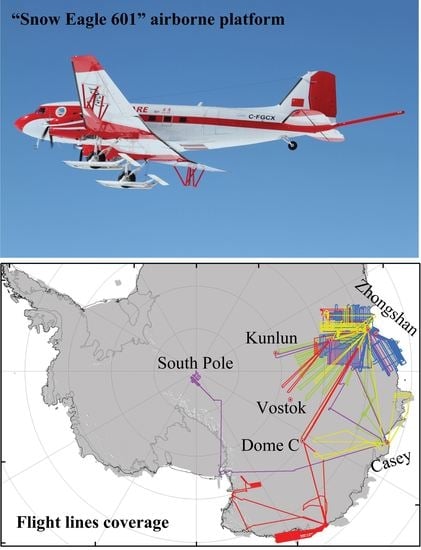
The Scientific Operations of Snow Eagle 601 in Antarctica in the Past Five Austral Seasons
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Snow Eagle 601 Airborne Surveying System
2.1. Airborne Platform
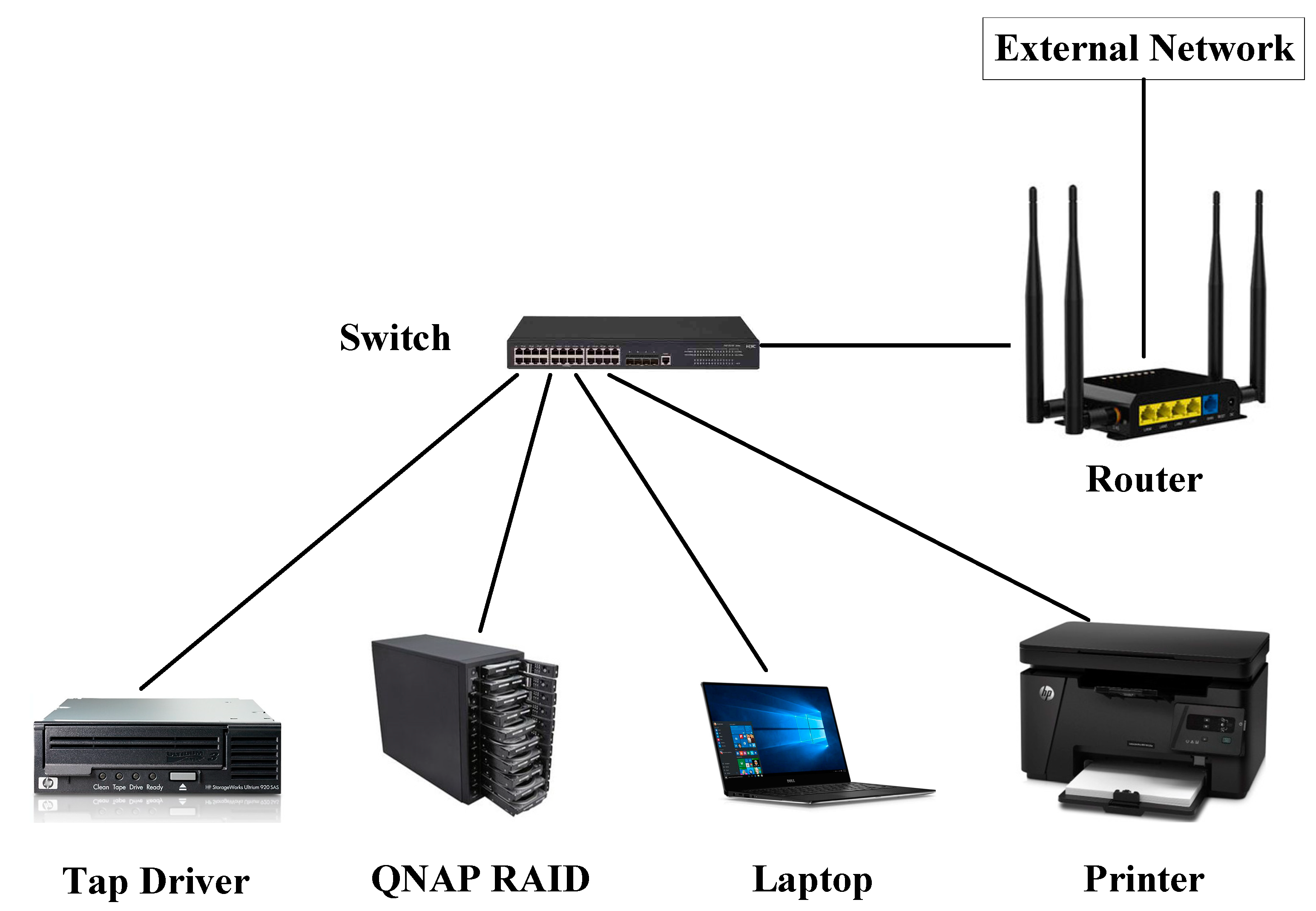
2.2. Base Stations
3. Aviation Support
3.1. Aviation Groups
3.2. Logistical Support
4. Airborne Survey and Data Processing
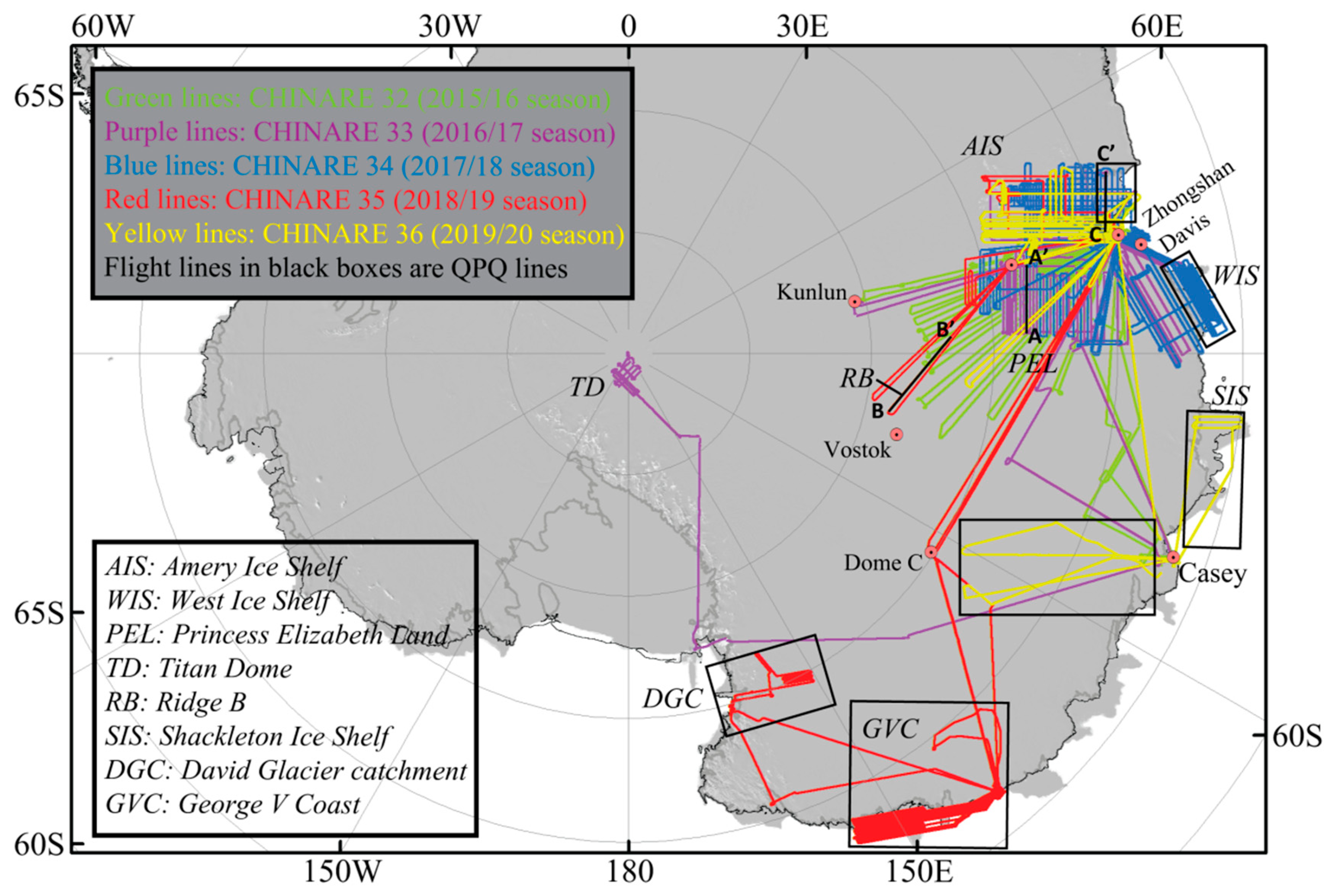
4.1. Flight Plan Design
4.2. Data Acquisition
4.3. Data Processing
4.4. Data Quality Control
4.5. Data and Documents Archive
5. Progress and Prospects
5.1. Progress
5.2. Future Work
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andrew, S.; Amanda, F.H.; Louise, F.S. Trends and connections across the Antarctic cryosphere. Nature 2018, 558, 223–232. [Google Scholar]
- Kennicutt, M.C.; Chown, S.L.; Cassano, J.J.; Liggett, D.; Massom, R.A.; Peck, L.S.; Rintoul, S.R.; Storey, J.W.V.; Vaughan, D.G.; Wilson, T.J.; et al. Polar research: Six priorities for Antarctic science. Nature 2014, 512, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennicutt ll, M.C.; Bromwich, D.; Liggett, D.; Njastad, B.; Peck, L.S.; Rintoul, S.R.; Ritz, C.; Siegert, M.J.; Aitken, A.R.A.; Brooks, C.M.; et al. Sustained Antarctic Research: A 21st Century Imperative. One Earth 2019, 1, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, S. Radio techniques for the measurement of ice thickness. Polar Record. 2019, 11, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Sun, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, D.; Li, X.; Tang, X.; Tian, G. A review of ice radar’s technical development in polar ice sheet investigation. Chin. J. Polar Res. 2009, 21, 322–335. [Google Scholar]
- Mirko, S.; Graeme, E.; Kirsty, T. Airborne platforms help answer questions in polar geosciences. Eos 2017, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, D.M.; Dowdeswell, J.A.; Siegert, M.J.; Bingham, R.; Chu, W.; Mackie, E.J.; Siegfried, M.R.; Vega, K.I.; Emmons, J.R.; Winstein, K. Multidecadal observations of the Antarctic ice sheet from restored analog radar records. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 18867–18873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, R.E.; Ferraccioli, F.; Creyts, T.T.; Braaten, D.; Corr, H.F.; Das, I.; Damaske, D.; Frearson, N.; Jordan, T.; Rose, K.; et al. Widespread Persistent Thickening of the East Antarctic Ice Sheet by Freezing from the Base. Science 2011, 331, 1592–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeofry, H.; Ross, N.; Corr, H.F.J.; Li, J.; Morlighem, M.; Gogineni, P.; Siegert, M.J. A new bed elevation model for the Weddell Sea sector of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2018, 10, 711–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, T.A.; Martin, C.; Ferraccioli, F.; Matsuoka, K.; Corr, H.F.; Forsberg, R.; Olesen, A.; Siegert, M. Anomalously high geothermal flux near the South Pole. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, D.A.; Wright, A.P.; Roberts, J.L.; Warner, R.C.; Young, N.W.; Greenbaum, J.S.; Schroeder, D.M.; Holt, J.W.; Sugden, D.E.; Blankenship, D.D.; et al. A dynamic early East Antarctic Ice Sheet suggested by ice-covered fjord landscapes. Nature 2011, 474, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenbaum, J.S.; Blankenship, D.D.; Young, D.A.; Richter, T.G.; Roberts, J.L.; Aitken, A.R.A.; Legresy, B.; Schroeder, D.M.; Warner, R.C.; van Ommen, T.D.; et al. Ocean access to a cavity beneath Totten Glacier in East Antarctica. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Greenbaum, J.S.; Beem, L.H.; Guo, J.; Ng, G.; Li, L.; Blankenship, D.; Sun, B. The First Fixed-wing Aircraft For Chinese Antarctic Expeditions: Airframe, Modifications, Scientific Instrumentation and Applications. J. Environ. Eng. Geophys. 2018, 23, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson, N.B.; Binder, T.; Eagles, G.; Helm, V.; Pattyn, F.; Van Liefferinge, B.; Eisen, O. Glaciological characteristics in the Dome Fuji region and new assessment for “Oldest Ice”. Cryosphere 2018, 12, 2413–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fretwell, P.T.; Pritchard, H.D.; Vaughan, D.G.; Bamber, J.L.; Barrand, N.E.; Bell, R.E.; Bianchi, C.; Bingham, R.G.; Blankenship, D.D.; Casassa, G.; et al. Bedmap2: Improved ice bed, surface and thickness datasets for Antarctica. Cryosphere 2012, 7, 375–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golynsky, A.V.; Ferraccioli, F.; Hong, J.; Golynsky, D.A.; Von Frese, R.R.; Young, D.A.; Blankenship, D.D.; Holt, J.W.; Ivanov, S.V.; Kiselev, A.V.; et al. New Magnetic Anomaly Map of the Antarctic. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 6437–6449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheinert, M.; Ferraccioli, F.; Schwabe, J.; Bell, R.E.; Studinger, M.; Damaske, D.; Jokat, W.; Aleshkova, N.; Jordan, T.; Leitchenkov, G.; et al. New Antarctic gravity anomaly grid for enhanced geodetic and geophysical studies in Antarctica. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 600–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, G.; Lindzey, L.E.; Young, D.A.; Buhl, D.P.; Kempf, S.D.; Beem, L.H.; Roberts, J.L.; Greenbaum, J.S.; Blankenship, D.D. UTIG’s Approach to Managing Polar Aerogeophysical Data in the Field: Philosophy and Examples from Fixed Wing and Helicopter Surveys; UTIG Technical Report; University of Texas, Institute for Geophysics: Austin, TX, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson, S.S.R.; Ross, N.; Greenbaum, J.S.; Young, D.A.; Aitken, A.R.A.; Roberts, J.L.; Blankenship, D.D.; Siegert, M.J. An extensive subglacial lake and canyon system in Princess Elizabeth Land, East Antarctica. Geology 2016, 44, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Jeofry, H.; Greenbaum, J.S.; Guo, J.; Li, L.; Lindzey, L.E.; Habbal, F.A.; Wei, W.; Young, D.A.; Ross, N.; et al. Bed topography of Princess Elizabeth Land in East Antarctica. Earth Syst. Sci. Data Discuss. 2020. in review. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, H.D.; Ligtenberg, S.R.M.; Fricker, H.A.; Vaughan, D.G.; Van den Broeke, M.R.; Padman, L. Antarctic ice-sheet loss driven by basal melting of ice shelves. Nature 2012, 484, 502–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolo, F.; Fricker, H.; Padman, L. Volume loss from Antarctic ice shelves is accelerating. Science 2015, 348, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rignot, E.; Mouginot, J.; Morlighem, M.; Seroussi, H.; Scheuchl, B. Widespread, rapid grounding line retreat of Pine Island, Thwaites, Smith, and Kohler glaciers, West Antarctica, from 1992 to 2011. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 3502–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Rignot, E.; Morlighem, M.; Mouginot, J.; Scheuchl, B. Grounding line retreat of Totten Glacier, east Antarctica, 1996 to 2013. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 8049–8056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rintoul, S.R.; Silvano, A.; Pena-Molino, B.; van Wijk, E.; Rosenberg, M.; Greenbaum, J.S.; Blankenship, D.D. Ocean heat drives rapid basal melt of the Totten ice shelf. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, E1601610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Liefferinge, B.; Pattyn, F. Using ice-flow models to evaluate potential sites of million year-old ice in Antarctica. Clim. Past 2013, 9, 2335–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beem, L.H.; Young, D.A.; Greenbaum, J.S.; Blankenship, D.D.; Guo, J.; Bo, S. Characterization of Titan Dome, East Antarctica, and potential as an ice core target. Cryosphere 2020. in review. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, Y. Geological surveys in East Antarctica by Chinese expeditions over the last 20 years: Progress and prospects. Chin. J. Polar Res. 2018, 30, 268–286. [Google Scholar]
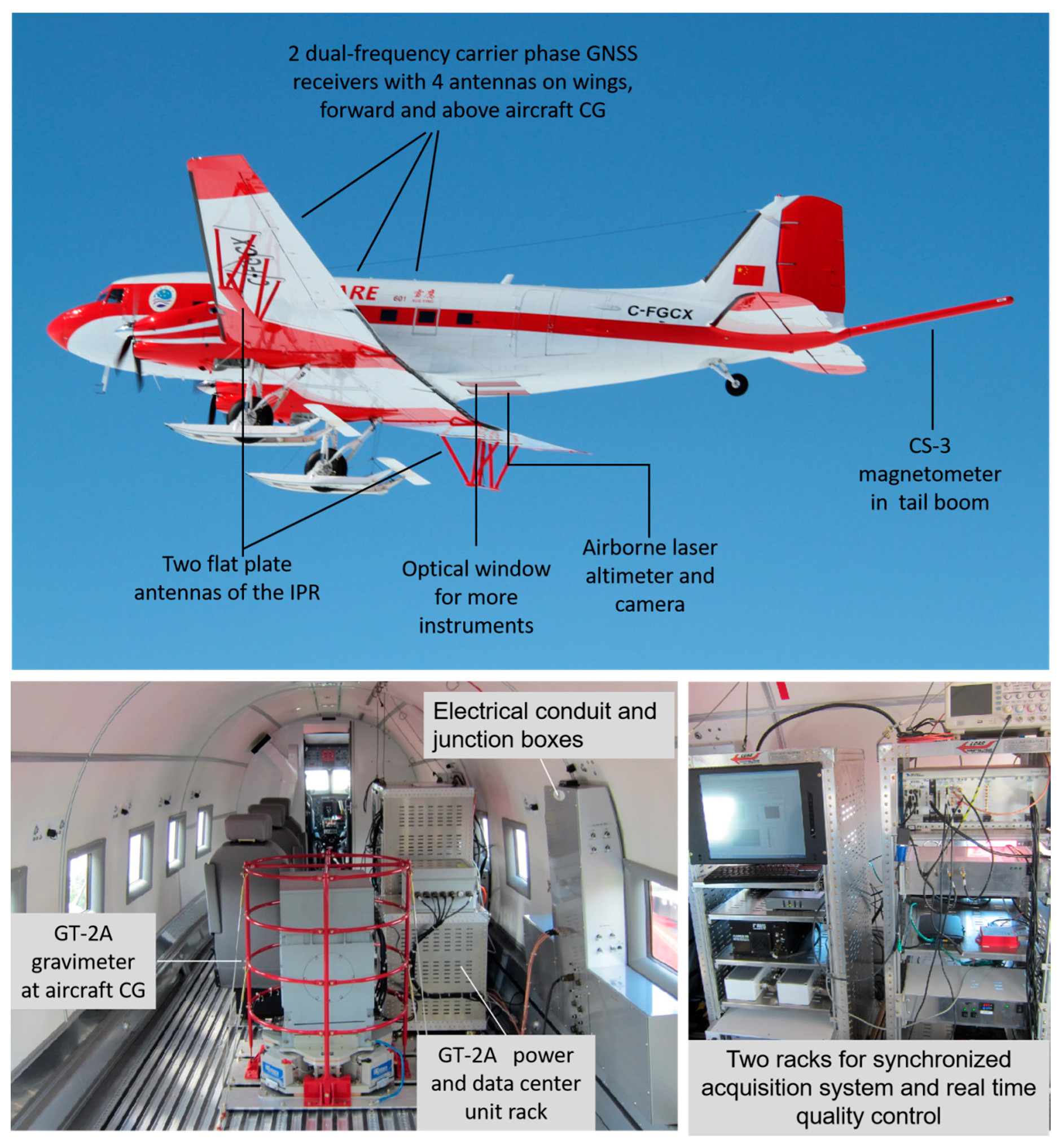



| Airborne Instruments | Performance | Targets |
|---|---|---|
| Ice-penetrating radar (IPR) | Deep penetrating ability: >4000 m; depth resolution: 5.6 m in ice; coherent system; both low gain and high gain channels; 500–1500 m nominal surface range | Map ice sheet geometry and subglacial topography; interpret subglacial conditions |
| GT-2A gravimeter | Improved performance over other conventional gravimeters: dynamic range (>1000 Gal) and sensitivity (resolution: 0.02 mGal); can be used in turbulence; functions well on draped surveys | Measure gravity anomalies; infer deep geological and tectonic structures, subglacial water and sediment depth; bathymetry under ice shelves [12] |
| CS-3 magnetometer | High sensitivity (resolution: 0.00032 nT) and very low noise (system noise: <0.0001 nT) | Measure magnetic anomalies; infer lithology, deep geological and tectonic structures |
| Laser altimeter | Maximum range: 1500 m; accuracy: 15 cm | Measure accurate flight height over the snow or ice surface |
| Camera | – | Characterize surface features |
| Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) | Dual frequency, four-channel carrier-phase GNSS receiver | Provides aircraft position and attitude |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, X.; Greenbaum, J.S.; Lang, S.; Zhao, X.; Li, L.; Guo, J.; Sun, B. The Scientific Operations of Snow Eagle 601 in Antarctica in the Past Five Austral Seasons. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2994. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12182994
Cui X, Greenbaum JS, Lang S, Zhao X, Li L, Guo J, Sun B. The Scientific Operations of Snow Eagle 601 in Antarctica in the Past Five Austral Seasons. Remote Sensing. 2020; 12(18):2994. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12182994
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Xiangbin, Jamin S. Greenbaum, Shinan Lang, Xi Zhao, Lin Li, Jingxue Guo, and Bo Sun. 2020. "The Scientific Operations of Snow Eagle 601 in Antarctica in the Past Five Austral Seasons" Remote Sensing 12, no. 18: 2994. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12182994
APA StyleCui, X., Greenbaum, J. S., Lang, S., Zhao, X., Li, L., Guo, J., & Sun, B. (2020). The Scientific Operations of Snow Eagle 601 in Antarctica in the Past Five Austral Seasons. Remote Sensing, 12(18), 2994. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12182994