Error Decomposition of Remote Sensing Soil Moisture Products Based on the Triple-Collocation Method Introducing an Unbiased Reference Dataset: A Case Study on the Tibetan Plateau
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
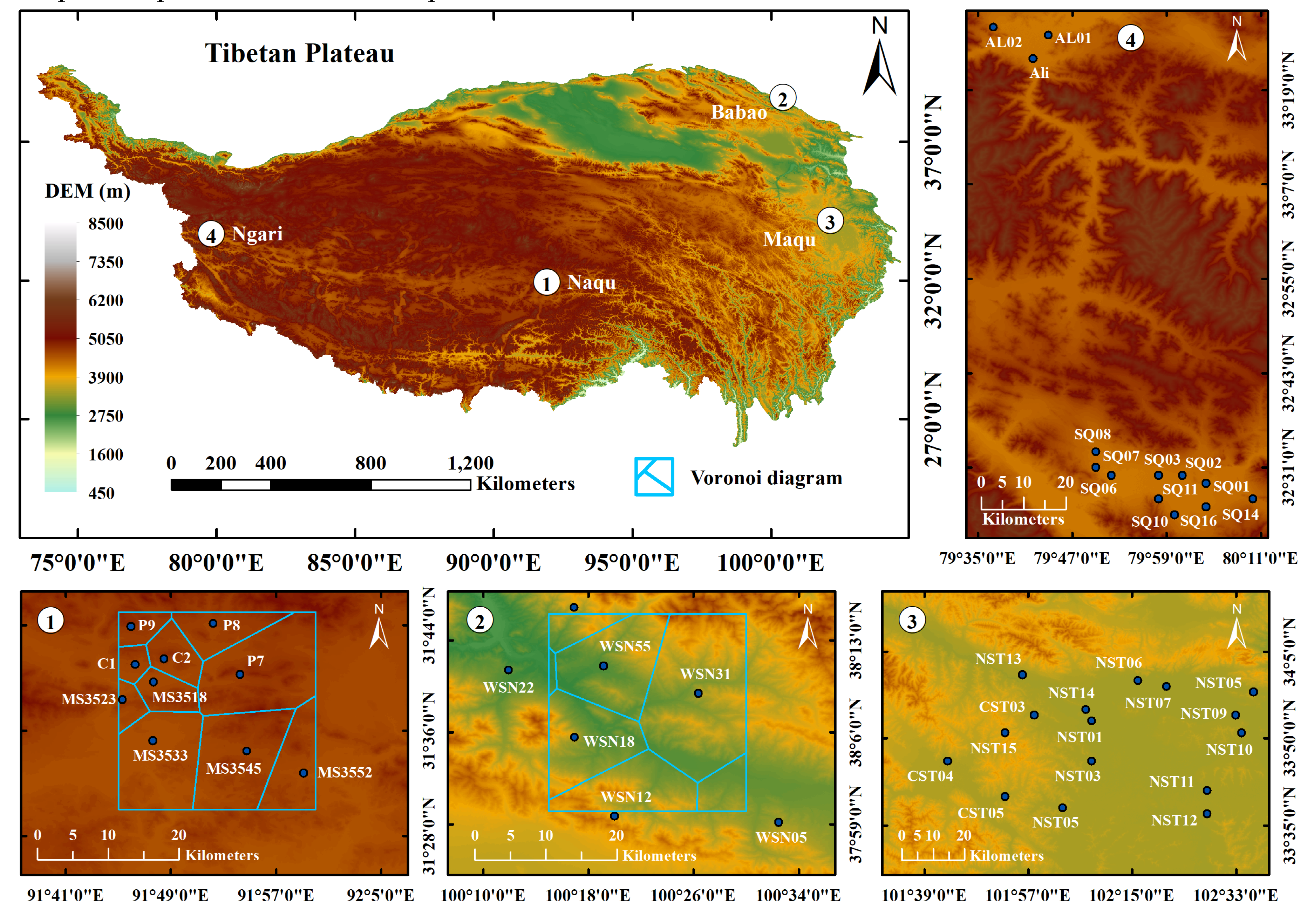
2.1. Study Area and Data
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. Error Decomposition
2.2.2. Determination of the Reference Dataset
3. A Case Study on the Error Structure of Remote Sensing Soil Moisture Product
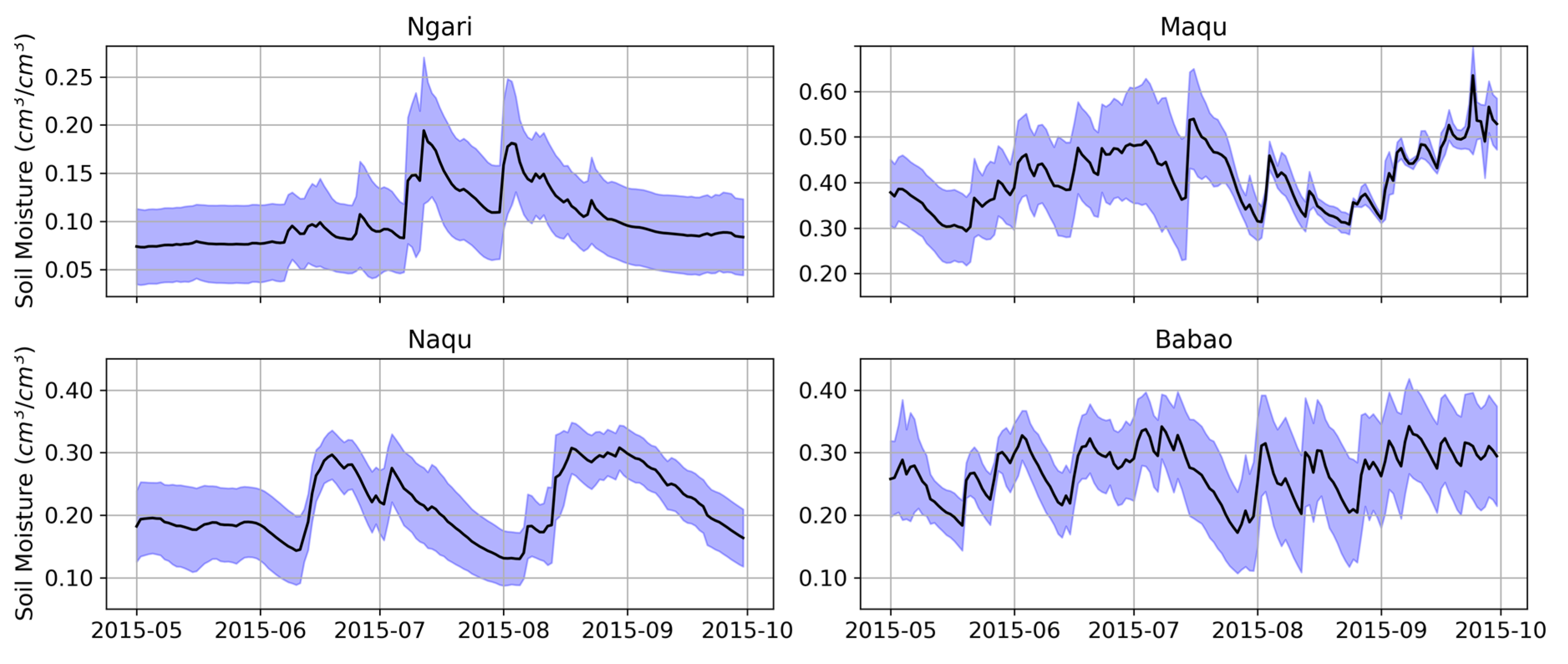
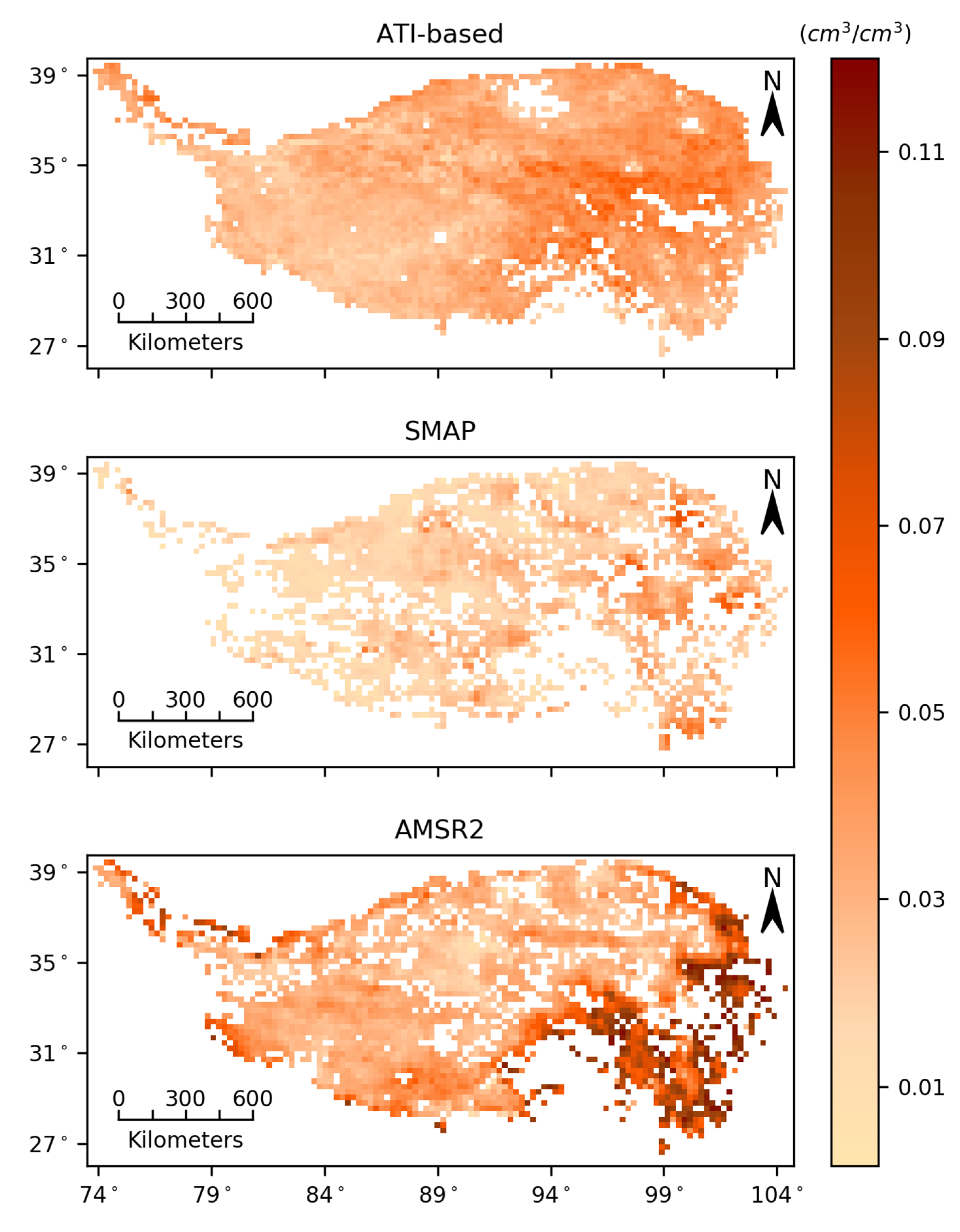
3.1. Obtaining the Soil Moisture Reference Dataset
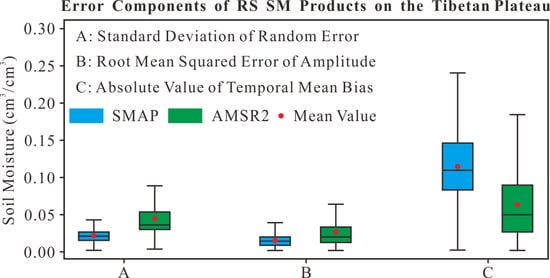
3.2. Error Decomposition
3.3. Analysis of Systematic Errors
3.4. Ground-based Validation of Error Decomposition
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tuttle, S.; Salvucci, G. Empirical evidence of contrasting soil moisture–precipitation feedbacks across the united states. Science 2016, 352, 825–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stéfanon, M.; Drobinski, P.; D’Andrea, F.; Lebeaupin-Brossier, C.; Bastin, S. Soil moisture-temperature feedbacks at meso-scale during summer heat waves over western europe. Clim. Dyn. 2014, 42, 1309–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mystakidis, S.; Davin, E.L.; Gruber, N.; Seneviratne, S.I. Influence of soil moisture-carbon cycle interactions on the terrestrial carbon cycle over Europe. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference, Vienna, Austria, 17–22 April 2016; 2016; p. 14125. [Google Scholar]
- Ochsner, T.E.; Cosh, M.H.; Cuenca, R.H.; Dorigo, W.A.; Draper, C.S.; Hagimoto, Y.; Kerr, Y.H.; Njoku, E.G.; Small, E.E.; Zreda, M. State of the art in large-scale soil moisture monitoring. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2013, 77, 1888–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seneviratne, S.I.; Corti, T.; Davin, E.L.; Hirschi, M.; Jaeger, E.B.; Lehner, I.; Orlowsky, B.; Teuling, A.J. Investigating soil moisture–climate interactions in a changing climate: A review. Earth Sci. Rev. 2010, 99, 125–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinnikov, K.Y.; Robock, A.; Qiu, S.; Entin, J.K. Optimal design of surface networks for observation of soil moisture. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 19743–19749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Dorigo, W.A.; Parinussa, R.M.; de Jeu, R.A.M.; Wagner, W.; McCabe, M.F.; Evans, J.P.; van Dijk, A.I.J.M. Trend-preserving blending of passive and active microwave soil moisture retrievals. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 123, 280–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, A.; Dorigo, W.A.; Crow, W.; Wagner, W. Triple collocation-based merging of satellite soil moisture retrievals. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 6780–6792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni-Meister, W. Recent advances on soil moisture data assimilation. Phys. Geogr. 2008, 29, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, W.; Scipal, K.; Pathe, C.; Gerten, D.; Lucht, W.; Rudolf, B. Evaluation of the agreement between the first global remotely sensed soil moisture data with model and precipitation data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichle, R.H.; Koster, R.D. Bias reduction in short records of satellite soil moisture. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Yaari, A.; Wigneron, J.P.; Ducharne, A.; Kerr, Y.; de Rosnay, P.; de Jeu, R.; Govind, A.; Al Bitar, A.; Albergel, C.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; et al. Global-scale evaluation of two satellite-based passive microwave soil moisture datasets (smos and amsr-e) with respect to land data assimilation system estimates. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 149, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Yaari, A.; Wigneron, J.-P.; Ducharne, A.; Kerr, Y.; Wagner, W.; De Lannoy, G.; Reichle, R.; Al Bitar, A.; Dorigo, W.; Richaume, P. Global-scale comparison of passive (smos) and active (ascat) satellite based microwave soil moisture retrievals with soil moisture simulations (merra-land). Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 614–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Hain, C.R.; Zhan, X.; Anderson, M.C. An inter-comparison of soil moisture data products from satellite remote sensing and a land surface model. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 48, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocca, L.; Hasenauer, S.; Lacava, T.; Melone, F.; Moramarco, T.; Wagner, W.; Dorigo, W.; Matgen, P.; Martínez-Fernández, J.; Llorens, P. Soil moisture estimation through ascat and amsr-e sensors: An intercomparison and validation study across europe. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 3390–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgin, M.S.; Colliander, A.; Njoku, E.G.; Chan, S.K.; Cabot, F.; Kerr, Y.H.; Bindlish, R.; Jackson, T.J.; Entekhabi, D.; Yueh, S.H. A comparative study of the smap passive soil moisture product with existing satellite-based soil moisture products. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 2959–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruhier, C.; Rosnay, P.d.; Hasenauer, S.; Holmes, T.; Jeu, R.d.; Kerr, Y.; Mougin, E.; Njoku, E.; Timouk, F.; Wagner, W. Soil moisture active and passive microwave products: Intercomparison and evaluation over a sahelian site. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Li, X.; Chen, K. The discrepancy between backscattering model simulations and radar observations caused by scaling issues: An uncertainty analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 5356–5372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nykanen, D.K.; Foufoula-Georgiou, E. Soil moisture variability and scale-dependency of nonlinear parameterizations in coupled land–atmosphere models. Adv. Water Res. 2001, 24, 1143–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara, M.; Vargas, R. Downscaling satellite soil moisture using geomorphometry and machine learning. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Jin, R.; Li, X. Regression kriging-based upscaling of soil moisture measurements from a wireless sensor network and multiresource remote sensing information over heterogeneous cropland. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Jin, R.; Li, X.; Ma, C.; Qin, J.; Zhang, Y. High spatio-temporal resolution mapping of soil moisture by integrating wireless sensor network observations and modis apparent thermal inertia in the babao river basin, china. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 191, 232–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlin, O.; Malbéteau, Y.; Notfi, Y.; Bacon, S.; Khabba, S.E.-R.S.; Jarlan, L. Performance metrics for soil moisture downscaling methods: Application to dispatch data in central morocco. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 3783–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Loew, A.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Niesel, J. Spatial downscaling of satellite soil moisture data using a vegetation temperature condition index. Geosci. Remote Sens. IEEE Trans. 2016, 54, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piles, M.; Camps, A.; Vall-Llossera, M.; Corbella, I.; Panciera, R.; Rüdiger, C.; Kerr, Y.H.; Walker, J. Downscaling smos-derived soil moisture using modis visible/infrared data. Geosci. Remote Sens. IEEE Trans. 2011, 49, 3156–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drusch, M.; Wood, E.F.; Gao, H. Observation operators for the direct assimilation of trmm microwave imager retrieved soil moisture. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosh, M.H.; Jackson, T.J.; Starks, P.; Heathman, G. Temporal stability of surface soil moisture in the little washita river watershed and its applications in satellite soil moisture product validation. J. Hydrol. 2006, 323, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, A.; Su, C.H.; Zwieback, S.; Crow, W.; Dorigo, W.; Wagner, W. Recent advances in (soil moisture) triple collocation analysis. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 45, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyaoka, K.; Gruber, A.; Ticconi, F.; Hahn, S.; Wagner, W.; Figa-Saldaña, J.; Anderson, C. Triple collocation analysis of soil moisture from metop-a ascat and smos against jra-55 and era-interim. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 2274–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigo, W.; Scipal, K.; Parinussa, R.; Liu, Y.; Wagner, W.; De Jeu, R.; Naeimi, V. Error characterisation of global active and passive microwave soil moisture datasets. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 2605–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Wen, J.; Dente, L.; Velde, R.; Wang, L.; Ma, Y.; Yang, K.; Hu, Z. The tibetan plateau observatory of plateau scale soil moisture and soil temperature (tibet-obs) for quantifying uncertainties in coarse resolution satellite and model products. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 2303–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Houser, P.R.; Jambor, U.; Gottschalck, J.; Mitchell, K.; Meng, C.J.; Arsenault, K.; Cosgrove, B.; Radakovich, J.; Bosilovich, M.; et al. The global land data assimilation system. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2004, 85, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam (Richard de Jeu); NASA GSFC (Manfred Owe). AMSR2/GCOM-W1 Surface Soil Moisture (LPRM) L3 1 Day 25 km x 25 km Ascending/Descending V001; Goddard Earth Sciences Data, Information Services Center (GES DISC) (Bill Teng), Eds.; Goddard Earth Sciences Data and Information Services Center (GES DISC): Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2014. [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, P.E.; Chan, S.; Njoku, E.G.; Jackson, T.; Bindlish, R.; Chaubell, J. SMAP L3 Radiometer Global Daily 36 km EASE-Grid Soil Moisture, Version 6; NASA National Snow and Ice Data Center Distributed Active Archive Center: Boulder, CO, USA, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Gruber, A.; De Lannoy, G.; Albergel, C.; Al-Yaari, A.; Brocca, L.; Calvet, J.C.; Colliander, A.; Cosh, M.; Crow, W.; Dorigo, W.; et al. Validation practices for satellite soil moisture retrievals: What are (the) errors? Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 244, 111806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McColl, K.A.; Vogelzang, J.; Konings, A.G.; Entekhabi, D.; Piles, M.; Stoffelen, A. Extended triple collocation: Estimating errors and correlation coefficients with respect to an unknown target. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 6229–6236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van doninck, J.; Peters, J.; De Baets, B.; De Clercq, E.M.; Ducheyne, E.; Verhoest, N.E.C. The potential of multitemporal aqua and terra modis apparent thermal inertia as a soil moisture indicator. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2011, 13, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwieback, S.; Scipal, K.; Dorigo, W.; Wagner, W. Structural and statistical properties of the collocation technique for error characterization. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 2012, 19, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

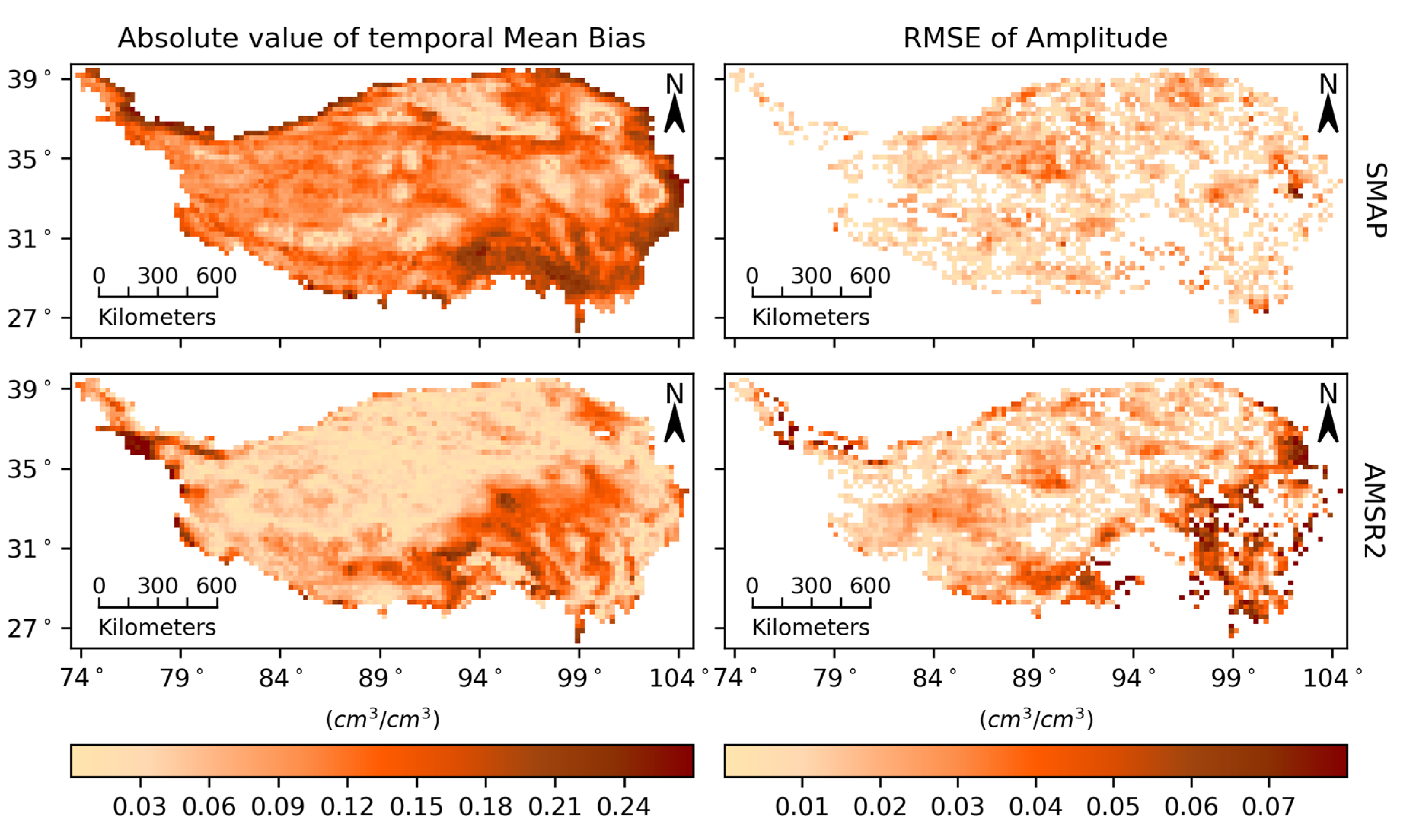
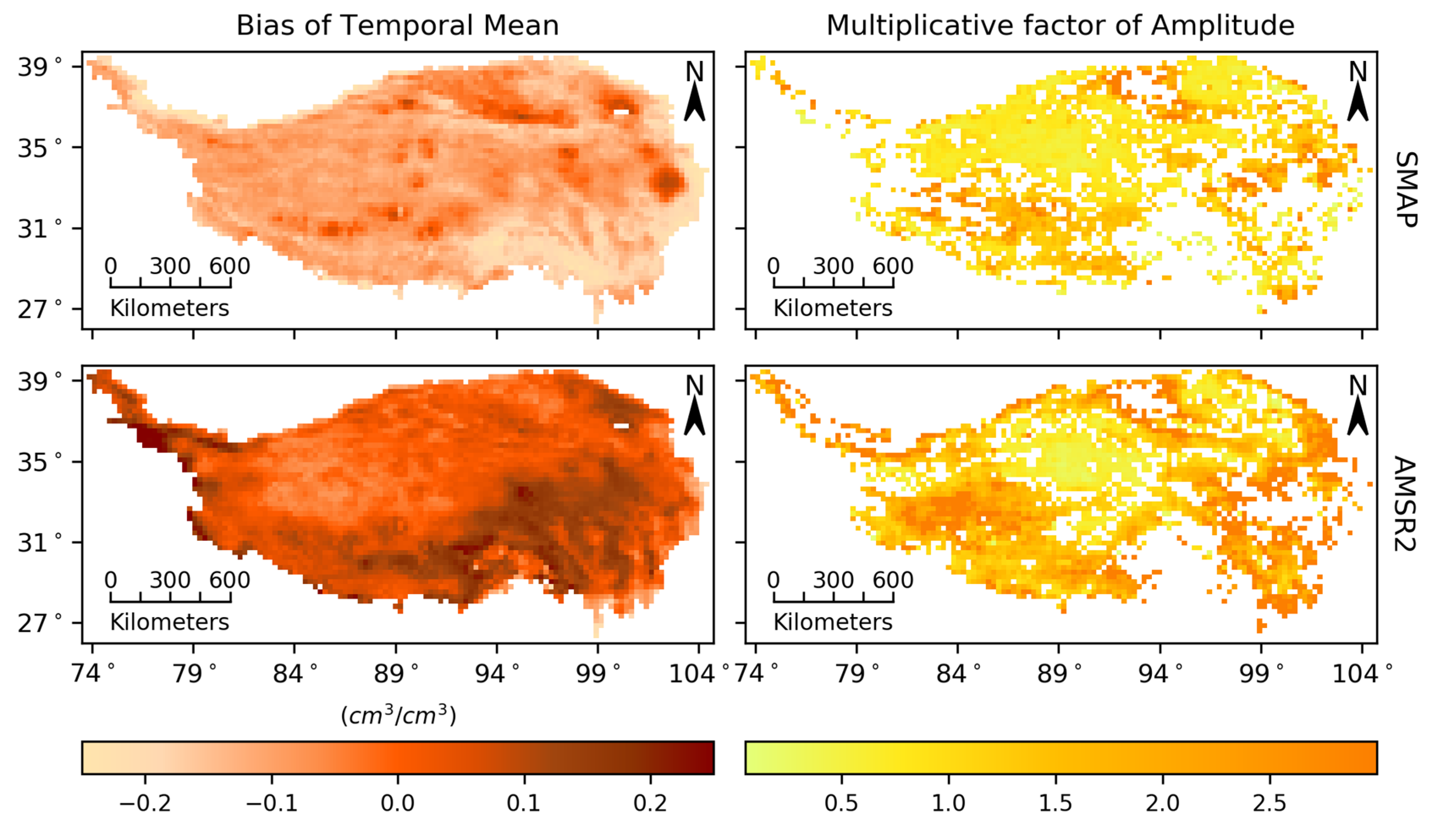
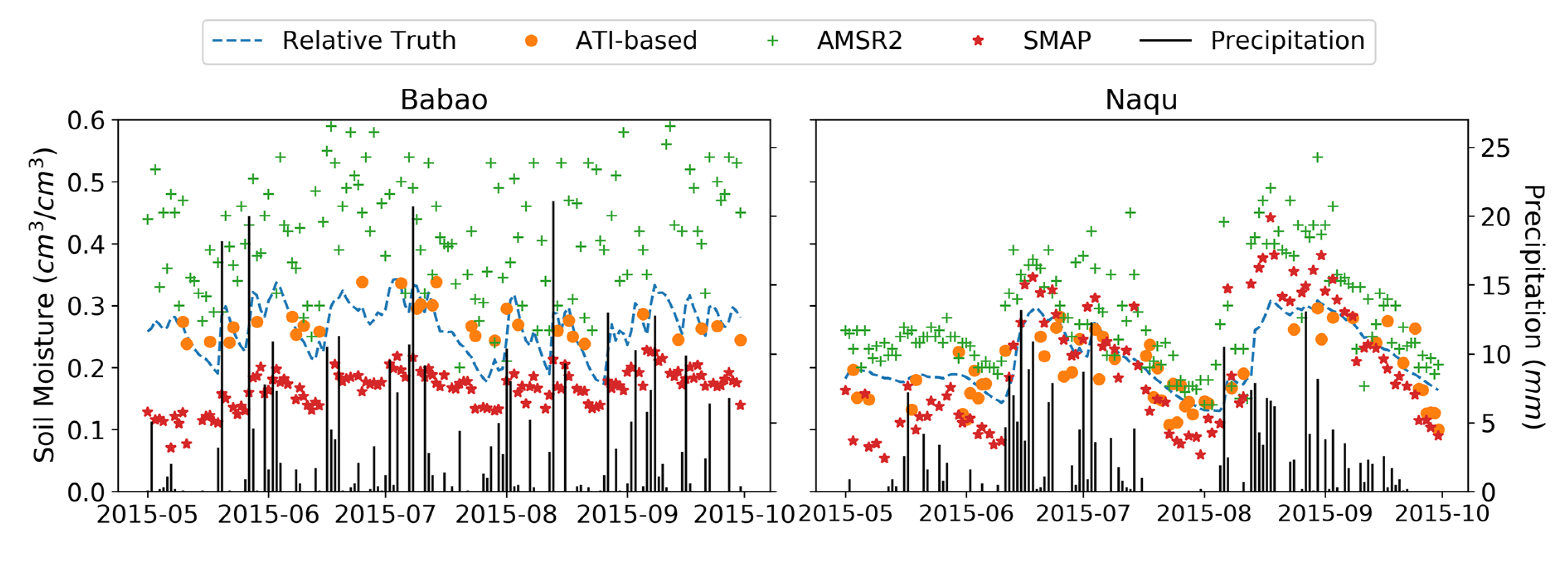
| Region | Babao | Naqu | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Index | Relative Truth | ATI-Based | GLDAS | Relative Truth | ATI-Based | GLDAS | |
| Mean (cm3/cm3) | 0.268 | 0.272 | 0.183 | 0.191 | 0.183 | 0.133 | |
| in Equation (1) | 1.0 | 0.768 | 0.707 | 1.0 | 0.891 | 0.319 | |
| Babao | Naqu | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (cm3/cm3) | Relative Truth | ATI-Based | SMAP | AMSR2 | Relative Truth | ATI-Based | SMAP | AMSR2 | |
| 0.017 | 0.018 | 0.019 | 0.062 | 0.009 | 0.034 | 0.026 | 0.026 | ||
| 0.032 | 0.024 | 0.014 | 0.044 | 0.052 | 0.046 | 0.085 | 0.069 | ||
| 0.268 | 0.272 | 0.153 | 0.367 | 0.191 | 0.183 | 0.162 | 0.245 | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, J.; Jin, R.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y. Error Decomposition of Remote Sensing Soil Moisture Products Based on the Triple-Collocation Method Introducing an Unbiased Reference Dataset: A Case Study on the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3087. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12183087
Kang J, Jin R, Li X, Zhang Y. Error Decomposition of Remote Sensing Soil Moisture Products Based on the Triple-Collocation Method Introducing an Unbiased Reference Dataset: A Case Study on the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(18):3087. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12183087
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Jian, Rui Jin, Xin Li, and Yang Zhang. 2020. "Error Decomposition of Remote Sensing Soil Moisture Products Based on the Triple-Collocation Method Introducing an Unbiased Reference Dataset: A Case Study on the Tibetan Plateau" Remote Sensing 12, no. 18: 3087. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12183087
APA StyleKang, J., Jin, R., Li, X., & Zhang, Y. (2020). Error Decomposition of Remote Sensing Soil Moisture Products Based on the Triple-Collocation Method Introducing an Unbiased Reference Dataset: A Case Study on the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sensing, 12(18), 3087. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12183087