.C.; Li, H.Y.; Han, F.; Hu, X.L.; Tian, W.; Tian, Y.; Pan, X.D.; Nian, Y.Y.; et al. Hydrological cycle in the heihe river basin and its implication for water resource management in endorheic basins. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 890–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cheng, G.D.; Liu, S.M.; Xiao, Q.; Ma, M.M.; Jin, R.; Che, T.; Liu, Q.H.; Wang, W.Z.; Qi, Y.; et al. Heihe watershed allied telemetry experimental research (HiWATER): Scientific objectives and experimental design. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 1145–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.M.; Li, X.; Xu, Z.W.; Che, T.; Xiao, Q.; Ma, M.G.; Liu, Q.H.; Jin, R.; Guo, J.W.; Wang, L.X.; et al. The Heihe integrated observatory network: A basin-scale land surface processes observatory in China. Vadose Zone J. 2018, 17, 180072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.M.; Xu, Z.W.; Song, L.S.; Zhao, Q.Y.; Ge, Y.; Xu, T.R.; Ma, Y.F.; Zhu, Z.L.; Jia, Z.Z.; Zhang, F. Upscaling evapotranspiration measurements from multi-site to the satellite pixel scale over heterogeneous land surfaces. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 230–231, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.M.; Xu, Z.W.; Wang, W.Z.; Jia, Z.Z.; Zhu, M.J.; Bai, J.W.; Wang, J.M. A comparison of eddy-covariance and large aperture scintillometer measurements with respect to the energy balance closure problem. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1291–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.W.; Liu, S.M.; Li, X.; Shi, S.J.; Wang, J.M.; Zhu, Z.L.; Xu, T.R.; Wang, W.Z.; Ma, M.G. Intercomparison of surface energy flux measurement systems used during the HiWATER-MUSOEXE. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 13140–13157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kustas, W.P.; Huang, C.L.; Nieto, H.; Haghighi, E.; Anderson, M.C.; Domingo, F.; Garcia, M.; Scott, L.R. Evaluating soil resistance formulations in thermal-based two-source energy balance (TSEB) model: Implications for heterogeneous semiarid and arid regions. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 1059–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Wang, J.M. A temperature prediction-correction method for estimating surface soil heat flux from soil temperature and moisture data. Sci. China Ser. Earth Sci. 2008, 51, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prueger, J.H.; Hatfield, J.L.; Kustas, W.P.; Hipps, L.E.; MacPherson, J.I.; Neale, C.M.U.; Eichinger, W.E.; Cooper, D.I.; Parkin, T.B. Tower and aircraft Eddy Covariance measurements of water vapor, energy, and carbon dioxide fluxes during SMACEX. J. Hydrometeorol. 2005, 6, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twine, T.E.; Kustas, W.P.; Norman, J.M.; Cook, D.R.; Houser, P.R.; Mayers, T.P.; Prueger, J.H.; Starks, P.J.; Wesely, M.L. Correcting eddy covariance flux underestimation over a grassland. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2000, 103, 279–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Chen, Z.X.; Gao, F.; Anderson, M.C.; Song, L.S.; Wang, L.M.; Hu, B.; Yang, Y. Reconstructing daily clear-sky land surface temperature for cloudy regions from Modis data. Comput. Geosci. 2017, 105, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaramuzza, P.; Micijevic, E.; Chander, G. SLC Gap-Filled Products Phase One Methodology. 2004. Available online: https://landsat.usgs.gov/sites/default/files/documents/SLC_Gap_Fill_Methodology.pdf (accessed on 28 May 2009).
- Yu, X.; Guo, X.; Wu, Z. Land surface temperature retrieval from landsat 8 tirs-comparison between radiative transfer equation-based method, split window algorithm and single channel method. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 9829–9852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutman, G.; Ignatov, A. The derivation of the green vegetation fraction from NOAA/AVHRR data for use in numerical weather prediction models. Int. J. Remote Sens 1998, 19, 1533–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, B.J. Relationships between vegetation indices, radiation absorption, and net photosynthesis evaluated by a sensitivity analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 1987, 22, 209–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, B.; Yang, A.X.; Nie, A.H.; Yao, Y.J.; Zhang, H.; Wu, S.L.; Liu, Q.H. Finer resolution land-cover mapping using multiple classifiers and multisource remotely sensed data in the Heihe River Basin. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 99, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, G.S.; Norman, J.M. An Introduction to Environmental Biophysics; Springer Science and Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 1998; p. 286. [Google Scholar]
- Colaizzi, P.D.; Agam, N.; Tolk, J.A.; Evett, S.R.; Howell, T.A.; Gowda, P.; O’Shaughnessy, S.A.; Kustas, W.P.; Anderson, M.C. Two source energy balance model to calculate E, T, and ET: Comparison of Priestly-Taylor and Penman-Monteith formulations and two time scaling methods. Trans. ASABE 2014, 57, 479–498. [Google Scholar]
- Colaizzi, P.D.; Evett, S.R.; Howell, T.A.; Gowda, P.; O’Shaughnessy, S.A.; Tolk, J.A.; Kustas, W.P.; Anderson, M.C. Two source energy balance model: Refinements and lysimeter tests in the Southern High Plains. Trans. ASABE 2012, 55, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustas, W.P.; Norman, J.M. A two-source energy balance approach using directional radiometric temperature observations for sparse canopy covered surfaces. J. Agron. 2000, 92, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Q.F.; Wu, B.F. Estimating evapotranspiration from an improved two-source energy balance model using ASTER satellite imagery. Water 2015, 7, 6673–6688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustas, W.P.; Daughtry, C.S.T. Estimation of the soil heat flux/net radiation ratio from spectral data. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1990, 49, 205–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morillas, L.; García, M.; Nieto, H.; Villagarcia, L.; Sandholt, I.; Gonzalez-Dugo, M.P.; Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Domingo, F. Using radiometric surface temperature for surface energy flux estimation in Mediterranean drylands from a two-source perspective. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 136, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.S.; Kustas, W.P.; Liu, S.M.; Colaizzi, P.D.; Nieto, H.; Xu, Z.W.; Ma, Y.F.; Li, M.S.; Xu, T.R.; Agam, N.; et al. Applications of a thermal-based two-source energy balance model using Priestley-Taylor approach for surface temperature partitioning under advective conditions. J. Hydrol. 2016, 540, 574–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustas, W.P.; Anderson, M.C. Advances in thermal infrared remote sensing for land surface modeling. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2009, 149, 2071–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Radeloff, V.C.; Ives, A.R. Improving the mapping of crop types in the midwestern USA by fusing landsat and modis satellite data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 58, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Tasumi, M.; Trezza, R. Satellite-based energy balance for Mapping Evapotranspiration with Internalized Calibration (METRIC)—Model. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2007, 133, 380–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop. Evapotranspiration—Guidelines for Computing Crop. Water Requirements—FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998; p. 300. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.T.; Long, D.; Guan, H.D.; Liang, W.; Simmons, C.; Batelaan, O. Comparison of three dual-source remote sensing evapotranspiration models during the MUSOEXE-12 campaign: Revisit of model physics. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 3145–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.S.; Liu, S.M.; Kustas, W.P.; Zhou, J.; Xu, Z.W.; Xia, T.; Li, M.S. Application of remote sensing-based two-source energy balance model for mapping field surface fluxes with composite and component surface temperatures. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 230–231, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.M.; Zhuang, J.X.; Wang, W.Z.; Liu, S.M.; Xu, Z.W. Assessment of uncertainties in Eddy Covariance flux measurement based on intensive flux matrix of HiWATER-MUSOEXE. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronato, F.R.; Bertiller, M.B. Precipitation and landscape related effects on soil moisture in semi-arid rangelands of Patagonia. J. Arid Environ. 1996, 34, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanzy, A.; Bruckler, L. Significance of soil surface moisture with respect to daily bare soil evaporation. Water Resour. Res. 1993, 29, 1113–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.M.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.Q. Determination of daily evaporation and evapotranspiration of winter wheat and maize by large-scale weighing lysimeter and micro-lysimeter. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2002, 111, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Yu, B.F.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.F.; Wang, G.Q. Water use efficiency and evapotranspiration partitioning for three typical ecosystems in the Heihe river basin, northwestern China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 253–254, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.S.; Kang, S.Z.; Li, F.S.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Tong, L. Evapotranspiration measurement and estimation using modified Priestley-Taylor model in an irrigated maize field with mulching. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 168, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Kang, S.Z.; Zhang, L.; Ortega-Farias, S.; Li, F.S.; Du, T.S.; Tong, L.; Wang, S.F.; Ingman, M.; Guo, W.H. Measuring and modeling maize evapotranspiration under plastic film-mulching condition. J. Hydrol. 2013, 503, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

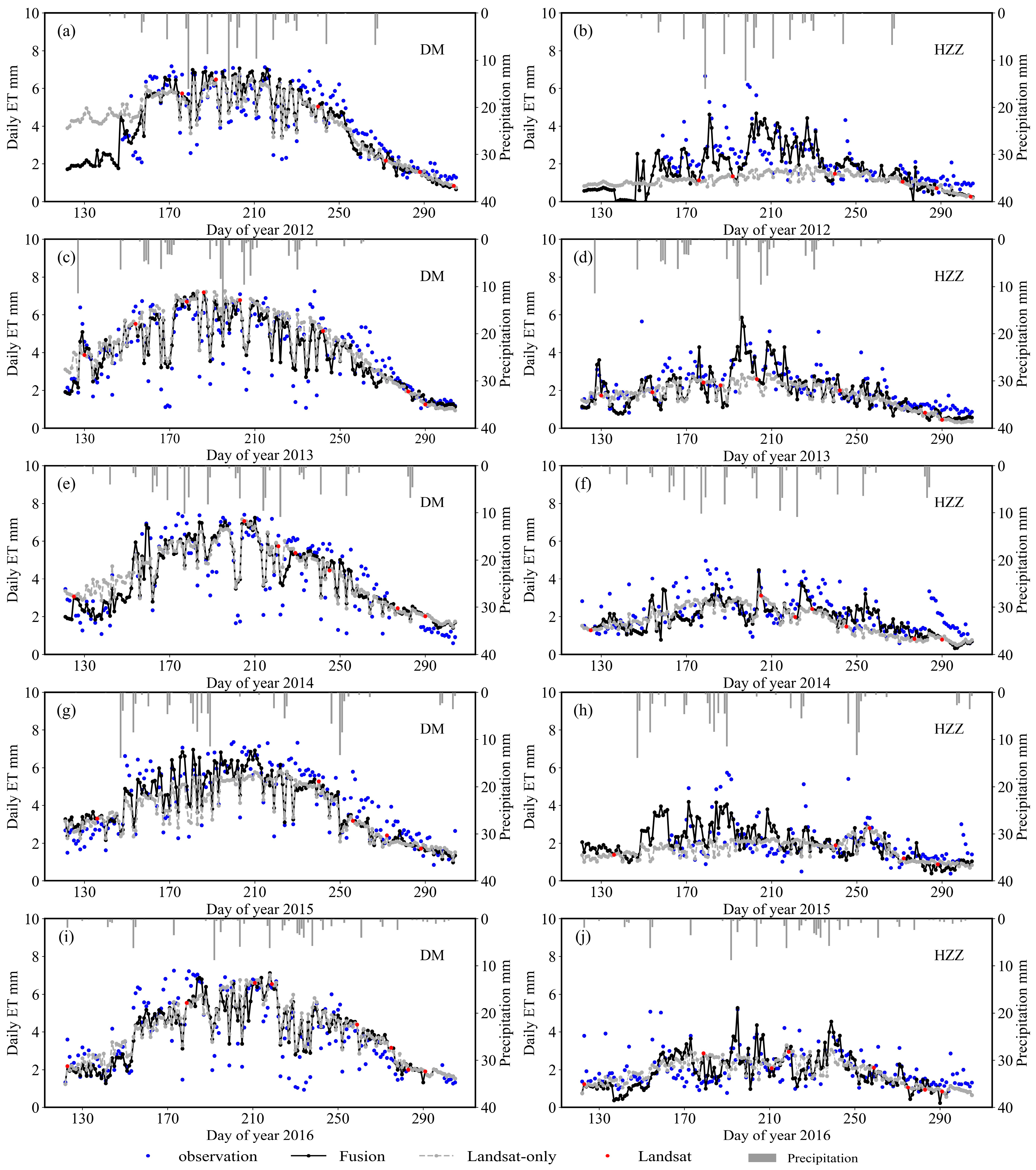
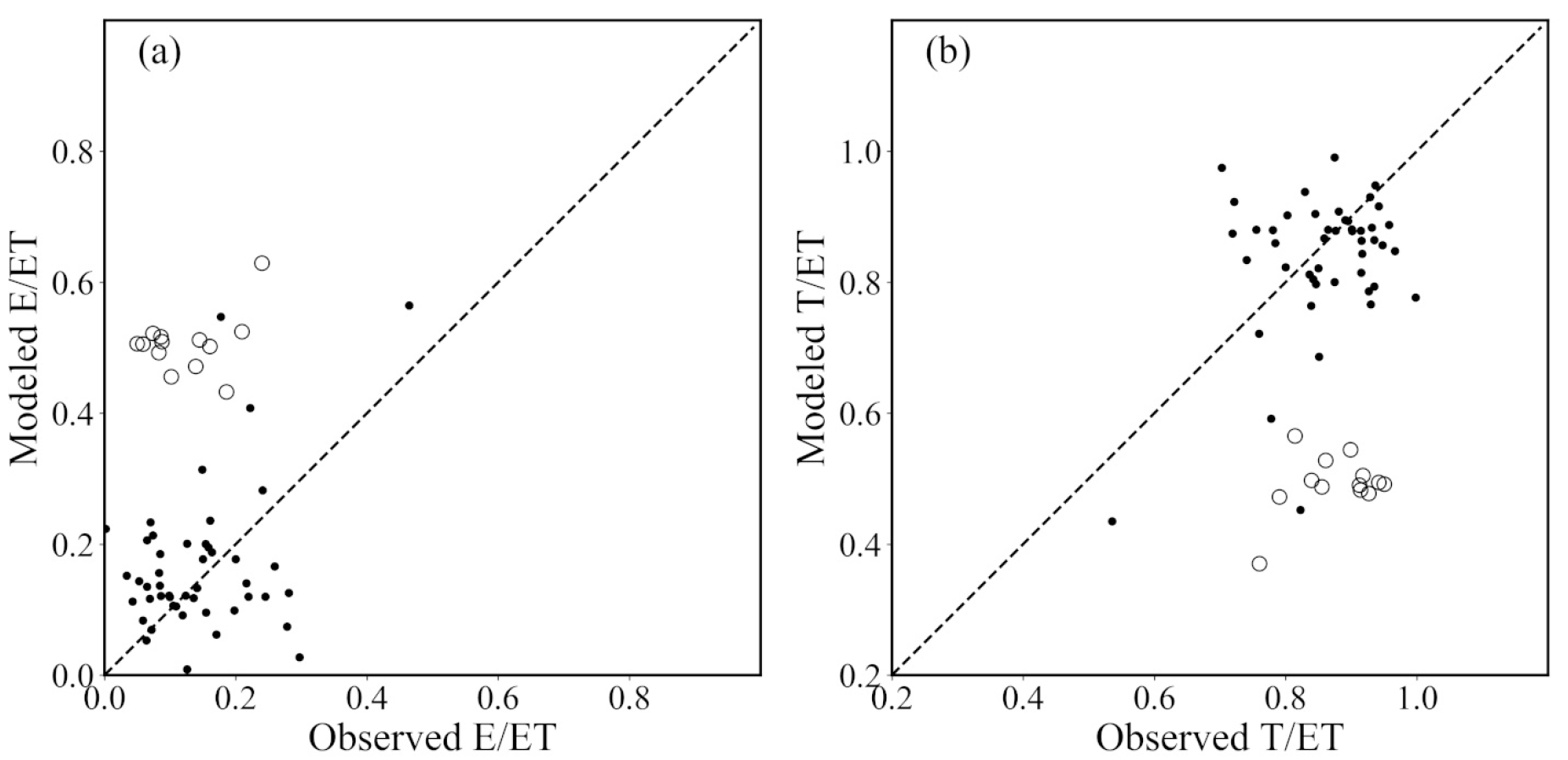

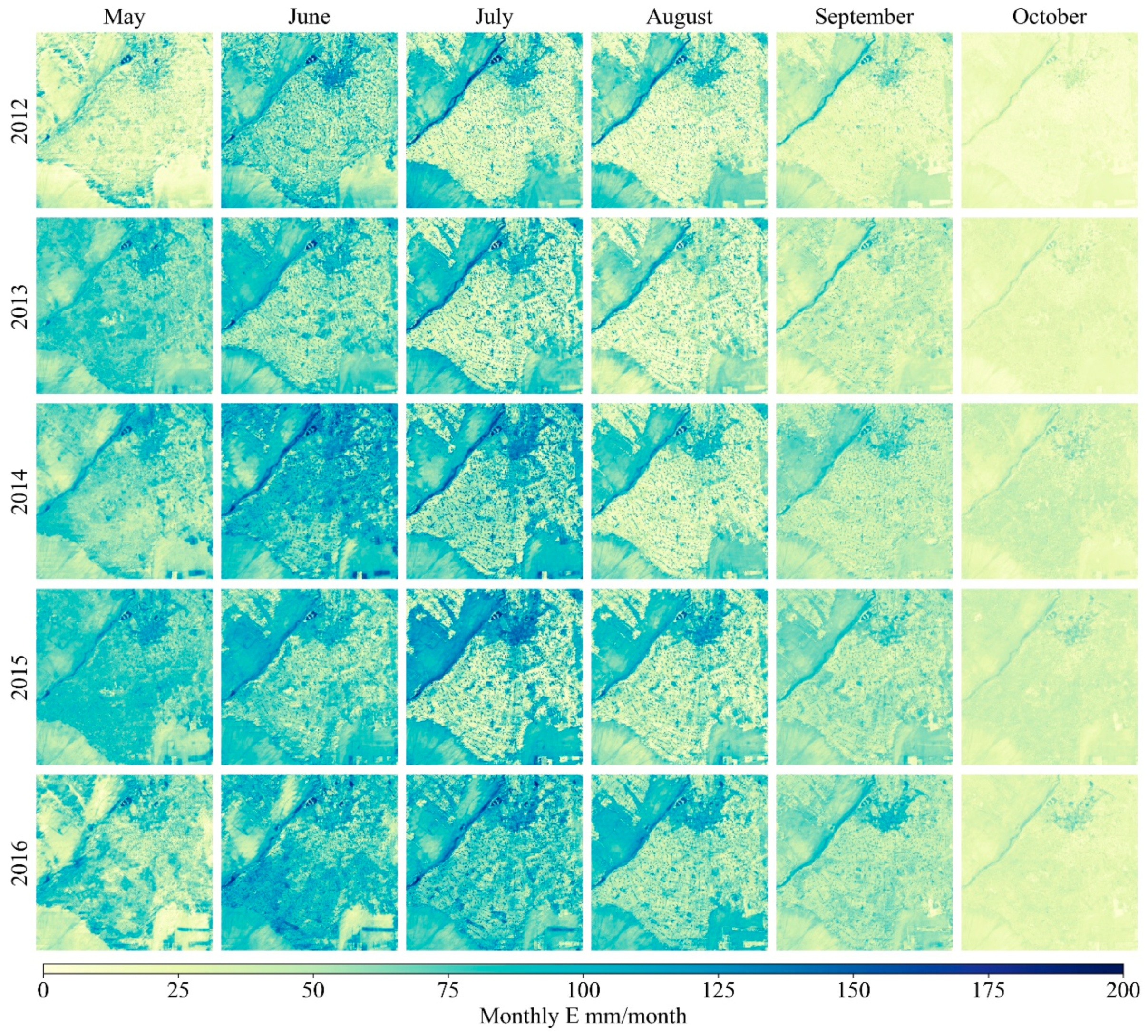
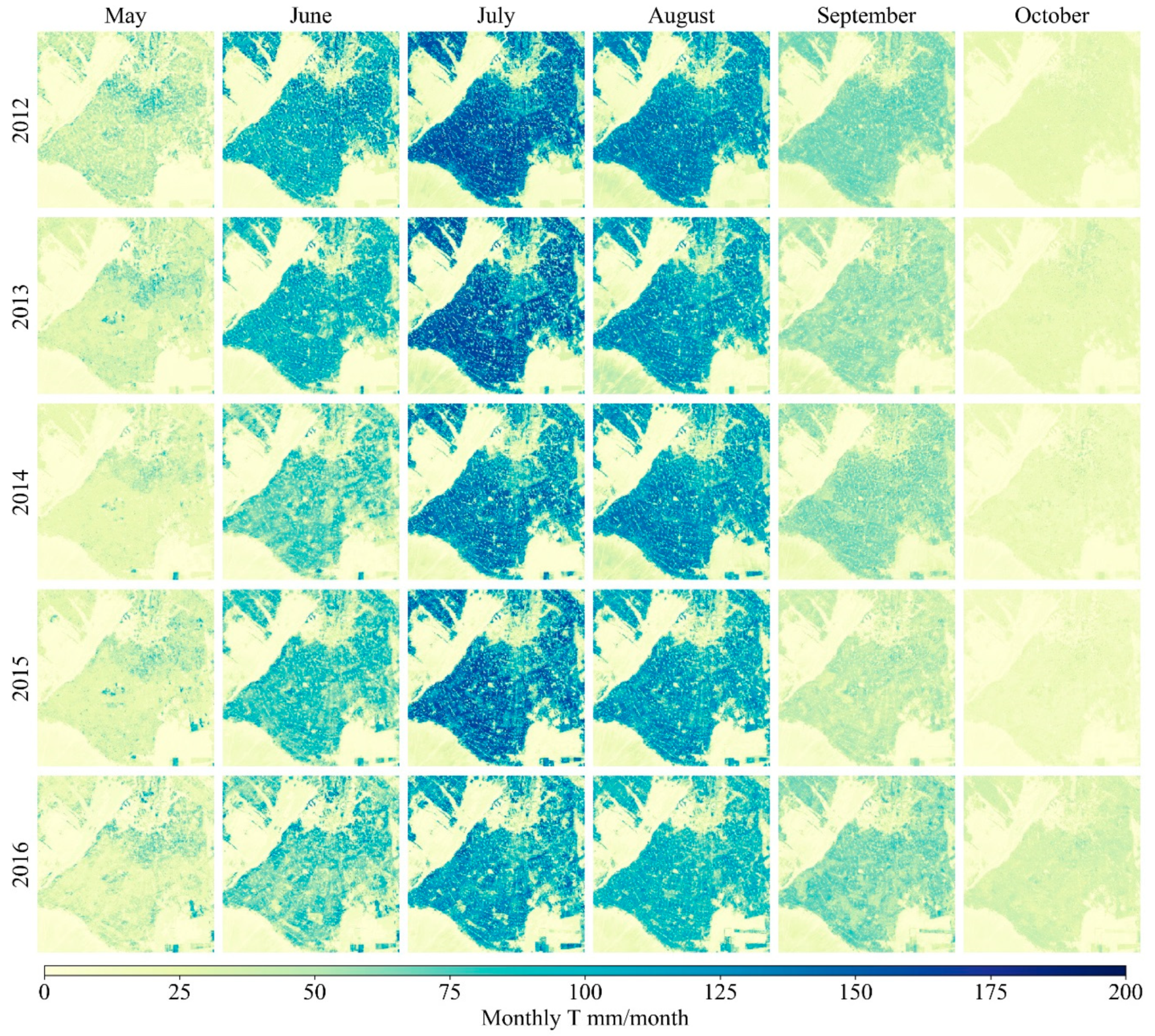

| Years | Number of Days with Useable MODIS Imagery | Day of Year (DOY) with A Clear Landsat 7 Overpass | DOY with A Clear Landsat 8 Overpass |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 | 92 | 176, 192, 240, 272, 288, 304 | ---- |
| 2013 | 90 | 130, 178, 242, 290 | 154, 186, 202, 282 |
| 2014 | 81 | 229, 245, 277, 290 | 125, 205, 221 |
| 2015 | 80 | 136 | 240, 256, 272, 288 |
| 2016 | 73 | 123, 219, 283 | 179, 211, 259, 275, 291 |
| Study Site | Number | Error Type | Rn (W/m2) | G (W/m2) | H (W/m2) | LE (W/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DM | 391 | Bias | 2 | 12 | −20 | 4 |
| RMSE | 22 | 41 | 54 | 61 | ||
| MAPD | 3% | 47% | 42% | 12% | ||
| HZZ | 395 | Bias | 1 | 13 | −24 | 10 |
| RMSE | 26 | 27 | 52 | 61 | ||
| MAPD | 4% | 22% | 19% | 32% |
| Study Site | Number | Error Type | Fusion | Landsat-Only |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DM | 825 | Bias (mm) | 0.01 | 0.04 |
| RMSE (mm) | 0.85 | 0.91 | ||
| MAPD | 16% | 17% | ||
| HZZ | 791 | Bias(mm) | −0.25 | −0.45 |
| RMSE (mm) | 0.84 | 1.00 | ||
| MAPD | 29% | 33% |
| Error Type | Overall (Number = 60) | DOY >170 (Number = 47) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| E/ET | Bias | 0.1 | 0 |
| RMSE | 0.2 | 0.11 | |
| MAPD | 107% | 53% | |
| T/ET | Bias | −0.1 | 0 |
| RMSE | 0.2 | 0.11 | |
| MAPD | 17% | 10% |
| Years | May | June | July | August | September | October |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 | 1.9 | 31.1 | 47.1 | 24.5 | 10.5 | 0.1 |
| 2013 | 18.5 | 33.0 | 58.9 | 17.9 | 3.0 | 0.0 |
| 2014 | 6.5 | 41.6 | 23.0 | 42.2 | 10.3 | 14.1 |
| 2015 | 18.2 | 31.2 | 30.4 | 12.0 | 33.1 | 9.4 |
| 2016 | 16.7 | 25.4 | 27.0 | 38.8 | 10.0 | 10.0 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Huang, C.; Kustas, W.P.; Nieto, H.; Sun, L.; Hou, J. Evapotranspiration Partitioning at Field Scales Using TSEB and Multi-Satellite Data Fusion in The Middle Reaches of Heihe River Basin, Northwest China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3223. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12193223
Li Y, Huang C, Kustas WP, Nieto H, Sun L, Hou J. Evapotranspiration Partitioning at Field Scales Using TSEB and Multi-Satellite Data Fusion in The Middle Reaches of Heihe River Basin, Northwest China. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(19):3223. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12193223
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yan, Chunlin Huang, William P. Kustas, Hector Nieto, Liang Sun, and Jinliang Hou. 2020. "Evapotranspiration Partitioning at Field Scales Using TSEB and Multi-Satellite Data Fusion in The Middle Reaches of Heihe River Basin, Northwest China" Remote Sensing 12, no. 19: 3223. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12193223
APA StyleLi, Y., Huang, C., Kustas, W. P., Nieto, H., Sun, L., & Hou, J. (2020). Evapotranspiration Partitioning at Field Scales Using TSEB and Multi-Satellite Data Fusion in The Middle Reaches of Heihe River Basin, Northwest China. Remote Sensing, 12(19), 3223. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12193223